Q_GLOBAL_STATIC宏
文章目录
- 目的
- Q_GLOBAL_STATIC
- 源代码分析
- 涉及到原子操作 以及静态变量初始化顺序
- 代码实现
目的
由Q_GLOBAL_STATIC宏, 引发的基于线程安全的Qt 单例模式的使用。
Q_GLOBAL_STATIC
/****************************************************************************
**
** Copyright (C) 2016 Intel Corporation.
** Contact: https://www.qt.io/licensing/
**
** This file is part of the QtCore module of the Qt Toolkit.
**
** $QT_BEGIN_LICENSE:LGPL$
** Commercial License Usage
** Licensees holding valid commercial Qt licenses may use this file in
** accordance with the commercial license agreement provided with the
** Software or, alternatively, in accordance with the terms contained in
** a written agreement between you and The Qt Company. For licensing terms
** and conditions see https://www.qt.io/terms-conditions. For further
** information use the contact form at https://www.qt.io/contact-us.
**
** GNU Lesser General Public License Usage
** Alternatively, this file may be used under the terms of the GNU Lesser
** General Public License version 3 as published by the Free Software
** Foundation and appearing in the file LICENSE.LGPL3 included in the
** packaging of this file. Please review the following information to
** ensure the GNU Lesser General Public License version 3 requirements
** will be met: https://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl-3.0.html.
**
** GNU General Public License Usage
** Alternatively, this file may be used under the terms of the GNU
** General Public License version 2.0 or (at your option) the GNU General
** Public license version 3 or any later version approved by the KDE Free
** Qt Foundation. The licenses are as published by the Free Software
** Foundation and appearing in the file LICENSE.GPL2 and LICENSE.GPL3
** included in the packaging of this file. Please review the following
** information to ensure the GNU General Public License requirements will
** be met: https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-2.0.html and
** https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.html.
**
** $QT_END_LICENSE$
**
****************************************************************************/#include <QtCore/qglobal.h>#ifndef QGLOBALSTATIC_H
#define QGLOBALSTATIC_H#include <QtCore/qatomic.h>QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACEnamespace QtGlobalStatic {
enum GuardValues {Destroyed = -2,Initialized = -1,Uninitialized = 0,Initializing = 1
};
}#if !QT_CONFIG(thread) || defined(Q_COMPILER_THREADSAFE_STATICS)
// some compilers support thread-safe statics
// The IA-64 C++ ABI requires this, so we know that all GCC versions since 3.4
// support it. C++11 also requires this behavior.
// Clang and Intel CC masquerade as GCC when compiling on Linux.
//
// Apple's libc++abi however uses a global lock for initializing local statics,
// which will block other threads also trying to initialize a local static
// until the constructor returns ...
// We better avoid these kind of problems by using our own locked implementation.#if defined(Q_OS_UNIX) && defined(Q_CC_INTEL)
// Work around Intel issue ID 6000058488:
// local statics inside an inline function inside an anonymous namespace are global
// symbols (this affects the IA-64 C++ ABI, so OS X and Linux only)
# define Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_INTERNAL_DECORATION Q_DECL_HIDDEN
#else
# define Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_INTERNAL_DECORATION Q_DECL_HIDDEN inline
#endif#define Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_INTERNAL(ARGS) \Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_INTERNAL_DECORATION Type *innerFunction() \{ \struct HolderBase { \~HolderBase() noexcept \{ if (guard.loadRelaxed() == QtGlobalStatic::Initialized) \guard.storeRelaxed(QtGlobalStatic::Destroyed); } \}; \static struct Holder : public HolderBase { \Type value; \Holder() \noexcept(noexcept(Type ARGS)) \: value ARGS \{ guard.storeRelaxed(QtGlobalStatic::Initialized); } \} holder; \return &holder.value; \}
#else
// We don't know if this compiler supports thread-safe global statics
// so use our own locked implementationQT_END_NAMESPACE
#include <QtCore/qmutex.h>
#include <mutex>
QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE#define Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_INTERNAL(ARGS) \Q_DECL_HIDDEN inline Type *innerFunction() \{ \static Type *d; \static QBasicMutex mutex; \int x = guard.loadAcquire(); \if (Q_UNLIKELY(x >= QtGlobalStatic::Uninitialized)) { \const std::lock_guard<QBasicMutex> locker(mutex); \if (guard.loadRelaxed() == QtGlobalStatic::Uninitialized) { \d = new Type ARGS; \static struct Cleanup { \~Cleanup() { \delete d; \guard.storeRelaxed(QtGlobalStatic::Destroyed); \} \} cleanup; \guard.storeRelease(QtGlobalStatic::Initialized); \} \} \return d; \}
#endif// this class must be POD, unless the compiler supports thread-safe statics
template <typename T, T *(&innerFunction)(), QBasicAtomicInt &guard>
struct QGlobalStatic
{typedef T Type;bool isDestroyed() const { return guard.loadRelaxed() <= QtGlobalStatic::Destroyed; }bool exists() const { return guard.loadRelaxed() == QtGlobalStatic::Initialized; }operator Type *() { if (isDestroyed()) return nullptr; return innerFunction(); }Type *operator()() { if (isDestroyed()) return nullptr; return innerFunction(); }Type *operator->(){Q_ASSERT_X(!isDestroyed(), "Q_GLOBAL_STATIC", "The global static was used after being destroyed");return innerFunction();}Type &operator*(){Q_ASSERT_X(!isDestroyed(), "Q_GLOBAL_STATIC", "The global static was used after being destroyed");return *innerFunction();}
};#define Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_WITH_ARGS(TYPE, NAME, ARGS) \namespace { namespace Q_QGS_ ## NAME { \typedef TYPE Type; \QBasicAtomicInt guard = Q_BASIC_ATOMIC_INITIALIZER(QtGlobalStatic::Uninitialized); \Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_INTERNAL(ARGS) \} } \static QGlobalStatic<TYPE, \Q_QGS_ ## NAME::innerFunction, \Q_QGS_ ## NAME::guard> NAME;#define Q_GLOBAL_STATIC(TYPE, NAME) \Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_WITH_ARGS(TYPE, NAME, ())QT_END_NAMESPACE
#endif // QGLOBALSTATIC_H源代码分析
Q_GLOBAL_STATIC
用于定义全局静态变量
#define Q_GLOBAL_STATIC(TYPE, NAME) \Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_WITH_ARGS(TYPE, NAME, ())
Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_WITH_ARGS
带有参数的全局静态变量宏
在匿名命名空间内定义了命名空间Q_QGS_ ## NAME,该命名空间内定义了
- 类型:typedef TYPE Type
- 原子操作变量:QBasicAtomicInt guard 初始化QtGlobalStatic::Uninitialized
- 内联函数:Type *innerFunction()
通过类模板QGlobalStatic来定义全局静态变量 NAME
#define Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_WITH_ARGS(TYPE, NAME, ARGS) \namespace { namespace Q_QGS_ ## NAME { \typedef TYPE Type; \QBasicAtomicInt guard = Q_BASIC_ATOMIC_INITIALIZER(QtGlobalStatic::Uninitialized); \Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_INTERNAL(ARGS) \} } \static QGlobalStatic<TYPE, \Q_QGS_ ## NAME::innerFunction, \Q_QGS_ ## NAME::guard> NAME;内联函数innerFunction
enum GuardValues {Destroyed = -2,Initialized = -1,Uninitialized = 0,Initializing = 1
};#define Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_INTERNAL(ARGS) \Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_INTERNAL_DECORATION Type *innerFunction() \{ \struct HolderBase { \~HolderBase() noexcept \{ if (guard.loadRelaxed() == QtGlobalStatic::Initialized) \guard.storeRelaxed(QtGlobalStatic::Destroyed); } \}; \static struct Holder : public HolderBase { \Type value; \Holder() \noexcept(noexcept(Type ARGS)) \: value ARGS \{ guard.storeRelaxed(QtGlobalStatic::Initialized); } \} holder; \return &holder.value; \}
#else
// We don't know if this compiler supports thread-safe global statics
// so use our own locked implementationQT_END_NAMESPACE
#include <QtCore/qmutex.h>
#include <mutex>
QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
采用双重检查方式来初始化全局静态变量
#define Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_INTERNAL(ARGS) \Q_DECL_HIDDEN inline Type *innerFunction() \{ \static Type *d; \static QBasicMutex mutex; \int x = guard.loadAcquire(); \if (Q_UNLIKELY(x >= QtGlobalStatic::Uninitialized)) { \const std::lock_guard<QBasicMutex> locker(mutex); \if (guard.loadRelaxed() == QtGlobalStatic::Uninitialized) { \d = new Type ARGS; \static struct Cleanup { \~Cleanup() { \delete d; \guard.storeRelaxed(QtGlobalStatic::Destroyed); \} \} cleanup; \guard.storeRelease(QtGlobalStatic::Initialized); \} \} \return d; \}
#endif
涉及到原子操作 以及静态变量初始化顺序
atomic
atomic_load与atomic_store
Load是C++11标准的介绍
用于原子访问全局和静态变量的新加载和存储操作。
load操作可以保证多线程环境下全局变量和静态变量的原子加载,
避免数据竞争和线程不安全问题
静态变量初始化顺序
- 全局变量初始化在主函数之前
- 静态局部变量初始化在第一次调用这个静态局部变量时
代码实现
mainwindow.h
static MainWindow* getInstance();
mainwindow.cpp
Q_GLOBAL_STATIC(MainWindow,mainwindow)static MainWindow* MainWindow::getInstance(){return mainwindow();
}
相关文章:

