pandas教程:Essential Functionality 索引 过滤 映射 排序
文章目录
- 5.2 Essential Functionality(主要功能)
- 1 Reindexing(重新索引)
- 2 Dropping Entries from an Axis (按轴删除记录)
- 3 Indexing, Selection, and Filtering(索引,选择,过滤)
- Selection with loc and iloc(用loc和iloc来选择)
- 4 Integer Indexes(整数索引)
- 5 Arithmetic and Data Alignment (算数和数据对齐)
- Arithmetic methods with fill values (带填充值的算数方法)
- Operations between DataFrame and Series (DataFrame和Series之间的操作)
- 6 Function Application and Mapping (函数应用和映射)
- 7 Sorting and Ranking (排序)
- 8 Axis Indexes with Duplicate Labels (有重复label的轴索引)
5.2 Essential Functionality(主要功能)
接下来介绍pandas中的一些主要功能,这里只介绍一些经常用到的。
1 Reindexing(重新索引)
pandas中一个重要的方法是reindex,已实施在创建object的时候遵照一个新的index。如下例:
import pandas as pd
obj = pd.Series([4.5, 7.2, -5.3, 3.6], index=['d', 'b', 'a', 'c'])
obj
d 4.5
b 7.2
a -5.3
c 3.6
dtype: float64
在series上调用reindex能更改index,如果没有对应index的话会引入缺失数据:
obj2 = obj.reindex(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
obj2
a -5.3
b 7.2
c 3.6
d 4.5
e NaN
dtype: float64
在处理时间序列这样的数据时,我们可能需要在reindexing的时候需要修改值。method选项能做到这一点,比如设定method为ffill:
obj3 = pd.Series(['bule', 'purple', 'yellow'], index=[0, 2, 4])
obj3
0 bule
2 purple
4 yellow
dtype: object
obj3.reindex(range(6), method='ffill')
0 bule
1 bule
2 purple
3 purple
4 yellow
5 yellow
dtype: object
对于DataFrame,reindex能更改row index,或column index。reindex the rows:
import numpy as np
frame = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3, 3),index=['a', 'c', 'd'],columns=['Ohio', 'Texas', 'California'])
frame
| Ohio | Texas | California | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| c | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| d | 6 | 7 | 8 |
frame2 = frame.reindex(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
frame2
| Ohio | Texas | California | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| b | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| c | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 |
| d | 6.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 |
更改columns index:
states = ['Texas', 'Utah', 'California']
frame.reindex(columns=states)
| Texas | Utah | California | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 1 | NaN | 2 |
| c | 4 | NaN | 5 |
| d | 7 | NaN | 8 |
还可以使用loc更简洁的reindex:
frame.loc[['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], states]
| Texas | Utah | California | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 1.0 | NaN | 2.0 |
| b | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| c | 4.0 | NaN | 5.0 |
| d | 7.0 | NaN | 8.0 |
2 Dropping Entries from an Axis (按轴删除记录)
对于series,drop回返回一个新的object,并删去你制定的axis的值:
obj = pd.Series(np.arange(5.), index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
obj
a 0.0
b 1.0
c 2.0
d 3.0
e 4.0
dtype: float64
new_obj = obj.drop('c')
new_obj
a 0.0
b 1.0
d 3.0
e 4.0
dtype: float64
obj.drop(['d', 'c'])
a 0.0
b 1.0
e 4.0
dtype: float64
对于DataFrame,index能按行或列的axis来删除:
data = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(16).reshape(4, 4),index=['Ohio', 'Colorado', 'Utah', 'New York'],columns=['one', 'two', 'three', 'four'])
data
| one | two | three | four | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ohio | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Colorado | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Utah | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| New York | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
行处理:如果a sequence of labels(一个标签序列)来调用drop,会删去row labels(axis 0):
data.drop(['Colorado', 'Ohio'])
| one | two | three | four | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| New York | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
列处理:drop列的话,设定axis=1或axis='columns':
data.drop('two', axis=1)
| one | three | four | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ohio | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| Colorado | 4 | 6 | 7 |
| Utah | 8 | 10 | 11 |
| New York | 12 | 14 | 15 |
data.drop(['two', 'four'], axis='columns')
| one | three | |
|---|---|---|
| Ohio | 0 | 2 |
| Colorado | 4 | 6 |
| Utah | 8 | 10 |
| New York | 12 | 14 |
drop也可以不返回一个新的object,而是直接更改series or dataframe in-place:
obj.drop('c', inplace=True)
obj
a 0.0
b 1.0
d 3.0
e 4.0
dtype: float64
3 Indexing, Selection, and Filtering(索引,选择,过滤)
series indexing(obj[...]) 相当于numpy的array indexing, 而且除了整数,还可以使用series的index:
obj = pd.Series(np.arange(4.), index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
obj
a 0.0
b 1.0
c 2.0
d 3.0
dtype: float64
obj['b']
1.0
obj[1]
1.0
obj[2:4]
c 2.0
d 3.0
dtype: float64
# 选中行
obj[['b', 'a', 'd']]
b 1.0
a 0.0
d 3.0
dtype: float64
obj[[1, 3]]
b 1.0
d 3.0
dtype: float64
obj[obj < 2]
a 0.0
b 1.0
dtype: float64
用label来slicing(切片)的时候,和python的切片不一样的在于,会包括尾节点:
obj['b':'c']
b 1.0
c 2.0
dtype: float64
可以直接给选中的label更改值:
obj['b':'c'] = 5
obj
a 0.0
b 5.0
c 5.0
d 3.0
dtype: float64
而对于DataFrame,indexing可以通过一个值或序列,选中一个以上的列:
data = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(16).reshape((4, 4)),index=['Ohio', 'Colorado', 'Utah', 'New York'],columns=['one', 'two', 'three', 'four'])
data
| one | two | three | four | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ohio | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Colorado | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Utah | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| New York | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
data['two']
Ohio 1
Colorado 5
Utah 9
New York 13
Name: two, dtype: int64
data[['three', 'one']]
| three | one | |
|---|---|---|
| Ohio | 2 | 0 |
| Colorado | 6 | 4 |
| Utah | 10 | 8 |
| New York | 14 | 12 |
dataframe的indexing有一些比较特别的方式。比如通过布尔数组:
data[:2]
| one | two | three | four | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ohio | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Colorado | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
data[data['three'] > 5]
| one | two | three | four | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorado | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Utah | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| New York | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
行选择的语法格式data[:2]是很方便的。给[]里传入一个list的话,可以选择列。
另一种方法是用boolean dataframe:
data < 5
| one | two | three | four | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ohio | True | True | True | True |
| Colorado | True | False | False | False |
| Utah | False | False | False | False |
| New York | False | False | False | False |
data[data < 5] = 0
data
| one | two | three | four | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ohio | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Colorado | 0 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Utah | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| New York | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
Selection with loc and iloc(用loc和iloc来选择)
对于label-indexing on rows, 我们介绍特别的索引符,loc and iloc. 这两个方法能通过axis labels(loc)或integer(iloc),来选择行或列。
一个列子,选中一行多列by label:
data
| one | two | three | four | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ohio | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Colorado | 0 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Utah | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| New York | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
data.loc['Colorado', ['two', 'three']]
two 5
three 6
Name: Colorado, dtype: int64
同iloc实现相同的效果:
data.iloc[2, [3, 0, 1]]
four 11
one 8
two 9
Name: Utah, dtype: int64
data.iloc[2] # 一行
one 8
two 9
three 10
four 11
Name: Utah, dtype: int64
data.iloc[[1, 2], [3, 0, 1]]
| four | one | two | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colorado | 7 | 0 | 5 |
| Utah | 11 | 8 | 9 |
indexing函数也能用于切片,不论是single labels或lists of labels:
data.loc[:'Utah', 'two']
Ohio 0
Colorado 5
Utah 9
Name: two, dtype: int64
data.iloc[:, :3][data.three > 5]
| one | two | three | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colorado | 0 | 5 | 6 |
| Utah | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| New York | 12 | 13 | 14 |
注意:当设计pandas的时候,作者发现frame[:, col]这样的语法是比较冗长的,因为这是会被经常用到的一个功能。作者把一些indexing的功能(lable or integer)集成在了ix这个方法上。实际中,因为这种label和integer都可以用的方式很方便,于是pandas team设计了loc和iloc来实现label-based和integer-based indexing.
