Linux驱动开发——网络设备驱动(理论篇)
目录
一、前言
二、网络层次结构
三、网络设备驱动核心数据结构和函数
一、前言
网络设备驱动是 Linux 的第三大类驱动,也是我们学习的最后一类 Linux 驱动。这里我们首先简单学习一下网络协议层次结构,然后简单讨论 Linux 内核中网络实现的层次结构。接下来着重介绍了网络设备驱动所涉及的核心数据结构和函数接口。在此基础之上实现了一个虚拟的网络设备驱动,并以该驱动框架为蓝本,分析了 DM9000 网卡的驱动。最后简单介绍了 NAPI的意义和实现过程。
二、网络层次结构
ISO (International Organization for Standardization, 国际标准化组织) 设计的 OSI(Open System Interconnection,开放系统互联)参考模型将网络划分成7个层次,这种参考模型虽然没有得到真正意义上的应用,但是几乎所有的互联系统的设计都参考了该模型,所以它称得上真正的参考模型。OSI在 Internet上的一个现实版的分层模型就是TCP/IP层次模型,两者的对应关系如图 所示。

Network Access(网络访问层)对应了 Data Link (数据链路层)和 Physical(物理层),包含了信号的电气特性,传输介质的机械特性(属于物理层) 和帧格式定义,差错处理,流量控制,链路的建立、维护和释放(属于数据链路层) 等的处理。每一个硬件设备都应该有一个唯一的ID,这个 ID 也叫硬件地址或 MAC 地址。
Internet (互联网络层) 对应了 Network (网络层),利用数据链路层提供的两个相邻端点之间的数据帧的传送功能,进一步管理网络中的数据通信,将数据设法从源端经过若干个中间节点传送到目的端,从而向运输层提供最基本的端到端的数据传送服务。本层提供重要的寻址和路由选择服务,在 TCP/IP 中,本层的地址是 IP 地址。
Host-to-Host(主机到主机)对应 Transport (传输层),提供端到端的传输,在 TCP/IP中,本层使用端口号进行寻址。
Application (应用层) 对应 Application、Presentation (表示层)和 Session (会话层),
从应用程序的角度来看网络连接,在两个应用之间建立通信连接之后,应用层负责传输实际的应用数据。
Linux 将网络协议实现在内核内部,整个系统的层次结构如图所示.
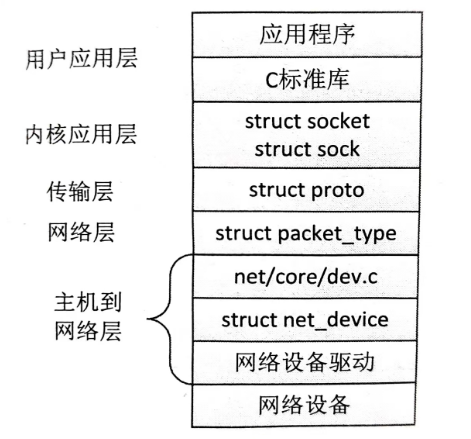
在这里,我们关注的是网络设备驱动,它负责了数据链路层的一部分工作。可以很容易地想见,网络设备驱动最主要的工作就是驱动网络设备 (通常也叫网卡) 将数据发送出去,或者将网络设备收到的数据往上层递交,更简单地说就是负责网络数据的收发。我们知道,网络数据是按包为单位来组织的,这样网络设备驱动就和块设备驱动非常类似。网络设备驱动负责将数据包“写入”网络或从网络中“读取”数据包,从而完成上层的请求。但是,它们之间还是有一些差别的。首先,网络设备没有设备节点,因此没有使用文件系统的那套接口对网络设备进行访问,使用的是另一套套接字编程接口。其次,网络设备通常是基于中断的方式工作的,在收到数据包后,会产生相应的中断,网络驱动从网卡中获取数据包后进行必要的验证,然后主动将数据包递交给上层。而块设备驱动在读取方向上也是被动地接受上层的请求。
(之前说的linux中万物皆文件不准却就是在这里,网络设备使用的是套接字接口而不是像文件系统那样抽象成一个文件驱操作)
网络设备驱动在这里担当了承上启下的作用,使上层的网络协议层不必关心底层的硬件细节信息。另外,驱动本身基本也与协议无关,不需要解析网络数据包,只负责数据包的收发。
当然,除了数据包收发的主要工作之外,网络设备驱动还要负责大量的管理任务,如设置硬件地址、修改传输参数、错误处理和统计、流量控制等。
三、网络设备驱动核心数据结构和函数
网络设备驱动中一个重要的数据结构是 struct net_device,这个结构非常庞大,以至设计这个结构的内核开发人员都在这个结构的定义前加这样一句注释“Actmally, thiswhole structure is a big mistake"。我们也只关心这个结构中和整动相关的一部分。
/** The DEVICE structure.* Actually, this whole structure is a big mistake. It mixes I/O* data with strictly "high-level" data, and it has to know about* almost every data structure used in the INET module.** FIXME: cleanup struct net_device such that network protocol info* moves out.*/struct net_device {/** This is the first field of the "visible" part of this structure* (i.e. as seen by users in the "Space.c" file). It is the name* of the interface.*/char name[IFNAMSIZ];/* device name hash chain, please keep it close to name[] */struct hlist_node name_hlist;/* snmp alias */char *ifalias;/** I/O specific fields* FIXME: Merge these and struct ifmap into one*/unsigned long mem_end; /* shared mem end */unsigned long mem_start; /* shared mem start */unsigned long base_addr; /* device I/O address */int irq; /* device IRQ number *//** Some hardware also needs these fields, but they are not* part of the usual set specified in Space.c.*/unsigned long state;struct list_head dev_list;struct list_head napi_list;struct list_head unreg_list;struct list_head close_list;/* directly linked devices, like slaves for bonding */struct {struct list_head upper;struct list_head lower;} adj_list;/* all linked devices, *including* neighbours */struct {struct list_head upper;struct list_head lower;} all_adj_list;/* currently active device features */netdev_features_t features;/* user-changeable features */netdev_features_t hw_features;/* user-requested features */netdev_features_t wanted_features;/* mask of features inheritable by VLAN devices */netdev_features_t vlan_features;/* mask of features inherited by encapsulating devices* This field indicates what encapsulation offloads* the hardware is capable of doing, and drivers will* need to set them appropriately.*/netdev_features_t hw_enc_features;/* mask of fetures inheritable by MPLS */netdev_features_t mpls_features;/* Interface index. Unique device identifier */int ifindex;int iflink;struct net_device_stats stats;atomic_long_t rx_dropped; /* dropped packets by core network* Do not use this in drivers.*/#ifdef CONFIG_WIRELESS_EXT/* List of functions to handle Wireless Extensions (instead of ioctl).* See <net/iw_handler.h> for details. Jean II */const struct iw_handler_def * wireless_handlers;/* Instance data managed by the core of Wireless Extensions. */struct iw_public_data * wireless_data;
#endif/* Management operations */const struct net_device_ops *netdev_ops;const struct ethtool_ops *ethtool_ops;const struct forwarding_accel_ops *fwd_ops;/* Hardware header description */const struct header_ops *header_ops;unsigned int flags; /* interface flags (a la BSD) */unsigned int priv_flags; /* Like 'flags' but invisible to userspace.* See if.h for definitions. */unsigned short gflags;unsigned short padded; /* How much padding added by alloc_netdev() */unsigned char operstate; /* RFC2863 operstate */unsigned char link_mode; /* mapping policy to operstate */unsigned char if_port; /* Selectable AUI, TP,..*/unsigned char dma; /* DMA channel */unsigned int mtu; /* interface MTU value */unsigned short type; /* interface hardware type */unsigned short hard_header_len; /* hardware hdr length *//* extra head- and tailroom the hardware may need, but not in all cases* can this be guaranteed, especially tailroom. Some cases also use* LL_MAX_HEADER instead to allocate the skb.*/unsigned short needed_headroom;unsigned short needed_tailroom;/* Interface address info. */unsigned char perm_addr[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* permanent hw address */unsigned char addr_assign_type; /* hw address assignment type */unsigned char addr_len; /* hardware address length */unsigned short neigh_priv_len;unsigned short dev_id; /* Used to differentiate devices* that share the same link* layer address*/spinlock_t addr_list_lock;struct netdev_hw_addr_list uc; /* Unicast mac addresses */struct netdev_hw_addr_list mc; /* Multicast mac addresses */struct netdev_hw_addr_list dev_addrs; /* list of device* hw addresses*/
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSFSstruct kset *queues_kset;
#endifbool uc_promisc;unsigned int promiscuity;unsigned int allmulti;/* Protocol specific pointers */#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_VLAN_8021Q)struct vlan_info __rcu *vlan_info; /* VLAN info */
#endif
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_NET_DSA)struct dsa_switch_tree *dsa_ptr; /* dsa specific data */
#endif
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_TIPC)struct tipc_bearer __rcu *tipc_ptr; /* TIPC specific data */
#endifvoid *atalk_ptr; /* AppleTalk link */struct in_device __rcu *ip_ptr; /* IPv4 specific data */struct dn_dev __rcu *dn_ptr; /* DECnet specific data */struct inet6_dev __rcu *ip6_ptr; /* IPv6 specific data */void *ax25_ptr; /* AX.25 specific data */struct wireless_dev *ieee80211_ptr; /* IEEE 802.11 specific data,assign before registering *//** Cache lines mostly used on receive path (including eth_type_trans())*/unsigned long last_rx; /* Time of last Rx* This should not be set in* drivers, unless really needed,* because network stack (bonding)* use it if/when necessary, to* avoid dirtying this cache line.*//* Interface address info used in eth_type_trans() */unsigned char *dev_addr; /* hw address, (before bcastbecause most packets areunicast) */#ifdef CONFIG_SYSFSstruct netdev_rx_queue *_rx;/* Number of RX queues allocated at register_netdev() time */unsigned int num_rx_queues;/* Number of RX queues currently active in device */unsigned int real_num_rx_queues;#endifrx_handler_func_t __rcu *rx_handler;void __rcu *rx_handler_data;struct netdev_queue __rcu *ingress_queue;unsigned char broadcast[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* hw bcast add *//** Cache lines mostly used on transmit path*/struct netdev_queue *_tx ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;/* Number of TX queues allocated at alloc_netdev_mq() time */unsigned int num_tx_queues;/* Number of TX queues currently active in device */unsigned int real_num_tx_queues;/* root qdisc from userspace point of view */struct Qdisc *qdisc;unsigned long tx_queue_len; /* Max frames per queue allowed */spinlock_t tx_global_lock;#ifdef CONFIG_XPSstruct xps_dev_maps __rcu *xps_maps;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_RFS_ACCEL/* CPU reverse-mapping for RX completion interrupts, indexed* by RX queue number. Assigned by driver. This must only be* set if the ndo_rx_flow_steer operation is defined. */struct cpu_rmap *rx_cpu_rmap;
#endif/* These may be needed for future network-power-down code. *//** trans_start here is expensive for high speed devices on SMP,* please use netdev_queue->trans_start instead.*/unsigned long trans_start; /* Time (in jiffies) of last Tx */int watchdog_timeo; /* used by dev_watchdog() */struct timer_list watchdog_timer;/* Number of references to this device */int __percpu *pcpu_refcnt;/* delayed register/unregister */struct list_head todo_list;/* device index hash chain */struct hlist_node index_hlist;struct list_head link_watch_list;/* register/unregister state machine */enum { NETREG_UNINITIALIZED=0,NETREG_REGISTERED, /* completed register_netdevice */NETREG_UNREGISTERING, /* called unregister_netdevice */NETREG_UNREGISTERED, /* completed unregister todo */NETREG_RELEASED, /* called free_netdev */NETREG_DUMMY, /* dummy device for NAPI poll */} reg_state:8;bool dismantle; /* device is going do be freed */enum {RTNL_LINK_INITIALIZED,RTNL_LINK_INITIALIZING,} rtnl_link_state:16;/* Called from unregister, can be used to call free_netdev */void (*destructor)(struct net_device *dev);#ifdef CONFIG_NETPOLLstruct netpoll_info __rcu *npinfo;
#endif#ifdef CONFIG_NET_NS/* Network namespace this network device is inside */struct net *nd_net;
#endif/* mid-layer private */union {void *ml_priv;struct pcpu_lstats __percpu *lstats; /* loopback stats */struct pcpu_sw_netstats __percpu *tstats;struct pcpu_dstats __percpu *dstats; /* dummy stats */struct pcpu_vstats __percpu *vstats; /* veth stats */};/* GARP */struct garp_port __rcu *garp_port;/* MRP */struct mrp_port __rcu *mrp_port;/* class/net/name entry */struct device dev;/* space for optional device, statistics, and wireless sysfs groups */const struct attribute_group *sysfs_groups[4];/* space for optional per-rx queue attributes */const struct attribute_group *sysfs_rx_queue_group;/* rtnetlink link ops */const struct rtnl_link_ops *rtnl_link_ops;/* for setting kernel sock attribute on TCP connection setup */
#define GSO_MAX_SIZE 65536unsigned int gso_max_size;
#define GSO_MAX_SEGS 65535u16 gso_max_segs;#ifdef CONFIG_DCB/* Data Center Bridging netlink ops */const struct dcbnl_rtnl_ops *dcbnl_ops;
#endifu8 num_tc;struct netdev_tc_txq tc_to_txq[TC_MAX_QUEUE];u8 prio_tc_map[TC_BITMASK + 1];#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_FCOE)/* max exchange id for FCoE LRO by ddp */unsigned int fcoe_ddp_xid;
#endif
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_CGROUP_NET_PRIO)struct netprio_map __rcu *priomap;
