ORDER BY limit 10比ORDER BY limit 100更慢
问题分析
pg数据库中执行sql时,ORDER BY limit 10比ORDER BY limit 100更慢
执行计划分析
SELECT*,(select cl.ITEM_DESC from tablelzl2 cl where item_name='name' and cl.ITEM_NO='abcdefg') AS "item"FROMtablelzl1 RIWHERE RI.column1='AAAA'AND RI.column2 = 'applyno20231112'ORDER BYRI.column3 DESC limit 10
Limit (cost=0.43..1522.66 rows=10 width=990)-> Index Scan Backward using idx_tablelzl1_column3 on tablelzl1 ri (cost=0.43..158007.45 rows=1038 width=990)Filter: (((column1)::text = 'AAAA'::text) AND ((column2)::text = 'applyno20231112'::text))SubPlan 1-> Index Scan using uk_tablelzl2_ii on tablelzl2 cl (cost=0.27..5.29 rows=1 width=18)Index Cond: (((item_no)::text = 'manualSign'::text) AND ((item_name)::text = (ri.manual_sign)::text))
主表没有走到column2索引,而是走column3排序字段索引的Index Scan Backward,scan index的cost非常高,而最终的cost比较低,实际执行需要9s
如果把limit 10改成limit 100,执行计划正常:
SELECT*,(select cl.ITEM_DESC from tablelzl2 cl where cl.ITEM_NAME = RI.MANUAL_SIGN AND cl.ITEM_NO='manualSign') AS "manualSign"FROMtablelzl1 RIWHERE RI.column1='AAAA'AND RI.column2 = 'applyno20231112'ORDER BYRI.column3 DESC limit 100
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Limit (cost=2632.28..3162.78 rows=100 width=990)-> Result (cost=2632.28..8138.87 rows=1038 width=990)-> Sort (cost=2632.28..2634.87 rows=1038 width=474)Sort Key: ri.column3 DESC-> Index Scan using idx_cri_column2 on tablelzl1 ri (cost=0.43..2592.61 rows=1038 width=474)Index Cond: ((column2)::text = 'applyno20231112'::text)Filter: ((column1)::text = 'AAAA'::text)SubPlan 1-> Index Scan using uk_tablelzl2_ii on tablelzl2 cl (cost=0.27..5.29 rows=1 width=18)Index Cond: (((item_no)::text = 'manualSign'::text) AND ((item_name)::text = (ri.manual_sign)::text))
(10 rows)
子查询执行计划不变,主表走到column2单列索引,回表后排序再limit,执行非常快。
不仅是limit,如果原sql仅更换column2的值,执行计划也正常。也就是说这个生产的sql只有极个别的column2的值时执行计划是异常的。
执行计划分析:
子查询前后没变可以不用分析,主要是索引选择上的不同。column2是过滤字段,column3是排序字段,两个执行计划分别选择了这2个字段的索引。
- 异常的limit 10执行计划:反向扫描排序字段索引->回表 ->limit。因为不需要额外排序,反向扫描索引时找到limit个数据就可以不用继续扫描了;扫描排序字段索引的预估代价非常高,最上层的limit最终代价预估很低。
- 正常的limit 100执行计划:访问过滤字段索引->回表 ->以排序字段排序 ->limit。因为要排序,需要把符合条件的所有索引条目全部找出来;本身访问过滤字段的索引代价预估低。
所以问题的关键在于部分反向扫描排序索引时,代价预估的过低
真实的执行情况
explain (analyze,buffers) 看下真实的执行情况
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Limit (cost=0.43..1521.93 rows=10 width=990) (actual time=23.311..8122.516 rows=10 loops=1)Buffers: shared hit=861100 read=42985 dirtied=7I/O Timings: read=6741.003-> Index Scan Backward using idx_tablelzl1_column3 on tablelzl1 ri (cost=0.43..157932.45 rows=1038 width=990) (actual time=23.309..8122.505 rows=10 loops=1)Filter: (((column1)::text = 'AAAA'::text) AND ((column2)::text = 'applyno20231112'::text))Rows Removed by Filter: 1521796Buffers: shared hit=861100 read=42985 dirtied=7I/O Timings: read=6741.003SubPlan 1-> Index Scan using uk_tablelzl2_ii on tablelzl2 cl (cost=0.27..5.29 rows=1 width=18) (actual time=0.005..0.005 rows=0 loops=10)Index Cond: (((item_no)::text = 'manualSign'::text) AND ((item_name)::text = (ri.manual_sign)::text))Buffers: shared hit=6Planning:Buffers: shared hit=121 read=28I/O Timings: read=1.476Planning Time: 2.314 msExecution Time: 8122.658 ms
