STL常用算法-C++
概述:
- 算法主要是由头文件
<algorithm><functional><numeric>组成。 <algorithm>是所有 STL 头文件中最大的一个,范围涉及是比较、交换、查找、遍历操作、复制、修改等等。<functional>定义了一些模板类,用以声明函数对象<numeric>体积很小,只包括几个在序列上面进行简单数学运算的模板函数
1. 常用的遍历算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的遍历算法
算法简介:
for_each// 遍历容器transform// 搬运容器到另一个容器中
1.1 for_each
功能描述:
- 实现遍历容器
函数原型:
- for_each(iterator beg, iterator end, _func);
// 遍历算法 遍历容器元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _func 函数或者函数对象
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;//1.普通函数
void print01(int val) {cout << val << " ";
}//2.仿函数
class print02
{
public:void operator()(int val) {cout << val << " ";}
};int main() {vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v.push_back(i);}for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print01);//普通函数cout << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());//仿函数的函数对象cout << endl;return 0;
}
总结:for_each 在实际开发中是最常用的遍历算法,需要熟练掌握
1.2 transform
功能描述:
- 搬运容器到另一个容器中
函数原型:
- transform(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, _func);
// beg1 源容器开始迭代器
// end1 源容器结束迭代器
// beg2 目标容器开始迭代器
// _func 函数或者函数对象(可以在搬运过程中对源容器中的元素做一些逻辑运算等操作)
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;//仿函数
class Transform
{
public:int operator()(int val) {//搬运过程中需要把元素返回回去,所以返回类型为搬运的元素类型return val;}
};class MyPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val) {cout << val << " ";}
};int main() {vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v.push_back(i);}vector<int> vTarget;vTarget.resize(v.size());//目标容器需要提前开辟预定大小的空间transform(v.begin(), v.end(), vTarget.begin(), Transform());for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), MyPrint());cout << endl;return 0;
}
总结:
- 搬运的目标容器必须要提前开辟预定大小的空间,否则无法正常搬运
- 搬运过程中需要把元素返回回去,所以仿函数的返回类型为 搬运的元素的类型
2. 常用查找算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的查找算法
算法简介:
- find // 查找元素
- find_if // 按条件查找元素
- adjacent_find // 查找相邻重复元素
- binary_search // 二分查找法
- count // 统计元素个数
- count_if // 按条件统计元素个数
2.1 find
功能描述:
- 查找指定元素,找到返回指定元素的迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器(end)
函数原型:
- find(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// 以迭代器的方式按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 查找的元素
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;class Person {
public:Person(string name, int age) {this->name = name;this->age = age;}bool operator==(const Person& p) {if (this->name == p.name && this->age == p.age) {return true;} else {return false;}}public:string name;int age;
};int main() {
//查找内置数据类型vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v.push_back(i);}vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 5);if (it == v.end()) {cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else {cout << "找到:" << *it << endl;}//查找自定义数据类型vector<Person> vp;Person p1("aaa", 10);Person p2("bbb", 20);Person p3("ccc", 30);Person p4("ddd", 40);vp.push_back(p1);vp.push_back(p2);vp.push_back(p3);vp.push_back(p4);Person pp("bbb", 20);//当使用 find 查找自定义数据类型时,要在自定义数据类型内部重载 == 运算符,让底层 find 知道如何对比自定义数据类型vector<Person>::iterator it = find(vp.begin(), vp.end(), pp);if (it == vp.end()) {cout << "没有找到" << endl;}else {cout << "找到:" << it->name << " " << it.age << endl;}return 0;
}
总结:
- 利用 find 可以在容器中找指定的元素,返回值是迭代器
- 当使用 find 查找自定义数据类型时,要在自定义数据类型内部重载 == 运算符,让底层 find 知道如何对比自定义数据类型
2.2 find_if
功能描述:
- 按条件查找元素
函数原型:
- find_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定元素迭代器位置,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _Pred 函数或者谓词(返回 bool 类型的仿函数)
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;//内置数据类型仿函数
class GreaterFive
{
public:bool operator()(int val) {return val > 5;}
};class Person {
public:Person(string name, int age) {this->name = name;this->age = age;}bool operator==(const Person& p) {if (this->name == p.name && this->age == p.age) {return true;} else {return false;}}public:string name;int age;
};//自定义数据类型仿函数
class Greater20
{
public:bool operator()(Person& p) {return p.age > 20;}
};int main() {
//查找内置数据类型vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v.push_back(i);}vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive());if (it == v.end()) {cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else {cout << "找到大于 5 的数字为:" << *it << endl;}//查找自定义数据类型vector<Person> vp;Person p1("aaa", 10);Person p2("bbb", 20);Person p3("ccc", 30);Person p4("ddd", 40);vp.push_back(p1);vp.push_back(p2);vp.push_back(p3);vp.push_back(p4);Person pp("bbb", 20);vector<Person>::iterator it = find(vp.begin(), vp.end(), Greater20());if (it == vp.end()) {cout << "没有找到" << endl;}else {cout << "找到:" << it->name << " " << it.age << endl;}return 0;
