Pure-Pursuit 跟踪双移线 Gazebo 仿真
Pure-Pursuit 跟踪双移线 Gazebo 仿真
主要参考学习下面的博客和开源项目
自动驾驶规划控制(A*、pure pursuit、LQR算法,使用c++在ubuntu和ros环境下实现)
https://github.com/NeXTzhao/planning
Pure-Pursuit 的理论基础见今年六月份的笔记
对参考轨迹进行调整,采用双移线轨迹
#include <geometry_msgs/PoseStamped.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/Quaternion.h>
#include <nav_msgs/Path.h>
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <std_msgs/String.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;// 双移线构造的参数
const float shape = 2.4;
const float dx1 = 25.0, dx2 = 21.95;
const float dy1 = 4.05, dy2 = 5.7;
const float Xs1 = 27.19, Xs2 = 56.46;
// 参考路径在 X 方向长度以及参考点的步长
const float length = 120.0;
const float step = 0.1;// 计算 Y 轴参考位置
inline float calculate_reference_y(const float ref_x)
{float z1 = shape / dx1 * (ref_x - Xs1) - shape / 2.0;float z2 = shape / dx2 * (ref_x - Xs2) - shape / 2.0;return dy1 / 2.0 * (1 + tanh(z1)) - dy2 / 2.0 * (1 + tanh(z2));
}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{ros::init(argc, argv, "DoubleLane");ros::NodeHandle nh;ros::Publisher path_pub = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Path>("/double_lane", 1000, true);nav_msgs::Path reference_path;reference_path.header.frame_id = "world";reference_path.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();geometry_msgs::PoseStamped pose;pose.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();pose.header.frame_id = "world";int points_size = length / step;reference_path.poses.resize(points_size + 1);for (int i = 0; i <= points_size; ++i){float ref_x = i * step;float ref_y = calculate_reference_y(ref_x);// cout << ref_x << "\t" << ref_y << endl;pose.pose.position.x = ref_x;pose.pose.position.y = ref_y;pose.pose.position.z = 0.0;pose.pose.orientation.x = 0.0;pose.pose.orientation.y = 0.0;pose.pose.orientation.z = 0.0;pose.pose.orientation.w = 0.0;reference_path.poses[i] = pose;}ros::Rate loop(10);while (ros::ok()){path_pub.publish(reference_path);ros::spinOnce();loop.sleep();}return 0;
}
编程方面进行了一些简单的优化,轨迹跟踪的算法在 poseCallback 中实现,和博主有所区别
#include <geometry_msgs/Twist.h>
#include <nav_msgs/Path.h>
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <tf/tf.h>
#include <tf/transform_broadcaster.h>#include <algorithm>
#include <cassert>
#include <cmath>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>#include "cpprobotics_types.h"
#include "cubic_spline.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/PoseStamped.h"#define PREVIEW_DIS 1.5 // 预瞄距离#define Ld 1.868 // 轴距using namespace std;
using namespace cpprobotics;ros::Publisher purepersuit_;
ros::Publisher path_pub_;
nav_msgs::Path path;float carVelocity = 0;
float preview_dis = 0;
float k = 0.1;// 计算四元数转换到欧拉角
std::array<float, 3> calQuaternionToEuler(const float x, const float y,const float z, const float w)
{std::array<float, 3> calRPY = {(0, 0, 0)};// roll = atan2(2(wx+yz),1-2(x*x+y*y))calRPY[0] = atan2(2 * (w * x + y * z), 1 - 2 * (x * x + y * y));// pitch = arcsin(2(wy-zx))calRPY[1] = asin(2 * (w * y - z * x));// yaw = atan2(2(wx+yz),1-2(y*y+z*z))calRPY[2] = atan2(2 * (w * z + x * y), 1 - 2 * (y * y + z * z));return calRPY;
}cpprobotics::Vec_f r_x_;
cpprobotics::Vec_f r_y_;int pointNum = 0; // 保存路径点的个数
int targetIndex = pointNum - 1;// 计算发送给模型车的转角
void poseCallback(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped ¤tWaypoint)