#endif/* phy device may attach itself for hardware timestamping */struct phy_device *phydev;struct lock_class_key *qdisc_tx_busylock;/* group the device belongs to */int group;struct pm_qos_request pm_qos_req;
};(真的多结构体里套一堆自定义类型)
name: 网络设备的名字,如ethx 表示以太网设备、pppx 表示 PPP 连接类型的设备isdnx 表示ISDN 卡、lo 表示环回设备。
mem_end、mem start: 如 PCI 网卡之类的网络设备的共享内存的结束地址和起始地址。
base_addr:如 PCI 网卡之类的网络设备的I/O 端口地址。
irq:网卡使用的中断号。
stats: 网卡的统计信息,包括rx_packets、tx_packets、rx_bytes、tx_bytes、rx_errors、tx_errors、rx_dropped、tx_dropped 之类的收发统计信息。
netdev_ops: 网络设备的操作方法集合,后面会更详细地进行描述。
ethtool_ops: 用户层 ethtool 工具在驱动中对应的操作方法集合,例如使用ethtooleth0 命令可以查看 etho 网络设备的所有寄存器内容。
mtu: 接口的 MTU(最大传输单元) 值,对于以太网设备来说通常是 1500 个字节
type: 接口的硬件类型。
flags;一组接口的标志。
hard_header_len:硬件头长度,以太网是 14 个字节。
addr_len; 硬件地址长度,以太网为 MAC 地址,长度为6 个字节
uc:单播 MAC 地址列表。
mc:多播 MAC 地址列表。
dev_addr: 指向硬件地址的指针
broadcast: 广播的硬件地址。
_tx: 网络设备的发送数据包队列。
num_tx_queues: 由 alloc_netdev_mq 函数分配的属于当前网络设备的发送队列的数量
real_num_tx_queues:当前活动的发送队列的数量。
tx_queue_len: 每个队列允许的最大帧数量。
trans_start: 用jiffies 表示的数据包开始发送的时间
watchdog_timeo: 数据包发送的超时时间。
watchdog_timer: 发送超时的定时器,如果超时时间到期,数据包还没被发送出去那么驱动提供的超时函数将会被调用。
网络设备的操作方法集合由 struct net_device_ops 结构来描述,该结构中有很多函数指针指向不同的函数,用于对网络设备进行不同的操作,但我们最关心的还是与数据的发送处理相关的内容,
/** This structure defines the management hooks for network devices.* The following hooks can be defined; unless noted otherwise, they are* optional and can be filled with a null pointer.** int (*ndo_init)(struct net_device *dev);* This function is called once when network device is registered.* The network device can use this to any late stage initializaton* or semantic validattion. It can fail with an error code which will* be propogated back to register_netdev** void (*ndo_uninit)(struct net_device *dev);* This function is called when device is unregistered or when registration* fails. It is not called if init fails.** int (*ndo_open)(struct net_device *dev);* This function is called when network device transistions to the up* state.** int (*ndo_stop)(struct net_device *dev);* This function is called when network device transistions to the down* state.** netdev_tx_t (*ndo_start_xmit)(struct sk_buff *skb,* struct net_device *dev);* Called when a packet needs to be transmitted.* Must return NETDEV_TX_OK , NETDEV_TX_BUSY.* (can also return NETDEV_TX_LOCKED iff NETIF_F_LLTX)* Required can not be NULL.** u16 (*ndo_select_queue)(struct net_device *dev, struct sk_buff *skb,* void *accel_priv, select_queue_fallback_t fallback);* Called to decide which queue to when device supports multiple* transmit queues.** void (*ndo_change_rx_flags)(struct net_device *dev, int flags);* This function is called to allow device receiver to make* changes to configuration when multicast or promiscious is enabled.** void (*ndo_set_rx_mode)(struct net_device *dev);* This function is called device changes address list filtering.* If driver handles unicast address filtering, it should set* IFF_UNICAST_FLT to its priv_flags.** int (*ndo_set_mac_address)(struct net_device *dev, void *addr);* This function is called when the Media Access Control address* needs to be changed. If this interface is not defined, the* mac address can not be changed.** int (*ndo_validate_addr)(struct net_device *dev);* Test if Media Access Control address is valid for the device.** int (*ndo_do_ioctl)(struct net_device *dev, struct ifreq *ifr, int cmd);* Called when a user request an ioctl which can't be handled by* the generic interface code. If not defined ioctl's return* not supported error code.** int (*ndo_set_config)(struct net_device *dev, struct ifmap *map);* Used to set network devices bus interface parameters. This interface* is retained for legacy reason, new devices should use the bus* interface (PCI) for low level management.** int (*ndo_change_mtu)(struct net_device *dev, int new_mtu);* Called when a user wants to change the Maximum Transfer Unit* of a device. If not defined, any request to change MTU will* will return an error.** void (*ndo_tx_timeout)(struct net_device *dev);* Callback uses when the transmitter has not made any progress* for dev->watchdog ticks.** struct rtnl_link_stats64* (*ndo_get_stats64)(struct net_device *dev,* struct rtnl_link_stats64 *storage);* struct net_device_stats* (*ndo_get_stats)(struct net_device *dev);* Called when a user wants to get the network device usage* statistics. Drivers must do one of the following:* 1. Define @ndo_get_stats64 to fill in a zero-initialised* rtnl_link_stats64 structure passed by the caller.* 2. Define @ndo_get_stats to update a net_device_stats structure* (which should normally be dev->stats) and return a pointer to* it. The structure may be changed asynchronously only if each* field is written atomically.* 3. Update dev->stats asynchronously and atomically, and define* neither operation.** int (*ndo_vlan_rx_add_vid)(struct net_device *dev, __be16 proto, u16t vid);* If device support VLAN filtering this function is called when a* VLAN id is registered.** int (*ndo_vlan_rx_kill_vid)(struct net_device *dev, unsigned short vid);* If device support VLAN filtering this function is called when a* VLAN id is unregistered.** void (*ndo_poll_controller)(struct net_device *dev);** SR-IOV management functions.* int (*ndo_set_vf_mac)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, u8* mac);* int (*ndo_set_vf_vlan)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, u16 vlan, u8 qos);* int (*ndo_set_vf_tx_rate)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, int rate);* int (*ndo_set_vf_spoofchk)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, bool setting);* int (*ndo_get_vf_config)(struct net_device *dev,* int vf, struct ifla_vf_info *ivf);* int (*ndo_set_vf_link_state)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, int link_state);* int (*ndo_set_vf_port)(struct net_device *dev, int vf,* struct nlattr *port[]);* int (*ndo_get_vf_port)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, struct sk_buff *skb);* int (*ndo_setup_tc)(struct net_device *dev, u8 tc)* Called to setup 'tc' number of traffic classes in the net device. This* is always called from the stack with the rtnl lock held and netif tx* queues stopped. This allows the netdevice to perform queue management* safely.** Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) offload functions.* int (*ndo_fcoe_enable)(struct net_device *dev);* Called when the FCoE protocol stack wants to start using LLD for FCoE* so the underlying device can perform whatever needed configuration or* initialization to support acceleration of FCoE traffic.** int (*ndo_fcoe_disable)(struct net_device *dev);* Called when the FCoE protocol stack wants to stop using LLD for FCoE* so the underlying device can perform whatever needed clean-ups to* stop supporting acceleration of FCoE traffic.** int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_setup)(struct net_device *dev, u16 xid,* struct scatterlist *sgl, unsigned int sgc);* Called when the FCoE Initiator wants to initialize an I/O that* is a possible candidate for Direct Data Placement (DDP). The LLD can* perform necessary setup and returns 1 to indicate the device is set up* successfully to perform DDP on this I/O, otherwise this returns 0.** int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_done)(struct net_device *dev, u16 xid);* Called when the FCoE Initiator/Target is done with the DDPed I/O as* indicated by the FC exchange id 'xid', so the underlying device can* clean up and reuse resources for later DDP requests.** int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_target)(struct net_device *dev, u16 xid,* struct scatterlist *sgl, unsigned int sgc);* Called when the FCoE Target wants to initialize an I/O that* is a possible candidate for Direct Data Placement (DDP). The LLD can* perform necessary setup and returns 1 to indicate the device is set up* successfully to perform DDP on this I/O, otherwise this returns 0.** int (*ndo_fcoe_get_hbainfo)(struct net_device *dev,* struct netdev_fcoe_hbainfo *hbainfo);* Called when the FCoE Protocol stack wants information on the underlying* device. This information is utilized by the FCoE protocol stack to* register attributes with Fiber Channel management service as per the* FC-GS Fabric Device Management Information(FDMI) specification.** int (*ndo_fcoe_get_wwn)(struct net_device *dev, u64 *wwn, int type);* Called when the underlying device wants to override default World Wide* Name (WWN) generation mechanism in FCoE protocol stack to pass its own* World Wide Port Name (WWPN) or World Wide Node Name (WWNN) to the FCoE* protocol stack to use.** RFS acceleration.* int (*ndo_rx_flow_steer)(struct net_device *dev, const struct sk_buff *skb,* u16 rxq_index, u32 flow_id);* Set hardware filter for RFS. rxq_index is the target queue index;* flow_id is a flow ID to be passed to rps_may_expire_flow() later.* Return the filter ID on success, or a negative error code.** Slave management functions (for bridge, bonding, etc).* int (*ndo_add_slave)(struct net_device *dev, struct net_device *slave_dev);* Called to make another netdev an underling.** int (*ndo_del_slave)(struct net_device *dev, struct net_device *slave_dev);* Called to release previously enslaved netdev.** Feature/offload setting functions.* netdev_features_t (*ndo_fix_features)(struct net_device *dev,* netdev_features_t features);* Adjusts the requested feature flags according to device-specific* constraints, and returns the resulting flags. Must not modify* the device state.** int (*ndo_set_features)(struct net_device *dev, netdev_features_t features);* Called to update device configuration to new features. Passed* feature set might be less than what was returned by ndo_fix_features()).* Must return >0 or -errno if it changed dev->features itself.** int (*ndo_fdb_add)(struct ndmsg *ndm, struct nlattr *tb[],* struct net_device *dev,* const unsigned char *addr, u16 flags)* Adds an FDB entry to dev for addr.* int (*ndo_fdb_del)(struct ndmsg *ndm, struct nlattr *tb[],* struct net_device *dev,* const unsigned char *addr)* Deletes the FDB entry from dev coresponding to addr.* int (*ndo_fdb_dump)(struct sk_buff *skb, struct netlink_callback *cb,* struct net_device *dev, int idx)* Used to add FDB entries to dump requests. Implementers should add* entries to skb and update idx with the number of entries.** int (*ndo_bridge_setlink)(struct net_device *dev, struct nlmsghdr *nlh)* int (*ndo_bridge_getlink)(struct sk_buff *skb, u32 pid, u32 seq,* struct net_device *dev, u32 filter_mask)** int (*ndo_change_carrier)(struct net_device *dev, bool new_carrier);* Called to change device carrier. Soft-devices (like dummy, team, etc)* which do not represent real hardware may define this to allow their* userspace components to manage their virtual carrier state. Devices* that determine carrier state from physical hardware properties (eg* network cables) or protocol-dependent mechanisms (eg* USB_CDC_NOTIFY_NETWORK_CONNECTION) should NOT implement this function.