Java-IO流
文章目录
- Java-IO流
- 文件字节流
- 文件字符流
- File类
- 缓冲流
- 转换流
- 打印流
- 数据流
- 对象流
Java-IO流
JDK提供了一套用于IO操作的框架,为了方便我们开发者使用,就定义了一个像水流一样,根据流的传输方向和读取单位,分为字节流InputStream和OutputStream以及字符流Reader和Writer的IO框架
这里的流指的是数据流,通过流,我们就可以一直从流中读取数据,直到读取到尽头,或是不断向其中写入数据,直到我们写入完成
文件字节流
FileInputStream通过它来获取文件的输入流:
public static void main(String[] args) {FileInputStream inputStream = null; //定义可以先放在try外部try {inputStream = new FileInputStream("路径");} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try { //建议在finally中进行,因为关闭流是任何情况都必须要执行的!if(inputStream != null) inputStream.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
在使用完成一个流之后,必须关闭这个流来完成对资源的释放,否则资源会被一直占用
JDK1.7新增了try-with-resource语法,用于简化资源释放的写法:
public static void main(String[] args) {//注意,这种语法只支持实现了AutoCloseable接口的类!try(FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("路径")) { //直接在try()中定义要在完成之后释放的资源} catch (IOException e) { //这里变成IOException是因为调用close()可能会出现,而FileNotFoundException是继承自IOException的e.printStackTrace();}//无需再编写finally语句块,因为在最后自动帮我们调用了close()
}
使用read方法读取文件内容:
public static void main(String[] args) {//test.txt:abcdtry(FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("test.txt")) {int tmp;while ((tmp = inputStream.read()) != -1){ //通过while循环来一次性读完内容System.out.println((char)tmp);}}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
使用available方法能查看当前可读的剩余字节数量
一个一个读取效率太低了,可以预置一个合适容量的byte[]数组来存放
public static void main(String[] args) {//test.txt:abcdtry(FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("test.txt")) {byte[] bytes = new byte[inputStream.available()]; //我们可以提前准备好合适容量的byte数组来存放System.out.println(inputStream.read(bytes)); //一次性读取全部内容(返回值是读取的字节数)System.out.println(new String(bytes)); //通过String(byte[])构造方法得到字符串}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
控制要读取数量:
System.out.println(inputStream.read(bytes, 1, 2)); //第二个参数是从给定数组的哪个位置开始放入内容,第三个参数是读取流中的字节数
一次性读取同单个读取一样,当没有任何数据可读时,依然会返回-1
通过skip()方法可以跳过指定数量的字节
FileInputStream是不支持reset()的,虽然有这个方法
write()操作向文件里写入内容:
public static void main(String[] args) {try(FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("output.txt", true)) { //true表示开启追加模式outputStream.write("lb".getBytes()); //现在只会进行追加写入,而不是直接替换原文件内容outputStream.flush();}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
文件拷贝:
public static void main(String[] args) {try(FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("output.txt");FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("test.txt")) { //可以写入多个byte[] bytes = new byte[10]; //使用长度为10的byte[]做传输媒介int tmp; //存储本地读取字节数while ((tmp = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1){ //直到读取完成为止outputStream.write(bytes, 0, tmp); //写入对应长度的数据到输出流}}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
文件字符流
字符流不同于字节,字符流是以一个具体的字符进行读取,因此它只适合读纯文本的文件,如果是其他类型的文件不适用:
public static void main(String[] args) {try(FileReader reader = new FileReader("test.txt")){char[] str = new char[10];reader.skip(1); //现在跳过的是一个字符reader.read(str);System.out.println(str); //直接读取到char[]中}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
Writer:
public static void main(String[] args) {try(FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("output.txt")){writer.getEncoding(); //支持获取编码(不同的文本文件可能会有不同的编码类型)writer.write('牛');writer.append('牛'); //其实功能和write一样writer.flush(); //刷新}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
append支持像StringBuilder那样的链式调用,返回的是Writer对象本身。
File类
File类是专门用于表示一个文件或文件夹,只不过它只是代表这个文件,但并不是这个文件本身。
通过File对象,可以更好地管理和操作硬盘上的文件。
public static void main(String[] args) {File file = new File("test.txt"); //直接创建文件对象,可以是相对路径,也可以是绝对路径System.out.println(file.exists()); //此文件是否存在System.out.println(file.length()); //获取文件的大小System.out.println(file.isDirectory()); //是否为一个文件夹System.out.println(file.canRead()); //是否可读System.out.println(file.canWrite()); //是否可写System.out.println(file.canExecute()); //是否可执行File file = new File("/");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(file.list())); //快速获取文件夹下的文件名称列表System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath()); //获取文件的绝对路径
}
直接将File作为参数传入字节流或是字符流,读取某个文件的内容:
File file = new File("test.txt");
try (FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file)){ //直接做参数System.out.println(inputStream.available());
}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();
