OpenMMlab导出yolox模型并用onnxruntime和tensorrt推理
导出onnx文件
直接使用脚本
import torch
from mmdet.apis import init_detector, inference_detectorconfig_file = './configs/yolox/yolox_tiny_8xb8-300e_coco.py'
checkpoint_file = 'yolox_tiny_8x8_300e_coco_20211124_171234-b4047906.pth'
model = init_detector(config_file, checkpoint_file, device='cpu') # or device='cuda:0'
torch.onnx.export(model, (torch.zeros(1, 3, 416, 416),), "yolox.onnx", opset_version=11)
导出的onnx结构如下:
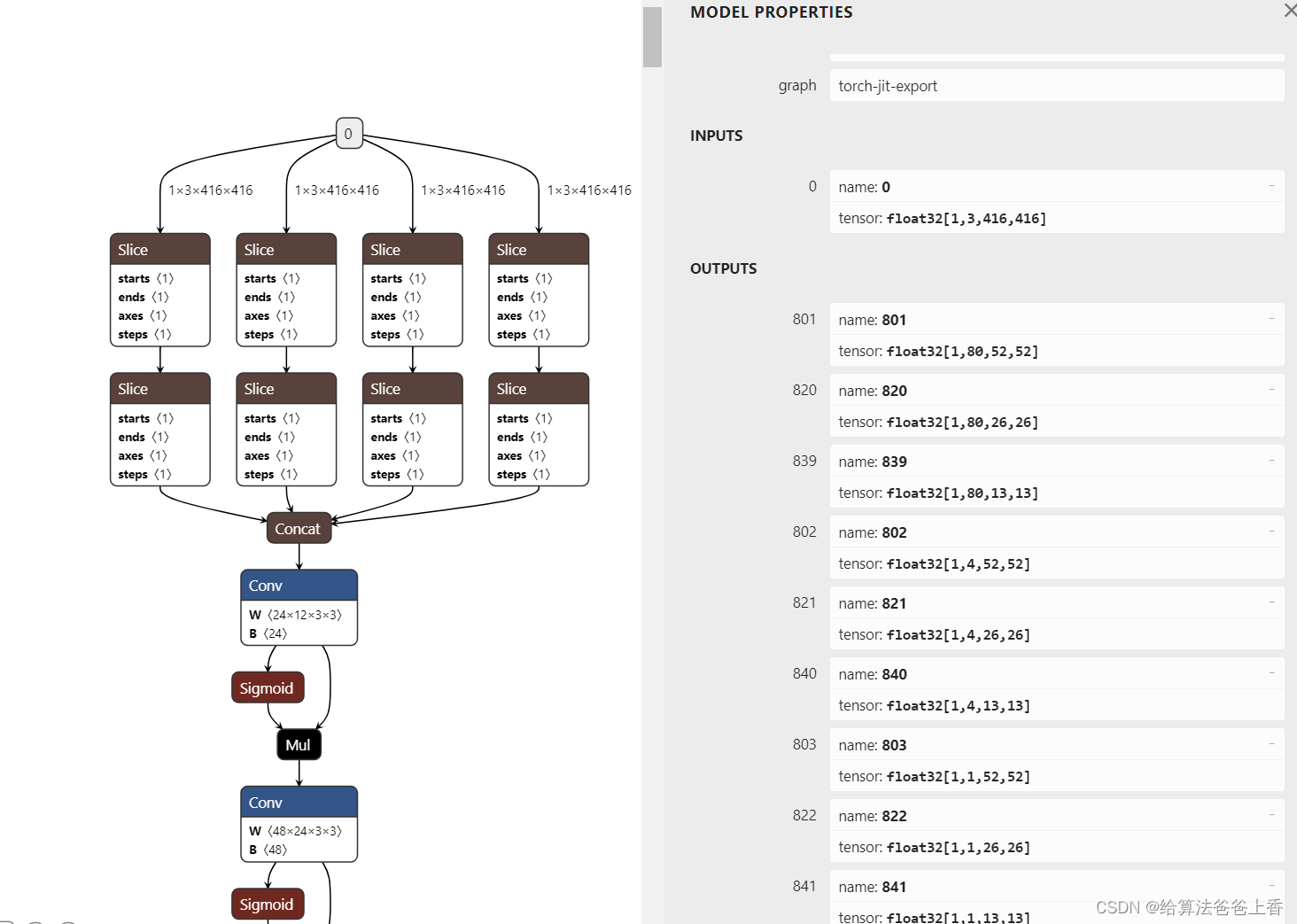
输出是包含多个检测头的输出。若需要合并检测结果,需要修改脚本如下:
import torch
import cv2
import numpy as np
from mmdet.apis import init_detector, inference_detectorconfig_file = './configs/yolox/yolox_tiny_8xb8-300e_coco.py'
checkpoint_file = 'yolox_tiny_8x8_300e_coco_20211124_171234-b4047906.pth'
model = init_detector(config_file, checkpoint_file, device='cpu') # or device='cuda:0'class YOLOX(torch.nn.Module):def __init__(self):super().__init__()self.model = init_detector(config_file, checkpoint_file, device='cpu')self.class_num = 80self.strides = [(8, 8), (16, 16), (32, 32)]def _meshgrid(self, x, y):yy, xx = torch.meshgrid(y, x)return xx.reshape(-1), yy.reshape(-1)def grid_priors(self, featmap_sizes):multi_level_priors = []for i in range(len(featmap_sizes)):feat_h, feat_w = featmap_sizes[i]stride_w, stride_h = self.strides[i]shift_x = torch.arange(0, feat_w) * stride_wshift_y = torch.arange(0, feat_h) * stride_hshift_xx, shift_yy = self._meshgrid(shift_x, shift_y)stride_w = shift_xx.new_full((shift_xx.shape[0], ), stride_w)stride_h = shift_xx.new_full((shift_yy.shape[0], ), stride_h)shifts = torch.stack([shift_xx, shift_yy, stride_w, stride_h], dim=-1) multi_level_priors.append(shifts)return multi_level_priorsdef bbox_decode(self, priors, bbox_preds):xys = (bbox_preds[..., :2] * priors[:, 2:]) + priors[:, :2]whs = bbox_preds[..., 2:].exp() * priors[:, 2:]tl_x = (xys[..., 0] - whs[..., 0] / 2)tl_y = (xys[..., 1] - whs[..., 1] / 2)br_x = (xys[..., 0] + whs[..., 0] / 2)br_y = (xys[..., 1] + whs[..., 1] / 2)decoded_bboxes = torch.stack([tl_x, tl_y, br_x, br_y], -1)return decoded_bboxesdef forward(self, x):x = self.model.backbone(x)x = self.model.neck(x)pred_maps = self.model.bbox_head(x)cls_scores, bbox_preds, objectnesses = pred_maps featmap_sizes = [cls_score.shape[2:] for cls_score in cls_scores] mlvl_priors = self.grid_priors(featmap_sizes)flatten_cls_scores = [cls_score.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(1, -1, self.class_num) for cls_score in cls_scores]flatten_bbox_preds = [bbox_pred.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(1, -1, 4) for bbox_pred in bbox_preds]flatten_objectness = [objectness.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(1, -1) for objectness in objectnesses]flatten_cls_scores = torch.cat(flatten_cls_scores, dim=1).sigmoid()flatten_bbox_preds = torch.cat(flatten_bbox_preds, dim=1)flatten_objectness = torch.cat(flatten_objectness, dim=1).sigmoid()flatten_priors = torch.cat(mlvl_priors)flatten_bboxes = self.bbox_decode(flatten_priors, flatten_bbox_preds)return flatten_bboxes, flatten_objectness, flatten_cls_scoresmodel = YOLOX().eval()
input = torch.zeros(1, 3, 416, 416, device='cpu')
torch.onnx.export(model, input, "yolox.onnx", opset_version=11)
导出的onnx结构如下:
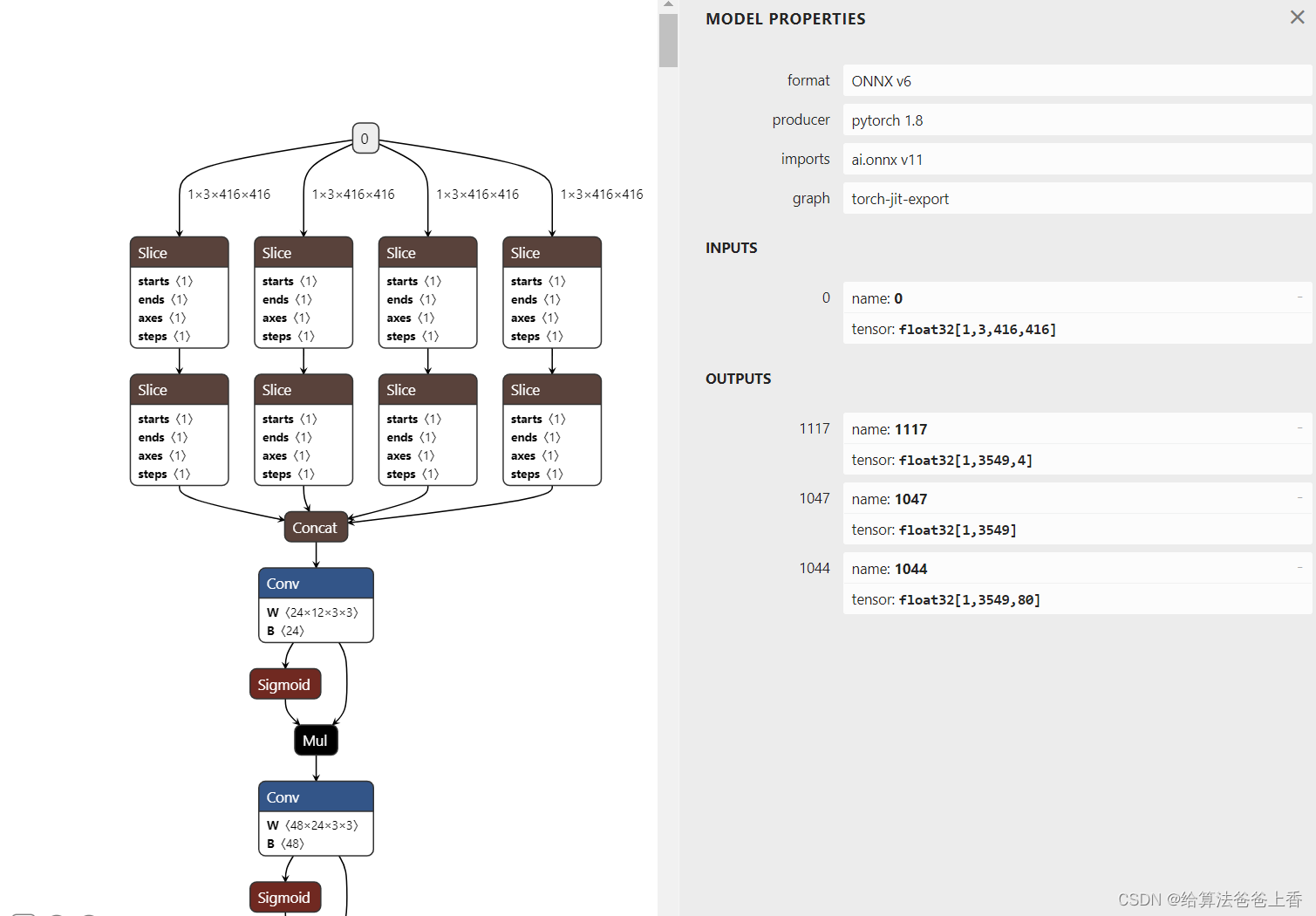
安装mmdeploy的话,可以通过下面脚本导出onnx模型。
from mmdeploy.apis import torch2onnx
from mmdeploy.backend.sdk.export_info import export2SDKimg = 'bus.jpg'
work_dir = './work_dir/onnx/yolox'
save_file = './end2end.onnx'
deploy_cfg = 'mmdeploy/configs/mmdet/detection/detection_onnxruntime_dynamic.py'
model_cfg = 'mmdetection/configs/yolox/yolox_tiny_8xb8-300e_coco.py'
model_checkpoint = 'checkpoints/yolox_tiny_8x8_300e_coco_20211124_171234-b4047906.pth'
device = 'cpu'# 1. convert model to onnx
torch2onnx(img, work_dir, save_file, deploy_cfg, model_cfg, model_checkpoint, device)# 2. extract pipeline info for sdk use (dump-info)
export2SDK(deploy_cfg, model_cfg, work_dir, pth=model_checkpoint, device=device)
onnx模型的结构如下: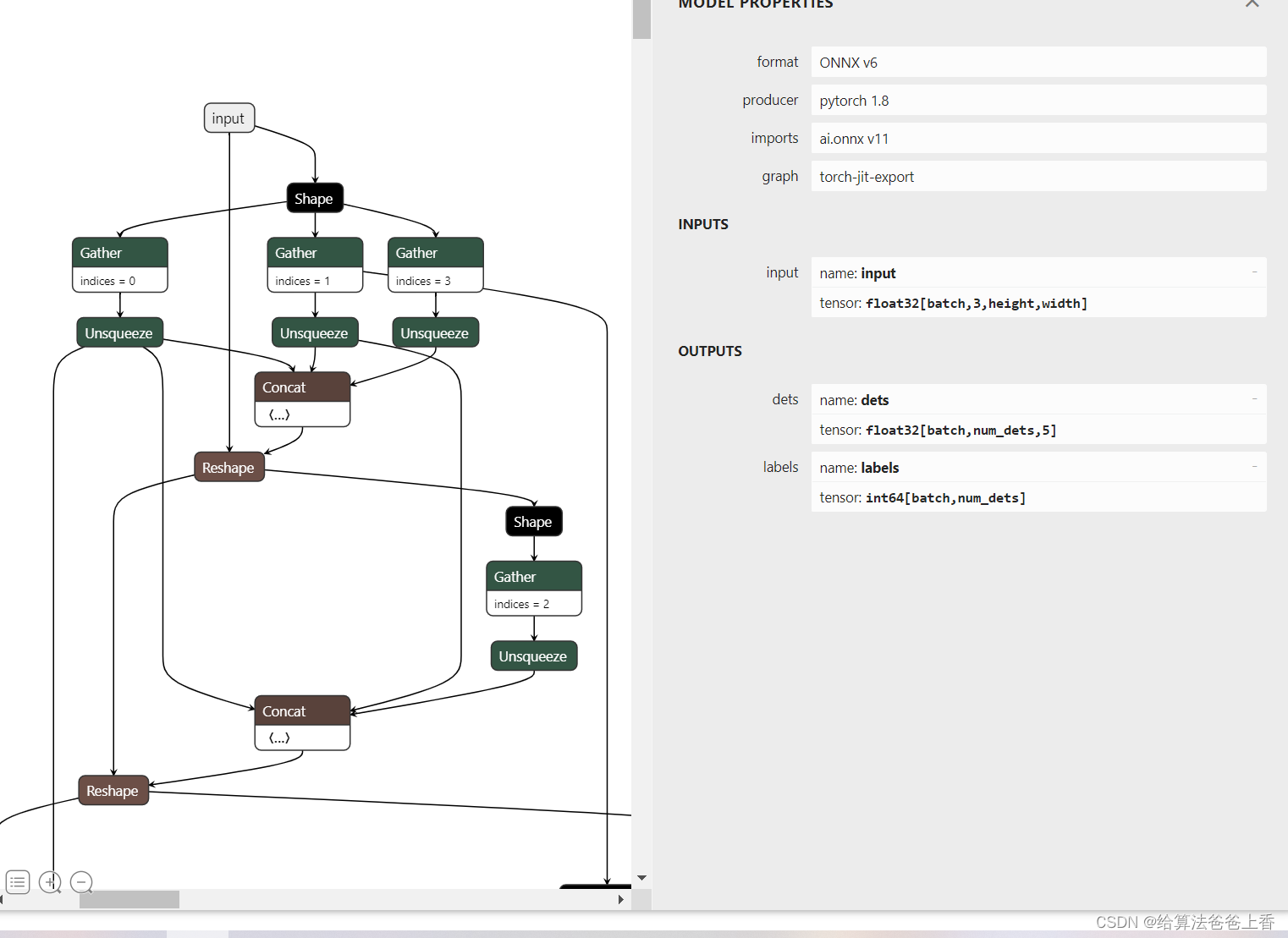
onnxruntime推理
手动导出的onnx模型使用onnxruntime推理:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import onnxruntimeclass_names = ['person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light','fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow','elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee','skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard','tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple','sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch','potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone','microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear','hair drier', 'toothbrush'] #coco80类别
input_shape = (416, 416)
score_threshold = 0.2
nms_threshold = 0.5
