PyTorch中的intrusive_ptr
PyTorch中的intrusive_ptr
前言
intrusive_ptr與unique_ptr,shared_ptr等一樣,都是smart pointer。但是intrusive_ptr比較特別,它所指向的物件類型必須繼承自intrusive_ptr_target,而intrusive_ptr_target必須實現引用計數相關的函數才行。
在PyTorch中,StorageImpl繼承自c10::intrusive_ptr_target,所以c10::intrusive_ptr可以與StorageImpl搭配使用。
同樣地,TensorImpl也繼承自c10::intrusive_ptr_target,而TensorBase就是透過 c10::intrusive_ptr<TensorImpl, UndefinedTensorImpl> impl_;這個成員變數來存取TensorImpl物件的。
想要循環引用時,如果使用shared_ptr會出現無法析構的問題,我們可以使用weak_ptr來解決。weak_ptr不會增加所指向物件的引用計數,所以從引用計數的角度來看,就不會有deadlock的問題。注意weak_ptr必須搭配shared_ptr來使用。
想要有多個指標指向同一物件時,如果使用shared_ptr會出現重複析構的問題。使用shared_ptr的話,引用計數是儲存在shared_ptr裡;使用intrusive_ptr的話,引用計數是儲存在指向的物件裡,一個物件只有一個引用計數,所以不會有重複析構的問題。
intrusive_ptr的缺點是無法使用weak_ptr,所以不能用在循環引用的場景中。
【C++11新特性】 C++11智能指针之weak_ptr
boost::intrusive_ptr原理介绍
Smart Ptr 一點訣 (1):使用 intrusive_ptr
c10::intrusive_ptr_target
c10/util/intrusive_ptr.h
提供引用計數功能的base class(基類):
class C10_API intrusive_ptr_target {// Note [Weak references for intrusive refcounting]// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~// Here's the scheme://// - refcount == number of strong references to the object// weakcount == number of weak references to the object,// plus one more if refcount > 0// An invariant: refcount > 0 => weakcount > 0//// - c10::StorageImpl stays live as long as there are any strong// or weak pointers to it (weakcount > 0, since strong// references count as a +1 to weakcount)//// - finalizers are called and data_ptr is deallocated when refcount == 0//// - Once refcount == 0, it can never again be > 0 (the transition// from > 0 to == 0 is monotonic)//// - When you access c10::StorageImpl via a weak pointer, you must// atomically increment the use count, if it is greater than 0.// If it is not, you must report that the storage is dead.//mutable std::atomic<size_t> refcount_;mutable std::atomic<size_t> weakcount_;// ...
};
boost::instrusive_ptr在循環引用時會有無法析構的問題,PyTorch中的intrusive_ptr為了避免出現這種情況,被設計成兼具intrusive_ptr和weak_ptr的功能,所以除了refcount_外,還有weakcount_成員變數。
constructors
constexpr intrusive_ptr_target() noexcept : refcount_(0), weakcount_(0) {}// intrusive_ptr_target supports copy and move: but refcount and weakcount// don't participate (since they are intrinsic properties of the memory// location)intrusive_ptr_target(intrusive_ptr_target&& /*other*/) noexcept: intrusive_ptr_target() {}intrusive_ptr_target& operator=(intrusive_ptr_target&& /*other*/) noexcept {return *this;}intrusive_ptr_target(const intrusive_ptr_target& /*other*/) noexcept: intrusive_ptr_target() {}intrusive_ptr_target& operator=(const intrusive_ptr_target& /*other*/) noexcept {return *this;}
destructor
// protected destructor. We never want to destruct intrusive_ptr_target*// directly.virtual ~intrusive_ptr_target() {
// Disable -Wterminate and -Wexceptions so we're allowed to use assertions
// (i.e. throw exceptions) in a destructor.
// We also have to disable -Wunknown-warning-option and -Wpragmas, because
// some other compilers don't know about -Wterminate or -Wexceptions and
// will show a warning about unknown warning options otherwise.
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && !defined(__clang__)
#pragma warning(push)
#pragma warning( \disable : 4297) // function assumed not to throw an exception but does
#else
#pragma GCC diagnostic push
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wpragmas"
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wunknown-warning-option"
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wterminate"
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wexceptions"
#endifTORCH_INTERNAL_ASSERT_DEBUG_ONLY(// Second condition is there to accommodate// unsafe_adapt_non_heap_allocated: since we are doing our own// deallocation in that case, it is correct for each// expected_decref to have happened (some user code tried to// decref and thus free the object, but it didn't happen right// away) or not (no user code tried to free the object, and// now it's getting destroyed through whatever mechanism the// caller of unsafe_adapt_non_heap_allocated wanted to// use). We choose our reference count such that the count// will not dip below INT_MAX regardless.refcount_.load() == 0 || refcount_.load() >= INT_MAX,"Tried to destruct an intrusive_ptr_target that still has intrusive_ptr to it; refcount was ",refcount_.load());TORCH_INTERNAL_ASSERT_DEBUG_ONLY(// See ~intrusive_ptr for optimization that will frequently result in 1// at destruction time.weakcount_.load() == 1 || weakcount_.load() == 0 ||weakcount_.load() == INT_MAX - 1 || weakcount_.load() == INT_MAX,"Tried to destruct an intrusive_ptr_target that still has weak_intrusive_ptr to it");
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && !defined(__clang__)
#pragma warning(pop)
#else
#pragma GCC diagnostic pop
#endif}
c10::raw::intrusive_ptr::incref/decref
用於增加及減少引用計數的函數:
namespace c10 {
// ...namespace raw {namespace intrusive_ptr {// WARNING: Unlike the reclaim() API, it is NOT valid to pass
// NullType::singleton to this function
inline void incref(intrusive_ptr_target* self) {if (self) {detail::atomic_refcount_increment(self->refcount_);}
}// WARNING: Unlike the reclaim() API, it is NOT valid to pass
// NullType::singleton to this function
inline void decref(intrusive_ptr_target* self) {// Let it diec10::intrusive_ptr<intrusive_ptr_target>::reclaim(self);// NB: Caller still has 'self' pointer, but it's now invalid.// If you want more safety, used the actual c10::intrusive_ptr class
}// ...} // namespace intrusive_ptr// ...} // namespace raw} // namespace c10
class C10_API intrusive_ptr_target {// ...friend inline void raw::intrusive_ptr::incref(intrusive_ptr_target* self);// ...
};
(但為何decref不是friend function?)
decref的作用看起來是reset不是把ref count減一?
c10::intrusive_ptr::reclaim
/*** Takes an owning pointer to TTarget* and creates an intrusive_ptr that takes* over ownership. That means the refcount is not increased.* This is the counter-part to intrusive_ptr::release() and the pointer* passed in *must* have been created using intrusive_ptr::release().*/static intrusive_ptr reclaim(TTarget* owning_ptr) {TORCH_INTERNAL_ASSERT_DEBUG_ONLY(owning_ptr == NullType::singleton() ||owning_ptr->refcount_.load() == 0 || owning_ptr->weakcount_.load(),"TTarget violates the invariant that refcount > 0 => weakcount > 0");return intrusive_ptr(owning_ptr, raw::DontIncreaseRefcount{});}
c10::StorageImpl
c10/core/StorageImpl.h
繼承自c10::intrusive_ptr_target的具體功能類:
struct C10_API StorageImpl : public c10::intrusive_ptr_target {//...
};
接下來看看c10::intrusive_ptr_target是怎麼與c10::intrusive_ptr搭配使用的。
使用案例一
at::detail::_empty_generic
aten/src/ATen/EmptyTensor.cpp
