java中的方法引用和Stream流
知识模块: 一.方法引用a.方法概述b.方法引用格式 二.Stream流1.Stream流概述2.Stream流操作步骤一.方法引用a.方法概述/*方法引用概述:当我们使用已有类中的方法作为Lambda表达式对应的接口中的抽象方法实现我们可以用方法引用来简化Lambda表达式*/
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.function.Consumer;/*方法引用概述:当我们使用已有类中的方法作为Lambda表达式对应的接口中的抽象方法实现我们可以用方法引用来简化Lambda表达式*/
public class MethodRef01 {@Testpublic void test01() {Consumer<String> c = str -> System.out.println(str);c.accept("abc");System.out.println(System.out);//java.io.PrintStream@f5f2bb7}@Testpublic void test02() {//Consumer<String> c = str -> System.out.println(str);Consumer<String>c=System.out::println; //System.out代表了我们要引用的类//::后面的println代表我们引用的方法c.accept("abc");}}
/*class MethodRefDemo$$Lambda$1 implements Consumer<sTRING>{public void accept(String str){System.out.println(str);//我们使用是PrintStream类中的println(String str)方法//作为str->System.out.println(str)对应的Consumer<String>//中accept(String str)的实现}}*/
b.方法引用格式方法引用使用的前提:(适用于1,2)引用的方法和Lambda表达式对应接口中的抽象方法中的形参类型保持一致
1.成员方法引用a.引用非静态成员方法/*非静态成员引用对象名::方法名*/
import java.util.Objects;public class Person {private String name;public Person(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +'}';}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (!(o instanceof Person person)) return false;return name.equals(person.name);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(name);}
}
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Supplier;/*方法引用使用的前提:引用的方法和Lambda表达式对应接口中的抽象方法中的形参类型保持一致非静态成员引用对象名::方法名*/
public class MethodRefDemo02 {Person p = new Person("老王");@Testpublic void test01() {//Supplier<String >s=()->p.getName();Supplier<String> s = p::getName;System.out.println(s.get());}@Testpublic void test02() {//Consumer<String> c = name -> p.setName(name);Consumer<String>c=p::setName;c.accept("老李");System.out.println(p);}@Testpublic void test03() {String str = "abc";//Supplier<Integer> s = () -> str.length();Supplier<Integer> s = str::length;System.out.println(s.get());}@Testpublic void test04() {String str = "abc";//Supplier<Character> s = () -> str.charAt(1);/* Supplier<Character>s=str::charAt; //一个有参,一个无参,不能简化System.out.println(s.get());*/}
}
b.引用静态成员方法/*静态方法引用类名::静态方法名Arrays,CollectionsArrays类中static String toString(int[] a)返回指定数组内容的字符串表示形式。Collections类public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List<T> list)根据元素的自然顺序 对指定列表按升序进行排序*/
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Function;/*静态方法引用类名::静态方法名Arrays,CollectionsArrays类中static String toString(int[] a)返回指定数组内容的字符串表示形式。Collections类public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List<T> list)根据元素的自然顺序 对指定列表按升序进行排序*/
public class MethodRefDemo03 {@Testpublic void test01() {int[] arr = {3, 7, 9};//Function<int[], String> f = array -> Arrays.toString(array);Function<int[],String>f=Arrays::toString;System.out.println(f.apply(arr));}@Testpublic void test02() {List<Integer> integers = Arrays.asList(1, 7, 12, 5, 23);//Consumer<List<Integer>> c = list -> Collections.sort(list);Consumer<List<Integer>> c = Collections::sort;c.accept(integers);System.out.println(integers);}
}
2.构造方法引用/*构造方法引用格式:类名::new*/
3.数组对象引用数组对象引用格式类型[]::new
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.function.Function;/*构造方法引用格式:类名::new数组对象引用格式类型[]::new*/
public class MethodRefDemo04 {@Testpublic void test01() {//创建一个Person类的对象,获取这个对象//Function<String, Person> f = name -> new Person(name);Function<String, Person> f = Person::new;System.out.println(f.apply("三丰"));}@Testpublic void test02() {//创建一个指定长度的数组,返回这个数组对象//Function<Integer, int[]> f = n -> new int[n];Function<Integer, int[]> f=int[]::new;System.out.println(f.apply(4).length);}
}
4.特殊的非静态方法/*特殊的非静态方法的引用格式:类名::非静态方法名***1.不再适用于放啊引用的前提条件2.当Lambda表达式第一个参数,作为实例(非静态)方法的调用者,第二个参数作为实例对象的参数,可以受用 类名::非静态方法名3.当Lambda表达式的参数作为一个空参实例方法的调用者时候,也可使用 类名::非静态方法名*/
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.function.BiPredicate;
import java.util.function.Function;/*特殊的非静态方法的引用格式:类名::非静态方法名1.不再适用于放啊引用的前提条件2.当Lambda表达式第一个参数,作为实例(非静态)方法的调用者,第二个参数作为实例对象的参数,可以受用 类名::非静态方法名3.当Lambda表达式的参数作为一个空参实例方法的调用者时候,也可使用 类名::非静态方法名*/
public class MethodRefDemo05 {@Testpublic void test01() {Person p1 = new Person("老王");Person p2 = new Person("老李");//BiPredicate<Person, Person> bp = (person1, person2) -> person1.equals(person2);BiPredicate<Person, Person> bp = Person::equals;System.out.println(bp.test(p1, p2));}@Testpublic void test02() {Person p1 = new Person("老王");//Function<Person, String> f = person -> person.getName();Function<Person, String> f = Person::getName;System.out.println(f.apply(p1));}