虽然ix indexing依然存在,但是已经过时,不推荐使用。
4 Integer Indexes(整数索引)
一些新手再用integer来index的时候,总是会被绊倒。因为这种方法和python用于list和tuple的indexing方法不同。
比如,你不希望下面的代码出现error:
ser = pd.Series(np.arange(3.))
ser
0 0.0
1 1.0
2 2.0
dtype: float64
ser[-1]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------KeyError Traceback (most recent call last)<ipython-input-61-3cbe0b873a9e> in <module>()
----> 1 ser[-1]/Users/xu/anaconda/envs/py35/lib/python3.5/site-packages/pandas/core/series.py in __getitem__(self, key)581 key = com._apply_if_callable(key, self)582 try:
--> 583 result = self.index.get_value(self, key)584 585 if not lib.isscalar(result):/Users/xu/anaconda/envs/py35/lib/python3.5/site-packages/pandas/indexes/base.py in get_value(self, series, key)1978 try:1979 return self._engine.get_value(s, k,
-> 1980 tz=getattr(series.dtype, 'tz', None))1981 except KeyError as e1:1982 if len(self) > 0 and self.inferred_type in ['integer', 'boolean']:pandas/index.pyx in pandas.index.IndexEngine.get_value (pandas/index.c:3332)()pandas/index.pyx in pandas.index.IndexEngine.get_value (pandas/index.c:3035)()pandas/index.pyx in pandas.index.IndexEngine.get_loc (pandas/index.c:4018)()pandas/hashtable.pyx in pandas.hashtable.Int64HashTable.get_item (pandas/hashtable.c:6610)()pandas/hashtable.pyx in pandas.hashtable.Int64HashTable.get_item (pandas/hashtable.c:6554)()KeyError: -1
看到了,pandas在整数索引上可能会出错。这里我们有一个index包括0,1,2,但是猜测用户想要什么是很困难的:
ser
0 0.0
1 1.0
2 2.0
dtype: float64
另一方面,如果用非整数来做index,就没有歧义了:
ser2 = pd.Series(np.arange(3.), index=['a', 'b', 'c'])
ser2[-1]
2.0
为了保持连贯性,如果axis index里包含integer,那么选择数据的时候,就会是label-oriented. 为了更精确地选择,使用loc(for label)或ilco(for integers):
ser[:1]
0 0.0
dtype: float64
ser.loc[:1]
0 0.0
1 1.0
dtype: float64
ser.iloc[:1]
0 0.0
dtype: float64
5 Arithmetic and Data Alignment (算数和数据对齐)
pandas一个有用的feature就是,不同index的obejct之间的算数计算。如果两个object相加,但他们各自的index并不相同,最后结果得到的index是这两个index的合集:
s1 = pd.Series([7.3, -2.5, 3.4, 1.5], index=['a', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
s2 = pd.Series([2.1, 3.6, -1.5, 4, 3.1], index=['a', 'c', 'e', 'f', 'g'])
s1
a 7.3
c -2.5
d 3.4
e 1.5
dtype: float64
s2
a 2.1
c 3.6
e -1.5
f 4.0
g 3.1
dtype: float64
s1 + s2
a 9.4
c 1.1
d NaN
e 0.0
f NaN
g NaN
dtype: float64
这种数据对齐的方式(internal data alignment)引入了很多缺失值在没有的位置上。这些缺失值会被用在之后的算数计算中。
在DataFrame中,数据对齐同时发生在行和列上:
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9.).reshape((3, 3)), columns=list('bcd'),index=['Ohio', 'Texas', 'Colorado'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12.).reshape((4, 3)), columns=list('bde'),index=['Utah', 'Ohio', 'Texas', 'Oregon'])
df1
| b | c | d | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ohio | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| Texas | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 |
| Colorado | 6.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 |
df2
| b | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| Ohio | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 |
| Texas | 6.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 |
| Oregon | 9.0 | 10.0 | 11.0 |
相加的结果就是两个DataFrame,行和列的合集:
df1 + df2
| b | c | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorado | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| Ohio | 3.0 | NaN | 6.0 | NaN |
| Oregon | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| Texas | 9.0 | NaN | 12.0 | NaN |
| Utah | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
因为'c'和'e'列都不在两个DataFrame里,所有全是缺失值。对于行,即使有相同的,但列不一样的话也会是缺失值。
如果两个DataFrame相加,而且没有column和row,结果会全是null:
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'B': [3, 4]})
df1
| A | |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
df2
| B | |
|---|---|
| 0 | 3 |
| 1 | 4 |
df1 - df2
| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | NaN | NaN |
| 1 | NaN | NaN |
Arithmetic methods with fill values (带填充值的算数方法)
对于上面那些缺失值,我们想要填上0:
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12.).reshape((3, 4)), columns=list('abcd'))df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20.).reshape((4, 5)), columns=list('abcde'))df2.loc[1, 'b'] = np.nan
df1
| a | b | c | d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 |
| 1 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 7.0 |
| 2 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 10.0 | 11.0 |
df2
| a | b | c | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
| 1 | 5.0 | NaN | 7.0 | 8.0 | 9.0 |
| 2 | 10.0 | 11.0 | 12.0 | 13.0 | 14.0 |
| 3 | 15.0 | 16.0 | 17.0 | 18.0 | 19.0 |
不使用添加方法的结果:
df1 + df2
| a | b | c | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 6.0 | NaN |
| 1 | 9.0 | NaN | 13.0 | 15.0 | NaN |
| 2 | 18.0 | 20.0 | 22.0 | 24.0 | NaN |
| 3 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
使用fill_value:
df1.add(df2, fill_value=0)
| a | b | c | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 4.0 |
| 1 | 9.0 | 5.0 | 13.0 | 15.0 | 9.0 |
| 2 | 18.0 | 20.0 | 22.0 | 24.0 | 14.0 |
| 3 | 15.0 | 16.0 | 17.0 | 18.0 | 19.0 |
每一个都有一个配对的,以 r 开头,意思是反转:
1 / df1