}
2.3 adjacent_find
功能描述:
- 查找相邻重复元素
函数原型:
- adjacent_find(iterator beg, iterator end);
// 查找相邻重复元素,返回相邻元素的第一个位置的迭代器;找不到返回结束迭代器位置。
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;int main() {
//查找内置数据类型vector<int> v;v.push_back(0);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(0);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(3);vector<int>::iterator it = adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());if (it == v.end()) {cout << "没有找到相邻重复元素!" << endl;}else {cout << "找到相邻重复元素:" << *it << endl;}return 0;
}
2.4 binary_search
功能描述:
- 查找指定元素是否存在
函数原型:
- bool binary_search(iterator beg, iterator end, val);
// 查找指定的元素,查到返回 true,否则 false
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 查找的元素
注意:容器必须是有序的序列,在无序序列中不可用。(如果是无序的序列,结果未知!)
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;int main() {
//查找内置数据类型vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v.push_back(i);}bool ret= binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 9);if (ret) {cout << "找到了元素!" << endl;}else {cout << "未找到!" << endl;}return 0;
}
总结:虽然二分查找法查找效率很高,但是值得注意的是查找的容器中元素必须是有序序列。
2.5 count
功能描述:
- 统计元素个数
函数原型:
- count(iterator beg, iterator end, val);
// 统计元素出现次数
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 统计的元素
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;class Person {
public:Person(string name, int age) {this->name = name;this->age = age;}bool operator==(const Person& p) {//底层要求必须加上 const,否则会报错if (this->age == p.age) {return true;} else {return false;}}public:string name;int age;
};int main() {
//统计内置数据类型vector<int> v;v.push_back(0);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(0);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(3);int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);cout << "3 的元素个数为:" << num << endl;//统计自定义数据类型vector<Person> vp;Person p1("aaa", 10);Person p2("bbb", 20);Person p3("ccc", 20);Person p4("ddd", 40);vp.push_back(p1);vp.push_back(p2);vp.push_back(p3);vp.push_back(p4);Person pp("eee", 20);//当使用 count 查找自定义数据类型时,要在自定义数据类型内部重载 == 运算符,让底层 count 知道如何对比自定义数据类型num = count(vp.begin(), vp.end(), pp);cout << "和 eee 的年龄相同 的元素个数为:" << num << endl;return 0;
}
总结:统计自定义数据类型的时候,需要配合重载 operator==
2.5 count_if
功能描述:
- 按条件统计元素个数
函数原型:
- count_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
// 按条件统计元素出现次数
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _Pred 谓词
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;class Greater2
{
public:bool operator()(int val) {return val > 2;}
};class Person {
public:Person(string name, int age) {this->name = name;this->age = age;}bool operator==(const Person& p) {//底层要求必须加上 const,否则会报错if (this->age == p.age) {return true;} else {return false;}}public:string name;int age;
};class AgeGreater20
{
public:bool operator()(const Person& p) {return p.age >= 20;}
};int main() {
//统计内置数据类型vector<int> v;v.push_back(0);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(0);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(3);int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater2());cout << "大于 2 的元素个数为:" << num << endl;//统计自定义数据类型vector<Person> vp;Person p1("aaa", 10);Person p2("bbb", 20);Person p3("ccc", 20);Person p4("ddd", 40);vp.push_back(p1);vp.push_back(p2);vp.push_back(p3);vp.push_back(p4);num = count(vp.begin(), vp.end(), AgeGreater20());cout << "age >= 20 的元素个数为:" << num << endl;return 0;
}
3. 常用排序算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的排序算法
算法简介:
- sort //对容器中元素进行排序
- random_shuffle //洗牌 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
- merge //容器元素合并,并存储在另一个容器中
- reverse //反转指定范围内的元素
3.1 sort
功能描述:
- 对容器内元素进行排序
函数原型:
- sort(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _Pred 谓词,可以选择填或不填,不填的话默认是一个从小到大的排序;如果填的话会按照指定的排序规则进行排序
// 返回值是 bool 类型
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;class Greater2
{
public:bool operator()(int val) {return val > 2;}
};//普通函数遍历
void myPrint(int val) {cout << val << " ";
}int main() {vector<int> v;v.push_back(0);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(4);sort(v.begin(), v.end());//1.默认升序排列for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());//2.使用内建函数对象降序排列for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;return 0;
}