}
缓冲流
普通的文件流读取文件数据非常便捷,但是每次都需要从外部I/O设备去获取数据,由于外部I/O设备的速度一般都达不到内存的读取速度,很有可能造成程序反应迟钝,因此性能还不够高。
缓冲流能够提供一个缓冲,提前将部分内容存入内存(缓冲区)在下次读取时,如果缓冲区中存在此数据,则无需再去请求外部设备。当向外部设备写入数据时,也是由缓冲区处理,而不是直接向外部设备写入。
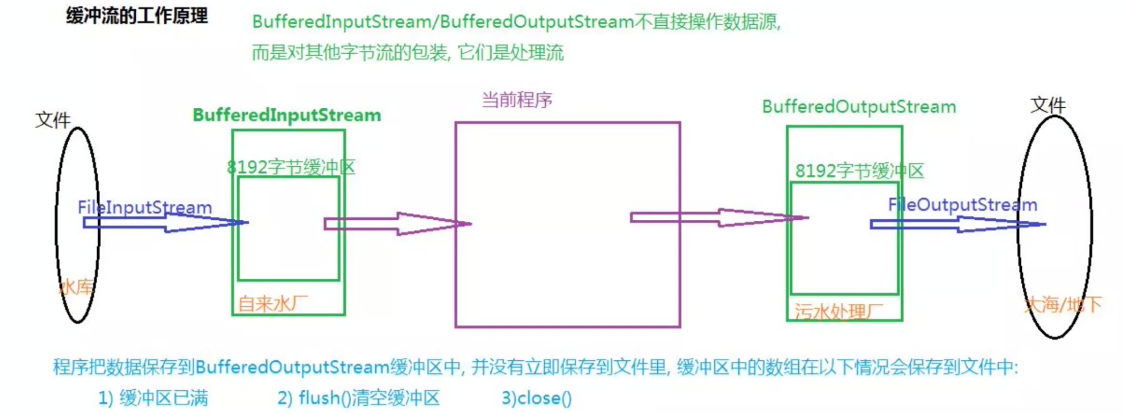
创建一个缓冲字节流:
public static void main(String[] args) {try (BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("test.txt"))){ //传入FileInputStreamSystem.out.println((char) bufferedInputStream.read()); //操作和原来的流是一样的}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
实际上进行I/O操作的并不是BufferedInputStream,而是我们传入的FileInputStream,而BufferedInputStream虽然有着同样的方法,但是进行了一些额外的处理然后再调用FileInputStream的同名方法,这样的写法称为装饰者模式
close方法源码:
public void close() throws IOException {byte[] buffer;while ( (buffer = buf) != null) {if (bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, null)) { //CAS无锁算法,并发会用到,暂时不需要了解InputStream input = in;in = null;if (input != null)input.close();return;}// Else retry in case a new buf was CASed in fill()}
}
BufferedInputStream中还存在一个专门用于缓存的数组:
/*** The internal buffer array where the data is stored. When necessary,* it may be replaced by another array of* a different size.*/
protected volatile byte buf[];
缓冲流提供了缓冲机制,一部分内容可以被暂时保存,BufferedInputStream支持reset()和mark()操作
当调用mark()之后,输入流会以某种方式保留之后读取的readlimit数量的内容,当读取的内容数量超过readlimit则之后的内容不会被保留,当调用reset()之后,会使得当前的读取位置回到mark()调用时的位置
其实mark()后保存的读取内容是取readlimit和BufferedInputStream类的缓冲区大小两者中的最大值
public static void main(String[] args) {try (BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("test.txt"))){bufferedInputStream.mark(1); //只保留之后的1个字符System.out.println((char) bufferedInputStream.read());System.out.println((char) bufferedInputStream.read());bufferedInputStream.reset(); //回到mark时的位置System.out.println((char) bufferedInputStream.read());System.out.println((char) bufferedInputStream.read());}catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
BufferedReader构造时需要传入一个Reader对象:
public static void main(String[] args) {try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("test.txt"))){System.out.println((char) reader.read());}catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
BufferedReader内部也包含一个缓存数组:
private char cb[];
BufferedReader支持按行读取:
public static void main(String[] args) {try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("test.txt"))){System.out.println(reader.readLine()); //按行读取}catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
把每一行内容依次转换为集合类提到的Stream流:
public static void main(String[] args) {try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("test.txt"))){reader.lines().limit(2).distinct().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);}catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
BufferedWriter在处理纯文本文件方便:
public static void main(String[] args) {try (BufferedWriter reader = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("output.txt"))){reader.newLine(); //使用newLine进行换行reader.write("汉堡做滴彳亍不彳亍"); //可以直接写入一个字符串reader.flush(); //清空缓冲区}catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
转换流
读取的是一个字符串或是一个个字符,但是我只能往一个OutputStream里输出,但是OutputStream又只支持byte类型,如果要往里面写入内容,进行数据转换就会很麻烦,那么能否有更加简便的方式来做这样的事情呢
public static void main(String[] args) {try(OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("test.txt"))){ //虽然给定的是FileOutputStream,但是现在支持以Writer的方式进行写入writer.write("lbwnb"); //以操作Writer的样子写入OutputStream}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
只拿到了一个InputStream,但是我们希望能够按字符的方式读取,我们就可以使用InputStreamReader来帮助我们实现:
public static void main(String[] args) {try(InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("test.txt"))){ //虽然给定的是FileInputStream,但是现在支持以Reader的方式进行读取System.out.println((char) reader.read());}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
打印流
System.out就是一个PrintStream,PrintStream也继承自FilterOutputStream类因此依然是装饰我们传入的输出流,但是它存在自动刷新机制。
PrintStream也永远不会抛出异常,而是使用内部检查机制checkError()方法进行错误检查。
它能够格式化任意的类型,将它们以字符串的形式写入到输出流。
System.out也是PrintStream,不过默认是向控制台打印,也可以让它向文件中打印:
public static void main(String[] args) {try(PrintStream stream = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("test.txt"))){stream.println("lbwnb"); //其实System.out就是一个PrintStream}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
println方法就是PrintStream中的方法,它会直接打印基本数据类型或是调用对象的toString()方法得到一个字符串,并将字符串转换为字符,放入缓冲区再经过转换流输出到给定的输出流上。