| a | b | c | d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | inf | 1.000000 | 0.500000 | 0.333333 |
| 1 | 0.250000 | 0.200000 | 0.166667 | 0.142857 |
| 2 | 0.125000 | 0.111111 | 0.100000 | 0.090909 |
df1.rdiv(1)
| a | b | c | d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | inf | 1.000000 | 0.500000 | 0.333333 |
| 1 | 0.250000 | 0.200000 | 0.166667 | 0.142857 |
| 2 | 0.125000 | 0.111111 | 0.100000 | 0.090909 |
在reindex(重建索引)的时候,也可以使用fill_value:
df1.reindex(columns=df2.columns, fill_value=0)
| a | b | c | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 0 |
| 1 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 0 |
| 2 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 10.0 | 11.0 | 0 |
Operations between DataFrame and Series (DataFrame和Series之间的操作)
先举个numpy的例子帮助理解,可以考虑成一个二维数组和它的一行:
arr = np.arange(12.).reshape((3, 4))
arr
array([[ 0., 1., 2., 3.],[ 4., 5., 6., 7.],[ 8., 9., 10., 11.]])
arr[0]
array([ 0., 1., 2., 3.])
arr - arr[0]
array([[ 0., 0., 0., 0.],[ 4., 4., 4., 4.],[ 8., 8., 8., 8.]])
可以看到,这个减法是用在了每一行上。这种操作叫broadcasting,在Appendix A有更详细的解释。DataFrame和Series的操作也类似:
frame = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12.).reshape((4, 3)),columns=list('bde'),index=['Utah', 'Ohio', 'Texas', 'Oregon'])
series = frame.iloc[0]
frame
| b | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| Ohio | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 |
| Texas | 6.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 |
| Oregon | 9.0 | 10.0 | 11.0 |
series
b 0.0
d 1.0
e 2.0
Name: Utah, dtype: float64
可以理解为series的index与dataframe的列匹配,broadcasting down the rows(向下按行广播):
frame - series
| b | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Ohio | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Texas | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
| Oregon | 9.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 |
如果一个index既不在DataFrame的column中,也不再series里的index中,那么结果也是合集:
series2 = pd.Series(range(3), index=['b', 'e', 'f'])
frame + series2
| b | d | e | f | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | 0.0 | NaN | 3.0 | NaN |
| Ohio | 3.0 | NaN | 6.0 | NaN |
| Texas | 6.0 | NaN | 9.0 | NaN |
| Oregon | 9.0 | NaN | 12.0 | NaN |
如果想要广播列,去匹配行,必须要用到算数方法:
series3 = frame['d']
frame
| b | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| Ohio | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 |
| Texas | 6.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 |
| Oregon | 9.0 | 10.0 | 11.0 |
series3
Utah 1.0
Ohio 4.0
Texas 7.0
Oregon 10.0
Name: d, dtype: float64
frame.sub(series3, axis='index')
| b | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | -1.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Ohio | -1.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Texas | -1.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Oregon | -1.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
axis参数就是用来匹配轴的。在这个例子里是匹配dataframe的row index(axis='index or axis=0),然后再广播。
6 Function Application and Mapping (函数应用和映射)
numpy的ufuncs(element-wise数组方法)也能用在pandas的object上:
frame = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(4, 3), columns=list('bde'), index=['Utah', 'Ohio', 'Texas', 'Oregon'])
frame
| b | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | -0.810435 | 0.194448 | -0.705901 |
| Ohio | -0.886275 | 0.553640 | 1.066754 |
| Texas | 0.189898 | -0.056108 | -0.159926 |
| Oregon | 0.448303 | 0.439650 | -1.351029 |
np.abs(frame)
| b | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | 0.810435 | 0.194448 | 0.705901 |
| Ohio | 0.886275 | 0.553640 | 1.066754 |
| Texas | 0.189898 | 0.056108 | 0.159926 |
| Oregon | 0.448303 | 0.439650 | 1.351029 |
另一个常用的操作是把一个用在一维数组上的函数,应用在一行或一列上。要用到DataFrame中的apply函数:
f = lambda x: x.max() - x.min()
frame.apply(f)
b 1.334579
d 0.609748
e 2.417783
dtype: float64
这里函数f,计算的是一个series中最大值和最小值的差,在frame中的每一列,这个函数被调用一次。作为结果的series,它的index就是frame的column。
如果你传入axis='column'用于apply,那么函数会被用在每一行:
frame.apply(f, axis='columns')
Utah 1.004883
Ohio 1.953030
Texas 0.349825
Oregon 1.799333
dtype: float64
像是sum, mean这样的数组统计方法,DataFrame中已经集成了,所以没必要用apply。
apply不会返回标量,只会返回一个含有多个值的series:
def f(x): return pd.Series([x.min(), x.max()], index=['min', 'max'])
frame
| b | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | -0.810435 | 0.194448 | -0.705901 |
| Ohio | -0.886275 | 0.553640 | 1.066754 |
| Texas | 0.189898 | -0.056108 | -0.159926 |
| Oregon | 0.448303 | 0.439650 | -1.351029 |
frame.apply(f)
| b | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|
| min | -0.886275 | -0.056108 | -1.351029 |
| max | 0.448303 | 0.553640 | 1.066754 |
element-wise的python函数也能用。假设想要格式化frame中的浮点数,变为string。可以用apply map:
format = lambda x: '%.2f' % x
frame.applymap(format)
| b | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | -0.81 | 0.19 | -0.71 |
| Ohio | -0.89 | 0.55 | 1.07 |
| Texas | 0.19 | -0.06 | -0.16 |
| Oregon | 0.45 | 0.44 | -1.35 |
applymap的做法是,series有一个map函数,能用来实现element-wise函数:
frame['e'].map(format)
Utah -0.71
Ohio 1.07
Texas -0.16
Oregon -1.35
