C++——解锁string常用接口
目录
string::npos;
1.测试string容量相关的接口:
1.1 string::size()
1.2 string::clear()
1.3 string::resize()
1.4 string::erase()
1.5 string::reserve() 保留
1.6 std::string::shrink_to_fit
2.string数据插入删除相关的接口
2.1 std::string::push_back 尾插
2.2 std::string::pop_back 尾删
2.3 std::string::insert 插入
3.string查找相关的接口
3.1 std::string::find
3.2 std::string::rfind
3.3string::find_first_of
参数
返回值
3.4 string::find_first_not_of
3.5 string::find_last_of
3.6 string::find_last_not_of
4.string的遍历(含迭代器接口)
4.1 std::string::begin
4.2 std::string::end
4.3 std::string::rbegin
4.4 std::string::rend
5. string 子字符串
5.1 std::string::substr
pos
lens
返回值
例
6.交换和替换string接口
6.1 std::string::replace
参数
6.2 std::string::swap
参数
7.比较赋值string接口
8.获取等效的 C 字符串
8.1 std::string::c_str
9.数字与字符串的转换
9.1 数字转字符串
string::to_string
返回值
例
9.2字符串转数字
std::stoi
参数
例
std::stol (std::stoll)
std::stof
std::stod
std::stold
10.算法中的string运用
10.1交换字符串
10.2反转字符串
本篇的内容是记录使用string接口的测试与使用,方便后续使用时查阅使用
首先介绍
string::npos;
size_t(无符号整型)的最大值。NPOS 是一个静态成员常量值,具有 size_t 类型元素的最大可能值。当此值用作字符串成员函数中 len(或 sublen)参数的值时,表示“直到字符串末尾”。作为返回值,它通常用于指示不匹配。此常量使用值 -1 定义,由于 size_t 是无符号整数类型,因此它是此类型的最大可能可表示值。
引用头文件和展开命名空间
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace1.测试string容量相关的接口:
1.1 string::size()
size_t size() const;字符串的返回长度返回字符串的长度(以字节为单位)。
这是符合字符串内容的实际字节数,不包括'\0',不一定等于其存储容量。
请注意,对象在处理字节时不知道最终可能用于对其包含的字符进行编码的编码。因此,返回的值可能与多字节或可变长度字符序列(如 UTF-8)中编码字符的实际数目不对应。string::size 和 string::length 都是同义词,返回相同的值。
string// string::size #include <iostream> #include <string>int main () {std::string str ("Test string");std::cout << "The size of str is " << str.size() << " bytes.\n";return 0; }
输出:
The size of str is 11 bytes
1.2 string::clear()
void clear();清除字符串擦除字符串的内容,该字符串将变为空字符串(长度为 0 个字符)。
其实就是将s中的字符串清空,注意清空时只是将size清0,不改变底层空间的大小
1.3 string::resize()
void resize (size_t n); void resize (size_t n, char c);● 如果 n 小于当前字符串长度,则当前值将缩短为其前 n 个字符,并删除第 n 个字符以外的字符。 ● 如果 n 大于当前字符串长度,则通过在末尾插入任意数量的字符来扩展当前内容,以达到 n 的大小。 ● 如果指定了 c,则新元素将初始化为 c 的副本,否则,它们是值初始化的字符(null 字符)void Teststring1() {// 注意:string类对象支持直接用cin和cout进行输入和输出string s("hello, zjc!!!");cout << s.size() << endl;cout << s.length() << endl;cout << s.capacity() << endl;cout << s << endl;// 将s中的字符串清空,注意清空时只是将size清0,不改变底层空间的大小s.clear();cout << s.size() << endl;cout << s.capacity() << endl;// 将s中有效字符个数增加到10个,多出位置用'a'进行填充// “aaaaaaaaaa”s.resize(10, 'a');cout << s.size() << endl;cout << s.capacity() << endl;//将s中有效字符个数增加到15个,多出位置用缺省值'\0'进行填充//”aaaaaaaaaaa\0\0“//注意此时s中有效个数已经增加到15个s.resize(15);cout << s.size() << endl;cout << s.capacity() << endl;cout << s << endl;//将s中有效数字符缩小到5个s.resize(5);cout << s.size() << endl;cout << s.capacity() <<endl;cout << s << endl;}
1.4 string::erase()
erase()函数用于从字符串中删除指定位置或指定范围的字符。它可以接受一个参数或两个参数。
1.当传递一个参数时,表示从指定位置开始删除到字符串的末尾的所有字符。
2.当传递两个参数时,表示从指定位置开始删除指定数量的字符。
3.l调用erase()后,字符串的长度会相应地减少,并且内存空间也可能会被重新分配以适应新的长度。
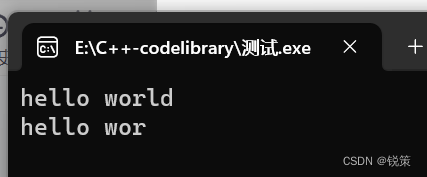
void Teststring2() {//clear()函数用于清空字符串的内容,将字符串变为空字符串,即不包含任何字符。//调用clear()后,字符串的长度将变为0,但内存空间不会被释放,仍然保留着。string s1("hello wolrd"); s1.clear();cout << "s1: " << s1 <<endl;cout << s1.size()<<endl<< s1.capacity()<<endl;//erase()函数用于从字符串中删除指定位置或指定范围的字符。它可以接受一个参数或两个参数。//当传递一个参数时,表示从指定位置开始删除到字符串的末尾的所有字符。string s2("hello wolrd");s2.erase(4);cout << "s2: " << s2 <<endl;cout << s2.size()<<endl<< s2.capacity()<<endl; //当传递两个参数时,表示从指定位置开始删除指定数量的字符。//调用erase()后,字符串的长度会相应地减少,并且内存空间也可能会被重新分配以适应新的长度。string s3("hello wolrd");s3.erase(7,3);cout << "s3: " << s3 <<endl;cout << s3.size()<<endl<< s3.capacity(); }
1.5 string::reserve() 保留
void reserve (size_t n = 0);请求更改容量请求使字符串容量适应计划的大小更改,长度不超过 n 个字符。
如果 n 大于当前字符串容量,则该函数会导致容器将其容量增加到 n 个字符(或更大(具体看编译器的设定))。
在所有其他情况下,它被视为收缩字符串容量的非绑定请求(在size大于n的情况下,请求缩小容积无效):容器实现可以自由地优化,并使字符串的容量大于 n。
此函数对字符串长度没有影响,并且无法更改其内容。void Teststring3() {string s;//测试reserve是否改变string中有效元素个数s.reserve(100);cout << s.size()<<endl;cout << s.capacity() <<endl;// 测试reserve参数小于string的底层空间大小,是否会将空间缩小s.reserve(50);cout << s.size()<<endl;cout << s.capacity() <<endl;//可以缩小空间 }
1.6 std::string::shrink_to_fit
void shrink_to_fit();收缩以适合请求字符串减小其容量以适合其大小。
可以理解为请求string::size() 缩小后。为了缩小占有空间,使用shrink_to_fit()缩小,此时string::size()不变。string::capacity可能会缩小有可能不变,如果string::capacity缩小,那么一定大于等于string::size。
例:
// string::shrink_to_fit #include <iostream> #include <string>int main () {std::string str (100,'x');std::cout << "1. capacity of str: " << str.capacity() << '\n';str.resize(10);std::cout << "2. capacity of str: " << str.capacity() << '\n';str.shrink_to_fit();std::cout << "3. capacity of str: " << str.capacity() << '\n';return 0; }可能的输出:
1. capacity of str: 100 2. capacity of str: 100 3. capacity of str: 10
2.string数据插入删除相关的接口
2.1 std::string::push_back 尾插
void push_back (char c);将字符附加到字符串将字符 c 追加到字符串的末尾,使其长度增加 1。
// string::push_back #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <string>int main () {std::string str1("hello world");std::string str2;for(auto e:str1){str2.push_back(e);}std::cout << str2 << '\n';return 0; }将字符串str1的字符从前到后尾插到str2中
