大话数据结构-迪杰斯特拉算法(Dijkstra)和弗洛伊德算法(Floyd)
6 最短路径
最短路径,对于图来说,是两顶点之间经过的边数最少的路径;对于网来说,是指两顶点之间经过的边上权值之和最小的路径。路径上第一个顶点为源点,最后一个顶点是终点。
6.1 迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法
以如下无向图为例:
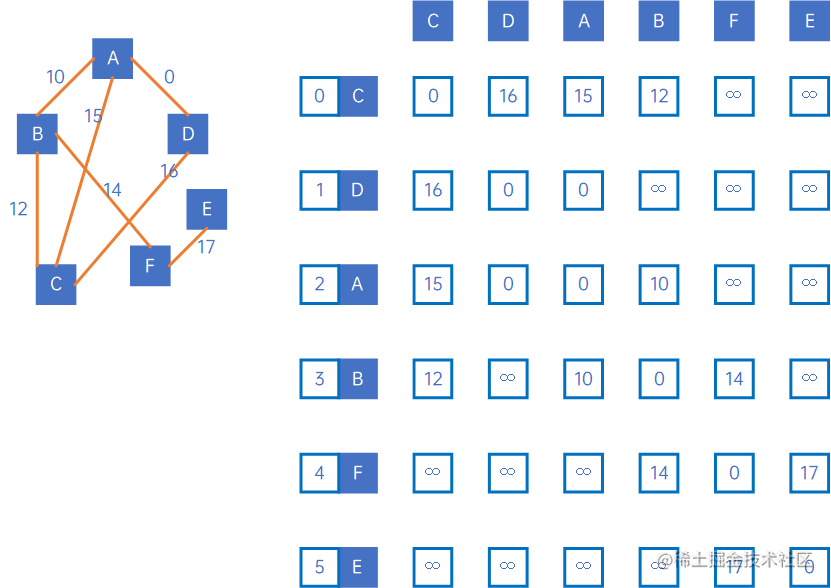
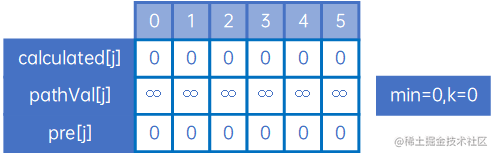
我们来计算下标为0的顶点,到其他顶点的最短路径,首先定义三个数组,calculated[j]表示0->j的最短路径是否已计算出来,pathVal[j]表示0->j的最短路径,目前还未进行计算,我们设置所有元素值均为无穷大,pre[j]表示0->j中经历的顶点,例如pre[1]=3、pre[3]=2、pre[2]=0,表示的:
(1) pre[1]=3表示0->1需要经过3;
(2) pre[3]=2表示0->3需要经过2;
(3) pre[2]=0表示0->2可以直达;
(4) 因此可以得出结论,0->1的路径是:0->2->3->1;
再定义一个变量min,表示“0->上一个顶点的最小权值”,k表示min对应的顶点的下标,因此初始情况如下所示:
接下来来看0到第0个顶点的最短路径,这个不需要计算,肯定是0,且不需要经过其他顶点,因此有如下情况:
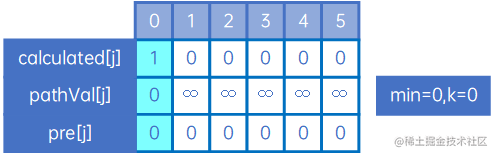
到目前为止,min仍然为0,k仍然为0,接下来看0到其他顶点的最短路径,我们把arc[0][j]与现有的pathVal[j]比较,规则是:
(1) calculated[j]=1表示已找到最短路径,不进行任何处理;
(2) 如果arc[0][j]+min<pathVal[j],则令pathVal[j]=arc[0][j]+min,令pre[j]=k,表示0->j至少要经过顶点k;
(3) 如果arc[0][j]+min>=pathVal[j],则pathVal[j]不变,pre[j]也不变,表示0->j不会经过顶点k;
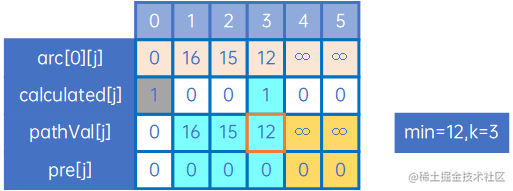
那么,有以下结果:
(1) calculated[0]=1,不进行任何处理;
(2) arc[0][1]+min=16+0<pathVal[1]=无穷大,令pathVal[1]=arc[0][1]+min=16,令pre[j]=k=0;
(3) arc[0][2]、arc[0][3]与arc[0][1]处理方式一致;
(4) arc[0][4]和arc[0][5]都为无穷大,加上min后等于pathVal[4]和pathVal[5],因此pathVal[4]、pathVal[5]和pre[4]、pre[5]不进行处理;
(5) 这时来看最新的pathVal[j],发现最小的权是pathVal[3],于是令min=pathVal[3]=12,令k=3,这也表示0->3的最短路径已找到,因此令calculated[3]=1,如下:
k=3,即其他未计算出的最短路径,都有可能会经过顶点3,因此我们把arc[3][j]与现有pathVal[j]比较,规则仍与arc[0][j]时一致,特别的,arc[3][2]+min=10+12=26>pathVal[2]=15,因此pathVal[2]和pre[2]不进行变更,当然,arc[3][1]也是同样的:
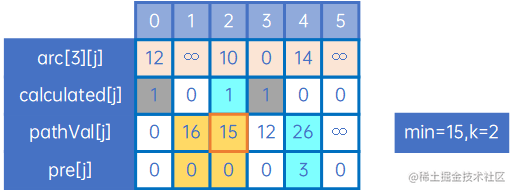
这时,min=15,k=2,因此处理arc[2][j],如下:
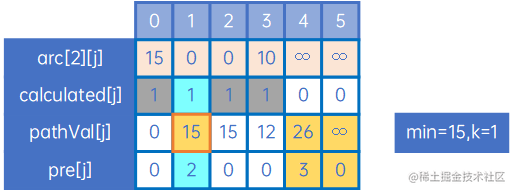
然后继续处理,直到calculated[j]的元素都为1:
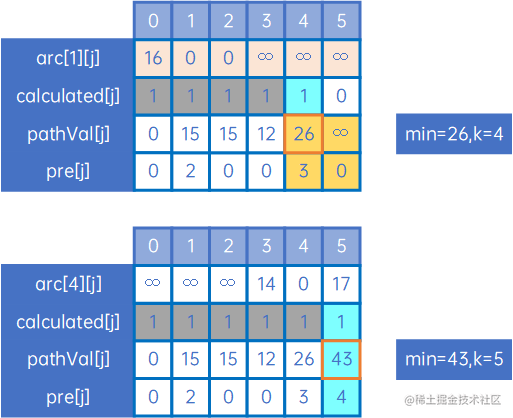
我们来看现在的pathVal[j]和pre[j]:
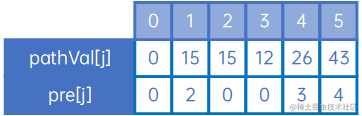
可以知道以下内容:
(1) 顶点5,即E,对应的pathVal[5]是43,pre[4]是4,因此顶点0->5,即C->E的最短路径是43,且中间肯定会经过顶点4即顶点F,即肯定有C->F->E;
(2) 顶点4,即F,对应的pathVal[4]是26,pre[4]是3,因此顶点0->4,即C->F的最短路径是26,且中间肯定会经过顶点3即顶点B,即肯定有C->B->F,结点(1),那么肯定有C->B->F->E;
(3) 顶点3,即B,对应的pathVal[3]是12,pre[3]是0,因此顶点0->3,即C->B的最短路径是12,且无中间顶点,那么,结点(1)和(2),得到结论;
1) C到B的最短路径是12,路径是C->B;
2) C到F的最短路径是26,路径是C->B->F;
3) C到E的最短路径是43,路径是C->B->F->E;
(4) 同样的规则,能分析到:
1) C到A的最短路径是15,路径是C->A;
2) C到D的最短路径是15,路径是C->A->D;
以上即为迪杰斯特拉算法。
由上也可知,邻接矩阵的迪杰斯特拉算法实现代码如下所示:
/*** 迪杰斯特拉算法获取最短路径** @param fromVertexIndex 起始顶点下标* @return 起始顶点到各顶点的最短路径及前驱顶点列表* @author Korbin* @date 2023-02-20 14:54:35**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object[][] shortestPathDijkstra(int fromVertexIndex) {// 最短路径权值,初始化为fromVertexIndex的权W[] pathVal = (W[]) Array.newInstance(infinity.getClass(), vertexNum);// 是否已计算,初始值为falseboolean[] calculated = new boolean[vertexNum];// 要到达此顶点应先从哪个顶点过来,初始值为fromVertexIndexInteger[] pre = new Integer[vertexNum];for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {pathVal[i] = arc[fromVertexIndex][i];pre[i] = fromVertexIndex;}// 最小权值W minWeight = null;// 最小权值对应的索引下标int minWeightIndex = fromVertexIndex;// 已计算的顶点数量,初始值为0int calculatedNum;// 从fromVertexIndex到fromVertexIndex,令pathVal[fromVertexIndex]为0,令pre[fromVertexIndex]为fromVertexIndex// ,令calculated[fromVertexIndex]为truepathVal[fromVertexIndex] = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);pre[fromVertexIndex] = fromVertexIndex;calculated[fromVertexIndex] = true;calculatedNum = 1;while (calculatedNum < vertexNum) {// 循环到所有顶点都计算完毕// 处理arc[minWeightIndex][j]for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {// 跳过calculated[j]为true的顶点if (!calculated[i]) {// 与现有pathVal[j]比较if (infinity instanceof Integer) {// 对于arc[minWeightIndex][i]为无穷大的也不处理if (!arc[minWeightIndex][i].equals(infinity)) {// 只处理权值是Integer的情况,其他类型的类似处理if (null == minWeight) {minWeight = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);}W arcI = (W) (Integer.valueOf((Integer) arc[minWeightIndex][i] + (Integer) minWeight));if (arcI.compareTo(pathVal[i]) < 0) {// 令pathVal[j]=arc[minWeightIndex][j] + minWeightpathVal[i] = arcI;// 令pre[j]=minWeightIndexpre[i] = minWeightIndex;}}}}}// 从pathVal和pre中取出新的minWeight和minWeightIndexminWeight = null;for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {// 跳过已计算最短路径的顶点if (!calculated[i] && (null == minWeight || minWeight.compareTo(pathVal[i]) > 0)) {minWeight = pathVal[i];minWeightIndex = i;}}// 设置minWeightIndex对应的顶点为已访问calculated[minWeightIndex] = true;calculatedNum++;// 用于测试System.out.println("min weight is " + minWeight + ", min weight index is " + minWeightIndex);StringBuilder builder1 = new StringBuilder("path val is [");StringBuilder builder2 = new StringBuilder("pre vertex is [");StringBuilder builder3 = new StringBuilder("calculated is [");for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {builder1.append(pathVal[i]).append(",");builder2.append(pre[i]).append(",");builder3.append(calculated[i]).append(",");}builder1.append("]");builder2.append("]\n\r");builder3.append("]");System.out.println(builder3);System.out.println(builder1);System.out.println(builder2);}Object[][] result = new Object[2][];result[0] = pathVal;result[1] = pre;return result;
}
邻接表代码如下:
/*** 迪杰斯特拉算法获取最短路径** @param fromVertexIndex 起始顶点下标* @return 起始顶点到各顶点的最短路径及前驱顶点列表* @author Korbin* @date 2023-02-20 14:54:35**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object[][] shortestPathDijkstra(int fromVertexIndex) {// 最短路径权值,初始化为fromVertexIndex的权W[] pathVal = (W[]) Array.newInstance(infinity.getClass(), vertexNum);// 是否已计算,初始值为falseboolean[] calculated = new boolean[vertexNum];// 要到达此顶点应先从哪个顶点过来,初始值为fromVertexIndexInteger[] pre = new Integer[vertexNum];for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {pre[i] = fromVertexIndex;pathVal[i] = infinity;}// 处理第一个顶点VertexNode<T, W> vertexNode = vertexes[fromVertexIndex];EdgeNode<W> edgeNode = vertexNode.getFirstEdge();while (null != edgeNode) {int refIndex = edgeNode.getIndex();W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();pathVal[refIndex] = weight;edgeNode = edgeNode.getNext();}// 最小权值W minWeight = null;// 最小权值对应的索引下标int minWeightIndex = fromVertexIndex;// 已计算的顶点数量,初始值为0int calculatedNum;// 从fromVertexIndex到fromVertexIndex,令pathVal[fromVertexIndex]为0,令pre[fromVertexIndex]为fromVertexIndex// ,令calculated[fromVertexIndex]为truepathVal[fromVertexIndex] = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);pre[fromVertexIndex] = fromVertexIndex;calculated[fromVertexIndex] = true;calculatedNum = 1;while (calculatedNum < vertexNum) {// 循环到所有顶点都计算完毕// 处理本顶点指向的顶点vertexNode = vertexes[minWeightIndex];edgeNode = vertexNode.getFirstEdge();while (null != edgeNode) {int refIndex = edgeNode.getIndex();W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();// 跳过calculated[j]为true的顶点if (!calculated[refIndex]) {// 与现有pathVal[j]比较if (infinity instanceof Integer) {// 对于weight为无穷大的也不处理if (!weight.equals(infinity)) {// 只处理权值是Integer的情况,其他类型的类似处理if (null == minWeight) {minWeight = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);}W arcI = (W) (Integer.valueOf((Integer) weight + (Integer) minWeight));if (arcI.compareTo(pathVal[refIndex]) < 0) {// 令pathVal[j]=arc[minWeightIndex][j] + minWeightpathVal[refIndex] = arcI;// 令pre[j]=minWeightIndexpre[refIndex] = minWeightIndex;}}}}edgeNode = edgeNode.getNext();}// 从pathVal和pre中取出新的minWeight和minWeightIndexminWeight = null;for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {// 跳过已计算最短路径的顶点if (!calculated[i] && (null == minWeight || minWeight.compareTo(pathVal[i]) > 0)) {minWeight = pathVal[i];minWeightIndex = i;}}// 设置minWeightIndex对应的顶点为已访问calculated[minWeightIndex] = true;calculatedNum++;// 用于测试System.out.println("min weight is " + minWeight + ", min weight