先來看看在aten/src/ATen/EmptyTensor.cpp 的at::detail::_empty_generic函數中intrusive_ptr是如何被使用的:
auto storage_impl = c10::make_intrusive<StorageImpl>(c10::StorageImpl::use_byte_size_t(),size_bytes,allocator,/*resizeable=*/true);
可以看到它呼叫了c10::make_intrusive,並以StorageImpl為模板參數,且傳入四個參數(這四個參數是StorageImpl建構子所需的)。
c10::make_intrusive
c10/util/intrusive_ptr.h
template <class TTarget,class NullType = detail::intrusive_target_default_null_type<TTarget>,class... Args>
inline intrusive_ptr<TTarget, NullType> make_intrusive(Args&&... args) {return intrusive_ptr<TTarget, NullType>::make(std::forward<Args>(args)...);
}
模板參數TTarget是StorageImpl,傳入四個型別分別為use_byte_size_t, SymInt size_bytes, at::Allocator*, bool的參數。
c10::intrusive_ptr::make
c10/util/intrusive_ptr.h
/*** Allocate a heap object with args and wrap it inside a intrusive_ptr and* incref. This is a helper function to let make_intrusive() access private* intrusive_ptr constructors.*/template <class... Args>static intrusive_ptr make(Args&&... args) {return intrusive_ptr(new TTarget(std::forward<Args>(args)...));}
模板參數TTarget是StorageImpl,這裡會將四個型別分別為use_byte_size_t, SymInt size_bytes, at::Allocator*, bool的參數接力傳給TTarget建構子。
此處透過new TTarget得到StorageImpl物件指標後,會接著呼叫intrusive_ptr的建構子。
c10::intrusive_ptr constructor
c10/util/intrusive_ptr.h
// raw pointer constructors are not public because we shouldn't make// intrusive_ptr out of raw pointers except from inside the make_intrusive(),// reclaim() and weak_intrusive_ptr::lock() implementations.// This constructor will increase the ref counter for you.// This constructor will be used by the make_intrusive(), and also pybind11,// which wrap the intrusive_ptr holder around the raw pointer and incref// correspondingly (pybind11 requires raw pointer constructor to incref by// default).explicit intrusive_ptr(TTarget* target): intrusive_ptr(target, raw::DontIncreaseRefcount{}) {if (target_ != NullType::singleton()) {// We just created result.target_, so we know no other thread has// access to it, so we know we needn't care about memory ordering.// (On x86_64, a store with memory_order_relaxed generates a plain old// `mov`, whereas an atomic increment does a lock-prefixed `add`, which is// much more expensive: https://godbolt.org/z/eKPzj8.)TORCH_INTERNAL_ASSERT_DEBUG_ONLY(target_->refcount_ == 0 && target_->weakcount_ == 0,"intrusive_ptr: Newly-created target had non-zero refcounts. Does its ""constructor do something strange like incref or create an ""intrusive_ptr from `this`?");target_->refcount_.store(1, std::memory_order_relaxed);target_->weakcount_.store(1, std::memory_order_relaxed);}}
接著調用同一個檔案下不同簽名的constructor:
// This constructor will not increase the ref counter for you.// We use the tagged dispatch mechanism to explicitly mark this constructor// to not increase the refcountexplicit intrusive_ptr(TTarget* target, raw::DontIncreaseRefcount) noexcept: target_(target) {}
做的事情實際上就只是更新TTarget*類型的成員變數target_。成員變數如下:
TTarget* target_;
在intrusive_ptr的類別宣告中有下面這麼一段注釋:
// the following static assert would be nice to have but it requires
// the target class T to be fully defined when intrusive_ptr<T> is instantiated
// this is a problem for classes that contain pointers to themselves
// static_assert(
// std::is_base_of<intrusive_ptr_target, TTarget>::value,
// "intrusive_ptr can only be used for classes that inherit from
// intrusive_ptr_target.");
這裡說明TTarget必須繼承自intrusive_ptr_target。
到c10/core/StorageImpl.h中檢查一下StorageImpl是否符合這個條件:
struct C10_API StorageImpl : public c10::intrusive_ptr_target {//...
};
使用案例二
c10::Storage constructor
torch/include/c10/core/Storage.h
c10/core/Storage.h
struct C10_API Storage {// ...Storage(c10::intrusive_ptr<StorageImpl> ptr): storage_impl_(std::move(ptr)) {}// ...protected:c10::intrusive_ptr<StorageImpl> storage_impl_;
}
Storage類別有一個成員變數storage_impl_,是經intrusive_ptr包裝過後的StorageImpl。記得我們之前看過StorageImpl是c10::intrusive_ptr_target的子類別,這也印證了剛才所說intrusive_ptr必須搭配intrusive_ptr_target使用的規定。
注意到這裡初始化storage_impl_時用到了std::move,也就是調用了c10::intrusive_ptr的move constructor。
c10::intrusive_ptr move constructor
c10/util/intrusive_ptr.h
c10::intrusive_ptr的move constructor如下。把rhs的target_佔為己有後,將rhs.target_設為空:
intrusive_ptr(intrusive_ptr&& rhs) noexcept : target_(rhs.target_) {rhs.target_ = NullType::singleton();}
下面這種move constructor支援不同類型的rhs,並多了相應的類型檢查功能,如果模板參數From可以被轉換成TTarget*(也就是target_的型別)才算成功:
template <class From, class FromNullType>/* implicit */ intrusive_ptr(intrusive_ptr<From, FromNullType>&& rhs) noexcept: target_(detail::assign_ptr_<TTarget, NullType, FromNullType>(rhs.target_)) {static_assert(std::is_convertible<From*, TTarget*>::value,"Type mismatch. intrusive_ptr move constructor got pointer of wrong type.");rhs.target_ = FromNullType::singleton();}
至於為何要使用move constructor呢?
根據Why would I std::move an std::shared_ptr?:
std::shared_ptr reference count is atomic. increasing or decreasing the reference count requires atomic increment or decrement. This is hundred times slower than non-atomic increment/decrement, not to mention that if we increment and decrement the same counter we wind up with the exact number, wasting a ton of time and resources in the process.By moving the shared_ptr instead of copying it, we "steal" the atomic reference count and we nullify the other shared_ptr. "stealing" the reference count is not atomic, and it is hundred times faster than copying the shared_ptr (and causing atomic reference increment or decrement).
如果使用copy constructor的話,就需要atomic地增/減smart pointer的引用計數,而這個操作是十分耗時的,改用move constructor就可以免去這個atomic操作,節省大量時間。
demo
#include <torch/torch.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <memory> //shared_ptr
#include <boost/intrusive_ptr.hpp>
#include <boost/detail/atomic_count.hpp> // boost::detail::atomic_count
#include <boost/checked_delete.hpp> // boost::checked_delete#define use_weak// #define use_shared
// #define use_boost
#define use_c10#ifdef use_c10
#define smart_ptr c10::intrusive_ptr
#define make_ptr c10::make_intrusive
#define weak_smart_ptr c10::weak_intrusive_ptr
#elif defined(use_boost)
#define smart_ptr boost::intrusive_ptr
#elif defined(use_shared)
#define smart_ptr std::shared_ptr
#define make_ptr std::make_shared
#define weak_smart_ptr std::weak_ptr
#endif#ifdef use_boost
template<class T>
class intrusive_ptr_base {