2.2 std::string::pop_back 尾删
void pop_back();删除最后一个字符擦除字符串的最后一个字符,从而有效地将其长度减少 1。
#include <iostream> #include <string>int main () {std::string str1("hello world");std::string str2;for(auto e:str1){str2.push_back(e);}std::cout << str2 << '\n';str2.pop_back();str2.pop_back();std::cout << str2 << '\n';return 0; }直接调用两次pop_back函数,删掉尾部两个字符。
2.3 std::string::insert 插入
这里我们
string (1) substrring (2) C -string (3) buffer(4) fill(5) char (6) range (7) 这里我们主要用到1235这三个重载函数。
// inserting into a string #include <iostream> #include <string>int main () {std::string str="to be question";std::string str2="the ";std::string str3="or not to be";std::string::iterator it;// used in the same order as described above:str.insert(6,str2); // to be (the )questionstr.insert(6,str3,3,4); // to be (not )the questionstr.insert(10,"that is cool",8); // to be not (that is )the questionstr.insert(10,"to be "); // to be not (to be )that is the questionstr.insert(15,1,':'); // to be not to be(:) that is the questionit = str.insert(str.begin()+5,','); // to be(,) not to be: that is the questionstr.insert (str.end(),3,'.'); // to be, not to be: that is the question(...)str.insert (it+2,str3.begin(),str3.begin()+3); // (or )std::cout << str << '\n';return 0; }
3.string查找相关的接口
3.1 std::string::find
字符串 (1) size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const; C string (2) size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const; 缓冲器 (3) size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const; 字符 (4) size_t find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const;在字符串中查找内容在字符串中搜索由其参数指定的序列的第一次匹配项,并返回第一个匹配项所在的第一个字符的位置。
指定 pos 时,搜索仅包括位置 pos 处或位置之后的字符,忽略任何可能出现的在 pos 之前包含字符的情况。
请注意,与成员find_first_of不同,每当搜索多个字符时,仅其中一个字符匹配是不够的,但整个(所搜索)序列必须匹配。参数
str
另一个包含要搜索的主题的字符串。
POS
要在搜索中考虑的字符串中第一个字符的位置。
如果这大于字符串长度,则函数永远不会找到匹配项。
注意:第一个字符由值 0(不是 1)表示:值 0 表示搜索整个字符串。s
指向字符数组的指针。
如果指定了参数 n (3),则要匹配的序列是数组中的前 n 个字符。
否则 (2),应为以 null 结尾的序列:要匹配的序列的长度由第一次出现 null 字符确定。n
要匹配的字符序列的长度。
c
要搜索的单个字符
size_t 是无符号整型(与成员类型相同)。string::size_type
返回值
第一个匹配项的第一个字符的位置。
如果未找到匹配项,该函数将返回 string::npos。void Teststring6() { //取出ur1中的域名string ur1("http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/find/");cout << ur1 << endl;size_t start = 0;size_t finish = ur1.find("://");if(start == string::npos){cout << "invalid ur1" << endl;return;}// string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;string address = ur1.substr(start,finish - start);cout << address << ' ';start += address.size()+3;do{finish = ur1.find('/',start); address = ur1.substr(start,finish - start);cout << address << ' '; start += address.size()+1;}while(finish!= (ur1.size()-1));cout << endl;// 删除ur1的协议前缀pos = ur1.find("://");ur1.erase(0, pos + 3);cout << ur1 <<endl; }使用find寻找C++图书馆网站的网址中://和/,来区分协议,域名等的。
string::size_type
3.2 std::string::rfind
std::string::rfind
string (1) c-string (2) buffer (3) character (4) 在字符串中搜索由其参数指定的序列的最后一次匹配项。
指定 pos 时,搜索仅包括从位置 pos 开始或之前开始的字符序列,忽略在 pos 之后开始的任何可能的匹配。这个与string::find类似,不过最大的区别是一个从前往后搜索,另一个从后往前搜索。
// string::rfind #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstddef>int main () {std::string str ("The sixth sick sheik's sixth sheep's sick.");std::string key ("sixth");std::size_t found = str.rfind(key);if (found!=std::string::npos)str.replace (found,key.length(),"seventh");std::cout << str << '\n';return 0; }这代码搜索sixth,并且替换成seventh,可以看到它是替换掉后面sixth而不是前面的sixth,可以证明该函数是从前后往前搜索的。
输出
The sixth sick sheik's seventh sheep's sick
string::find_first_of
string::find_first_not_of
string::find_last_of
string::find_list_not_of
这四个接口十分类似,这里不一一列举,主要讲解string::find_first_of,其他简单介绍。
3.3string::find_first_of
字符串 (1) C 弦 (2) 缓冲器 (3) 字符 (4) 在字符串中搜索与其参数中指定的任何字符匹配的第一个字符。
指定 pos 时,搜索仅包括位置 pos 处或位置之后的字符,忽略 pos 之前可能出现的任何字符。参数
str
另一个包含要搜索的字符的字符串。
POS
要在搜索中考虑的字符串中第一个字符的位置。
如果这大于字符串长度,则函数永远不会找到匹配项。
注意:第一个字符由值 0(不是 1)表示:值 0 表示搜索整个字符串。s
指向字符数组的指针。
如果指定了参数 n (3),则搜索数组中的前 n 个字符。
否则 (2),应为以 null 结尾的序列:包含要匹配的字符的序列的长度由第一次出现 null 字符确定。n
要搜索的字符值数。
c
要搜索的单个字符。
size_t是无符号整型(与成员类型相同)。string::size_typestring::size_type
返回值
匹配的第一个字符的位置。
如果未找到匹配项,该函数将返回 string::npos。代码演示
// string::find_first_of #include <iostream> // std::cout #include <string> // std::string #include <cstddef> // std::size_tint main () {std::string str ("Please, replace the vowels in this sentence by asterisks.");std::size_t found = str.find_first_of("aeiou");while (found!=std::string::npos){str[found]='*';found=str.find_first_of("aeiou",found+1);}std::cout << str << '\n';return 0; }找到任何字符匹配的第一个字符,即是字符串中“aeiou”的任意一个字符匹配,就把它替换成
‘*’。
输出
Pl**s*, r*pl*c* th* v*w*ls *n th*s s*nt*nc* by *st*r*sks.
3.4 string::find_first_not_of
接口参数和string::find_first_of一样,但是查找的是字符串中缺少字符(没有出现的字符),返回它的位置。
3.5 string::find_last_of
