负载均衡lvs
简介
ipvsadm 是 Linux 内核中的 IP 虚拟服务器(IPVS)管理工具。IPVS是 Linux 内核提供的一种负载均衡解决方案,它允许将入站的网络流量分发到多个后端服务器,以实现负载均衡和高可用性。IPVS通过在内核中维护一个虚拟服务器表,根据特定的负载均衡调度算法将请求转发到后端服务器。
实践
启动几台nginx 作为后台服务器
docker run -d nginx
集群服务管理
查看
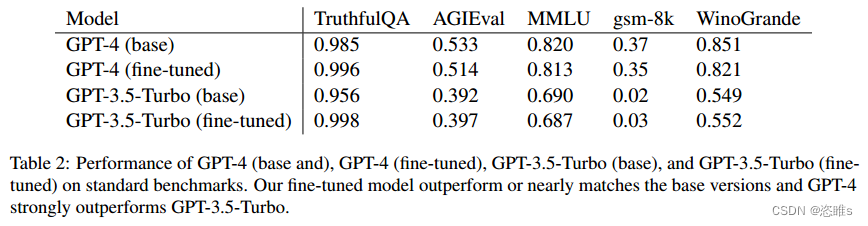
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn新增
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -A -t 192.124.95.67:80 -s rr
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.124.95.67:80 rr修改
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -E -t 192.124.95.67:80 -s wlc
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.124.95.67:80 wlc删除
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -D -t 192.124.95.67:8080
No such service
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -D -t 192.124.95.67:80
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn删除整个集群
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -A -t 192.124.95.67:801 -s rr
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]#
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -A -t 192.124.95.67:80 -s rr
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.124.95.67:80 rr
TCP 192.124.95.67:801 rr
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -C
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn真实服务器管理
新增
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -A -t 192.124.95.67:80 -s rr
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 192.124.95.67:80 -r 172.17.0.2:80 -m
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 192.124.95.67:80 -r 172.17.0.3:80 -m
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.124.95.67:80 rr-> 172.17.0.2:80 Masq 1 0 0-> 172.17.0.3:80 Masq 1 0 0修改
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -e -t 192.124.95.67:80 -r 172.17.0.3:80 -m -w 2
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.124.95.67:80 rr-> 172.17.0.2:80 Masq 1 0 0-> 172.17.0.3:80 Masq 2 0 0删除
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.124.95.67:80 rr-> 172.17.0.2:80 Masq 1 0 0-> 172.17.0.3:80 Masq 2 0 0-> 172.17.0.3:81 Masq 1 0 0
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -d -t 192.124.95.67:80 -r 172.17.0.3:81
[root@192-124-95-67 ~]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.124.95.67:80 rr-> 172.17.0.2:80 Masq 1 0 0-> 172.17.0.3:80 Masq 2 0 0规则表的备份与还原
[root@192-124-95-67 home]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.124.95.67:80 rr-> 172.17.0.2:80 Masq 1 0 0-> 172.17.0.3:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 192.124.95.67:801 rr
[root@192-124-95-67 home]# ipvsadm -S > ipvs.bak
[root@192-124-95-67 home]# ipvsadm -C
[root@192-124-95-67 home]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
[root@192-124-95-67 home]# ipvsadm -R < ipvs.bak
[root@192-124-95-67 home]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.124.95.67:80 rr-> 172.17.0.2:80 Masq 1 0 0-> 172.17.0.3:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 192.124.95.67:801 rr[root@192-124-95-67 home]# cat ipvs.bak
-A -t 192-124-95-67:http -s rr
-a -t 192-124-95-67:http -r 172.17.0.2:http -m -w 1
-a -t 192-124-95-67:http -r 172.17.0.3:http -m -w 1
-A -t 192-124-95-67:device -s rr帮助手册
Synopsis
ipvsadm -A|E -t|u|f service-address [-s scheduler]
[-p [timeout]] [-O] [-M netmask]
ipvsadm -D -t|u|f service-address
ipvsadm -C
ipvsadm -R
ipvsadm -S [-n]
ipvsadm -a|e -t|u|f service-address -r server-address
[-g|i|m] [-w weight] [-x upper] [-y lower]
ipvsadm -d -t|u|f service-address -r server-address
ipvsadm -L|l [options]
ipvsadm -Z [-t|u|f service-address]
ipvsadm --set tcp tcpfin udp
ipvsadm --start-daemon state [–mcast-interface interface]
[–syncid syncid]
ipvsadm --stop-daemon state
ipvsadm -h
Description
Ipvsadm(8) is used to set up, maintain or inspect the virtual server table in the Linux kernel. The Linux Virtual Server can be used to build scalable network services based on a cluster of two or more nodes. The active node of the cluster redirects service requests to a collection of server hosts that will actually perform the services. Supported features include two protocols (TCP and UDP), three packet-forwarding methods (NAT, tunneling, and direct routing), and eight load balancing algorithms (round robin, weighted round robin, least-connection, weighted least-connection, locality-based least-connection, locality-based least-connection with replication, destination-hashing, and source-hashing).
The command has two basic formats for execution:
ipvsadm COMMAND [protocol] service-address
[scheduling-method] [persistence options]
ipvsadm command [protocol] service-address
server-address [packet-forwarding-method] [weight options]
The first format manipulates a virtual service and the algorithm for assigning service requests to real servers. Optionally, a persistent timeout and network mask for the granularity of a persistent service may be specified. The second format manipulates a real server that is associated with an existing virtual service. When specifying a real server, the packet-forwarding method and the weight of the real server, relative to other real servers for the virtual service, may be specified, otherwise defaults will be used.
COMMANDS
ipvsadm(8) recognises the commands described below. Upper-case commands maintain virtual services. Lower-case commands maintain real servers that are associated with a virtual service.
-A, --add-service
Add a virtual service. A service address is uniquely defined by a triplet: IP address, port number, and protocol. Alternatively, a virtual service may be defined by a firewall-mark.
-E, --edit-service
Edit a virtual service.
-D, --delete-service
Delete a virtual service, along with any associated real servers.
-C, --clear
Clear the virtual server table.
-R, --restore
Restore Linux Virtual Server rules from stdin. Each line read from stdin will be treated as the command line options to a separate invocation of ipvsadm. Lines read from stdin can optionally begin with “ipvsadm”. This option is useful to avoid executing a large number or ipvsadm commands when constructing an extensive routing table.
-S, --save
Dump the Linux Virtual Server rules to stdout in a format that can be read by -R|–restore.
-a, --add-server
Add a real server to a virtual service.
-e, --edit-server
Edit a real server in a virtual service.
-d, --delete-server
Remove a real server from a virtual service.