Name: e, dtype: object
7 Sorting and Ranking (排序)
按row或column index来排序的话,可以用sort_index方法,会返回一个新的object:
obj = pd.Series(range(4), index=['d', 'a', 'b', 'c'])
obj.sort_index()
a 1
b 2
c 3
d 0
dtype: int64
在DataFrame,可以用index或其他axis来排序:
frame = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(8).reshape((2, 4)),index=['three', 'one'],columns=['d', 'a', 'b', 'c'])
frame
| d | a | b | c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| three | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| one | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
frame.sort_index()
| d | a | b | c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| one | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| three | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
frame.sort_index(axis=1)
| a | b | c | d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| three | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| one | 5 | 6 | 7 | 4 |
默认是升序,可以设置降序:
frame.sort_index(axis=1, ascending=False)
| d | c | b | a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| three | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| one | 4 | 7 | 6 | 5 |
通过值来排序,用sort_values方法:
obj = pd.Series([4, 7, -3, 2])
obj.sort_values()
2 -3
3 2
0 4
1 7
dtype: int64
缺失值会被排在最后:
obj = pd.Series([4, np.nan, 7, np.nan, -3, 2])
obj.sort_values()
4 -3.0
5 2.0
0 4.0
2 7.0
1 NaN
3 NaN
dtype: float64
对于一个DataFrame,可以用一列或多列作为sort keys。这样的话,只需要把一列多多列的名字导入到sort_values即可:
frame = pd.DataFrame({'b': [4, 7, -3, 2], 'a': [0, 1, 0, 1]})
frame
| a | b | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 1 | 1 | 7 |
| 2 | 0 | -3 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 |
frame.sort_values(by='b')
| a | b | |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0 | -3 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 1 | 1 | 7 |
多列排序的话,传入一个list of names:
frame.sort_values(by=['a', 'b'])
| a | b | |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0 | -3 |
| 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | 7 |
ranking(排名)是给有效的数据分配数字。rank方法能用于series和DataFrame,rank方法默认会给每个group一个mean rank(平均排名)。rank 表示在这个数在原来的Series中排第几名,有相同的数,取其排名平均(默认)作为值:
obj = pd.Series([7, -5, 7, 4, 2, 0, 4])
obj
0 7
1 -5
2 7
3 4
4 2
5 0
6 4
dtype: int64
obj.sort_values()
1 -5
5 0
4 2
3 4
6 4
0 7
2 7
dtype: int64
obj.rank()
0 6.5
1 1.0
2 6.5
3 4.5
4 3.0
5 2.0
6 4.5
dtype: float64
在obj中,4和4的排名是第4名和第五名,取平均得4.5。7和7的排名分别是第六名和第七名,则其排名取平均得6.5。
rank也可以根据数据被观测到的顺序来设定:
obj
0 7
1 -5
2 7
3 4
4 2
5 0
6 4
dtype: int64
obj.rank(method='first')
0 6.0
1 1.0
2 7.0
3 4.0
4 3.0
5 2.0
6 5.0
dtype: float64
这里没有给0和2(指两个数字7)赋予average rank 6.5,而是给第一个看到的7(label 0)设置rank为6,第二个看到的7(label 2)设置rank为7。
也可以设置降序:
# Assign tie values the maximum rank in the group
obj.rank(ascending=False, method='max')
0 2.0
1 7.0
2 2.0
3 4.0
4 5.0
5 6.0
6 4.0
dtype: float64
dataframe 可以根据行或列来计算rank:
frame = pd.DataFrame({'b': [4.3, 7, -3, 2],'a': [0, 1, 0, 1],'c': [-2, 5, 8, -2.5]})
frame
| a | b | c | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 4.3 | -2.0 |
| 1 | 1 | 7.0 | 5.0 |
| 2 | 0 | -3.0 | 8.0 |
| 3 | 1 | 2.0 | -2.5 |
frame.rank(axis='columns') # columns表示列与列之间的排序(即每一行里数据间的排序)
| a | b | c | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 1.0 |
| 1 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 |
| 2 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| 3 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 1.0 |
8 Axis Indexes with Duplicate Labels (有重复label的轴索引)
我们看到的所有例子都有unique axis labels(index values),唯一的轴标签(索引值)。一些pandas函数(reindex),需要label是唯一的,但这并是不强制的。比如下面有一个重复的索引:
obj = pd.Series(range(5), index=['a', 'a', 'b', 'b', 'c'])
obj
a 0
a 1
b 2
b 3
c 4
dtype: int64
index的is_unique特性能告诉我们label是否是唯一的:
obj.index.is_unique
False
数据选择对于重复label则表现有点不同。如果一个label有多个值,那么就会返回一个series, 如果是label只对应一个值的话,会返回一个标量:
obj['a']
a 0
a 1
dtype: int64
obj['c']
4
这个选择的逻辑也应用于DataFrame:
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(4, 3), index=['a', 'a', 'b', 'b'])
df
| 0 | 1 | 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | -0.314526 | -1.313861 | 0.823529 |
| a | 0.994028 | -0.442338 | -0.846985 |
| b | -1.340453 | -0.031612 | 0.044791 |
| b | -0.919341 | -0.409164 | -1.297257 |
df.loc['b']
| 0 | 1 | 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| b | -1.340453 | -0.031612 | 0.044791 |
| b | -0.919341 | -0.409164 | -1.297257 |
相关文章:

pandas教程:Essential Functionality 索引 过滤 映射 排序
文章目录 5.2 Essential Functionality(主要功能)1 Reindexing(重新索引)2 Dropping Entries from an Axis (按轴删除记录)3 Indexing, Selection, and Filtering(索引,选择,过滤)Selection with loc and i…...
pyspark连接mysql数据库报错
使用pyspark连接mysql数据库代码如下 spark_conf SparkConf().setAppName("MyApp").setMaster("local")spark SparkSession.builder.config(confspark_conf).getOrCreate()url "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicodetrue&characterE…...

HK WEB3 MONTH Polkadot Hong Kong 火热报名中!
HK Web3 Month 11月除了香港金融科技周外,HK Web3 Month又是一大盛事,从10月29日开始开幕直到11月18日结束。此次将齐聚世界各地的Web3产业从业者、开发者、社群成员和学生来参与本次盛会。除外,超过75位产业知名的讲者与超过50场工作坊将为…...

