ASM字节码操作类库(打开java语言世界通往字节码世界的大门) | 京东云技术团队
前言:授人以鱼不如授人以渔,应用asm的文章有很多,简单demo的也很多,那么ASM都具备哪些能力呢?如何去学习编写ASM代码呢?什么样的情景需要用到ASM呢?让我们带着这些问题阅读这篇文章吧。
这里由于篇幅限制做了删减(第六部分TreeApi和CoreApi的比较、核心API类的介绍等),如果有兴趣可以联系作者进行交流,
个人认为核心在于第五部分如何查看一个想写的类的ASM代码如何写,以及全面了解ASM都有哪些能力,这样在后面的特定场景下我们才会知道可以通过它来实现想做的功能
一、ASM介绍
1、ASM 是什么
ASM是一个通用的Java字节码操作和分析框架。它可以用于修改现有类或直接以二进制形式动态生成类。ASM提供了一些常见的字节码转换和分析算法,可以从中构建定制的复杂转换和代码分析工具。ASM提供了与其他Java字节码框架类似的功能,但侧重于性能。由于它的设计和实现尽可能小和快,因此非常适合在动态系统中使用(但当然也可以以静态方式使用,例如在编译器中)。
一个.java文件经过Java编译器(javac)编译之后会生成一个.class文件。在.class文件中,存储的是字节码(ByteCode)数据。ASM所操作的对象是字节码(ByteCode),而在许多情况下,字节码(ByteCode)的具体表现形式是.class文件。
ASM处理字节码(ByteCode)的方式是“拆分-修改-合并”。
| 字节码工具 | 类创建 | 实现接口 | 方法调用 | 类扩展 | 父类方法调用 | 优点 | 缺点 | 常见使用 | 学习成本 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| java-proxy | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 不支持 | 不支持 | 简单动态代理首选 | 功能有限,不支持扩展 | spring-aop,MyBatis | 1星 |
| asm | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 任意字节码插入,几乎不受限制 | 学习难度大,编写代码多 | cglib | 5星 |
| javaassit | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | java原始语法,字符串形式插入,写入直观 | 不支持jdk1.5以上的语法,如泛型,增强for | Fastjson,MyBatis | 2星 |
| cglib | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 与bytebuddy看起来差不多 | 正在被bytebuddy淘汰 | EasyMock,jackson-databind | 3星 |
| bytebuddy | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持任意维度的拦截,可以获取原始类、方法,以及代理类和全部参数 | 不太直观,学习理解有些成本,API非常多 | SkyWalking,Mockito,Hibernate,powermock | 3星 |
比较表格参考: http://xingyun.jd.com/shendeng/article/detail/7826
- ASM官网:https://asm.ow2.io/
- ASM源码:https://gitlab.ow2.org/asm/asm
- 开发者指南:https://asm.ow2.io/developer-guide.html
2、ASM能做什么
生成、修改、删除(接口、类、字段、方法…)ASM能够对字节码数据进行analyze、generate、transformation,ASM可以形象的理解为“Java语言世界”边缘上一扇大门,通过这扇大门,可以帮助我们进入到“字节码的世界”。
3、ASM实际的使用场景
3.1、Spring当中的ASM
第一个应用场景,是Spring框架当中的AOP。 在很多Java项目中,都会使用到Spring框架,而Spring框架当中的AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)是依赖于ASM的。具体来说,Spring的AOP,可以通过JDK的动态代理来实现,也可以通过CGLIB实现。其中,CGLib (Code Generation Library)是在ASM的基础上构建起来的,所以,Spring AOP是间接的使用了ASM。(参考自 Spring Framework Reference Documentation的 8.6 Proxying mechanisms)。
3.2、JDK当中的ASM
第二个应用场景,是JDK当中的Lambda表达式。 在Java 8中引入了一个非常重要的特性,就是支持Lambda表达式。Lambda表达式,允许把方法作为参数进行传递,它能够使代码变的更加简洁紧凑。但是,我们可能没有注意到,其实,在现阶段(Java 8版本),Lambda表达式的调用是通过ASM来实现的。
在rt.jar文件的jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm包当中,就包含了JDK内置的ASM代码。在JDK 8版本当中,它所使用的ASM 5.0版本。
如果我们跟踪Lambda表达式的编码实现,就会找到InnerClassLambdaMetafactory.spinInnerClass()方法。在这个方法当中,我们就会看到:JDK会使用jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm.ClassWriter来生成一个类,将lambda表达式的代码包装起来。
LambdaMetafactory.metafactory() 第一步,找到这个方法 InnerClassLambdaMetafactory.buildCallSite() 第二步,找到这个方法
InnerClassLambdaMetafactory.spinInnerClass() 第三步,找到这个方法
4、 ASM的两个组成部分
从组成结构上来说,ASM分成两部分,一部分为Core API,另一部分为Tree API。
其中,Core API包括asm.jar、asm-util.jar和asm-commons.jar;其中,Tree API包括asm-tree.jar和asm-analysis.jar。
asm.jar内核心类:ClassReader、ClassVisitor、ClassWriter、FieldVisitor、FieldWriter、MethodVisitor、MethodWriter、Label、Opcodes、Type
ClassReader类,负责读取.class文件里的内容,然后拆分成各个不同的部分。ClassVisitor类,负责对.class文件中某一部分里的信息进行修改。ClassWriter类,负责将各个不同的部分重新组合成一个完整的.class文件。
asm-util.jar内核心类
以Check开头的类,主要负责检查(Check)生成的.class文件内容是否正确。以Trace开头的类,主要负责将.class文件的内容打印成文字输出。根据输出的文字信息,可以探索或追踪(Trace).class文件的内部信息。
5、ClassFile
我们都知道,在.class文件中,存储的是ByteCode数据。但是,这些ByteCode数据并不是杂乱无章的,而是遵循一定的数据结构。
这个.class文件遵循的数据结构就是由 Java Virtual Machine Specification中定义的 The class File Format
6、常见的字节码类库
Apache Commons BCEL:其中BCEL为Byte Code Engineering Library首字母的缩写。
Javassist:Javassist表示Java programming assistant
ObjectWeb ASM:本课程的研究对象。
Byte Buddy:在ASM基础上实现的一个类库。
二、无中生有
1、生成新的接口
预期目标:
生成一个正常接口结构定义的.class文件
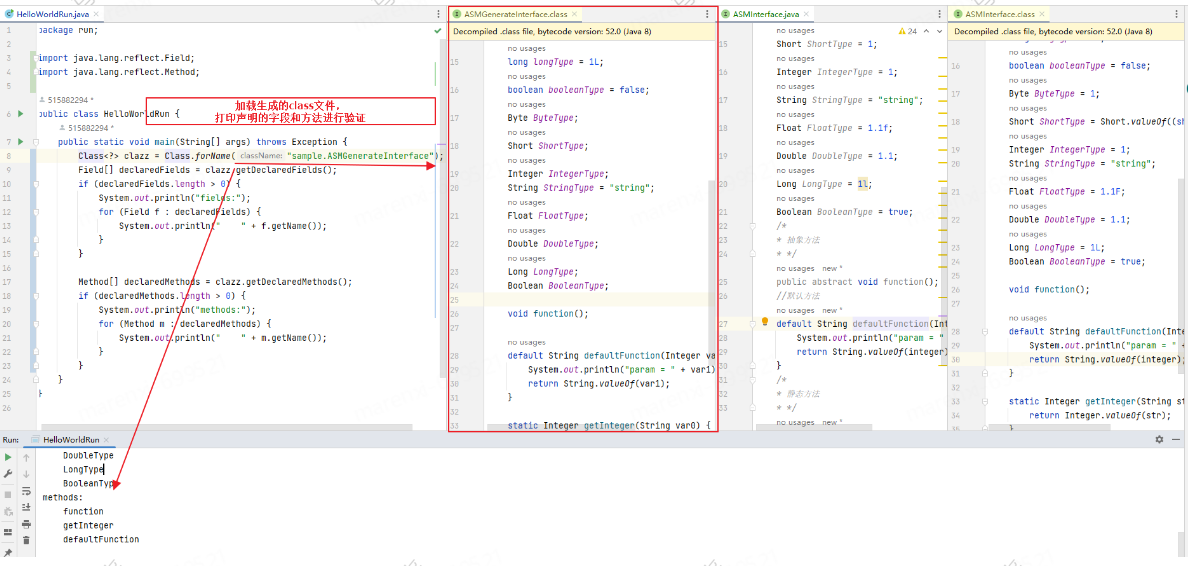
public interface ASMInterface {byte byteType = 1;short shortType = 1;int intType = 1;char charType = 's';float floatType = 1.1F;double doubleType = 1.2;long longType = 1L;boolean booleanType = false;Byte ByteType = 1;Short ShortType = Short.valueOf((short)1);Integer IntegerType = 1;String StringType = "s";Float FloatType = 1.1F;Double DoubleType = 1.1;Long LongType = 1L;Boolean BooleanType = true;void function();default String defaultFunction(Integer integer) {System.out.println("param = " + integer);return String.valueOf(integer);}static Integer getInteger(String str) {return Integer.valueOf(str);}
}
编码实现:
public class InterfaceGenerateCore {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {String relative_path = "sample/ASMGenerateInterface.class";String filepath = FileUtils.getFilePath(relative_path);// (1) 生成byte[]内容byte[] bytes = dump();// (2) 保存byte[]到文件FileUtils.writeBytes(filepath, bytes);}public static byte[] dump() throws Exception {// (1) 创建ClassWriter对象ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);// (2) 调用visitXxx()方法,调用顺序和说明如下/** visit* [visitSource][visitModule][visitNestHost][visitPermittedSubclass][visitOuterClass]* (visitAnnotation |* visitTypeAnnotation |* visitAttribute)** (visitNestMember |* visitInnerClass |* visitRecordComponent |* visitField |* visitMethod)** visitEnd* []: 表示最多调用一次,可以不调用,但最多调用一次。* ()和|: 表示在多个方法之间,可以选择任意一个,并且多个方法之间不分前后顺序。* *: 表示方法可以调用0次或多次。* *///定义接口/**visit(version, access, name, signature, superName, interfaces)*version: 表示当前类的版本信息。在下述示例代码中,其取值为Opcodes.V1_8,表示使用Java 8版本。*access: 表示当前类的访问标识(access flag)信息。在下面的示例中,access的取值是ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_ABSTRACT + ACC_INTERFACE,也可以写成ACC_PUBLIC | ACC_ABSTRACT | ACC_INTERFACE。如果想进一步了解这些标识的含义,可以参考Java Virtual Machine Specification的Chapter 4. The class File Format部分。*name: 表示当前类的名字,它采用的格式是Internal Name的形式。在.java文件中,我们使用Java语言来编写代码,使用类名的形式是Fully Qualified Class Name,例如java.lang.String;将.java文件编译之后,就会生成.class文件;在.class文件中,类名的形式会发生变化,称之为Internal Name,例如java/lang/String。因此,将Fully Qualified Class Name转换成Internal Name的方式就是,将.字符转换成/字符。*signature: 表示当前类的泛型信息。因为在这个接口当中不包含任何的泛型信息,因此它的值为null。*superName: 表示当前类的父类信息,它采用的格式是Internal Name的形式。*interfaces: 表示当前类实现了哪些接口信息。**/cw.visit(V1_8, // versionACC_PUBLIC + ACC_ABSTRACT + ACC_INTERFACE, // access"sample/ASMGenerateInterface", // namenull, // signature"java/lang/Object", // superNamenull // interfaces);//定义字段-基本类型/** visitField(access, name, descriptor, signature, value)*access参数:表示当前字段或方法带有的访问标识(access flag)信息,例如ACC_PUBLIC、ACC_STATIC和ACC_FINAL等。*name参数:表示当前字段或方法的名字。*descriptor参数:表示当前字段或方法的描述符。这些描述符,与我们平时使用的Java类型是有区别的。byte-B、short-S、int-I、char-C、具体可以参考如下示例代码*signature参数:表示当前字段或方法是否带有泛型信息。换句话说,如果不带有泛型信息,提供一个null就可以了;如果带有泛型信息,就需要给它提供某一个具体的值。*value参数:是visitField()方法的第5个参数。这个参数的取值,与当前字段是否为常量有关系。如果当前字段是一个常量,就需要给value参数提供某一个具体的值;如果当前字段不是常量,那么使用null就可以了。* */{FieldVisitor fv1 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "byteType", "B", null, new Integer(1));fv1.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv2 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "shortType", "S", null, new Integer(1));fv2.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv3 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "intType", "I", null, new Integer(1));fv3.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv4 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "charType", "C", null, 's');fv4.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv5 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "floatType", "F", null, new Float("1.1"));fv5.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv6 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "doubleType", "D", null, new Double("1.2"));fv6.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv7 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "longType", "J", null, new Long(1L));fv7.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv8 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "booleanType", "Z", null, new Integer(0));fv8.visitEnd();}//定义变量-包装类型{FieldVisitor fv11 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "ByteType", "Ljava/lang/Byte;", null, null);fv11.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv12 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "ShortType", "Ljava/lang/Short;", null,null);fv12.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv13 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "IntegerType", "Ljava/lang/Integer;", null,null);fv13.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv14 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "StringType", "Ljava/lang/String;", null, "s");fv14.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv15 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "FloatType", "Ljava/lang/Float;", null,null);fv15.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv16 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "DoubleType", "Ljava/lang/Double;", null,null);fv16.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv17 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "LongType", "Ljava/lang/Long;", null, null);fv17.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv18 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_STATIC + ACC_FINAL, "BooleanType", "Ljava/lang/Boolean;", null, null);fv18.visitEnd();}//定义方法-抽象方法/** visitMethod(access, name, descriptor, signature, exceptions)*access参数:表示当前字段或方法带有的访问标识(access flag)信息,例如ACC_PUBLIC、ACC_STATIC和ACC_FINAL等。*name参数:表示当前字段或方法的名字。*descriptor参数:表示当前字段或方法的描述符。这些描述符,与我们平时使用的Java类型是有区别的。()内为入参,后面为反参*signature参数:表示当前字段或方法是否带有泛型信息。换句话说,如果不带有泛型信息,提供一个null就可以了;如果带有泛型信息,就需要给它提供某一个具体的值。*exceptions参数:是visitMethod()方法的第5个参数。这个参数的取值,与当前方法声明中是否具有throws XxxException相关。* */{MethodVisitor mv1 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_ABSTRACT, "function", "()V", null, null);mv1.visitEnd();}//定义方法-默认方法{MethodVisitor mv2 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC, "defaultFunction", "(Ljava/lang/Integer;)Ljava/lang/String;", null, null);mv2.visitCode();mv2.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");mv2.visitTypeInsn(NEW, "java/lang/StringBuilder");mv2.visitInsn(DUP);mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESPECIAL, "java/lang/StringBuilder", "<init>", "()V", false);mv2.visitLdcInsn("param = ");mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/lang/StringBuilder", "append", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;", false);mv2.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 1);mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/lang/StringBuilder", "append", "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;", false);mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/lang/StringBuilder", "toString", "()Ljava/lang/String;", false);mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);mv2.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 1);mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/String", "valueOf", "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/String;", false);mv2.visitInsn(ARETURN);mv2.visitMaxs(3, 2);mv2.visitEnd();}//定义方法-静态方法{MethodVisitor mv3 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC | ACC_STATIC, "getInteger", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Integer;", null, null);mv3.visitCode();mv3.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);mv3.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Integer", "valueOf", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Integer;", false);mv3.visitInsn(ARETURN);mv3.visitMaxs(1, 1);mv3.visitEnd();}{MethodVisitor mv4 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_STATIC, "<clinit>", "()V", null, null);mv4.visitCode();mv4.visitInsn(ICONST_1);mv4.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Byte", "valueOf", "(B)Ljava/lang/Byte;", false);mv4.visitFieldInsn(PUTSTATIC, "sample/ASMInterface", "ByteType", "Ljava/lang/Byte;");mv4.visitInsn(ICONST_1);mv4.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Short", "valueOf", "(S)Ljava/lang/Short;", false);mv4.visitFieldInsn(PUTSTATIC, "sample/ASMInterface", "ShortType", "Ljava/lang/Short;");mv4.visitInsn(ICONST_1);mv4.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Integer", "valueOf", "(I)Ljava/lang/Integer;", false);mv4.visitFieldInsn(PUTSTATIC, "sample/ASMInterface", "IntegerType", "Ljava/lang/Integer;");mv4.visitLdcInsn(new Float("1.1"));mv4.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Float", "valueOf", "(F)Ljava/lang/Float;", false);mv4.visitFieldInsn(PUTSTATIC, "sample/ASMInterface", "FloatType", "Ljava/lang/Float;");mv4.visitLdcInsn(new Double("1.1"));mv4.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Double", "valueOf", "(D)Ljava/lang/Double;", false);mv4.visitFieldInsn(PUTSTATIC, "sample/ASMInterface", "DoubleType", "Ljava/lang/Double;");mv4.visitInsn(LCONST_1);mv4.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Long", "valueOf", "(J)Ljava/lang/Long;", false);mv4.visitFieldInsn(PUTSTATIC, "sample/ASMInterface", "LongType", "Ljava/lang/Long;");mv4.visitInsn(ICONST_1);mv4.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Boolean", "valueOf", "(Z)Ljava/lang/Boolean;", false);mv4.visitFieldInsn(PUTSTATIC, "sample/ASMInterface", "BooleanType", "Ljava/lang/Boolean;");mv4.visitInsn(RETURN);mv4.visitMaxs(2, 0);mv4.visitEnd();}cw.visitEnd(); // 注意,最后要调用visitEnd()方法// (3) 调用toByteArray()方法return cw.toByteArray();}