-L, -l, --list
List the virtual server table if no argument is specified. If a service-address is selected, list this service only. If the -c option is selected, then display the connection table. The exact output is affected by the other arguments given.
-Z, --zero
Zero the packet, byte and rate counters in a service or all services.
–set tcp tcpfin udp
Change the timeout values used for IPVS connections. This command always takes 3 parameters, representing the timeout values (in seconds) for TCP sessions, TCP sessions after receiving a FIN packet, and UDP packets, respectively. A timeout value 0 means that the current timeout value of the corresponding entry is preserved.
–start-daemon state
Start the connection synchronization daemon. The state is to indicate that the daemon is started as master or backup. The connection synchronization daemon is implemented inside the Linux kernel. The master daemon running at the primary load balancer multicasts changes of connections periodically, and the backup daemon running at the backup load balancers receives multicast message and creates corresponding connections. Then, in case the primary load balancer fails, a backup load balancer will takeover, and it has state of almost all connections, so that almost all established connections can continue to access the service.
The sync daemon currently only supports IPv4 connections.
–stop-daemon
Stop the connection synchronization daemon.
-h, --help
Display a description of the command syntax.
PARAMETERS
The commands above accept or require zero or more of the following parameters.
-t, --tcp-service service-address
Use TCP service. The service-address is of the form host[:port]. Host may be one of a plain IP address or a hostname. Port may be either a plain port number or the service name of port. The Port may be omitted, in which case zero will be used. A Port of zero is only valid if the service is persistent as the -p|–persistent option, in which case it is a wild-card port, that is connections will be accepted to any port.
-u, --udp-service service-address
Use UDP service. See the -t|–tcp-service for the description of the service-address.
-f, --fwmark-service integer
Use a firewall-mark, an integer value greater than zero, to denote a virtual service instead of an address, port and protocol (UDP or TCP). The marking of packets with a firewall-mark is configured using the -m|–mark option to iptables(8). It can be used to build a virtual service assoicated with the same real servers, covering multiple IP address, port and protocol tripplets. If IPv6 addresses are used, the -6 option must be used.
Using firewall-mark virtual services provides a convenient method of grouping together different IP addresses, ports and protocols into a single virtual service. This is useful for both simplifying configuration if a large number of virtual services are required and grouping persistence across what would otherwise be multiple virtual services.
-s, --scheduler scheduling-method
scheduling-method Algorithm for allocating TCP connections and UDP datagrams to real servers. Scheduling algorithms are implemented as kernel modules. Ten are shipped with the Linux Virtual Server:
rr - Robin Robin: distributes jobs equally amongst the available real servers.
wrr - Weighted Round Robin: assigns jobs to real servers proportionally to there real servers’ weight. Servers with higher weights receive new jobs first and get more jobs than servers with lower weights. Servers with equal weights get an equal distribution of new jobs.
lc - Least-Connection: assigns more jobs to real servers with fewer active jobs.
wlc - Weighted Least-Connection: assigns more jobs to servers with fewer jobs and relative to the real servers’ weight (Ci/Wi). This is the default.
lblc - Locality-Based Least-Connection: assigns jobs destined for the same IP address to the same server if the server is not overloaded and available; otherwise assign jobs to servers with fewer jobs, and keep it for future assignment.
lblcr - Locality-Based Least-Connection with Replication: assigns jobs destined for the same IP address to the least-connection node in the server set for the IP address. If all the node in the server set are over loaded, it picks up a node with fewer jobs in the cluster and adds it in the sever set for the target. If the server set has not been modified for the specified time, the most loaded node is removed from the server set, in order to avoid high degree of replication.
dh - Destination Hashing: assigns jobs to servers through looking up a statically assigned hash table by their destination IP addresses.
sh - Source Hashing: assigns jobs to servers through looking up a statically assigned hash table by their source IP addresses.
sed - Shortest Expected Delay: assigns an incoming job to the server with the shortest expected delay. The expected delay that the job will experience is (Ci + 1) / Ui if sent to the ith server, in which Ci is the number of jobs on the the ith server and Ui is the fixed service rate (weight) of the ith server.
nq - Never Queue: assigns an incoming job to an idle server if there is, instead of waiting for a fast one; if all the servers are busy, it adopts the Shortest Expected Delay policy to assign the job.
-p, --persistent [timeout]
Specify that a virtual service is persistent. If this option is specified, multiple requests from a client are redirected to the same real server selected for the first request. Optionally, the timeout of persistent sessions may be specified given in seconds, otherwise the default of 300 seconds will be used. This option may be used in conjunction with protocols such as SSL or FTP where it is important that clients consistently connect with the same real server.
Note: If a virtual service is to handle FTP connections then persistence must be set for the virtual service if Direct Routing or Tunnelling is used as the forwarding mechanism. If Masquerading is used in conjunction with an FTP service than persistence is not necessary, but the ip_vs_ftp kernel module must be used. This module may be manually inserted into the kernel using insmod(8).
-M, --netmask netmask