Limit (cost=2632.28..3162.78 rows=100 width=990) (actual time=150.101..150.122 rows=14 loops=1)Buffers: shared hit=700 read=274I/O Timings: read=146.903-> Result (cost=2632.28..8138.87 rows=1038 width=990) (actual time=150.100..150.119 rows=14 loops=1)Buffers: shared hit=700 read=274I/O Timings: read=146.903-> Sort (cost=2632.28..2634.87 rows=1038 width=474) (actual time=150.072..150.073 rows=14 loops=1)Sort Key: ri.column3 DESCSort Method: quicksort Memory: 30kBBuffers: shared hit=694 read=274I/O Timings: read=146.903-> Index Scan using idx_cri_column2 on tablelzl1 ri (cost=0.43..2592.61 rows=1038 width=474) (actual time=0.418..149.973 rows=14 loops=1)Index Cond: ((column2)::text = 'applyno20231112'::text)Filter: ((column1)::text = 'AAAA'::text)Rows Removed by Filter: 1218Buffers: shared hit=691 read=274I/O Timings: read=146.903SubPlan 1-> Index Scan using uk_tablelzl2_ii on tablelzl2 cl (cost=0.27..5.29 rows=1 width=18) (actual time=0.002..0.002 rows=0 loops=14)Index Cond: (((item_no)::text = 'manualSign'::text) AND ((item_name)::text = (ri.manual_sign)::text))Buffers: shared hit=6Planning Time: 0.334 msExecution Time: 150.257 ms
limit 10的执行计划,执行8s,内存读shared hit=861100 磁盘读read=42985 ,丢弃了1521796行
limit 100的执行计划执行0.1s shared hit=694 read=274,丢弃了1218行
limit 10的执行计划明显是不正常,读了太多的数据才找到符合条件的行,这是sql执行过慢的原因
统计信息分析
本身预估的代价不高,但是实际上需要扫描非常多的索引行,首先想到是否是统计信息是否准确
表的统计信息:
[postgres@cnsz381785:7169/(rasesql)phmamp][10-30.15:01:26]M=# select relpages,reltuples::bigint from pg_class where relname='tablelzl1';relpages | reltuples
----------+-----------91172 | 2280874 --count出来差不多
字段的统计信息:
[phmampopr@cnsz381785:7169/(rasesql)phmamp][10-27.17:08:48]M=> select * from pg_stats where tablename='tablelzl1' and attname='column2';
-[ RECORD 1 ]----------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
schemaname | public
tablename | tablelzl1
attname | column2
inherited | f
null_frac | 0
avg_width | 18
n_distinct | -0.11990886
most_common_vals | {applyno20231112,DY20190723006650,DY20200102012899,DY20180827000557,DY20190524001304,DY20190529001885,DY20190728002359}
most_common_freqs | {0.0005,0.00026666667,0.00023333334,0.0002,0.0002,0.0002,0.0002}
histogram_bounds | {CULZF0000121605605,DSNEW0000126854232,DSNEW0000137652871,DY20160516001057,DY20161104005509,DY20170306002677,DY20170703010428,DY20170928013517,DY20180410007383,DY20180615002936,DY20180
correlation | 0.3131596
most_common_elems | [null]
most_common_elem_freqs | [null]
elem_count_histogram | [null]
这个column2 applyno20231112刚好就是排第一的most_common_vals,出现预估概率是0.0005,用预估的行2280874*0.0005=1140,与实际的行数1232差不多
[postgres@cnsz381785:7169/(rasesql)phmamp][10-30.15:05:28]M=# select count(*) from tablelzl1 where column2 = 'applyno20231112';count
-------1232
说明统计信息是准确的,实际上运行analze收集统计信息也不会解决这个问题
数据分布不均的计算
用当前统计信息计算出来的符合条件的行有1140个,那么预计从排序字段的索引上找到第一条数据平均要扫描2280874/1140=2000个索引行。如果找10条便是20000个索引行,100条便是200000个索引行。
把sort禁用,让limit 100语句强行走排序字段的索引
M=# set enable_sort=off;
SET
--limit 100的执行计划Limit (cost=0.43..15222.69 rows=100 width=990)-> Index Scan Backward using idx_tablelzl1_column3 on tablelzl1 ri (cost=0.43..158007.45 rows=1038 width=990)Filter: (((column1)::text = 'AAAA'::text) AND ((column2)::text = 'applyno20231112'::text))SubPlan 1-> Index Scan using uk_tablelzl2_ii on tablelzl2 cl (cost=0.27..5.29 rows=1 width=18)Index Cond: (((item_no)::text = 'manualSign'::text) AND ((item_name)::text = (ri.manual_sign)::text))
limit 10改成limit 100后的执行计划,代价从1522.66升到了15222.69,基本上只是简单的*10。limit 100的代价15222.69大于了走过滤字段索引的执行计划cost 3162.78,所以limit 10和limit 100执行计划不同,选择了不同的索引。
以上的估算都是以数据零散的放在排序列的索引上 为前提的,实际情况有可能数据在最后一条(反向扫描索引),很快就能找到;也有可能数据全部在索引叶节点前面的几个pages,此时几乎是扫描全部索引并回表,代价便非常高。
那么两个字段的关联度,数据在索引上的分布情况,决定了使用排序字段的索引 的效率。
再看下真实的执行扫描了多少行数据:
-> Index Scan Backward using idx_tablelzl1_column3 on tablelzl1 ri (cost=0.43..157932.45 rows=1038 width=990) (actual time=23.309..8122.505 rows=10 loops=1)Filter: (((column1)::text = 'AAAA'::text) AND ((column2)::text = 'applyno20231112'::text))Rows Removed by Filter: 1521796
实际上差不多扫描了1521796行才找到这10条数据,本来预估的是20000,整整相差了76倍!