}验证结果:
生成的接口是否正确
public class HelloWorldRun {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();Class<?> clazz = classLoader.loadClass("sample.ASMGenerateInterface");Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();if (declaredFields.length > 0) {System.out.println("fields:");for (Field f : declaredFields) {Object value = f.get(null);System.out.println(" " + f.getName() + ": " + value);}}Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();if (declaredMethods.length > 0) {System.out.println("methods:");for (Method m : declaredMethods) {System.out.println(" " + m.getName());}}}
}
效果图如下:
2、生成新的类
预期目标:
生成一个正常类结构定义的.class文件
public class ASMClass {//定义变量-基本类型byte byteType = 1;short shortType = 1;int intType = 1;char charType = 's';float floatType = 1.1f;double doubleType = 1.2;long longType = 1;boolean booleanType = false;//定义变量-包装类型Byte ByteType = 1;Short ShortType = 1;Integer IntegerType = 1;String StringType = "string";Float FloatType = 1.1f;Double DoubleType = 1.1;Long LongType = 1l;@DeprecatedBoolean BooleanType = true;/** 静态方法* */public static Integer getInteger(String str) {return Integer.valueOf(str);}/** 实例方法* */public String instanceMethod(Integer integer) {return String.valueOf(integer);}
}编码实现:
public class ClassGenerateCore {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {String relative_path = "sample/ASMGenerateClass.class";String filepath = FileUtils.getFilePath(relative_path);// (1) 生成byte[]内容byte[] bytes = dump();// (2) 保存byte[]到文件FileUtils.writeBytes(filepath, bytes);}public static byte[] dump() throws Exception {// (1) 创建ClassWriter对象ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);// (2) 调用visitXxx()方法,调用顺序和说明如下/** visit* [visitSource][visitModule][visitNestHost][visitPermittedSubclass][visitOuterClass]* (visitAnnotation |* visitTypeAnnotation |* visitAttribute)** (visitNestMember |* visitInnerClass |* visitRecordComponent |* visitField |* visitMethod)** visitEnd* []: 表示最多调用一次,可以不调用,但最多调用一次。* ()和|: 表示在多个方法之间,可以选择任意一个,并且多个方法之间不分前后顺序。* *: 表示方法可以调用0次或多次。* *///定义接口/**visit(version, access, name, signature, superName, interfaces)*version: 表示当前类的版本信息。在下述示例代码中,其取值为Opcodes.V1_8,表示使用Java 8版本。*access: 表示当前类的访问标识(access flag)信息。在下面的示例中,access的取值是ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_ABSTRACT + ACC_INTERFACE,也可以写成ACC_PUBLIC | ACC_ABSTRACT | ACC_INTERFACE。如果想进一步了解这些标识的含义,可以参考Java Virtual Machine Specification的Chapter 4. The class File Format部分。*name: 表示当前类的名字,它采用的格式是Internal Name的形式。在.java文件中,我们使用Java语言来编写代码,使用类名的形式是Fully Qualified Class Name,例如java.lang.String;将.java文件编译之后,就会生成.class文件;在.class文件中,类名的形式会发生变化,称之为Internal Name,例如java/lang/String。因此,将Fully Qualified Class Name转换成Internal Name的方式就是,将.字符转换成/字符。*signature: 表示当前类的泛型信息。因为在这个接口当中不包含任何的泛型信息,因此它的值为null。*superName: 表示当前类的父类信息,它采用的格式是Internal Name的形式。*interfaces: 表示当前类实现了哪些接口信息。**/cw.visit(V1_8, // versionACC_PUBLIC + ACC_SUPER, // access"sample/ASMGenerateClass", // namenull, // signature"java/lang/Object", // superNamenull // interfaces);//定义字段-基本类型/** visitField(access, name, descriptor, signature, value)*access参数:表示当前字段或方法带有的访问标识(access flag)信息,例如ACC_PUBLIC、ACC_STATIC和ACC_FINAL等。*name参数:表示当前字段或方法的名字。*descriptor参数:表示当前字段或方法的描述符。这些描述符,与我们平时使用的Java类型是有区别的。byte-B、short-S、int-I、char-C、具体可以参考如下示例代码*signature参数:表示当前字段或方法是否带有泛型信息。换句话说,如果不带有泛型信息,提供一个null就可以了;如果带有泛型信息,就需要给它提供某一个具体的值。*value参数:是visitField()方法的第5个参数。这个参数的取值,与当前字段是否为常量有关系。如果当前字段是一个常量,就需要给value参数提供某一个具体的值;如果当前字段不是常量,那么使用null就可以了。* */{FieldVisitor fv1 = cw.visitField(0, "byteType", "B", null, new Byte("1"));fv1.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv2 = cw.visitField(0, "shortType", "S", null, new Short("1"));fv2.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv3 = cw.visitField(0, "intType", "I", null, new Integer(1));fv3.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv4 = cw.visitField(0, "charType", "C", null, "s");fv4.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv5 = cw.visitField(0, "floatType", "F", null, new Float("1.1"));fv5.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv6 = cw.visitField(0, "doubleType", "D", null, new Double("1.2"));fv6.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv7 = cw.visitField(0, "longType", "J", null, new Long(1));fv7.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv8 = cw.visitField(0, "booleanType", "Z", null, false);fv8.visitEnd();}//定义变量-包装类型{FieldVisitor fv11 = cw.visitField(0, "ByteType", "Ljava/lang/Byte;", null, 1);fv11.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv12 = cw.visitField(0, "ShortType", "Ljava/lang/Short;", null, 1);fv12.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv13 = cw.visitField(0, "IntegerType", "Ljava/lang/Integer;", null, 1);fv13.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv14 = cw.visitField(0, "StringType", "Ljava/lang/String;", null, "s");fv14.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv15 = cw.visitField(0, "FloatType", "Ljava/lang/Float;", null, 1.1f);fv15.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv16 = cw.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC, "DoubleType", "Ljava/lang/Double;", null, 1.1);fv16.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv17 = cw.visitField(0, "LongType", "Ljava/lang/Long;", null, 1l);fv17.visitEnd();}{FieldVisitor fv18 = cw.visitField(ACC_DEPRECATED, "BooleanType", "Ljava/lang/Boolean;", null, true);{AnnotationVisitor annotationVisitor0 = fv18.visitAnnotation("Ljava/lang/Deprecated;", true);annotationVisitor0.visitEnd();}fv18.visitEnd();}/** visitMethod(access, name, descriptor, signature, exceptions)*access参数:表示当前字段或方法带有的访问标识(access flag)信息,例如ACC_PUBLIC、ACC_STATIC和ACC_FINAL等。*name参数:表示当前字段或方法的名字。*descriptor参数:表示当前字段或方法的描述符。这些描述符,与我们平时使用的Java类型是有区别的。()内为入参,后面为反参*signature参数:表示当前字段或方法是否带有泛型信息。换句话说,如果不带有泛型信息,提供一个null就可以了;如果带有泛型信息,就需要给它提供某一个具体的值。*exceptions参数:是visitMethod()方法的第5个参数。这个参数的取值,与当前方法声明中是否具有throws XxxException相关。* *///定义方法-静态代码块{MethodVisitor mv2 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_STATIC, "<clinit>", "()V", null, null);mv2.visitCode();mv2.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");mv2.visitLdcInsn("class initialization method");mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);mv2.visitInsn(RETURN);mv2.visitMaxs(2, 0);mv2.visitEnd();}//定义方法-无参构造器{MethodVisitor methodVisitor = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC, "<init>", "()V", null, null);methodVisitor.visitCode();methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESPECIAL, "java/lang/Object", "<init>", "()V", false);methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitInsn(ICONST_1);methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "byteType", "B");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitInsn(ICONST_1);methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "shortType", "S");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitInsn(ICONST_1);methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "intType", "I");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitIntInsn(BIPUSH, 115);methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "charType", "C");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitLdcInsn(new Float("1.1"));methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "floatType", "F");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitLdcInsn(new Double("1.2"));methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "doubleType", "D");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitInsn(LCONST_1);methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "longType", "J");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitInsn(ICONST_0);methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "booleanType", "Z");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitInsn(ICONST_1);methodVisitor.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Byte", "valueOf", "(B)Ljava/lang/Byte;", false);methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "ByteType", "Ljava/lang/Byte;");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitInsn(ICONST_1);methodVisitor.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Short", "valueOf", "(S)Ljava/lang/Short;", false);methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "ShortType", "Ljava/lang/Short;");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitInsn(ICONST_1);methodVisitor.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Integer", "valueOf", "(I)Ljava/lang/Integer;", false);methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "IntegerType", "Ljava/lang/Integer;");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitLdcInsn("string");methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "StringType", "Ljava/lang/String;");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitLdcInsn(new Float("1.1"));methodVisitor.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Float", "valueOf", "(F)Ljava/lang/Float;", false);methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "FloatType", "Ljava/lang/Float;");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitLdcInsn(new Double("1.1"));methodVisitor.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Double", "valueOf", "(D)Ljava/lang/Double;", false);methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "DoubleType", "Ljava/lang/Double;");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitInsn(LCONST_1);methodVisitor.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Long", "valueOf", "(J)Ljava/lang/Long;", false);methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "LongType", "Ljava/lang/Long;");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);methodVisitor.visitInsn(ICONST_1);methodVisitor.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Boolean", "valueOf", "(Z)Ljava/lang/Boolean;", false);methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(PUTFIELD, "sample/ASMGenerateClass", "BooleanType", "Ljava/lang/Boolean;");methodVisitor.visitInsn(RETURN);methodVisitor.visitMaxs(3, 1);methodVisitor.visitEnd();}//定义方法-静态方法{MethodVisitor mv1 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC | ACC_STATIC, "getInteger", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Integer;", null, null);mv1.visitCode();mv1.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);mv1.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Integer", "valueOf", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Integer;", false);mv1.visitInsn(ARETURN);mv1.visitMaxs(1, 1);mv1.visitEnd();}//定义方法-实例方法{MethodVisitor mv2 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC, "instanceMethod", "(Ljava/lang/Integer;)Ljava/lang/String;", null, null);mv2.visitCode();mv2.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 1);mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/String", "valueOf", "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/String;", false);mv2.visitInsn(ARETURN);mv2.visitMaxs(1, 2);mv2.visitEnd();}cw.visitEnd(); // 注意,最后要调用visitEnd()方法// (3) 调用toByteArray()方法return cw.toByteArray();}
}
验证结果:
public class HelloWorldRun {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("sample.ASMGenerateClass");Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("instanceMethod",Integer.class);Object instance = clazz.newInstance();Object invoke = method.invoke(instance, new Integer(12));Class<?> aClass = invoke.getClass();System.out.println("aClass = " + aClass);}
}
或者
public class HelloWorldRun {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();Class<?> clazz = classLoader.loadClass("sample.ASMGenerateClass");Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();if (declaredFields.length > 0) {for (Field f : declaredFields) {Object value = f.get(null);System.out.println(" " + f.getName() + ": " + value);}}Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();if (declaredMethods.length > 0) {for (Method m : declaredMethods) {System.out.println(" " + m.getName());}}}
}
效果图如下:

ClassVisitor中visitXxx()的调用顺序
visit
[visitSource][visitModule][visitNestHost][visitPermittedSubclass][visitOuterClass]
(visitAnnotation |visitTypeAnnotation |visitAttribute
)*
(visitNestMember |visitInnerClass |visitRecordComponent |visitField |visitMethod
)*
visitEnd
其中,涉及到一些符号,它们的含义如下:
[]: 表示最多调用一次,可以不调用,但最多调用一次。
()和|: 表示在多个方法之间,可以选择任意一个,并且多个方法之间不分前后顺序。
*: 表示方法可以调用0次或多次。
FieldVisitor中visitXxx()的调用顺序
(visitAnnotation |visitTypeAnnotation |visitAttribute
)*
visitEnd
MethodVisitor中visitXxx()的调用顺序
(visitParameter)*
[visitAnnotationDefault]
(visitAnnotation | visitAnnotableParameterCount | visitParameterAnnotation | visitTypeAnnotation | visitAttribute)*
[visitCode(visitFrame |visitXxxInsn |visitLabel |visitInsnAnnotation |visitTryCatchBlock |visitTryCatchAnnotation |visitLocalVariable |visitLocalVariableAnnotation |visitLineNumber)*visitMaxs
]
visitEnd
第一组,在visitCode()方法之前的方法。这一组的方法,主要负责parameter、annotation和attributes等内容
第二组,在visitCode()方法和visitMaxs()方法之间的方法。这一组的方法,主要负责当前方法的“方法体”内的opcode内容。其中,visitCode()方法,标志着方法体的开始,而visitMaxs()方法,标志着方法体的结束。
第三组,是visitEnd()方法。这个visitEnd()方法,是最后一个进行调用的方法。
不同的MethodVisitor对象,它们的visitXxx()方法是彼此独立的,只要各自遵循方法的调用顺序,就能够得到正确的结果。
三、狸猫换太子
1、修改类的版本
ClassVisitor子类实现
public class ClassChangeVersionVisitor extends ClassVisitor {public ClassChangeVersionVisitor(int api, ClassVisitor classVisitor) {super(api, classVisitor);}@Overridepublic void visit(int version, int access, String name, String signature, String superName, String[] interfaces) {super.visit(Opcodes.V1_7, access, name, signature, superName, interfaces);}
}
使用ClassVisitor的子类ClassChangeVersionVisitor进行类的版本修改
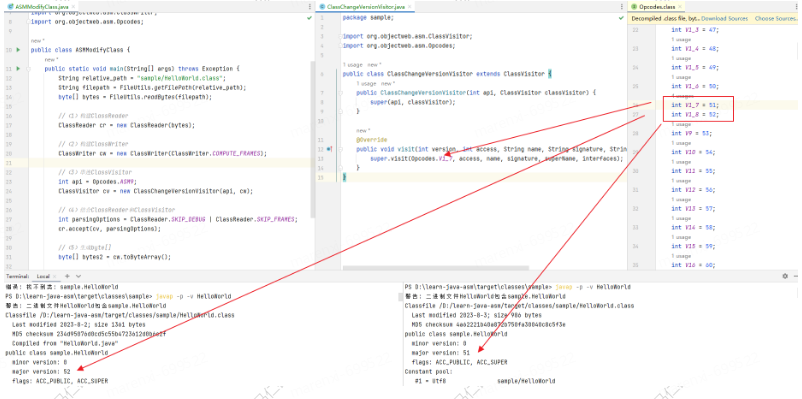
public class ASMModifyClass {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {String relative_path = "sample/HelloWorld.class";String filepath = FileUtils.getFilePath(relative_path);byte[] bytes = FileUtils.readBytes(filepath);//(1)构建ClassReaderClassReader cr = new ClassReader(bytes);//(2)构建ClassWriterClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);//(3)串连ClassVisitorint api = Opcodes.ASM9;ClassVisitor cv = new ClassChangeVersionVisitor(api, cw);//(4)结合ClassReader和ClassVisitorint parsingOptions = ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG | ClassReader.SKIP_FRAMES;cr.accept(cv, parsingOptions);//(5)生成byte[]byte[] bytes2 = cw.toByteArray();FileUtils.writeBytes(filepath, bytes2);}
}
验证&效果
通过javap -p -v HelloWorld命令可以看到版本号信息已从52调整位51
2.给每个方法添加计算调用时间
对目标类进行方法改造调换—为每个方法添加用时计算
public class HelloWorld {public int add(int a, int b) throws InterruptedException {int c = a + b;Random rand = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());int num = rand.nextInt(300);Thread.sleep(100 + num);return c;}public int sub(int a, int b) throws InterruptedException {int c = a - b;Random rand = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());int num = rand.nextInt(400);Thread.sleep(100 + num);return c;}
}
ASM编码实现
public class MethodTimerVisitor2 extends ClassVisitor {private String owner;private boolean isInterface;public MethodTimerVisitor2(int api, ClassVisitor classVisitor) {super(api, classVisitor);}@Overridepublic void visit(int version, int access, String name, String signature, String superName, String[] interfaces) {super.visit(version, access, name, signature, superName, interfaces);owner = name;isInterface = (access & ACC_INTERFACE) != 0;}@Overridepublic MethodVisitor visitMethod(int access, String name, String descriptor, String signature, String[] exceptions) {MethodVisitor mv = super.visitMethod(access, name, descriptor, signature, exceptions);if (!isInterface && mv != null && !"<init>".equals(name) && !"<clinit>".equals(name)) {boolean isAbstractMethod = (access & ACC_ABSTRACT) != 0;boolean isNativeMethod = (access & ACC_NATIVE) != 0;if (!isAbstractMethod && !isNativeMethod) {// 每遇到一个合适的方法,就添加一个相应的字段FieldVisitor fv = super.visitField(ACC_PUBLIC | ACC_STATIC, getFieldName(name), "J", null, null);if (fv != null) {fv.visitEnd();}mv = new MethodTimerAdapter2(api, mv, owner, name);}}return mv;}private String getFieldName(String methodName) {return "timer_" + methodName;}private class MethodTimerAdapter2 extends MethodVisitor {private final String owner;private final String methodName;public MethodTimerAdapter2(int api, MethodVisitor mv, String owner, String methodName) {super(api, mv);this.owner = owner;this.methodName = methodName;}@Overridepublic void visitCode() {// 首先,处理自己的代码逻辑super.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, owner, getFieldName(methodName), "J"); // 注意,字段名字要对应super.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/System", "currentTimeMillis", "()J", false);super.visitInsn(LSUB);super.visitFieldInsn(PUTSTATIC, owner, getFieldName(methodName), "J"); // 注意,字段名字要对应// 其次,调用父类的方法实现super.visitCode();}@Overridepublic void visitInsn(int opcode) {// 首先,处理自己的代码逻辑if ((opcode >= IRETURN && opcode <= RETURN) || opcode == ATHROW) {super.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, owner, getFieldName(methodName), "J"); // 注意,字段名字要对应super.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/System", "currentTimeMillis", "()J", false);super.visitInsn(LADD);super.visitFieldInsn(PUTSTATIC, owner, getFieldName(methodName), "J"); // 注意,字段名字要对应}// 其次,调用父类的方法实现super.visitInsn(opcode);}}
}
对方法进行转换
public class HelloWorldTransformCore {private static final int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 1024 * 4;public static void main(String[] args) {String relative_path = "sample/HelloWorld.class";String dir = HelloWorldTransformCore.class.getResource("/").getPath();String filepath = dir + relative_path;File file = new File(filepath);try {InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);in = new BufferedInputStream(in);ByteArrayOutputStream bao = new ByteArrayOutputStream();copyLarge(in, bao, new byte[DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE]);byte[] bytes1 = bao.toByteArray();//(1)构建ClassReaderClassReader cr = new ClassReader(bytes1);//(2)构建ClassWriterClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);//(3)串连ClassVisitorint api = Opcodes.ASM9;ClassVisitor cv = new MethodTimerVisitor2(api, cw);//(4)结合ClassReader和ClassVisitorint parsingOptions = ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG | ClassReader.SKIP_FRAMES;cr.accept(cv, parsingOptions);//(5)生成byte[]byte[] bytes2 = cw.toByteArray();OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(filepath);BufferedOutputStream buff = new BufferedOutputStream(out);buff.write(bytes2);buff.flush();buff.close();System.out.println("file://" + filepath);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static long copyLarge(final InputStream input, final OutputStream output, final byte[] buffer)throws IOException {long count = 0;int n;while (-1 != (n = input.read(buffer))) {output.write(buffer, 0, n);count += n;}return count;}
}
验证结果
public class HelloWorldRun {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 第一部分,先让“子弹飞一会儿”,让程序运行一段时间HelloWorld instance = new HelloWorld();Random rand = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {boolean flag = rand.nextBoolean();int a = rand.nextInt(50);int b = rand.nextInt(50);if (flag) {int c = instance.add(a, b);String line = String.format("%d + %d = %d", a, b, c);System.out.println(line);}else {int c = instance.sub(a, b);String line = String.format("%d - %d = %d", a, b, c);System.out.println(line);}}// 第二部分,来查看方法运行的时间Class<?> clazz = HelloWorld.class;Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();for (Field f : declaredFields) {String fieldName = f.getName();f.setAccessible(true);if (fieldName.startsWith("timer")) {Object FieldValue = f.get(null);System.out.println(fieldName + " = " + FieldValue);}}}
}
3、打印方法参数和返回值
对目标类进行方法改造—为每个方法添加打印入参和出参
public class HelloWorld {public int test(String name, int age, long idCard, Object obj) {int hashCode = 0;hashCode += name.hashCode();hashCode += age;hashCode += (int) (idCard % Integer.MAX_VALUE);hashCode += obj.hashCode();return hashCode;}
}
我们想实现的预期目标:打印出“方法接收的参数值”和“方法的返回值”。
public class HelloWorld {public int test(String name, int age, long idCard, Object obj) {int hashCode = 0;hashCode += name.hashCode();hashCode += age;hashCode += (int) (idCard % Integer.MAX_VALUE);hashCode += obj.hashCode();System.out.println(hashCode);return hashCode;}
}
实现这个功能的思路:在“方法进入”的时候,打印出“方法接收的参数值”;在“方法退出”的时候,打印出“方法的返回值”。
首先,我们添加一个ParameterUtils类,在这个类定义了许多print方法,这些print方法可以打印不同类型的数据。
public class ParameterUtils {private static final DateFormat fm = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");public static void printValueOnStack(boolean value) {System.out.println(" " + value);}public static void printValueOnStack(byte value) {System.out.println(" " + value);}public static void printValueOnStack(char value) {System.out.println(" " + value);}public static void printValueOnStack(short value) {System.out.println(" " + value);}public static void printValueOnStack(int value) {System.out.println(" " + value);}public static void printValueOnStack(float value) {System.out.println(" " + value);}public static void printValueOnStack(long value) {System.out.println(" " + value);}public static void printValueOnStack(double value) {System.out.println(" " + value);}public static void printValueOnStack(Object value) {if (value == null) {System.out.println(" " + value);}else if (value instanceof String) {System.out.println(" " + value);}else if (value instanceof Date) {System.out.println(" " + fm.format(value));}else if (value instanceof char[]) {System.out.println(" " + Arrays.toString((char[])value));}else {System.out.println(" " + value.getClass() + ": " + value.toString());}}public static void printText(String str) {System.out.println(str);}
}
在下面的MethodParameterVisitor2类当中,我们将使用ParameterUtils类帮助我们打印信息。
ASM编码实现
public class MethodParameterVisitor2 extends ClassVisitor {public MethodParameterVisitor2(int api, ClassVisitor classVisitor) {super(api, classVisitor);}@Overridepublic MethodVisitor visitMethod(int access, String name, String descriptor, String signature, String[] exceptions) {MethodVisitor mv = super.visitMethod(access, name, descriptor, signature, exceptions);if (mv != null && !name.equals("<init>")) {boolean isAbstractMethod = (access & ACC_ABSTRACT) != 0;boolean isNativeMethod = (access & ACC_NATIVE) != 0;if (!isAbstractMethod && !isNativeMethod) {mv = new MethodParameterAdapter2(api, mv, access, name, descriptor);}}return mv;}private static class MethodParameterAdapter2 extends MethodVisitor {private final int methodAccess;private final String methodName;private final String methodDesc;public MethodParameterAdapter2(int api, MethodVisitor mv, int methodAccess, String methodName, String methodDesc) {super(api, mv);this.methodAccess = methodAccess;this.methodName = methodName;this.methodDesc = methodDesc;}@Overridepublic void visitCode() {// 首先,处理自己的代码逻辑boolean isStatic = ((methodAccess & ACC_STATIC) != 0);int slotIndex = isStatic ? 0 : 1;printMessage("Method Enter: " + methodName + methodDesc);Type methodType = Type.getMethodType(methodDesc);Type[] argumentTypes = methodType.getArgumentTypes();for (Type t : argumentTypes) {int sort = t.getSort();int size = t.getSize();String descriptor = t.getDescriptor();int opcode = t.getOpcode(ILOAD);super.visitVarInsn(opcode, slotIndex);if (sort >= Type.BOOLEAN && sort <= Type.DOUBLE) {String methodDesc = String.format("(%s)V", descriptor);printValueOnStack(methodDesc);}else {printValueOnStack("(Ljava/lang/Object;)V");}slotIndex += size;}// 其次,调用父类的方法实现super.visitCode();}@Overridepublic void visitInsn(int opcode) {// 首先,处理自己的代码逻辑if ((opcode >= IRETURN && opcode <= RETURN) || opcode == ATHROW) {printMessage("Method Exit: " + methodName + methodDesc);if (opcode >= IRETURN && opcode <= DRETURN) {Type methodType = Type.getMethodType(methodDesc);Type returnType = methodType.getReturnType();int size = returnType.getSize();String descriptor = returnType.getDescriptor();if (size == 1) {super.visitInsn(DUP);}else {super.visitInsn(DUP2);}String methodDesc = String.format("(%s)V", descriptor);printValueOnStack(methodDesc);}else if (opcode == ARETURN) {super.visitInsn(DUP);printValueOnStack("(Ljava/lang/Object;)V");}else if (opcode == RETURN) {printMessage(" return void");}else {printMessage(" abnormal return");}}// 其次,调用父类的方法实现super.visitInsn(opcode);}private void printMessage(String str) {super.visitLdcInsn(str);super.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "sample/ParameterUtils", "printText", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);}private void printValueOnStack(String descriptor) {super.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "sample/ParameterUtils", "printValueOnStack", descriptor, false);}}
}
进行转换
public class HelloWorldTransformCore {public static void main(String[] args) {String relative_path = "sample/HelloWorld.class";String filepath = FileUtils.getFilePath(relative_path);byte[] bytes1 = FileUtils.readBytes(filepath);//(1)构建ClassReaderClassReader cr = new ClassReader(bytes1);//(2)构建ClassWriterClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);//(3)串连ClassVisitorint api = Opcodes.ASM9;ClassVisitor cv = new MethodParameterVisitor2(api, cw);//(4)结合ClassReader和ClassVisitorint parsingOptions = ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG | ClassReader.SKIP_FRAMES;cr.accept(cv, parsingOptions);//(5)生成byte[]byte[] bytes2 = cw.toByteArray();FileUtils.writeBytes(filepath, bytes2);}