}
二.Stream流1.Stream流概述Strean流的出现是为了增强集合和数组的操作,Stream流更专注于数据的转换,过滤,获取等一系列操作同时Stream流提高了操作集合和数组的小笼包,简化了代码
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;/*Stream流的概述统计后缀名为.txt文件名称的个数*/
public class StreamDemo01 {@Testpublic void test01() {ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<String>();al.add("1.txt");al.add("2.txt");al.add("3.pdf");al.add("4.docx");int count=0;for (String s : al) {if (s.endsWith(".txt")) {count++;}}System.out.println(count);}@Testpublic void test02() {List<String> list = Arrays.asList("1.txt", "2.txt", "3.pdf", "4.docx");/*long count = list.stream().filter(str -> str.endsWith(".txt")).count();System.out.println(count);*/System.out.println(list.stream().filter(str -> str.endsWith(".txt")).count());}
}
2.Stream流操作步骤1.根据数据源获取一个Stream对象/*集合或数组流对象的获取集合:Collection体系:都是通过Stream()方法来获取一个流对象ListSetMap体系: 需要转换到Collection体系的集合,才能调用stream()方法获取一个流对象HashMap数组:static <T> Stream<T> of(T... values)返回一个元素为指定值的顺序排列的流。*/
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.stream.Stream;/*集合或数组流对象的获取集合:Collection体系:都是通过Stream()方法来获取一个流对象ListSetMap体系: 需要转换到Collection体系的集合,才能调用stream()方法获取一个流对象HashMap数组:static <T> Stream<T> of(T... values)返回一个元素为指定值的顺序排列的流。*/
public class StreamDemo02 {@Testpublic void test01() {Stream<Stream> stream1 = new ArrayList<Stream>().stream();//Stream流上的泛型和集合中元素的类型相对应//当我们通过集合对象来调用stream()方法,相当于//将集合中的元素添加到Stream流中等待操作Stream<Integer> stream2 = new HashSet<Integer>().stream();//Stream流上的泛型和集合中元素的类型相对应}@Testpublic void test02() {new HashMap<Integer,Stream>().keySet().stream();//需要将Map转换成Collection体系的集合,就可以使用stream()方法获取流对象//将一个个key添加到stream中new HashMap<Integer,String>().entrySet().stream();//将一个entry对象{key=value}添加到stream流中}@Testpublic void test03() {int[] arr = {1, 3, 9};Stream<int[]> stream1 = Stream.of(arr);//如果通过基本类型数组获取一个流对象,此时六种只有一个元素:这个数组对象Integer[] arr2 = {1, 3, 9};Stream<Integer> stream2 = Stream.of(arr2);//我们通过基本类型对应的包装类的引用类型数组,获取流对象,此时相当于将数组中的元素添加到流中Stream<String> stream3 = Stream.of("abc", "def", "ghk");//通过一串数据获取流对象Stream<Integer> stream4 = Stream.of(3, 5, 7);}
}2.通过Stream对象可以进行0次或多次中间操作/*中间操作:过滤操作filter:传入一个Predicate,根据Predicate中的条件对流中的元素做一个筛选,满足条件保留,不满足的剔除排序操作:sorted:可以根据指定的规则,将流中的元素从小到大排序去重操作distinct:去除流中重复的元素截取操作limit:根据传入的值,来决定截取流总元素的个数skip: 根据传入的值,决定跳过流中的元素个数映射操作map:讲义中数据根据指定操作映射成另一种数据mapToIntmapToDoublemapToLong*/
public class Student {//学生姓名private String name;//语文成绩private double chineseScore;//数学成绩private double mathScore;public Student(String name, double chineseScore, double mathScore) {this.name = name;this.chineseScore = chineseScore;this.mathScore = mathScore;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public double getChineseScore() {return chineseScore;}public void setChineseScore(double chineseScore) {this.chineseScore = chineseScore;}public double getMathScore() {return mathScore;}public void setMathScore(double mathScore) {this.mathScore = mathScore;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", chineseScore=" + chineseScore +", mathScore=" + mathScore +'}';}
}
/*中间操作:过滤操作filter:传入一个Predicate,根据Predicate中的条件对流中的元素做一个筛选,满足条件保留,不满足的剔除排序操作:sorted:可以根据指定的规则,将流中的元素从小到大排序去重操作distinct:去除流中重复的元素截取操作limit:根据传入的值,来决定截取流总元素的个数skip: 根据传入的值,决定跳过流中的元素个数映射操作map:讲义中数据根据指定操作映射成另一种数据mapToIntmapToDoublemapToLong班级中有5个人姓名,语文成绩,数学成绩分别如下李雷, 70, 90韩梅梅, 30, 100李宁, 85, 80王松,70,60张家界,90,73需求:1.打印语文成绩>80的学生信息2.打印数学成绩前三名的学生信息3.打印数学成绩倒数第一和倒数第二的学生信息4.获取全班数学的平均成绩5.获取全班语文成绩(不包含重复成绩)6.将语文成绩或数学成绩在[80,90]之间的学生的姓名收集到一个集合中*/import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class StreamDemo04 {//@Before会在所有的@Test注解之前执行List<Student> students;@Beforepublic void init() {//初始化数据源students= Arrays.asList(new Student("李雷", 70, 90),new Student("韩梅梅", 30, 100),new Student("李宁", 85, 80),new Student("王松", 70, 60),new Student("张家界", 90, 73));}@Testpublic void test02() {//1.打印语文成绩>80的学生信息students.stream().filter(stu -> stu.getChineseScore() > 80).forEach(System.out::println);}@Testpublic void test03() {//2.打印数学成绩前三名的学生信息/*a.首先需要对学生的成绩从大到小排序b.获取前三名的信息*/students.stream().sorted((stu1,stu2)->(int)(stu2.getMathScore()-stu1.getMathScore())).limit(3)//截取流中的前三个元素.forEach(System.out::println);}@Testpublic void test04() {// 3.打印数学成绩倒数第一和倒数第二的学生信息/*a.首先需要对学生的数学成绩从大到小排序b.获取倒数第一和倒数第二*/students.stream().sorted((stu1, stu2) -> (int) (stu2.getMathScore() - stu1.getMathScore())).skip(students.size() - 2).forEach(System.out::println);}@Testpublic void test05() {//4.获取全班数学的平均成绩//将流中的以恶搞个学生对象映射成每个学生对应的数学成绩double avgScore = students.stream().mapToDouble(stu -> stu.getMathScore()).average().getAsDouble();System.out.println(avgScore);}@Testpublic void test06() {// 5.