Q_GLOBAL_STATIC宏
文章目录 目的Q_GLOBAL_STATIC源代码分析涉及到原子操作 以及静态变量初始化顺序代码实现 目的 由Q_GLOBAL_STATIC宏, 引发的基于线程安全的Qt 单例模式的使用。 Q_GLOBAL_STATIC /***************************************************************************…...

[批处理]_[初级]_[如何删除变量值里的双引号]
场景 在使用Visual Studio开发本地程序的时,需要在项目属性,生成事件->生成后事件里增加一些资源的打包,复制,删除等操作,那么就需要用到批处理来进行。而传递带空格的路径给外部的批处理文件时就需要双引号引用从…...
51单片机电子钟闹钟温度LCD1602液晶显示设计( proteus仿真+程序+原理图+设计报告+讲解视频)
51单片机电子钟闹钟温度液晶显示设计( proteus仿真程序原理图设计报告讲解视频) 1.主要功能:2.仿真3. 程序代码4. 原理图5. 设计报告6. 设计资料内容清单&&下载链接资料下载链接(可点击): 🌟51单片…...

怎样学好java
最近在看一本java方面的书。《java从入门到精通》,里面看到一段如何学习java的话,觉得非常好,下面我分享一下。 如何学好java语言,是所有初学者都需要面对的问题。其实,每种语言的学习方法都大同小异。初学者需要注意…...

HarmonyOS 数据管理与应用数据持久化(二)
通过键值型数据库实现数据持久化 场景介绍 键值型数据库存储键值对形式的数据,当需要存储的数据没有复杂的关系模型,比如存储商品名称及对应价格、员工工号及今日是否已出勤等,由于数据复杂度低,更容易兼容不同数据库版本和设备…...
Hadoop环境搭建及Demo
参考博客 Windows 10安装Hadoop 3.3.0教程 (kontext.tech) Hadoop入门篇——伪分布模式安装 & WordCount词频统计 | Liu Baoshuai’s Blog Hadoop安装教程 Linux版_linux和hadoop的安装_lnlnldczxy的博客-CSDN博客 hadoop启动出错 The value of property bind.address …...
更新一下数据集
UCI Machine Learning Repository UCI的数据集还是挺老牌的,最近换了地址,我就再记录一下。 左边是比较常见的数据集,比如Iris很经典,Heart Disease这也是,包括Wine,通常对于初学者学习比较好,…...

web3之跨链预言机SupraOracles:什么是Supra
文章目录 web3之跨链预言机SupraOracles什么是Supra什么是DORA(分布式Oracle协议)使用场景web3之跨链预言机SupraOracles 什么是Supra 官网:https://supraoracles.com/ 预言机的核心价值就在于数据传输,数据传输的速度、准确性、安全性更是重中之重。Supra Oracles 就是这…...

关系型数据库 期末复习(未完
关系型数据库 绪论概念间的关系数据库的历史信息和数据数据模型 关系模型数据结构关系完整性关系操作语言 关系代数语言 绪论 概念间的关系 数据->数据库->数据库管理系统->数据库系统 数据库的历史 人工管理阶段 -> 文件系统阶段 -> 数据库系统阶段 数据库…...