Specify the granularity with which clients are grouped for persistent virtual services. The source address of the request is masked with this netmask to direct all clients from a network to the same real server. The default is 255.255.255.255, that is, the persistence granularity is per client host. Less specific netmasks may be used to resolve problems with non-persistent cache clusters on the client side. IPv6 netmasks should be specified as a prefix length between 1 and 128. The default prefix length is 128.
-r, --real-server server-address
Real server that an associated request for service may be assigned to. The server-address is the host address of a real server, and may plus port. Host can be either a plain IP address or a hostname. Port can be either a plain port number or the service name of port. In the case of the masquerading method, the host address is usually an RFC 1918 private IP address, and the port can be different from that of the associated service. With the tunneling and direct routing methods, port must be equal to that of the service address. For normal services, the port specified in the service address will be used if port is not specified. For fwmark services, port may be omitted, in which case the destination port on the real server will be the destination port of the request sent to the virtual service.
[packet-forwarding-method]
-g, --gatewaying Use gatewaying (direct routing). This is the default.
-i, --ipip Use ipip encapsulation (tunneling).
-m, --masquerading Use masquerading (network access translation, or NAT).
Note: Regardless of the packet-forwarding mechanism specified, real servers for addresses for which there are interfaces on the local node will be use the local forwarding method, then packets for the servers will be passed to upper layer on the local node. This cannot be specified by ipvsadm, rather it set by the kernel as real servers are added or modified.
-w, --weight weight
Weight is an integer specifying the capacity of a server relative to the others in the pool. The valid values of weight are 0 through to 65535. The default is 1. Quiescent servers are specified with a weight of zero. A quiescent server will receive no new jobs but still serve the existing jobs, for all scheduling algorithms distributed with the Linux Virtual Server. Setting a quiescent server may be useful if the server is overloaded or needs to be taken out of service for maintenance.
-x, --u-threshold uthreshold
uthreshold is an integer specifying the upper connection threshold of a server. The valid values of uthreshold are 0 through to 65535. The default is 0, which means the upper connection threshold is not set. If uthreshold is set with other values, no new connections will be sent to the server when the number of its connections exceeds its upper connection threshold.
-y, --l-threshold lthreshold
lthreshold is an integer specifying the lower connection threshold of a server. The valid values of lthreshold are 0 through to 65535. The default is 0, which means the lower connection threshold is not set. If lthreshold is set with other values, the server will receive new connections when the number of its connections drops below its lower connection threshold. If lthreshold is not set but uthreshold is set, the server will receive new connections when the number of its connections drops below three forth of its upper connection threshold.
–mcast-interface interface
Specify the multicast interface that the sync master daemon sends outgoing multicasts through, or the sync backup daemon listens to for multicasts.
–syncid syncid
Specify the syncid that the sync master daemon fills in the SyncID header while sending multicast messages, or the sync backup daemon uses to filter out multicast messages not matched with the SyncID value. The valid values of syncid are 0 through to 255. The default is 0, which means no filtering at all.
-c, --connection
Connection output. The list command with this option will list current IPVS connections.
–timeout
Timeout output. The list command with this option will display the timeout values (in seconds) for TCP sessions, TCP sessions after receiving a FIN packet, and UDP packets.
–daemon
Daemon information output. The list command with this option will display the daemon status and its multicast interface.
–stats
Output of statistics information. The list command with this option will display the statistics information of services and their servers.
–rate
Output of rate information. The list command with this option will display the rate information (such as connections/second, bytes/second and packets/second) of services and their servers.
–thresholds
Output of thresholds information. The list command with this option will display the upper/lower connection threshold information of each server in service listing.
–persistent-conn
Output of persistent connection information. The list command with this option will display the persistent connection counter information of each server in service listing. The persistent connection is used to forward the actual connections from the same client/network to the same server.
–sort
Sort the list of virtual services and real servers. The virtual service entries are sorted in ascending order by <protocol, address, port>. The real server entries are sorted in ascending order by <address, port>. (default)
–nosort
Do not sort the list of virtual services and real servers.
-O, --ops
Specify that a virtual service uses one-packet scheduling. This option can be used only for UDP services. If this option is specified, all connections are created only to schedule one packet. Option is useful to schedule UDP packets from same client port to different real servers.
-n, --numeric
Numeric output. IP addresses and port numbers will be printed in numeric format rather than as as host names and services respectively, which is the default.
–exact
Expand numbers. Display the exact value of the packet and byte counters, instead of only the rounded number in K’s (multiples of 1000) M’s (multiples of 1000K) or G’s (multiples of 1000M). This option is only relevant for the -L command.
-6
Use with -f to signify fwmark rule uses IPv6 addresses.
参考文档
http://124.220.104.235/web/chatgpt
http://www.linuxvirtualserver.org/Documents.html
https://linux.die.net/man/8/ipvsadm?__cf_chl_rt_tk=RzdazyyWRreeHdlH9SxBQsYksmP74r7Bkr7woz3Gcak-1700633510-0-gaNycGzNDaU
相关文章:

负载均衡lvs
简介 ipvsadm 是 Linux 内核中的 IP 虚拟服务器(IPVS)管理工具。IPVS是 Linux 内核提供的一种负载均衡解决方案,它允许将入站的网络流量分发到多个后端服务器,以实现负载均衡和高可用性。IPVS通过在内核中维护一个虚拟服务器表&a…...

【腾讯云云上实验室】探索向量数据库背后的安全监控机制
当今数字化时代,数据安全成为了企业和个人最为关注的重要议题之一。随着数据规模的不断增长和数据应用的广泛普及,如何保护数据的安全性和隐私性成为了迫切的需求。 今天,我将带领大家一起探索腾讯云云上实验室所推出的向量数据库,…...
阅读笔记——《Removing RLHF Protections in GPT-4 via Fine-Tuning》
【参考文献】Zhan Q, Fang R, Bindu R, et al. Removing RLHF Protections in GPT-4 via Fine-Tuning[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.05553, 2023.【注】本文仅为作者个人学习笔记,如有冒犯,请联系作者删除。 目录 摘要 一、介绍 二、背景 三、方法…...

electron实现截图的功能
Electron是一种跨平台的桌面应用程序开发框架,可以使用HTML、CSS和JavaScript等Web技术构建桌面应用程序。下面是一种使用Electron实现截图的简单方法: 安装Electron和截图库 首先,需要安装Electron和一个截图库,例如electron-sc…...

11、动态数码管显示
数码管驱动方式 1、单片机直接扫描:硬件设备简单,但会消耗大量的单片机CPU时间 2、专用驱动芯片:内部自带显存、扫描电路,单片机只需告诉他显示什么即可 #include <REGX52.H> //数组代表显示亮灯的内容0、1、2、3、4、5、…...

Linux的基本指令(三)
目录 前言 echo指令(简述) Linux的设计理念 输出重定向操作符 > 追加输出重定向操作符 >> 输入重定向操作符 < 补充知识 学前补充 more指令 less指令 head指令 tail指令 查看文件中间的内容 利用输出重定向实现 利用管道“ |…...
使用python 实现华为设备的SFTP文件传输
实验目的: 公司有一台CE12800的设备,管理地址位172.16.1.2,现在需要编写自动化脚本,通过SFTP实现简单的上传下载操作。 实验拓扑: 实验步骤: 步骤1:将本地电脑和ensp的设备进行桥接ÿ…...

高防cdn防护原理是什么,是否可以防护服务器吗
随着互联网业务的迅速发展,网络安全问题日益凸显。在这样的背景下,高防CDN作为一种有效的网络安全解决方案,受到了越来越多的关注。那么高防CDN的防护原理是什么呢?接下来就跟小德一起深入了解下吧! 1. 高防CDN的基本概念 我们要明确什么是…...
)
SELinux零知识学习三十五、SELinux策略语言之角色和用户(6)
接前一篇文章:SELinux零知识学习三十四、SELinux策略语言之角色和用户(5) 三、SELinux策略语言之角色和用户 SELinux提供了一种依赖于类型强制(类型增强,TE)的基于角色的访问控制(Role-Based Access Control),角色用于组域类型和限制域类型与用户之间的关系,SELinux…...

初学Flink 学后总结
最近开始学习Flink,一边学习一边记录,以下是基于【尚硅谷】Flink1.13实战教程总结的笔记,方便后面温习 目录 初始 Flink 一:基础概念 1.Flink是什么 2.Flink主要应用场景...

CSS新手入门笔记整理:CSS基本介绍
CSS,指的是“Cascading Style Sheet(层叠样式表)”,用于控制网页外观。 CSS引入方式 外部样式表 独立建立一个.CSS文件,在HTML中使用 link标签 来引用CSS文件。link标签放置在head标签内部。 语法 <link rel&qu…...

【华为OD】B\C卷真题 100%通过:需要打开多少监控器 C/C++实现
【华为OD】B\C卷真题 100%通过:需要打开多少监控器 C/C实现 目录 题目描述: 示例1 代码实现: 题目描述: 某长方形停车场,每个车位上方都有对应监控器,当且仅当在当前车位或者前后左右四个方向任意一个…...

HarmonyOS开发(七):构建丰富页面
1、组件状态管理 1.1、概述 在应用中,界面一般都是动态的。界面会根据不同状态展示不一样的效果。 ArkUI作为一种声明式UI,具有状态驱动UI更新的特点,当用户进行界面交互或有外部事件引起状态改变时,状态的变会会触发组件的自动…...
--rsa - RSA加密解密)
LuatOS-SOC接口文档(air780E)--rsa - RSA加密解密
示例 -- 请在电脑上生成私钥和公钥, 当前最高支持4096bit, 一般来说2048bit就够用了 -- openssl genrsa -out privkey.pem 2048 -- openssl rsa -in privkey.pem -pubout -out public.pem -- privkey.pem 是私钥, public.pem 是公钥 -- 私钥用于 加密 和 签名, 通常保密, 放在…...
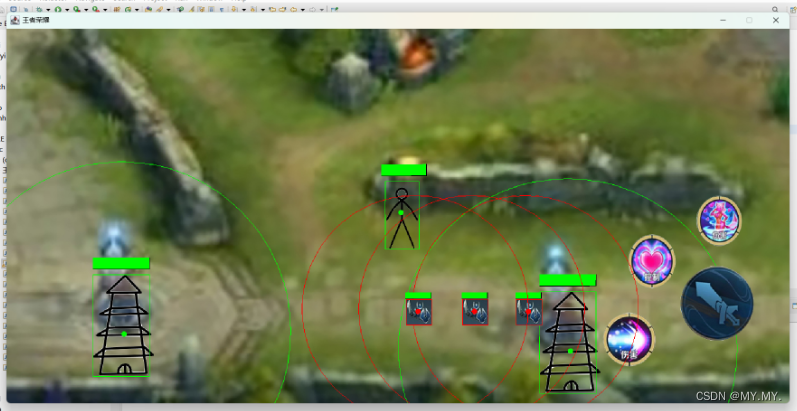
简易版王者荣耀
所有包和类 GameFrame类 package newKingOfHonor;import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter; import java.awt.event.KeyEvent; import java.io.File; import java.util.ArrayList;im…...