获取全班语文成绩(不包含重复成绩)// 需要使用mapToDouble//students.stream().mapToDouble(stu->stu.getChineseScore()).distinct().forEach(System.out::println);//students.stream().map(stu->stu.getChineseScore()).distinct().forEach(System.out::println);students.stream().map(Student::getChineseScore).distinct().forEach(System.out::println);}@Testpublic void test07() {// 6.将语文成绩或数学成绩在[80,90]之间的学生的姓名收集到一个集合中//a.语文成绩在[80,90]之间的学生(Predicate) 或者 数学成绩在[80,90]之间(Predicate)//b.将过滤后的一个个学生对象映射成一个个学生姓名//c.将过滤和映射中间操作后的数据收集到以恶搞集合中Predicate<Student>p1=stu->stu.getChineseScore()>=80&&stu.getChineseScore()<=90;Predicate<Student>p2=stu->stu.getMathScore()>=80&&stu.getMathScore()<=90;List<String> names = students.stream().filter(p1.or(p2)).map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(names);}
}
3.进行一次最终操作获取最终结果/*Stream流的最终操作:1.迭代forEach:逐个消费流中的元素2.统计count:统计流中元素的个数max :按照一定比较规则(Comparator接口实现规则),来获取流中最大元素min :按照一定比较规则(Comparator接口实现规则),来获取流中最小元素3.查找findFirst4.匹配allMatch:只有流中所有的元素都满足Predicate(条件),allMatch方法才返回true,否则返回falseanyMatch:只有流中有一个元素满足Predicate(条件),anyMatch方法才返回true,否则返回falsenoneMatch:只有流中所有的元素都不满足Predicate(条件),noneMatch方法才返回true,否则返回false5.收集collect:我们可以将最终操作结果收集到一个集合(List,Set,Map)我们主要通过Collections.toList(),Collections.toSet(),Collections.toMap(),将最终操作结果收集到不同集合中中间操作:sorted*/
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;/*Stream流的最终操作:1.迭代forEach:逐个消费流中的元素2.统计count:统计流中元素的个数max :按照一定比较规则(Comparator接口实现规则),来获取流中最大元素min :按照一定比较规则(Comparator接口实现规则),来获取流中最小元素3.查找findFirst4.匹配allMatch:只有流中所有的元素都满足Predicate(条件),allMatch方法才返回true,否则返回falseanyMatch:只有流中有一个元素满足Predicate(条件),anyMatch方法才返回true,否则返回falsenoneMatch:只有流中所有的元素都不满足Predicate(条件),noneMatch方法才返回true,否则返回false5.收集collect:我们可以将最终操作结果收集到一个集合(List,Set,Map)我们主要通过Collections.toList(),Collections.toSet(),Collections.toMap(),将最终操作结果收集到不同集合中中间操作:sorted*/
public class StreamDemo03 {List<String> list = Arrays.asList("zhangsan", "lisi", "laowang");@Testpublic void test01() {//list.stream().forEach(str-> System.out.println(str));list.stream().forEach(System.out::println);}@Testpublic void test02() {long count = list.stream().count();System.out.println(count);}@Testpublic void test03() {list.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);//字符串的默认排序方式是字典顺序System.out.println("------------");/*Comparator接口的int compare(T o1, T o2);如果compare方法返回一个正数,默认为o1>o2如果compare方法返回一个负数,默认为o1<o2如果compare方法返回0,默认为o1=o2sorted方法默认按照元素从小到大排序比较流程:str1="lisi"str2="zhangsan"str1.length() - str2.length()<0 => "lisi"<"zhangsan"第二种情况:str2.length() - str1.length() >0 =>"lisi">"zhangsan"str1="laowang"str2="zhangsan"str1.lemgth() - str2.length() => "laowang"<"zhangsan"第二种情况: str2.length() - str1.length()>0 =>"laowang">"zhangsan"str1="laowang"str2="lisi"str1.length() - str2.length() => "laiwang">"lisi"第二种情况: str2.length() - str1.length()<0 => "laowang"<"kisi"最终结果: list<laowang<zhangsan第二种情况最终结果: zhangsan<laowang<lisi*/list.stream().sorted((str1, str2) -> str1.length() - str2.length()).forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("-------------------");list.stream().sorted((str1, str2) -> str2.length() - str1.length()).forEach(System.out::println);}//List<String> list = Arrays.asList("zhangsan", "lisi", "laowang");@Testpublic void test04() {//获取最大长度的字符串System.out.println(list.stream().max((str1, str2) -> str1.length() - str2.length()).get());//获取最小长度字符串System.out.println(list.stream().min((str1, str2) -> str1.length() - str2.length()).get());}@Testpublic void test05() {System.out.println(list.stream().findFirst().get());}@Testpublic void test06() {System.out.println(list.stream().allMatch(str -> str.length() > 4));//falseSystem.out.println(list.stream().anyMatch(str -> str.length() > 4));//trueSystem.out.println(list.stream().noneMatch(str -> str.length() > 4));//true}@Testpublic void test07() {Stream<String> stream = list.stream();List<String> l = stream.collect(Collectors.toList());//将流中的数据收集到List集合中System.out.println(l.getClass());System.out.println(l.size());}@Testpublic void test08() {Set<String> set = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());System.out.println(set);}@Testpublic void test09() {//将字符串的长度作为ley,字符串的值作为value去构造一个mapMap<Integer, String> map = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(str -> str.length(), str -> str));System.out.println(map);}
}
相关文章:

java中的方法引用和Stream流
知识模块: 一.方法引用a.方法概述b.方法引用格式 二.Stream流1.Stream流概述2.Stream流操作步骤一.方法引用a.方法概述/*方法引用概述:当我们使用已有类中的方法作为Lambda表达式对应的接口中的抽象方法实现我们可以用方法引用来简化Lambda表达式*/impor…...