接口参数和string::find_first_of一样,查找的是字符串中字符,返回它的位置,与string::find_first_of不同的是从后往前寻找。
3.6 string::find_last_not_of
接口参数和string::find_first_of一样,与 string::find_last_of类似但是查找的是字符串中缺少字符(没有出现的字符)。
4.string的遍历(含迭代器接口)
3种遍历方式:
需要注意的以下三种方式除了遍历string对象,还可以遍历修改string中的字符,
另外以下三种方式对于string而言,第一种使用最多void Teststring5() {string s("hello world");//1.for + operator[]for(size_t i = 0; i< s.size();++i)cout << s[i] <<" ";cout << endl;//2.迭代器string::iterator it = s.begin();while(it != s.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it; }cout << endl; // string::reverse_iterator = s.rbegin();//C++11之后。直接使用auto定义迭代器,让编译器推导迭代器的类型auto rit = s.rbegin(); while(rit != s.rend()){cout << *rit << endl;rit++;} //3.范围for(底层也是运用迭代器)for(auto ch : s) //如果要修改的话,使用引用 cout << ch << " ";cout << endl; }
4.1 std::string::begin
iterator end(); const_iterator end() const;将迭代器返回到开头返回指向字符串的第一个字符的迭代器。(运用如上代码所示)
4.2 std::string::end
iterator end(); const_iterator end() const;将迭代器返回到 end返回一个迭代器,该迭代器指向字符串的末尾字符。(运用如上代码所示)
过去结束字符是理论上的字符,它将跟随字符串中的最后一个字符。不得取消引用。
由于标准库的函数使用的范围不包括其关闭迭代器所指向的元素,因此此函数通常与 string::begin 结合使用,以指定包含字符串中所有字符的范围。
如果对象是空字符串,则此函数返回与 string::begin 相同的结果。
4.3 std::string::rbegin
reverse_iterator rbegin(); const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const;返回反向迭代器以反向开始返回指向字符串最后一个字符(即其反向开头)的反向迭代器。
反向迭代器向后迭代:增加它们会使它们向字符串的开头移动。
rbegin 指向 member end 将指向的字符之前的字符。(运用如上代码所示)
4.4 std::string::rend
reverse_iterator rend(); const_reverse_iterator rend() const;将反向迭代器返回到反向端返回一个反向迭代器,该迭代器指向字符串第一个字符(被视为其反向末尾)之前的理论元素。
string::rbegin 和 string::rend 之间的范围包含字符串的所有字符(顺序相反)。(运用如上代码所示)
5. string 子字符串
5.1 std::string::substr
string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;生成子字符串
返回一个新构造的对象,其值初始化为此对象的子字符串的副本。子字符串是对象的一部分,它从字符位置开始并跨越字符(或直到字符串的末尾,以先到者为准)。
pos
要作为子字符串复制的第一个字符的位置。
如果这等于字符串长度,则该函数返回一个空字符串。
如果这大于字符串长度,则会抛出out_of_range。
注意:第一个字符由值 0(而不是 1)表示。
lens
要包含在子字符串中的字符数(如果字符串较短,则使用尽可能多的字符)。
值 string::npos 表示字符串末尾之前的所有字符。
返回值
一个字符串对象,具有此对象的子字符串。
例
// string::substr #include <iostream> #include <string>int main () {std::string str="We think in generalities, but we live in details.";// (quoting Alfred N. Whitehead)std::string str2 = str.substr (3,5); // "think"std::size_t pos = str.find("live"); // position of "live" in strstd::string str3 = str.substr (pos); // get from "live" to the endstd::cout << str2 << ' ' << str3 << '\n';return 0; }输出
think live in details.演示了加lens和不加lens的情况
6.交换和替换string接口
6.1 std::string::replace
string (1) string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str); string& replace (iterator i1, iterator i2, const string& str); substring (2) string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str,size_t subpos, size_t sublen); C string (3) string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, const char* s); string& replace (iterator i1, iterator i2, const char* s); 缓冲器 (4) string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, const char* s, size_t n); string& replace (iterator i1, iterator i2, const char* s, size_t n); full (5) string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, size_t n, char c); string& replace (iterator i1, iterator i2, size_t n, char c); range (6) template <class InputIterator>string& replace (iterator i1, iterator i2,InputIterator first, InputIterator last);主要用到前四个接口。
很简单的概括就是前面规划出要被替换的字符串和后面规划出要替换的字符串。
参数
pos
原来字符串位置
len
要替换的长度
例子
#include <iostream> #include <string>int main () {std::string base="this is a test string.";std::string str2="n example";std::string str3="sample phrase";std::string str4="useful.";// replace signatures used in the same order as described above:// Using positions: 0123456789*123456789*12345std::string str=base; // "this is a test string."str.replace(9,5,str2); // "this is an example string." (1)str.replace(19,6,str3,7,6); // "this is an example phrase." (2)str.replace(8,10,"just a"); // "this is just a phrase." (3)str.replace(8,6,"a shorty",7); // "this is a short phrase." (4)str.replace(22,1,3,'!'); // "this is a short phrase!!!" (5)// Using iterators: 0123456789*123456789*str.replace(str.begin(),str.end()-3,str3); // "sample phrase!!!" (1)str.replace(str.begin(),str.begin()+6,"replace"); // "replace phrase!!!" (3)str.replace(str.begin()+8,str.begin()+14,"is coolness",7); // "replace is cool!!!" (4)str.replace(str.begin()+12,str.end()-4,4,'o'); // "replace is cooool!!!" (5)str.replace(str.begin()+11,str.end(),str4.begin(),str4.end());// "replace is useful." (6)std::cout << str << '\n';return 0; }
6.2 std::string::swap
void swap (string& str);交换字符串值通过 str 的内容交换容器的内容,str 是另一个字符串对象。长度可能不同。
调用此成员函数后,此对象的值是 str 在调用之前的值,str 的值是此对象在调用之前的值。
请注意,存在一个具有相同名称的非成员函数 swap,该算法使用行为类似于此成员函数的优化重载该算法。
参数
str
另一个字符串对象,其值与此字符串的值交换。
例
// swap strings #include <iostream> #include <string>main () {std::string buyer ("money");std::string seller ("goods");std::cout << "Before the swap, buyer has " << buyer;std::cout << " and seller has " << seller << '\n';seller.swap (buyer);std::cout << " After the swap, buyer has " << buyer;std::cout << " and seller has " << seller << '\n';return 0; }输出:
Before the swap, buyer has money and seller has goodsAfter the swap, buyer has goods and seller has mone
7.比较赋值string接口
直接运用>、<、<=、>=、!=、==、运算比较即可
库函数已经进行运算符重载就不需要用类似string::compare()的接口增加记忆成本
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main ()
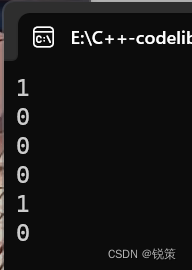
{string str1("string");string str2("string1");string str3("string1");cout << (str1 < str2) <<endl;cout << (str1 == str2) <<endl;cout << (str1 > str2) <<endl;cout << (str3 < str2) <<endl;cout << (str3 == str2) <<endl;cout << (str3 > str2) <<endl;}输出:
8.获取等效的 C 字符串
8.1 std::string::c_str
const char* c_str() const;用于C和C++是兼容的,在有时候常常会用到C接口,要使用到C字符串。
std::string::c_str()就是因此而诞生的。
获取等效的 C 字符串返回指向数组的指针,该数组包含以 null 结尾的字符序列(即 C 字符串),该字符表示字符串对象的当前值。
此数组包含构成字符串对象值的相同字符序列,以及末尾的附加终止 null 字符 ('\0')。// strings and c-strings #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <string>int main () {std::string str ("Please split this sentence into tokens");char * cstr = new char [str.length()+1];std::strcpy (cstr, str.c_str());// cstr now contains a c-string copy of strchar * p = std::strtok (cstr," ");while (p!=0){std::cout << p << '\n';p = std::strtok(NULL," ");}delete[] cstr;return 0; }输出:
Please split this sentence into tokens
9.数字与字符串的转换
9.1 数字转字符串
string::to_string
string to_string (int val); string to_string (long val); string to_string (long long val); string to_string (unsigned val); string to_string (unsigned long val); string to_string (unsigned long long val); string to_string (float val); string to_string (double val); string to_string (long double val);将数值转换为字符串返回表示为 val 的字符串。
使用的格式与 printf 为相应类型打印的格式相同:The format used is the same that printf would print for the corresponding type:
type of val printf equivalent description int "%d" Decimal-base representation of val.
The representations of negative values are preceded with a minus sign (-).long "%ld long long "%lld unsigned "%u" Decimal-base representation of val. unsigned long "%lu unsigned long long "%llu float "%f" As many digits are written as needed to represent the integral part, followed by the decimal-point character and six decimal digits.
inf (or infinity) is used to represent infinity.
nan (followed by an optional sequence of characters) to represent NaNs (Not-a-Number).
The representations of negative values are preceded with a minus sign (-).double "%f long double "%Lf 返回值
一个 字符串对象,将 val 表示为字符序列例
// to_string example #include <iostream> // std::cout #include <string> // std::string, std::to_stringint main () {std::string pi = "pi is " + std::to_string(3.1415926);std::string perfect = std::to_string(1+2+4+7+14) + " is a perfect number";std::cout << pi << '\n';std::cout << perfect << '\n';return 0; }可能的输出:
pi is 3.141593 28 is a perfect numbe
9.2字符串转数字
std::stoi
int stoi (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0, int base = 10); int stoi (const wstring& str, size_t* idx = 0, int base = 10);将字符串转换为整数解析 str 并将其内容解释为指定基数的整数,该整数作为 int 值返回。
如果 idx 不是空指针,则该函数还会将 idx 的值设置为 str 中第一个字符在数字之后的位置。
参数
str
表示整数的 String 对象。
IDX的
指向 size_t 类型的对象的指针,该对象的值由函数设置为 str 中下一个字符在数值之后的位置。
此参数也可以是 null 指针,在这种情况下,不使用它。基础
确定有效字符及其解释的数字基数(基数)。
如果此值为 0,则使用的基数由序列中的格式决定(有关详细信息,请参见 strtol)。请注意,默认情况下,此参数为 10,而不是 0。
例
// stoi example #include <iostream> // std::cout #include <string> // std::string, std::stoiint main () {std::string str_dec = "2001, A Space Odyssey";std::string str_hex = "40c3";std::string str_bin = "-10010110001";std::string str_auto = "0x7f";std::string::size_type sz; // alias of size_tint i_dec = std::stoi (str_dec,&sz); //sz是为了得到2001的下一个字符的位置,默认10进制字符串转换成十进制整数int i_hex = std::stoi (str_hex,nullptr,16);//16进制字符串转换成十进制整数int i_bin = std::stoi (str_bin,nullptr,2);//2进制字符串转换成十进制整数int i_auto = std::stoi (str_auto,nullptr,0);//如果此值为 0,则使用的基数由序列中的格式决定std::cout << str_dec << ": " << i_dec << " and [" << str_dec.substr(sz) << "]\n";std::cout << str_hex << ": " << i_hex << '\n';std::cout << str_bin << ": " << i_bin << '\n';std::cout << str_auto << ": " << i_auto << '\n';return 0; }输出:
2001, A Space Odyssey: 2001 and [, A Space Odyssey] 40c3: 16579 -10010110001: -1201 0x7f: 127
下面接口跟std::stoi相似,这里简单介绍一下
std::stol (std::stoll)
long stol (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0, int base = 10); long stol (const wstring& str, size_t* idx = 0, int base = 10);
std::stof
float stof (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0); float stof (const wstring& str, size_t* idx = 0);
std::stod
std::stold
10.算法中的string运用
10.1反转字符串
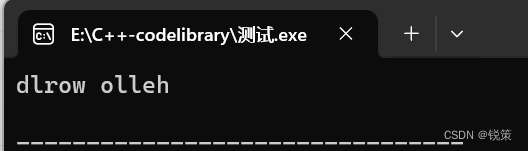
输出:#include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; int main () {string str1("hello world");reverse(str1.begin(),str1.end());cout << str1 <<endl; }
相关文章:

C++——解锁string常用接口
目录 string::npos; 1.测试string容量相关的接口: 1.1 string::size() 1.2 string::clear() 1.3 string::resize() 1.4 string::erase() 1.5 string::reserve() 保留 1.6 std::string::shrink_to_fit 2.string数据插入删除相关的接口 2.1 std::string::pus…...

Stable Video Diffusion(SVD)参数使用教程
Stable Video Diffusion(SVD)安装和测试 官网 github | https://github.com/Stability-AI/generative-modelsHugging Face | https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-video-diffusion-img2vid-xtPaper | https://stability.ai/research/stable-vid…...

【传智杯】排排队、小卡与质数 2、1024 程序员节发橙子题解
🍎 博客主页:🌙披星戴月的贾维斯 🍎 欢迎关注:👍点赞🍃收藏🔥留言 🍇系列专栏:🌙 蓝桥杯 🌙请不要相信胜利就像山坡上的蒲公英一样唾手…...

Oracle
1.解释冷备份和热备份的不同点以及各自的优点 冷备份 发生在数据库已经正常关闭的情况下,将关键性文件拷贝到另外位置的一种说法。适用于所有模式的数据库。 优点 是非常快速的备份方法(只需拷贝文件)容易归档(简单拷贝即可&a…...
2023年c语言程序设计大赛
7-1 这是一道送分题 为了让更多的同学参与程序设计中来,这里给同学们一个送分题,让各位感受一下程序设计的魅力,并祝贺各位同学在本次比赛中取得好成绩。 注:各位同学只需将输入样例里的代码复制到右侧编译器,然后直…...
:spu管理页面的新增和修改)
9.vue3项目(九):spu管理页面的新增和修改
目录 一、SPU和SKU概念 二、SPU静态搭建 1.代码编辑 2.效果展示 三、封装接口以及出参入参...