【学习笔记】CF1895G Two Characters, Two Colors
感谢grass8sheep提供的思路。 首先,我们可以用 D P DP DP解决这个问题。 设 f i , j f_{i,j} fi,j表示前 i i i个数中有 j j j个为 1 1 1的位置为红色的最大价值。则转移如下: f i , j ← f i − 1 , j b i f_{i,j}\gets f_{i-1,j}b_i fi,j←fi−…...
GZ035 5G组网与运维赛题第10套
2023年全国职业院校技能大赛 GZ035 5G组网与运维赛项(高职组) 赛题第10套 一、竞赛须知 1.竞赛内容分布 竞赛模块1--5G公共网络规划部署与开通(35分) 子任务1:5G公共网络部署与调试(15分) 子…...

基于SSM的教学管理系统(有报告)。Javaee项目。
演示视频: 基于SSM的教学管理系统(有报告)。Javaee项目。 项目介绍: 采用M(model)V(view)C(controller)三层体系结构,通过Spring SpringMvc My…...
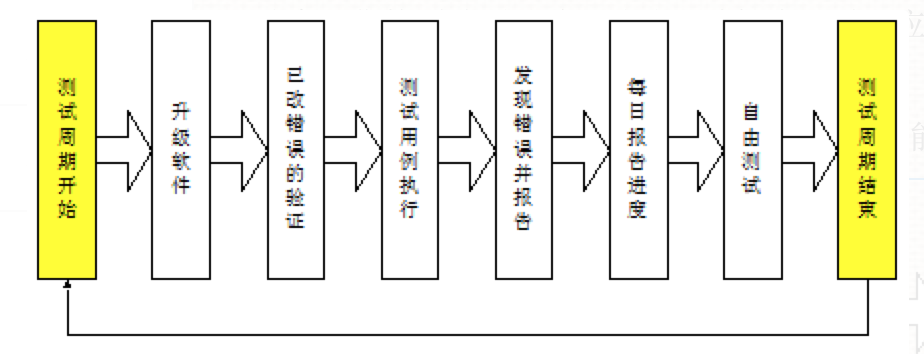
软件测试工作流程
流程体系介绍 在以往的项目工作中,我参与过,需求评审、测试计划制定、测试用例编写、测试用例执行、测试脚本编写、测试脚本的执行,进行回归测试、验收测试、编写阶段性测试报告等工作 需求分析,需求评审(RPD、产品原…...
高级文本编辑软件 UltraEdit mac中文版介绍说明
UltraEdit mac是一款在Windows系统中非常出名的文本编辑器, UltraEdit for mac对于IT程序猿来说,更是必不可少,可以使用UltraEdit编辑配置文件、查看16进制文件、代码高亮显示等,虽然Mac上已经有了很多优秀的文本编辑器࿰…...
python模块的介绍和导入