Scanner使用的是系统提供的输入流,也可以使用Scanner来扫描其他的输入流:
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(new FileInputStream("秘制小汉堡.txt")); //将文件内容作为输入流进行扫描
}
数据流
数据流DataInputStream也是FilterInputStream的子类,同样采用装饰者模式,最大的不同是它支持基本数据类型的直接读取:
public static void main(String[] args) {try (DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("test.txt"))){System.out.println(dataInputStream.readBoolean()); //直接将数据读取为任意基本数据类型}catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
用于写入基本数据类型:
public static void main(String[] args) {try (DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("output.txt"))){dataOutputStream.writeBoolean(false);}catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
写入的是二进制数据,并不是写入的字符串,使用DataInputStream可以读取,一般他们是配合一起使用的。
对象流
ObjectOutputStream不仅支持基本数据类型,通过对对象的序列化操作,以某种格式保存对象,来支持对象类型的IO,它不是继承自FilterInputStream的。
public static void main(String[] args) {try (ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("output.txt"));ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("output.txt"))){People people = new People("lbw");outputStream.writeObject(people);outputStream.flush();people = (People) inputStream.readObject();System.out.println(people.name);}catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}static class People implements Serializable{ //必须实现Serializable接口才能被序列化String name;public People(String name){this.name = name;}
}
后续的操作中,有可能会使得这个类的一些结构发生变化,而原来保存的数据只适用于之前版本的这个类,因此我们需要一种方法来区分类的不同版本:
static class People implements Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 123456; //在序列化时,会被自动添加这个属性,它代表当前类的版本,我们也可以手动指定版本。String name;public People(String name){this.name = name;}
}
当发生版本不匹配时,会无法反序列化为对象
如果我们不希望某些属性参与到序列化中进行保存,我们可以添加transient关键字
static class People implements Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 1234567;transient String name;public People(String name){this.name = name;}
}
ialVersionUID = 123456; //在序列化时,会被自动添加这个属性,它代表当前类的版本,我们也可以手动指定版本。
String name;public People(String name){this.name = name;
}
}
当发生版本不匹配时,会无法反序列化为对象如果我们不希望某些属性参与到序列化中进行保存,我们可以添加`transient`关键字~~~java
static class People implements Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 1234567;transient String name;public People(String name){this.name = name;}
}
transient关键字,使得某些属性不参与序列化,取消这些不必要保存的属性,可以节省数据空间占用以及减少序列化时间。
相关文章:

Java-IO流
文章目录 Java-IO流文件字节流文件字符流File类缓冲流转换流打印流数据流对象流 Java-IO流 JDK提供了一套用于IO操作的框架,为了方便我们开发者使用,就定义了一个像水流一样,根据流的传输方向和读取单位,分为字节流InputStream和…...
04、Python 爬取免费小说思路
目录 Python 爬取免费小说思路代码解析爬取东西基本的四行代码:user-agent安装模块从 bs4 导入 BeautifulSoup ,查询某个标签开头的数据筛选遍历获取小说的章节名称每章小说的链接获取请求网址的响应获取小说的内容筛选内容整理内容爬取下载到指定文件夹完整代码:Python 爬取…...
【前端vue面试】vue2
目录 computed和watchv-show和v-ifkey 的重要性v-for 和 v-if 不能一起使用!click的event修饰符事件修饰符表单项修饰符 父子组件通讯生命周期父子组件生命周期顺序 $nextTickslot 插槽动态组件异步组件keep-alivemixin computed和watch computed 有缓存࿰…...

自然语言处理---Transformer机制详解之GPT模型介绍
1 GPT介绍 GPT是OpenAI公司提出的一种语言预训练模型.OpenAI在论文<< Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training >>中提出GPT模型.OpenAI后续又在论文<< Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners >>中提出GPT2模型.…...
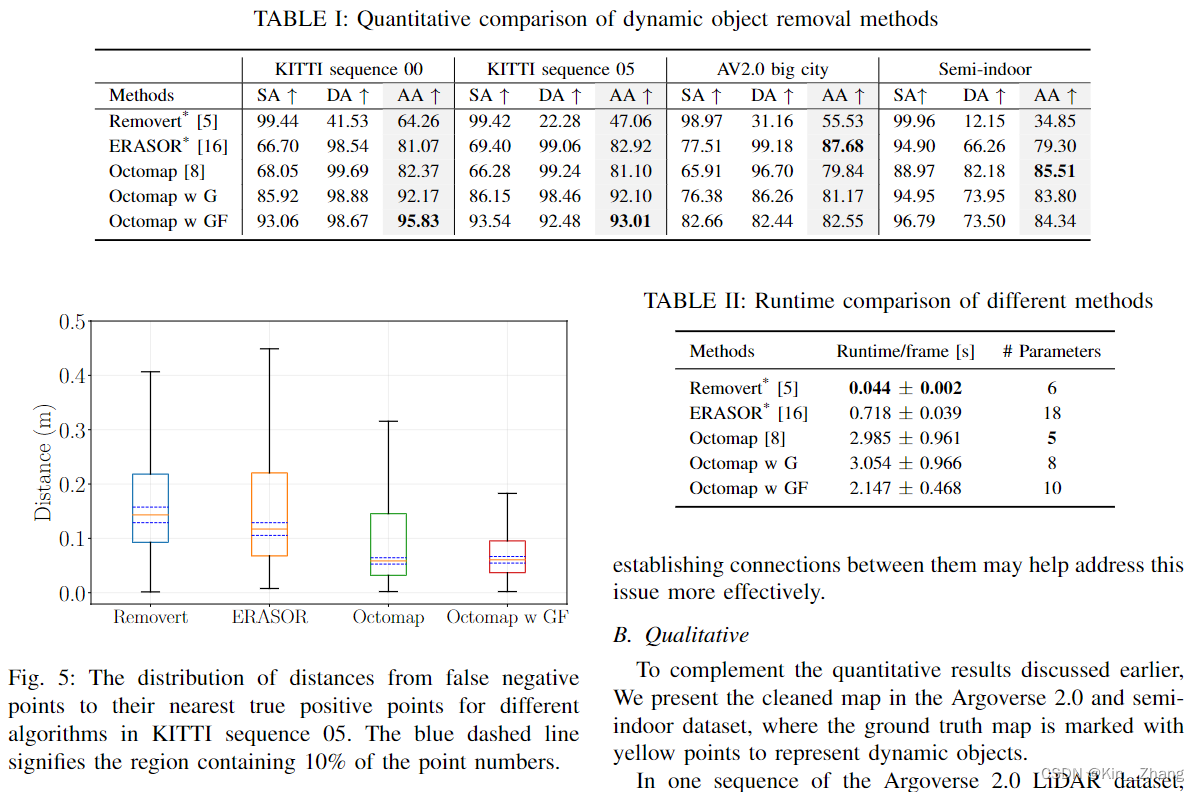
【论文阅读】点云地图动态障碍物去除基准 A Dynamic Points Removal Benchmark in Point Cloud Maps
【论文阅读】点云地图动态障碍物去除基准 A Dynamic Points Removal Benchmark in Point Cloud Maps 终于一次轮到了讲自己的paper了 hahaha,写个中文的解读放在博客方便大家讨论 Title Picture Reference and prenotes paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.07260 …...
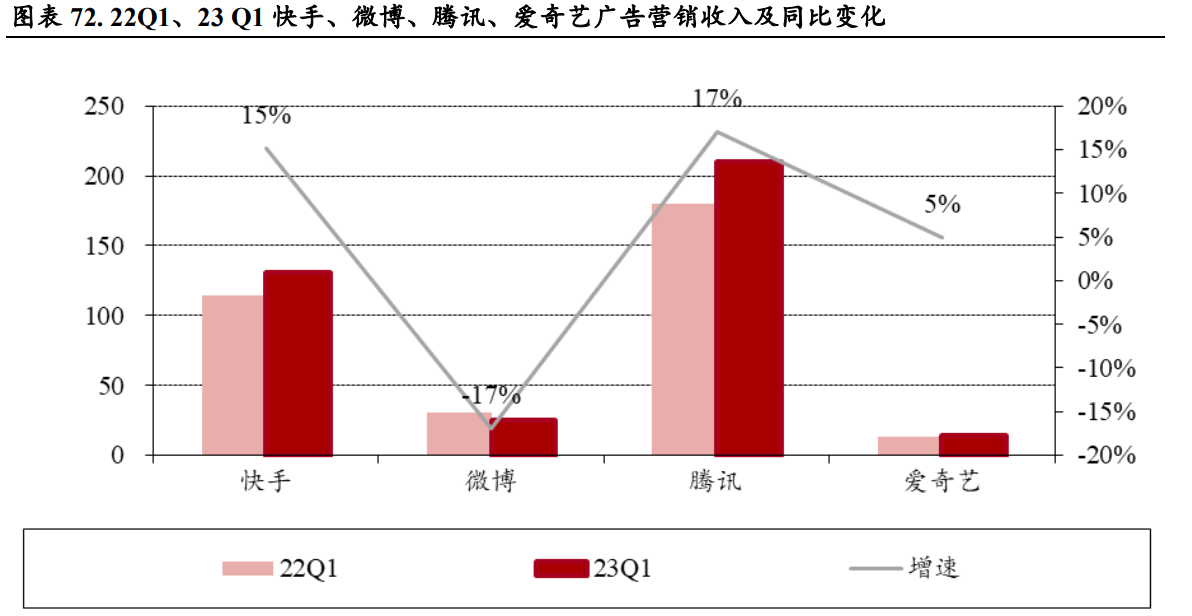
2023年传媒行业中期策略 AIGC从三个不同层次为内容产业赋能
基本面和新题材共振,推动传媒互联网行情上涨 AIGC 概念带动,传媒板块领涨 A 股 2023 年第一个交易日(1 月 3 日)至 6 月 2 日,申万传媒指数区间涨幅高达 48.38%,同时期沪深 300 跌幅为 0.25%,…...