{auto currentPositionX = currentWaypoint.pose.position.x;auto currentPositionY = currentWaypoint.pose.position.y;auto currentPositionZ = 0.0;auto currentQuaternionX = currentWaypoint.pose.orientation.x;auto currentQuaternionY = currentWaypoint.pose.orientation.y;auto currentQuaternionZ = currentWaypoint.pose.orientation.z;auto currentQuaternionW = currentWaypoint.pose.orientation.w;std::array<float, 3> calRPY =calQuaternionToEuler(currentQuaternionX, currentQuaternionY,currentQuaternionZ, currentQuaternionW);cout << currentPositionX << "\t" << currentPositionY << "\t" << calRPY[2] << endl;for (int i = pointNum - 1; i >= 0; --i){float distance = sqrt(pow((r_x_[i] - currentPositionX), 2) +pow((r_y_[i] - currentPositionY), 2));if (distance < preview_dis){targetIndex = i + 1;break;}}if (targetIndex >= pointNum){targetIndex = pointNum - 1;}float alpha =atan2(r_y_[targetIndex] - currentPositionY, r_x_[targetIndex] - currentPositionX) -calRPY[2];// 当前点和目标点的距离Idfloat dl = sqrt(pow(r_y_[targetIndex] - currentPositionY, 2) +pow(r_x_[targetIndex] - currentPositionX, 2));// 发布小车运动指令及运动轨迹if (targetIndex == pointNum - 1 && dl < 0.2) // 离终点很近时停止运动{geometry_msgs::Twist vel_msg;vel_msg.linear.x = 0;vel_msg.angular.z = 0;purepersuit_.publish(vel_msg);}else{float theta = atan(2 * Ld * sin(alpha) / dl);geometry_msgs::Twist vel_msg;vel_msg.linear.x = 3;vel_msg.angular.z = theta;purepersuit_.publish(vel_msg);// 发布小车运动轨迹geometry_msgs::PoseStamped this_pose_stamped;this_pose_stamped.pose.position.x = currentPositionX;this_pose_stamped.pose.position.y = currentPositionY;geometry_msgs::Quaternion goal_quat = tf::createQuaternionMsgFromYaw(theta);this_pose_stamped.pose.orientation.x = currentQuaternionX;this_pose_stamped.pose.orientation.y = currentQuaternionY;this_pose_stamped.pose.orientation.z = currentQuaternionZ;this_pose_stamped.pose.orientation.w = currentQuaternionW;this_pose_stamped.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();this_pose_stamped.header.frame_id = "world";path.poses.push_back(this_pose_stamped);}path_pub_.publish(path);
}void velocityCall(const geometry_msgs::TwistStamped &carWaypoint)
{carVelocity = carWaypoint.twist.linear.x;// 预瞄距离计算preview_dis = k * carVelocity + PREVIEW_DIS;
}void pointCallback(const nav_msgs::Path &msg)
{// 避免参考点重复赋值if (pointNum != 0){return;}// geometry_msgs/PoseStamped[] posespointNum = msg.poses.size();// 提前开辟内存r_x_.resize(pointNum);r_y_.resize(pointNum);for (int i = 0; i < pointNum; i++){r_x_[i] = msg.poses[i].pose.position.x;r_y_[i] = msg.poses[i].pose.position.y;}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{// 创建节点ros::init(argc, argv, "pure_pursuit");// 创建节点句柄ros::NodeHandle n;// 创建Publisher,发送经过pure_pursuit计算后的转角及速度purepersuit_ = n.advertise<geometry_msgs::Twist>("/smart/cmd_vel", 20);path_pub_ = n.advertise<nav_msgs::Path>("/rvizpath", 100, true);// ros::Rate loop_rate(10);path.header.frame_id = "world";// 设置时间戳path.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();geometry_msgs::PoseStamped pose;pose.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();// 设置参考系pose.header.frame_id = "world";ros::Subscriber splinePath = n.subscribe("/double_lane", 20, pointCallback);ros::Subscriber carVel = n.subscribe("/smart/velocity", 20, velocityCall);ros::Subscriber carPose = n.subscribe("/smart/rear_pose", 20, poseCallback);ros::spin();return 0;