总结:sort 属于开发中最常用的算法之一,需熟练掌握
3.2 random_shuffle
功能描述:
- 洗牌:对指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
函数原型:
- random_shuffle(iterator beg, iterator end);
// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;//普通函数遍历
void myPrint(int val) {cout << val << " ";
}int main() {vector<int> v;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10; i++) {v.push_back(i);}//1.利用洗牌算法打乱顺序,但每次打乱顺序是一样的//random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());//2.利用洗牌算法打乱顺序,加入随机种子真实打乱srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;return 0;
}
总结:random_shuffle 洗牌算法比较实用,使用时记得加随机数种子
3.3 merge
功能描述:
- 两个容器元素合并,并存储到另一个容器中
函数原型:
- merge(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
注意:默认情况下两个容器必须都是升序序列,合并后依然是一个升序序列;如果都是降序序列的话,需要在参数列表中第 6 个形参的位置填写 谓词参数 指定规则。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;//普通函数遍历
void myPrint(int val) {cout << val << " ";
}int main() {vector<int> v1;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10; i++) {v1.push_back(i);}vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10; i++) {v2.push_back(i+3);}vector<int> vTarget;vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());//提前给目标容器分配空间merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;return 0;
}
总结:
- 默认情况下 merge 合并的两个容器必须都是升序序列,合并后依然是一个升序序列。
- 必须提前给目标容器分配空间
3.3 reverse
功能描述:
- 将容器内元素进行反转
函数原型:
- reverse(iterator beg, iterator end);
// 反转指定范围内的元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;//普通函数遍历
void myPrint(int val) {cout << val << " ";
}int main() {vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);cout << "反转前" << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;cout << "反转后" << endl;reverse(v.begin(), v.end());//1.for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;return 0;
}
总结:
- reverse 反转区间内元素,面试题可能涉及到
4. 常用拷贝和替换算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的拷贝和替换算法
算法简介:
- copy // 容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一个容器中
- replace // 将容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素
- replace_if // 容器内指定范围满足条件的元素替换为新元素
- swap // 互换两个容器的元素
4.1 copy
功能描述:
- 容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一个容器中
函数原型:
- copy(iterator beg, iterator end, iterator dest);
// 将源容器中的数据拷贝到目标容器中
// beg 源容器的起始迭代器
// end 源容器的结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器的起始迭代器
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;//普通函数遍历
void myPrint(int val) {cout << val << " ";
}int main() {vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;vector<int> v2;v2.resize(v.size());//提前开辟空间copy(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin());//1.for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;return 0;
}
总结:
- 利用 copy 算法在拷贝时,目标容器记得提前开辟空间。
- 在实际工程中以容器直接赋值为主,copy 算法拷贝使用较少。
4.2 replace
功能描述:
- 容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素
函数原型:
- replace(iterator beg, iterator end, oldvalue, newvalue);
// 将区间内旧元素替换成新元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// oldvalue 旧元素
// newvalue 新元素
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;//普通函数遍历
void myPrint(int val) {cout << val << " ";
}int main() {vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;replace(v.begin(), v.end(), 20, 2000);//1.for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;return 0;
}
总结:
- replace 会替换区间内满足条件的元素
4.3 replace_if
功能描述:
- 将区间内满足条件的元素,替换成指定元素
函数原型:
- replace_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _pred, newvalue);
// 按条件替换元素,将区间内满足条件的旧元素替换成新元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _pred 谓词
// newvalue 替换的新元素
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;//普通函数遍历
void myPrint(int val) {cout << val << " ";
}class Greater30 {
public:bool operator()(int val) {return val >= 30;}
};int main() {vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater30(), 3000);//1.for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;return 0;
}
总结:
- replace_if 按条件查找,可以利用仿函数灵活筛选满足的条件
4.4 swap
功能描述:
- 互换两个容器
函数原型:
- swap(container c1, container c2);
// 互换两个容器
// c1:容器 1
// c2:容器 2
同种类型的容器才可以做交换。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;//普通函数遍历
void myPrint(int val) {cout << val << " ";
}int main() {vector<int> v1;v1.push_back(10);v1.push_back(30);v1.push_back(50);v1.push_back(20);v1.push_back(40);vector<int> v2;v2.push_back(300);v2.push_back(500);v2.push_back(200);v2.push_back(400);for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;swap(v1, v2);//1.for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;return 0;