iOS上架App Store的全攻略
iOS上架App Store的全攻略 第一步:申请开发者账号 在开始将应用上架到App Store之前,你需要申请一个开发者账号。 1.1 打开苹果开发者中心网站:https://developer.apple.com/ 1.2 使用Apple ID和密码登录(如果没有账号则需要注册…...
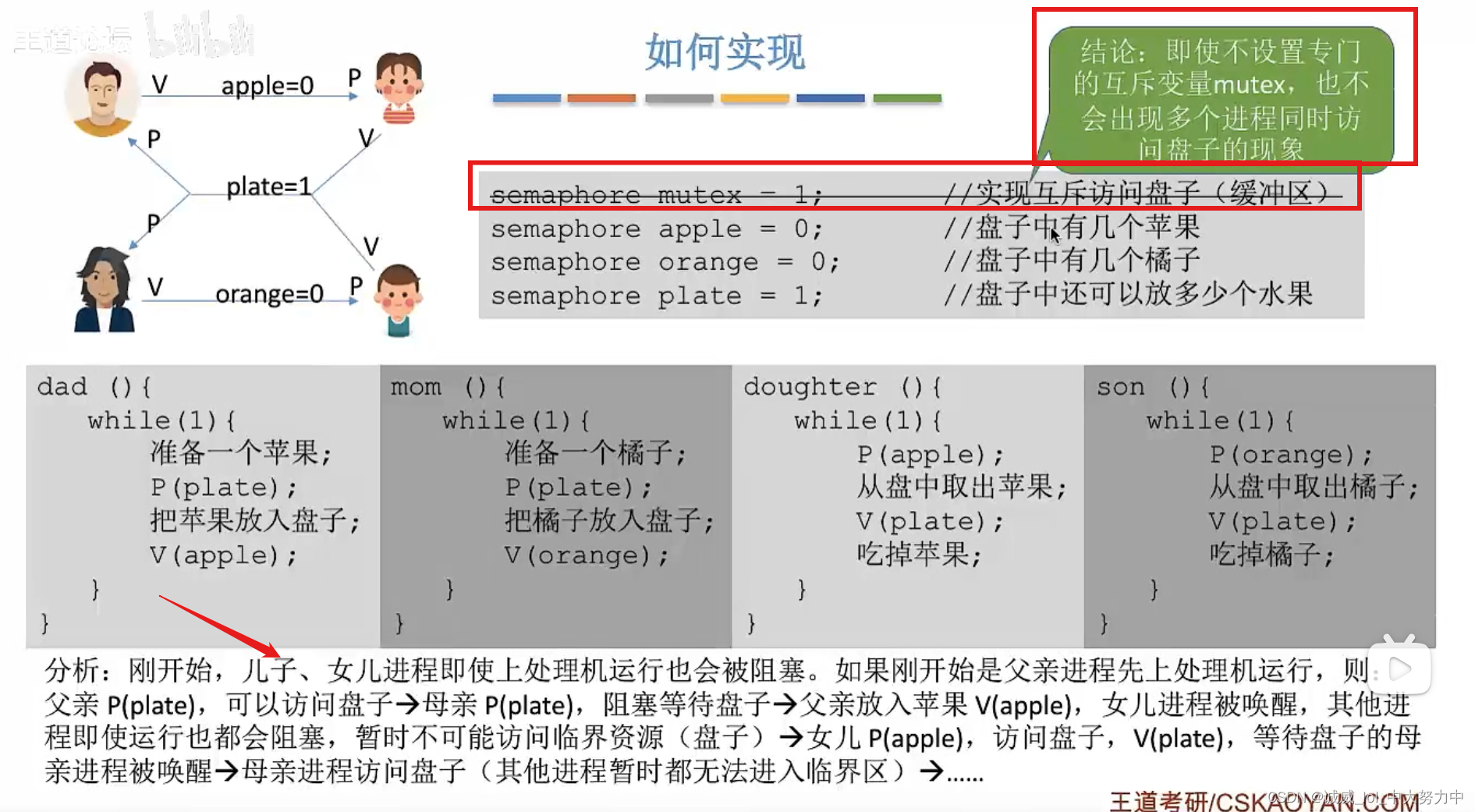
操作系统——多个类别产品的生产者-消费者问题(王道视频p33、课本ch6)
1.问题解剖——得到的是 1个“互斥信号量” 3个“同步信号量” 其中特别注意,对于盘子plate可以清空的设计4个对象的,但是只用这一个同步信号量就可以实现 2.代码—— 3.由于这里的同步信号量的初值都是1,所以,即使不设置互斥信…...
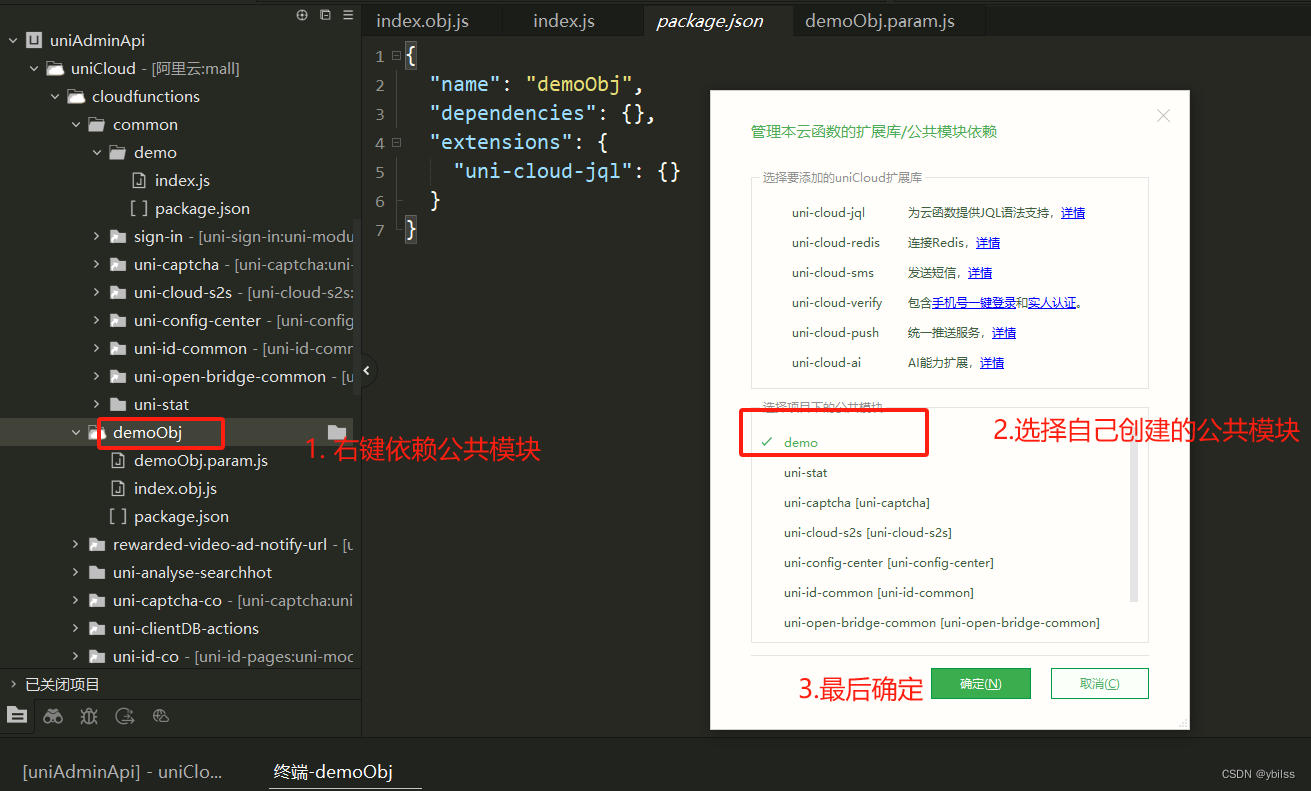
uniapp(uncloud) 使用生态开发接口详情5(云公共模块)
1.uniCloud官网 云对象中云公共模块: 网站: https://uniapp.dcloud.net.cn/uniCloud/cf-common.html // 官网介绍 cloudfunctions├─common // 云函数公用模块目录| └─hello-common // 云函数公用模块| ├─package.json| └─index.js // 公用模块代码࿰…...
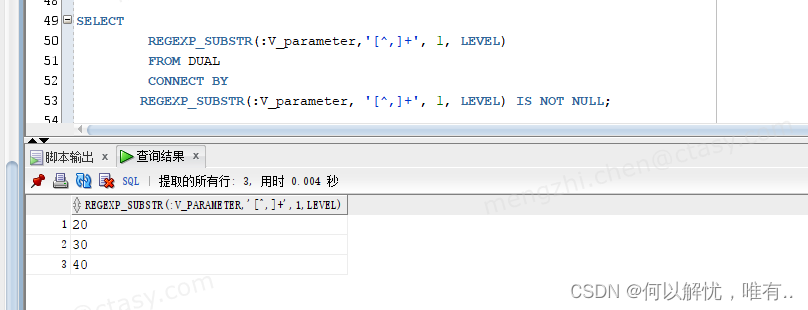
Oracle数据中如何在 where in() 条件传参
一、问题场景描述 在sql 条件中,如何在 where in()中想传入参数,如果直接 where in(:seqList),当传入单个值,seqList: ‘80’ 是没问题的,但是初入多个值时,seqList: ‘80,90’ ,因缺少单引号&…...