python模块的介绍和导入 概念 在Python中,每个Python代码文件都是一个模块。写程序时,我们可以将代码分散在不同的模块(文件)中,然后在一个模块中引用另一个模块的内容。 导入格式 1、在一个模块中引用(导入)另一个模块可以使用import语句…...
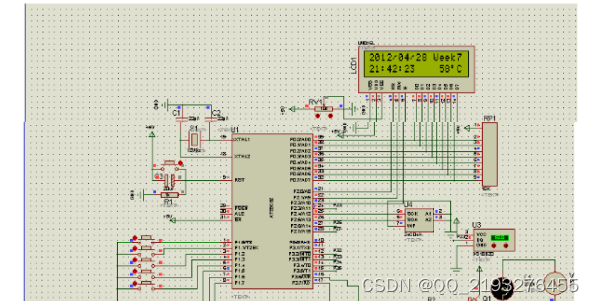
基于单片机的智能饮水机系统
收藏和点赞,您的关注是我创作的动力 文章目录 概要 一、系统设计方案分析2.1 设计功能及性能分析2.2设计方案分析 二、系统的硬件设计3.1 系统设计框图系统软件设计4.1 总体介绍原理图 四、 结论 概要 现在很多学校以及家庭使用的饮水机的功能都是比较单一的&#…...
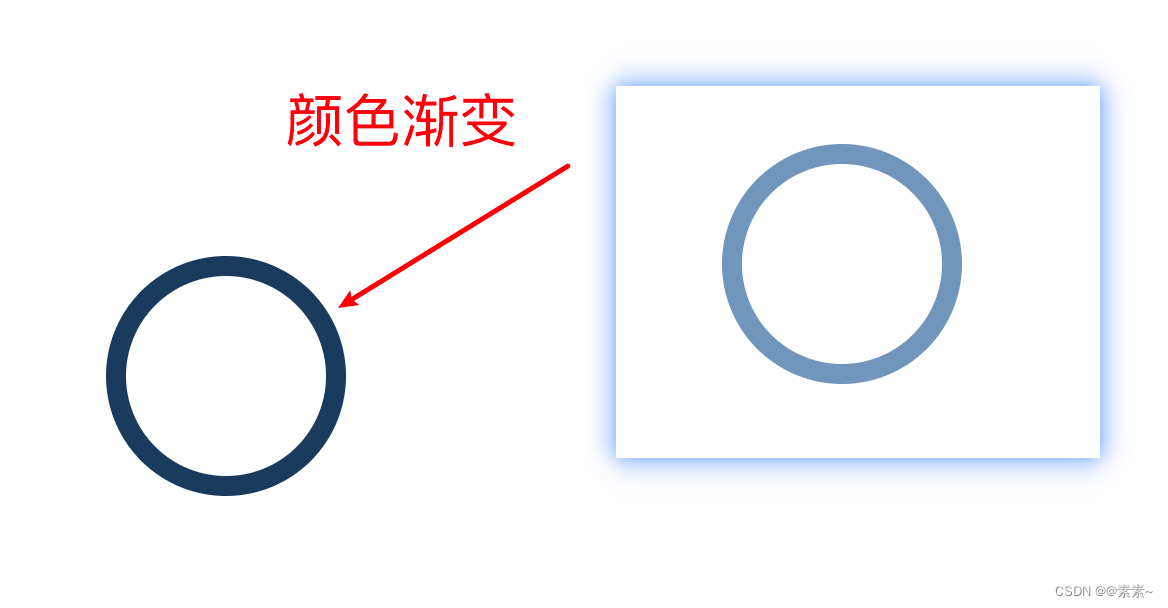
CSS画圆以及CSS实现动态圆
CSS画圆以及CSS实现动态圆 1. 先看基础(静态圆)1.1 效果如下:1.2 代码如下: 2. 动态圆2.1 一个动态圆2.1.1 让圆渐变2.1.2 圆渐变8秒后消失2.1.3 转动的圆(单个圆) 2.2 多个动态圆 1. 先看基础(…...
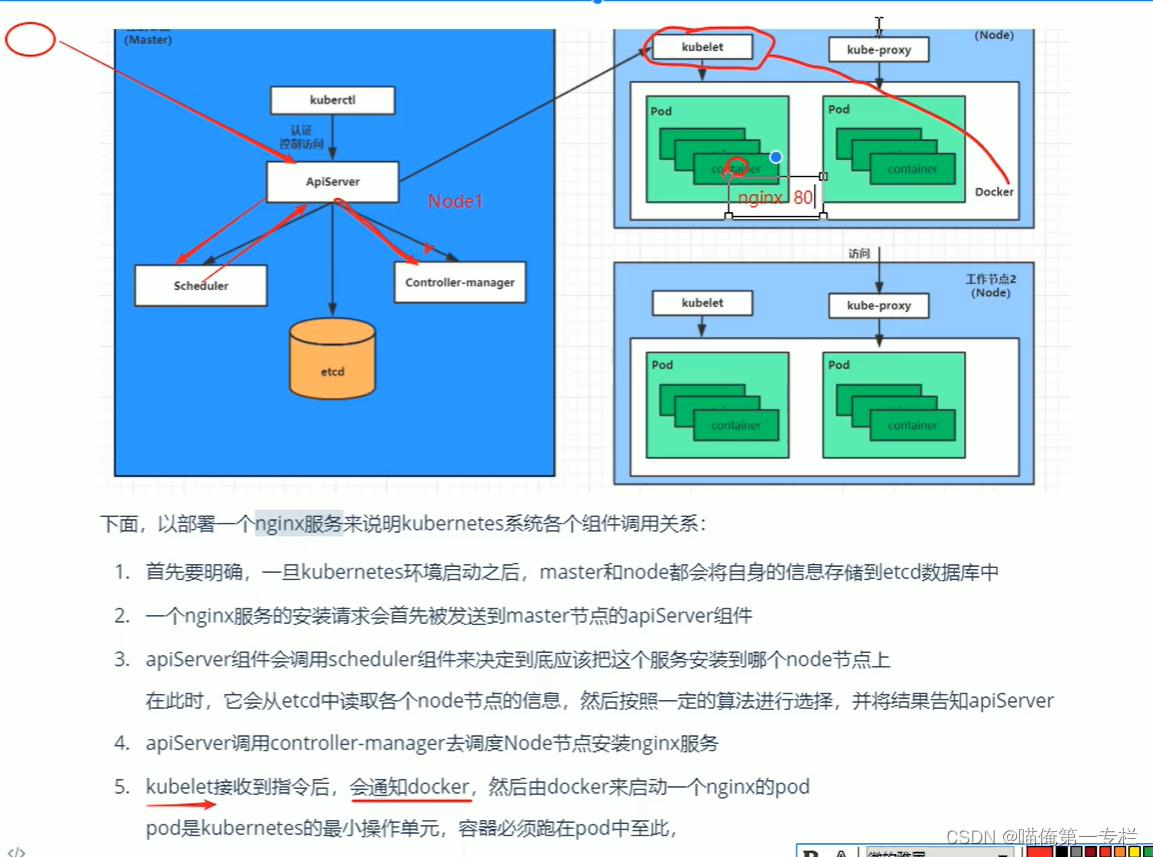
K8S知识点(一)
(1)应用部署方式转变 (2)K8S介绍 容器部署容易出现编排问题,为了解决就出现了大量的编排软件,这里将的是K8S编排问题的解决佼佼者 弹性伸缩:当流量从1000变为1200可以,自动开启一个…...
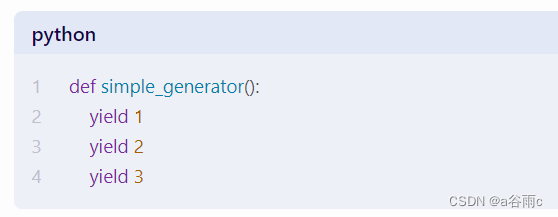
人工智能师求职面试笔试题及答案汇总
人工智能师求职面试笔试题及答案汇总 1.如何在Python中实现一个生成器? 答:在Python中,生成器是一种特殊类型的迭代器。生成器允许你在需要时才生成值,从而节省内存。生成器函数在Python中是通过关键字yield来实现的。例如&…...