触发场景
- 必须有where +order by+limit语句
- 排序字段和过滤字段都必须有索引
- 一般limit不会特别大
- 数据分布不均
解决办法
改写sql语句:添加表达式,不让order by字段走索引即可
SELECT*,(select cl.ITEM_DESC from tablelzl2 cl where cl.ITEM_NAME = RI.MANUAL_SIGN AND cl.ITEM_NO='manualSign') AS "manualSign"FROMtablelzl1 RIWHERE RI.column1='AAAA'AND RI.column2 = 'applyno20231112'ORDER BYRI.column3 +'0' DESC limit 10
oracle是怎么做的
执行计划cost的预估差异
从上面的执行计划分析,pg的执行计划cost看起来不太适应,上层的cost小于内层的cost,不像oracle这样阶梯式的累加计算
这里做一个oracle和pg的实验,一张表仅存储colname='x’的数据,看下pg和oracle的对cost计算的区别:
[postgres@cnsz381785:7169/(rasesql)dbmgr][10-31.14:32:19]M=# explain select * from testlzl where col1='x' limit 1;QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------Limit (cost=0.00..0.02 rows=1 width=2)-> Seq Scan on testlzl (cost=0.00..17747.20 rows=1048576 width=2)Filter: ((col1)::text = 'x'::text)
[postgres@cnsz381785:7169/(rasesql)dbmgr][10-31.14:32:30]M=# explain select * from testlzl where col1='xx' limit 1;QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------Limit (cost=0.00..17747.20 rows=1 width=2)-> Seq Scan on testlzl (cost=0.00..17747.20 rows=1 width=2)Filter: ((col1)::text = 'xx'::text)
col1='x’立马就能找到,limit的算法没有推入到全表扫描的成本中,total cost是17747.20,跟扫描完表的成本是一样的。limit的成本cost虽然没有下推到内层的cost做计算,但是rows计算了!
来看下oracle是执行计划是怎么做的:
SYS@t8icss1> select * from dbmgr.testlzl where a='x' and rownum<=1;1 row selected.Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 2045386539------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 2 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | COUNT STOPKEY | | | | | |
|* 2 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| TESTLZL | 1 | 2 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------1 - filter(ROWNUM<=1)2 - filter("A"='x')
SYS@t8icss1> select * from dbmgr.testlzl where a='xx' and rownum<=1;no rows selectedExecution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 2045386539------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 2 | 302 (2)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | COUNT STOPKEY | | | | | |
|* 2 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| TESTLZL | 1 | 2 | 302 (2)| 00:00:01 |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------1 - filter(ROWNUM<=1)2 - filter("A"='xx')
对于oracle的计划,a='x’的数据可以立即找到的话,STOPKEY的代价算进了内层的cost中,cost只有2,实际上扫描全表的代价比较高302。
这一点是oracle与pg关于cost计算的一个重要区别:
- oracle的外层cost必然>=内层cost;pg则不一定
- oracle的内层cost计算包含了外层的算子(比如stopkey);但是pg不会包含,直接给子路径的全部成本
oracle的数据分布不均问题
知道了数据分布不均的原理,造一条数据把他放在排序索引的开头即可
create table tlzl(a char(100) not null,b char(100) not null);
--插入批量数据
begin
for i in 1..100000 loop
insert into tlzl values('test','test');
end loop;
end;
/
--插入特殊数据
insert into tlzl values('aaaa','aaaa');
insert into tlzl values('zzzz','zzzz');
--创建索引
create index idx_a on tlzl(a);
create index idx_b on tlzl(b);
--收集统计信息
EXEC DBMS_STATS.GATHER_TABLE_STATS(OWNNAME=>'SYS',TABNAME=>'TLZL',estimate_percent => 10, degree=>1,METHOD_OPT=>'FOR ALL COLUMNS SIZE AUTO',cascade=>true);
select * from (select /*+ index(tlzl idx_a)*/* from tlzl where b='aaaa' order by a) where rownum<=1;
select * from (select /*+ index(tlzl idx_a)*/* from tlzl where b='zzzz' order by a) where rownum<=1;
SYS@t8icss1> select * from (select /*+ index(tlzl idx_a)*/* from tlzl where b='aaaa' order by a) where rownum<=1; Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3674066029---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 204 | 2210 (1)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | COUNT STOPKEY | | | | | |
| 2 | VIEW | | 1 | 204 | 2210 (1)| 00:00:01 |
|* 3 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| TLZL | 1 | 202 | 2210 (1)| 00:00:01 |
| 4 | INDEX FULL SCAN | IDX_A | 98830 | | 779 (1)| 00:00:01 |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SYS@t8icss1> select * from (select /*+ index(tlzl idx_a)*/* from tlzl where b='zzzz' order by a) where rownum<=1; Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3674066029---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 204 | 2210 (1)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | COUNT STOPKEY | | | | | |
| 2 | VIEW | | 1 | 204 | 2210 (1)| 00:00:01 |
|* 3 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| TLZL | 1 | 202 | 2210 (1)| 00:00:01 |
| 4 | INDEX FULL SCAN | IDX_A | 98830 | | 779 (1)| 00:00:01 |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
oracle的优化器也是一样的,优化器并不知道数据到底放在索引的哪个地方,没有办法,放在索引的第一条和最后一条都是估算的同一代价。
不过oracle有很多方法可以解决这个问题,如extended statistic、Automatic Column Group Detection、固化执行计划等。
参考
http://www.postgres.cn/v2/news/viewone/1/717
https://oracle-base.com/articles/12c/automatic-column-group-detection-extended-statistics-12cr1
相关文章:

ORDER BY limit 10比ORDER BY limit 100更慢
问题分析 pg数据库中执行sql时,ORDER BY limit 10比ORDER BY limit 100更慢 执行计划分析 SELECT*,(select cl.ITEM_DESC from tablelzl2 cl where item_namename and cl.ITEM_NOabcdefg) AS "item"FROMtablelzl1 RIWHERE RI.column1AAAAAND RI.colum…...