public:/*** 缺省构造函数*/intrusive_ptr_base(): ref_count(0) {// std::cout << "intrusive_ptr_base default constructor" << std::endl;}/*** 不允许拷贝构造,只能使用intrusive_ptr来构造另一个intrusive_ptr*/intrusive_ptr_base(intrusive_ptr_base<T> const&): ref_count(0) {std::cout << "intrusive_ptr_base copy constructor" << std::endl;}~intrusive_ptr_base(){std::cout << "intrusive_ptr_base destructor" << std::endl;}/*** 不允许进行赋值操作*/intrusive_ptr_base& operator=(intrusive_ptr_base const& rhs) {std::cout << "Assignment operator" << std::endl;return *this;}/*** 递增引用计数(放到基类中以便compiler能找到,否则需要放到boost名字空间中)*/friend void intrusive_ptr_add_ref(intrusive_ptr_base<T> const* s) {std::cout << "intrusive_ptr_base add ref" << std::endl;assert(s->ref_count >= 0);assert(s != 0);++s->ref_count;}/*** 递减引用计数*/friend void intrusive_ptr_release(intrusive_ptr_base<T> const* s) {std::cout << "intrusive_ptr_base release" << std::endl;assert(s->ref_count > 0);assert(s != 0);if (--s->ref_count == 0)boost::checked_delete(static_cast<T const*>(s)); //s的实际类型就是T,intrusive_ptr_base<T>为基类}/*** 类似于shared_from_this()函数*/boost::intrusive_ptr<T> self() {return boost::intrusive_ptr<T>((T*)this);}boost::intrusive_ptr<const T> self() const {return boost::intrusive_ptr<const T>((T const*)this);}int refcount() const {return ref_count;}private:///should be modifiable even from const intrusive_ptr objectsmutable boost::detail::atomic_count ref_count;};
#endif#ifdef use_c10
class MyVector : public c10::intrusive_ptr_target {
#elif defined(use_boost)
class MyVector : public intrusive_ptr_base<MyVector> {
#elif defined(use_shared)
class MyVector {
#endif
public:MyVector(const std::vector<int>& d) : data(d) {std::cout << "MyVector constructor" << std::endl;}~MyVector() {std::cout << "MyVector destructor" << std::endl;}std::vector<int> data;
};class A;
class B;#ifdef use_c10
class A : public c10::intrusive_ptr_target {
#elif defined(use_boost)
class A : public intrusive_ptr_base<A> {
#elif defined(use_shared)
class A {
#endif
public:A() {// std::cout << "A constructor" << std::endl;}~A() {std::cout << "A destructor" << std::endl;}#ifdef use_weakweak_smart_ptr<B> pointer;
#elsesmart_ptr<B> pointer;
#endif
};#ifdef use_c10
class B : public c10::intrusive_ptr_target {
#elif defined(use_boost)
class B : public intrusive_ptr_base<B> {
#elif defined(use_shared)
class B {
#endif
public:B() {// std::cout << "B constructor" << std::endl;}~B() {std::cout << "B destructor" << std::endl;}#ifdef use_weakweak_smart_ptr<A> pointer;
#elsesmart_ptr<A> pointer;
#endif
};int main() {{// 循環引用std::cout << "Circular reference" << std::endl;
#if defined(use_c10)smart_ptr<A> a_ptr = make_ptr<A>();smart_ptr<B> b_ptr = make_ptr<B>();
#elseA* a_raw_ptr = new A();B* b_raw_ptr = new B();std::cout << "Create A's smart pointer" << std::endl;smart_ptr<A> a_ptr(a_raw_ptr);std::cout << "Create B's smart pointer" << std::endl;smart_ptr<B> b_ptr(b_raw_ptr);
#endif#if !defined(use_boost)std::cout << "A ref count: " << a_ptr.use_count() << std::endl;std::cout << "B ref count: " << b_ptr.use_count() << std::endl;
#elsestd::cout << "A ref count: " << a_ptr->refcount() << std::endl;std::cout << "B ref count: " << b_ptr->refcount() << std::endl;
#endifstd::cout << "A's smart pointer references to B" << std::endl;a_ptr->pointer = b_ptr;std::cout << "B's smart pointer references to A" << std::endl;b_ptr->pointer = a_ptr;#if !defined(use_boost)std::cout << "A ref count: " << a_ptr.use_count() << std::endl;std::cout << "B ref count: " << b_ptr.use_count() << std::endl;
#elsestd::cout << "A ref count: " << a_ptr->refcount() << std::endl;std::cout << "B ref count: " << b_ptr->refcount() << std::endl;
#endif// shared_ptr, boost::intrusive_ptr: 引用計數都由1變成2,最後destructor不會被調用}std::cout << std::endl;{// 多指標指向同一物件std::cout << "Multiple smart pointer point to the same object" << std::endl;std::vector<int> vec({1,2,3});MyVector* raw_ptr = new MyVector(vec);smart_ptr<MyVector> ip, ip2;
#if defined(use_c10)std::cout << "Create 1st smart pointer" << std::endl;ip.reclaim(raw_ptr);// 無法用一個refcount非0的raw pointer創建c10::intrusive_ptr// std::cout << "Create 2nd smart pointer" << std::endl;// ip2.reclaim(raw_ptr);/*terminate called after throwing an instance of 'c10::Error'what(): owning_ptr == NullType::singleton() || owning_ptr->refcount_.load() == 0 || owning_ptr->weakcount_.load() INTERNAL ASSERT FAILED at "/root/Documents/installation/libtorch/include/c10/util/intrusive_ptr.h":471, please report a bug to PyTorch. TTarget violates the invariant that refcount > 0 => weakcount > 0Exception raised from reclaim at /root/Documents/installation/libtorch/include/c10/util/intrusive_ptr.h:471 (most recent call first):*/
#elsestd::cout << "Create 1st smart pointer" << std::endl;ip = smart_ptr<MyVector>(raw_ptr);std::cout << "Create 2nd smart pointer" << std::endl;ip2 = smart_ptr<MyVector>(raw_ptr);
#endif// shared_ptr: MyVector的destructor會被調用兩次,會出現Segmentation fault (core dumped)// boost::intrusive_ptr: 最後destructor會被調用}return 0;
}
rm -rf * && cmake -DCMAKE_PREFIX_PATH="<libtorch_installation_path>;<boost_installation_path>" .. && make && ./intrusive_ptr
循環引用
std::shared_ptr
Circular reference
Create A's smart pointer
Create B's smart pointer
A ref count: 1
B ref count: 1
A's smart pointer references to B
B's smart pointer references to A
A ref count: 2
B ref count: 2
改用std::weak_ptr
Circular reference
Create A's smart pointer
Create B's smart pointer
A ref count: 1
B ref count: 1
A's smart pointer references to B
B's smart pointer references to A
A ref count: 1
B ref count: 1
B destructor
A destructor
如果將A和B的成員改成std::weak_ptr,在循環引用後它們的reference count不會增加,並且在離開scope後A跟B的destructor都會被調用。
boost::intrusive_ptr
Circular reference
Create A's smart pointer
intrusive_ptr_base add ref
Create B's smart pointer
intrusive_ptr_base add ref
A ref count: 1
B ref count: 1
A's smart pointer references to B
intrusive_ptr_base add ref
B's smart pointer references to A
intrusive_ptr_base add ref
A ref count: 2
B ref count: 2
intrusive_ptr_base release
intrusive_ptr_base release
c10::intrusive_ptr
Circular reference
A ref count: 1
B ref count: 1
A's smart pointer references to B
B's smart pointer references to A
A ref count: 2
B ref count: 2
如果改用c10::weak_intrusive_ptr,因為它沒有default constructor,會出現以下錯誤:
error: no matching function for call to 'c10::weak_intrusive_ptr<B>::wea
k_intrusive_ptr()'
多指標指向同一物件
std::shared_ptr
Multiple smart pointer point to the same object
MyVector constructor
Create 1st smart pointer
Create 2nd smart pointer
MyVector destructor
MyVector destructor
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
boost::intrusive_ptr
Multiple smart pointer point to the same object
MyVector constructor
Create 1st smart pointer
intrusive_ptr_base add ref
Create 2nd smart pointer
intrusive_ptr_base add ref
intrusive_ptr_base release
intrusive_ptr_base release
MyVector destructor
intrusive_ptr_base destructor
c10::intrusive_ptr
Multiple smart pointer point to the same object
MyVector constructor
Create 1st smart pointer
相关文章:

PyTorch中的intrusive_ptr
PyTorch中的intrusive_ptr 前言 intrusive_ptr與unique_ptr,shared_ptr等一樣,都是smart pointer。但是intrusive_ptr比較特別,它所指向的物件類型必須繼承自intrusive_ptr_target,而intrusive_ptr_target必須實現引用計數相關的…...

webrtc-stream编译报错记录
磁盘空间不足错误 错误信息 677.2 fatal: cannot create directory at blink/web_tests/external/wpt: No space left on device说明:这个错误是由于本地在配置docker资源时所给磁盘空间太小导致,直接根据镜像大小合理分配资源大小即可 pushd和popd执…...

什么是Docker CLI
Docker CLI(命令行界面)是一个工具,允许用户通过命令行或终端与Docker进行交互。Docker是一个开源平台,用于开发、运送和运行应用程序。Docker使用容器化技术来打包应用程序及其依赖项,以确保在不同环境中的一致性和隔…...

Java项目_家庭记账(简易版)
文章目录 简介代码实现 简介 该项目主要用来练习,Java的变量,运算符,分支结构和循环结构的知识点。 程序界面如下: 登记收入 登记支出 收支明细 程序退出 代码实现 package project;import java.util.Scanner;import sta…...

vscode json文件添加注释报错
在vscode中创建json文件,想要注释一波时,发现报了个错:Comments are not permitted in JSON. (521),意思是JSON中不允许注释 以下为解决方法: 在vscode的右下角中找到这个,点击 在出现的弹窗中输入json wit…...

vue3移动端嵌入pdf的两种办法
1.使用embed嵌入 好处:简单,代码量少,功能齐全 缺点:有固定样式,难以修改,不可定制 <embed class"embedPdf" :src"pdfurl" type"application/pdf">2.使用vue-pdf-e…...