}
这里和 CarSim-Simulink 联合仿真的代码类似
function [sys,x0,str,ts] = MY_MPCController3(t,x,u,flag)
% 该函数是写的第3个S函数控制器(MATLAB版本:R2011a)
% 限定于车辆运动学模型,控制量为速度和前轮偏角,使用的QP为新版本的QP解法
% [sys,x0,str,ts] = MY_MPCController3(t,x,u,flag)
%
% is an S-function implementing the MPC controller intended for use
% with Simulink. The argument md, which is the only user supplied
% argument, contains the data structures needed by the controller. The
% input to the S-function block is a vector signal consisting of the
% measured outputs and the reference values for the controlled
% outputs. The output of the S-function block is a vector signal
% consisting of the control variables and the estimated state vector,
% potentially including estimated disturbance states.switch flag,case 0[sys,x0,str,ts] = mdlInitializeSizes; % Initializationcase 2sys = mdlUpdates(t,x,u); % Update discrete statescase 3sys = mdlOutputs(t,x,u); % Calculate outputscase {1,4,9} % Unused flagssys = [];otherwiseerror(['unhandled flag = ',num2str(flag)]); % Error handling
end
% End of dsfunc.%==============================================================
% Initialization
%==============================================================function [sys,x0,str,ts] = mdlInitializeSizes
% Call simsizes for a sizes structure, fill it in, and convert it
% to a sizes array.
sizes = simsizes;
sizes.NumContStates = 0;
sizes.NumDiscStates = 4; % this parameter doesn't matter
sizes.NumOutputs = 1;
sizes.NumInputs = 5;
sizes.DirFeedthrough = 1; % Matrix D is non-empty.
sizes.NumSampleTimes = 1;
sys = simsizes(sizes);
x0 =[0.00001;0.00001;0.00001;0.00001];
global U; % store current ctrl vector:[vel_m, delta_m]
U=[0];global cx;
cx = 0:0.01:160;
global cy;
shape=2.4;%参数名称,用于参考轨迹生成
dx1=25;dx2=21.95;%没有任何实际意义,只是参数名称
dy1=4.05;dy2=5.7;%没有任何实际意义,只是参数名称
Xs1=27.19;Xs2=56.46;%参数名称
for i = 1:length(cx) %全局路径c(y)生成 路径初始化z1=shape/dx1*(cx(i)-Xs1)-shape/2;z2=shape/dx2*(cx(i)-Xs2)-shape/2;cy(i) = dy1/2*(1+tanh(z1))-dy2/2*(1+tanh(z2));
end% Initialize the discrete states.
str = []; % Set str to an empty matrix.
ts = [0.05 0]; % sample time: [period, offset]
%End of mdlInitializeSizes%==============================================================
% Update the discrete states
%==============================================================
function sys = mdlUpdates(t,x,u)sys = x;
%End of mdlUpdate.%==============================================================
% Calculate outputs
%==============================================================
function sys = mdlOutputs(t,x,u)global U; %store chi_tilde=[vel-vel_ref; delta - delta_ref]global cx;global cy;pi = 3.1415926;ticfprintf('Update start, t=%6.3f\n',t);x = u(1);y = u(2);yaw_angle =u(3)*pi/180;%CarSim输出的Yaw angle为角度,角度转换为弧度v = u(4) / 3.6;k = 0.1; % look forward gain 前向预测距离所用增益Lfc = 3; % 基础预瞄距离L = 2.7; % [m] wheel base of vehicleLd = k * v + Lfc;N = length(cx);ind = N;for i = N : -1 : 1distance = sqrt((cx(i)-x)^2 + (cy(i)-y)^2);if distance < Ldind = i + 1;break;endendif ind > Nind = N; endtx = cx(ind);ty = cy(ind);Ld = sqrt((tx-x)^2 + (ty-y)^2);alpha = atan((ty-y)/(tx-x))-yaw_angle; %该处定义向左转为alpha=beta-Fai,所以向右转就输出-alphadelta = atan(2*L * sin(alpha)/Ld); %前轮转角U = delta;sys= U; % vel, steering, x, ytoc
% End of mdlOutputs.
注意处理接近终点的情况,不加限制的话容易出现绕着终点转圈的现象