}
验证结果
public class HelloWorldRun {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {HelloWorld instance = new HelloWorld();int hashCode = instance.test("Tomcat", 10, System.currentTimeMillis(), new Object());int remainder = hashCode % 2;if (remainder == 0) {System.out.println("hashCode is even number.");}else {System.out.println("hashCode is odd number.");}}
}
四、非顺序结构
1、if语句
public class HelloWorld {public void test(int value) {if (value == 0) {System.out.println("value is 0");}else {System.out.println("value is not 0");}}
}
ASM编码实现
public class HelloWorldGenerateCore {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {String relative_path = "sample/HelloWorld.class";String filepath = FileUtils.getFilePath(relative_path);// (1) 生成byte[]内容byte[] bytes = dump();// (2) 保存byte[]到文件FileUtils.writeBytes(filepath, bytes);}public static byte[] dump() throws Exception {// (1) 创建ClassWriter对象ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);// (2) 调用visitXxx()方法cw.visit(V1_8, ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_SUPER, "sample/HelloWorld",null, "java/lang/Object", null);{MethodVisitor mv1 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC, "<init>", "()V", null, null);mv1.visitCode();mv1.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);mv1.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESPECIAL, "java/lang/Object", "<init>", "()V", false);mv1.visitInsn(RETURN);mv1.visitMaxs(0, 0);mv1.visitEnd();}{MethodVisitor mv2 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC, "test", "(I)V", null, null);Label elseLabel = new Label();Label returnLabel = new Label();// 第1段mv2.visitCode();mv2.visitVarInsn(ILOAD, 1);mv2.visitJumpInsn(IFNE, elseLabel);mv2.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");mv2.visitLdcInsn("value is 0");mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);mv2.visitJumpInsn(GOTO, returnLabel);// 第2段mv2.visitLabel(elseLabel);mv2.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");mv2.visitLdcInsn("value is not 0");mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);// 第3段mv2.visitLabel(returnLabel);mv2.visitInsn(RETURN);mv2.visitMaxs(0, 0);mv2.visitEnd();}cw.visitEnd();// (3) 调用toByteArray()方法return cw.toByteArray();}
}
验证结果
public class HelloWorldRun {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("sample.HelloWorld");Object obj = clazz.newInstance();Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("test", int.class);method.invoke(obj, 0);method.invoke(obj, 1);}
}
2、switch语句
public class HelloWorld {public void test(int val) {switch (val) {case 1:System.out.println("val = 1");break;case 2:System.out.println("val = 2");break;case 3:System.out.println("val = 3");break;case 4:System.out.println("val = 4");break;default:System.out.println("val is unknown");}}
}
ASM编码实现
public class HelloWorldGenerateCore {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {String relative_path = "sample/HelloWorld.class";String filepath = FileUtils.getFilePath(relative_path);// (1) 生成byte[]内容byte[] bytes = dump();// (2) 保存byte[]到文件FileUtils.writeBytes(filepath, bytes);}public static byte[] dump() throws Exception {// (1) 创建ClassWriter对象ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);// (2) 调用visitXxx()方法cw.visit(V1_8, ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_SUPER, "sample/HelloWorld",null, "java/lang/Object", null);{MethodVisitor mv1 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC, "<init>", "()V", null, null);mv1.visitCode();mv1.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);mv1.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESPECIAL, "java/lang/Object", "<init>", "()V", false);mv1.visitInsn(RETURN);mv1.visitMaxs(0, 0);mv1.visitEnd();}{MethodVisitor mv2 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC, "test", "(I)V", null, null);Label caseLabel1 = new Label();Label caseLabel2 = new Label();Label caseLabel3 = new Label();Label caseLabel4 = new Label();Label defaultLabel = new Label();Label returnLabel = new Label();// 第1段mv2.visitCode();mv2.visitVarInsn(ILOAD, 1);mv2.visitTableSwitchInsn(1, 4, defaultLabel, new Label[]{caseLabel1, caseLabel2, caseLabel3, caseLabel4});// 第2段mv2.visitLabel(caseLabel1);mv2.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");mv2.visitLdcInsn("val = 1");mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);mv2.visitJumpInsn(GOTO, returnLabel);// 第3段mv2.visitLabel(caseLabel2);mv2.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");mv2.visitLdcInsn("val = 2");mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);mv2.visitJumpInsn(GOTO, returnLabel);// 第4段mv2.visitLabel(caseLabel3);mv2.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");mv2.visitLdcInsn("val = 3");mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);mv2.visitJumpInsn(GOTO, returnLabel);// 第5段mv2.visitLabel(caseLabel4);mv2.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");mv2.visitLdcInsn("val = 4");mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);mv2.visitJumpInsn(GOTO, returnLabel);// 第6段mv2.visitLabel(defaultLabel);mv2.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");mv2.visitLdcInsn("val is unknown");mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);// 第7段mv2.visitLabel(returnLabel);mv2.visitInsn(RETURN);mv2.visitMaxs(0, 0);mv2.visitEnd();}cw.visitEnd();// (3) 调用toByteArray()方法return cw.toByteArray();}
}
验证结果
import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class HelloWorldRun {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("sample.HelloWorld");Object obj = clazz.newInstance();Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("test", int.class);for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++) {method.invoke(obj, i);}}
}
3、for语句
public class HelloWorld {public void test() {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(i);}}
}
ASM编码实现
import org.objectweb.asm.*;import static org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes.*;public class HelloWorldGenerateCore {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {String relative_path = "sample/HelloWorld.class";String filepath = FileUtils.getFilePath(relative_path);// (1) 生成byte[]内容byte[] bytes = dump();// (2) 保存byte[]到文件FileUtils.writeBytes(filepath, bytes);}public static byte[] dump() throws Exception {// (1) 创建ClassWriter对象ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);// (2) 调用visitXxx()方法cw.visit(V1_8, ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_SUPER, "sample/HelloWorld",null, "java/lang/Object", null);{MethodVisitor mv1 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC, "<init>", "()V", null, null);mv1.visitCode();mv1.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);mv1.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESPECIAL, "java/lang/Object", "<init>", "()V", false);mv1.visitInsn(RETURN);mv1.visitMaxs(0, 0);mv1.visitEnd();}{MethodVisitor methodVisitor = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC, "test", "()V", null, null);Label conditionLabel = new Label();Label returnLabel = new Label();// 第1段methodVisitor.visitCode();methodVisitor.visitInsn(ICONST_0);methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ISTORE, 1);// 第2段methodVisitor.visitLabel(conditionLabel);methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ILOAD, 1);methodVisitor.visitIntInsn(BIPUSH, 10);methodVisitor.visitJumpInsn(IF_ICMPGE, returnLabel);methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(ILOAD, 1);methodVisitor.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(I)V", false);methodVisitor.visitIincInsn(1, 1);methodVisitor.visitJumpInsn(GOTO, conditionLabel);// 第3段methodVisitor.visitLabel(returnLabel);methodVisitor.visitInsn(RETURN);methodVisitor.visitMaxs(0, 0);methodVisitor.visitEnd();}cw.visitEnd();// (3) 调用toByteArray()方法return cw.toByteArray();}
}
验证结果
public class HelloWorldRun {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("sample.HelloWorld");Object obj = clazz.newInstance();Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("test");method.invoke(obj);}
}
4、try-catch语句
public class HelloWorld {public void test() {try {System.out.println("Before Sleep");Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println("After Sleep");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
ASM编码实现
public class HelloWorldGenerateCore {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {String relative_path = "sample/HelloWorld.class";String filepath = FileUtils.getFilePath(relative_path);// (1) 生成byte[]内容byte[] bytes = dump();// (2) 保存byte[]到文件FileUtils.writeBytes(filepath, bytes);}public static byte[] dump() throws Exception {// (1) 创建ClassWriter对象ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);// (2) 调用visitXxx()方法cw.visit(V1_8, ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_SUPER, "sample/HelloWorld",null, "java/lang/Object", null);{MethodVisitor mv1 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC, "<init>", "()V", null, null);mv1.visitCode();mv1.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);mv1.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESPECIAL, "java/lang/Object", "<init>", "()V", false);mv1.visitInsn(RETURN);mv1.visitMaxs(0, 0);mv1.visitEnd();}{MethodVisitor mv2 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC, "test", "()V", null, null);Label startLabel = new Label();Label endLabel = new Label();Label exceptionHandlerLabel = new Label();Label returnLabel = new Label();// 第1段mv2.visitCode();// visitTryCatchBlock可以在这里访问mv2.visitTryCatchBlock(startLabel, endLabel, exceptionHandlerLabel, "java/lang/InterruptedException");// 第2段mv2.visitLabel(startLabel);mv2.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");mv2.visitLdcInsn("Before Sleep");mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);mv2.visitLdcInsn(new Long(1000L));mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Thread", "sleep", "(J)V", false);mv2.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");mv2.visitLdcInsn("After Sleep");mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);// 第3段mv2.visitLabel(endLabel);mv2.visitJumpInsn(GOTO, returnLabel);// 第4段mv2.visitLabel(exceptionHandlerLabel);mv2.visitVarInsn(ASTORE, 1);mv2.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 1);mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/lang/InterruptedException", "printStackTrace", "()V", false);// 第5段mv2.visitLabel(returnLabel);mv2.visitInsn(RETURN);// 第6段// visitTryCatchBlock也可以在这里访问// mv2.visitTryCatchBlock(startLabel, endLabel, exceptionHandlerLabel, "java/lang/InterruptedException");mv2.visitMaxs(0, 0);mv2.visitEnd();}cw.visitEnd();// (3) 调用toByteArray()方法return cw.toByteArray();}
}
验证结果
public class HelloWorldRun {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("sample.HelloWorld");Object obj = clazz.newInstance();Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("test");method.invoke(obj);}
}
五、查看class文件的ASM代码
1.打印
当我们想对某一类进行ASM学习或者对想要实现的功能不知道如何实现时可以使用如下类进行ASM代码输出并查看
public class ASMPrint {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// (1) 设置参数String className = "sample.HelloWorld";int parsingOptions = ClassReader.SKIP_FRAMES | ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG;boolean asmCode = true;// (2) 打印结果Printer printer = asmCode ? new ASMifier() : new Textifier();PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(System.out, true);TraceClassVisitor traceClassVisitor = new TraceClassVisitor(null, printer, printWriter);new ClassReader(className).accept(traceClassVisitor, parsingOptions);}
}
className值设置为类的全限定名,可以是我们自己写的类,例如sample.HelloWorld,也可以是JDK自带的类,例如java.lang.Comparable。
asmCode值设置为true或false。如果是true,可以打印出对应的ASM代码;如果是false,可以打印出方法对应的Instruction。
parsingOptions值设置为ClassReader.SKIP_CODE、ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG、ClassReader.SKIP_FRAMES、ClassReader.EXPAND_FRAMES的组合值,也可以设置为0,可以打印出详细程度不同的信息。
2.插件
如果你是IDEA可以安装ASM ByteCode Viewer,然后选择要查看得java文件右键选择后可以在右侧看到ASPPlugin上看到对应得ByteCode、ASMified、Groovified。或者是插件ASM Bytecode Outline(本人用得社区版IDEA未达到效果)
六、TreeApi
Core API和Tree API的区别
- Tree API的优势:易用性:如果一个人在之前并没有接触过Core API和Tree API,那么Tree API更容易入手。功能性:在实现比较复杂的功能时,Tree API比Core API更容易实现。
- Core API的优势:执行效率:在实现相同功能的前提下,Core API要比Tree API执行效率高,花费时间少。内存使用:Core API比Tree API占用的内存空间少。
- 第一点,在ASM当中,不管是Core API,还是Tree API,都能够进行Class Generation、Class Transformation和Class Analysis操作。
- 第二点,Core API和Tree API是两者有各自的优势。Tree API易于使用、更容易实现复杂的操作;Core API执行速度更快、占用内存空间更少。
这里由于篇幅限制做了删减,如果有兴趣可以联系作者进行交流
七、文中用到的工具类
1、FileUtils
public class FileUtils {public static String getFilePath(String relativePath) {String dir = FileUtils.class.getResource("/").getPath();return dir + relativePath;}
}
八、思考对于ASM我们以后能用于做些什么?
1、生成类----根据模版生成类(结合脚手架快速搭建项目以及项目初期模块快速搭建)
2、修改类----根据模版修改类(结合特定结构在java源代码编译生成.class字节码文件时对类进行修改以达到提升系统效率和释放开发人力的目的,可以结合IDEA插件开发开发类似于lombok或更为强大的插件)
作者:京东健康 马仁喜
来源:京东云开发者社区 转载请注明来源
相关文章:

ASM字节码操作类库(打开java语言世界通往字节码世界的大门) | 京东云技术团队
前言:授人以鱼不如授人以渔,应用asm的文章有很多,简单demo的也很多,那么ASM都具备哪些能力呢?如何去学习编写ASM代码呢?什么样的情景需要用到ASM呢?让我们带着这些问题阅读这篇文章吧。 这里由…...
SpringBoot 拦截器高级篇
Springboot 拦截器 定义使用场景拦截器与过滤器的区别实现步骤全局拦截器的局限性全局拦截器VS局部拦截器局部拦截器自定义局部拦截器使用多个局部拦截器 定义 拦截器是Spring MVC框架中的一个重要组件,它是一种AOP(面向切面编程)的实现方式&…...
)
Android frameworks 开发总结之十(lock screen message Battery Last full charge)
1.設置lock screen message後不显示 XXXt設備設置lock screen message後,發現鎖頻界面不顯示內容,像時間日期都不顯示。只在右上角顯示一個鎖圖標,需要向下滑動一下才能顯示出來。布局文件位置: frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/res-keygu…...

[建议收藏] 一个网站集合所有最新最全的AI工具
今天给大家推荐一个宝藏的AI工具合集网站,有了这个网站,你们再也不用去其他地方找AI工具了。 名称:AI-BOT工具集 这个网站精选1000AI工具,并持续每天更新添加,包括AI写作、AI绘画、AI音视频处理、AI平面设计、AI自动编…...