中文编程开发语言工具系统化教程初级1上线
中文编程系统化教程初级1 学习编程捷径:(不论是正在学习编程的大学生,还是IT人士或者是编程爱好者,在学习编程的过程中用正确的学习方法 可以达到事半功倍的效果。对于初学者,可以通过下面的方法学习编程,…...

零售数据分析模板分享(通用型)
零售数据来源多,数据量大,导致数据的清洗整理工作量大,由于零售的特殊性,其指标计算组合更是多变,进一步导致了零售数据分析工作量激增,往往很难及时分析数据,发现问题。那怎么办?可…...
Spring Cloud之微服务
目录 微服务 微服务架构 微服务架构与单体架构 特点 框架 总结 SpringCloud 常用组件 与SpringBoot关系 版本 微服务 微服务:从字面上理解即:微小的服务; 微小:微服务体积小,复杂度低,一个微服…...
之date)
Linux命令(104)之date
linux命令之date 1.date介绍 linux命令date用来设置和显示系统日期和时间 2.date用法 date [参数] date参数 参数说明-s修改并设置时间-d可以显示以前和未来的时间%H小时%M分钟%S秒%X等价于%H %M %S%F显示当前所有时间属性%Y完整年份%m月%d日%A星期的全称 3.实例 3.1.当前…...
微信小程序投票管理系统:打造智能、便捷的投票体验
前言 随着社交网络的兴起和移动互联网的普及,人们对于参与和表达意见的需求越来越强烈。在这个背景下,微信小程序投票管理系统应运而生。它为用户提供了一个智能、便捷的投票平台,使用户可以轻松创建和参与各种类型的投票活动。本文将详细介…...
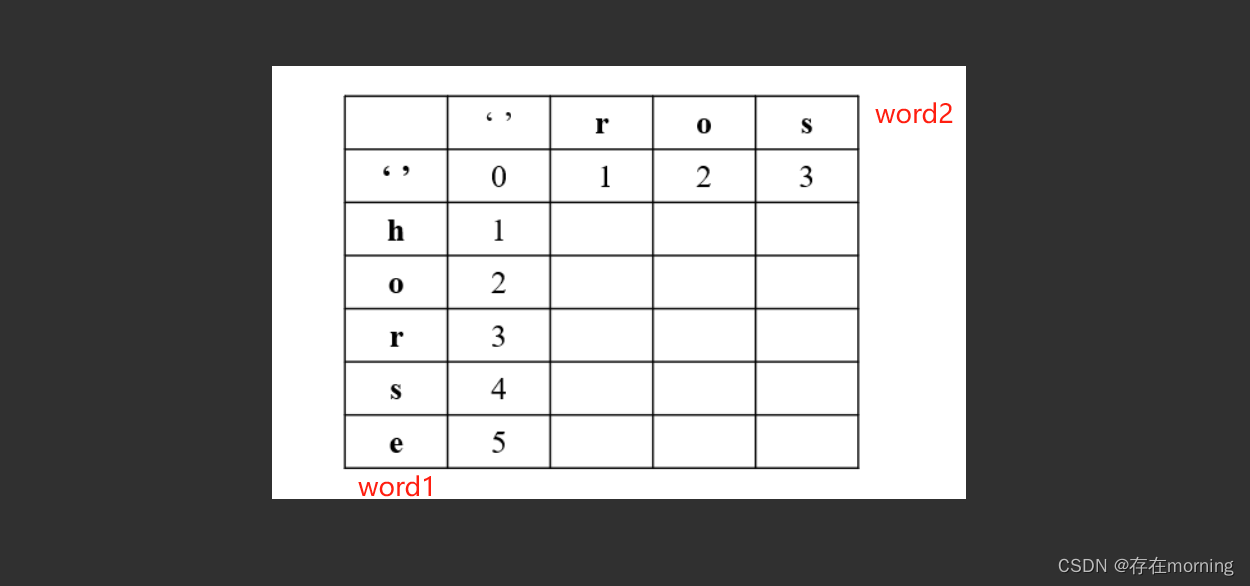
【算法训练-动态规划 五】【二维DP问题】编辑距离
废话不多说,喊一句号子鼓励自己:程序员永不失业,程序员走向架构!本篇Blog的主题是【动态规划】,使用【数组】这个基本的数据结构来实现,这个高频题的站点是:CodeTop,筛选条件为&…...
Windows电脑如何录制电脑桌面?
如果你使用的电脑是Windows系统,那你是不是想知道如何在Windows电脑上录制电脑桌面? 本文以win10为例,好消息是,Windows 10电脑自带录屏工具,你可以直接使用此录屏工具轻松录制视频,而无需下载其他第三方软…...
ubuntu18.04双系统安装(2023最新最详细)以及解决重启后发现进不了Ubuntu问题
目录 一.简介 二.安装教程 1.首先确定了电脑的引导格式是UEFIGPT还是BIOSMBR 2. 使用Windows磁盘管理划分足够的磁盘空间 3. 开始安装 三.重启后发现自动进入WIN10系统了,进不了Ubuntu? 一.简介 Linux是一种自由和开放源代码的操作系统内核&#x…...

Springboot + screw 数据库快速开发文档
1、方式1 引入依赖 <dependency><groupId>cn.smallbun.screw</groupId><artifactId>screw-core</artifactId><version>1.0.5</version></dependency> /*** 文档生成 Springboot2.X screw数据库快速开发文档(74&…...

2 第一个Go程序
概述 在上一节的内容中,我们介绍了Go的前世今生,包括:Go的诞生、发展历程、特性和应用领域。从本节开始,我们将正式学习Go语言。Go语言是一种编译型语言,也就是说,Go语言在运行之前需要先进行编译ÿ…...