Python:函数篇(每周练习)
编程题: Python第四章作业(初级) (educoder.net) 题一:无参无返回值函数 def print_hi_human(): # 函数名用小写字母print("人类,你好!")if __name__ __main__:print_hi_human() 题二&#…...

为Element Plus封装业务组件FormDialog,将所有需要填写表单的弹窗组件封装,方便快速配置
使用FormDialog组件能够对表单弹窗进行快速配置,不用每次单独写弹窗表单业务组件,快速实现表单弹窗业务功能。 调用页面demo.vue validateRules.js引用 <script setup lang"ts"> import FormDialog from /components/FormDialog/index…...

ubuntu 设置和取消代理
背景 因为国内环境限制,在 linux 上安装一些软件的时候,因为限制就安装不了, 此时就可以通过设置代理的方式来规避这种问题,下面是具体的设置方式 步骤 sudo vim /etc/profile.d/proxy.sh添加以下内容到文件中 export http_pro…...
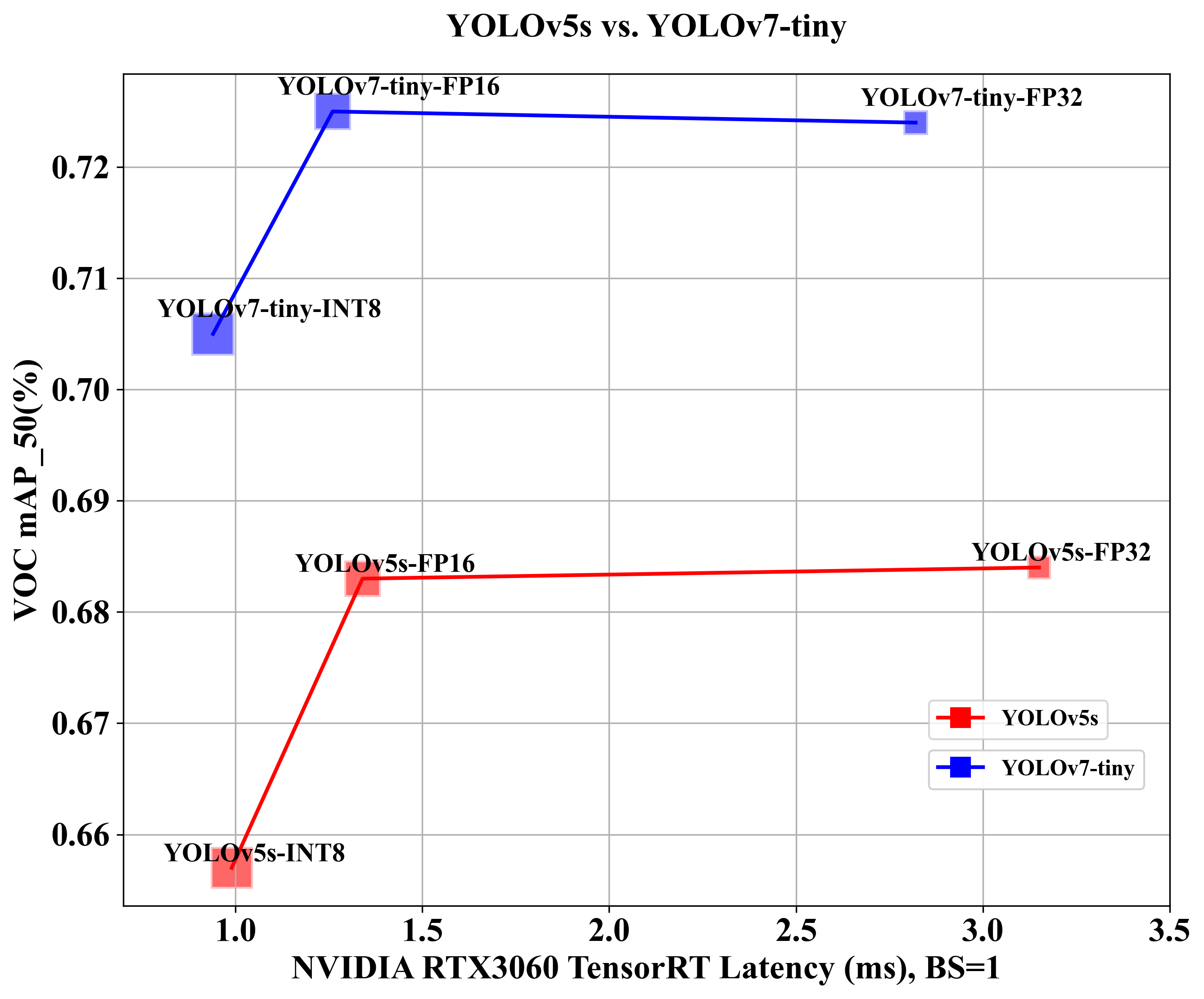
YOLOv7-PTQ量化部署
目录 前言一、PTQ量化浅析二、YOLOv7模型训练1. 项目的克隆和必要的环境依赖1.1 项目的克隆1.2 项目代码结构整体介绍1.3 环境安装 2. 数据集和预训练权重的准备2.1 数据集2.2 预训练权重准备 3. 训练模型3.1 修改模型配置文件3.2 修改数据配置文件3.3 训练模型3.4 mAP测试 三、…...
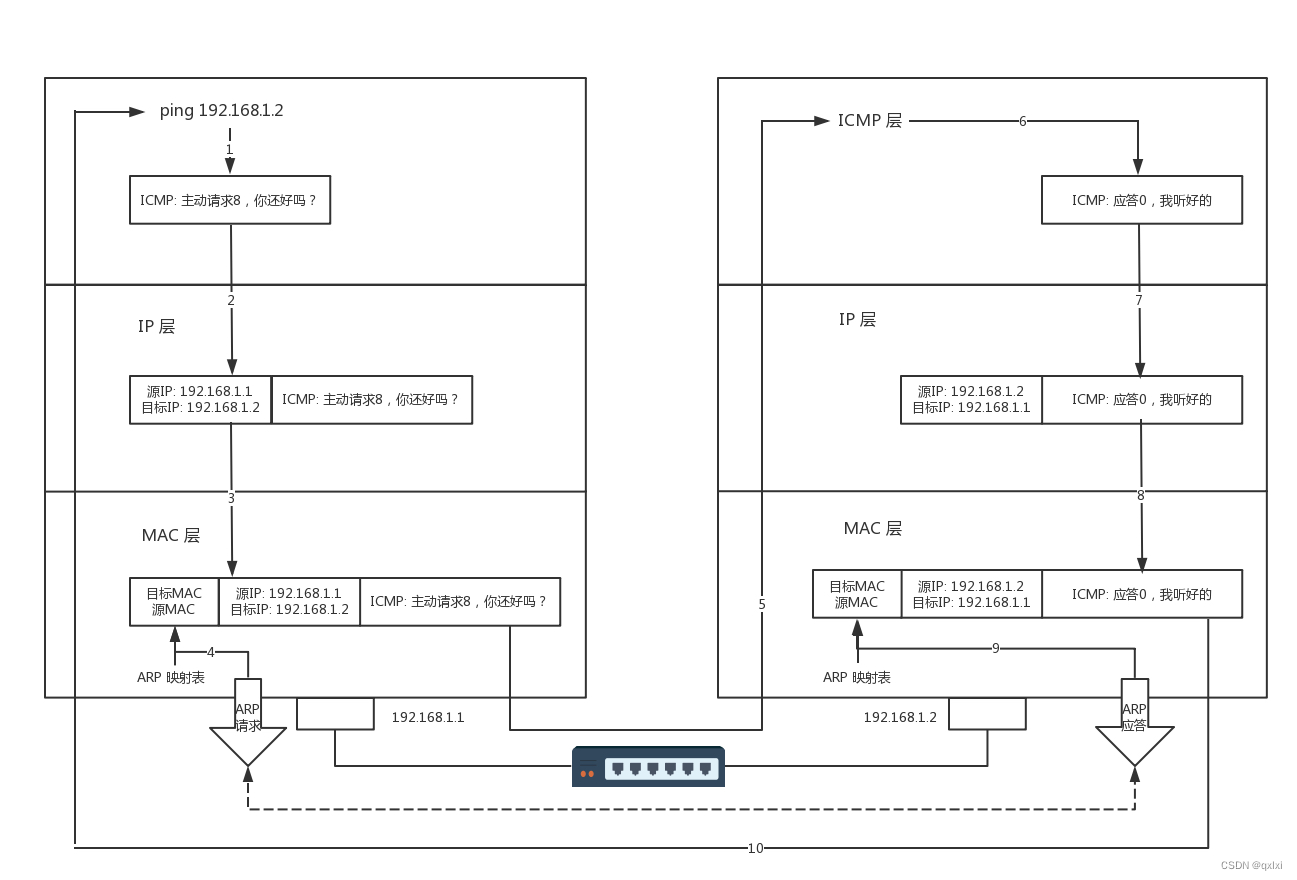
【网络协议】聊聊ICMP与ping是如何测试网络联通性
ICMP协议格式 ping是基于iCMP协议工作的,ICMP全称Internet Control Message Protocol,就是互联网控制报文协议。其实就是有点类似于古代行军打仗,哨探进行前方探明具体情况。 IMCP本身处于网络层,将报文封装在IP包里,…...