限制后整体的跟踪效果尚可,但在终点处仍旧会出现异常的偏航,仍有较大的优化空间




相关文章:

Pure-Pursuit 跟踪双移线 Gazebo 仿真
Pure-Pursuit 跟踪双移线 Gazebo 仿真 主要参考学习下面的博客和开源项目 自动驾驶规划控制(A*、pure pursuit、LQR算法,使用c在ubuntu和ros环境下实现) https://github.com/NeXTzhao/planning Pure-Pursuit 的理论基础见今年六月…...

Selenium学习(Java + Edge)
Selenium /səˈliːniəm/ 1. 简介 Selenium是一个用于Web应用程序自动化测试工具。Selenium测试直接运行在浏览器中,就像真正的用户在操作一样。支持的浏览器包括IE、Mozilla Firefox、Safari、Google Chrome、Opera、Edge等。 适用于自动化测试&#x…...

项目管理-组织战略类型和层次讲解
组织战略类型和层次 对于不同的组织战略可能会采用不同的项目管理形式,组织作为项目管理的载体,其战略决策对项目管理体系的架构,对组织与项目之间责权利的划分具有深远的影响,组织的战略文化也会影响到项目的组织文化氛围。因此…...
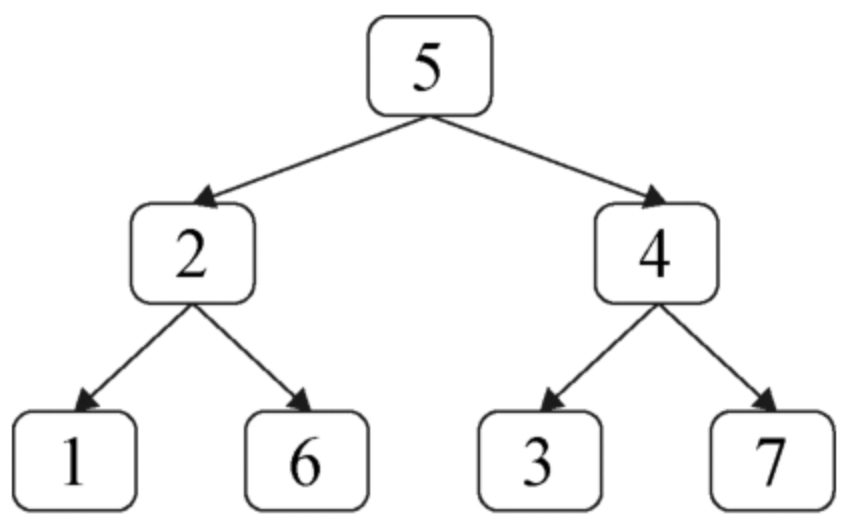
面试算法50:向下的路径节点值之和
题目 给定一棵二叉树和一个值sum,求二叉树中节点值之和等于sum的路径的数目。路径的定义为二叉树中顺着指向子节点的指针向下移动所经过的节点,但不一定从根节点开始,也不一定到叶节点结束。例如,在如图8.5所示中的二叉树中有两条…...

dbeaver查看表,解决证书报错current license is non-compliant for [jdbc]
http://localhost:9200/_license { “license” : { “status” : “active”, “uid” : “b91ae0e0-b04d-4e20-8730-cf0bca7b2035”, “type” : “basic”, “issue_date” : “2023-02-22T14:33:27.648Z”, “issue_date_in_millis” : 1677076407648, “max_nodes” : 10…...
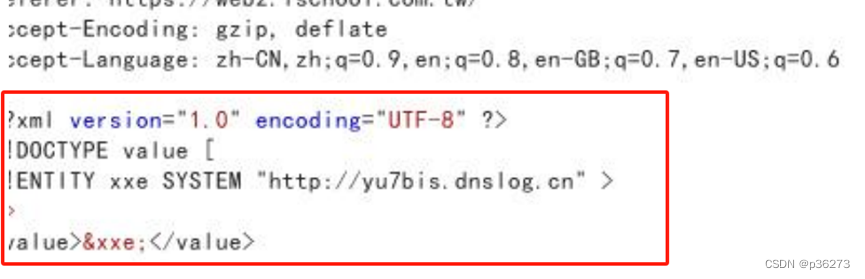
网络安全进阶学习第二十一课——XXE
文章目录 一、XXE简介二、XXE原理三、XXE危害四、XXE如何寻找五、XXE限制条件六、XXE分类七、XXE利用1、读取任意文件1.1、有回显1.2、没有回显 2、命令执行(情况相对较少见)3、内网探测/SSRF4、拒绝服务攻击(DDoS)4.1、内部实体4.2、参数实体 八、绕过基…...
如何将 ruby 打包类似于jdk在另一台相同架构的机器上面开箱即用
需求 目前工作中使用到了ruby作为java 项目的中转语言,但是部署ruby的时候由于环境的不同会出现安装依赖包失败的问题,如何找到一种开箱即用的方式类似于java 中的jdk内置jvm这种方式 解决 TruffleRuby 完美解决问题,TruffleRuby 是使用 T…...

vue封装独立组件:实现分格密码输入框/验证码输入框
目录 第一章 实现效果 第二章 核心实现思路 第三章 封装组件代码实现 第一章 实现效果 为了方便小编的父组件随便找了个页面演示的通过点击按钮,展示子组件密码输入的输入框通过点击子组件输入框获取焦点,然后输入验证码数字即可子组件的确定按钮是验…...