Leetcode—2678.老人的数目【简单】
2023每日刷题(八) Leetcode—2678.老人的数目 int countSeniors(char ** details, int detailsSize){ int ans 0; int i; int tens 0; int ones 0; for(i 0; i < detailsSize; i) { tens ((details i) 11) - ‘0’; ones ((details i) 12)…...
解决 /bin/bash^M: bad interpreter: No such file or directory
问题描述 linux 系统中知行*.sh 文件报/bin/bash^M: bad interpreter: No such file or directory 原因: .sh文件是在windows系统编写的,在linux执行就有问题 解决过程 转化下格式执行如下命令 # dos2unix app.sh 结果bash: dos2unix: command not …...
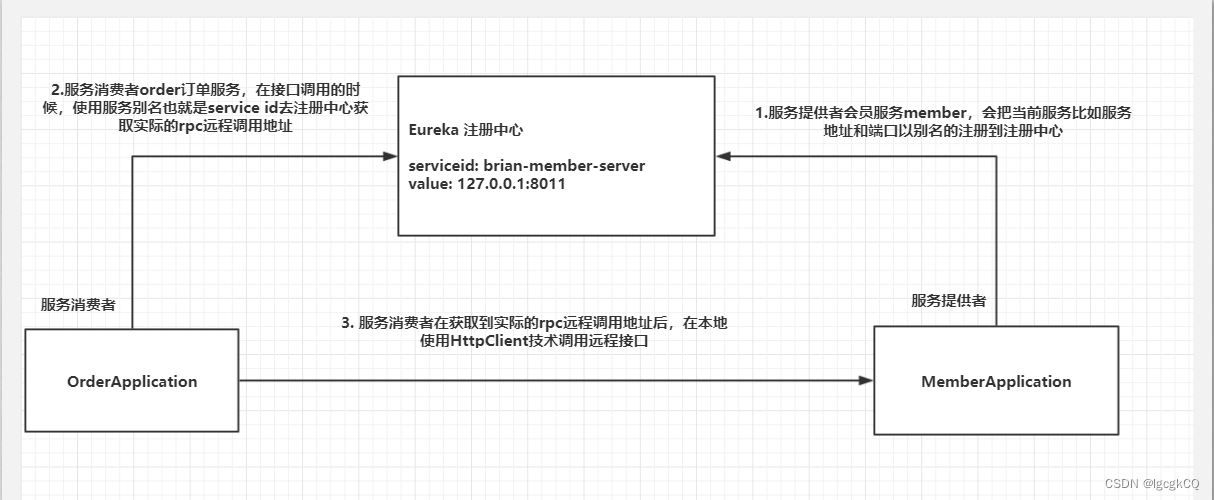
Spring Cloud之服务注册与发现(Eureka)
目录 Eureka 介绍 角色 实现流程 单机构建 注册中心 服务提供者 服务消费者 集群搭建 注册中心 服务提供者 自我保护机制 原理分析 Eureka 介绍 Eureka是spring cloud中的一个负责服务注册与发现的组件,本身是基于REST的服务,同时还提供了…...
Rust-后端服务调试入坑记
这篇文章收录于Rust 实战专栏。这个专栏中的相关代码来自于我开发的笔记系统。它启动于是2023年的9月14日。相关技术栈目前包括:Rust,Javascript。关注我,我会通过这个项目的开发给大家带来相关实战技术的分享。 如果你关注过我的Rust 实战里…...
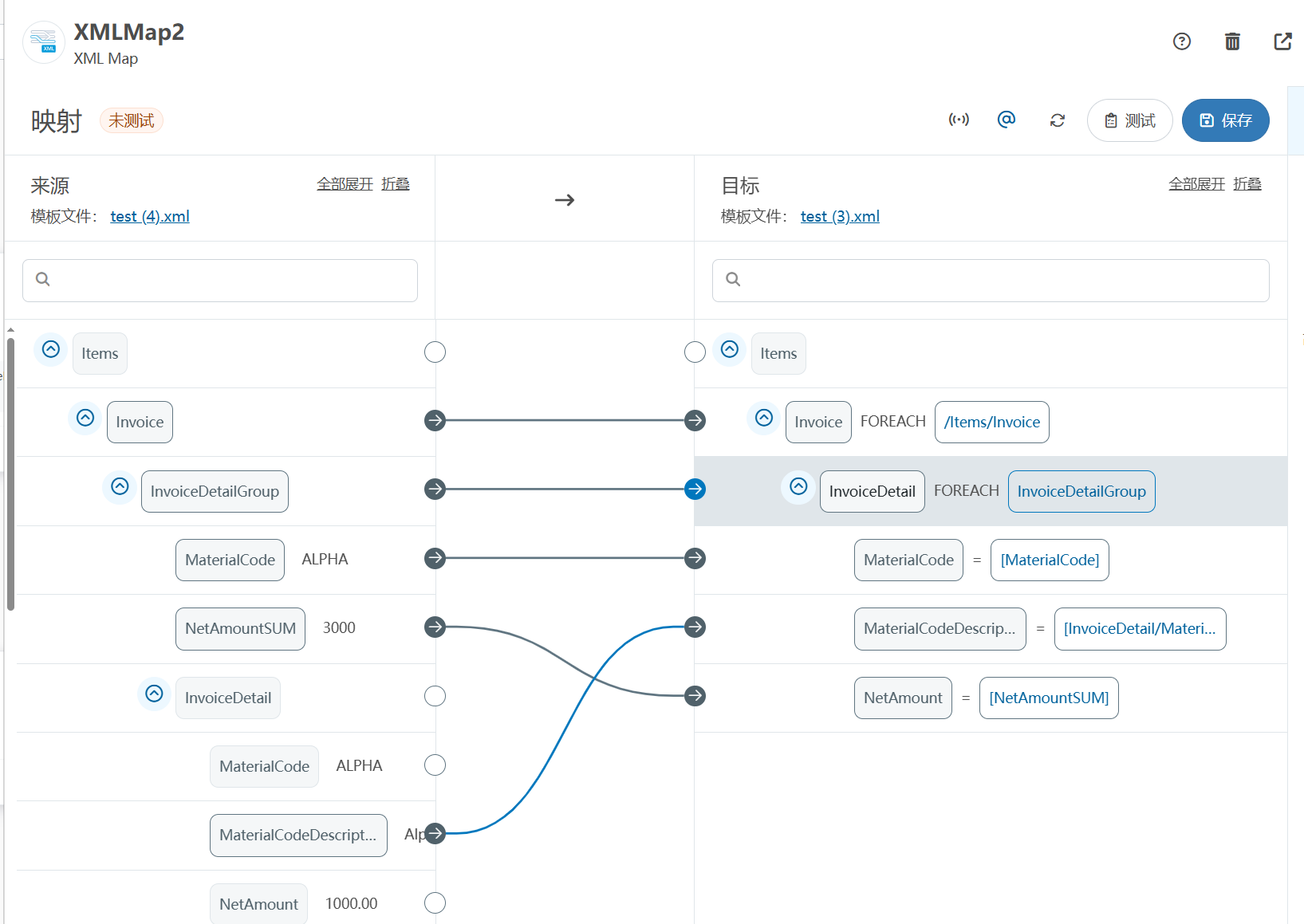
XML Group端口详解
在XML数据映射过程中,经常需要对数据进行分组聚合操作。例如,当处理包含多个物料明细的XML文件时,可能需要将相同物料号的明细归为一组,或对相同物料号的数量进行求和计算。传统实现方式通常需要编写脚本代码,增加了开…...

