【rl-agents代码学习】02——DQN算法
文章目录
- Highway-env Intersection
- rl-agents之DQN
- *Implemented variants*:
- *References*:
- Query agent for actions sequence
- 探索策略
- 神经网络实现
- 小结1
- Record the experience
- Replaybuffer
- compute_bellman_residual
- step_optimizer
- update_target_network
- 小结2
- exploration_policy
- Greedy
- ϵ \epsilon ϵ-Greedy
- Boltzmann
- 运行结果
Highway-env Intersection
本文将继续探索rl-agents中相关DQN算法的实现。下面的介绍将会以intersection这个环境为例,首先介绍一下Highway-env中的intersection-v1。Highway-env中相关文档——http://highway-env.farama.org/environments/intersection/。
highway-env中的环境可以通过配置文件进行修改, observations, actions, dynamics 以及rewards等信息都是以字典的形式存储在配置文件中。
PS:DQN、DuelingDQN算法原理可参考【强化学习】10 —— DQN算法【强化学习】11 —— Double DQN算法与Dueling DQN算法
import gymnasium as gym
import pprint
from matplotlib import pyplot as pltenv = gym.make("intersection-v1", render_mode='rgb_array')
pprint.pprint(env.unwrapped.config)
输出config,可以看到如下信息:
{'action': {'dynamical': True,'lateral': True,'longitudinal': True,'steering_range': [-1.0471975511965976, 1.0471975511965976],'type': 'ContinuousAction'},'arrived_reward': 1,'centering_position': [0.5, 0.6],'collision_reward': -5,'controlled_vehicles': 1,'destination': 'o1','duration': 13,'high_speed_reward': 1,'initial_vehicle_count': 10,'manual_control': False,'normalize_reward': False,'observation': {'features': ['presence','x','y','vx','vy','long_off','lat_off','ang_off'],'type': 'Kinematics','vehicles_count': 5},'offroad_terminal': False,'offscreen_rendering': False,'other_vehicles_type': 'highway_env.vehicle.behavior.IDMVehicle','policy_frequency': 1,'real_time_rendering': False,'render_agent': True,'reward_speed_range': [7.0, 9.0],'scaling': 7.15,'screen_height': 600,'screen_width': 600,'show_trajectories': False,'simulation_frequency': 15,'spawn_probability': 0.6}
之后可以通过以下代码输出图像:
plt.imshow(env.render())
plt.show()

输出observation,可以看到是一个5*8的array,:
[[ 1.0000000e+00 9.9999998e-03 1.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00-1.2500000e-01 6.3297665e+01 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00][ 1.0000000e+00 1.3849856e-01 -1.0000000e+00 -9.9416278e-021.2500000e-01 8.1300293e+01 1.0361128e-15 0.0000000e+00][ 1.0000000e+00 -2.0000000e-02 -1.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+002.2993930e-01 6.5756187e+01 2.8473811e-15 0.0000000e+00][ 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+000.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00][ 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+000.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00]]
observation的解释如下,

通过以下代码,可以将action的类型变为离散的空间。
env.unwrapped.configure({"action": {'longitudinal': True,"type": "DiscreteMetaAction"}
})
rl-agents之DQN
A neural-network model is used to estimate the state-action value function and produce a greedy optimal policy.
Implemented variants:
- Double DQN
- Dueling architecture
- N-step targets
References:
Playing Atari with Deep Reinforcement Learning, Mnih V. et al (2013).
Deep Reinforcement Learning with Double Q-learning, van Hasselt H. et al. (2015).
Dueling Network Architectures for Deep Reinforcement Learning, Wang Z. et al. (2015).
Query agent for actions sequence
由上一节所知,通过调用run_episodes函数,进行具体的agent训练。其中会调用step函数,并执行self.agent.plan(self.observation)。对于DQNAgent的实现,首先由AbstractAgent类实现plan,之后plan函数会调用act函数:
def step(self):"""Plan a sequence of actions according to the agent policy, and step the environment accordingly."""# Query agent for actions sequenceactions = self.agent.plan(self.observation)
// rl_agents/agents/common/abstract.py
class AbstractAgent(Configurable, ABC):def __init__(self, config=None):super(AbstractAgent, self).__init__(config)self.writer = None # Tensorboard writerself.directory = None # Run directory@abstractmethoddef act(self, state):"""Pick an action:param state: s, the current state of the agent:return: a, the action to perform"""raise NotImplementedError()def plan(self, state):"""Plan an optimal trajectory from an initial state.:param state: s, the initial state of the agent:return: [a0, a1, a2...], a sequence of actions to perform"""return [self.act(state)]
DQN抽象类AbstractDQNAgent继承自AbstractStochasticAgent,AbstractStochasticAgent继承自AbstractAgent,在DQN抽象类AbstractDQNAgent中实现对act函数的重写:
def act(self, state, step_exploration_time=True):"""Act according to the state-action value model and an exploration policy:param state: current state:param step_exploration_time: step the exploration schedule:return: an action"""self.previous_state = stateif step_exploration_time:self.exploration_policy.step_time()# Handle multi-agent observations# TODO: it would be more efficient to forward a batch of statesif isinstance(state, tuple):return tuple(self.act(agent_state, step_exploration_time=False) for agent_state in state)# Single-agent settingvalues = self.get_state_action_values(state)self.exploration_policy.update(values)return self.exploration_policy.sample()
探索策略
首先来看一下exploration_policy 的实现:
self.exploration_policy = exploration_factory(self.config["exploration"], self.env.action_space)
探索策略加载的配置文件部分:
"exploration": {"method": "EpsilonGreedy","tau": 15000,"temperature": 1.0,"final_temperature": 0.05
}
跳转到exploration_factory,可以看到主要实现了三类探索策略,具体的内容会在后面部分进行介绍:
- Greedy
- ϵ \epsilon ϵ-Greedy
- Boltzmann
def exploration_factory(exploration_config, action_space):"""Handles creation of exploration policies:param exploration_config: configuration dictionary of the policy, must contain a "method" key:param action_space: the environment action space:return: a new exploration policy"""from rl_agents.agents.common.exploration.boltzmann import Boltzmannfrom rl_agents.agents.common.exploration.epsilon_greedy import EpsilonGreedyfrom rl_agents.agents.common.exploration.greedy import Greedyif exploration_config['method'] == 'Greedy':return Greedy(action_space, exploration_config)elif exploration_config['method'] == 'EpsilonGreedy':return EpsilonGreedy(action_space, exploration_config)elif exploration_config['method'] == 'Boltzmann':return Boltzmann(action_space, exploration_config)else:raise ValueError("Unknown exploration method")
神经网络实现
接着获取 Q ( s , a ) Q(s,a) Q(s,a)值
def get_state_action_values(self, state):""":param state: s, an environment state:return: [Q(a1,s), ..., Q(an,s)] the array of its action-values for each actions"""return self.get_batch_state_action_values([state])[0]
调用了抽象方法get_batch_state_action_values
@abstractmethoddef get_batch_state_action_values(self, states):"""Get the state-action values of several states:param states: [s1; ...; sN] an array of states:return: values:[[Q11, ..., Q1n]; ...] the array of all action values for each state"""raise NotImplementedError
接着来看DQNAgent中的具体实现:
class DQNAgent(AbstractDQNAgent):def __init__(self, env, config=None):super(DQNAgent, self).__init__(env, config)size_model_config(self.env, self.config["model"])self.value_net = model_factory(self.config["model"])self.target_net = model_factory(self.config["model"])self.target_net.load_state_dict(self.value_net.state_dict())self.target_net.eval()logger.debug("Number of trainable parameters: {}".format(trainable_parameters(self.value_net)))self.device = choose_device(self.config["device"])self.value_net.to(self.device)self.target_net.to(self.device)self.loss_function = loss_function_factory(self.config["loss_function"])self.optimizer = optimizer_factory(self.config["optimizer"]["type"],self.value_net.parameters(),**self.config["optimizer"])self.steps = 0def get_batch_state_action_values(self, states):return self.value_net(torch.tensor(states, dtype=torch.float).to(self.device)).data.cpu().numpy()
value_net的实现依赖于model_factory,其中的配置文件部分如下:
"model": {"type": "MultiLayerPerceptron","layers": [128, 128]},
再进入model_factory,主要实现了四类网络:
- MultiLayerPerceptron
- DuelingNetwork
- ConvolutionalNetwork
- EgoAttentionNetwork
这里我们暂且先分析多层感知机MultiLayerPerceptron(即普通DQN)。
// rl_agents/agents/common/models.py
def model_factory(config: dict) -> nn.Module:if config["type"] == "MultiLayerPerceptron":return MultiLayerPerceptron(config)elif config["type"] == "DuelingNetwork":return DuelingNetwork(config)elif config["type"] == "ConvolutionalNetwork":return ConvolutionalNetwork(config)elif config["type"] == "EgoAttentionNetwork":return EgoAttentionNetwork(config)else:raise ValueError("Unknown model type")
MultiLayerPerceptron类继承自BaseModule,BaseModule继承自torch.nn.Module。根据配置文件baseline.json,可以看到MultiLayerPerceptron类的sizes为[128, 128],激活函数为RELU。我们可以注意到,网络实现中有reshape操作,因为state的输入是5*8的矩阵,通过reshape,可以将其转换为一维的向量。最终网络结构类似于下图。