}
总结:
- swap 交换容器时,注意交换的容器要同种类型
5. 常用的算术生成算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的算术生成算法
注意:
- 算术生成算法属于小型算法,使用是包含的头文件为
#include <numeric>
算法简介:
accumulate// 计算容器元素累积总和fill// 往容器中添加元素
5.1 accumulate
功能描述:
- 计算区间内的容器元素累计总和
函数原型:
- accumulate(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// 计算容器元素累积总和
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 初始的累加值
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;//普通函数遍历
void myPrint(int val) {cout << val << " ";
}int main() {vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {v.push_back(i);}for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;int total = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0);//1.cout << "total = " << total << endl;return 0;
}
总结:
- accumulate 使用时头文件注意是 numeric,这个算法很实用
5.2 fill
功能描述:
- 向容器中填充指定的元素
函数原型:
- fill(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// 向容器中填充元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 填充的值
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;//普通函数遍历
void myPrint(int val) {cout << val << " ";
}int main() {vector<int> v;v.resize(10);fill(v.begin(), v.end(), 100);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;return 0;
}
总结:
- 利用 fill 可以将容器区间内元素填充为 指定的值。
6. 常用集合算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的集合算法
算法简介:
- set_intersection //求两个容器的交集
- set_union //求两个容器的并集
- set_difference //求两个容器的差集
6.1 set_intersection
功能描述:
- 求两个容器的交集
函数原型:
- set_intersection(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// 求两个容器的交集
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
// 返回目标容器中交集结束的迭代器
注意:两个集合(两个源容器)必须是有序序列(默认升序,降序谓词)。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;//普通函数遍历
void myPrint(int val) {cout << val << " ";
}int main() {vector<int> v1;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10; i++) {v1.push_back(i);}vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10; i++) {v2.push_back(i+3);}vector<int> vTarget;vTarget.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));//提前给目标容器分配空间vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());//1.返回值是目标容器中交集结束的迭代器for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint);cout << endl;return 0;
}
总结:
- 求交集的两个集合(两个源容器)必须是有序序列(默认升序,降序谓词)。
- 目标容器开辟空间需要从两个容器中取小值
- set_intersection 返回值 是交集中最后一个元素的下一个位置,在遍历交集的时候使用返回值的迭代器。
6.2 set_union
功能描述:
- 求两个容器的并集
函数原型:
- set_union(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// 求两个容器的并集
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
// 返回目标容器中并集结束的迭代器
注意:两个集合(两个源容器)必须是有序序列(默认升序,降序谓词)。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;//普通函数遍历
void myPrint(int val) {cout << val << " ";
}int main() {vector<int> v1;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10; i++) {v1.push_back(i);}vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10; i++) {v2.push_back(i+3);}vector<int> vTarget;vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());//提前给目标容器分配空间vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());//1.返回值是目标容器中并集结束的迭代器for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint);cout << endl;return 0;
}
总结:
- 求并集的两个集合(两个源容器)必须是有序序列(默认升序,降序谓词)。
- 目标容器开辟空间需要两个容器相加
- set_union 返回值 是并集中最后一个元素的下一个位置,在遍历并集的时候使用返回值的迭代器。
6.3 set_difference
功能描述:
- 求两个容器的差集
v1 和 v2 容器的差集:v1 - v1 ∩ v2
v2 和 v1 容器的差集:v2 - v1 ∩ v2
函数原型:
- set_difference(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// 求两个容器的差集
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
// 返回目标容器中差集结束的迭代器
注意:两个集合(两个源容器)必须是有序序列(默认升序,降序谓词)。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;//普通函数遍历
void myPrint(int val) {cout << val << " ";
}int main() {vector<int> v1;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10; i++) {v1.push_back(i);}vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10; i++) {v2.push_back(i+3);}vector<int> vTarget;vTarget.resize(max(v1.size(), v2.size()));//提前给目标容器分配空间cout << "v1 和 v2 的差集是:" << endl;vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());//1.返回值是目标容器中差集结束的迭代器for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint);cout << endl;cout << "v2 和 v1 的差集是:" << endl;vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), vTarget.begin());//2.返回值是目标容器中差集结束的迭代器for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint);cout << endl;return 0;
}
总结:
- 求差集的两个集合(两个源容器)必须是有序序列(默认升序,降序谓词)。
- 目标容器开辟空间需要从两个容器中取较大值
- set_difference 返回值 是差集中最后一个元素的下一个位置,在遍历差集的时候使用返回值的迭代器。
相关文章:

STL常用算法-C++
概述: 算法主要是由头文件 <algorithm> <functional> <numeric> 组成。<algorithm> 是所有 STL 头文件中最大的一个,范围涉及是比较、交换、查找、遍历操作、复制、修改等等。<functional> 定义了一些模板类,…...

一、Lua基础
文章目录 一、Lua是什么二、Lua特性(一)轻量级(二)可扩展(三)其它特性 三、Lua安装四、Lua应用 看到评论说,C让我见识了语言的严谨与缜密,lua让我见识到了语言的精巧与创新ÿ…...

vue3 webSocket 封装及使用
vue3 webSocket 封装及使用 封装 import { ref, onUnmounted } from vue; interface SocketOptions {heartbeatInterval?: number;reconnectInterval?: number;maxReconnectAttempts?: number; }class Socket {url: string;ws: WebSocket | null null;opts: SocketOption…...
)
记录vscode常用插件集合(extensions)
名称用处Chinese (Simplified) (简体中文) Language Pack for Visual Studio Code适用于 VS Code 的中文(简体)语言包Dev ContainersVisual Studio代码开发容器ES7 React/Redux/GraphQL/React-Native snippetsES7 React/Redux/GraphQL/Rect Native代码段…...

正则表达式详解
一、正则表达式概述 正则表达式是一组由字母和符号组成的特殊文本,它可以用来从文本中找出满足你想要的格式的句子。通俗的讲就是按照某种规则去匹配符合条件的字符串 一个正则表达式是一种从左到右匹配主体字符串的模式。 “Regular expression”这个词比较拗口&a…...

【限时免费】20天拿下华为OD笔试之【双指针】2023Q1A-两数之和绝对值最小【欧弟算法】全网注释最详细分类最全的华为OD真题题解
文章目录 题目描述与示例题目描述输入输出示例一输入输出说明 解题思路代码解法一pythonjavacpp 解法二pythonjavacpp 时空复杂度 华为OD算法/大厂面试高频题算法练习冲刺训练 题目描述与示例 题目描述 给定一个整数数组nums,请你在该数组中找出两个数,…...