aws亚马逊云:置以使用 Amazon EC2!!!
完成本部分中的任务,以便为首次启动 Amazon EC2 实例进行设置: 注册一个 AWS 账户 创建管理用户 创建密钥对 创建安全组 完成后,您将准备好学习 Amazon EC2 入门教程。 注册一个 AWS 账户 如果您还没有 AWS 账户,请完成以下…...
、 torch.add()、torch.subtract()、torch.subtract()和torch.div()函数详解和示例)
torch.cat()、 torch.add()、torch.subtract()、torch.subtract()和torch.div()函数详解和示例
本文通过原理和示例对torch.cat()、 torch.add()、torch.subtract()、torch.subtract()、torch.div()和torch.linalg.solve() 函数进行详解,以帮助大家理解和使用。 目录 torch.cat()函数torch.add()函数torch.subtract()函数逐元素减法示例矩阵减法示例 torch.mul…...
jetsonTX2 nx配置tensorRT加速yolov5推理
环境说明 Ubuntu 18conda环境python3.9cuda10.2,硬件平台是Jetson tx2 nx 前提你已经能运行YOLOV5代码后,再配置tensorRT进行加速。 目前只试了图片检测和C打开USB摄像头进行视频检测,希望是使用python配合D435i深度相机来实现检测ÿ…...

<<C++primer>>函数模板与类模板相关知识点整理
1.类型萃取的原理 类型萃取利用模板形参的推演方式使得类型去掉了引用性质: //消除引用,保留原始特性 //类型萃取 /// </summary> /// <param name"it"></param> template<class _Ty> struct my_remove_reference …...

一小时学习 Git 笔记
一小时Git教程传送门 git 基础 1. 起始配置 # 配置自己的姓名 git config --global user.name "Your Name" # 配置自己的邮箱 git config --global user.email "emailexample.com" 注意1.命令之间有空格2.上面的两个命令只需要运行一次即可, 如果输入错…...
简单漂亮的登录页面
效果图 说明 开发环境:vue3,sass 代码 <template><div class"container"><div class"card-container"><div class"card-left"><span><h1>Dashboard</h1><p>Lorem ip…...
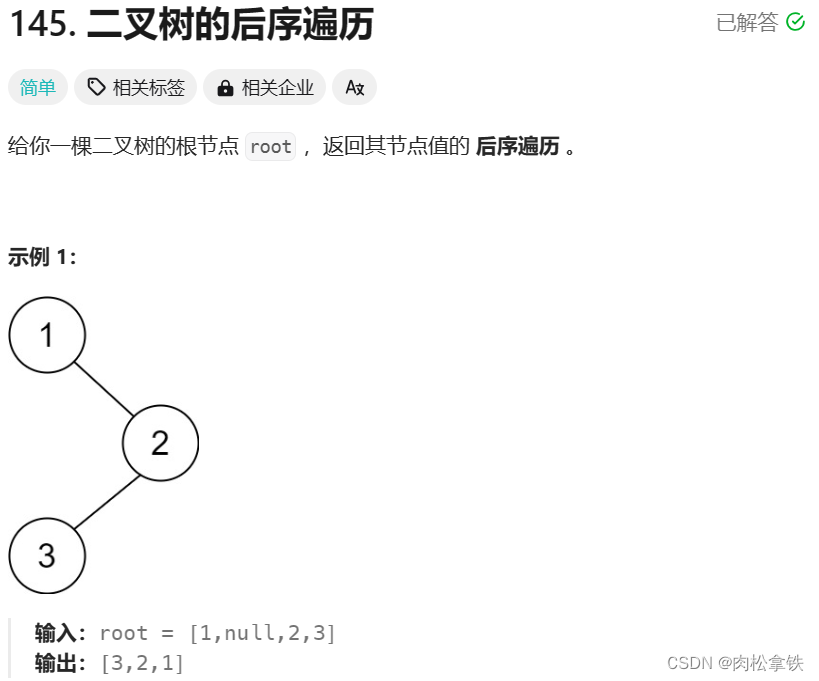
Leetcode-145 二叉树的后序遍历
递归 /*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this…...

详解JDBC
JDBC简介 概念: jdbc就是使用java语言操作关系型数据库的一套API 全称 : (Java DataBase Connectivity) Java数据库连接 本质: 官方(sun公司)定义的一套操作所有关系型数据库的规则,即接口; 各个数据库厂商实现这套接口,提供数据库驱动j…...

江门車馬炮汽车金融中心 11月11日开张
江门车马炮汽车金融中心于11月11日正式开张,这是江门市汽车金融服务平台,旨在为广大车主提供更加便捷、高效的汽车金融服务。 江门市作为广东省的一个经济发达城市,汽车保有量持续增长,但车主在购车、用车、养车等方面仍存在诸多不…...