class MultiLayerPerceptron(BaseModule, Configurable):def __init__(self, config):super().__init__()Configurable.__init__(self, config)sizes = [self.config["in"]] + self.config["layers"] self.activation = activation_factory(self.config["activation"])layers_list = [nn.Linear(sizes[i], sizes[i + 1]) for i in range(len(sizes) - 1)]self.layers = nn.ModuleList(layers_list)if self.config.get("out", None):self.predict = nn.Linear(sizes[-1], self.config["out"])@classmethoddef default_config(cls):return {"in": None,"layers": [64, 64],"activation": "RELU","reshape": "True","out": None}def forward(self, x):if self.config["reshape"]:x = x.reshape(x.shape[0], -1) # We expect a batch of vectorsfor layer in self.layers:x = self.activation(layer(x))if self.config.get("out", None):x = self.predict(x)return x
获取 Q Q Q之后,探索策略进行更新,并sample一个action。以 ϵ \epsilon ϵ-Greedy为例,因为 ϵ \epsilon ϵ-Greedy继承DiscreteDistribution,所以主要关注DiscreteDistribution中的相关实现。
def act(self, state, step_exploration_time=True):...self.exploration_policy.update(values)return self.exploration_policy.sample()
rl_agents/agents/common/exploration/epsilon_greedy.pydef update(self, values):"""Update the action distribution parameters:param values: the state-action values:param step_time: whether to update epsilon schedule"""self.optimal_action = np.argmax(values)self.epsilon = self.config['final_temperature'] + \(self.config['temperature'] - self.config['final_temperature']) * \np.exp(- self.time / self.config['tau'])if self.writer:self.writer.add_scalar('exploration/epsilon', self.epsilon, self.time)
class DiscreteDistribution(Configurable, ABC):def __init__(self, config=None, **kwargs):super(DiscreteDistribution, self).__init__(config)self.np_random = None@abstractmethoddef get_distribution(self):""":return: a distribution over actions {action:probability}"""raise NotImplementedError()def sample(self):""":return: an action sampled from the distribution"""distribution = self.get_distribution()return self.np_random.choice(list(distribution.keys()), 1, p=np.array(list(distribution.values())))[0]
可以看到首先需要获得action的一个分布,这部分在 ϵ \epsilon ϵ-Greedy中的实现为:
def get_distribution(self):distribution = {action: self.epsilon / self.action_space.n for action in range(self.action_space.n)}distribution[self.optimal_action] += 1 - self.epsilonreturn distribution
get_distribution 函数返回一个动作的概率分布字典。字典的键是动作,字典的值是动作被选择的概率。概率分布的计算方式为:每个动作都有一个基础概率 self.epsilon / self.action_space.n,其中 self.action_space.n 是动作的总数,即每个动作被选择的概率相等,这是基于探索的角度。同时,最优动作 self.optimal_action 会额外获得一个概率增量 1 - self.epsilon,这是基于利用的角度,即利用已知的最优动作。
sample 函数根据 get_distribution 函数得到的动作概率分布进行采样,返回一个动作。具体地,使用 np_random.choice 函数,其参数包括动作列表和对应的动作概率分布列表,返回的是一个根据给定概率分布随机采样的动作。
小结1
到此,act函数返回一个待执行的action,此部分的框图如下所示:
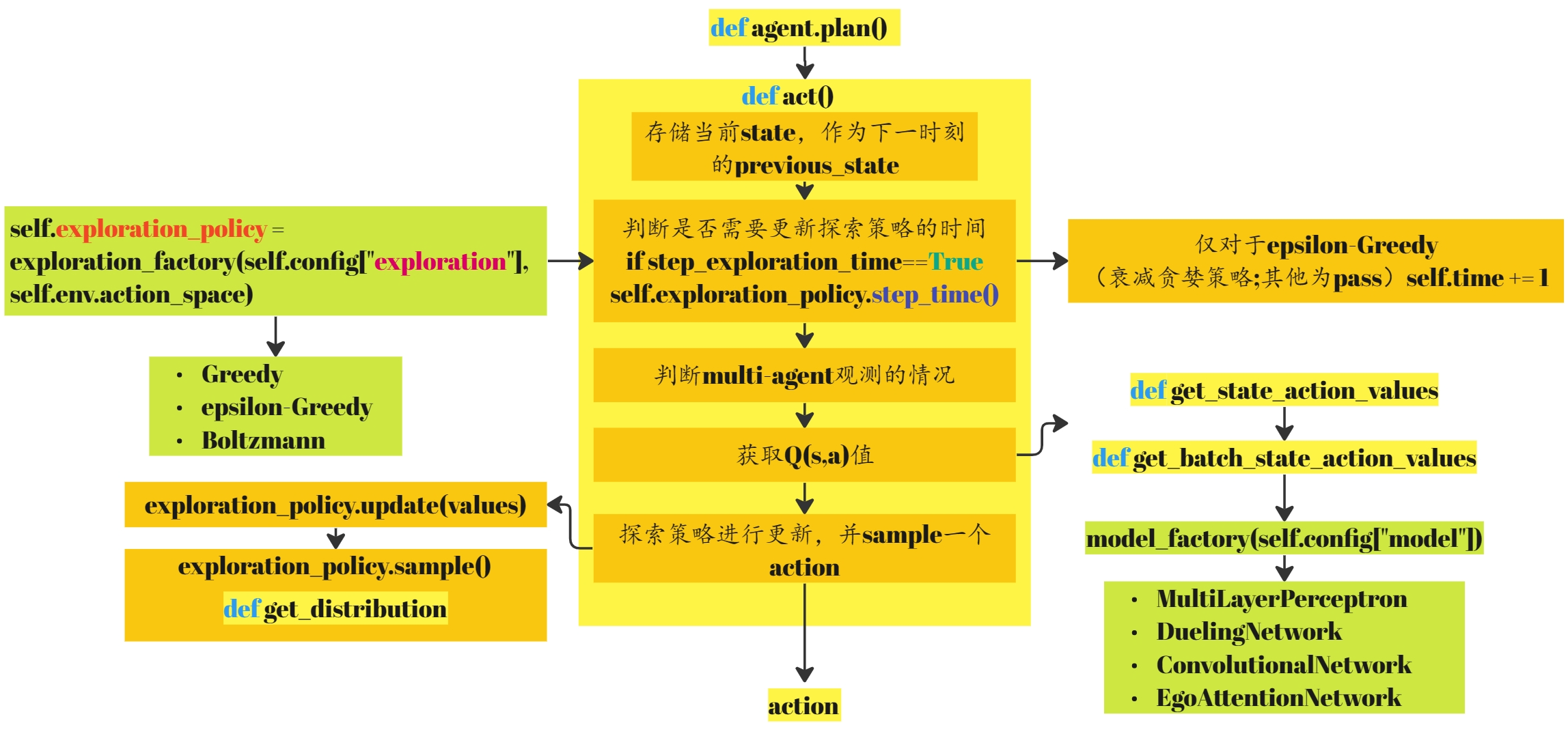
之后这几步在上一讲已经讨论过http://t.csdnimg.cn/ddpVJ。
# Forward the actions to the environment viewertry:self.env.unwrapped.viewer.set_agent_action_sequence(actions)except AttributeError:pass# Step the environmentprevious_observation, action = self.observation, actions[0]transition = self.wrapped_env.step(action)self.observation, reward, done, truncated, info = transitionterminal = done or truncated# Call callbackif self.step_callback_fn is not None:self.step_callback_fn(self.episode, self.wrapped_env, self.agent, transition, self.writer)
Record the experience
现在step函数中只剩下这一步,我们再来看这一步的实现。
# Record the experience.try:self.agent.record(previous_observation, action, reward, self.observation, done, info)except NotImplementedError:pass
直接跳转到AbstractDQNAgent类中查看相关实现
def record(self, state, action, reward, next_state, done, info):"""Record a transition by performing a Deep Q-Network iteration- push the transition into memory- sample a minibatch- compute the bellman residual loss over the minibatch- perform one gradient descent step- slowly track the policy network with the target network:param state: a state:param action: an action:param reward: a reward:param next_state: a next state:param done: whether state is terminal"""if not self.training:returnif isinstance(state, tuple) and isinstance(action, tuple): # Multi-agent setting[self.memory.push(agent_state, agent_action, reward, agent_next_state, done, info)for agent_state, agent_action, agent_next_state in zip(state, action, next_state)]else: # Single-agent settingself.memory.push(state, action, reward, next_state, done, info)batch = self.sample_minibatch()if batch:loss, _, _ = self.compute_bellman_residual(batch)self.step_optimizer(loss)self.update_target_network()
Replaybuffer
self.memory是Replaybuffer的一个实现
self.memory = ReplayMemory(self.config)
- push函数的实现可以提升运算速率。
- 在强化学习中,经常需要从经验回放缓存(这里就是
self.memory)中抽样出一批数据来更新模型。而这里的n-step是一个常用的技巧,它表明在预测下一个状态时,不仅仅使用当前的状态和动作,还使用接下来的n-1个状态和动作。当n为1时,这就是常见的单步过渡;当n大于1时,这就是n步采样。
rl_agents/agents/common/memory.py
class ReplayMemory(Configurable):"""Container that stores and samples transitions."""def __init__(self, config=None, transition_type=Transition):super(ReplayMemory, self).__init__(config)self.capacity = int(self.config['memory_capacity'])self.transition_type = transition_typeself.memory = []self.position = 0@classmethoddef default_config(cls):return dict(memory_capacity=10000,n_steps=1,gamma=0.99)def push(self, *args):"""Saves a transition."""if len(self.memory) < self.capacity:self.memory.append(None)self.position = len(self.memory) - 1elif len(self.memory) > self.capacity:self.memory = self.memory[:self.capacity]# Faster than append and popself.memory[self.position] = self.transition_type(*args)self.position = (self.position + 1) % self.capacitydef sample(self, batch_size, collapsed=True):"""Sample a batch of transitions.If n_steps is greater than one, the batch will be composed of lists of successive transitions.:param batch_size: size of the batch:param collapsed: whether successive transitions must be collapsed into one n-step transition.:return: the sampled