expect脚本在自动化部署中的具体应用案例
#expect脚本在自动化部署中的具体应用 expect脚本是一个非常好的交互式应用脚本,在自动化部署中,可以使用这个脚本来实现全自动的自动化部署。下面是一些具体的应用案例。 场景一:自动安装mysql 可以使用expect脚本来实现mysql自动安装&…...
【Java+SQL Server】前后端连接小白教程
目录 📋 流程总览 ⛳️【SQL Server】数据库操作 1. 新建数据库text 2. 新建表 3. 编辑表 ⛳️【IntelliJ IDEA】操作 1. 导入jar包 2. 运行显示错误 📋 流程总览 ⛳️【SQL Server】数据库操作 打开SQL Server数据库-->sa登录-->新建数据库…...
Xilinx Zynq-7000系列FPGA多路视频处理:图像缩放+视频拼接显示,提供工程源码和技术支持
目录 1、前言免责声明 2、相关方案推荐FPGA图像处理方案FPGA图像缩放方案FPGA视频拼接叠加融合方案推荐 3、设计思路详解HLS 图像缩放介绍Video Mixer介绍 4、vivado工程介绍PL 端 FPGA 逻辑设计PS 端 SDK 软件设计 5、工程移植说明vivado版本不一致处理FPGA型号不一致处理其他…...

Web语言基础课程期末代做
《Web语言基础》课程期末考核要求综合运用课程所学知识,使用VS和SQL及相关开发工具,结合DIVCSS等前端设计技术,完成一个具备新闻发布和考试功能的动态系统,要求包括但不限于:用户注册、登录功能、新闻展示功能、后台数…...
Scanner常用知识点
在Java中,Scanner类是用于读取用户输入的工具类,可以从多种输入源读取数据,如标准输入流、文件或字符串。以下是一些Scanner类的常用知识点: Scanner的初始化:在使用Scanner类之前,需要先将其导入到你的Ja…...
uniapp页面使用多个echarts出现数据渲染错乱问题解决
首先,uniapp当中使用echarts是在通过使用renderjs的script模板的前提下实现的,在官方提供的案例当中,核心代码是这一部分: 但如果将其封装为组件,并在一个页面当中引用多次来生成多个charts图标,那么这个时…...

PHP连接数据库 错误抑制 三元运算符 学习资料
PHP连接数据库 PHP可以通过不同的扩展和库来连接各种类型的数据库。下面是一个使用MySQL数据库的连接示例: <?php $servername "localhost"; $username "your_username"; $password "your_password"; $dbname "your_d…...
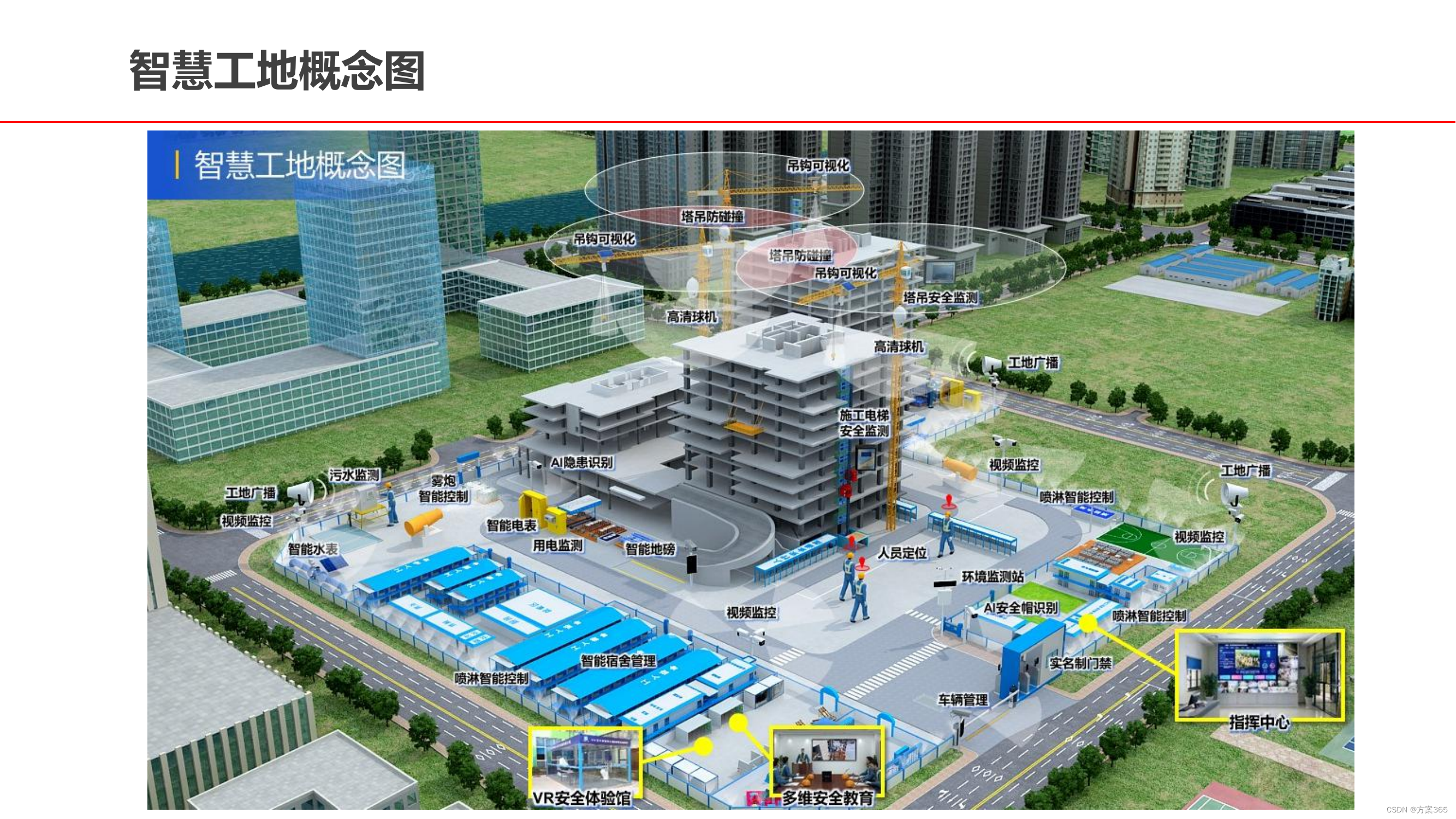
5G智慧工地整体解决方案:文件全文115页,附下载
关键词:5G智慧工地,智慧工地建设方案,智慧工地管理平台系统,智慧工地建设调研报告,智慧工地云平台建设 一、5G智慧工地建设背景 5G智慧工地是利用5G技术、物联网、大数据、云计算、AI等信息技术,围绕“人…...