confidence_threshold = 0.2 def nms(boxes, scores, score_threshold, nms_threshold):x1 = boxes[:, 0]y1 = boxes[:, 1]x2 = boxes[:, 2]y2 = boxes[:, 3]areas = (y2 - y1 + 1) * (x2 - x1 + 1)keep = []index = scores.argsort()[::-1] while index.size > 0:i = index[0]keep.append(i)x11 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[index[1:]]) y11 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[index[1:]])x22 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[index[1:]])y22 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[index[1:]])w = np.maximum(0, x22 - x11 + 1) h = np.maximum(0, y22 - y11 + 1) overlaps = w * hious = overlaps / (areas[i] + areas[index[1:]] - overlaps)idx = np.where(ious <= nms_threshold)[0]index = index[idx + 1]return keepdef filter_box(outputs): outputs0, outputs1, outputs2 = outputsflag = outputs1 > confidence_thresholdoutput0 = outputs0[flag].reshape(-1, 4)output1 = outputs1[flag].reshape(-1, 1)classes_scores = outputs2[flag].reshape(-1, 80)outputs = np.concatenate((output0, output1, classes_scores), axis=1)boxes = []scores = []class_ids = []for i in range(len(classes_scores)):class_id = np.argmax(classes_scores[i])outputs[i][4] *= classes_scores[i][class_id]outputs[i][5] = class_idif outputs[i][4] > score_threshold:boxes.append(outputs[i][:6])scores.append(outputs[i][4])class_ids.append(outputs[i][5])boxes = np.array(boxes)scores = np.array(scores)indices = nms(boxes, scores, score_threshold, nms_threshold) output = boxes[indices]return outputdef letterbox(im, new_shape=(416, 416), color=(114, 114, 114)):# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraintsshape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]# Scale ratio (new / old)r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])# Compute paddingnew_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r)) dw, dh = (new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0])/2, (new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1])/2 # wh padding top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resizeim = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add borderreturn imdef scale_boxes(boxes, shape):# Rescale boxes (xyxy) from input_shape to shapegain = min(input_shape[0] / shape[0], input_shape[1] / shape[1]) # gain = old / newpad = (input_shape[1] - shape[1] * gain) / 2, (input_shape[0] - shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh paddingboxes[..., [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x paddingboxes[..., [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y paddingboxes[..., :4] /= gainboxes[..., [0, 2]] = boxes[..., [0, 2]].clip(0, shape[1]) # x1, x2boxes[..., [1, 3]] = boxes[..., [1, 3]].clip(0, shape[0]) # y1, y2return boxesdef draw(image, box_data):box_data = scale_boxes(box_data, image.shape)boxes = box_data[...,:4].astype(np.int32) scores = box_data[...,4]classes = box_data[...,5].astype(np.int32)for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):top, left, right, bottom = boxcv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 1)cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(class_names[cl], score), (top, left), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 1)if __name__=="__main__":image = cv2.imread('bus.jpg')input = letterbox(image, input_shape)input = cv2.resize(image, input_shape)input = input[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1).astype(dtype=np.float32) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHWinput = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0)onnx_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession('yolox.onnx', providers=['CPUExecutionProvider'])input_name = []for node in onnx_session.get_inputs():input_name.append(node.name)output_name = []for node in onnx_session.get_outputs():output_name.append(node.name)inputs = {}for name in input_name:inputs[name] = inputoutputs = onnx_session.run(None, inputs)boxes = filter_box(outputs)draw(image, boxes)cv2.imwrite('result.jpg', image)
mmdeploy导出的onnx模型使用onnxruntime推理:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import onnxruntimeclass_names = ['person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light','fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow','elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee','skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard','tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple','sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch','potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone','microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear','hair drier', 'toothbrush'] #coco80类别
input_shape = (416, 416)