Arthas设置参数以Json形式输出
进入arthas控制台后,先输入options json-format true命令,即可让结果、参数以json的方式输出,比如之后用watch命令查看参数,输出的形式就会是json了,这样的格式,就比较好复制出参数,在本地复现试…...
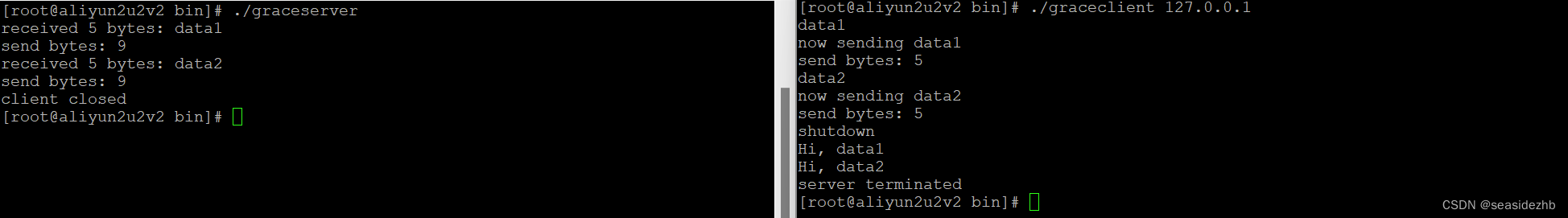
优雅关闭TCP的函数shutdown效果展示
《TCP关闭的两种方法概述》里边理论基础,下边是列出代码,并且进行实验。 服务端代码graceserver.c的内容如下: #include "lib/common.h"static int count;static void sig_int(int signo) {printf("\nreceived %d datagrams\…...

商品管理幻灯图片更换实现
<?xml version"1.0" encoding"UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace"com.java1234.mapper.ProductMappe…...
tomcat下载与使用教程
1. tomcat下载 官网:https://tomcat.apache.org/ 镜像地址:https://mirrors.huaweicloud.com/apache/tomcat/ 1、选择一个版本下载,官网下载速度缓慢,推荐镜像 2、对压缩包进行解压,无需进行安装,解压放…...
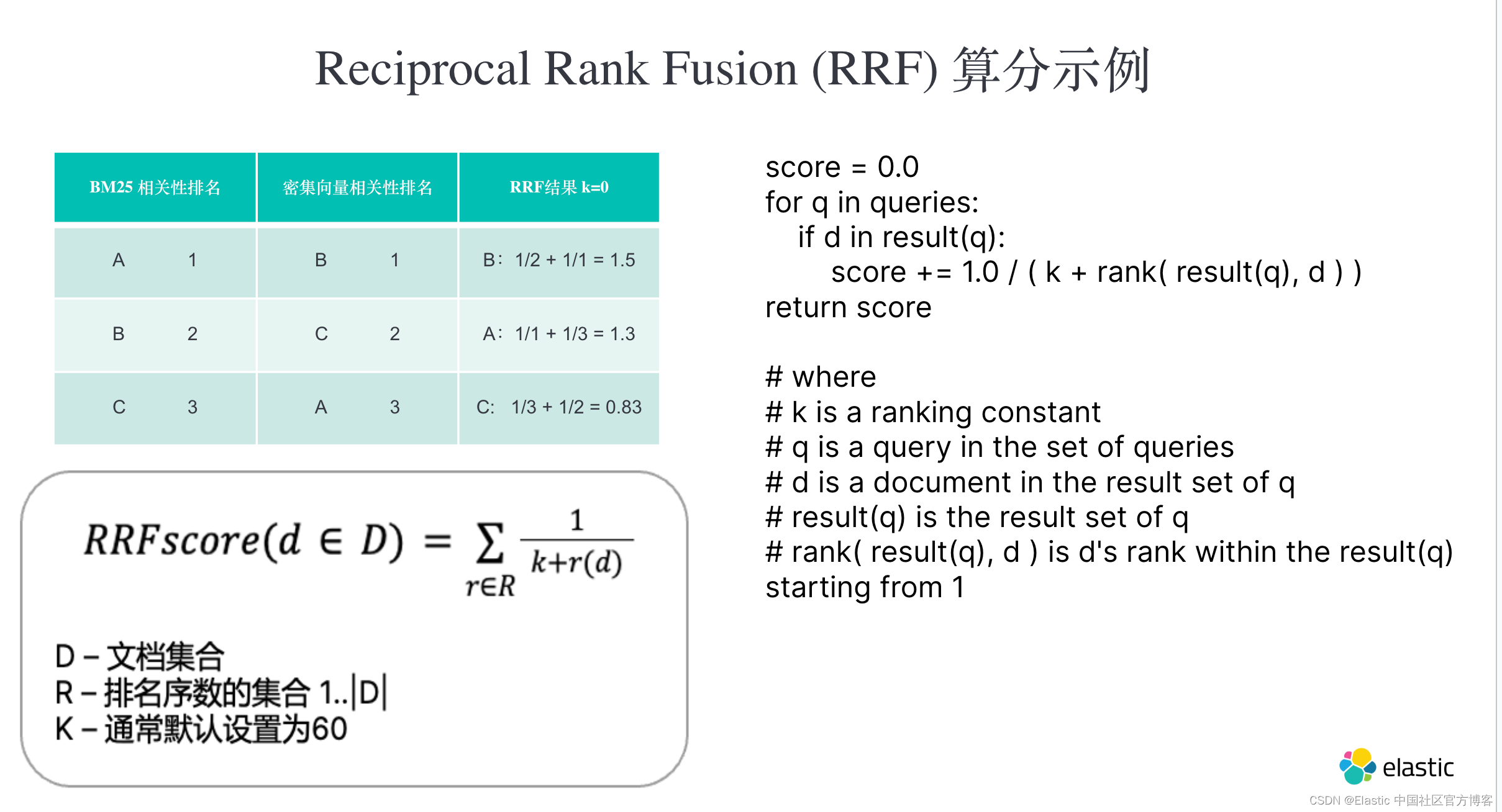
通过 Elasticsearch 和 Go 使用混合搜索进行地鼠狩猎
作者:CARLY RICHMOND,LAURENT SAINT-FLIX 就像动物和编程语言一样,搜索也经历了不同实践的演变,很难在其中做出选择。 在本系列的最后一篇博客中,Carly Richmond 和 Laurent Saint-Flix 将关键字搜索和向量搜索结合起…...