batch"""# TODO: use agent's np_random for seedingif self.config["n_steps"] == 1:# Directly sample transitionsreturn random.sample(self.memory, batch_size)else:# Sample initial transition indexesindexes = random.sample(range(len(self.memory)), batch_size)# Get the batch of n-consecutive-transitions starting from sampled indexesall_transitions = [self.memory[i:i+self.config["n_steps"]] for i in indexes]# Collapse transitionsreturn map(self.collapse_n_steps, all_transitions) if collapsed else all_transitionsdef collapse_n_steps(self, transitions):"""Collapse n transitions <s,a,r,s',t> of a trajectory into one transition <s0, a0, Sum(r_i), sp, tp>.We start from the initial state, perform the first action, and then the return estimate is formed byaccumulating the discounted rewards along the trajectory until a terminal state or the end of thetrajectory is reached.:param transitions: A list of n successive transitions:return: The corresponding n-step transition"""state, action, cumulated_reward, next_state, done, info = transitions[0]discount = 1for transition in transitions[1:]:if done:breakelse:_, _, reward, next_state, done, info = transitiondiscount *= self.config['gamma']cumulated_reward += discount*rewardreturn state, action, cumulated_reward, next_state, done, infodef __len__(self):return len(self.memory)def is_full(self):return len(self.memory) == self.capacitydef is_empty(self):return len(self.memory) == 0
回到record代码中,首先将采样到的数据放入Replaybuffer,当采样数据量大于batch_size时,从Replaybuffer中采样。
def sample_minibatch(self):if len(self.memory) < self.config["batch_size"]:return Nonetransitions = self.memory.sample(self.config["batch_size"])return Transition(*zip(*transitions))
compute_bellman_residual
之后便利用bellman方程进行更新:
loss, _, _ = self.compute_bellman_residual(batch)
def compute_bellman_residual(self, batch, target_state_action_value=None):# Compute concatenate the batch elementsif not isinstance(batch.state, torch.Tensor):# logger.info("Casting the batch to torch.tensor")state = torch.cat(tuple(torch.tensor([batch.state], dtype=torch.float))).to(self.device)action = torch.tensor(batch.action, dtype=torch.long).to(self.device)reward = torch.tensor(batch.reward, dtype=torch.float).to(self.device)next_state = torch.cat(tuple(torch.tensor([batch.next_state], dtype=torch.float))).to(self.device)terminal = torch.tensor(batch.terminal, dtype=torch.bool).to(self.device)batch = Transition(state, action, reward, next_state, terminal, batch.info)# Compute Q(s_t, a) - the model computes Q(s_t), then we select the# columns of actions takenstate_action_values = self.value_net(batch.state)state_action_values = state_action_values.gather(1, batch.action.unsqueeze(1)).squeeze(1)if target_state_action_value is None:with torch.no_grad():# Compute V(s_{t+1}) for all next states.next_state_values = torch.zeros(batch.reward.shape).to(self.device)if self.config["double"]:# Double Q-learning: pick best actions from policy network_, best_actions = self.value_net(batch.next_state).max(1)# Double Q-learning: estimate action values from target networkbest_values = self.target_net(batch.next_state).gather(1, best_actions.unsqueeze(1)).squeeze(1)else:best_values, _ = self.target_net(batch.next_state).max(1)next_state_values[~batch.terminal] = best_values[~batch.terminal]# Compute the expected Q valuestarget_state_action_value = batch.reward + self.config["gamma"] * next_state_values# Compute lossloss = self.loss_function(state_action_values, target_state_action_value)return loss, target_state_action_value, batch
with torch.no_grad():用于禁止在其作用域内进行梯度计算- 实现了DoubleDQN
self.loss_function = loss_function_factory(self.config["loss_function"])loss函数包括以下几种:
def loss_function_factory(loss_function):if loss_function == "l2":return F.mse_losselif loss_function == "l1":return F.l1_losselif loss_function == "smooth_l1":return F.smooth_l1_losselif loss_function == "bce":return F.binary_cross_entropyelse:raise ValueError("Unknown loss function : {}".format(loss_function))
step_optimizer
对梯度进行了截断
def step_optimizer(self, loss):# Optimize the modelself.optimizer.zero_grad()loss.backward()for param in self.value_net.parameters():param.grad.data.clamp_(-1, 1)self.optimizer.step()
update_target_network
更新目标网络
def update_target_network(self):self.steps += 1if self.steps % self.config["target_update"] == 0:self.target_net.load_state_dict(self.value_net.state_dict())
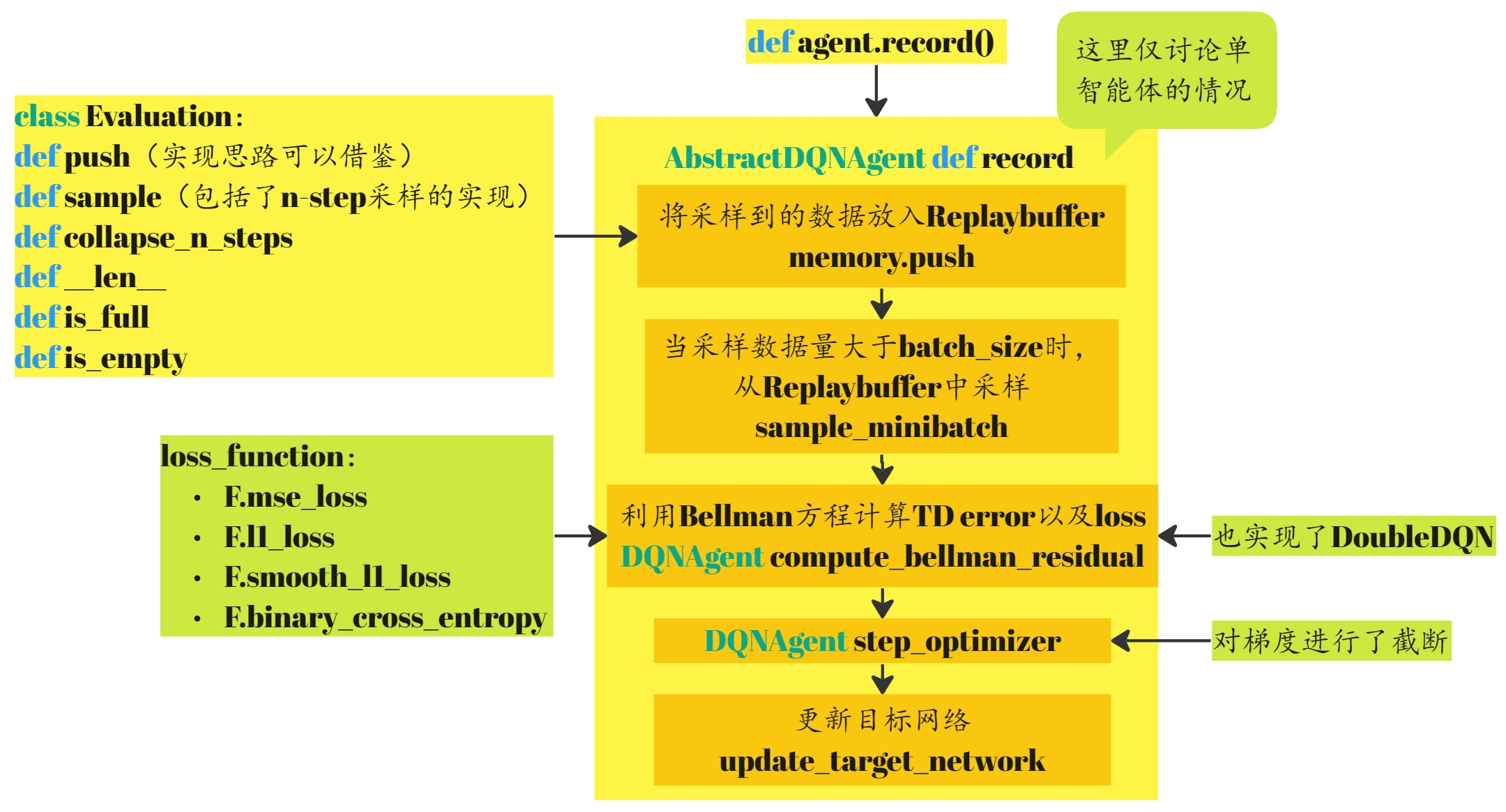
小结2
到此,整个DQN算法实现完毕,record部分的框图如下:
exploration_policy
这部分主要实现了三种策略:
- Greedy
- ϵ \epsilon ϵ-Greedy
- Boltzmann
此部分可以参考:【强化学习】02—— 探索与利用
Greedy
Greedy贪婪策略即选择最优的策略 a t = arg max a ∈ A Q ( s , a ) a_t=\argmax_{a\in\mathcal{A}}Q(s,a) at=argmaxa∈AQ(s,a)
class Greedy(DiscreteDistribution):"""Always use the optimal action"""def __init__(self, action_space, config=None):super(Greedy, self).__init__(config)self.action_space = action_spaceif isinstance(self.action_space, spaces.Tuple):self.action_space = self.action_space.spaces[0]if not isinstance(self.action_space, spaces.Discrete):raise TypeError("The action space should be discrete")self.values = Noneself.seed()def get_distribution(self):optimal_action = np.argmax(self.values)return {action: 1 if action == optimal_action else 0 for action in range(self.action_space.n)}def update(self, values):self.values = values
ϵ \epsilon ϵ-Greedy
ϵ \epsilon ϵ-Greedy公式如下:
a t = { arg max a ∈ A Q ^ ( a ) , 采样概率:1- ϵ 从 A 中随机选择 , 采样概率: ϵ a_t=\begin{cases}\arg\max_{a\in\mathcal{A}}\hat{Q}(a),&\text{采样概率:1-}\epsilon\\\text{从 }\mathcal{A}\text{ 中随机选择},&\text{采样概率: }\epsilon&\end{cases} at={argmaxa∈AQ^(a),从 A 中随机选择,采样概率:1-ϵ采样概率: ϵ
这里实现的其实是衰减贪心策略,衰减曲线如下图所示。
ϵ = final-temperature + ( temperature − final-temperature ) ∗ e − t τ \begin{aligned}\epsilon &= \text{final-temperature}+(\text{temperature}-\text{final-temperature})*e^{\frac{-t}{\tau}}\end{aligned} ϵ=final-temperature+(temperature−final-temperature)∗eτ−t