从2D圆形到3D椭圆
要将一个2D圆形转换成3D椭圆,我们需要使用CSS的transform属性和一些基本的几何知识。首先,让我们创建一个HTML元素,如下所 html <div class"circle"></div> 然后,使用CSS样式将其转换成3D椭圆 css .circ…...
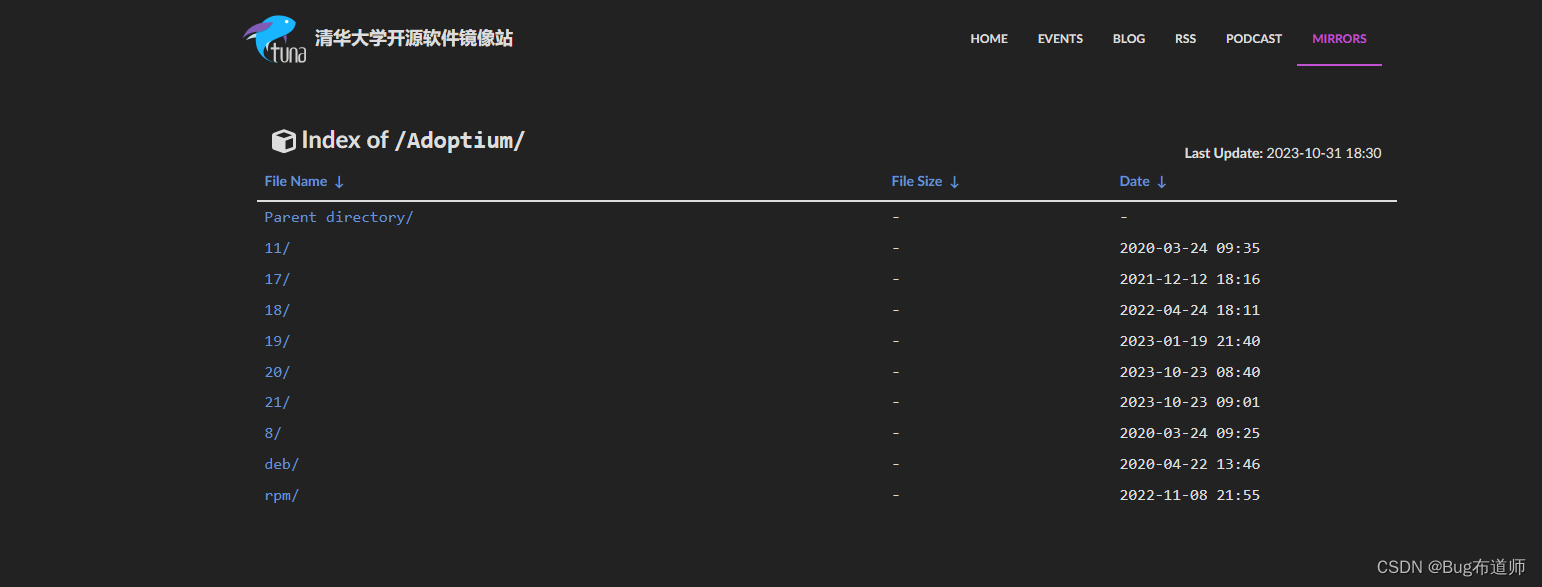
Linux CentOS7.9安装OpenJDK17
Linux CentOS7.9安装OpenJDK17 一、OpenJDK下载 清华大学开源软件镜像站 国内的站点,下载速度贼快 二、上传解压 文件上传到服务器后,解压命令: tar -zxvf jdk-xxxx-linux-x64.tar.gz三、配置环境 export JAVA_HOME/home/local/java/j…...
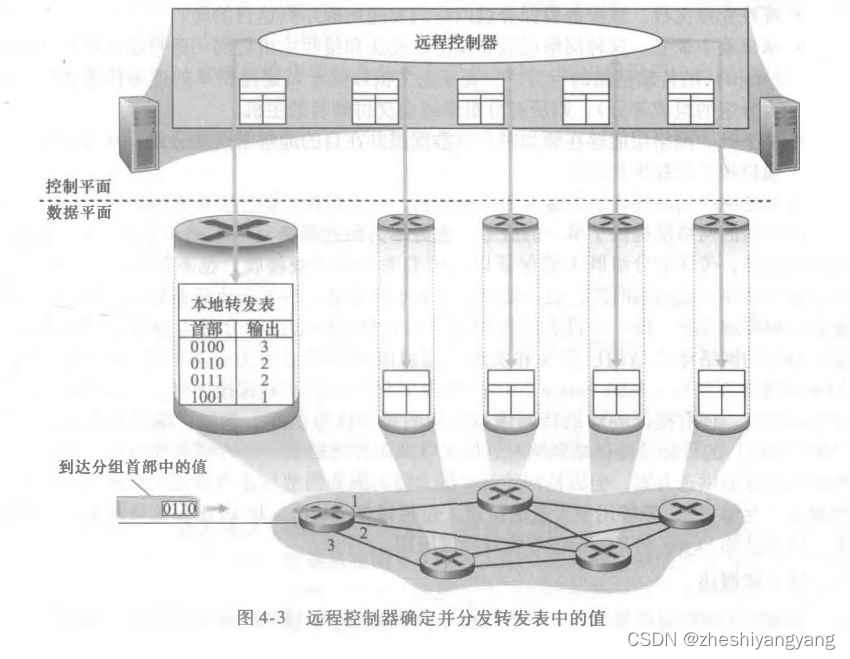
计算机网络第4章-网络层(1)
引子 网络层能够被分解为两个相互作用的部分: 数据平面和控制平面。 网络层概述 路由器具有截断的协议栈,即没有网络层以上的部分。 如下图所示,是一个简单网络: 转发和路由选择:数据平面和控制平面 网络层的作用…...
单元测试学习
回顾测试理论基础 单元测试基础知识 什么是单元测试 单元测试流程、测试计划 测试策略设计、实现 单元测试 - 执行 HTML 报告生成 1 软件测试分类 目标 回顾测试理论知识-测试分类 1. 测 试分类 代码可见度上-划分分类: 1. 黑盒测试 2. 灰盒测试 3. …...
python编写接口测试文档(以豆瓣搜索为例)
📢专注于分享软件测试干货内容,欢迎点赞 👍 收藏 ⭐留言 📝 如有错误敬请指正!📢交流讨论:欢迎加入我们一起学习!📢资源分享:耗时200小时精选的「软件测试」资…...