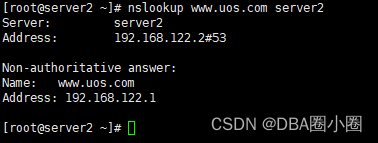
【LIUNX】配置缓存DNS服务
配置缓存DNS服务 A.安装bind bind-utils1.尝试修改named.conf配置文件2.测试nslookup B.修改named.conf配置文件1.配置文件2.再次测试 缓存DNS服务器:只提供域名解析结果的缓存功能,目的在于提高数据查询速度和效率,但是没有自己控制的区域地…...
)
Arduino驱动A01NYUB防水超声波传感器(超声波传感器)
目录 1、传感器特性 2、控制器和传感器连线图 3、通信协议 4、驱动程序 A01NYUB超声波测距传感器是一款通过发射和接收机械波来感应物体距离的电子传感器。该款产品具有监测距离远、范围广、防水等优点,且具有一定的穿透能力(烟雾、粉尘等)。该产品带有可拆卸式喇叭口,安…...
curl(八)时间和环境变量以及配置
一 时间 ① --connect-timeout 连接超时时间 ② -m | --max-time 数据最大传输时间 -m: 限制curl 完成时间(overall time limit)-m,--max-time <seconds> 整个交互完成的超时时间场景: 通过设置-m参数,可以避免请求时间过长而导致的超时错误…...
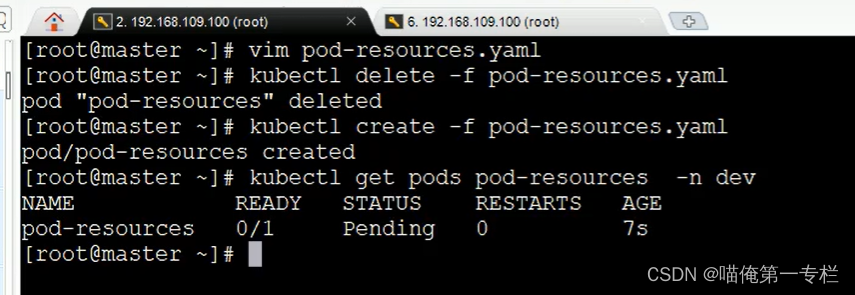
K8S知识点(十)
(1)Pod详解-启动命令 创建Pod,里面的两个容器都正常运行 (2)Pod详解-环境变量 (3)Pod详解-端口设置 (4)Pod详解-资源配额 修改:memory 不满足条件是不能正常…...
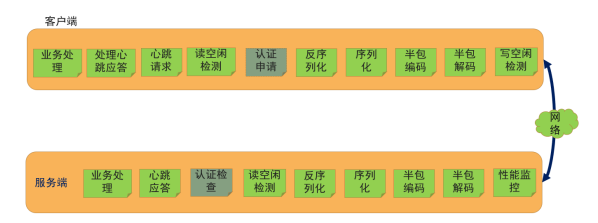
Netty实现通信框架
一、LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder的参数解释 1、LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder的构造方法参数 看下最多参数的构造方法 /*** Creates a new instance.** param byteOrder* the {link ByteOrder} of the length field* param maxFrameLength* the maximum len…...