功能测试进阶建议,学习思路讲解
1. 深入了解测试理论: 了解测试的原理、方法和最佳实践,包括黑盒测试、白盒测试、灰盒测试等。可以阅读相关的书籍或参加在线课程。 2. 学习相关测试工具: 掌握常用的测试工具,如缺陷发现工具、性能测试工具、安全测试工具等。可以…...

AI数字人与虚拟人:区别与应用场景
随着人工智能和虚拟技术的不断发展,AI数字人和虚拟人成为了数字世界中的两个重要概念。本文将介绍AI数字人和虚拟人的区别,并探讨它们在不同领域的应用场景。 一、AI数字人与虚拟人的区别 定义和概念: AI数字人:是利用人工智能技术…...
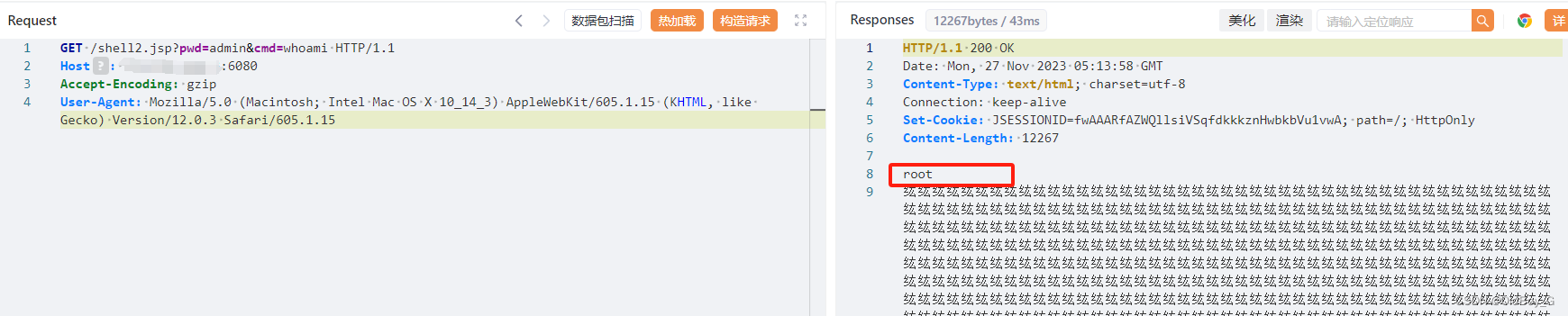
金蝶Apusic应用服务器 任意文件上传漏洞复现
0x01 产品简介 金蝶Apusic应用服务器(Apusic Application Server,AAS)是一款标准、安全、高效、集成并具丰富功能的企业级应用服务器软件,全面支持JakartaEE8/9的技术规范,提供满足该规范的Web容器、EJB容器以及WebSer…...
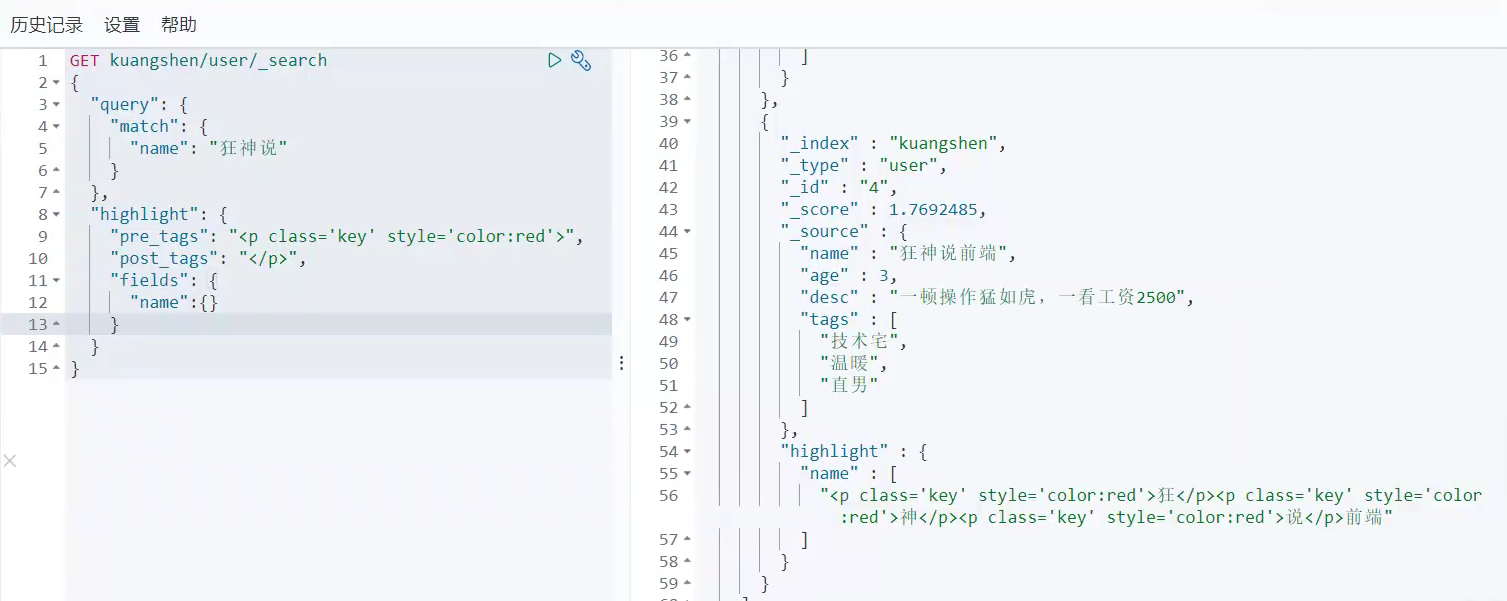
ElasticSearch学习笔记(狂神说)
ElasticSearch学习笔记(狂神说) 视频地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV17a4y1x7zq 在学习ElasticSearch之前,先简单了解一下Lucene: Doug Cutting开发是apache软件基金会 jakarta项目组的一个子项目是一个开放…...