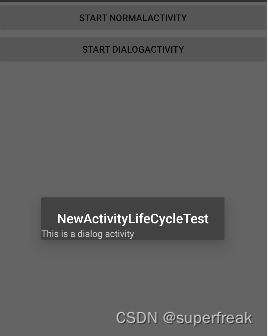
《第一行代码:Android》第三版-3.4.4体验Activity的生命周期
本文的代码是在主Activity中,重载了几个生命周期函数,在日志中打印出对应的日志信息,有两个按钮,负责启动另外的Activity,并回到主Activity 由此查看日志,来体会生命周期。 MainActivity.kt 文件如下 pac…...

用java编写一个网络聊天室
网络聊天室 服务器: 1.启动服务器,在服务器端循环监听客户端的连接 try {ServerSocket serverSocketnew ServerSocket(6622);System.out.println("服务器已启动");while(true){//把客户端实例添加到sockets里Socket socketserverSocket.acc…...

Opencv颜色追踪
废话不多说直接上代码!! # 这是一个示例 Python 脚本。 import cv2 import numpy as npdef track_object():# 打开摄像头外接cap cv2.VideoCapture(0)while True:# 读取摄像头帧# ret(Return Value)是一个布尔值,表示…...
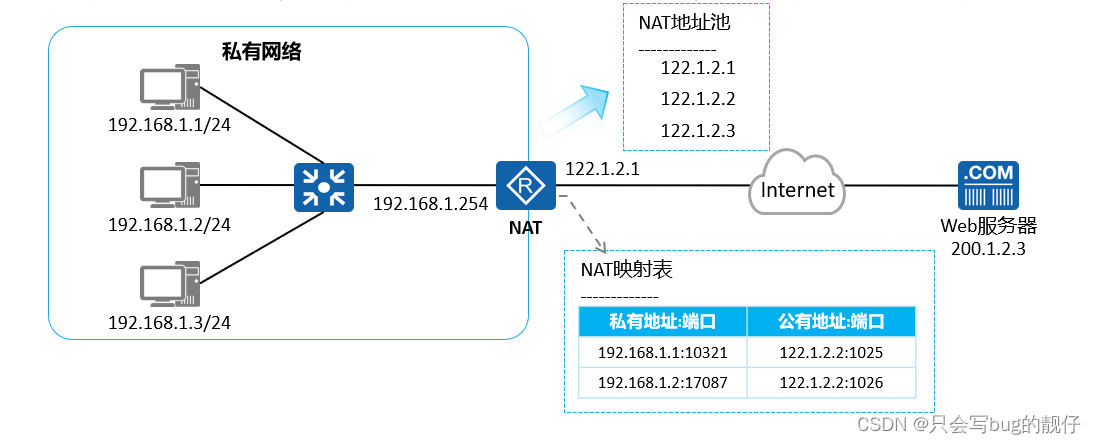
计算机网络——网络可靠性及网络出口配置
1. 前言: 学习目标: 1.了解链路聚合的作用 2. 了解ACL的工作原理 3. 了解NAT的工作原理和配置 2. 网络可靠性方案 网络可靠性是指网络在面对各种异常情况或故障时,能够维持正常运行和提供服务的能力。这包括防止网络中断、减小数据丢失的可能…...
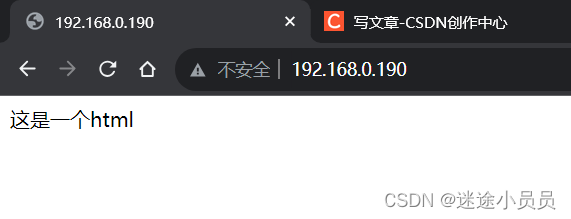
在虚拟机搭建nignx,和使用本地访问nginx的情况
下载nginx yum install nginx 查看nginx是否安装成功。 nginx -v nginx的配置文件的目录和资源的目录。 先到nginx.conf的目录下,在 /etc/nginx/nginx.conf,编辑它。 vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf 可以看到默认的html的目录。在 /usr/share/nginx/html 下面…...
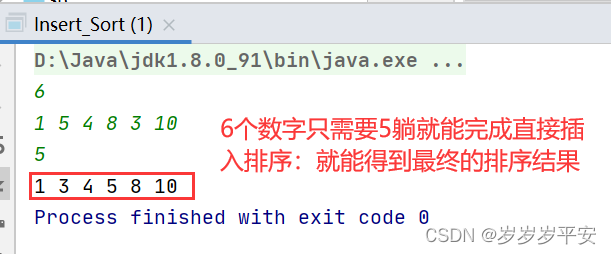
Java数据结构之《直接插入排序》问题
一、前言: 这是怀化学院的:Java数据结构中的一道难度中等的一道编程题(此方法为博主自己研究,问题基本解决,若有bug欢迎下方评论提出意见,我会第一时间改进代码,谢谢!) 后面其他编程题只要我写完…...