嵌入式硬件基础知识——1
目录 SOC、MCU、MPU、CPU SPI STM32的时钟系统 can是什么 串口和并口 传感器输出引脚高阻抗好还是低阻抗好? iic 运算放大器特点 MOS管和三极管 同步电路和异步电路 SOC、MCU、MPU、CPU SOC 片上系统 手机的核心芯片 MCU 微控系统 单片机 MPU 嵌入式微处…...

Spring如何在多线程下保持事务的一致性
Spring如何在多线程下保持事务的一致性 方法:每个线程都开启各自的事务去执行相关业务,等待所有线程的业务执行完成,统一提交或回滚。 下面我们通过具体的案例来演示Spring如何在多线程下保持事务的一致性。 1、项目结构 2、数据库SQL CR…...

外部中断为什么会误触发?
今天在写外部中断的程序的时候,发现中断特别容易受到干扰,我把手放在对应的中断引脚上,中断就一直触发,没有停过。经过一天的学习,找到了几个解决方法,所以写了这篇笔记。如果你的中断也时不时会误触发&…...
【数据库】聊聊一颗B+树 可以存储多少数据
我们知道数据库使用的数据结构是B树,但是B树可以存储多少数据呢,在面试中也是经常会问的问题,所以我们从根上理解这个问题。 操作系统层面 数据都是存储在磁盘中的,而磁盘中的数据都是以最新单位扇区进行分割。一个扇区的大小是…...