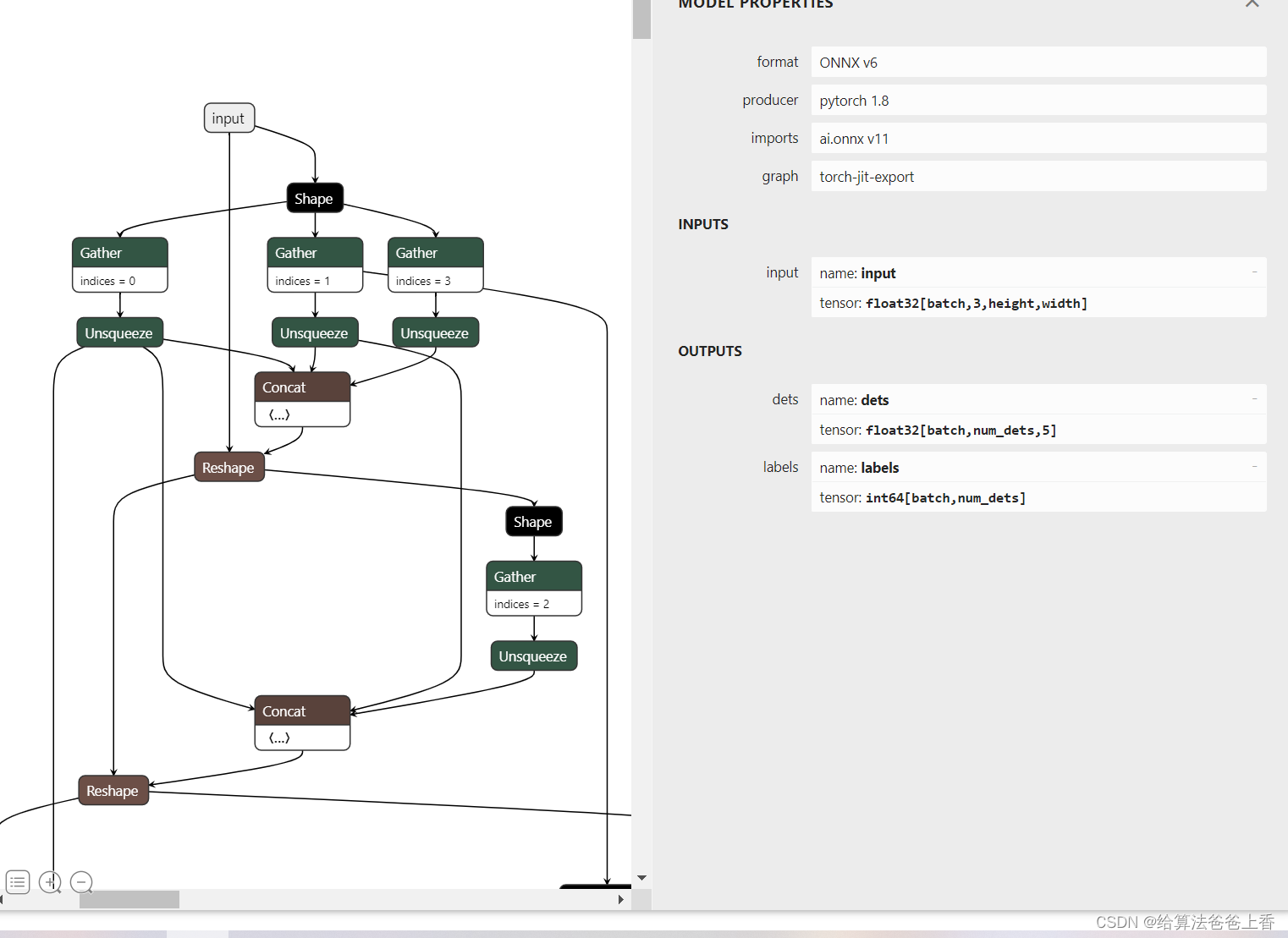
OpenMMlab导出yolox模型并用onnxruntime和tensorrt推理
导出onnx文件 直接使用脚本 import torch from mmdet.apis import init_detector, inference_detectorconfig_file ./configs/yolox/yolox_tiny_8xb8-300e_coco.py checkpoint_file yolox_tiny_8x8_300e_coco_20211124_171234-b4047906.pth model init_detector(config_fi…...

Vue记事本应用实现教程
文章目录 1. 项目介绍2. 开发环境准备3. 设计应用界面4. 创建Vue实例和数据模型5. 实现记事本功能5.1 添加新记事项5.2 删除记事项5.3 清空所有记事 6. 添加样式7. 功能扩展:显示创建时间8. 功能扩展:记事项搜索9. 完整代码10. Vue知识点解析10.1 数据绑…...

k8s从入门到放弃之Ingress七层负载
k8s从入门到放弃之Ingress七层负载 在Kubernetes(简称K8s)中,Ingress是一个API对象,它允许你定义如何从集群外部访问集群内部的服务。Ingress可以提供负载均衡、SSL终结和基于名称的虚拟主机等功能。通过Ingress,你可…...