未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?
编辑:陈萍萍的公主一点人工一点智能 未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?RWM通过双自回归机制有效解决了复合误差、部分可观测性和随机动力学等关键挑战,在不依赖领域特定归纳偏见的条件下实现了卓越的预测准…...

C++初阶-list的底层
目录 1.std::list实现的所有代码 2.list的简单介绍 2.1实现list的类 2.2_list_iterator的实现 2.2.1_list_iterator实现的原因和好处 2.2.2_list_iterator实现 2.3_list_node的实现 2.3.1. 避免递归的模板依赖 2.3.2. 内存布局一致性 2.3.3. 类型安全的替代方案 2.3.…...

FFmpeg 低延迟同屏方案
引言 在实时互动需求激增的当下,无论是在线教育中的师生同屏演示、远程办公的屏幕共享协作,还是游戏直播的画面实时传输,低延迟同屏已成为保障用户体验的核心指标。FFmpeg 作为一款功能强大的多媒体框架,凭借其灵活的编解码、数据…...

ssc377d修改flash分区大小
1、flash的分区默认分配16M、 / # df -h Filesystem Size Used Available Use% Mounted on /dev/root 1.9M 1.9M 0 100% / /dev/mtdblock4 3.0M...
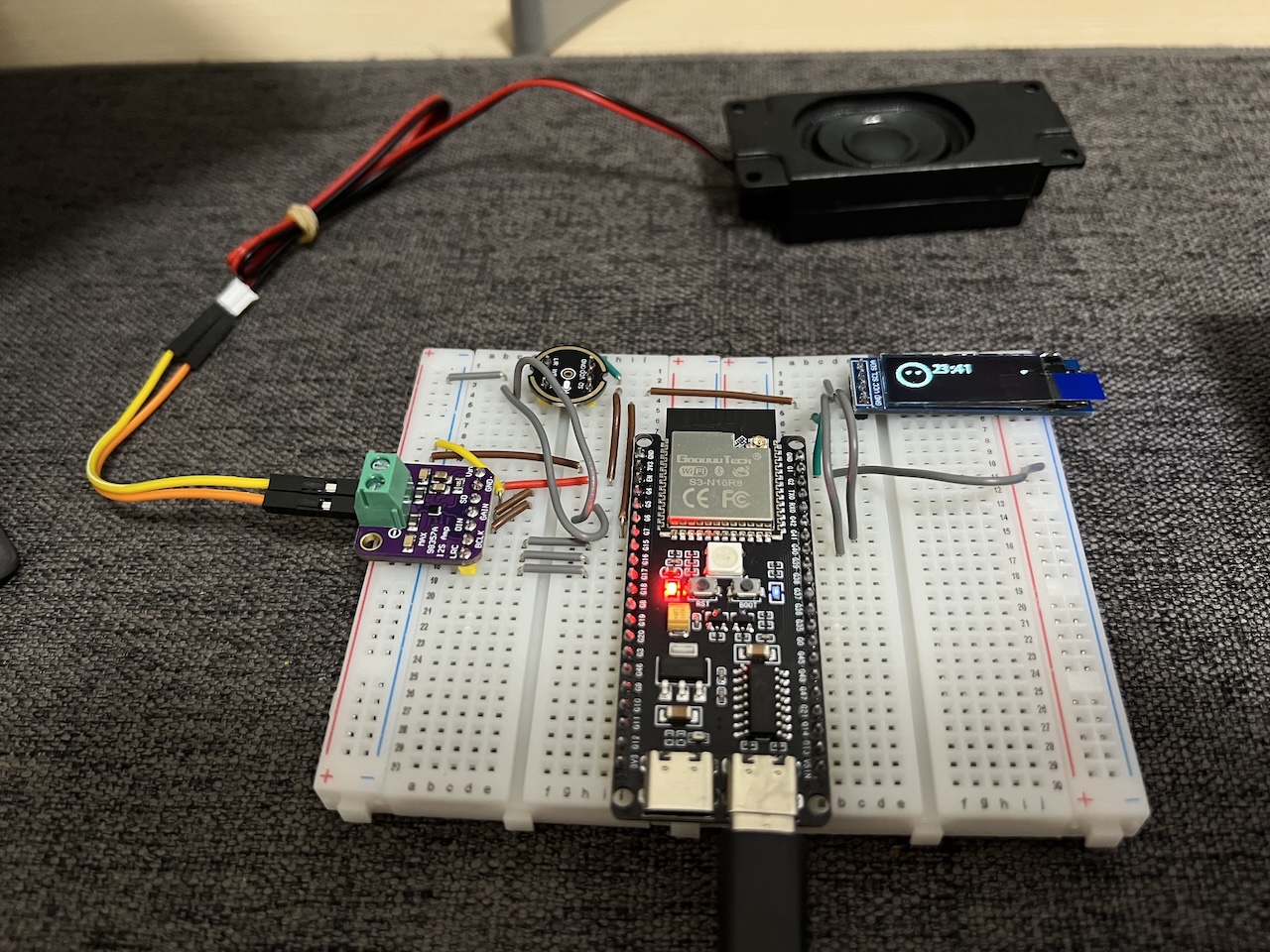
DIY|Mac 搭建 ESP-IDF 开发环境及编译小智 AI
前一阵子在百度 AI 开发者大会上,看到基于小智 AI DIY 玩具的演示,感觉有点意思,想着自己也来试试。 如果只是想烧录现成的固件,乐鑫官方除了提供了 Windows 版本的 Flash 下载工具 之外,还提供了基于网页版的 ESP LA…...