数据结构 / 内存的动态申请和释放
1.内存的动态申请 malloc malloc 的头文件: #include <stdlib.h>格式: void *malloc(size_t size);参数: size_t size: 申请堆区内存大小, 单位是字节;size_t: 是数据类型, 是 unsigned long的宏定义的别名;返回值: void *: 通用类型指针,使用时需要强转为具…...

Android手电筒、闪光灯、torch、flash
1. 仅开启手电筒 单纯的开启手电筒我们可以使用CameraManager的.setTorchMode()方法。 cameraCharacteristics.get(CameraCharacteristics.FLASH_INFO_AVAILABLE)获取该相机特征是否可获取闪光灯。 CameraManager cameraManager (CameraManager) getSystemService(CAMERA_SE…...

C语言--每日选择题--Day26
第一题 1.在C语言中,表示一次性地给数组a的10元素赋值() int a[10];scanf("%d",a); A:正确 B:错误 答案及解析 B 我们知道单独的数组名就是首元素地址,但是也有…...

[ACTF2020 新生赛]BackupFile
打开题目就一句话:尝试找到源文件 和上一题一样,用dirsearch扫描网站找到了一下内容 flag.php,0B,虚假flag 瞅一眼index.php.bak是啥 下载了一个文件,把bak后缀删掉,打开了index.php源码 is_numeric()&am…...

WPF面试题:WPF绘图技术介绍
作者:令狐掌门 技术交流QQ群:675120140 csdn博客:https://mingshiqiang.blog.csdn.net/ 文章目录 WPF绘图基本用法绘制直线在XAML中绘制直线在C#代码中绘制直线使用Path绘制直线注意矩形绘制在XAML中绘制矩形在C#代码中绘制矩形设置矩形的位置使用圆角矩形画刷1. SolidColor…...
三、Lua变量
文章目录 一、变量分类二、变量赋值三、索引 一、变量分类 lua变量分为全局变量,局部变量。 全局变量:默认,全局有效。 局部变量:从作用范围开始到作用范围结束,需加local 修饰。 a1function ff()local b1 endprint(a…...
UE5 学习系列(二)用户操作界面及介绍
这篇博客是 UE5 学习系列博客的第二篇,在第一篇的基础上展开这篇内容。博客参考的 B 站视频资料和第一篇的链接如下: 【Note】:如果你已经完成安装等操作,可以只执行第一篇博客中 2. 新建一个空白游戏项目 章节操作,重…...