“第六十三天”
这两天怎么做的这么别扭,为什么我的vs 的strlen函数包括终止字符了; 哦哦,明白了,fgets函数读取在未达到指定字长,或者遇见空白符之前,会读取前面的所有字符,所以会读取换行符,而get…...

常用排序算法实现
时间复杂度 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) void func1(int n){int count 100;count; } void func2(int n){int count 100;for(int i 0; i < count;i){} } int func3(int n){return n; }O ( n ) O(n) O(n) void func1(int n){int count 100;for(int i 0; i < n;i){count;} …...
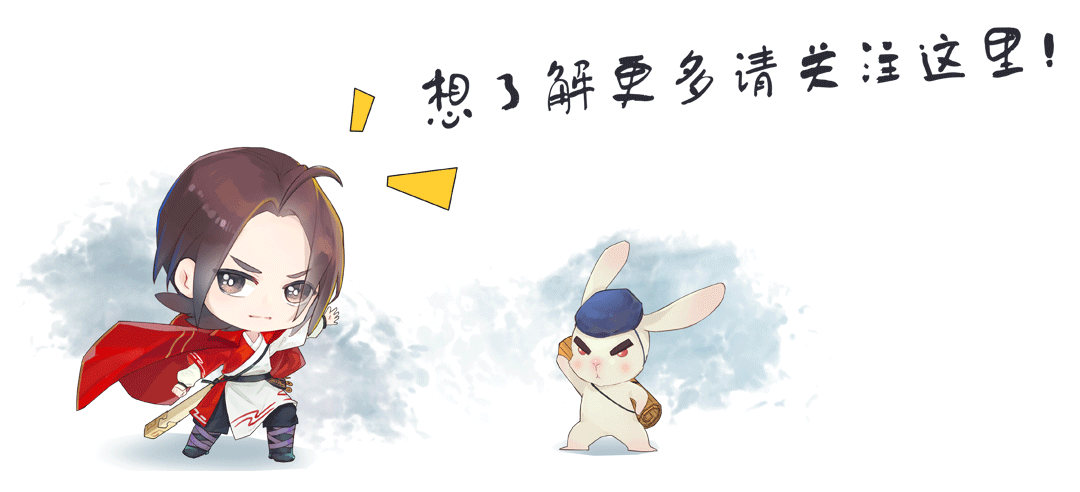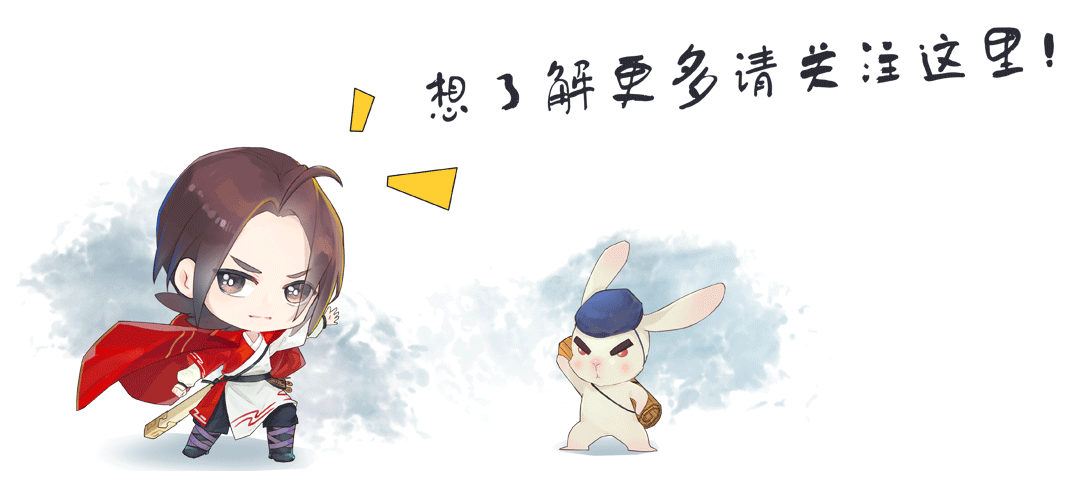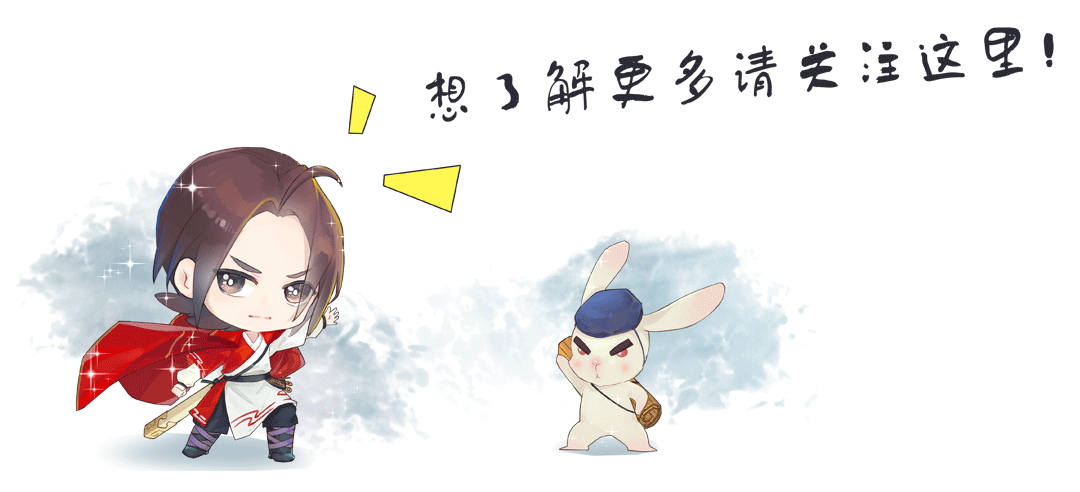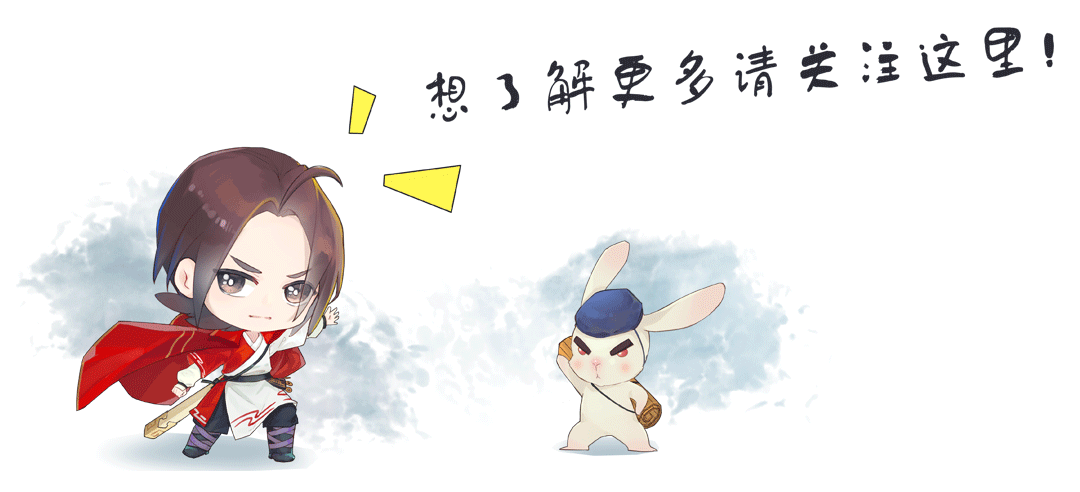
使用表单登录方法模拟登录通信人家园,要求发送登录请求后打印出来的用户名下的用户组类别
目标网站:https://www.txrjy.com/forum.php 一、进入网页,右键“检查” 二、输入用户名和密码,点击“登录”,点击“Network”,上划加载项找到蓝色框中的内容 三、点击第一个加载项,找到URL 四、相关代码: …...