【Java学习笔记】Arrays类
Arrays 类 1. 导入包:import java.util.Arrays 2. 常用方法一览表 方法描述Arrays.toString()返回数组的字符串形式Arrays.sort()排序(自然排序和定制排序)Arrays.binarySearch()通过二分搜索法进行查找(前提:数组是…...
visual studio 2022更改主题为深色
visual studio 2022更改主题为深色 点击visual studio 上方的 工具-> 选项 在选项窗口中,选择 环境 -> 常规 ,将其中的颜色主题改成深色 点击确定,更改完成...
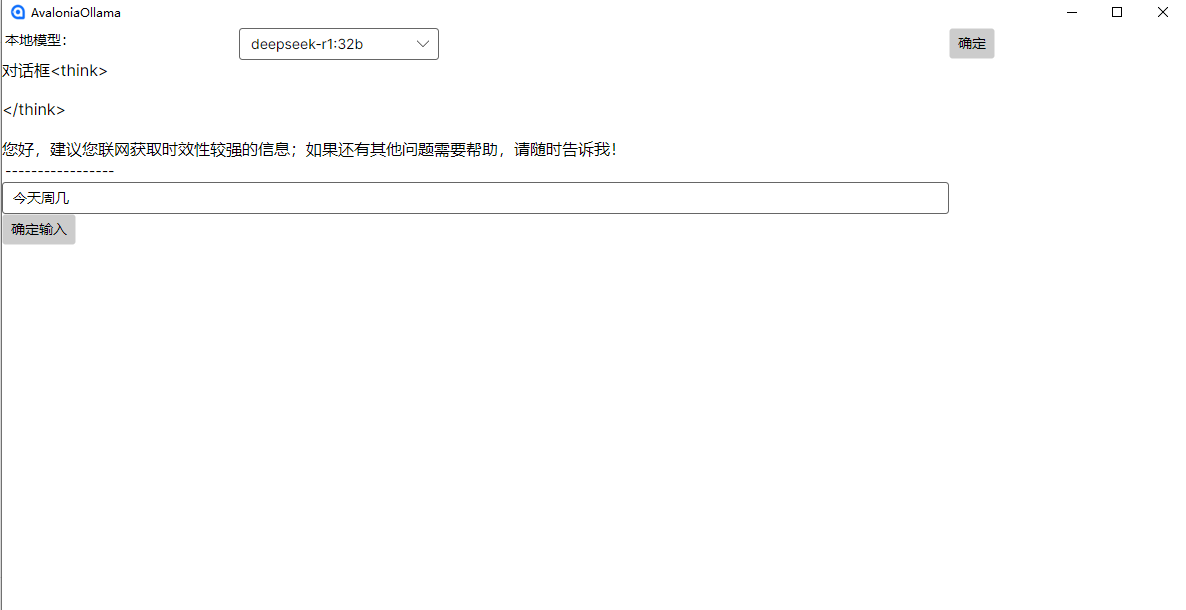
c#开发AI模型对话
AI模型 前面已经介绍了一般AI模型本地部署,直接调用现成的模型数据。这里主要讲述讲接口集成到我们自己的程序中使用方式。 微软提供了ML.NET来开发和使用AI模型,但是目前国内可能使用不多,至少实践例子很少看见。开发训练模型就不介绍了&am…...

IoT/HCIP实验-3/LiteOS操作系统内核实验(任务、内存、信号量、CMSIS..)
文章目录 概述HelloWorld 工程C/C配置编译器主配置Makefile脚本烧录器主配置运行结果程序调用栈 任务管理实验实验结果osal 系统适配层osal_task_create 其他实验实验源码内存管理实验互斥锁实验信号量实验 CMISIS接口实验还是得JlINKCMSIS 简介LiteOS->CMSIS任务间消息交互…...

DeepSeek 技术赋能无人农场协同作业:用 AI 重构农田管理 “神经网”
目录 一、引言二、DeepSeek 技术大揭秘2.1 核心架构解析2.2 关键技术剖析 三、智能农业无人农场协同作业现状3.1 发展现状概述3.2 协同作业模式介绍 四、DeepSeek 的 “农场奇妙游”4.1 数据处理与分析4.2 作物生长监测与预测4.3 病虫害防治4.4 农机协同作业调度 五、实际案例大…...
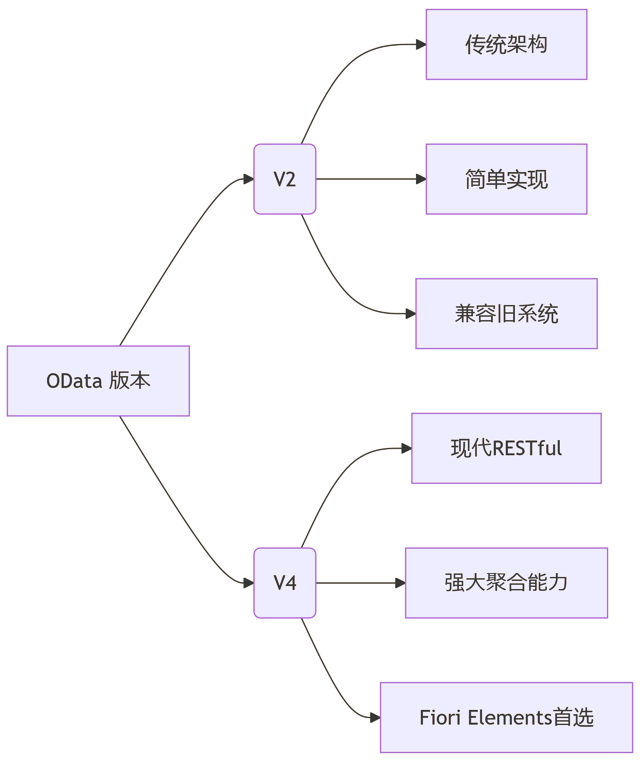
SAP学习笔记 - 开发26 - 前端Fiori开发 OData V2 和 V4 的差异 (Deepseek整理)
上一章用到了V2 的概念,其实 Fiori当中还有 V4,咱们这一章来总结一下 V2 和 V4。 SAP学习笔记 - 开发25 - 前端Fiori开发 Remote OData Service(使用远端Odata服务),代理中间件(ui5-middleware-simpleproxy)-CSDN博客…...