<6>-MySQL表的增删查改
目录 一,create(创建表) 二,retrieve(查询表) 1,select列 2,where条件 三,update(更新表) 四,delete(删除表…...
)
进程地址空间(比特课总结)
一、进程地址空间 1. 环境变量 1 )⽤户级环境变量与系统级环境变量 全局属性:环境变量具有全局属性,会被⼦进程继承。例如当bash启动⼦进程时,环 境变量会⾃动传递给⼦进程。 本地变量限制:本地变量只在当前进程(ba…...
)
椭圆曲线密码学(ECC)
一、ECC算法概述 椭圆曲线密码学(Elliptic Curve Cryptography)是基于椭圆曲线数学理论的公钥密码系统,由Neal Koblitz和Victor Miller在1985年独立提出。相比RSA,ECC在相同安全强度下密钥更短(256位ECC ≈ 3072位RSA…...
Appium+python自动化(十六)- ADB命令
简介 Android 调试桥(adb)是多种用途的工具,该工具可以帮助你你管理设备或模拟器 的状态。 adb ( Android Debug Bridge)是一个通用命令行工具,其允许您与模拟器实例或连接的 Android 设备进行通信。它可为各种设备操作提供便利,如安装和调试…...

抖音增长新引擎:品融电商,一站式全案代运营领跑者
抖音增长新引擎:品融电商,一站式全案代运营领跑者 在抖音这个日活超7亿的流量汪洋中,品牌如何破浪前行?自建团队成本高、效果难控;碎片化运营又难成合力——这正是许多企业面临的增长困局。品融电商以「抖音全案代运营…...

376. Wiggle Subsequence
376. Wiggle Subsequence 代码 class Solution { public:int wiggleMaxLength(vector<int>& nums) {int n nums.size();int res 1;int prediff 0;int curdiff 0;for(int i 0;i < n-1;i){curdiff nums[i1] - nums[i];if( (prediff > 0 && curdif…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个医院查看报告小程序
一、开发环境准备 工具安装: 下载安装DevEco Studio 4.0(支持HarmonyOS 5)配置HarmonyOS SDK 5.0确保Node.js版本≥14 项目初始化: ohpm init harmony/hospital-report-app 二、核心功能模块实现 1. 报告列表…...
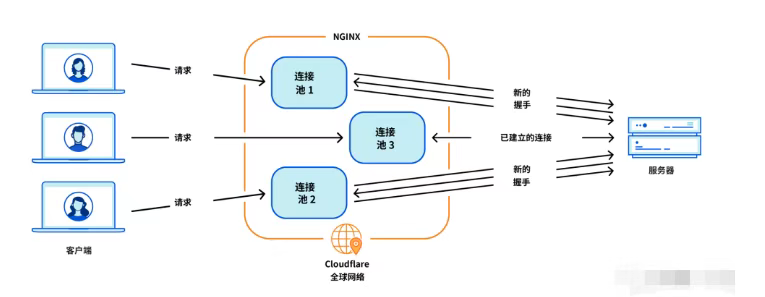
Cloudflare 从 Nginx 到 Pingora:性能、效率与安全的全面升级
在互联网的快速发展中,高性能、高效率和高安全性的网络服务成为了各大互联网基础设施提供商的核心追求。Cloudflare 作为全球领先的互联网安全和基础设施公司,近期做出了一个重大技术决策:弃用长期使用的 Nginx,转而采用其内部开发…...

用机器学习破解新能源领域的“弃风”难题
音乐发烧友深有体会,玩音乐的本质就是玩电网。火电声音偏暖,水电偏冷,风电偏空旷。至于太阳能发的电,则略显朦胧和单薄。 不知你是否有感觉,近两年家里的音响声音越来越冷,听起来越来越单薄? —…...