confidence_threshold = 0.2def filter_box(outputs): #删除置信度小于confidence_threshold的BOXflag = outputs[0][..., 4] > confidence_thresholdboxes = outputs[0][flag] class_ids = outputs[1][flag].reshape(-1, 1) output = np.concatenate((boxes, class_ids), axis=1) return outputdef letterbox(im, new_shape=(416, 416), color=(114, 114, 114)):# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraintsshape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]# Scale ratio (new / old)r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])# Compute paddingnew_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r)) dw, dh = (new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0])/2, (new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1])/2 # wh padding top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resizeim = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add borderreturn imdef scale_boxes(input_shape, boxes, shape):# Rescale boxes (xyxy) from input_shape to shapegain = min(input_shape[0] / shape[0], input_shape[1] / shape[1]) # gain = old / newpad = (input_shape[1] - shape[1] * gain) / 2, (input_shape[0] - shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh paddingboxes[..., [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x paddingboxes[..., [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y paddingboxes[..., :4] /= gainboxes[..., [0, 2]] = boxes[..., [0, 2]].clip(0, shape[1]) # x1, x2boxes[..., [1, 3]] = boxes[..., [1, 3]].clip(0, shape[0]) # y1, y2return boxesdef draw(image, box_data):box_data = scale_boxes(input_shape, box_data, image.shape)boxes = box_data[...,:4].astype(np.int32) scores = box_data[...,4]classes = box_data[...,5].astype(np.int32)for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):top, left, right, bottom = boxcv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 1)cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(class_names[cl], score), (top, left), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 1)if __name__=="__main__":images = cv2.imread('bus.jpg')input = letterbox(images, input_shape)input = input[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1).astype(dtype=np.float32) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHWinput = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0)onnx_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession('../work_dir/onnx/yolox/end2end.onnx', providers=['CPUExecutionProvider'])input_name = []for node in onnx_session.get_inputs():input_name.append(node.name)output_name = []for node in onnx_session.get_outputs():output_name.append(node.name)inputs = {}for name in input_name:inputs[name] = inputoutputs = onnx_session.run(None, inputs)boxes = filter_box(outputs)draw(images, boxes)cv2.imwrite('result.jpg', images)
直接使用mmdeploy的api推理:
from mmdeploy.apis import inference_modelmodel_cfg = 'mmdetection/configs/yolox/yolox_tiny_8xb8-300e_coco.py'
deploy_cfg = 'mmdeploy/configs/mmdet/detection/detection_onnxruntime_dynamic.py'
img = 'bus.jpg'
backend_files = ['work_dir/onnx/yolox/end2end.onnx']
device = 'cpu'result = inference_model(model_cfg, deploy_cfg, backend_files, img, device)
print(result)
或者:
from mmdeploy_runtime import Detector
import cv2# 读取图片
img = cv2.imread('bus.jpg')# 创建检测器
detector = Detector(model_path='work_dir/onnx/yolox', device_name='cpu')# 执行推理
bboxes, labels, _ = detector(img)
# 使用阈值过滤推理结果,并绘制到原图中
indices = [i for i in range(len(bboxes))]
for index, bbox, label_id in zip(indices, bboxes, labels):[left, top, right, bottom], score = bbox[0:4].astype(int), bbox[4]if score < 0.3:continuecv2.rectangle(img, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 255, 0))
cv2.imwrite('result.jpg', img)
导出engine文件
这里通过trtexec转换onnx文件,LZ的版本是TensorRT-8.2.1.8。
./trtexec.exe --onnx=yolox.onnx --saveEngine=yolox.engine --workspace=20480
tensorrt推理
手动导出的模型使用tensorrt推理:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import tensorrt as trt
import pycuda.autoinit
import pycuda.driver as cuda class_names = ['person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light','fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow','elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee','skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard','tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple','sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch','potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone','microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear','hair drier', 'toothbrush'] #coco80类别
input_shape = (416, 416)
score_threshold = 0.2
nms_threshold = 0.5
confidence_threshold = 0.2 def nms(boxes, scores, score_threshold, nms_threshold):x1 = boxes[:, 0]y1 = boxes[:, 1]x2 = boxes[:, 2]y2 = boxes[:, 3]areas = (y2 - y1 + 1) * (x2 - x1 + 1)keep = []index = scores.argsort()[::-1] while index.size > 0:i = index[0]keep.append(i)x11 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[index[1:]]) y11 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[index[1:]])x22 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[index[1:]])y22 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[index[1:]])w = np.maximum(0, x22 - x11 + 1) h = np.maximum(0, y22 - y11 + 1) overlaps = w * hious = overlaps / (areas[i] + areas[index[1:]] - overlaps)idx = np.where(ious <= nms_threshold)[0]index = index[idx + 1]return keepdef filter_box(outputs): outputs0, outputs1, outputs2 = outputsflag = outputs1 > confidence_thresholdoutput0 = outputs0[flag].reshape(-1, 4)output1 = outputs1[flag].reshape(-1, 1)classes_scores = outputs2[flag].reshape(-1, 80)outputs = np.concatenate((output0, output1, classes_scores), axis=1)boxes = []scores = []class_ids = []for i in range(len(classes_scores)):class_id = np.argmax(classes_scores[i])outputs[i][4] *= classes_scores[i][class_id]outputs[i][5] = class_idif