人工智能:让生活更便捷、更智能——探讨人工智能在生活中的作用与挑战
文章目录 前言人工智能的定义与分类人工智能的领域一、智能语音助手改变日常生活二、智能驾驶带来出行革命三、人工智能在医疗健康领域的应用四、教育领域的人工智能创新 人工智能的应用生活方面的影响工作方面的影响 应对AI带来的挑战后记 前言 人工智能相关的领域࿰…...
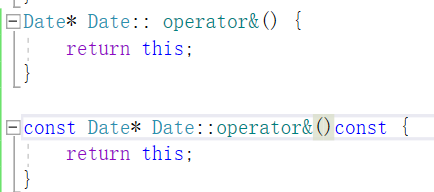
【C++】类和对象——const修饰成员函数和取地址操作符重载
在上篇博客中,我们已经对于日期类有了较为全面的实现,但是,还有一个问题,比如说,我给一个const修饰的日期类的对象 这个对象是不能调用我们上篇博客写的函数的,因为&d1是const Date*类型的ÿ…...
express+mySql实现用户注册、登录和身份认证
expressmySql实现用户注册、登录和身份认证 注册 注册时需要对用户密码进行加密入库,提高账户的安全性。用户登录时再将密码以相同的方式进行加密,再与数据库中存储的密码进行比对,相同则表示登录成功。 安装加密依赖包bcryptjs cnpm insta…...
加载数据集)
【PyTorch】(二)加载数据集
文章目录 1. 创建数据集1.1. 直接继承Dataset类1.2. 使用TensorDataset类 2. 加载数据集3. 将数据转移到GPU 1. 创建数据集 主要是将数据集读入内存,并用Dataset类封装。 1.1. 直接继承Dataset类 必须要重写__getitem__方法,用于根据索引获得相应样本…...
如何提高3D建模技能?
无论是制作影视动画还是视频游戏,提高3D建模技能对于你的工作都至关重要的。那么如何能创建出精美的3D模型呢?本文给大家一些3D建模技能方面的建议。 3D建模通过专门的软件完成,涉及制作三维对象。这项技能在视频游戏开发、建筑、动画和产品…...