Redis 的缓存击穿,穿透,雪崩及其解决方案
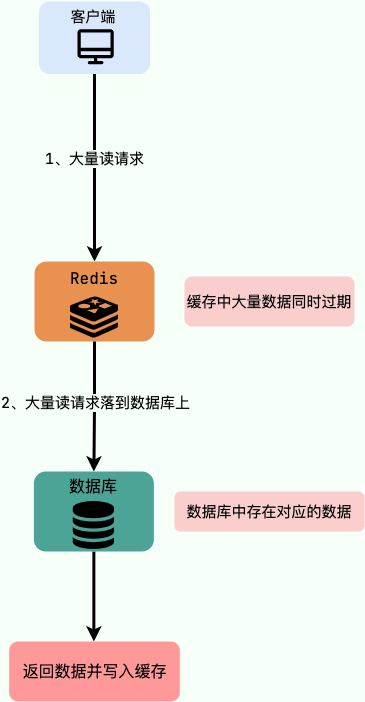
1 缓存穿透 什么是缓存穿透? 大量请求的 key 是不合理的,根本不存在于缓存中,也不存在于数据库中 。导致这些请求直接到了数据库上,根本没有经过缓存这一层,对数据库造成了巨大的压力,可能直接就被这么多…...
JWT原理分析——JWT
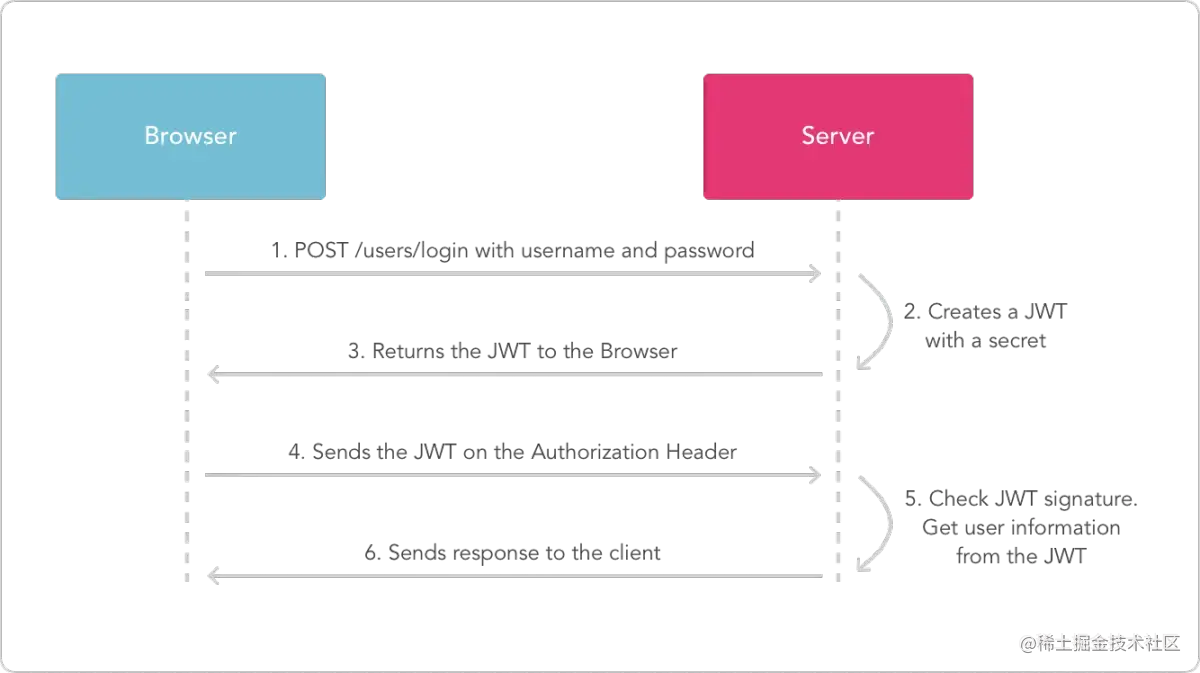
了解为什么会有JWT的出现? 首先不得不提到一个知识叫做跨域身份验证,JWT的出现就是为了更好的解决这个问题,但是在没有JWT的时候,我们一般怎么做呢?一般使用Cookie和Session,流程大体如下所示:…...