class EpsilonGreedy(DiscreteDistribution):"""Uniform distribution with probability epsilon, and optimal action with probability 1-epsilon"""def __init__(self, action_space, config=None):super(EpsilonGreedy, self).__init__(config)self.action_space = action_spaceif isinstance(self.action_space, spaces.Tuple):self.action_space = self.action_space.spaces[0]if not isinstance(self.action_space, spaces.Discrete):raise TypeError("The action space should be discrete")self.config['final_temperature'] = min(self.config['temperature'], self.config['final_temperature'])self.optimal_action = Noneself.epsilon = 0self.time = 0self.writer = Noneself.seed()@classmethoddef default_config(cls):return dict(temperature=1.0,final_temperature=0.1,tau=5000)def get_distribution(self):distribution = {action: self.epsilon / self.action_space.n for action in range(self.action_space.n)}distribution[self.optimal_action] += 1 - self.epsilonreturn distributiondef update(self, values):"""Update the action distribution parameters:param values: the state-action values:param step_time: whether to update epsilon schedule"""self.optimal_action = np.argmax(values)self.epsilon = self.config['final_temperature'] + \(self.config['temperature'] - self.config['final_temperature']) * \np.exp(- self.time / self.config['tau'])if self.writer:self.writer.add_scalar('exploration/epsilon', self.epsilon, self.time)def step_time(self):self.time += 1def set_time(self, time):self.time = timedef set_writer(self, writer):self.writer = writer
Boltzmann
玻尔兹曼分布(Boltzmann Distribution)是描述分子在热力学平衡时分布的概率分布函数。它表明在给定的能量状态下,不同的微观状态出现的概率是不同的,且符合一个指数函数形式。
在热力学中,任何物质在一定温度下都会具有一定的热运动,这些热运动状态可以用分子内能或动能来描述。而玻尔兹曼分布表明了在相同温度下,分子在所有可能状态之间的分布概率。其表达式为:
P ( E i ) = e − E i / k T ∑ j e − E j / k T P(E_i) = \frac{e^{-E_i/kT}}{\sum_{j} e^{-E_j/kT}} P(Ei)=∑je−Ej/kTe−Ei/kT
其中, P ( E i ) P(E_i) P(Ei)为分子处于能量状态 E i E_i Ei的概率, k k k为玻尔兹曼常数, T T T为温度, E j E_j Ej为所有可以达到的能量状态。
可以看到,玻尔兹曼分布中每个能量状态的出现概率与其能量成负指数关系,因此能量较小的状态出现的概率更大。这符合熵增加的趋势,即越有序的状态出现的概率越小。
class Boltzmann(DiscreteDistribution):"""Uniform distribution with probability epsilon, and optimal action with probability 1-epsilon"""def __init__(self, action_space, config=None):super(Boltzmann, self).__init__(config)self.action_space = action_spaceif not isinstance(self.action_space, spaces.Discrete):raise TypeError("The action space should be discrete")self.values = Noneself.seed()@classmethoddef default_config(cls):return dict(temperature=0.5)def get_distribution(self):actions = range(self.action_space.n)if self.config['temperature'] > 0:weights = np.exp(self.values / self.config['temperature'])else:weights = np.zeros((len(actions),))weights[np.argmax(self.values)] = 1return {action: weights[action] / np.sum(weights) for action in actions}def update(self, values):self.values = values运行结果
运行命令与方法在上一讲已经介绍【rl-agents代码学习】01——总体框架。
超参数设置采用默认设置,使用DQN算法分别运行4000steps和20000steps。使用Tensorboard查看结果:
tensorboard --logdir C:\Users\16413\Desktop\rl-agents-master\scripts\out\IntersectionEnv\DQNAgent\baseline_20231113-123234_7944\
4000steps