【Windows-软件-FFmpeg】(01)通过CMD运行FFmpeg进行操作,快速上手
前言 通过"cmd"运行"ffmpeg"进行操作,快速上手; 实操 【实操一】 说明 使用"ffmpeg"来合并音频文件和视频文件 ; 环境 Windows 11 专业版(22621.2428); 代码 …...

Python爬虫实战:研究MechanicalSoup库相关技术
一、MechanicalSoup 库概述 1.1 库简介 MechanicalSoup 是一个 Python 库,专为自动化交互网站而设计。它结合了 requests 的 HTTP 请求能力和 BeautifulSoup 的 HTML 解析能力,提供了直观的 API,让我们可以像人类用户一样浏览网页、填写表单和提交请求。 1.2 主要功能特点…...

前端倒计时误差!
提示:记录工作中遇到的需求及解决办法 文章目录 前言一、误差从何而来?二、五大解决方案1. 动态校准法(基础版)2. Web Worker 计时3. 服务器时间同步4. Performance API 高精度计时5. 页面可见性API优化三、生产环境最佳实践四、终极解决方案架构前言 前几天听说公司某个项…...
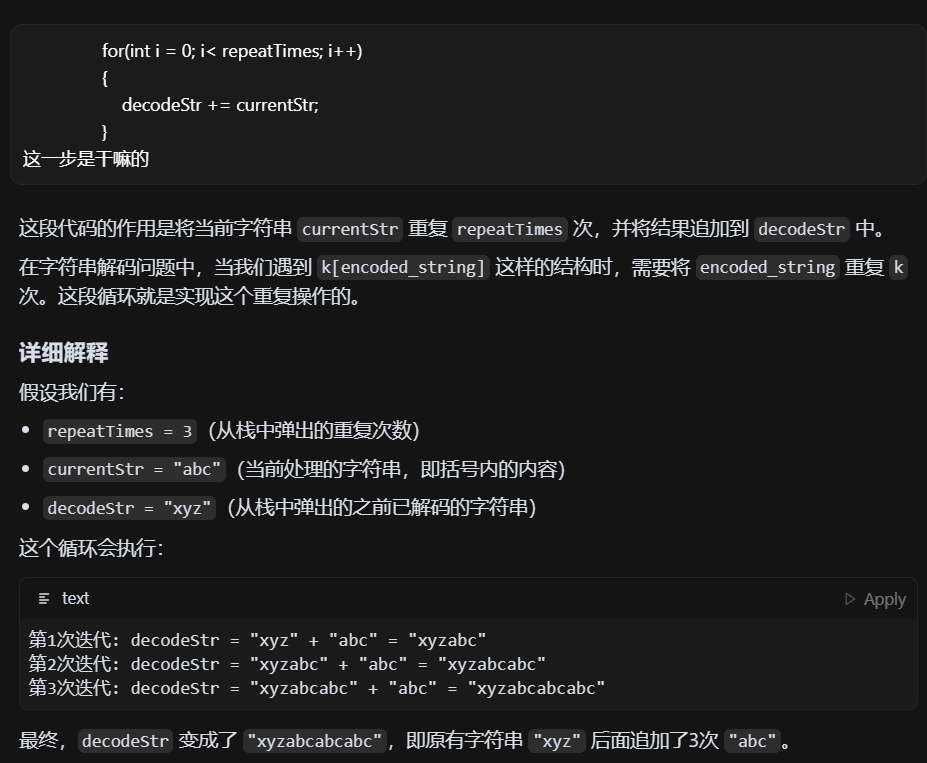
LeetCode - 394. 字符串解码
题目 394. 字符串解码 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路 使用两个栈:一个存储重复次数,一个存储字符串 遍历输入字符串: 数字处理:遇到数字时,累积计算重复次数左括号处理:保存当前状态&a…...