nginx tomcat 动静分离
动静分离: 访问静态和动态页面分开 实现动态和静态页面负载均衡。 五台虚拟机 实验1,动静分离 思路: 需要设备:三台虚拟机 一台nginx 代理又是静态 两台tomcat 请求动态页面 在全局模块中配置upstream tomcat 新建location…...

java读取指定文件夹下的全部文件,并输出文件名,文件大小,文件创建时间
import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.file.*; import java.nio.file.attribute.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Path startingDir Paths.get("你的目…...

leetcode 105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
2023.10.21 本题需要根据前序遍历序列和中序遍历序列来构造出一颗二叉树。类似于从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 。使用递归, java代码如下: /*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* …...

【试题039】 多个逻辑或例题
题目:设int n;,执行表达式(n0)||(n1)||(n2)||(n3)后,n的值是?代码分析: //设int n; , 执行表达式(n 0) || (n 1) ||(n 2) ||(n 3)后, n的值是?int n;printf("n%d\n", (n 0) || (n 1) || (n 2) || (n 3));//分析࿱…...

打卡go学习第一天
8.1 下面展示一些 代码。 package mainimport ("fmt""net""os""time" )type Clock struct {Name stringAddr string } func main() {clocks : []Clock{{Name: "New York", Addr: "localhost:8000"…...

连锁超市冷库节能解决方案:如何实现超市降本增效
在连锁超市冷库运营中,高能耗、设备损耗快、人工管理低效等问题长期困扰企业。御控冷库节能解决方案通过智能控制化霜、按需化霜、实时监控、故障诊断、自动预警、远程控制开关六大核心技术,实现年省电费15%-60%,且不改动原有装备、安装快捷、…...
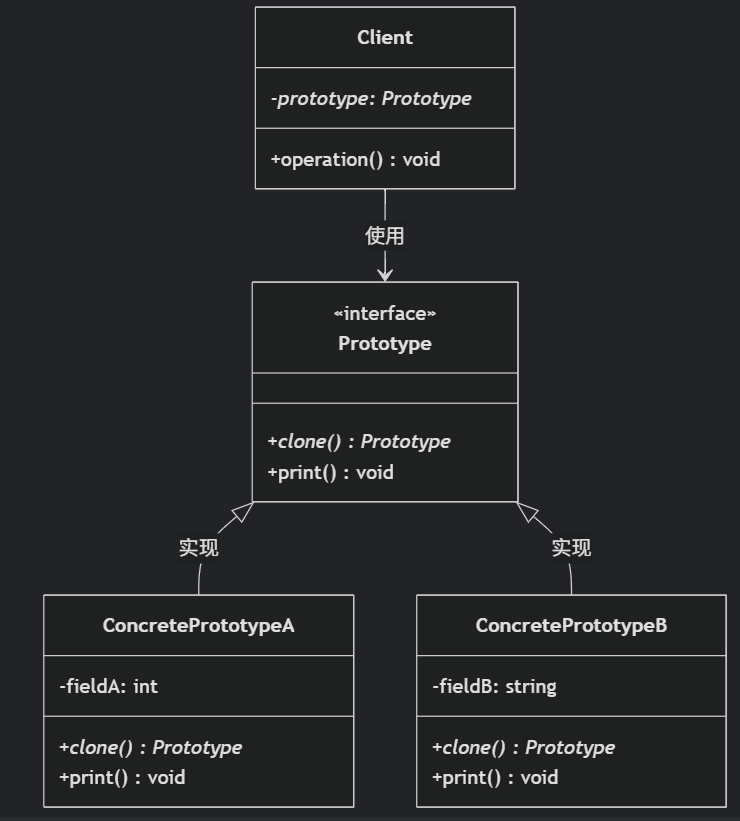
(二)原型模式
原型的功能是将一个已经存在的对象作为源目标,其余对象都是通过这个源目标创建。发挥复制的作用就是原型模式的核心思想。 一、源型模式的定义 原型模式是指第二次创建对象可以通过复制已经存在的原型对象来实现,忽略对象创建过程中的其它细节。 📌 核心特点: 避免重复初…...

页面渲染流程与性能优化
页面渲染流程与性能优化详解(完整版) 一、现代浏览器渲染流程(详细说明) 1. 构建DOM树 浏览器接收到HTML文档后,会逐步解析并构建DOM(Document Object Model)树。具体过程如下: (…...
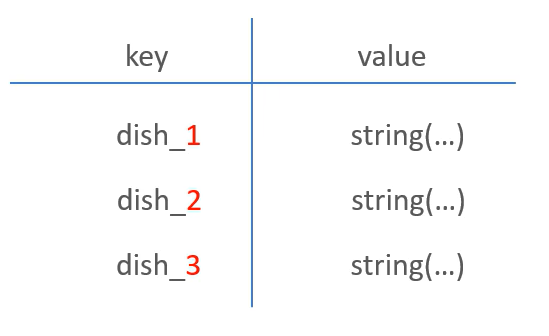
苍穹外卖--缓存菜品
1.问题说明 用户端小程序展示的菜品数据都是通过查询数据库获得,如果用户端访问量比较大,数据库访问压力随之增大 2.实现思路 通过Redis来缓存菜品数据,减少数据库查询操作。 缓存逻辑分析: ①每个分类下的菜品保持一份缓存数据…...