可以看到最后的episode reward大致在3左右。
20000steps

可以看到最后的episode reward大致在3左右。
相关文章:

【rl-agents代码学习】02——DQN算法
文章目录 Highway-env Intersectionrl-agents之DQN*Implemented variants*:*References*:Query agent for actions sequence探索策略神经网络实现小结1 Record the experienceReplaybuffercompute_bellman_residualstep_optimizerupdate_target_network小结2 exploration_polic…...

关于使用 Java 反射技术来实现解耦?
关于使用 Java 反射技术来实现解耦? 文章目录 关于使用 Java 反射技术来实现解耦?一、基本说明二、代码示例三、注意 一、基本说明 Java 反射技术允许程序在运行时加载、探索和使用类和对象。通过反射,我们可以在程序运行期间动态地创建对象…...
使用清华智谱ChatGLM2大模型搭建本地私有知识库
首先放上该方案项目的git地址:https://github.com/chatchat-space/Langchain-Chatchat 以下是我的搭建和踩坑经验记录 一、环境准备 1、python安装 在环境中安装python,我安装的是3.9版本的python,官方要求的是Python 3.8 - 3.10 版本。不知…...

MES系统如何赋能制造企业实现4M防错追溯?
生产过程4M管理和MES系统的结合是现代制造业中关键的质量管理实践,它有助于提高生产效率、降低生产成本并保证产品质量。本文将深入探讨4M管理的概念,以及MES系统如何赋能制造企业实现4M防错追溯。 一、4M管理的概念 4M管理是指在制造过程中管理和控制四…...

Mybatis保存时参数携带了逗号和空格导致SQL保存异常
起初发现这个问题是因为导入文件时,用户输入的导入参数不规范,在字段中有逗号和空格一起出现,就会导致mybatis保存时发生sql异常。 异常数据张这样: INSERT INTO enterprise_stratification (id,create_date,create_by,update_da…...
vscode launch.json
有时新的服务器进行调试时,需要设置调试的launch.json的结果 然后就可以打开一个launch.json 其内容如下 {// 使用 IntelliSense 了解相关属性。 // 悬停以查看现有属性的描述。// 欲了解更多信息,请访问: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid83…...
绿盟远程安全评估系统 RSAS 使用体验-难用
最近领导让我用公司采购的RSAS对产品进行漏洞扫描,学习并使用了这个软件,体验就是真的很难用。使用遇到问题时,咨询售后服务,机器人需要有公司认证,不能随便问问题,也是无语了。咨询客服,客服回…...

【Linux】 mdir命令使用
mdir 为mtools工具指令,模拟MS-DOS的dir指令,可显示MS-DOS文件系统中的目录内容。 语法 mdir [参数][目录] mdir命令 -Linux手册页 命令选项及作用 执行令 mdir--help 执行命令结果 参数 -a 显示隐藏文件。-f 不显示磁盘所剩余的可用空间。-w…...
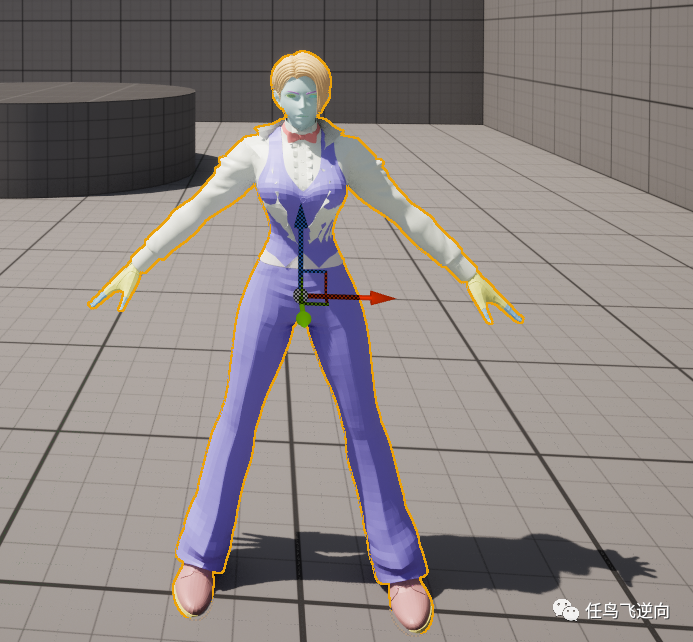
解压游戏资源,导出游戏模型
游戏中有很多好看的角色,地图等等资源。 你有没有想过,把他们导出到自己的游戏中进行魔改又或则玩换肤等操作呢? 相信很多同学都喜欢拳皇中的角色, 那么我们今天就拿拳皇15举例子,导出他的资源。 首先要先安装好这个…...