** int (*ndo_get_phys_port_id)(struct net_device *dev,* struct netdev_phys_port_id *ppid);* Called to get ID of physical port of this device. If driver does* not implement this, it is assumed that the hw is not able to have* multiple net devices on single physical port.** void (*ndo_add_vxlan_port)(struct net_device *dev,* sa_family_t sa_family, __be16 port);* Called by vxlan to notiy a driver about the UDP port and socket* address family that vxlan is listnening to. It is called only when* a new port starts listening. The operation is protected by the* vxlan_net->sock_lock.** void (*ndo_del_vxlan_port)(struct net_device *dev,* sa_family_t sa_family, __be16 port);* Called by vxlan to notify the driver about a UDP port and socket* address family that vxlan is not listening to anymore. The operation* is protected by the vxlan_net->sock_lock.** void* (*ndo_dfwd_add_station)(struct net_device *pdev,* struct net_device *dev)* Called by upper layer devices to accelerate switching or other* station functionality into hardware. 'pdev is the lowerdev* to use for the offload and 'dev' is the net device that will* back the offload. Returns a pointer to the private structure* the upper layer will maintain.* void (*ndo_dfwd_del_station)(struct net_device *pdev, void *priv)* Called by upper layer device to delete the station created* by 'ndo_dfwd_add_station'. 'pdev' is the net device backing* the station and priv is the structure returned by the add* operation.* netdev_tx_t (*ndo_dfwd_start_xmit)(struct sk_buff *skb,* struct net_device *dev,* void *priv);* Callback to use for xmit over the accelerated station. This* is used in place of ndo_start_xmit on accelerated net* devices.*/
struct net_device_ops {int (*ndo_init)(struct net_device *dev);void (*ndo_uninit)(struct net_device *dev);int (*ndo_open)(struct net_device *dev);int (*ndo_stop)(struct net_device *dev);netdev_tx_t (*ndo_start_xmit) (struct sk_buff *skb,struct net_device *dev);u16 (*ndo_select_queue)(struct net_device *dev,struct sk_buff *skb,void *accel_priv,select_queue_fallback_t fallback);void (*ndo_change_rx_flags)(struct net_device *dev,int flags);void (*ndo_set_rx_mode)(struct net_device *dev);int (*ndo_set_mac_address)(struct net_device *dev,void *addr);int (*ndo_validate_addr)(struct net_device *dev);int (*ndo_do_ioctl)(struct net_device *dev,struct ifreq *ifr, int cmd);int (*ndo_set_config)(struct net_device *dev,struct ifmap *map);int (*ndo_change_mtu)(struct net_device *dev,int new_mtu);int (*ndo_neigh_setup)(struct net_device *dev,struct neigh_parms *);void (*ndo_tx_timeout) (struct net_device *dev);struct rtnl_link_stats64* (*ndo_get_stats64)(struct net_device *dev,struct rtnl_link_stats64 *storage);struct net_device_stats* (*ndo_get_stats)(struct net_device *dev);int (*ndo_vlan_rx_add_vid)(struct net_device *dev,__be16 proto, u16 vid);int (*ndo_vlan_rx_kill_vid)(struct net_device *dev,__be16 proto, u16 vid);
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_POLL_CONTROLLERvoid (*ndo_poll_controller)(struct net_device *dev);int (*ndo_netpoll_setup)(struct net_device *dev,struct netpoll_info *info,gfp_t gfp);void (*ndo_netpoll_cleanup)(struct net_device *dev);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLLint (*ndo_busy_poll)(struct napi_struct *dev);
#endifint (*ndo_set_vf_mac)(struct net_device *dev,int queue, u8 *mac);int (*ndo_set_vf_vlan)(struct net_device *dev,int queue, u16 vlan, u8 qos);int (*ndo_set_vf_tx_rate)(struct net_device *dev,int vf, int rate);int (*ndo_set_vf_spoofchk)(struct net_device *dev,int vf, bool setting);int (*ndo_get_vf_config)(struct net_device *dev,int vf,struct ifla_vf_info *ivf);int (*ndo_set_vf_link_state)(struct net_device *dev,int vf, int link_state);int (*ndo_set_vf_port)(struct net_device *dev,int vf,struct nlattr *port[]);int (*ndo_get_vf_port)(struct net_device *dev,int vf, struct sk_buff *skb);int (*ndo_setup_tc)(struct net_device *dev, u8 tc);
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_FCOE)int (*ndo_fcoe_enable)(struct net_device *dev);int (*ndo_fcoe_disable)(struct net_device *dev);int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_setup)(struct net_device *dev,u16 xid,struct scatterlist *sgl,unsigned int sgc);int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_done)(struct net_device *dev,u16 xid);int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_target)(struct net_device *dev,u16 xid,struct scatterlist *sgl,unsigned int sgc);int (*ndo_fcoe_get_hbainfo)(struct net_device *dev,struct netdev_fcoe_hbainfo *hbainfo);
#endif#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_LIBFCOE)
#define NETDEV_FCOE_WWNN 0
#define NETDEV_FCOE_WWPN 1int (*ndo_fcoe_get_wwn)(struct net_device *dev,u64 *wwn, int type);
#endif#ifdef CONFIG_RFS_ACCELint (*ndo_rx_flow_steer)(struct net_device *dev,const struct sk_buff *skb,u16 rxq_index,u32 flow_id);
#endifint (*ndo_add_slave)(struct net_device *dev,struct net_device *slave_dev);int (*ndo_del_slave)(struct net_device *dev,struct net_device *slave_dev);netdev_features_t (*ndo_fix_features)(struct net_device *dev,netdev_features_t features);int (*ndo_set_features)(struct net_device *dev,netdev_features_t features);int (*ndo_neigh_construct)(struct neighbour *n);void (*ndo_neigh_destroy)(struct neighbour *n);int (*ndo_fdb_add)(struct ndmsg *ndm,struct nlattr *tb[],struct net_device *dev,const unsigned char *addr,u16 flags);int (*ndo_fdb_del)(struct ndmsg *ndm,struct nlattr *tb[],struct net_device *dev,const unsigned char *addr);int (*ndo_fdb_dump)(struct sk_buff *skb,struct netlink_callback *cb,struct net_device *dev,int idx);int (*ndo_bridge_setlink)(struct net_device *dev,struct nlmsghdr *nlh);int (*ndo_bridge_getlink)(struct sk_buff *skb,u32 pid, u32 seq,struct net_device *dev,u32 filter_mask);int (*ndo_bridge_dellink)(struct net_device *dev,struct nlmsghdr *nlh);int (*ndo_change_carrier)(struct net_device *dev,bool new_carrier);int (*ndo_get_phys_port_id)(struct net_device *dev,struct netdev_phys_port_id *ppid);void (*ndo_add_vxlan_port)(struct net_device *dev,sa_family_t sa_family,__be16 port);void (*ndo_del_vxlan_port)(struct net_device *dev,sa_family_t sa_family,__be16 port);void* (*ndo_dfwd_add_station)(struct net_device *pdev,struct net_device *dev);void (*ndo_dfwd_del_station)(struct net_device *pdev,void *priv);netdev_tx_t (*ndo_dfwd_start_xmit) (struct sk_buff *skb,struct net_device *dev,void *priv);
};
ndo_init: 当网络设备注册后,该函数被调用,用于网络设备的后期初始化操作,没有特殊要求则为 NULL。
ndo_open: 当激活网络设备时,该函数被调用。
ndo_stop: 当网络设备被禁用时,该函数被调用。\
ndo_start_xmit:当一个网络数据包需要发送时,该函数被调用,函数应该返回
ndo_set_mac address:当需要改变 MAC 地址时,该函数被调用,可以为NULL。
NETDEV_TX_OK 或 NETDEV_TX_BUSY。
ndo_validate_addr: 用于验证 MAC 地址是否合法有效
ndo_do_ioctl: 用于处理通用接口代码不能处理的用户请求。
ndo_change_mtu:当用户想要改变设备的 MTU时,该函数被调用。
ndo_tx_timeout: 当发送超时时,该函数被调用。
ndo_get_stats: 用于获取网络设备的统计信息。
围绕 struct net_device 结构的主要函数和宏如下。
alloc_netdev(sizeof_priv, name, setup)
void *netdev_priv(const struct net_device *dev);
void free_netdev(struct net_device *dev);
void ether_setup(struct net_device *dev);
alloc_etherdev(sizeof_priv)
int register_netdev(struct net_device *dev) ;
void unregister_netdev(struct net_device *dev); alloc_netdev: 用于分配并且初始化一个 struct net_device 结构对象,并且还在该对象的后面分配了 sizeof_priv 字节大小的空间用于存放驱动的私有数据。为了提高访问的效率,驱动私有的数据开始地址对齐到 32字节的边界,所以在内存上的布局大致如图所示。
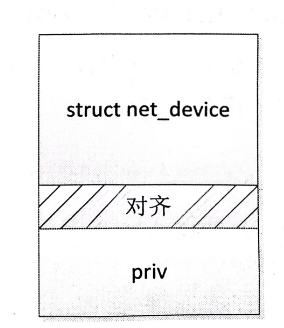
参数 name 是网络设备的名字,参数 setup 是一个指向用于进一步初始化 struct net_device 结构对象的函数指针。
netdev_priv:用于获取驱动私有数据区的起始地址
free_netdev:释放 struct net_device 结构对象。
alloc_etherdev:是专门针对分配并初始化以太网设备的 struct net_device 结构对象的一个宏,它的名字为 eth%d,也就是 eth 后面跟一个设备序号的数字,setup 方法为ether_setup。另外,这个宏还给该网络设备在发送方向和接收方向上分别分配了一个队列。
ether_setup:针对以太网设备的 struct net_device 结构对象中相关成员的初始化。代码如下。
void ether_setup(struct net_device *dev)
{dev->header_ops = ð_header_ops;dev->type = ARPHRD_ETHER;dev->hard_header_len = ETH_HLEN;dev->mtu = ETH_DATA_LEN;dev->addr_len = ETH_ALEN;dev->tx_queue_len = 1000; /* Ethernet wants good queues */dev->flags = IFF_BROADCAST | IFF_MULTICAST;dey->priv_flags |= IFF_TX_SKB_SHARING;memset (dev->broadcast, 0xFF, ETH_ALEN);
};
上面设置了以太网协议头的操作方法集为 et_header_ops, 然后对类型、硬件头长度MTU、硬件地址长度、发送队列的最大数目、一些标志和广播地址进行了设管。
register_netdev:注册网络设备。
unregister_netdev:注销网络设备。
网络数据的收发是基于队列的,在收发方向上各有单独的队列,上层要发送的数据包先送入发送队列,然后再通过网络设备驱动发送,网卡接收到的数据包放入接收队列,然后上层从接收队列中取出数据包进行协议解析。与队列相关的主要操作有如下的函数。
void netif_start_queue (struct net_device *dev) .
void netif_stop_queue(struct net_device *dev);netif_start_queue: 允许上层通过 hard_start_xmit 函数发送数据包
netif_stop_queue: 禁止上层通过 hard_start_xmit 函数发送数据包,这样可以在网络设备驱动中完成流控。
上面的数据包操作都是关于发送的,在网络设备操作方法集合里也没有数据包接收方向的接口函数。其实我们在前面也说过,网络设备驱动应该在收到数据包的时候“主动”将数据包递交给上层,一般这是发生在网卡的接收中断函数中的 (网卡一般都是按中断的方式工作的)。前面学习软中断时我们也提到过,网卡的接收中断的下半部完成对数据包的进一步处理,包括校验和拆包等,这样就完成了数据包向上层逐层传递的过程。这个向上层递交数据包的操作通过下面的函数来进行。
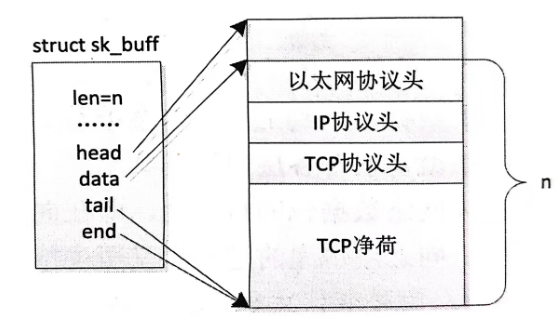
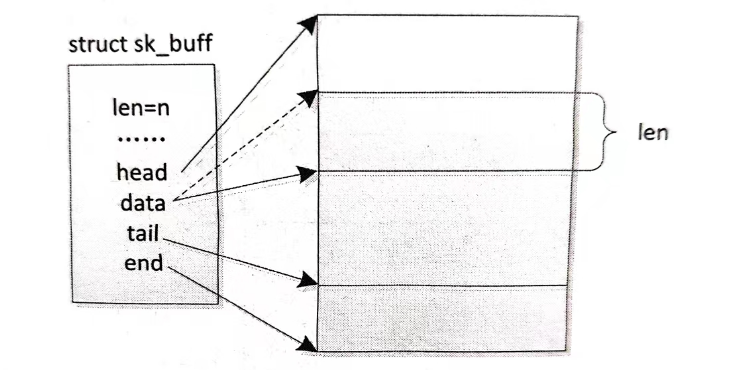
int netif_rx(struct sk_buff *skb);该函数返回 NET_RX_SUCCESS 表示成功,返回 NET_RX_DROP 表示包被丢弃。这里又引出一个关键的数据结构 struct sk_buff,即套接缓冲区,用于在各层之间传递数据包。但是该缓冲区不仅仅是一片容纳数据包的内存,还需要有额外的一些管理信息。数据包在网络协议层之间流动,处理它的效率必须要高。假如在下层向上层的递交过程中,下层的协议去掉协议头后将剩下的数据复制到上层,这会涉及大量的复制工作,显然这会影响效率。解决这个问题的方法就是要在各层协议间共享同一个缓冲区,在层与层之间传递缓冲区的指针。不过,因为网络数据包的特殊性,即在向下层传递的过程中要添加协议包头和可能在尾部的校验,向上层传递的过程中又要去掉协议包头和可能的尾部校验,因此层与层之间传递的指针必须要变化才行。struct sk_buff 这个巧妙的数据结构就能实现这一功能,如果不考虑分散/聚集 I/O 的处理,那么要理解它还是比较容易的。下面列出该结构最主要的成员。
struct sk_buff
{struct sk_buff *next;struct sk_buff *prev;ktime_t tstamp;struct net_device *dev;unsigned int len, data_len;__be16 protocol;__u16 transport_header;__u16 network_header;__u16 mac_header;sk_buff_data_t tail;sk_buff_data_t end;unaighed char *head,*data;unsigned int truesize;
};
nex、prev: 链接 skb (套接字缓冲区,以后用 skb 来称这个数据结对象)的指针
tstammp: 收到数据包的时间戳。
dev: 指向收到该数包的网络设备结构对象的指针。
len: 所有数据的长度,包括了用于分散/聚集 (分片) 数据的长度。
data_len:分片数据的长度。
protocol: 网络设备驱动收到的数据包的协议类型。
transport_header:传输层的数据包头的偏移地址。
network_header: 网络层数据包头的偏移地址。
mac_header: 数据链路层的数据包头的偏移地址。
tail: 如果没有使用偏移来表示,那么 tail 是指向有效数据的尾部的指针,否则是有效数据尾部的偏移地址。
end: 如果没有使用偏来表示,那么 end 是指向数据缓冲区 (没有分片)的尾部的指针,否则是缓冲区尾部的偏移地址。
head: 指向数据缓冲区的头部。
data: 指向有效数据的头部。
可以通过一个比较简单的无分片 skb 来直观展示上述关键成员,如图所示
围绕 struct sk_buf 结构有一些操作函数,现在将最常用的函数和宏分别罗列如下,并给出操作的示意图。
struct sk_buff *alloc_skb(unsigned int size, gfp_t priority);
struct sk_buff *dev_alloc_skb (unsigned int length);
void kfree_skb(struct sk_buff *skb);
dev_kfree_skb(a);
alloc_skb、dev_alloc_skb: 用于分配并初始化 skb, size 或 lengh 是级冲区的大小,priority 是内存分配掩码。dev_alloc_skb 用于不能休眠的上下文中
kfree_skb、 dev_kfree_skb:释放skb, kfree_skb 和 alloc_skb 配对使用, dev_kfree_skb和dev_alloc_skb 配对使用。
刚分配的 skb 示意图如图所示,为了简化问题,忽略了为提高缓冲区访问效率的对齐处理。
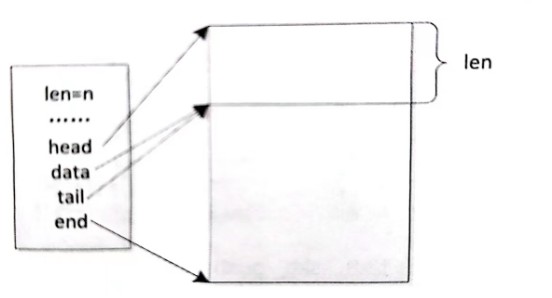
static inline void skb_reserve(struct sk_buff *skb, int len)
{skb->data += len; skb->tail += len;
}skb_reserve: 通过源码我们知道,该函数是将 data 和 tail 同时向 end 方向偏移 len 个字节。通常是在刚分配好 skb 后为了预留足够的协议头空间或为了对齐的操作,如图所示。
unsigned char *skb_put (struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len)
{
......skb->tail += len;skb->len += len;
.....
}
skb_put: 将 tail 向 end 方向偏 len 个字节,如图所示。在 put 操作之前, tail处于实线箭头的位置;在 put 操作之后,tail 在虚线箭头的位置,函数返回 put 操作之前的 tail 指针,通常用于添加尾部数据。