Neo4j 集群管理:原理、技术与最佳实践深度解析
Neo4j 的集群技术是其企业级高可用性、可扩展性和容错能力的核心。通过深入分析官方文档,本文将系统阐述其集群管理的核心原理、关键技术、实用技巧和行业最佳实践。 Neo4j 的 Causal Clustering 架构提供了一个强大而灵活的基石,用于构建高可用、可扩展且一致的图数据库服务…...
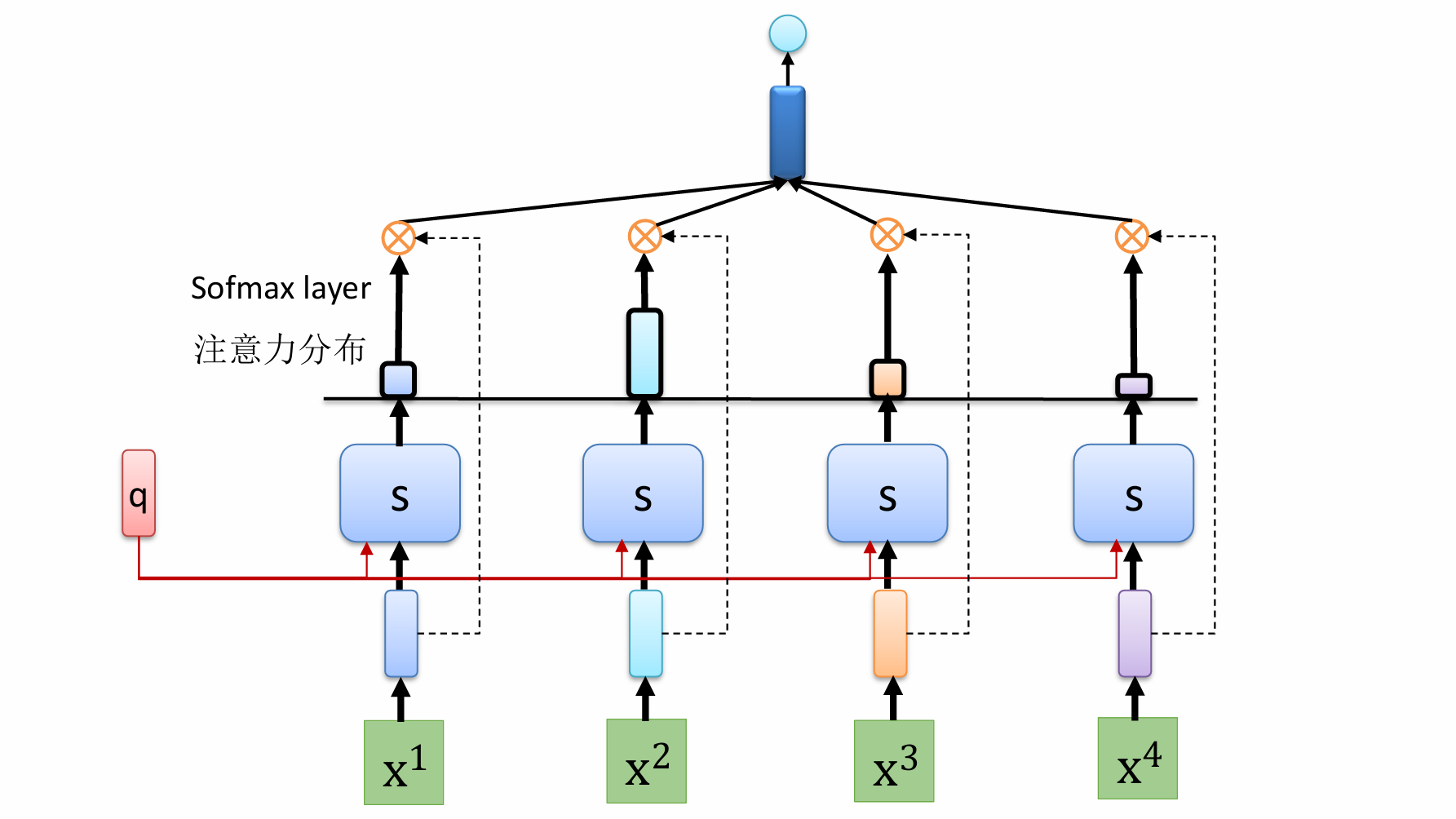
自然语言处理——循环神经网络
自然语言处理——循环神经网络 循环神经网络应用到基于机器学习的自然语言处理任务序列到类别同步的序列到序列模式异步的序列到序列模式 参数学习和长程依赖问题基于门控的循环神经网络门控循环单元(GRU)长短期记忆神经网络(LSTM)…...

ios苹果系统,js 滑动屏幕、锚定无效
现象:window.addEventListener监听touch无效,划不动屏幕,但是代码逻辑都有执行到。 scrollIntoView也无效。 原因:这是因为 iOS 的触摸事件处理机制和 touch-action: none 的设置有关。ios有太多得交互动作,从而会影响…...
)
【HarmonyOS 5 开发速记】如何获取用户信息(头像/昵称/手机号)
1.获取 authorizationCode: 2.利用 authorizationCode 获取 accessToken:文档中心 3.获取手机:文档中心 4.获取昵称头像:文档中心 首先创建 request 若要获取手机号,scope必填 phone,permissions 必填 …...

Java编程之桥接模式
定义 桥接模式(Bridge Pattern)属于结构型设计模式,它的核心意图是将抽象部分与实现部分分离,使它们可以独立地变化。这种模式通过组合关系来替代继承关系,从而降低了抽象和实现这两个可变维度之间的耦合度。 用例子…...
 + 力扣解决)
LRU 缓存机制详解与实现(Java版) + 力扣解决
📌 LRU 缓存机制详解与实现(Java版) 一、📖 问题背景 在日常开发中,我们经常会使用 缓存(Cache) 来提升性能。但由于内存有限,缓存不可能无限增长,于是需要策略决定&am…...