【科研新手指南2】「NLP+网安」相关顶级会议期刊 投稿注意事项+会议等级+DDL+提交格式
「NLP网安」相关顶级会议&期刊投稿注意事项 写在最前面一、会议ACL (The Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics)IH&MMSec (The ACM Workshop on Information Hiding, Multimedia and Security)CCS (The ACM Conference on Computer and Co…...

220kV环形网络的动态无功补偿方案初步设计
摘 要 动态无功补偿系统应用广泛,比如电子设备、发电系统、输电线路等方面,都会运用到动态无功补偿系统或工具。更高效率和更高稳定性的动态无功补偿系统一直是研究的热点。在电力系统中,动态无功补偿系统随处可见,因为运行稳…...
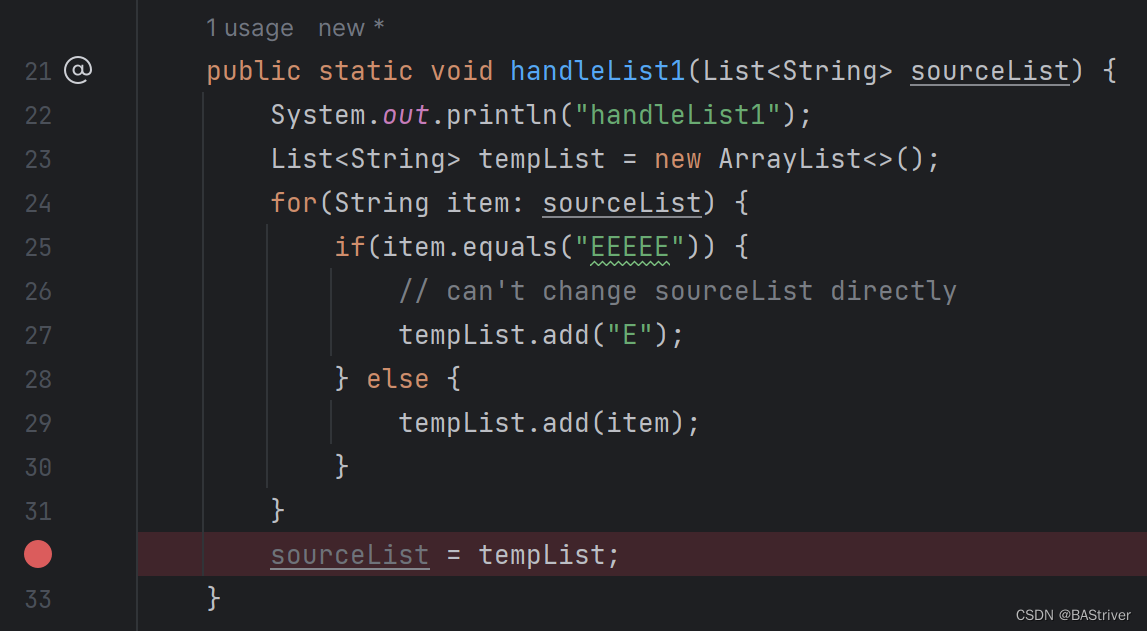
关于值传递和引用传递的问题记录
目录 1. 问题概述 1.1 测试 1.2 结果 2. ArrayList和Arrays.ArrayList 1. 问题概述 最近忙着写论文很久没更新了,趁现在有时间简单记录一下最近遇到的一个坑。 对于Java中的List<>类型的对象,按我以前理解是引用传递,但有一点要注…...

律师咨询小程序搭建流程
一、需求分析 在律师咨询小程序的开发过程中,需求分析是至关重要的一步。首先,我们需要明确小程序的定位和目标用户,了解用户的需求和痛点。在此基础上,我们需要细化功能需求,如在线咨询、案件查询、文书生成等。同时…...