向量场中的几个恒等式
向量场中的几个恒等式 1. ∇ 2 A ∇ ∇ ⋅ A − ∇ ∇ A \nabla ^2 A \nabla \nabla\cdot A-\nabla \times\nabla\times A ∇2A∇∇⋅A−∇∇A 2. ∇ ⋅ ∇ A 0 \nabla \cdot \nabla \times A 0 ∇⋅∇A0 3. ∇ ∇ ϕ 0 \nabla \times \nabla \phi0 ∇∇ϕ0...
)
异行星低代码平台--第三方插件对接:钉钉平台对接(一)
异行星低代码平台可以集成钉钉,实现单点登录、消息推送和组织机构同步。 提示 此功能需要企业版授权才能使用。 钉钉集成 单点登录 异行星低代码平台集成到钉钉后,只要使用钉钉账户登录钉钉客户端,即可在钉钉中直接使用管理后台&#…...

MyBatis使用教程详解<下>
回顾上一篇博文,我们讲了如何使用注解/XML的方式来操作数据库,实际上,一个Mapper接口的实现,这两种方式是可以并存的. 上一篇博文中,我们演示的都是比较简单的SQL语句,没有设计到复杂的逻辑,本篇博文会讲解复杂SQL的实现及一些细节处理.话不多说,让我们开始吧. 一. #{}和${} …...
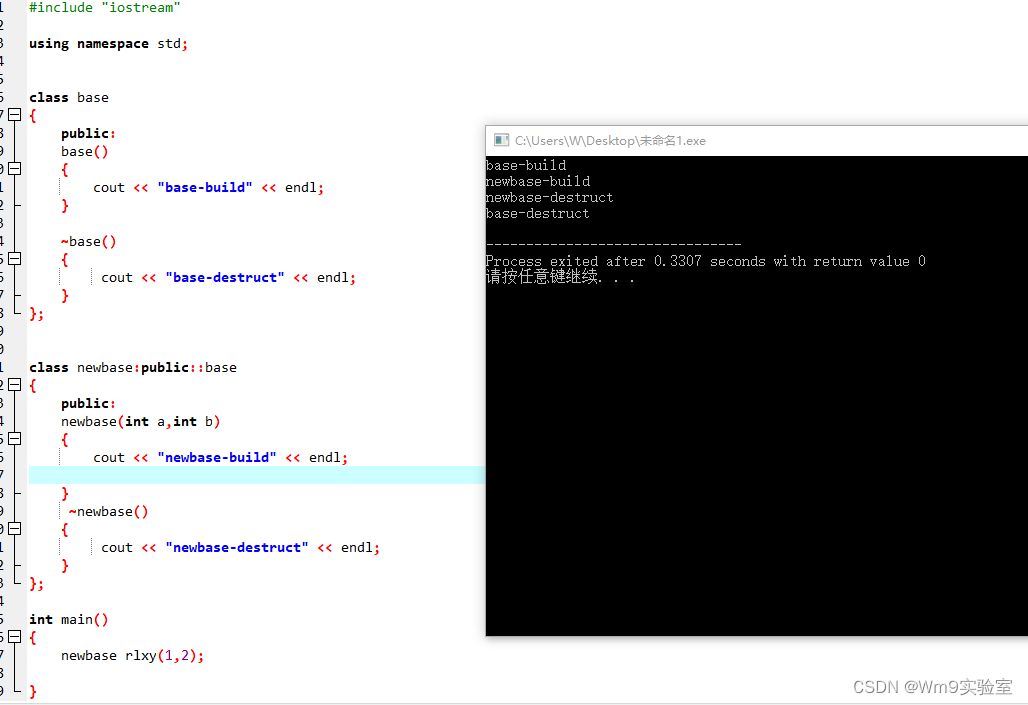
C++基础 -17-继承中 基类与派生构造和析构调用顺序
首先声明 定义了派生类会同时调用基类和派生的构造函数 定义了派生类会同时调用基类和派生的析构函数 那么顺序如何如下图 构造由上往下顺序执行 析构则完全相反 #include "iostream"using namespace std;class base {public:base(){cout << "base-bui…...
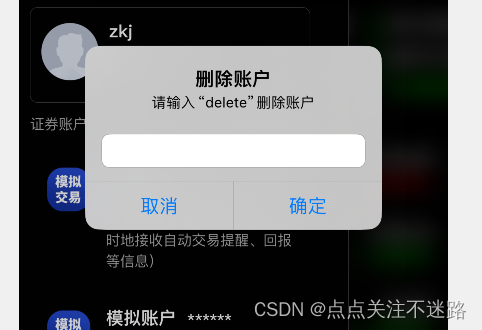
uniapp实现表单弹窗
uni.showModal({title: 删除账户,confirmColor:#3A3A3A,cancelColor:#999999,confirmText:确定,editable:true,//显示content:请输入“delete”删除账户,success: function (res) {console.log(res)if(res.confirm){if(res.contentdelete){console.log(123123123213)uni.setSto…...

Ajax 是什么? 如何创建一个 Ajax?
Ajax(Asynchronous JavaScript and XML)是一种使用客户端JavaScript发送异步HTTP请求到服务器的技术,以便在不重新加载整个页面的情况下更新部分网页内容。 使用Ajax的原因有很多,以下是其中一些: 改善用户体验&…...

【LeetCode】101. 对称二叉树
101. 对称二叉树 难度:简单 题目 给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。 示例 1: 输入:root [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 输出:true示例 2: 输入:root [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 输出&#…...

O-Star|再相识
暑去秋来,岁月如梭,几名"O-Star"们已经入职一段时间,在这期间他们褪去青涩,逐渐适应了公司的工作环境和文化,迈向沉稳~ 为了进一步加深校招生之间的交流与了解,提高校招生的凝聚力和…...