【机器学习 | ARIMA】经典时间序列模型ARIMA定阶最佳实践,确定不来看看?
🤵♂️ 个人主页: AI_magician 📡主页地址: 作者简介:CSDN内容合伙人,全栈领域优质创作者。 👨💻景愿:旨在于能和更多的热爱计算机的伙伴一起成长!!&…...
Python web自动化测试 —— 文件上传
文件上传三种方式: (一)查看元素标签,如果是input,则可以参照文本框输入的形式进行文件上传 方法:和用户输入是一样的,使用send_keys 步骤:1、找到定位元素,2&#…...
wpf使用CefSharp.OffScreen模拟网页登录,并获取身份cookie,C#后台执行js
目录 框架信息:MainWindow.xamlMainWindow.xaml.cs爬取逻辑模拟登录拦截请求Cookie获取 CookieVisitorHandle 框架信息: CefSharp.OffScreen.NETCore 119.1.20 MainWindow.xaml <Window x:Class"Wpf_CHZC_Img_Identy_ApiDataGet.MainWindow&qu…...
【代码随想录刷题】Day18 二叉树05
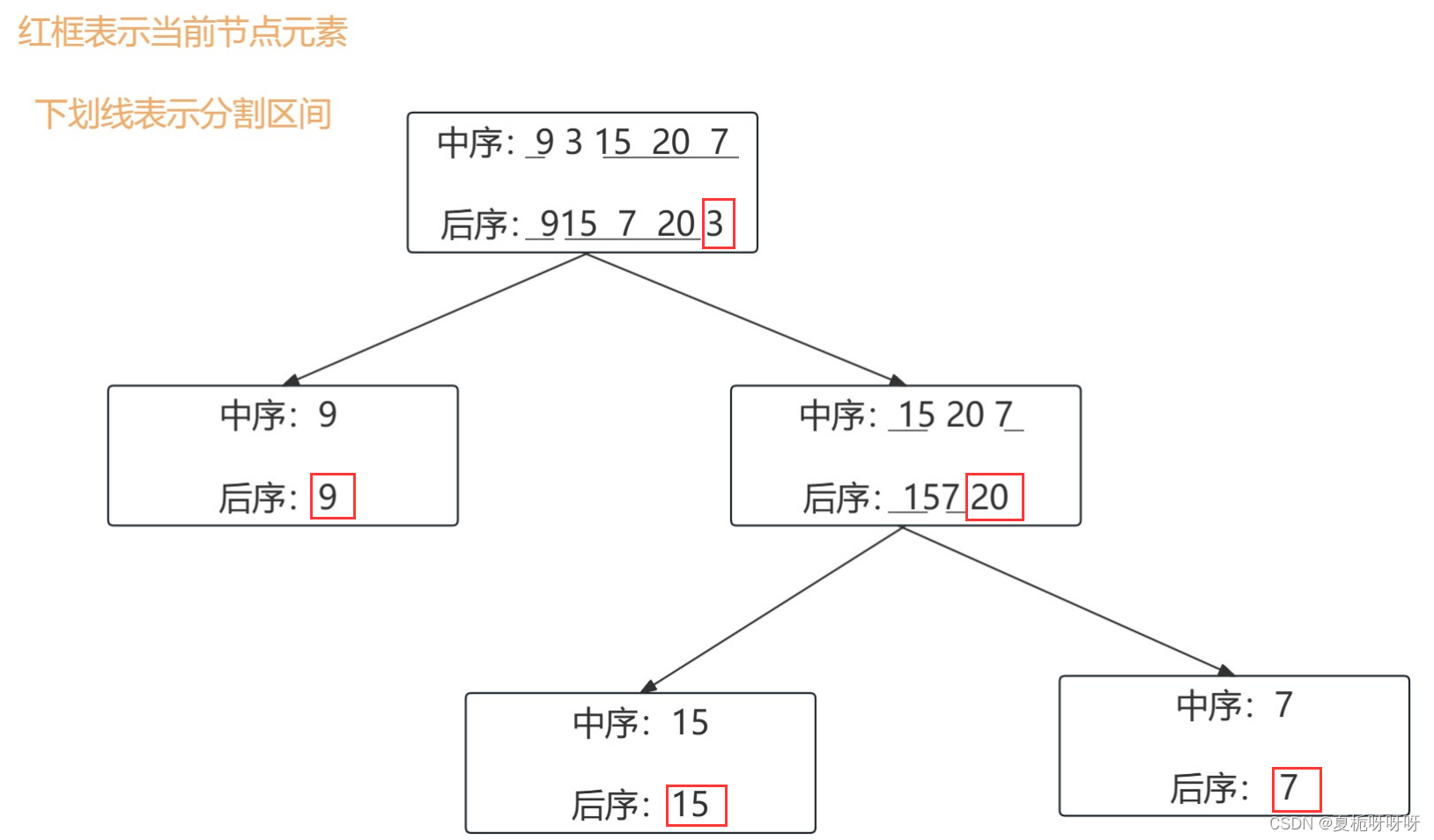
文章目录 1.【513】找树左下角的值1.1题目描述1.2 解题思路1.2.1 迭代法思路1.2.2 递归法思路 1.3 java代码实现1.3.1 迭代法java代码实现1.3.2 递归法java代码实现 2. 【112】路径总和2.1题目描述2.2 解题思路2.3 java代码实现 3.【106】从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树3.1题目…...
2023.11.25更新关于mac开发APP(flutter)的笔记与整理(实机开发一)
我自己写的笔记很杂,下面的笔记是我在chatgpt4的帮助下完成的,希望可以帮到正在踩坑mac开发APP(flutter)的小伙伴 目标:通过MAC电脑使用flutter框架开发一款适用于苹果手机的一个APP应用 本博客的阅读顺序是…...

万宾科技可燃气体监测仪的功能有哪些?
随着城市人口的持续增长和智慧城市不断发展,燃气作为一种重要的能源供应方式,已经广泛地应用于居民生活和工业生产的各个领域。然而燃气泄漏和安全事故的风险也随之增加,对城市的安全和社会的稳定构成了潜在的威胁。我国燃气管道安全事故的频…...

Binlog vs. Redo Log:数据库日志的较劲【高级】
🎏:你只管努力,剩下的交给时间 🏠 :小破站 Binlog vs. Redo Log:数据库日志的较劲【高级】 前言第一:事务的生命周期事务的生命周期Binlog和Redo Log记录事务的一致性和持久性Binlog的记录过程R…...
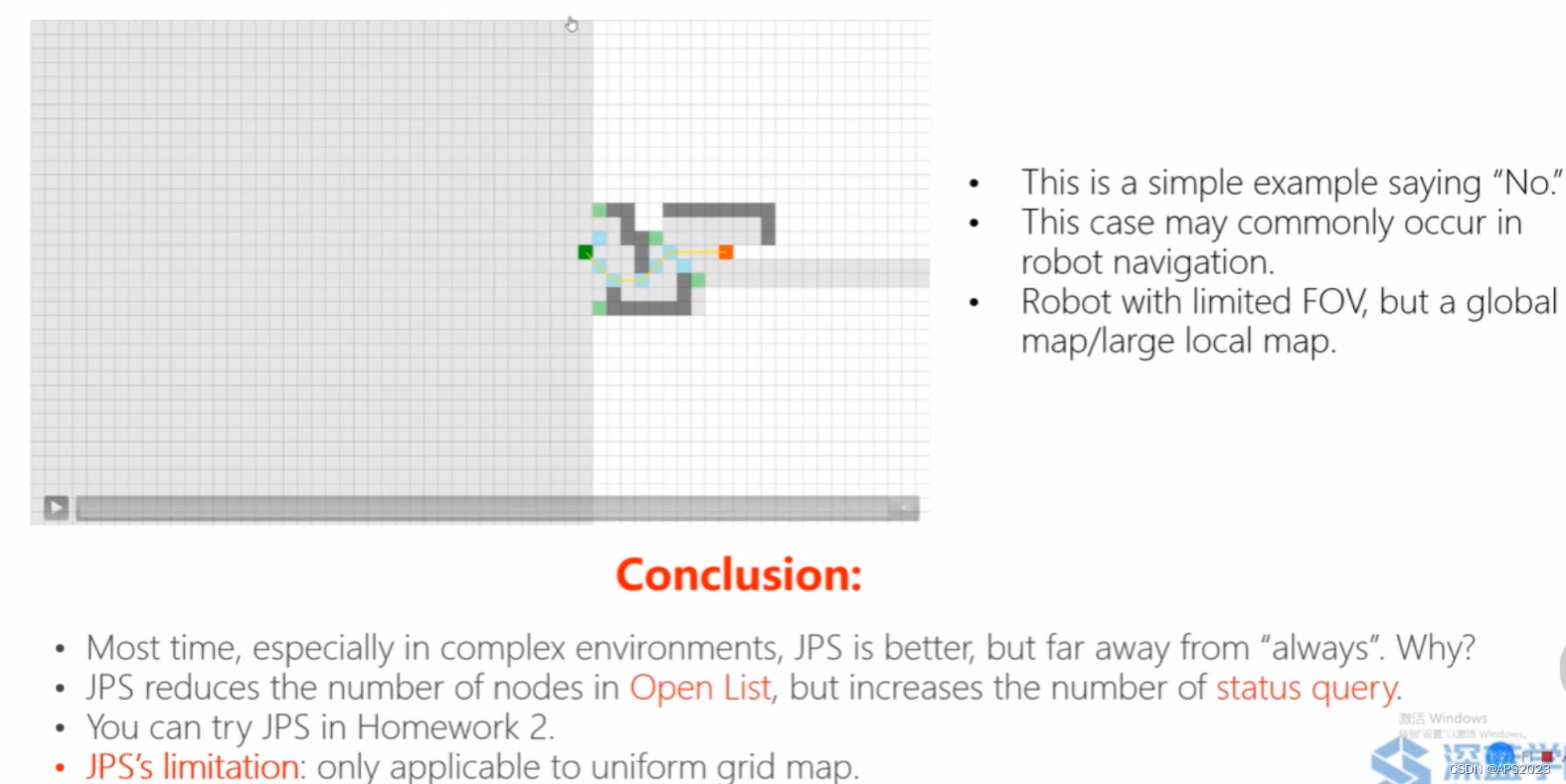
移动机器人路径规划(二)--- 图搜索基础,Dijkstra,A*,JPS
目录 1 图搜索基础 1.1 机器人规划的配置空间 Configuration Space 1.2 图搜索算法的基本概念 1.3 启发式的搜索算法 Heuristic search 2 A* Dijkstra算法 2.1 Dijkstra算法 2.2 A*&&Weighted A*算法 2.3 A* 算法的工程实践中的应用 3 JPS 1 图搜索基础 1.1…...
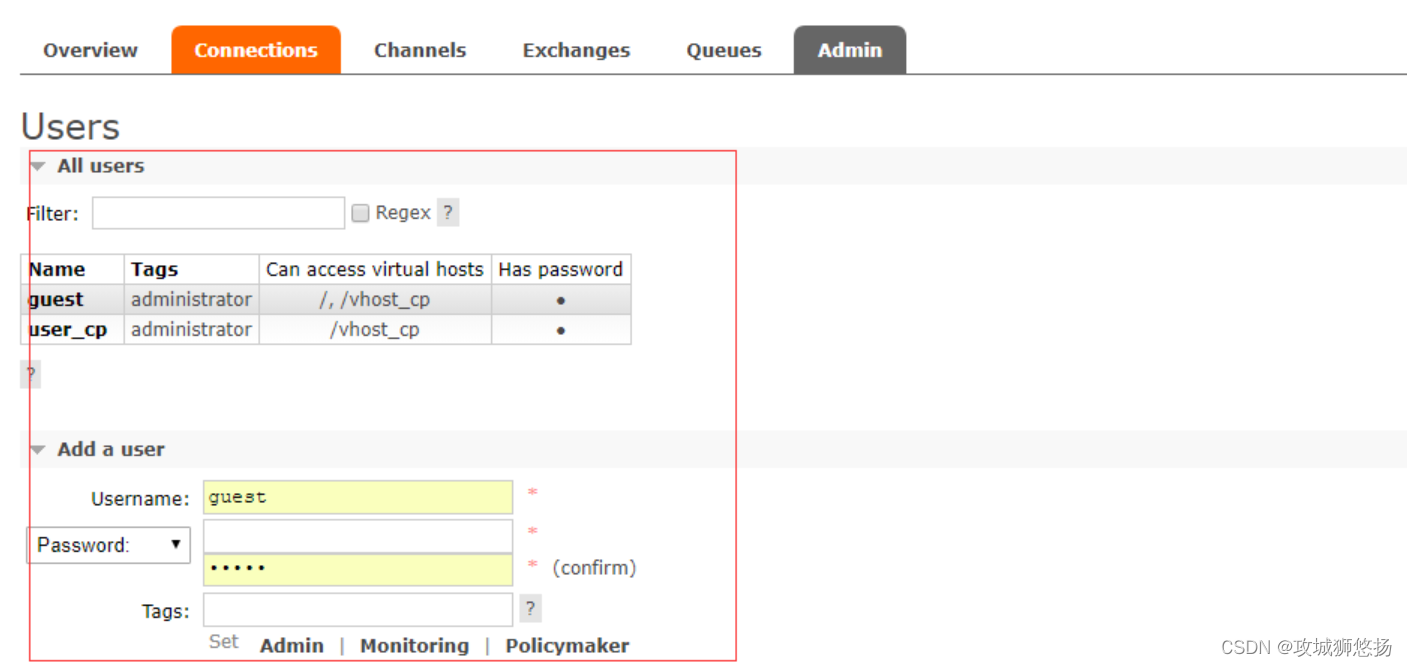
消息中间件——RabbitMQ(四)命令行与管控台的基本操作!
前言 在前面的文章中我们介绍过RabbitMQ的搭建:RabbitMQ的安装过以及各大主流消息中间件的对比:,本章就主要来介绍下我们之前安装的管控台是如何使用以及如何通过命令行进行操作。 1. 命令行操作 1.1 基础服务的命令操作 rabbitmqctl sto…...