unsigned char *skb_push (struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len)
{skb->data -= len;skb->len += len;
......
}
skb_push: 将 data 向 head 方向偏移 len 个字节,如下图所示。在 push 操作之前data 处于实线箭头的位置;在 push 操作之后,data 在虚线箭头的位置。函数返回push 操作之后的 data 指针,通常用于添加协议头数据。
unsigned char *skb_pull(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len)
{
......skb->len -= len;
......return skb->data += len;
}; skb_pull: 将 data 向 end 方向偏 len 个字节,如图所示。在 pull 操作之前,data处于实线箭头的位置;在 push 作之后,data 在虚线箭头的位置。通数返回 pull 操作之后的 data 指针,通常用于去掉协议头数据。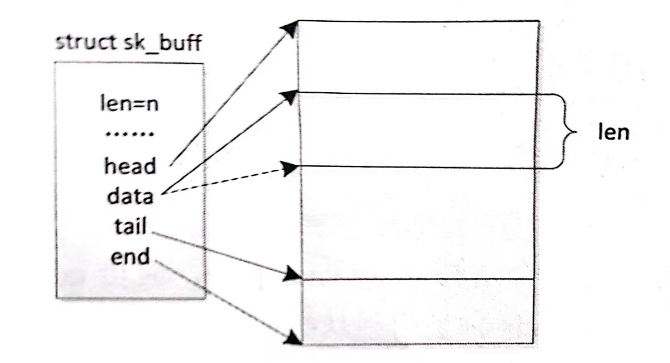
相关文章:

Linux驱动开发——网络设备驱动(理论篇)
目录 一、前言 二、网络层次结构 三、网络设备驱动核心数据结构和函数 一、前言 网络设备驱动是 Linux 的第三大类驱动,也是我们学习的最后一类 Linux 驱动。这里我们首先简单学习一下网络协议层次结构,然后简单讨论 Linux 内核中网络实现的层次结构。…...

simulink仿真
1)系统问题 连续系统,离散系统(采样周期问题) 系统分析问题 2)求解器问题 变步长,定步长,步长时间与采样周期问题、 3)积分器问题 连续积分,离散积分问题ÿ…...
PC端页面进去先出现加载效果
自定义指令v-loading,只需要绑定Boolean即可 v-loading“loading” <el-table :data"list" border style"width: 100%" v-loading"loading"><el-table-column align"center" label"序号" width"5…...
磁盘清理在哪里?学会这4个方法,快速清理内存!
“在使用电脑的过程中,我可能经常会保存一些文件到电脑上,这也导致电脑经常出现内存不足的情况。我想问问磁盘清理在哪里呀?我应该如何打开呢?” 随着使用电脑的时间增长,用户可能经常会遇到磁盘空间不足的情况&#x…...
Error opening terminal: xterm.”的解决方法
主要是看下面这两个变量是否设置正确 $ echo $TERM $ echo $TERMINFO 通常TERM的默认值为xterm-265color, 要查看支持的term,可以ls -al /lib/terminfo/x/ 如果TERM是xterm-265color的话,TERMINFO设置为/usr/lib/terminfo make menuconfig时提示“Err…...