outputs[i][4] > score_threshold:boxes.append(outputs[i][:6])scores.append(outputs[i][4])class_ids.append(outputs[i][5])boxes = np.array(boxes)scores = np.array(scores)indices = nms(boxes, scores, score_threshold, nms_threshold) output = boxes[indices]return outputdef letterbox(im, new_shape=(416, 416), color=(114, 114, 114)):# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraintsshape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]# Scale ratio (new / old)r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])# Compute paddingnew_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r)) dw, dh = (new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0])/2, (new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1])/2 # wh padding top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resizeim = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add borderreturn imdef scale_boxes(boxes, shape):# Rescale boxes (xyxy) from input_shape to shapegain = min(input_shape[0] / shape[0], input_shape[1] / shape[1]) # gain = old / newpad = (input_shape[1] - shape[1] * gain) / 2, (input_shape[0] - shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh paddingboxes[..., [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x paddingboxes[..., [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y paddingboxes[..., :4] /= gainboxes[..., [0, 2]] = boxes[..., [0, 2]].clip(0, shape[1]) # x1, x2boxes[..., [1, 3]] = boxes[..., [1, 3]].clip(0, shape[0]) # y1, y2return boxesdef draw(image, box_data):box_data = scale_boxes(box_data, image.shape)boxes = box_data[...,:4].astype(np.int32) scores = box_data[...,4]classes = box_data[...,5].astype(np.int32)for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):top, left, right, bottom = boxcv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 1)cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(class_names[cl], score), (top, left), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 1)if __name__=="__main__":logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)with open("yolox.engine", "rb") as f, trt.Runtime(logger) as runtime:engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())context = engine.create_execution_context()h_input = cuda.pagelocked_empty(trt.volume(context.get_binding_shape(0)), dtype=np.float32)h_output0 = cuda.pagelocked_empty(trt.volume(context.get_binding_shape(1)), dtype=np.float32)h_output1 = cuda.pagelocked_empty(trt.volume(context.get_binding_shape(2)), dtype=np.float32)h_output2 = cuda.pagelocked_empty(trt.volume(context.get_binding_shape(3)), dtype=np.float32)d_input = cuda.mem_alloc(h_input.nbytes)d_output0 = cuda.mem_alloc(h_output0.nbytes)d_output1 = cuda.mem_alloc(h_output1.nbytes)d_output2 = cuda.mem_alloc(h_output2.nbytes)stream = cuda.Stream()image = cv2.imread('bus.jpg')input = letterbox(image, input_shape)input = input[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1).astype(dtype=np.float32) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHWinput = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0) np.copyto(h_input, input.ravel())with engine.create_execution_context() as context:cuda.memcpy_htod_async(d_input, h_input, stream)context.execute_async_v2(bindings=[int(d_input), int(d_output0), int(d_output1), int(d_output2)], stream_handle=stream.handle)cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(h_output0, d_output0, stream)cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(h_output1, d_output1, stream)cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(h_output2, d_output2, stream)stream.synchronize() h_output = []h_output.append(h_output2.reshape(1, 3549, 4))h_output.append(h_output1.reshape(1, 3549))h_output.append(h_output0.reshape(1, 3549, 80))boxes = filter_box(h_output)draw(image, boxes)cv2.imwrite('result.jpg', image)
使用mmdeploy的api推理:
from mmdeploy.apis import torch2onnx
from mmdeploy.backend.sdk.export_info import export2SDKimg = 'bus.jpg'
work_dir = './work_dir/onnx/yolox'
save_file = './end2end.onnx'
deploy_cfg = 'mmdeploy/configs/mmdet/detection/detection_onnxruntime_dynamic.py'
model_cfg = 'mmdetection/configs/yolox/yolox_tiny_8xb8-300e_coco.py'
model_checkpoint = 'checkpoints/yolox_tiny_8x8_300e_coco_20211124_171234-b4047906.pth'
device = 'cpu'# 1. convert model to onnx
torch2onnx(img, work_dir, save_file, deploy_cfg, model_cfg, model_checkpoint, device)# 2. extract pipeline info for sdk use (dump-info)
export2SDK(deploy_cfg, model_cfg, work_dir, pth=model_checkpoint, device=device)
或者
from mmdeploy_runtime import Detector
import cv2# 读取图片
img = cv2.imread('bus.jpg')# 创建检测器
detector = Detector(model_path='work_dir/trt/yolox', device_name='cuda')# 执行推理
bboxes, labels, _ = detector(img)
# 使用阈值过滤推理结果,并绘制到原图中
indices = [i for i in range(len(bboxes))]
for index, bbox, label_id in zip(indices, bboxes, labels):[left, top, right, bottom], score = bbox[0:4].astype(int), bbox[4]if score < 0.3:continuecv2.rectangle(img, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 255, 0))
cv2.imwrite('result.jpg', img)
相关文章:

OpenMMlab导出yolox模型并用onnxruntime和tensorrt推理
导出onnx文件 直接使用脚本 import torch from mmdet.apis import init_detector, inference_detectorconfig_file ./configs/yolox/yolox_tiny_8xb8-300e_coco.py checkpoint_file yolox_tiny_8x8_300e_coco_20211124_171234-b4047906.pth model init_detector(config_fi…...

CMake语法解读 | Qt6需要用到
CMake 入门CMakeLists.txtmain.cpp编译示例cmake常用参数入门 Hello CMake CMake 是一个用于配置跨平台源代码项目应该如何配置的工具建立在给定的平台上。 ├── CMakeLists.txt # 希望运行的 CMake命令 ├── main.cpp # 带有main 的源文件 ├── include # 头文件目录 …...

jenkins 参数构建
整体思路 依赖环境及工具 GitCentos7及以上GitlabJenkinsshellansible 创建一个jenkins项目 应用保存,测试构建 在gitlab创建新项目,编写index.html [rootjenkins-node1 .ssh]# ssh-keygen Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in …...
DBT踩坑第二弹
总结下dbt-spark踩到的坑,连接方式采用的是thrift连接 Kerberos认证。考虑到开源组件Kyuubi也是基于Hiveserver2,使用的thrift协议,所以采用Kyuubi执行SparkSQL。 官方文档给出的Thrift方式连接示例真的是简单,但是真是用起来真是…...