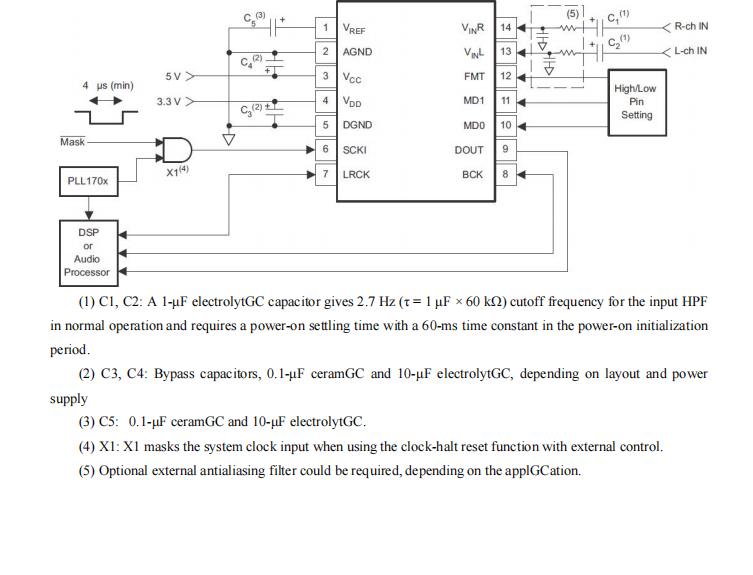
GC1808高性能24位立体声音频ADC芯片解析
1. 芯片概述 GC1808是一款24位立体声音频模数转换器(ADC),支持8kHz~96kHz采样率,集成Δ-Σ调制器、数字抗混叠滤波器和高通滤波器,适用于高保真音频采集场景。 2. 核心特性 高精度:24位分辨率,…...
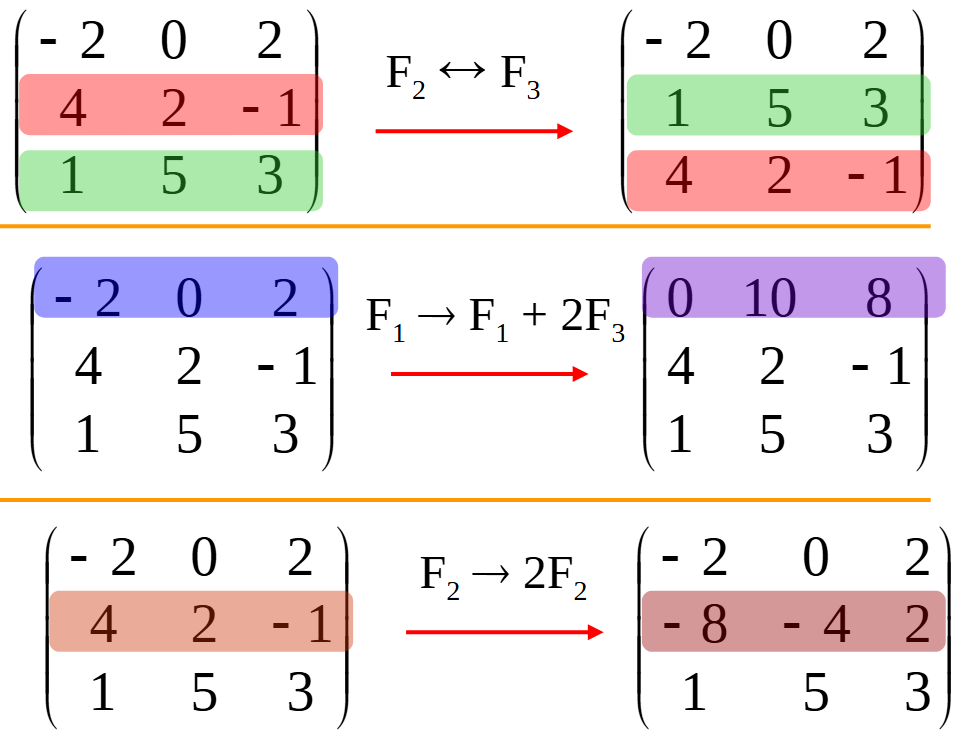
使用 SymPy 进行向量和矩阵的高级操作
在科学计算和工程领域,向量和矩阵操作是解决问题的核心技能之一。Python 的 SymPy 库提供了强大的符号计算功能,能够高效地处理向量和矩阵的各种操作。本文将深入探讨如何使用 SymPy 进行向量和矩阵的创建、合并以及维度拓展等操作,并通过具体…...
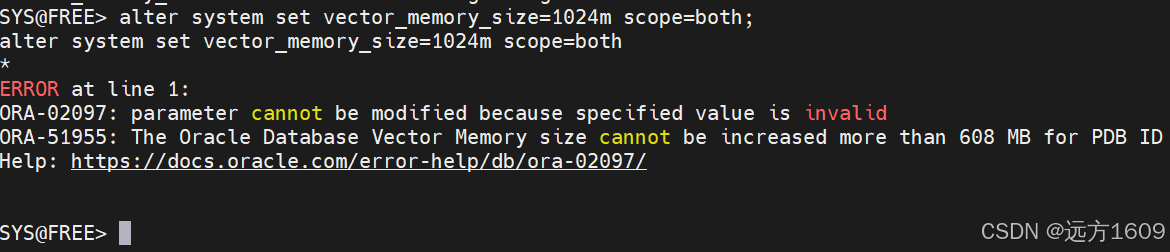
10-Oracle 23 ai Vector Search 概述和参数
一、Oracle AI Vector Search 概述 企业和个人都在尝试各种AI,使用客户端或是内部自己搭建集成大模型的终端,加速与大型语言模型(LLM)的结合,同时使用检索增强生成(Retrieval Augmented Generation &#…...

【生成模型】视频生成论文调研
工作清单 上游应用方向:控制、速度、时长、高动态、多主体驱动 类型工作基础模型WAN / WAN-VACE / HunyuanVideo控制条件轨迹控制ATI~镜头控制ReCamMaster~多主体驱动Phantom~音频驱动Let Them Talk: Audio-Driven Multi-Person Conversational Video Generation速…...