使用Matplotlib创建炫酷的3D散点图:数据可视化的新维度
文章目录 基础实现代码代码解析进阶技巧1. 自定义点的大小和颜色2. 添加图例和样式美化3. 真实数据应用示例实用技巧与注意事项完整示例(带样式)应用场景在数据科学和可视化领域,三维图形能为我们提供更丰富的数据洞察。本文将手把手教你如何使用Python的Matplotlib库创建引…...
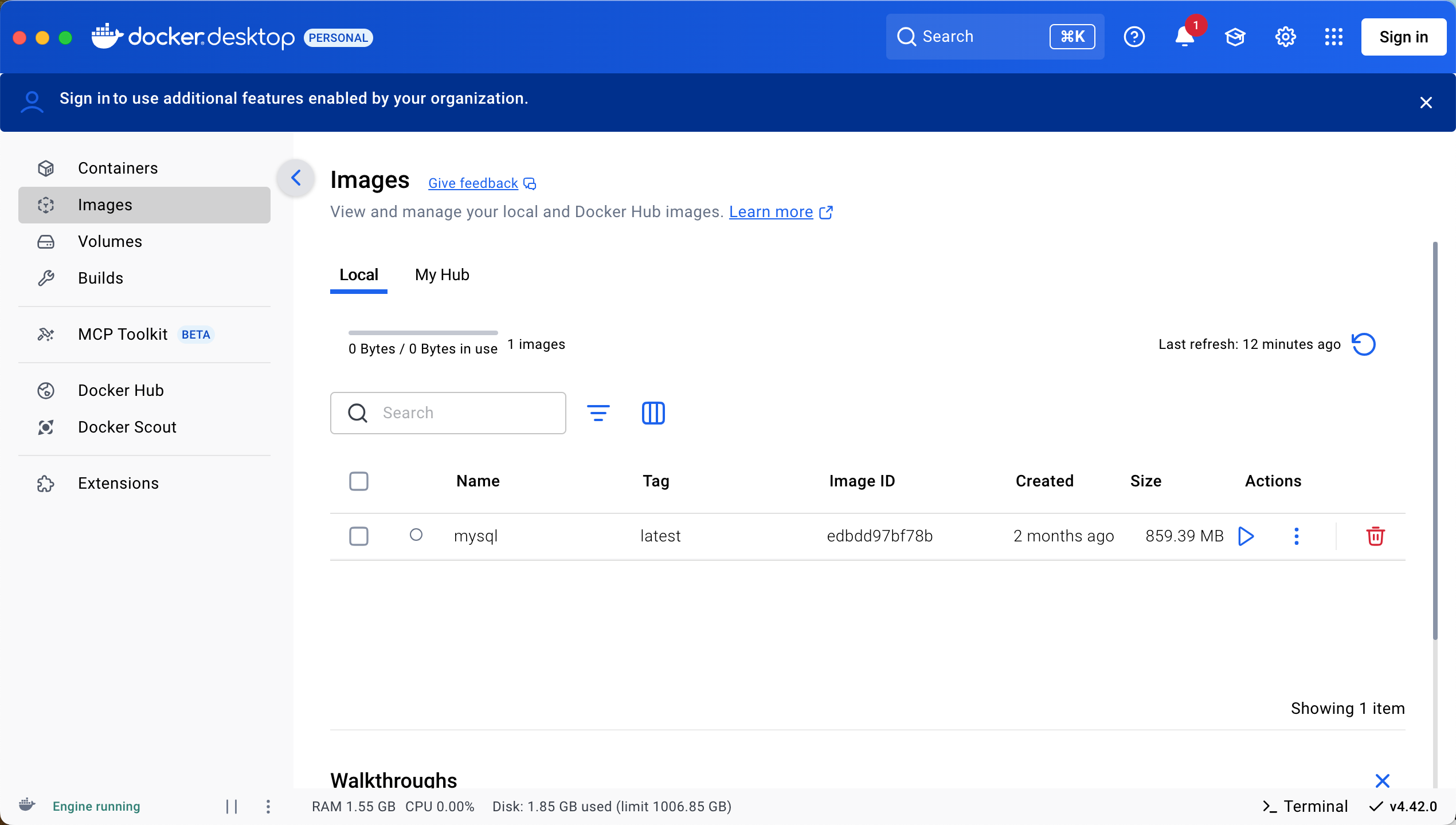
Docker 本地安装 mysql 数据库
Docker: Accelerated Container Application Development 下载对应操作系统版本的 docker ;并安装。 基础操作不再赘述。 打开 macOS 终端,开始 docker 安装mysql之旅 第一步 docker search mysql 》〉docker search mysql NAME DE…...