elasticsearch Connection reset by peer如何处理
如何处理: 代码的心跳代码删除,服务linux内核参数修改 客户端时间要小于服务端时间#异常代码 public RestHighLevelClient elasticsearchClient() {// 初始化 RestClient, hostName 和 port 填写集群的内网 IP 地址与端口 // String[] hosts nod…...

IO和NIO的区别 BIO,NIO,AIO 有什么区别? Files的常用方法都有哪些?
文章目录 IO和NIO的区别BIO,NIO,AIO 有什么区别?Files的常用方法都有哪些? 今天来对java中的io, nio, bio, aio进行了解,有何区别。 IO和NIO的区别 NIO与IO区别 IO是面向流的,NIO是面向缓冲区的Java IO面向流意味着每次从流中读一个或多个字…...
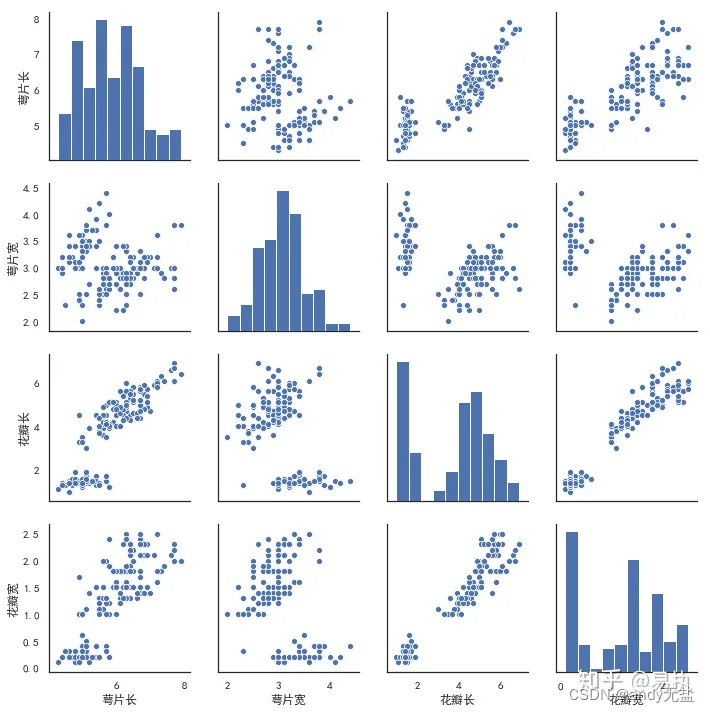
pairplot
Python可视化 | Seaborn5分钟入门(七)——pairplot - 知乎 (zhihu.com) Seaborn是基于matplotlib的Python可视化库。它提供了一个高级界面来绘制有吸引力的统计图形。Seaborn其实是在matplotlib的基础上进行了更高级的API封装,从而使得作图更加容易,不需…...
pytest系列——pytest_collection_modifyitems钩子函数修改测试用例执行顺序
前言 pytest默认执行用例是根据项目下的文件名称按ascii码去收集运行的;文件中的用例是从上往下按顺序执行的。 pytest_collection_modifyitems 这个函数顾名思义就是收集测试用例、改变用例的执行顺序的。 【严格意义上来说,我们在用例设计原则上用例…...
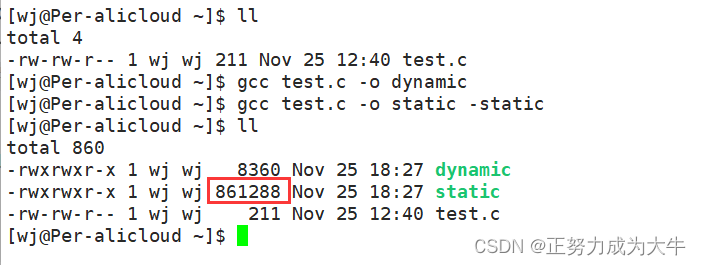
【Linux】gcc和g++
👦个人主页:Weraphael ✍🏻作者简介:目前正在学习c和Linux还有算法 ✈️专栏:Linux 🐋 希望大家多多支持,咱一起进步!😁 如果文章有啥瑕疵,希望大佬指点一二 …...
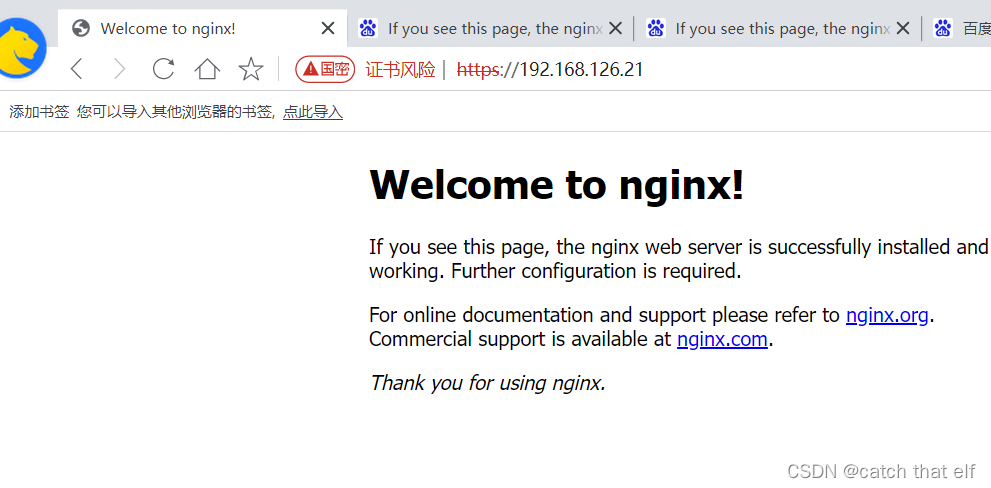
nginx国密ssl测试
文章目录 文件准备编译部署nginx申请国密数字证书配置证书并测试 文件准备 下载文件并上传到服务器,这里使用centos 7.8 本文涉及的程序文件已打包可以直接下载。 点击下载 下载国密版openssl https://www.gmssl.cn/gmssl/index.jsp 下载稳定版nginx http://n…...