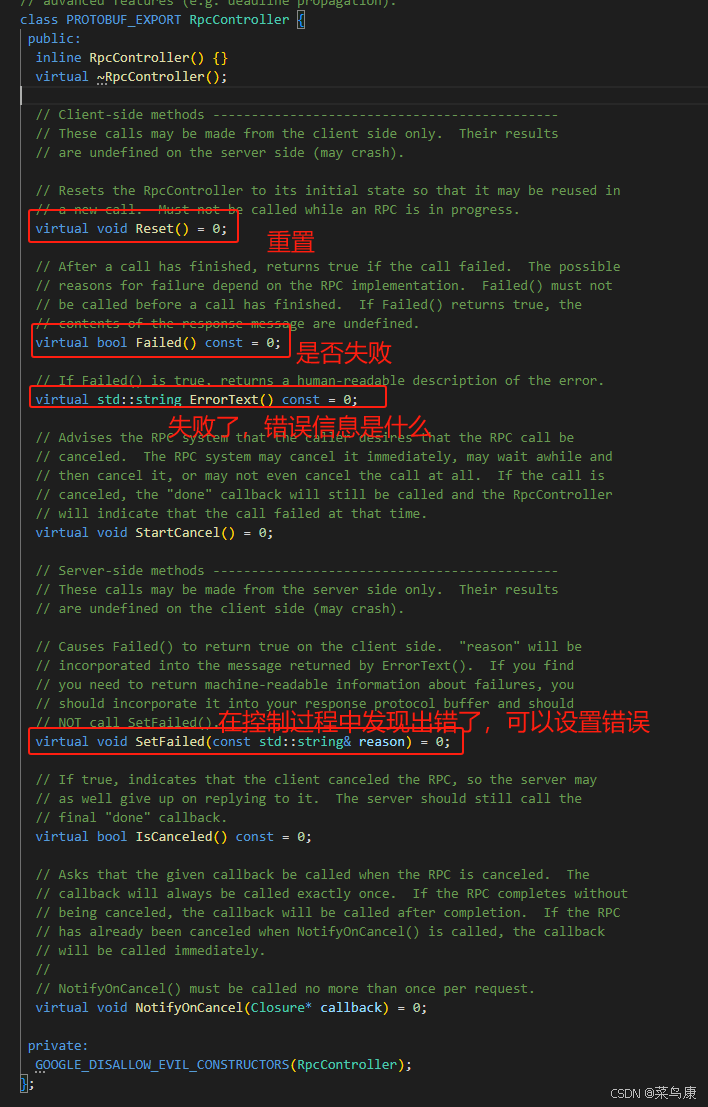
C++实现分布式网络通信框架RPC(3)--rpc调用端
目录 一、前言 二、UserServiceRpc_Stub 三、 CallMethod方法的重写 头文件 实现 四、rpc调用端的调用 实现 五、 google::protobuf::RpcController *controller 头文件 实现 六、总结 一、前言 在前边的文章中,我们已经大致实现了rpc服务端的各项功能代…...

Auto-Coder使用GPT-4o完成:在用TabPFN这个模型构建一个预测未来3天涨跌的分类任务
通过akshare库,获取股票数据,并生成TabPFN这个模型 可以识别、处理的格式,写一个完整的预处理示例,并构建一个预测未来 3 天股价涨跌的分类任务 用TabPFN这个模型构建一个预测未来 3 天股价涨跌的分类任务,进行预测并输…...

成都鼎讯硬核科技!雷达目标与干扰模拟器,以卓越性能制胜电磁频谱战
在现代战争中,电磁频谱已成为继陆、海、空、天之后的 “第五维战场”,雷达作为电磁频谱领域的关键装备,其干扰与抗干扰能力的较量,直接影响着战争的胜负走向。由成都鼎讯科技匠心打造的雷达目标与干扰模拟器,凭借数字射…...
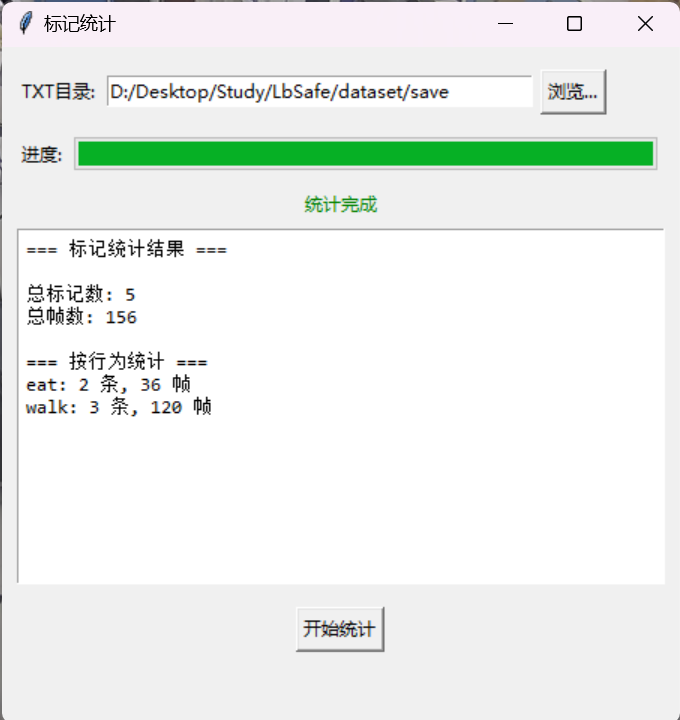
视频行为标注工具BehaviLabel(源码+使用介绍+Windows.Exe版本)
前言: 最近在做行为检测相关的模型,用的是时空图卷积网络(STGCN),但原有kinetic-400数据集数据质量较低,需要进行细粒度的标注,同时粗略搜了下已有开源工具基本都集中于图像分割这块,…...

【无标题】路径问题的革命性重构:基于二维拓扑收缩色动力学模型的零点隧穿理论
路径问题的革命性重构:基于二维拓扑收缩色动力学模型的零点隧穿理论 一、传统路径模型的根本缺陷 在经典正方形路径问题中(图1): mermaid graph LR A((A)) --- B((B)) B --- C((C)) C --- D((D)) D --- A A -.- C[无直接路径] B -…...