最新PHP熊猫头图片表情斗图生成源码
这是一款能生成熊猫头表情斗图的自适应系统源码,无论是在电脑还是手机上都可以正常使用!这个源码集成了搜狗搜索图片接口,可以轻松地一键搜索数百万张图片,并且还包含了表情制作等功能模块。对于一些新站来说,这是一个…...

子虔科技出席2023WAIC“智能制造融合创新论坛”
7月7日,2023世界人工智能大会(WAIC)闵行会场在大零号湾举办。子虔科技联合创始人周洋作为专家嘉宾受邀参与智能制造融合创新论坛大会。会上探讨了工业和制造业数字化转型的机遇、挑战和对策。其中,周洋提到,工业制造业…...
递归算法学习——二叉树的伪回文路径
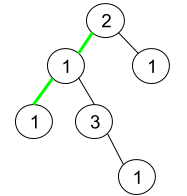
1,题目 给你一棵二叉树,每个节点的值为 1 到 9 。我们称二叉树中的一条路径是 「伪回文」的,当它满足:路径经过的所有节点值的排列中,存在一个回文序列。 请你返回从根到叶子节点的所有路径中 伪回文 路径的数目。 示例…...
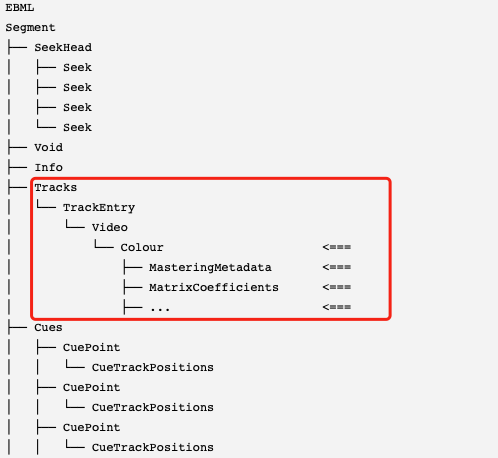
Android端极致画质体验之HDR播放
高动态范围HDR视频通过扩大亮度分量的动态范围(从100cd/m2到1000cd/m2),以及采用更宽的色彩空间BT2020,提供极致画质体验。从Android10开始,支持HDR视频播放。 一、HDR技术 HDR技术标准包括:Dolby-Vision、HDR10、HLG、PQ。支持…...
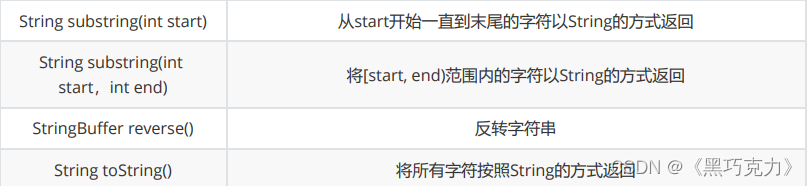
【Java SE】带你在String类世界中遨游!!!
🌹🌹🌹我的主页🌹🌹🌹 🌹🌹🌹【Java SE 专栏】🌹🌹🌹 🌹🌹🌹上一篇文章:带你走近Java的…...
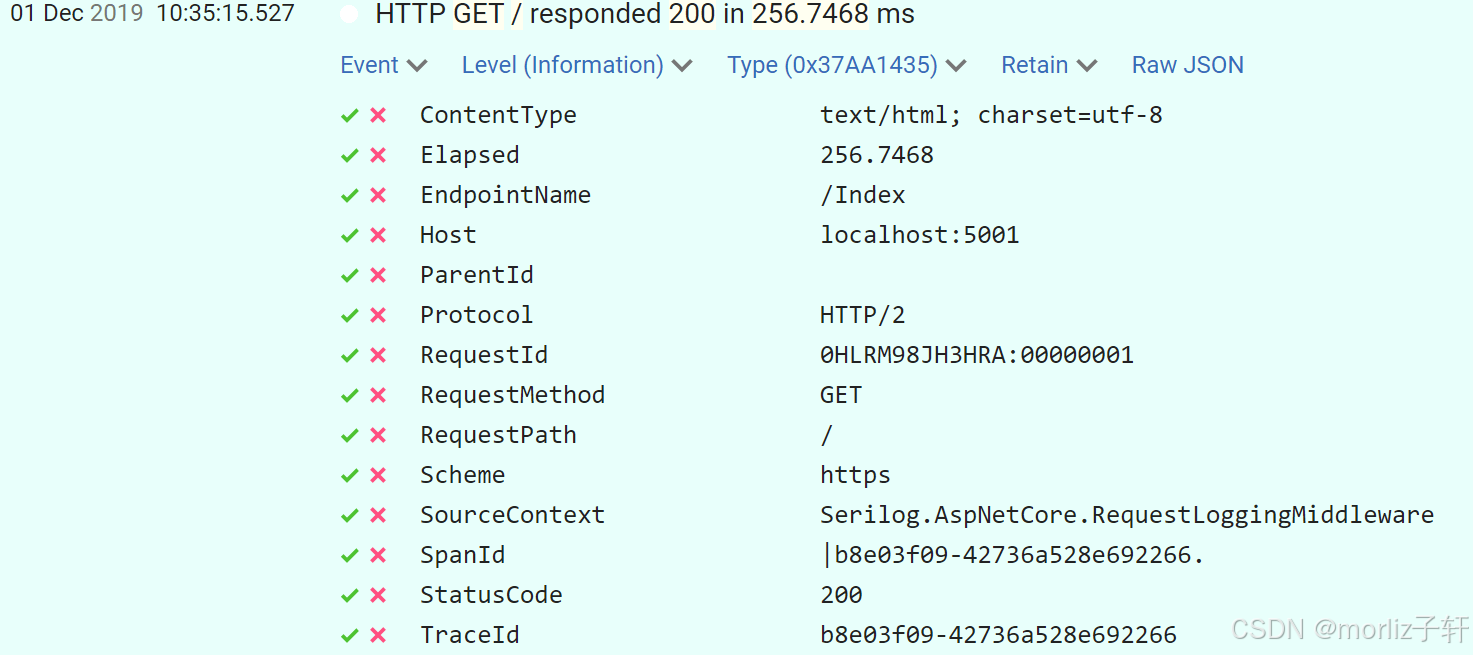
深入浅出Asp.Net Core MVC应用开发系列-AspNetCore中的日志记录
ASP.NET Core 是一个跨平台的开源框架,用于在 Windows、macOS 或 Linux 上生成基于云的新式 Web 应用。 ASP.NET Core 中的日志记录 .NET 通过 ILogger API 支持高性能结构化日志记录,以帮助监视应用程序行为和诊断问题。 可以通过配置不同的记录提供程…...