H5 清除浮动
1、为什么要清除浮动? 为了解决块级元素浮动后父元素塌陷问题。 2、为什么会产生 父元素塌陷? 首先父元素没有设置高度,父元素的高度是由子元素中最高的控件决定,撑开 简单可以这样理解,原本是在和父元素在同一层级上…...
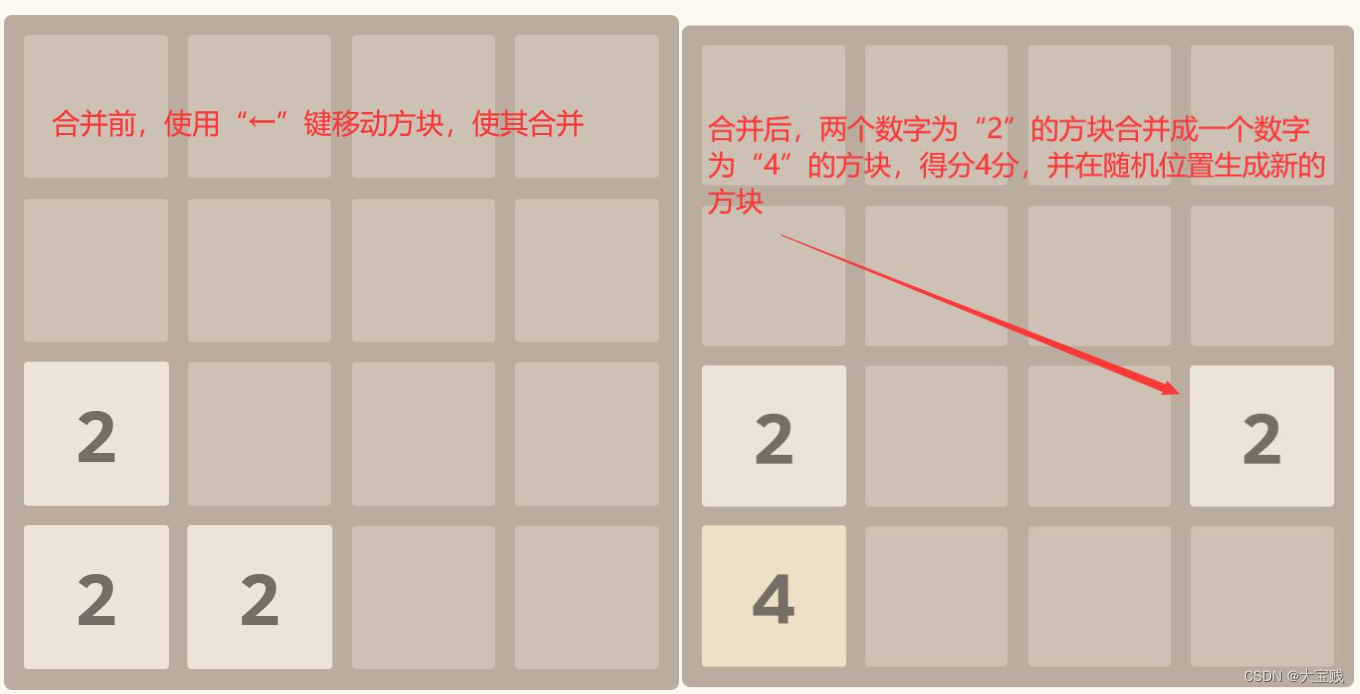
h5小游戏--2048
2048 经典2048小游戏,基于JS、Html5改写版 效果预览 点我下载源代码 下载代码解压后,双击index.html即可开始本游戏。 Game Rule 游戏规则 以下为游戏默认规则,若需要修改规则请修改代码。 移动箭头键来移动方块,当两个相同数…...

随手写了个博客多平台发布脚本:Python自动发布文章到Wordpress
引言 作为一名技术博主,提高博客发布效率是我们始终追求的目标。在这篇文章中,我将分享一个基于Python的脚本,能够实现博客多平台发布,具体来说,是自动发布文章到WordPress。通过这个简单而高效的脚本,…...

通义灵码,你的智能编码助手,免费公测啦!
目录 编辑 1、介绍 2、安装 3、功能介绍 行/函数级实时续写 自然语言生成代码 单元测试生成 代码注释生成 代码解释 研发智能问答 多编程语言、多编辑器全方位支持 4、视频 🍃作者介绍:双非本科大三网络工程专业在读,阿里云专家…...
QT Day01 qt概述,创建项目,窗口属性,按钮,信号与槽
1.qt概述 1.什么是qt Qt 是一个跨平台的 C 图形用户界面应用程序框架。它为应用程序开发者提供建立艺 术级图形界面所需的所有功能。它是完全面向对象的,很容易扩展,并且允许真正的组 件编程。 2.支持的平台 Windows – XP 、 Vista 、 Win7 、 Win8…...
在WSL单机搭建Kafka伪集群)
Kafka(一)在WSL单机搭建Kafka伪集群
目录 1 运行Kafka单实例1.1 Windws1.1.1 安装包下载1.1.2 修改环境变量1.1.3 修改配置文件1.1.4 启动Kafka单机版 1.2 Linux1.2.1 安装包下载1.2.2 创建目录1.2.3 添加环境变量1.2.4 修改配置文件1.2.5 运行Kafka1.2.6 停止Kafka 2 搭建Kafka集群2.1 搭建Zookeeper集群2.2 搭建…...
centos7 keepalived 探测哪个是当前节点
前提 nginx 默认页面内容中需要加上各节点的ip nginx web页面修改 nginx配置文件路径:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf,该配置文件引用了/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf 打开/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf配置文件可以看到html页面的路径 /usr/share/nginx…...

【iOS】数据持久化(二)之归档和解档(iOS 13以后)
在之前介绍的数据存储方法中,不管是NSUserDefaults还是plist文件都不能对自定义对象进行存储,OC提供的解归档恰好解决了这个问题 本片文章对 iOS13 以后的版本 归档和解档 进行介绍。老版本的解归档见这篇文章:【iOS】文件(对象数…...
OpenHarmony模块化编译
一、环境配置 OpenHarmony版本:OpenHarmony 4.0 Release 编译环境:WSL2 Ubuntu 18.04 平台设备:RK3568 二、配置hb OpenHarmony 代码构建有build.sh和hb两种方式: #方式一、build.sh ./build.sh --product-name rk3568 --ccache#方式二、…...
Java游戏制作——王者荣耀
一.准备工作 首先创建一个新的Java项目命名为“王者荣耀”,并在src下创建两个包分别命名为“com.sxt"、”com.stx.beast",在相应的包中创建所需的类。 创建一个名为“img”的文件夹来储存所需的图片素材。 二.代码呈现 package com.sxt;import javax.sw…...

ssc377d修改flash分区大小
1、flash的分区默认分配16M、 / # df -h Filesystem Size Used Available Use% Mounted on /dev/root 1.9M 1.9M 0 100% / /dev/mtdblock4 3.0M...