Java数值运算常见陷阱与规避方法
整数除法中的舍入问题 问题现象 当开发者预期进行浮点除法却误用整数除法时,会出现小数部分被截断的情况。典型错误模式如下: void process(int value) {double half = value / 2; // 整数除法导致截断// 使用half变量 }此时...

【JavaSE】多线程基础学习笔记
多线程基础 -线程相关概念 程序(Program) 是为完成特定任务、用某种语言编写的一组指令的集合简单的说:就是我们写的代码 进程 进程是指运行中的程序,比如我们使用QQ,就启动了一个进程,操作系统就会为该进程分配内存…...

日常一水C
多态 言简意赅:就是一个对象面对同一事件时做出的不同反应 而之前的继承中说过,当子类和父类的函数名相同时,会隐藏父类的同名函数转而调用子类的同名函数,如果要调用父类的同名函数,那么就需要对父类进行引用&#…...
【Veristand】Veristand环境安装教程-Linux RT / Windows
首先声明,此教程是针对Simulink编译模型并导入Veristand中编写的,同时需要注意的是老用户编译可能用的是Veristand Model Framework,那个是历史版本,且NI不会再维护,新版本编译支持为VeriStand Model Generation Suppo…...
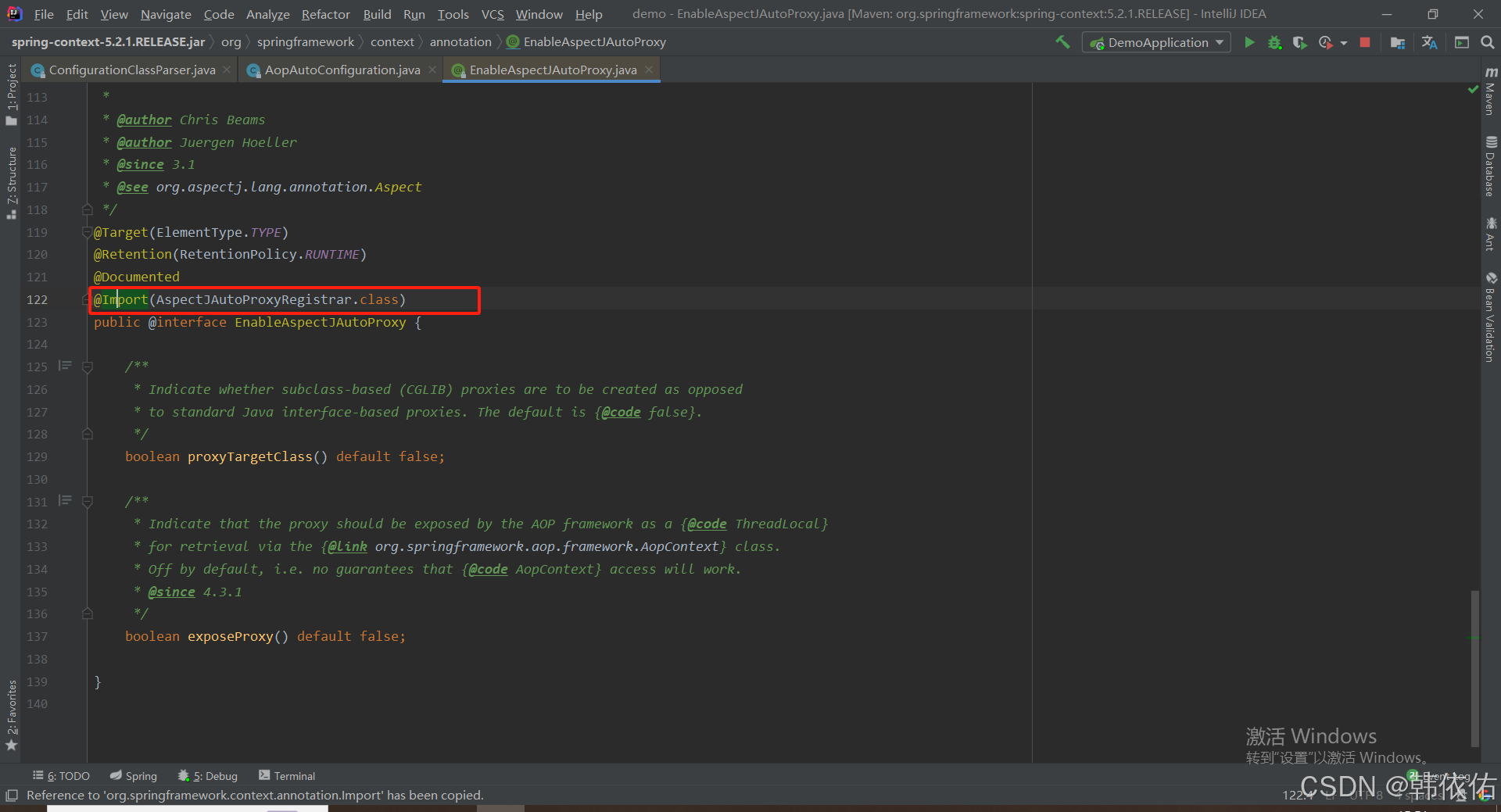
Spring AOP代理对象生成原理
代理对象生成的关键类是【AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator】,这个类继承了【BeanPostProcessor】是一个后置处理器 在bean对象生命周期中初始化时执行【org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization】方法时…...