怎么在uni-app中使用Vuex 深度解刨
本文深入研究Vuex,一个Vue.js状态管理库。我们将介绍创建它是为了解决的问题、其背后的核心概念、如何设置它,当然,还将在每一步中使用代码示例。 Vuex是一个由Vue团队构建的状态管理库,用于管理Vue.js应用程序中的数据。它提供了一种集中管理跨应用程序使用的数据的方式,…...
圆角(border-radius)不起作用的问题)
兼容iphone(ios)圆角(border-radius)不起作用的问题
一、出现场景:使用mosowe-swiper:适用于uni-app的轮播图插件,圆弧无效 ios手机会在transform的时候导致border-radius失效解决方法:在使用动画效果带transform的元素的上一级div元素的css加上下面语句: transform: rot…...
车间部署MES管理系统后有哪些变化
随着智能制造技术的飞速发展,工厂车间正经历着一场由数字化管理和智能化协调优化驱动的变革。这场变革的核心便是MES管理系统。实施MES管理系统在提升生产效率、降低成本、提高产品质量和优化资源投入方面发挥着重要作用,助力工厂实现整体运作的协作管理…...
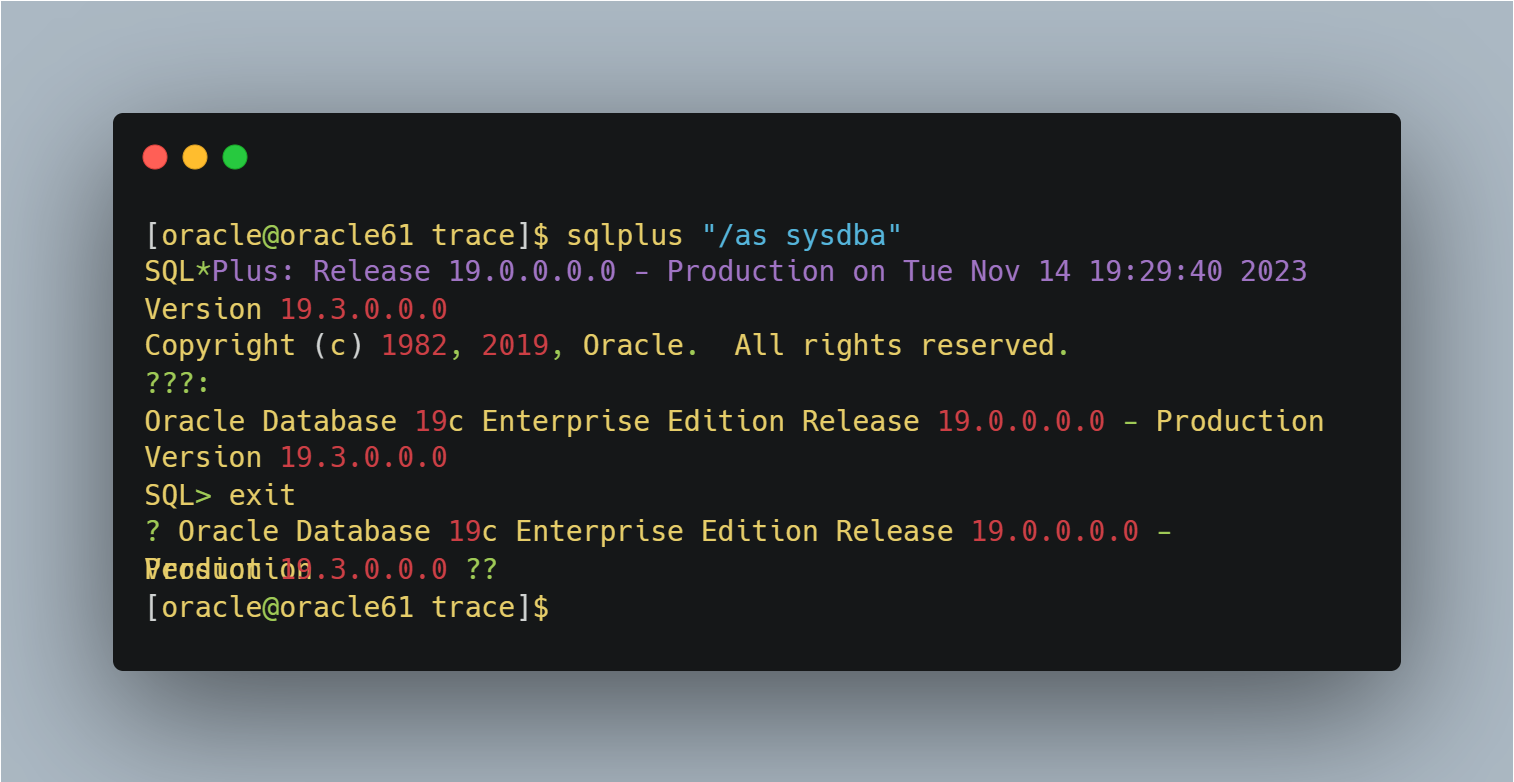
19C进入数据库出现问号
问题情况如图所示: 解决方法: su - oracle echo "NLS_LANGAMERICAN_AMERICA.ZHS16GBK;export NLS_LANG" >> ~/.bash_profilesource ~/.bash_profileofile...
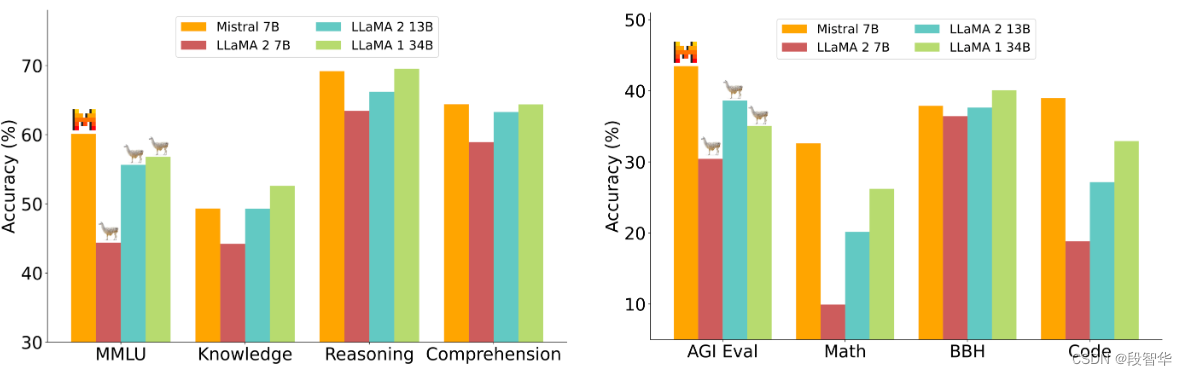
Mistral 7B 比Llama 2更好的开源大模型 (一)
Mistral 7B 简介 Mistral 7B Mistral 7B 是一个 7.3B 参数模型: 在所有基准测试中优于 Llama 2 13B在许多基准测试中优于 Llama 1 34B接近 CodeLlama 7B 的代码性能,同时保持擅长英语任务使用分组查询注意力 (GQA) 加快推理速度使用滑动窗口注意力 (SWA) 以更低的成本处…...
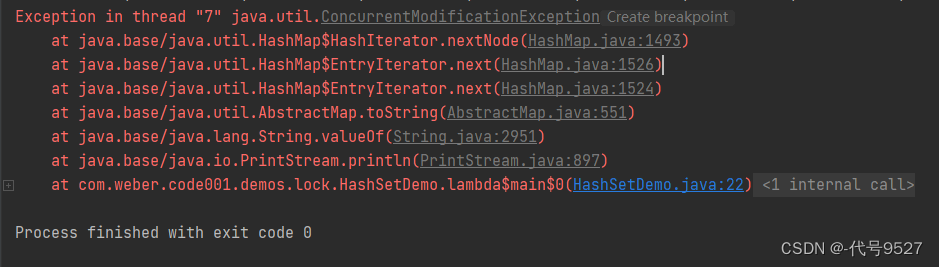
【JUC】三、集合的线程安全
文章目录 1、ArrayList集合线程安全问题分析2、解决方式一:Vector或synchronizedList( )3、解决方式二:CopyOnWriteArrayList 写时复制4、HashSet集合线程不安全的分析与解决5、HashMap集合线程不安全的分析与解决 1、ArrayList集合线程安全问题分析 对…...
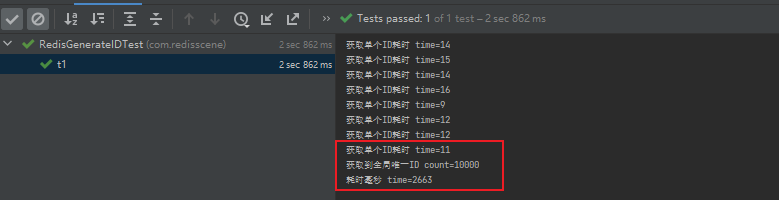
使用 Redis 实现生成分布式全局唯一ID(使用SpringBoot环境实现)
目录 一、前言二、如何通过Redis设计一个分布式全局唯一ID生成工具2.1、使用 Redis 计数器实现2.2、使用 Redis Hash结构实现 三、通过代码实现分布式全局唯一ID工具3.1、编写获取工具3.2、测试获取工具 四、总结 一、前言 在很多项目中生成类似订单编号、用户编号等有唯一性数…...
wordpress后台更新后 前端没变化的解决方法
使用siteground主机的wordpress网站,会出现更新了网站内容和修改了php模板文件、js文件、css文件、图片文件后,网站没有变化的情况。 不熟悉siteground主机的新手,遇到这个问题,就很抓狂,明明是哪都没操作错误&#x…...

基于距离变化能量开销动态调整的WSN低功耗拓扑控制开销算法matlab仿真
目录 1.程序功能描述 2.测试软件版本以及运行结果展示 3.核心程序 4.算法仿真参数 5.算法理论概述 6.参考文献 7.完整程序 1.程序功能描述 通过动态调整节点通信的能量开销,平衡网络负载,延长WSN生命周期。具体通过建立基于距离的能量消耗模型&am…...
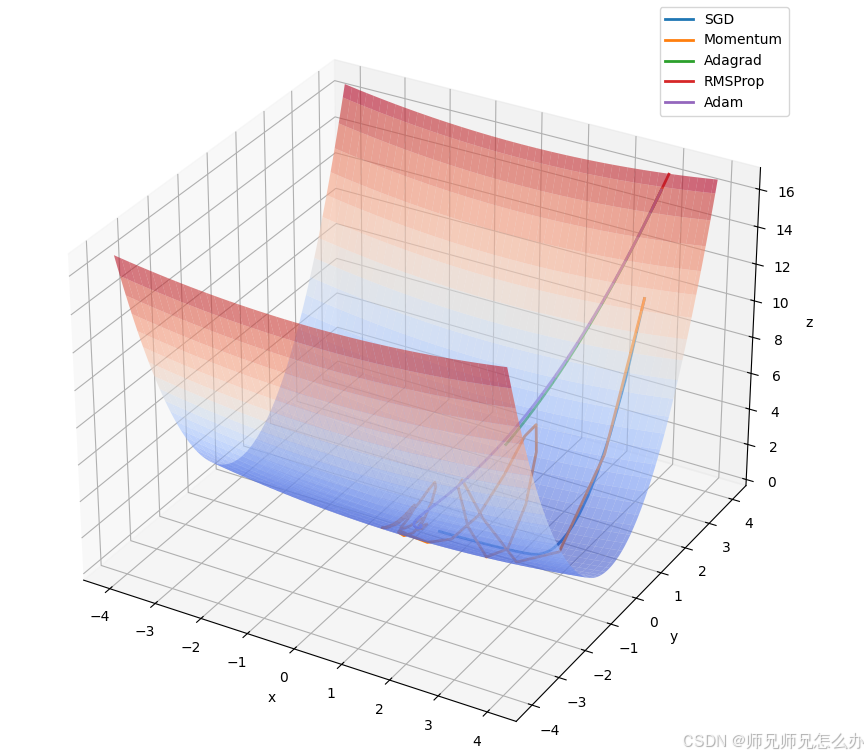
【人工智能】神经网络的优化器optimizer(二):Adagrad自适应学习率优化器
一.自适应梯度算法Adagrad概述 Adagrad(Adaptive Gradient Algorithm)是一种自适应学习率的优化算法,由Duchi等人在2011年提出。其核心思想是针对不同参数自动调整学习率,适合处理稀疏数据和不同参数梯度差异较大的场景。Adagrad通…...