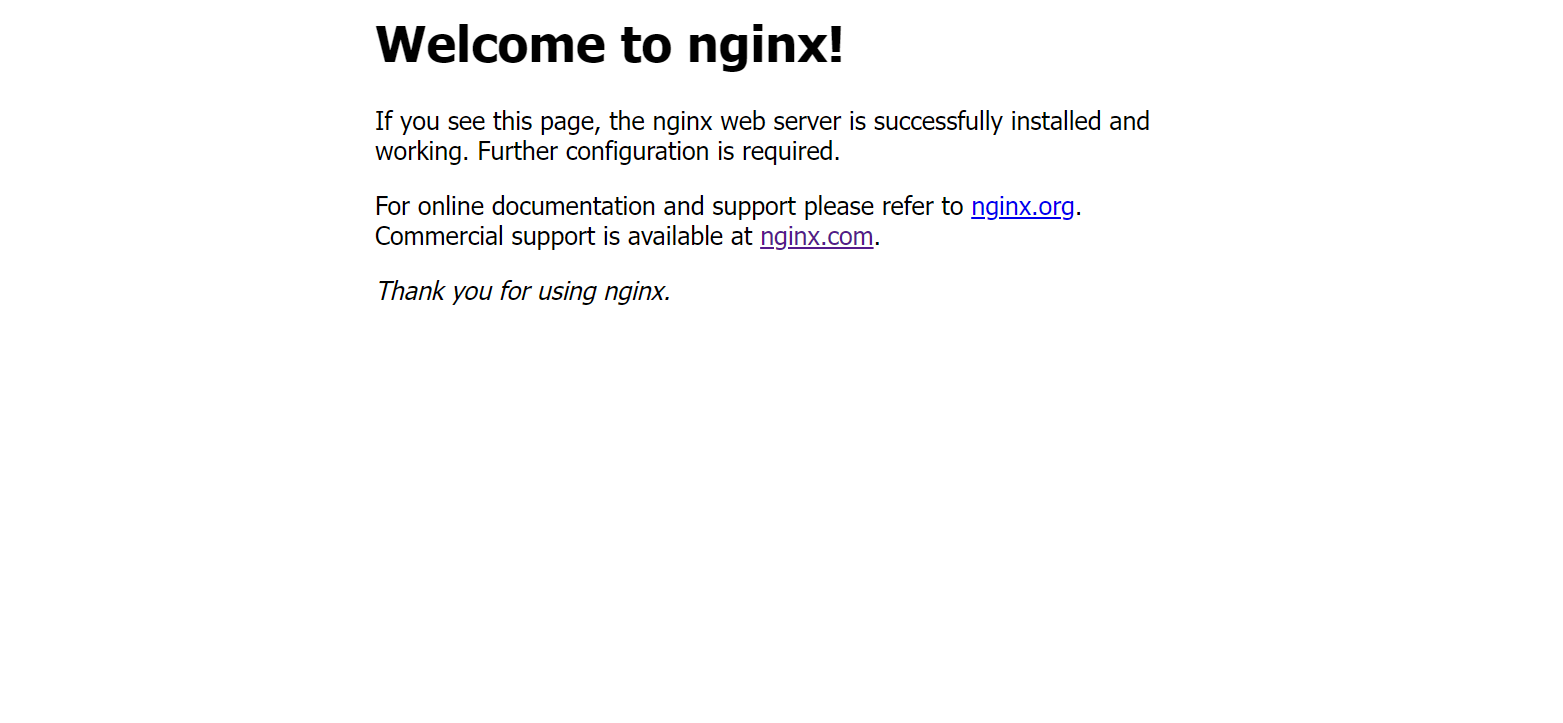
linux之kylin系统nginx的安装
一、nginx的作用 1.可做高性能的web服务器 直接处理静态资源(HTML/CSS/图片等),响应速度远超传统服务器类似apache支持高并发连接 2.反向代理服务器 隐藏后端服务器IP地址,提高安全性 3.负载均衡服务器 支持多种策略分发流量…...

ubuntu搭建nfs服务centos挂载访问
在Ubuntu上设置NFS服务器 在Ubuntu上,你可以使用apt包管理器来安装NFS服务器。打开终端并运行: sudo apt update sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server创建共享目录 创建一个目录用于共享,例如/shared: sudo mkdir /shared sud…...

大型活动交通拥堵治理的视觉算法应用
大型活动下智慧交通的视觉分析应用 一、背景与挑战 大型活动(如演唱会、马拉松赛事、高考中考等)期间,城市交通面临瞬时人流车流激增、传统摄像头模糊、交通拥堵识别滞后等问题。以演唱会为例,暖城商圈曾因观众集中离场导致周边…...