C#常见的设计模式-结构型模式
引言 设计模式是软件工程中用于解决常见问题的可复用解决方案。在C#编程中,常见的设计模式具有广泛的应用。本篇博客将重点介绍C#中常见的结构型设计模式,包括适配器模式、装饰器模式、代理模式、组合模式和享元模式。 目录 引言1. 适配器模式(Adapter …...

Redis分片备库切换操作
Redis分片备库切换操作 场景描述: 分片集群: 1.ipa:5001-ipa:5002 2.ipb:5001-ipb:5002 需将两个分片备库互置完成灾备 操作步骤 准备工作 主机密码:1qaz!QAZ 获取节点信息命令 /redispath/bin/redis-cli -a password -h ip -p port red…...
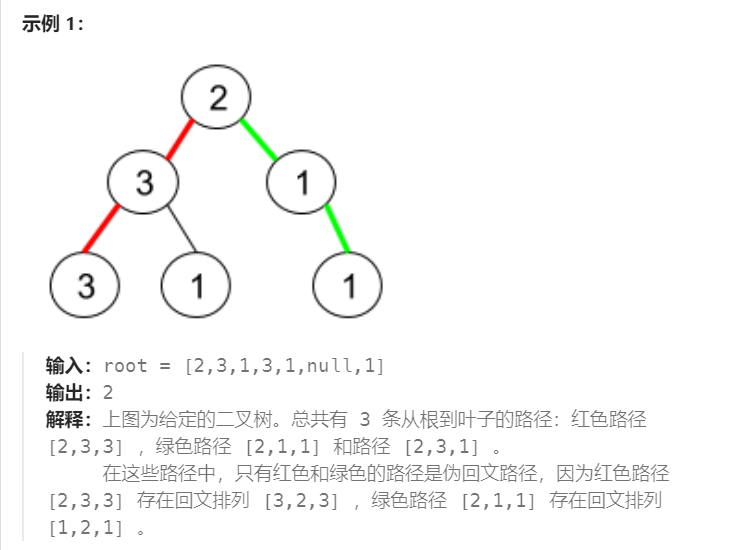
二叉树:leetcode1457. 二叉树中的伪回文路径
给你一棵二叉树,每个节点的值为 1 到 9 。我们称二叉树中的一条路径是 「伪回文」的,当它满足:路径经过的所有节点值的排列中,存在一个回文序列。 请你返回从根到叶子节点的所有路径中 伪回文 路径的数目。 给定二叉树的节点数目…...
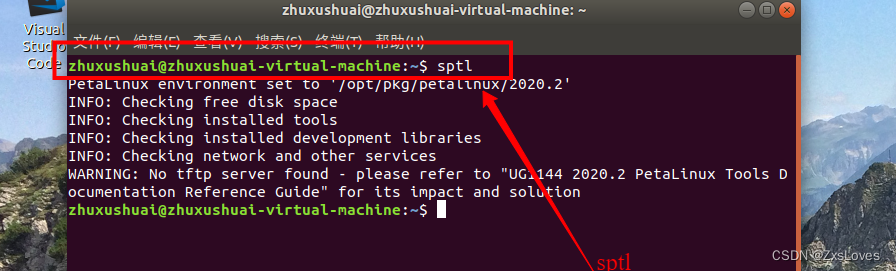
【【Linux下的Petallinux 以及其他的配置】】
Linux下的Petallinux 以及其他的配置 sudo apt-get install iproute2 gawk python3 python build-essential gcc git make net-tools libncurses5-dev tftpd zlib1g-dev libssl-dev flex bison libselinux1 gnupg wget git-core diffstat chrpath socat xterm autoconf libtoo…...

13、深度学习之神经网络
深度学习是机器学习中重要的一个学科分支,它的特点就在于需要构建多层“深度”的神经网络。 人们在探索人工智能初期,就曾设想构建一个用数学方式来表达的模型,它可以模拟人的大脑,大脑我们都知道,有很多神经元,每个神经元之间通过突触链接。 神经网络的设计就是模仿了这…...

js的数组去重方法
目录 es6数组中对象去重 1. filter()用法 2. findIndex()用法 3. 去重 其他方法: 方法二:reduce()去重 1. reduce()用法 1.1 找出字符长度最长的数组成员。 1.2 扁平化二维数组 1.3 扁平化多维数组 三、总结方案: 使用Set…...