线程与协程
1. 线程与协程 1.1. “函数调用级别”的切换、上下文切换 1. 函数调用级别的切换 “函数调用级别的切换”是指:像函数调用/返回一样轻量地完成任务切换。 举例说明: 当你在程序中写一个函数调用: funcA() 然后 funcA 执行完后返回&…...

vue3 字体颜色设置的多种方式
在Vue 3中设置字体颜色可以通过多种方式实现,这取决于你是想在组件内部直接设置,还是在CSS/SCSS/LESS等样式文件中定义。以下是几种常见的方法: 1. 内联样式 你可以直接在模板中使用style绑定来设置字体颜色。 <template><div :s…...

提升移动端网页调试效率:WebDebugX 与常见工具组合实践
在日常移动端开发中,网页调试始终是一个高频但又极具挑战的环节。尤其在面对 iOS 与 Android 的混合技术栈、各种设备差异化行为时,开发者迫切需要一套高效、可靠且跨平台的调试方案。过去,我们或多或少使用过 Chrome DevTools、Remote Debug…...
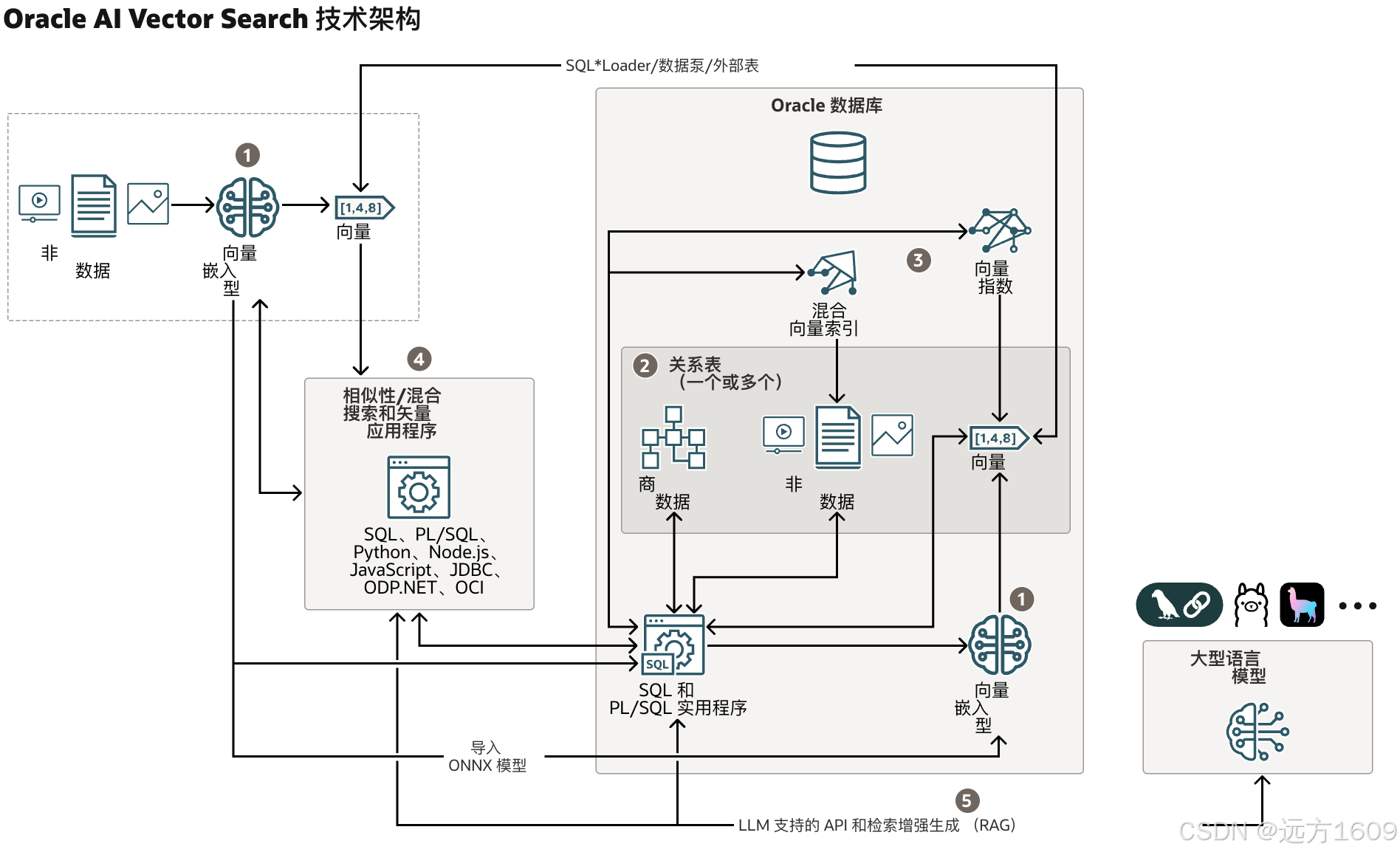
9-Oracle 23 ai Vector Search 特性 知识准备
很多小伙伴是不是参加了 免费认证课程(限时至2025/5/15) Oracle AI Vector Search 1Z0-184-25考试,都顺利拿到certified了没。 各行各业的AI 大模型的到来,传统的数据库中的SQL还能不能打,结构化和非结构的话数据如何和…...

GeoServer发布PostgreSQL图层后WFS查询无主键字段
在使用 GeoServer(版本 2.22.2) 发布 PostgreSQL(PostGIS)中的表为地图服务时,常常会遇到一个小问题: WFS 查询中,主键字段(如 id)莫名其妙地消失了! 即使你在…...

【题解-洛谷】P10480 可达性统计
题目:P10480 可达性统计 题目描述 给定一张 N N N 个点 M M M 条边的有向无环图,分别统计从每个点出发能够到达的点的数量。 输入格式 第一行两个整数 N , M N,M N,M,接下来 M M M 行每行两个整数 x , y x,y x,y,表示从 …...

npm安装electron下载太慢,导致报错
npm安装electron下载太慢,导致报错 背景 想学习electron框架做个桌面应用,卡在了安装依赖(无语了)。。。一开始以为node版本或者npm版本太低问题,调整版本后还是报错。偶尔执行install命令后,可以开始下载…...

Gitlab + Jenkins 实现 CICD
CICD 是持续集成(Continuous Integration, CI)和持续交付/部署(Continuous Delivery/Deployment, CD)的缩写,是现代软件开发中的一种自动化流程实践。下面介绍 Web 项目如何在代码提交到 Gitlab 后,自动发布…...

codeforces C. Cool Partition
目录 题目简述: 思路: 总代码: https://codeforces.com/contest/2117/problem/C 题目简述: 给定一个整数数组,现要求你对数组进行分割,但需满足条件:前一个子数组中的值必须在后一个子数组中…...