如何为服务器生成TLS证书
TLS(Transport Layer Security)证书是确保网络通信安全的重要手段,它通过加密技术保护传输的数据不被窃听和篡改。在服务器上配置TLS证书,可以使用户通过HTTPS协议安全地访问您的网站。本文将详细介绍如何在服务器上生成一个TLS证…...

Spring AI与Spring Modulith核心技术解析
Spring AI核心架构解析 Spring AI(https://spring.io/projects/spring-ai)作为Spring生态中的AI集成框架,其核心设计理念是通过模块化架构降低AI应用的开发复杂度。与Python生态中的LangChain/LlamaIndex等工具类似,但特别为多语…...

MySQL账号权限管理指南:安全创建账户与精细授权技巧
在MySQL数据库管理中,合理创建用户账号并分配精确权限是保障数据安全的核心环节。直接使用root账号进行所有操作不仅危险且难以审计操作行为。今天我们来全面解析MySQL账号创建与权限分配的专业方法。 一、为何需要创建独立账号? 最小权限原则…...

Fabric V2.5 通用溯源系统——增加图片上传与下载功能
fabric-trace项目在发布一年后,部署量已突破1000次,为支持更多场景,现新增支持图片信息上链,本文对图片上传、下载功能代码进行梳理,包含智能合约、后端、前端部分。 一、智能合约修改 为了增加图片信息上链溯源,需要对底层数据结构进行修改,在此对智能合约中的农产品数…...

Java求职者面试指南:Spring、Spring Boot、MyBatis框架与计算机基础问题解析
Java求职者面试指南:Spring、Spring Boot、MyBatis框架与计算机基础问题解析 一、第一轮提问(基础概念问题) 1. 请解释Spring框架的核心容器是什么?它在Spring中起到什么作用? Spring框架的核心容器是IoC容器&#…...

A2A JS SDK 完整教程:快速入门指南
目录 什么是 A2A JS SDK?A2A JS 安装与设置A2A JS 核心概念创建你的第一个 A2A JS 代理A2A JS 服务端开发A2A JS 客户端使用A2A JS 高级特性A2A JS 最佳实践A2A JS 故障排除 什么是 A2A JS SDK? A2A JS SDK 是一个专为 JavaScript/TypeScript 开发者设计的强大库ÿ…...
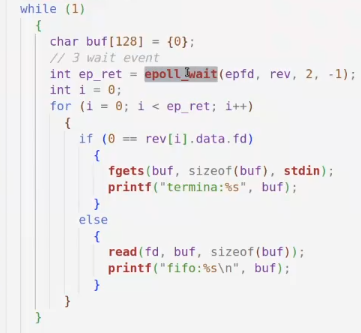
day36-多路IO复用
一、基本概念 (服务器多客户端模型) 定义:单线程或单进程同时监测若干个文件描述符是否可以执行IO操作的能力 作用:应用程序通常需要处理来自多条事件流中的事件,比如我现在用的电脑,需要同时处理键盘鼠标…...