index is " + minWeightIndex);StringBuilder builder1 = new StringBuilder("path val is [");StringBuilder builder2 = new StringBuilder("pre vertex is [");StringBuilder builder3 = new StringBuilder("calculated is [");for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {builder1.append(pathVal[i]).append(",");builder2.append(pre[i]).append(",");builder3.append(calculated[i]).append(",");}builder1.append("]");builder2.append("]\n\r");builder3.append("]");System.out.println(builder3);System.out.println(builder1);System.out.println(builder2);}Object[][] result = new Object[2][];result[0] = pathVal;result[1] = pre;return result;
}
十字链表的迪杰斯特拉算法实现:
/*** 迪杰斯特拉算法获取最短路径** @param fromVertexIndex 起始顶点下标* @return 起始顶点到各顶点的最短路径及前驱顶点列表* @author Korbin* @date 2023-02-20 14:54:35**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object[][] shortestPathDijkstra(int fromVertexIndex) {// 最短路径权值,初始化为fromVertexIndex的权W[] pathVal = (W[]) Array.newInstance(infinity.getClass(), vertexNum);// 是否已计算,初始值为falseboolean[] calculated = new boolean[vertexNum];// 要到达此顶点应先从哪个顶点过来,初始值为fromVertexIndexInteger[] pre = new Integer[vertexNum];for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {pre[i] = fromVertexIndex;pathVal[i] = infinity;}// 处理第一个顶点AcrossLinkVertexNode<T, W> vertexNode = vertexes[fromVertexIndex];AcrossLinkEdgeNode<W> edgeNode = vertexNode.getFirstOut();while (null != edgeNode) {int refIndex = edgeNode.getHeadIndex();W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();pathVal[refIndex] = weight;edgeNode = edgeNode.getNextHead();}// 最小权值W minWeight = null;// 最小权值对应的索引下标int minWeightIndex = fromVertexIndex;// 已计算的顶点数量,初始值为0int calculatedNum;// 从fromVertexIndex到fromVertexIndex,令pathVal[fromVertexIndex]为0,令pre[fromVertexIndex]为fromVertexIndex// ,令calculated[fromVertexIndex]为truepathVal[fromVertexIndex] = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);pre[fromVertexIndex] = fromVertexIndex;calculated[fromVertexIndex] = true;calculatedNum = 1;while (calculatedNum < vertexNum) {// 循环到所有顶点都计算完毕// 处理本顶点指向的顶点vertexNode = vertexes[minWeightIndex];edgeNode = vertexNode.getFirstOut();while (null != edgeNode) {int refIndex = edgeNode.getHeadIndex();W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();// 跳过calculated[j]为true的顶点if (!calculated[refIndex]) {// 与现有pathVal[j]比较if (infinity instanceof Integer) {// 对于weight为无穷大的也不处理if (!weight.equals(infinity)) {// 只处理权值是Integer的情况,其他类型的类似处理if (null == minWeight) {minWeight = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);}W arcI = (W) (Integer.valueOf((Integer) weight + (Integer) minWeight));if (arcI.compareTo(pathVal[refIndex]) < 0) {// 令pathVal[j]=arc[minWeightIndex][j] + minWeightpathVal[refIndex] = arcI;// 令pre[j]=minWeightIndexpre[refIndex] = minWeightIndex;}}}}edgeNode = edgeNode.getNextHead();}// 从pathVal和pre中取出新的minWeight和minWeightIndexminWeight = null;for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {// 跳过已计算最短路径的顶点if (!calculated[i] && (null == minWeight || minWeight.compareTo(pathVal[i]) > 0)) {minWeight = pathVal[i];minWeightIndex = i;}}// 设置minWeightIndex对应的顶点为已访问calculated[minWeightIndex] = true;calculatedNum++;// 用于测试System.out.println("min weight is " + minWeight + ", min weight index is " + minWeightIndex);StringBuilder builder1 = new StringBuilder("path val is [");StringBuilder builder2 = new StringBuilder("pre vertex is [");StringBuilder builder3 = new StringBuilder("calculated is [");for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {builder1.append(pathVal[i]).append(",");builder2.append(pre[i]).append(",");builder3.append(calculated[i]).append(",");}builder1.append("]");builder2.append("]\n\r");builder3.append("]");System.out.println(builder3);System.out.println(builder1);System.out.println(builder2);}Object[][] result = new Object[2][];result[0] = pathVal;result[1] = pre;return result;
}
邻接多重表的迪杰斯特拉算法实现如下:
/*** 迪杰斯特拉算法获取最短路径** @param fromVertexIndex 起始顶点下标* @return 起始顶点到各顶点的最短路径及前驱顶点列表* @author Korbin* @date 2023-02-20 14:54:35**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object[][] shortestPathDijkstra(int fromVertexIndex) {// 最短路径权值,初始化为fromVertexIndex的权W[] pathVal = (W[]) Array.newInstance(infinity.getClass(), vertexNum);// 是否已计算,初始值为falseboolean[] calculated = new boolean[vertexNum];// 要到达此顶点应先从哪个顶点过来,初始值为fromVertexIndexInteger[] pre = new Integer[vertexNum];for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {pre[i] = fromVertexIndex;pathVal[i] = infinity;}// 处理第一个顶点AdjacencyMultiVertexNode<T, W> vertexNode = vertexes[fromVertexIndex];AdjacencyMultiEdgeNode<W> edgeNode = vertexNode.getFirstEdge();boolean firstEdge = true;while (null != edgeNode) {int refIndex = 0;W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();if (firstEdge) {refIndex = edgeNode.getJVex();edgeNode = edgeNode.getILink();firstEdge = false;} else {int iVex = edgeNode.getIVex();int jVex = edgeNode.getJVex();if (iVex == fromVertexIndex) {refIndex = jVex;edgeNode = edgeNode.getJLink();} else if (jVex == fromVertexIndex) {refIndex = iVex;edgeNode = edgeNode.getILink();}}pathVal[refIndex] = weight;}// 最小权值W minWeight = null;// 最小权值对应的索引下标int minWeightIndex = fromVertexIndex;// 已计算的顶点数量,初始值为0int calculatedNum;// 从fromVertexIndex到fromVertexIndex,令pathVal[fromVertexIndex]为0,令pre[fromVertexIndex]为fromVertexIndex// ,令calculated[fromVertexIndex]为truepathVal[fromVertexIndex] = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);pre[fromVertexIndex] = fromVertexIndex;calculated[fromVertexIndex] = true;calculatedNum = 1;while (calculatedNum < vertexNum) {// 循环到所有顶点都计算完毕// 处理本顶点指向的顶点vertexNode = vertexes[minWeightIndex];edgeNode = vertexNode.getFirstEdge();firstEdge = true;while (null != edgeNode) {int refIndex = 0;W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();if (firstEdge) {refIndex = edgeNode.getJVex();edgeNode = edgeNode.getILink();firstEdge = false;} else {int iVex = edgeNode.getIVex();int jVex = edgeNode.getJVex();if (iVex == fromVertexIndex) {refIndex = jVex;edgeNode = edgeNode.getJLink();} else if (jVex == fromVertexIndex) {refIndex = iVex;edgeNode = edgeNode.getILink();}}// 跳过calculated[j]为true的顶点if (!calculated[refIndex]) {// 与现有pathVal[j]比较if (infinity instanceof Integer) {// 对于weight为无穷大的也不处理if (!weight.equals(infinity)) {// 只处理权值是Integer的情况,其他类型的类似处理if (null == minWeight) {minWeight = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);}W arcI = (W) (Integer.valueOf((Integer) weight + (Integer) minWeight));if (arcI.compareTo(pathVal[refIndex]) < 0) {// 令pathVal[j]=arc[minWeightIndex][j] + minWeightpathVal[refIndex] = arcI;// 令pre[j]=minWeightIndexpre[refIndex] = minWeightIndex;}}}}}// 从pathVal和pre中取出新的minWeight和minWeightIndexminWeight = null;for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {// 跳过已计算最短路径的顶点if (!calculated[i] && (null == minWeight || minWeight.compareTo(pathVal[i]) > 0)) {minWeight = pathVal[i];minWeightIndex = i;}}// 设置minWeightIndex对应的顶点为已访问calculated[minWeightIndex] = true;calculatedNum++;// 用于测试System.out.println("min weight is " + minWeight + ", min weight index is " + minWeightIndex);StringBuilder builder1 = new StringBuilder("path val is [");StringBuilder builder2 = new StringBuilder("pre vertex is [");StringBuilder builder3 = new StringBuilder("calculated is [");for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {builder1.append(pathVal[i]).append(",");builder2.append(pre[i]).append(",");builder3.append(calculated[i]).append(",");}builder1.append("]");builder2.append("]\n\r");builder3.append("]");System.out.println(builder3);System.out.println(builder1);System.out.println(builder2);}Object[][] result = new Object[2][];result[0] = pathVal;result[1] = pre;return result;