C++查看Class类结构
cl指令 cl test.cpp /d1reportSingleClassLayout 类名 注意。上面指令是d1,1是数字1 , 不是字母l;...
appium如何连接多台设备
我们在做app自动化的时候,若要考虑兼容性问题,需要跑几台设备,要是一台一台的跑比较耗时,因此需要考虑使用多线程来同时操作多台设备。 1.我们拿两台设备来模拟操作下,使用:adb devices查看连接状况&#…...

VUE el-form组件不绑定model时进行校验
在el-form中如果要使用:rules规则校验时,需要在el-form标签绑定 :model 如何不绑定model而进行校验字段: 思路: 1.假设规则为非空判断 2.获取该字段,进行非空判断,记录该字段是否校验完成,添加到校验标识中 3.表单或数据提交时,判断校验标识 required 红星星 :error 提示项 …...

计算机视觉的监督学习与无监督学习
什么是监督学习? 监督学习是一种机器学习算法,它从一组已标记的 合成数据生成器中生成的训练数据中学习。这意味着数据科学家已经用正确的标签(例如,“猫”或“狗”)标记了训练集中的每个数据点,以便算法可…...

Linux-lvds接口
lvds接口 单6 单8 双6 双8...

Android 自定义View一
1.继承已有VIew,改写尺寸:重写onMeasure SquareImageView 2.完全自定义重写onMeasure 3.自定义Layout 重写onMeasure onLayout 1.继承已有VIew,改写尺寸:重写onMeasure 流程: 重写onMeasure 用getmeasureedWidth …...
11、电路综合-集总参数电路结构的S参数模型计算与Matlab
11、电路综合-集总参数电路结构的S参数模型 电路综合专栏的大纲如下: 网络综合和简化实频理论学习概述 前面介绍了许多微带线电路综合的实际案例,如: 3、电路综合原理与实践—单双端口理想微带线(伪)手算S参数与时域…...
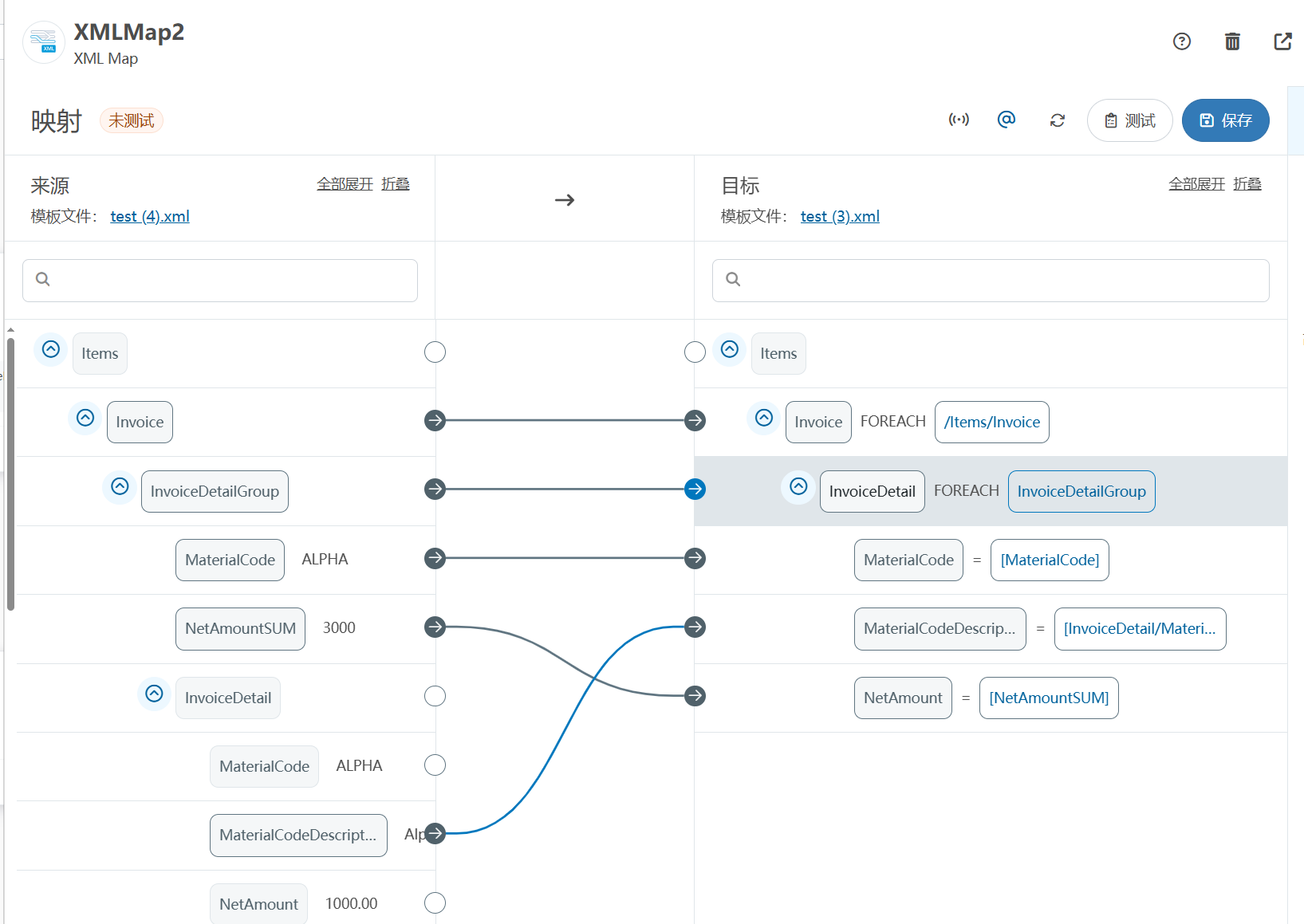
XML Group端口详解
在XML数据映射过程中,经常需要对数据进行分组聚合操作。例如,当处理包含多个物料明细的XML文件时,可能需要将相同物料号的明细归为一组,或对相同物料号的数量进行求和计算。传统实现方式通常需要编写脚本代码,增加了开…...
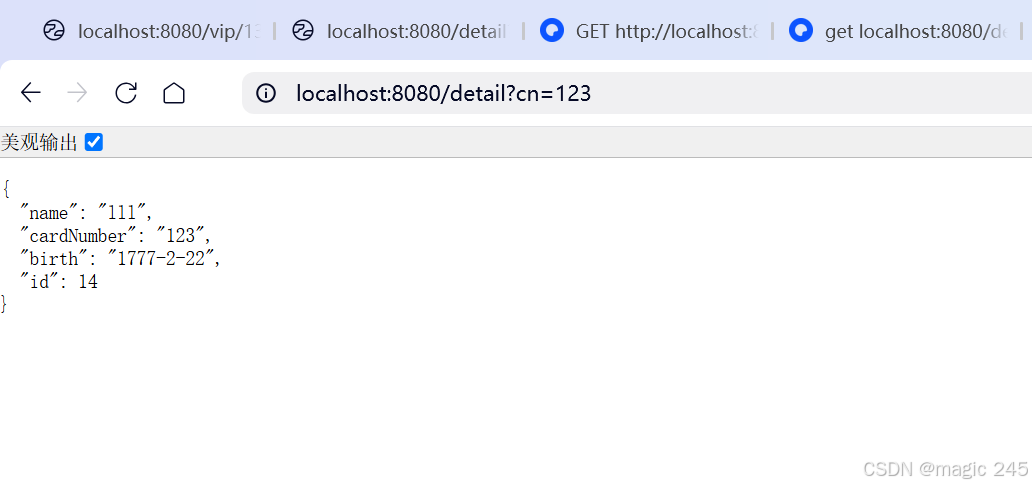
Lombok 的 @Data 注解失效,未生成 getter/setter 方法引发的HTTP 406 错误
HTTP 状态码 406 (Not Acceptable) 和 500 (Internal Server Error) 是两类完全不同的错误,它们的含义、原因和解决方法都有显著区别。以下是详细对比: 1. HTTP 406 (Not Acceptable) 含义: 客户端请求的内容类型与服务器支持的内容类型不匹…...