在 Next 14 的 appRouter 模式中接入 React-Redux
在 Next 14 的 appRouter 模式中接入 React-Redux 说明 Next.js 版本升级到 14 后,相比 13 版本是一个改动很大的大版本升级,很多概念或者使用方式 13 版本都有较大的区别,因此这里记录一些学习 14 版本的 Next.js 的心得体会或者问题。因为…...

aspose-words 跳过证书验证jar
优先用 aspose-words-19.3.jar ,不需要读取license.xml,导出后直接水印,jar包最好直接放在项目resource目录下直接引用,要不下载不下来 public static String doc2pdf(String fileName, String filePath) {try {String oldFile f…...

【开题报告】基于uniapp的瑜伽学习交流小程序的设计与实现
1.选题背景 瑜伽在现代社会中越来越受到人们的关注和喜爱。它不仅可以帮助人们塑造健美的身材,还能促进身心健康、提高生活质量。然而,由于瑜伽动作的复杂性和技巧性,很多初学者在学习过程中会遇到困难和挑战。 同时,由于工作和…...
)
【蓝桥杯单片机】应用手势传感器(串口2)
手势传感器:串口通信,可以识别左滑、右滑、单击三种手势,输出相应的固定串口数据。 控制器:IAP15F2K61S2单片机。 引脚连接: 单片机 手势传感器 P46 -> TX P47 -> RX VCC -> 5V GND->gnd main.c 程序说明:传感器与单片机的串口2进行数据交互,这里使用的是开…...
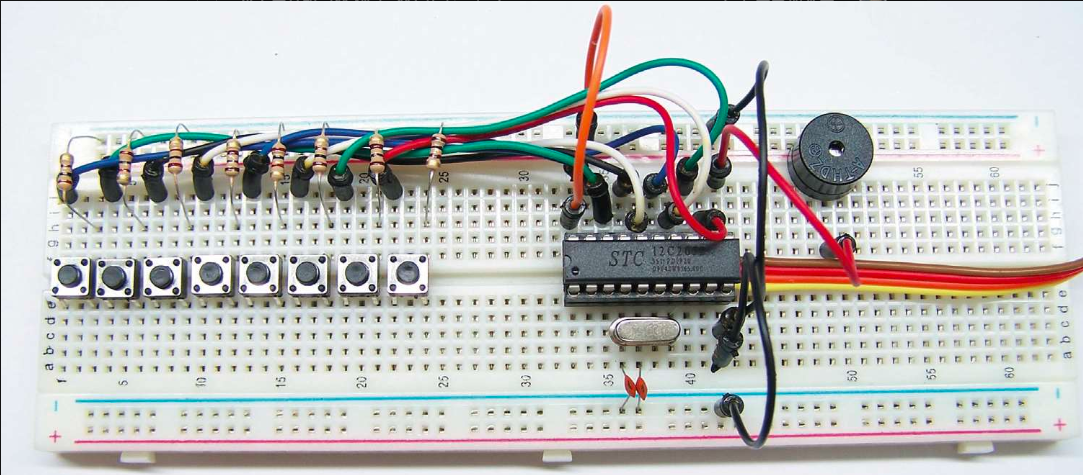
51单片机蜂鸣器发出悦耳的声音
51单片机蜂鸣器发出悦耳的声音 1.概述 这篇文章介绍单片机控制蜂鸣器入门小实验,通过该实验掌握蜂鸣器发声的原理,控制声音发出我们想听的音乐。 2.蜂鸣器发声 2.1.硬件原理 1.蜂鸣器正极接单片机20号引脚VCC,负极接19号引脚P1.7 2.20MH…...

Web3.0时代:区块链DAPP将如何颠覆传统模式
小编介绍:10年专注商业模式设计及软件开发,擅长企业生态商业模式,商业零售会员增长裂变模式策划、商业闭环模式设计及方案落地;扶持10余个电商平台做到营收过千万,数百个平台达到百万会员,欢迎咨询。 随着…...
JAVA 算法面试总结
1、二分查找 二分查找又叫折半查找,要求待查找的序列有序。每次取中间位置的值与待查关键字比较,如果中间位置 的值比待查关键字大,则在前半部分循环这个查找的过程,如果中间位置的值比待查关键字小, 则在后半部分循环…...
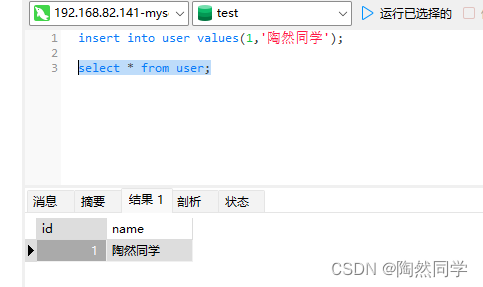
【Docker】安装MySQL 通俗易懂 亲测没有任何问题
目录 1.拉取镜像 2.运行容器 3.创建mysql配置文件 4.测试 1.拉取镜像 dockerhub官网:Docker 如果需要其他版本mysql docker pull mysql:xxx(版本) docker pull mysql #默认拉取最新版本 latest 2.运行容器 docker run -d -p 3306:33…...

【React】打包优化-配置CDN
CDN 是一种内容分发网络服务,当用户请求网站内容时,由离用户最近的服务器将缓存的资源内容传递给用户。 哪些资源可以放到CDN服务器?(比如react、 react-dom) 体积较大,需要利用CDN文件在浏览器的缓存特性…...

未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?
编辑:陈萍萍的公主一点人工一点智能 未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?RWM通过双自回归机制有效解决了复合误差、部分可观测性和随机动力学等关键挑战,在不依赖领域特定归纳偏见的条件下实现了卓越的预测准…...

java_网络服务相关_gateway_nacos_feign区别联系
1. spring-cloud-starter-gateway 作用:作为微服务架构的网关,统一入口,处理所有外部请求。 核心能力: 路由转发(基于路径、服务名等)过滤器(鉴权、限流、日志、Header 处理)支持负…...