基于Uniapp开发HarmonyOS 5.0旅游应用技术实践
一、技术选型背景 1.跨平台优势 Uniapp采用Vue.js框架,支持"一次开发,多端部署",可同步生成HarmonyOS、iOS、Android等多平台应用。 2.鸿蒙特性融合 HarmonyOS 5.0的分布式能力与原子化服务,为旅游应用带来…...

OkHttp 中实现断点续传 demo
在 OkHttp 中实现断点续传主要通过以下步骤完成,核心是利用 HTTP 协议的 Range 请求头指定下载范围: 实现原理 Range 请求头:向服务器请求文件的特定字节范围(如 Range: bytes1024-) 本地文件记录:保存已…...

UR 协作机器人「三剑客」:精密轻量担当(UR7e)、全能协作主力(UR12e)、重型任务专家(UR15)
UR协作机器人正以其卓越性能在现代制造业自动化中扮演重要角色。UR7e、UR12e和UR15通过创新技术和精准设计满足了不同行业的多样化需求。其中,UR15以其速度、精度及人工智能准备能力成为自动化领域的重要突破。UR7e和UR12e则在负载规格和市场定位上不断优化…...

智能分布式爬虫的数据处理流水线优化:基于深度强化学习的数据质量控制
在数字化浪潮席卷全球的今天,数据已成为企业和研究机构的核心资产。智能分布式爬虫作为高效的数据采集工具,在大规模数据获取中发挥着关键作用。然而,传统的数据处理流水线在面对复杂多变的网络环境和海量异构数据时,常出现数据质…...
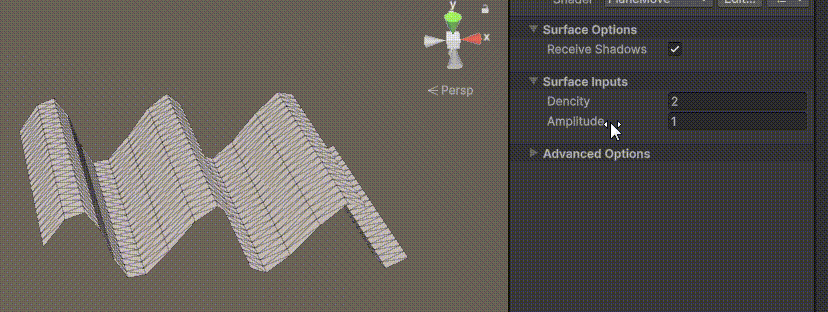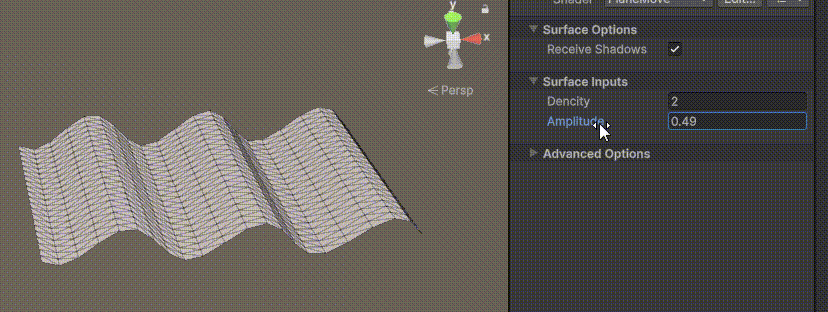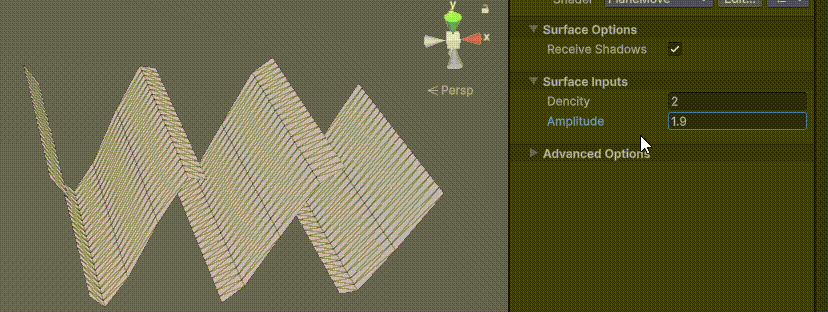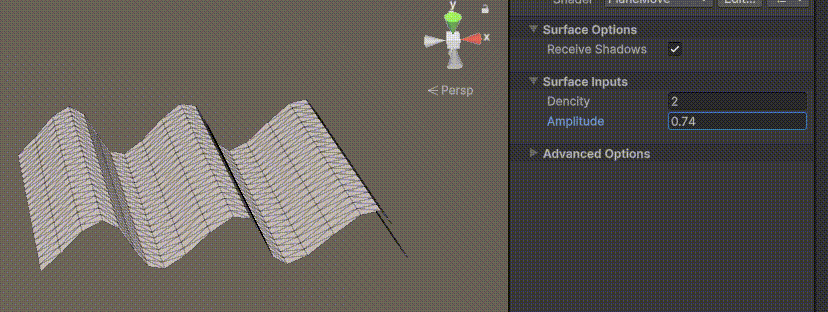
Unity | AmplifyShaderEditor插件基础(第七集:平面波动shader)
目录 一、👋🏻前言 二、😈sinx波动的基本原理 三、😈波动起来 1.sinx节点介绍 2.vertexPosition 3.集成Vector3 a.节点Append b.连起来 4.波动起来 a.波动的原理 b.时间节点 c.sinx的处理 四、🌊波动优化…...
Mobile ALOHA全身模仿学习
一、题目 Mobile ALOHA:通过低成本全身远程操作学习双手移动操作 传统模仿学习(Imitation Learning)缺点:聚焦与桌面操作,缺乏通用任务所需的移动性和灵活性 本论文优点:(1)在ALOHA…...

Linux C语言网络编程详细入门教程:如何一步步实现TCP服务端与客户端通信
文章目录 Linux C语言网络编程详细入门教程:如何一步步实现TCP服务端与客户端通信前言一、网络通信基础概念二、服务端与客户端的完整流程图解三、每一步的详细讲解和代码示例1. 创建Socket(服务端和客户端都要)2. 绑定本地地址和端口&#x…...