今日科技热点速览
🔥 今日科技热点速览 🎮 任天堂Switch 2 正式发售 任天堂新一代游戏主机 Switch 2 今日正式上线发售,主打更强图形性能与沉浸式体验,支持多模态交互,受到全球玩家热捧 。 🤖 人工智能持续突破 DeepSeek-R1&…...
ABAP设计模式之---“简单设计原则(Simple Design)”
“Simple Design”(简单设计)是软件开发中的一个重要理念,倡导以最简单的方式实现软件功能,以确保代码清晰易懂、易维护,并在项目需求变化时能够快速适应。 其核心目标是避免复杂和过度设计,遵循“让事情保…...

算法笔记2
1.字符串拼接最好用StringBuilder,不用String 2.创建List<>类型的数组并创建内存 List arr[] new ArrayList[26]; Arrays.setAll(arr, i -> new ArrayList<>()); 3.去掉首尾空格...

基于Java Swing的电子通讯录设计与实现:附系统托盘功能代码详解
JAVASQL电子通讯录带系统托盘 一、系统概述 本电子通讯录系统采用Java Swing开发桌面应用,结合SQLite数据库实现联系人管理功能,并集成系统托盘功能提升用户体验。系统支持联系人的增删改查、分组管理、搜索过滤等功能,同时可以最小化到系统…...

WebRTC从入门到实践 - 零基础教程
WebRTC从入门到实践 - 零基础教程 目录 WebRTC简介 基础概念 工作原理 开发环境搭建 基础实践 三个实战案例 常见问题解答 1. WebRTC简介 1.1 什么是WebRTC? WebRTC(Web Real-Time Communication)是一个支持网页浏览器进行实时语音…...
 Module Federation:Webpack.config.js文件中每个属性的含义解释)
MFE(微前端) Module Federation:Webpack.config.js文件中每个属性的含义解释
以Module Federation 插件详为例,Webpack.config.js它可能的配置和含义如下: 前言 Module Federation 的Webpack.config.js核心配置包括: name filename(定义应用标识) remotes(引用远程模块࿰…...
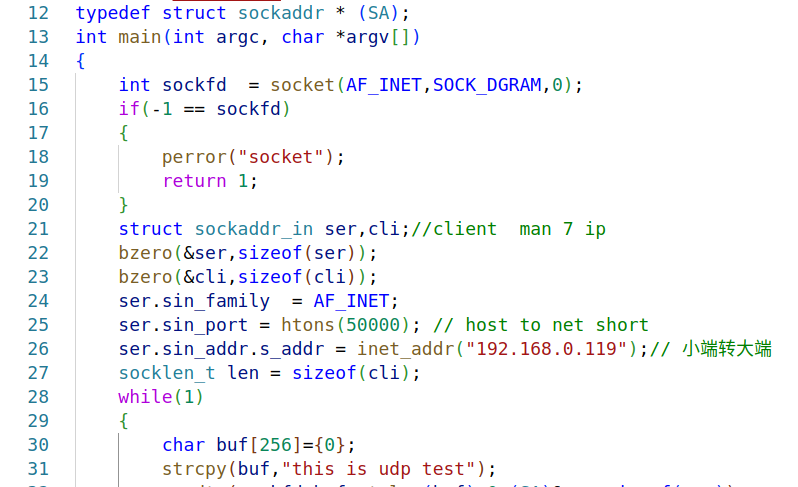
嵌入式学习之系统编程(九)OSI模型、TCP/IP模型、UDP协议网络相关编程(6.3)
目录 一、网络编程--OSI模型 二、网络编程--TCP/IP模型 三、网络接口 四、UDP网络相关编程及主要函数 编辑编辑 UDP的特征 socke函数 bind函数 recvfrom函数(接收函数) sendto函数(发送函数) 五、网络编程之 UDP 用…...

从零开始了解数据采集(二十八)——制造业数字孪生
近年来,我国的工业领域正经历一场前所未有的数字化变革,从“双碳目标”到工业互联网平台的推广,国家政策和市场需求共同推动了制造业的升级。在这场变革中,数字孪生技术成为备受关注的关键工具,它不仅让企业“看见”设…...