从WWDC看苹果产品发展的规律
WWDC 是苹果公司一年一度面向全球开发者的盛会,其主题演讲展现了苹果在产品设计、技术路线、用户体验和生态系统构建上的核心理念与演进脉络。我们借助 ChatGPT Deep Research 工具,对过去十年 WWDC 主题演讲内容进行了系统化分析,形成了这份…...
Cesium相机控制)
三维GIS开发cesium智慧地铁教程(5)Cesium相机控制
一、环境搭建 <script src"../cesium1.99/Build/Cesium/Cesium.js"></script> <link rel"stylesheet" href"../cesium1.99/Build/Cesium/Widgets/widgets.css"> 关键配置点: 路径验证:确保相对路径.…...
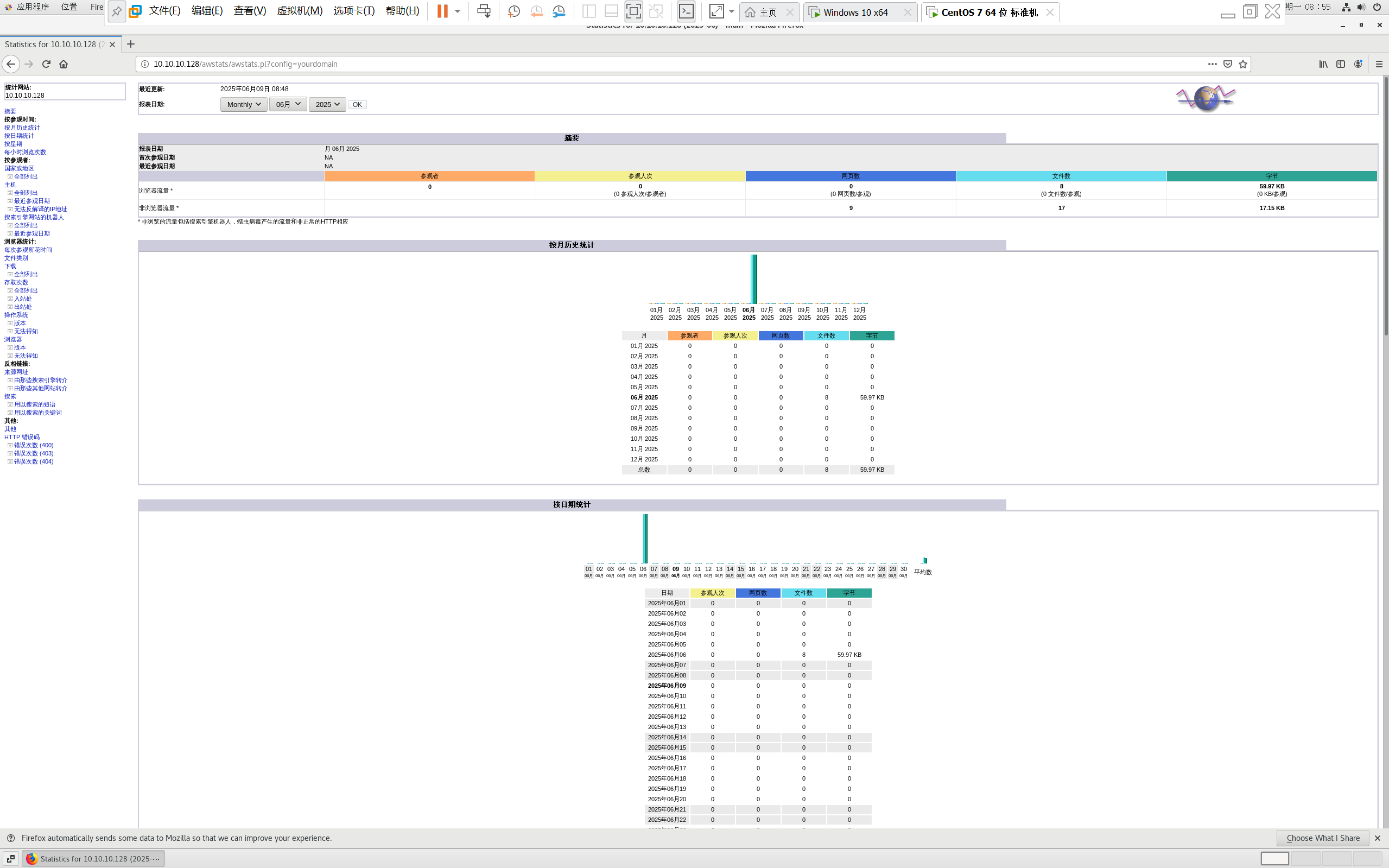
centos 7 部署awstats 网站访问检测
一、基础环境准备(两种安装方式都要做) bash # 安装必要依赖 yum install -y httpd perl mod_perl perl-Time-HiRes perl-DateTime systemctl enable httpd # 设置 Apache 开机自启 systemctl start httpd # 启动 Apache二、安装 AWStats࿰…...

AtCoder 第409场初级竞赛 A~E题解
A Conflict 【题目链接】 原题链接:A - Conflict 【考点】 枚举 【题目大意】 找到是否有两人都想要的物品。 【解析】 遍历两端字符串,只有在同时为 o 时输出 Yes 并结束程序,否则输出 No。 【难度】 GESP三级 【代码参考】 #i…...
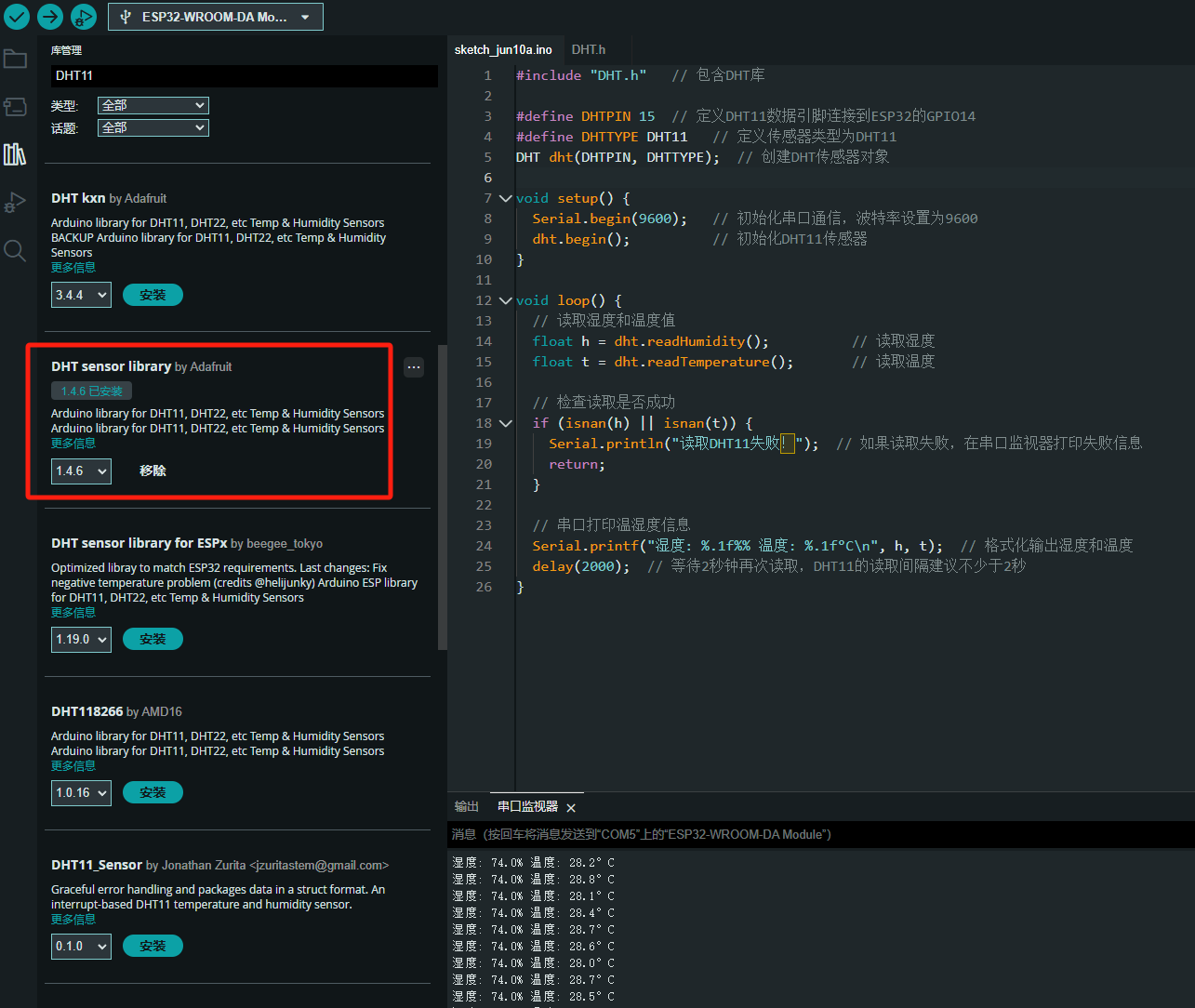
ESP32读取DHT11温湿度数据
芯片:ESP32 环境:Arduino 一、安装DHT11传感器库 红框的库,别安装错了 二、代码 注意,DATA口要连接在D15上 #include "DHT.h" // 包含DHT库#define DHTPIN 15 // 定义DHT11数据引脚连接到ESP32的GPIO15 #define D…...

【Zephyr 系列 10】实战项目:打造一个蓝牙传感器终端 + 网关系统(完整架构与全栈实现)
🧠关键词:Zephyr、BLE、终端、网关、广播、连接、传感器、数据采集、低功耗、系统集成 📌目标读者:希望基于 Zephyr 构建 BLE 系统架构、实现终端与网关协作、具备产品交付能力的开发者 📊篇幅字数:约 5200 字 ✨ 项目总览 在物联网实际项目中,**“终端 + 网关”**是…...

Hive 存储格式深度解析:从 TextFile 到 ORC,如何选对数据存储方案?
在大数据处理领域,Hive 作为 Hadoop 生态中重要的数据仓库工具,其存储格式的选择直接影响数据存储成本、查询效率和计算资源消耗。面对 TextFile、SequenceFile、Parquet、RCFile、ORC 等多种存储格式,很多开发者常常陷入选择困境。本文将从底…...
:观察者模式)
JS设计模式(4):观察者模式
JS设计模式(4):观察者模式 一、引入 在开发中,我们经常会遇到这样的场景:一个对象的状态变化需要自动通知其他对象,比如: 电商平台中,商品库存变化时需要通知所有订阅该商品的用户;新闻网站中࿰…...