【前端开发】Next.js与Nest.js之间的差异2023
在快节奏的网络开发领域,JavaScript已成为构建可靠且引人入胜的在线应用程序的标准语言。然而,随着对适应性强、高效的在线服务的需求不断增加,开发人员通常不得不从广泛的库和框架中进行选择,以满足其项目的要求。Next.js和Nest.…...

【CAN通信】CanIf模块详细介绍
目录 1.内容简介 2.CanIf详细设计 2.1 CanIf功能简介 2.2 一些关键概念 2.3依赖的上下层模块 2.4 功能详细设计 2.4.1 Hardware object handles 2.4.2 Static L-PDUs 2.4.3 Dynamic L-PDUs 2.4.4 Dynamic Transmit L-PDUs 2.4.5 Dynamic receive L-PDUs 2.4.6Physi…...

PS最新磨皮软件Portraiture4.1.2
Portraiture是一款好用的PS磨皮滤镜插件,拥有磨皮美白的功能,操作也很简单,一键点击即可实现美白效果,软件还保留了人物的皮肤质感让照片看起来更加真实。portraiture体积小巧,不会占用过多的电脑内存哦。 内置了多种…...
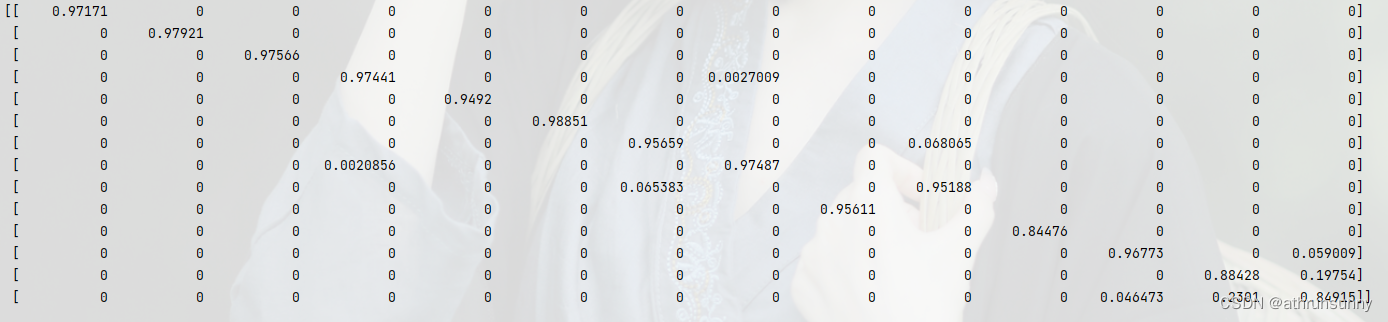
旋转框(obb)目标检测计算iou的方法
首先先定义一组多边形,这里的数据来自前后帧的检测结果 pre [[[860.0, 374.0], [823.38, 435.23], [716.38, 371.23], [753.0, 310.0]],[[829.0, 465.0], [826.22, 544.01], [684.0, 539.0], [686.78, 459.99]],[[885.72, 574.95], [891.0, 648.0], [725.0, 660.0]…...

render函数举例
在这段代码中,renderButton是一个对象吗 还有render为什么不能写成render() {} 代码原文链接 <template><div><renderButton /></div> </template><script setup> import { h, ref } from "vue"; const renderButt…...

微信小程序文件预览和下载-文件系统
文件预览和下载 在下载之前,我们得先调用接口获取文件下载的url 然后通过wx.downloadFile将下载文件资源到本地 wx.downloadFile({url: res.data.url,success: function (res) {console.log(数据,res);} })tempFilePath就是临时临时文件路径。 通过wx.openDocume…...
图解Redis适用场景
Redis以其速度而闻名。 1 业务数据缓存 1.1 通用数据缓存 string,int,list,map。Redis 最常见的用例是缓存对象以加速 Web 应用程序。 此用例中,Redis 将频繁请求的数据存储在内存。允许 Web 服务器快速返回频繁访问的数据。这…...
掌握Python BentoML:构建、部署和管理机器学习模型
更多资料获取 📚 个人网站:ipengtao.com BentoML是一个开源的Python框架,旨在简化机器学习模型的打包、部署和管理。本文将深入介绍BentoML的功能和用法,提供详细的示例代码和解释,帮助你更好地理解和应用这个强大的工…...