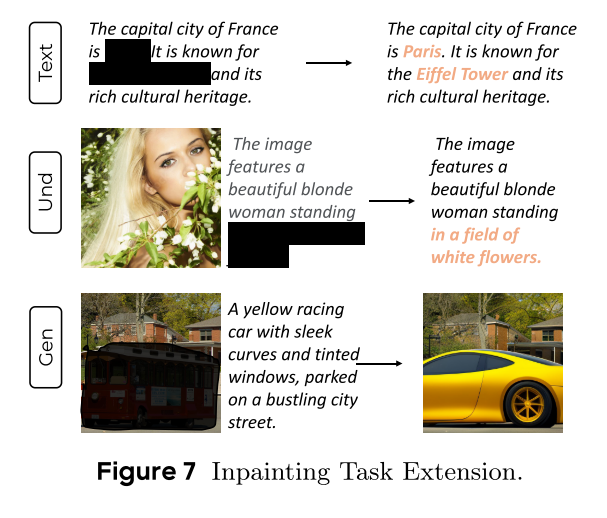
MMaDA: Multimodal Large Diffusion Language Models
CODE : https://github.com/Gen-Verse/MMaDA Abstract 我们介绍了一种新型的多模态扩散基础模型MMaDA,它被设计用于在文本推理、多模态理解和文本到图像生成等不同领域实现卓越的性能。该方法的特点是三个关键创新:(i) MMaDA采用统一的扩散架构…...

Java - Mysql数据类型对应
Mysql数据类型java数据类型备注整型INT/INTEGERint / java.lang.Integer–BIGINTlong/java.lang.Long–––浮点型FLOATfloat/java.lang.FloatDOUBLEdouble/java.lang.Double–DECIMAL/NUMERICjava.math.BigDecimal字符串型CHARjava.lang.String固定长度字符串VARCHARjava.lang…...

数据链路层的主要功能是什么
数据链路层(OSI模型第2层)的核心功能是在相邻网络节点(如交换机、主机)间提供可靠的数据帧传输服务,主要职责包括: 🔑 核心功能详解: 帧封装与解封装 封装: 将网络层下发…...
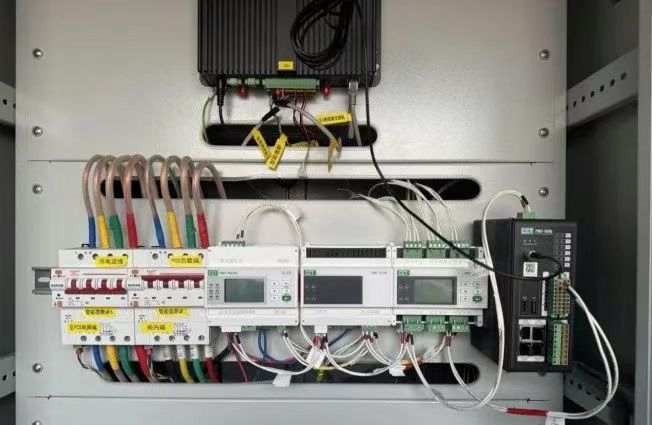
IT供电系统绝缘监测及故障定位解决方案
随着新能源的快速发展,光伏电站、储能系统及充电设备已广泛应用于现代能源网络。在光伏领域,IT供电系统凭借其持续供电性好、安全性高等优势成为光伏首选,但在长期运行中,例如老化、潮湿、隐裂、机械损伤等问题会影响光伏板绝缘层…...

Web 架构之 CDN 加速原理与落地实践
文章目录 一、思维导图二、正文内容(一)CDN 基础概念1. 定义2. 组成部分 (二)CDN 加速原理1. 请求路由2. 内容缓存3. 内容更新 (三)CDN 落地实践1. 选择 CDN 服务商2. 配置 CDN3. 集成到 Web 架构 …...
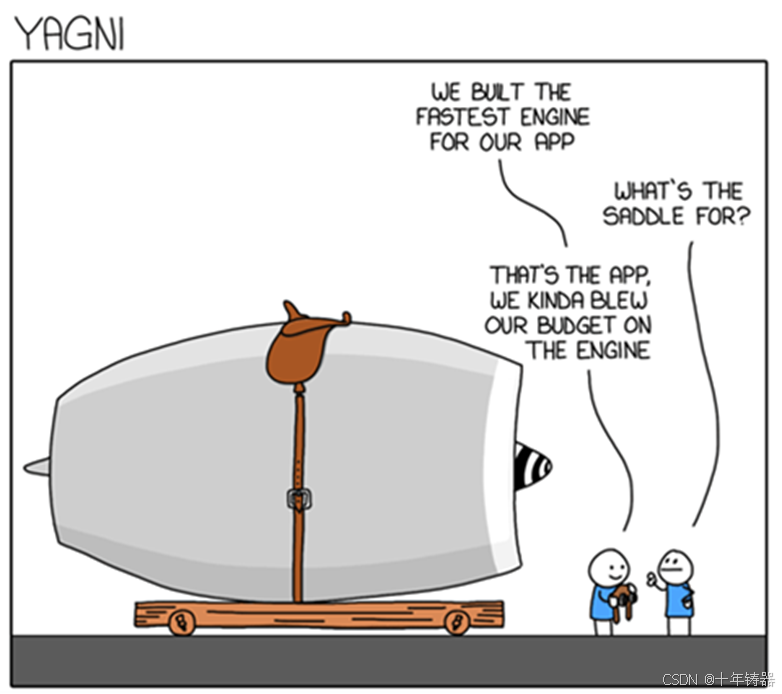
ABAP设计模式之---“简单设计原则(Simple Design)”
“Simple Design”(简单设计)是软件开发中的一个重要理念,倡导以最简单的方式实现软件功能,以确保代码清晰易懂、易维护,并在项目需求变化时能够快速适应。 其核心目标是避免复杂和过度设计,遵循“让事情保…...