Jprofiler/ VisualVM 定位内存溢出OOM
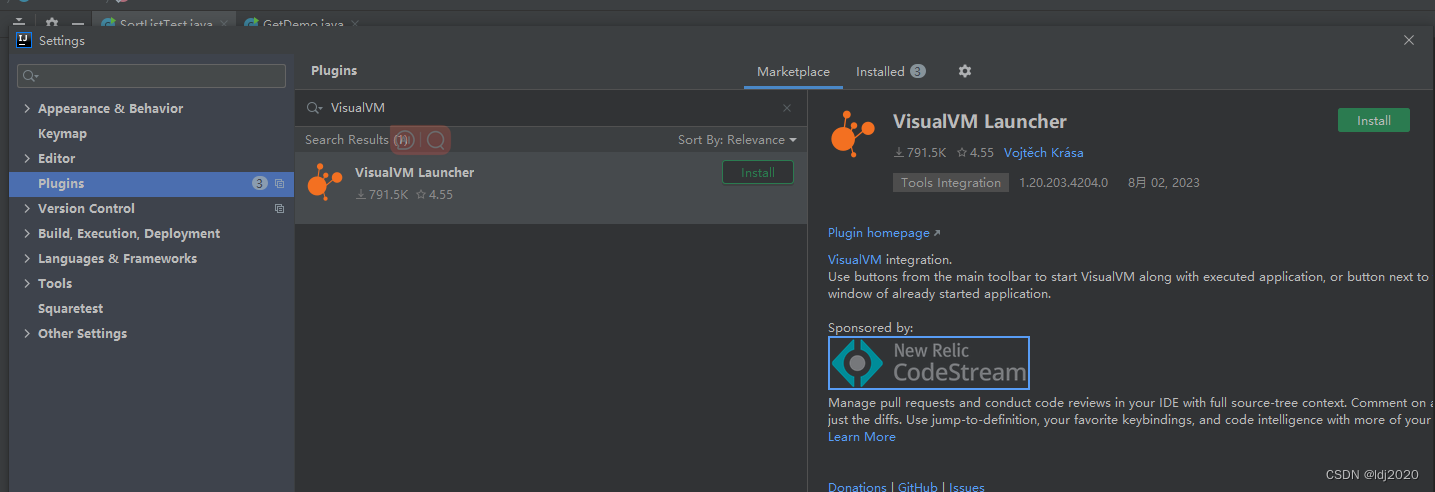
下载,接受协议下一步下一步,最后选择与IDEA集成OK ej-technologies - Java APM, Java Profiler, Java Installer Builder IDEA配置参数: # F:\study\spring-test\dump 为dump文件保存路径-XX:HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:HeapDumpPathF:\study\spring-test\dumppackage …...

NOIP2023模拟13联测34 competition
题目大意 有一场题目数量为 m m m的比赛,有一个团队想要来参加。 这个团队有 n n n个选手,编号为 i i i的选手能做第 l i ∼ r i l_i \sim r_i li∼ri道题,每题他都有 100 % 100\% 100%的概率做出来。 这个团队会随机派出一只队伍来参…...
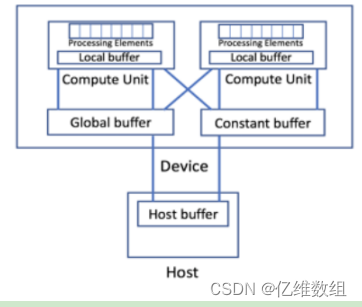
Intel oneAPI笔记(2)--jupyter官方文档(oneAPI_Intro)学习笔记
前言 本文是对jupyterlab中oneAPI_Essentials/01_oneAPI_Intro文档的学习记录,包含对SYCL、DPC extends SYCL、oneAPI Programming models等介绍和SYCL代码的初步演示等内容 oneAPI编程模型综述 oneAPI编程模型提供了一个全面而统一的开发人员工具组合࿰…...
用 QT 开发软件会吃官司吗?
之前我写过我们现在使用 QT 开发跨平台软件,有朋友留言,QT 虽好,当心收到律师函。今天就来聊聊这个话题。 在开始这个话题之前,我们先把使用盗版 QT 排除在外,只讨论在合法且遵从版权协议的前提下,能否使用…...

远程运维用什么软件?可以保障更安全?
远程运维顾名思义就是通过远程的方式IT设备等运行、维护。远程运维适用场景包含因疫情居家办公,包含放假期间出现运维故障远程解决,包含项目太远需要远程操作等等。但远程运维过程存在一定风险,安全性无法保障,所以一定要选择靠谱…...

数据结构与算法C语言版学习笔记(2)-线性表、顺序存储结构的线性表
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 文章目录 数据结构部分的知识框架一、线性表的定义和特点1.定义2.特点 二、线性表的实际案例引入1.案例一:多项式的加减乘除2.案例二:当多项式是稀疏多…...
【vite】vite.defineConfig is not a function/npm无法安装第三方包问题
当使用vite命令 npm init vite-app 项目名称时配置 import vue from vitejs/plugin-vueexport default defineConfig({plugins: [vue()] })会报错vite.defineConfig is not a function 还有就是npm下载的时候也会报错 原因vite插件vitejs/plugin-vue和vite版本问题 解决 调…...

234. 回文链表 --力扣 --JAVA
题目 给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。 解题思路 判断链表是否为回文链表取决于链表中各个节点的值,所以可以通过存储各节点的值进行对比判断&…...
【JAVA学习笔记】65 - 文件类,IO流--节点流、处理流、对象流、转换流、打印流
项目代码 https://github.com/yinhai1114/Java_Learning_Code/tree/main/IDEA_Chapter19/src/com/yinhai 文件 一、文件,流 文件,对我们并不陌生,文件是保存数据的地方,比如大家经常使用的word文档,txt文件,excel文件..都是文件。它既可以保存一张图片…...

R语言 复习 习题图片
这是日天土申哥不知道从哪淘来的R语言复习知识点图片,大部分内容都是课后习题的答案 加油吧,骚年,考个好分数...
c语言 结构体 简单实例
结构体 简单例子 要求: 结构体保存学生信息操作 代码 #include <stdio.h>//定义结构体 struct student{int ID;char name[20];char sex;char birthday[8];int grade; };int main(){int number;printf("请输入学生个数:");scanf(&quo…...

【ChatGPT】ChatGPT的自定义指令
ChatGPT的自定义指令 关于ChatGPT自定义指令的常见问题解答概述可用性如何使用您的数据自定义指令设置将应用于所有新聊天。启动新聊天可查看更改iOS & AndroidWeb 示例常见问题使用自定义指令的好处字符限制我的ChatGPT数据导出中是否包含自定义指令?当我删除我…...

反射获取方法和属性
Java反射获取方法 在Java中,反射(Reflection)是一种强大的机制,允许程序在运行时访问和操作类的内部属性和方法。通过反射,可以动态地创建对象、调用方法、改变属性值,这在很多Java框架中如Spring和Hiberna…...