性能压测工具:wrk
一般我们压测的时候,需要了解衡量系统性能的一些参数指标,比如。 1、性能指标简介 1.1 延迟 简单易懂。green:一般指响应时间 95线:P95。平均100%的请求中95%已经响应的时间 99线:P99。平均100%的请求中99%已经响应的时间 平…...
[Matlab有限元分析] 2.杆单元有限元分析
1. 一维杆单元有限元分析程序 一维刚单元的局部坐标系(单元坐标系)与全局坐标系相同。 1.1 线性杆单元 如图所示是一个杆单元,由两个节点i和j,局部坐标系的X轴沿着杆的方向,由i节点指向j节点,每个节点有…...
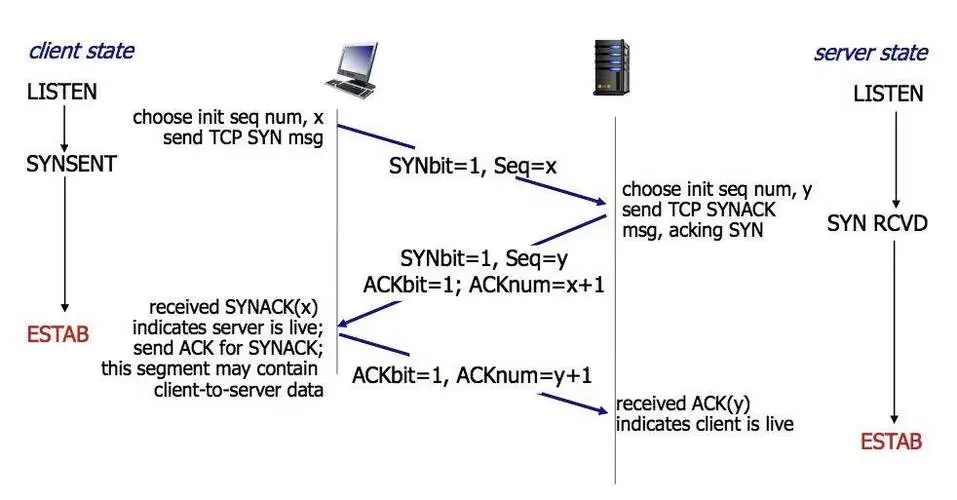
透过对话聊天聊网络tcp三次握手四次挥手
序 说起来网络,就让我想起的就是一张图。我在网上可以为所欲为,反正你又不能顺着网线来打我。接下来我们来详细说一下网络到底是怎么连接的。 TCP三次打招呼 首先我会用男女生之间的聊天方式,来举一个例子。 从tcp三次握手来说,…...
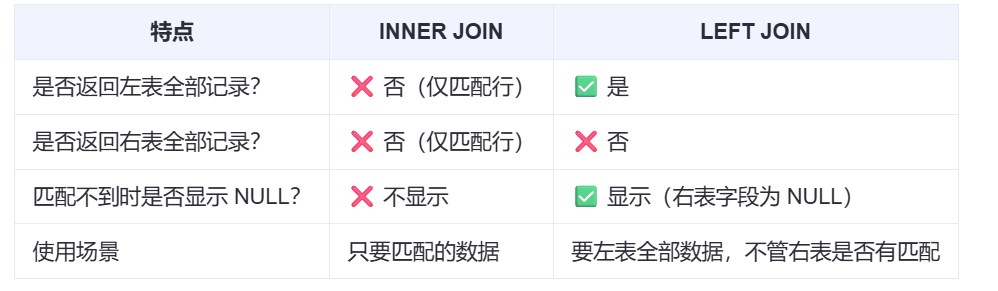
【SQL学习笔记1】增删改查+多表连接全解析(内附SQL免费在线练习工具)
可以使用Sqliteviz这个网站免费编写sql语句,它能够让用户直接在浏览器内练习SQL的语法,不需要安装任何软件。 链接如下: sqliteviz 注意: 在转写SQL语法时,关键字之间有一个特定的顺序,这个顺序会影响到…...
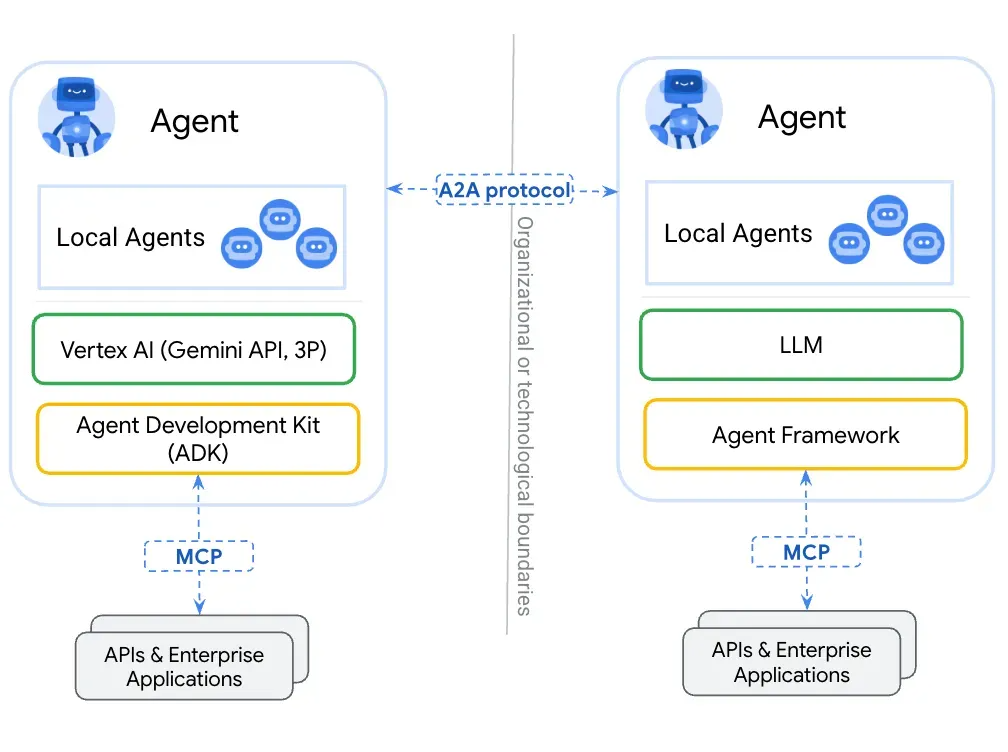
第一篇:Agent2Agent (A2A) 协议——协作式人工智能的黎明
AI 领域的快速发展正在催生一个新时代,智能代理(agents)不再是孤立的个体,而是能够像一个数字团队一样协作。然而,当前 AI 生态系统的碎片化阻碍了这一愿景的实现,导致了“AI 巴别塔问题”——不同代理之间…...

算法笔记2
1.字符串拼接最好用StringBuilder,不用String 2.创建List<>类型的数组并创建内存 List arr[] new ArrayList[26]; Arrays.setAll(arr, i -> new ArrayList<>()); 3.去掉首尾空格...

rnn判断string中第一次出现a的下标
# coding:utf8 import torch import torch.nn as nn import numpy as np import random import json""" 基于pytorch的网络编写 实现一个RNN网络完成多分类任务 判断字符 a 第一次出现在字符串中的位置 """class TorchModel(nn.Module):def __in…...

AGain DB和倍数增益的关系
我在设置一款索尼CMOS芯片时,Again增益0db变化为6DB,画面的变化只有2倍DN的增益,比如10变为20。 这与dB和线性增益的关系以及传感器处理流程有关。以下是具体原因分析: 1. dB与线性增益的换算关系 6dB对应的理论线性增益应为&…...

android13 app的触摸问题定位分析流程
一、知识点 一般来说,触摸问题都是app层面出问题,我们可以在ViewRootImpl.java添加log的方式定位;如果是touchableRegion的计算问题,就会相对比较麻烦了,需要通过adb shell dumpsys input > input.log指令,且通过打印堆栈的方式,逐步定位问题,并找到修改方案。 问题…...
通过 Ansible 在 Windows 2022 上安装 IIS Web 服务器
拓扑结构 这是一个用于通过 Ansible 部署 IIS Web 服务器的实验室拓扑。 前提条件: 在被管理的节点上安装WinRm 准备一张自签名的证书 开放防火墙入站tcp 5985 5986端口 准备自签名证书 PS C:\Users\azureuser> $cert New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName &…...
Linux部署私有文件管理系统MinIO
最近需要用到一个文件管理服务,但是又不想花钱,所以就想着自己搭建一个,刚好我们用的一个开源框架已经集成了MinIO,所以就选了这个 我这边对文件服务性能要求不是太高,单机版就可以 安装非常简单,几个命令就…...

c# 局部函数 定义、功能与示例
C# 局部函数:定义、功能与示例 1. 定义与功能 局部函数(Local Function)是嵌套在另一个方法内部的私有方法,仅在包含它的方法内可见。 • 作用:封装仅用于当前方法的逻辑,避免污染类作用域,提升…...
【Veristand】Veristand环境安装教程-Linux RT / Windows
首先声明,此教程是针对Simulink编译模型并导入Veristand中编写的,同时需要注意的是老用户编译可能用的是Veristand Model Framework,那个是历史版本,且NI不会再维护,新版本编译支持为VeriStand Model Generation Suppo…...