西南科技大学模拟电子技术实验二(二极管特性测试及其应用电路)预习报告
目录 一、计算/设计过程 二、画出并填写实验指导书上的预表 三、画出并填写实验指导书上的虚表 四、粘贴原理仿真、工程仿真截图 一、计算/设计过程 说明:本实验是验证性实验,计算预测验证结果。是设计性实验一定要从系统指标计算出元件参数过程,越详细越好。用公式输入…...

[2025CVPR]DeepVideo-R1:基于难度感知回归GRPO的视频强化微调框架详解
突破视频大语言模型推理瓶颈,在多个视频基准上实现SOTA性能 一、核心问题与创新亮点 1.1 GRPO在视频任务中的两大挑战 安全措施依赖问题 GRPO使用min和clip函数限制策略更新幅度,导致: 梯度抑制:当新旧策略差异过大时梯度消失收敛困难:策略无法充分优化# 传统GRPO的梯…...

golang循环变量捕获问题
在 Go 语言中,当在循环中启动协程(goroutine)时,如果在协程闭包中直接引用循环变量,可能会遇到一个常见的陷阱 - 循环变量捕获问题。让我详细解释一下: 问题背景 看这个代码片段: fo…...

FFmpeg 低延迟同屏方案
引言 在实时互动需求激增的当下,无论是在线教育中的师生同屏演示、远程办公的屏幕共享协作,还是游戏直播的画面实时传输,低延迟同屏已成为保障用户体验的核心指标。FFmpeg 作为一款功能强大的多媒体框架,凭借其灵活的编解码、数据…...
【HarmonyOS 5.0】DevEco Testing:鸿蒙应用质量保障的终极武器
——全方位测试解决方案与代码实战 一、工具定位与核心能力 DevEco Testing是HarmonyOS官方推出的一体化测试平台,覆盖应用全生命周期测试需求,主要提供五大核心能力: 测试类型检测目标关键指标功能体验基…...
` 方法)
深入浅出:JavaScript 中的 `window.crypto.getRandomValues()` 方法
深入浅出:JavaScript 中的 window.crypto.getRandomValues() 方法 在现代 Web 开发中,随机数的生成看似简单,却隐藏着许多玄机。无论是生成密码、加密密钥,还是创建安全令牌,随机数的质量直接关系到系统的安全性。Jav…...
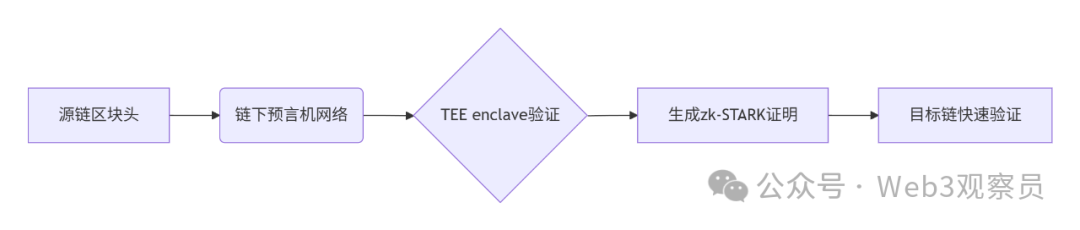
跨链模式:多链互操作架构与性能扩展方案
跨链模式:多链互操作架构与性能扩展方案 ——构建下一代区块链互联网的技术基石 一、跨链架构的核心范式演进 1. 分层协议栈:模块化解耦设计 现代跨链系统采用分层协议栈实现灵活扩展(H2Cross架构): 适配层…...

数据库分批入库
今天在工作中,遇到一个问题,就是分批查询的时候,由于批次过大导致出现了一些问题,一下是问题描述和解决方案: 示例: // 假设已有数据列表 dataList 和 PreparedStatement pstmt int batchSize 1000; // …...

SQL慢可能是触发了ring buffer
简介 最近在进行 postgresql 性能排查的时候,发现 PG 在某一个时间并行执行的 SQL 变得特别慢。最后通过监控监观察到并行发起得时间 buffers_alloc 就急速上升,且低水位伴随在整个慢 SQL,一直是 buferIO 的等待事件,此时也没有其他会话的争抢。SQL 虽然不是高效 SQL ,但…...

Mysql8 忘记密码重置,以及问题解决
1.使用免密登录 找到配置MySQL文件,我的文件路径是/etc/mysql/my.cnf,有的人的是/etc/mysql/mysql.cnf 在里最后加入 skip-grant-tables重启MySQL服务 service mysql restartShutting down MySQL… SUCCESS! Starting MySQL… SUCCESS! 重启成功 2.登…...
[ACTF2020 新生赛]Include 1(php://filter伪协议)
题目 做法 启动靶机,点进去 点进去 查看URL,有 ?fileflag.php说明存在文件包含,原理是php://filter 协议 当它与包含函数结合时,php://filter流会被当作php文件执行。 用php://filter加编码,能让PHP把文件内容…...