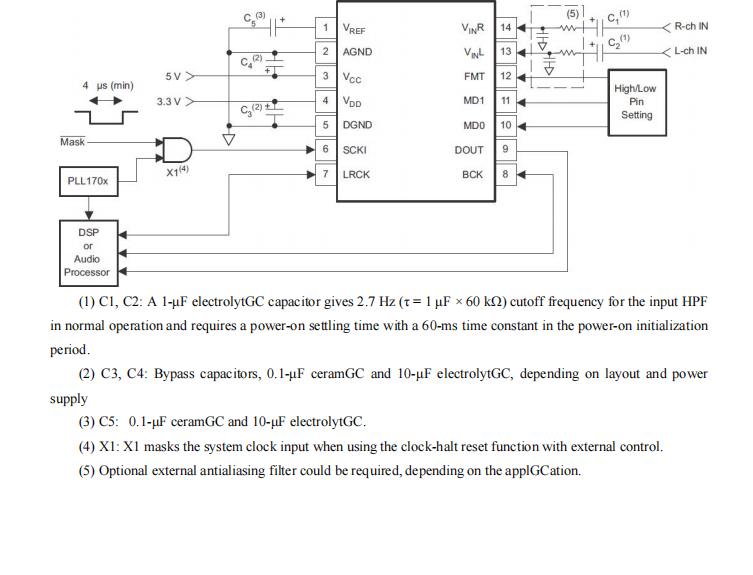
GC1808高性能24位立体声音频ADC芯片解析
1. 芯片概述 GC1808是一款24位立体声音频模数转换器(ADC),支持8kHz~96kHz采样率,集成Δ-Σ调制器、数字抗混叠滤波器和高通滤波器,适用于高保真音频采集场景。 2. 核心特性 高精度:24位分辨率,…...
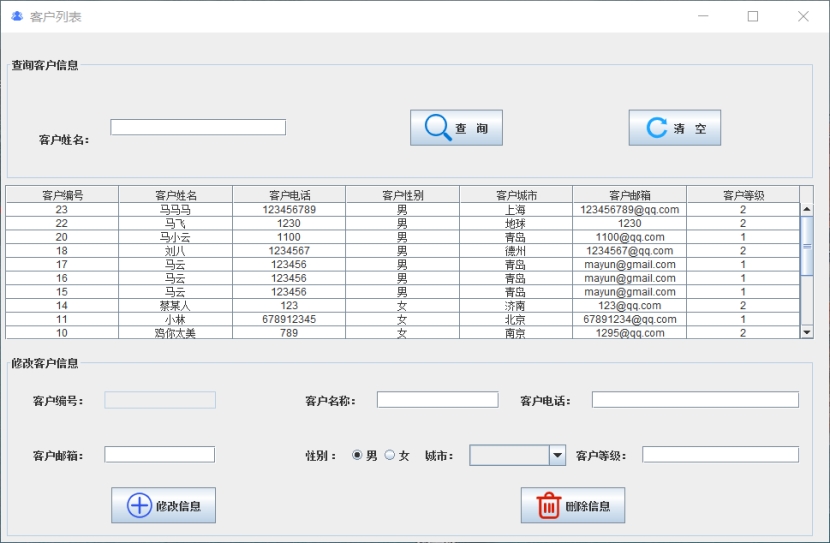
基于Java+MySQL实现(GUI)客户管理系统
客户资料管理系统的设计与实现 第一章 需求分析 1.1 需求总体介绍 本项目为了方便维护客户信息为了方便维护客户信息,对客户进行统一管理,可以把所有客户信息录入系统,进行维护和统计功能。可通过文件的方式保存相关录入数据,对…...
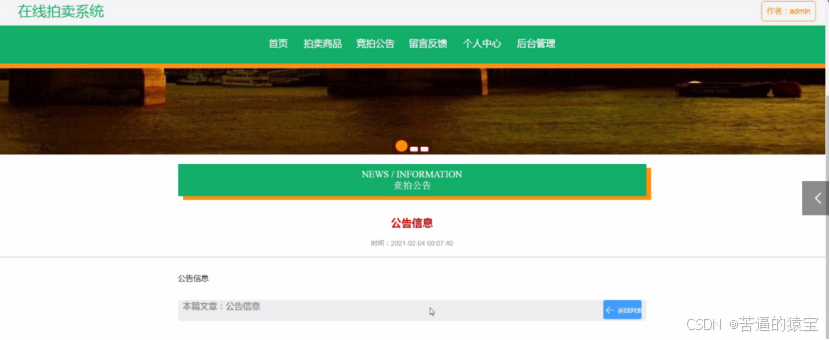
基于SpringBoot在线拍卖系统的设计和实现
摘 要 随着社会的发展,社会的各行各业都在利用信息化时代的优势。计算机的优势和普及使得各种信息系统的开发成为必需。 在线拍卖系统,主要的模块包括管理员;首页、个人中心、用户管理、商品类型管理、拍卖商品管理、历史竞拍管理、竞拍订单…...
论文阅读:LLM4Drive: A Survey of Large Language Models for Autonomous Driving
地址:LLM4Drive: A Survey of Large Language Models for Autonomous Driving 摘要翻译 自动驾驶技术作为推动交通和城市出行变革的催化剂,正从基于规则的系统向数据驱动策略转变。传统的模块化系统受限于级联模块间的累积误差和缺乏灵活性的预设规则。…...

21-Oracle 23 ai-Automatic SQL Plan Management(SPM)
小伙伴们,有没有迁移数据库完毕后或是突然某一天在同一个实例上同样的SQL, 性能不一样了、业务反馈卡顿、业务超时等各种匪夷所思的现状。 于是SPM定位开始,OCM考试中SPM必考。 其他的AWR、ASH、SQLHC、SQLT、SQL profile等换作下一个话题…...
)
iOS 项目怎么构建稳定性保障机制?一次系统性防错经验分享(含 KeyMob 工具应用)
崩溃、内存飙升、后台任务未释放、页面卡顿、日志丢失——稳定性问题,不一定会立刻崩,但一旦积累,就是“上线后救不回来的代价”。 稳定性保障不是某个工具的功能,而是一套贯穿开发、测试、上线全流程的“观测分析防范”机制。 …...

使用 uv 工具快速部署并管理 vLLM 推理环境
uv:现代 Python 项目管理的高效助手 uv:Rust 驱动的 Python 包管理新时代 在部署大语言模型(LLM)推理服务时,vLLM 是一个备受关注的方案,具备高吞吐、低延迟和对 OpenAI API 的良好兼容性。为了提高部署效…...
持续交付的进化:从DevOps到AI驱动的IT新动能
文章目录 一、持续交付的本质:从手动到自动的交付飞跃关键特性案例:电商平台的高效部署 二、持续交付的演进:从CI到AI驱动的未来发展历程 中国…...

React、Git、计网、发展趋势等内容——前端面试宝典(字节、小红书和美团)
React React Hook实现架构、.Hook不能在循环嵌套语句中使用 , 为什么,Fiber架构,面试向面试官介绍,详细解释 用户: React Hook实现架构、.Hook不能在循环嵌套语句中使用 , 为什么,Fiber架构,面试向面试官介绍&#x…...