}
边集数组的迪杰斯特拉算法实现如下:
/*** 迪杰斯特拉算法获取最短路径** @param fromVertexIndex 起始顶点下标* @return 起始顶点到各顶点的最短路径及前驱顶点列表* @author Korbin* @date 2023-02-20 14:54:35**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object[][] shortestPathDijkstra(int fromVertexIndex) {// 最短路径权值,初始化为fromVertexIndex的权W[] pathVal = (W[]) Array.newInstance(infinity.getClass(), vertexNum);// 是否已计算,初始值为falseboolean[] calculated = new boolean[vertexNum];// 要到达此顶点应先从哪个顶点过来,初始值为fromVertexIndexInteger[] pre = new Integer[vertexNum];for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {pre[i] = fromVertexIndex;pathVal[i] = infinity;}for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; i++) {EdgeListEdgeNode<W> edgeNode = arc[i];int begin = edgeNode.getBegin();int end = edgeNode.getEnd();W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();if (begin == fromVertexIndex) {pathVal[end] = weight;}}// 最小权值W minWeight = null;// 最小权值对应的索引下标int minWeightIndex = fromVertexIndex;// 已计算的顶点数量,初始值为0int calculatedNum;// 从fromVertexIndex到fromVertexIndex,令pathVal[fromVertexIndex]为0,令pre[fromVertexIndex]为fromVertexIndex// ,令calculated[fromVertexIndex]为truepathVal[fromVertexIndex] = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);pre[fromVertexIndex] = fromVertexIndex;calculated[fromVertexIndex] = true;calculatedNum = 1;while (calculatedNum < vertexNum) {// 循环到所有顶点都计算完毕// 处理本顶点指向的顶点for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; i++) {EdgeListEdgeNode<W> edgeNode = arc[i];int begin = edgeNode.getBegin();int end = edgeNode.getEnd();W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();int refIndex = -1;if (type.equals(BusinessConstants.GRAPH_TYPE.DIRECTED_NETWORK)) {if (begin == minWeightIndex) {refIndex = end;}} else {if (begin == minWeightIndex) {refIndex = end;} else if (end == minWeightIndex) {refIndex = begin;}}// 跳过calculated[j]为true的顶点if (refIndex >= 0 && !calculated[refIndex]) {// 与现有pathVal[j]比较if (infinity instanceof Integer) {// 对于weight为无穷大的也不处理if (!weight.equals(infinity)) {// 只处理权值是Integer的情况,其他类型的类似处理if (null == minWeight) {minWeight = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);}W arcI = (W) (Integer.valueOf((Integer) weight + (Integer) minWeight));if (arcI.compareTo(pathVal[refIndex]) < 0) {// 令pathVal[j]=arc[minWeightIndex][j] + minWeightpathVal[refIndex] = arcI;// 令pre[j]=minWeightIndexpre[refIndex] = minWeightIndex;}}}}}// 从pathVal和pre中取出新的minWeight和minWeightIndexminWeight = null;for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {// 跳过已计算最短路径的顶点if (!calculated[i] && (null == minWeight || minWeight.compareTo(pathVal[i]) > 0)) {minWeight = pathVal[i];minWeightIndex = i;}}// 设置minWeightIndex对应的顶点为已访问calculated[minWeightIndex] = true;calculatedNum++;// 用于测试System.out.println("min weight is " + minWeight + ", min weight index is " + minWeightIndex);StringBuilder builder1 = new StringBuilder("path val is [");StringBuilder builder2 = new StringBuilder("pre vertex is [");StringBuilder builder3 = new StringBuilder("calculated is [");for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {builder1.append(pathVal[i]).append(",");builder2.append(pre[i]).append(",");builder3.append(calculated[i]).append(",");}builder1.append("]");builder2.append("]\n\r");builder3.append("]");System.out.println(builder3);System.out.println(builder1);System.out.println(builder2);}Object[][] result = new Object[2][];result[0] = pathVal;result[1] = pre;return result;
}
6.2 弗洛伊德(Floyd)算法
我们仍然以以下无向网举例:
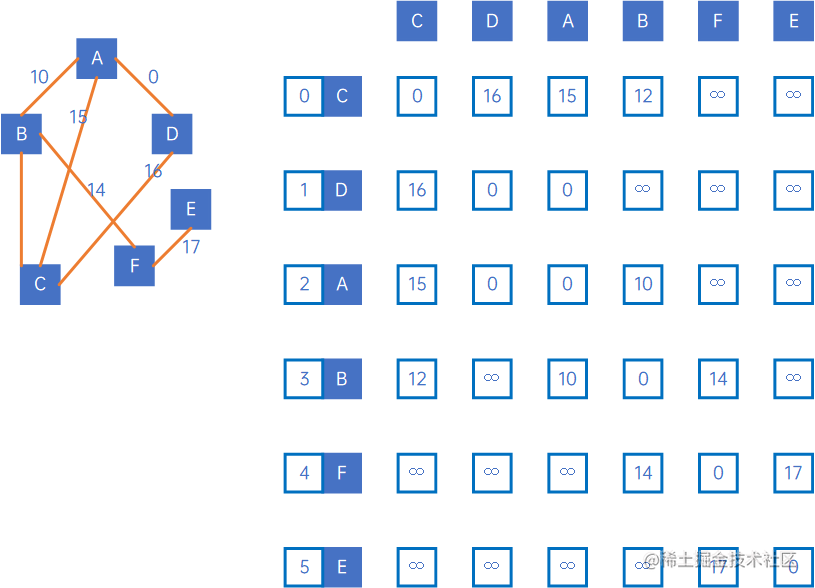
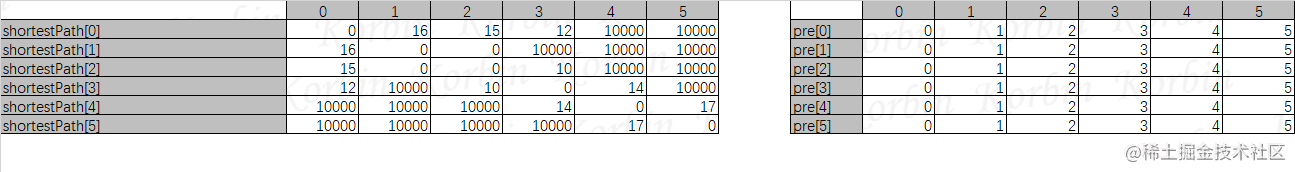
首先,我们定义两个矩阵,一为shortestPath,表示最短路径矩阵,一为pre,表示前驱矩阵,初始化shortestPath=arc即无向网的邻接矩阵,令pre[i][j]=j。
然后我们开始处理,我们把这个过程放到Excel里面进行展示,为了方便计算,我们将“∞\infty∞”设置为一个大于所有权值的值,例如10000,那么,有如下表格:
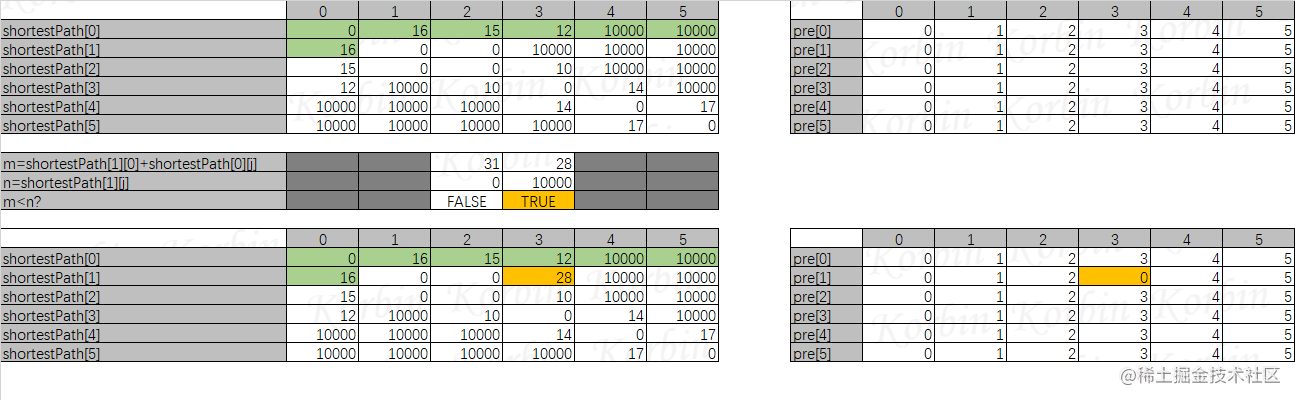
我们先令所有顶点都通过顶点0中转一下后,再连接到其他顶点,来比较直接连接的权和中转连接的权值,假设起始顶点是i,终止顶点是j,那么直接连接的权是n=shortestPath[i][j],通过顶点0中转的权是m=shortestPath[i][0]+shortestPath[0][j],而如果m<n,则表示顶点i通过顶点0中转后,再连到顶点j的代价更小,这种情况,我们将pre[i][j]设置为pre[i][0],将shortestPath[i][j]设置为shortestPath[i][0]+shortestPath[0][j]。
注意到,在这个计算过程中,如果shortestPath[i][0]或者shortestPath[0][j]为无穷大,那么它们加起来的权值和肯定为无穷大,无论shortestPath[i][j]权值是多少,肯定大于shortestPath[i][j],因此当shortestPath[i][0]或者shortestPath[0][j]为无穷大时,不需要进行计算。
先来看i=1的情况,计算后,我们发现shortestPath[1][0]+shortestPath[0][3]小于shortestPath[1][3],因此令shortestPath[1][3]=shortestPath[1][0]+shortestPath[0][3],令pre[1][3]=pre[1][0],如下:
再来看i=2的情况,所有的m都大于n,不进行任何处理:
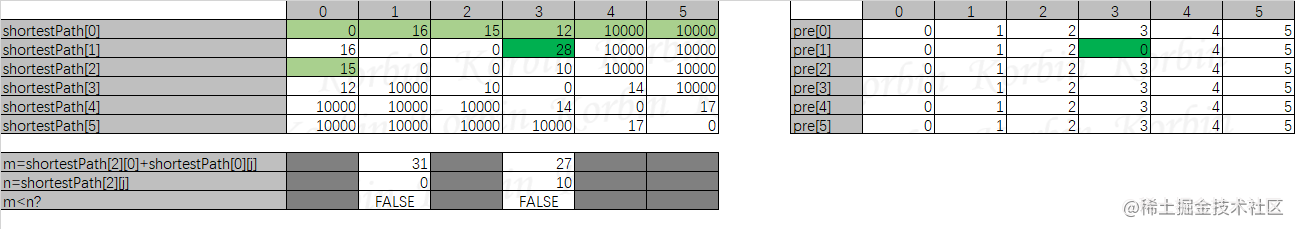
i=3时,shortestPath[3][0]+shortestPath[0][1]<shortestPath[3][1],令shortestPath[3][1]=shortestPath[3][0]+shortestPath[0][1],令pre[3][1]=pre[3][0]:
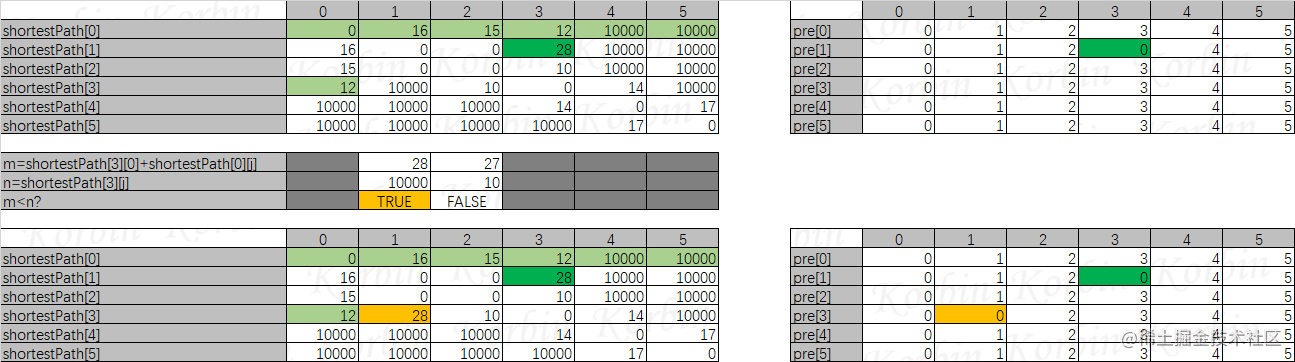
当i=4和i=5时,shortestPath[4][0]和shortestPath[5][0]都为无穷大,无论shortestPath[0][j](j=4或5)为多少,权值和肯定大于shortestPath[i][j](i=4或5,j=4或5),因此不需要计算。
到这里,所有顶点通过顶点0与其他顶点连通的处理已完毕。
接下来看所有顶点通过顶点1与其他顶点连通的情况,注意,处理时是基于前面已处理的shortestPath二维数组进行处理的。
我们发现,所有的shortestPath[i][1]+shortestPath[1][j]都大于shortestPath[i][j],因此不进行任何处理:

然后再看所有顶点通过顶点2连通其他顶点的情况,处理逻辑一致,结果如下:
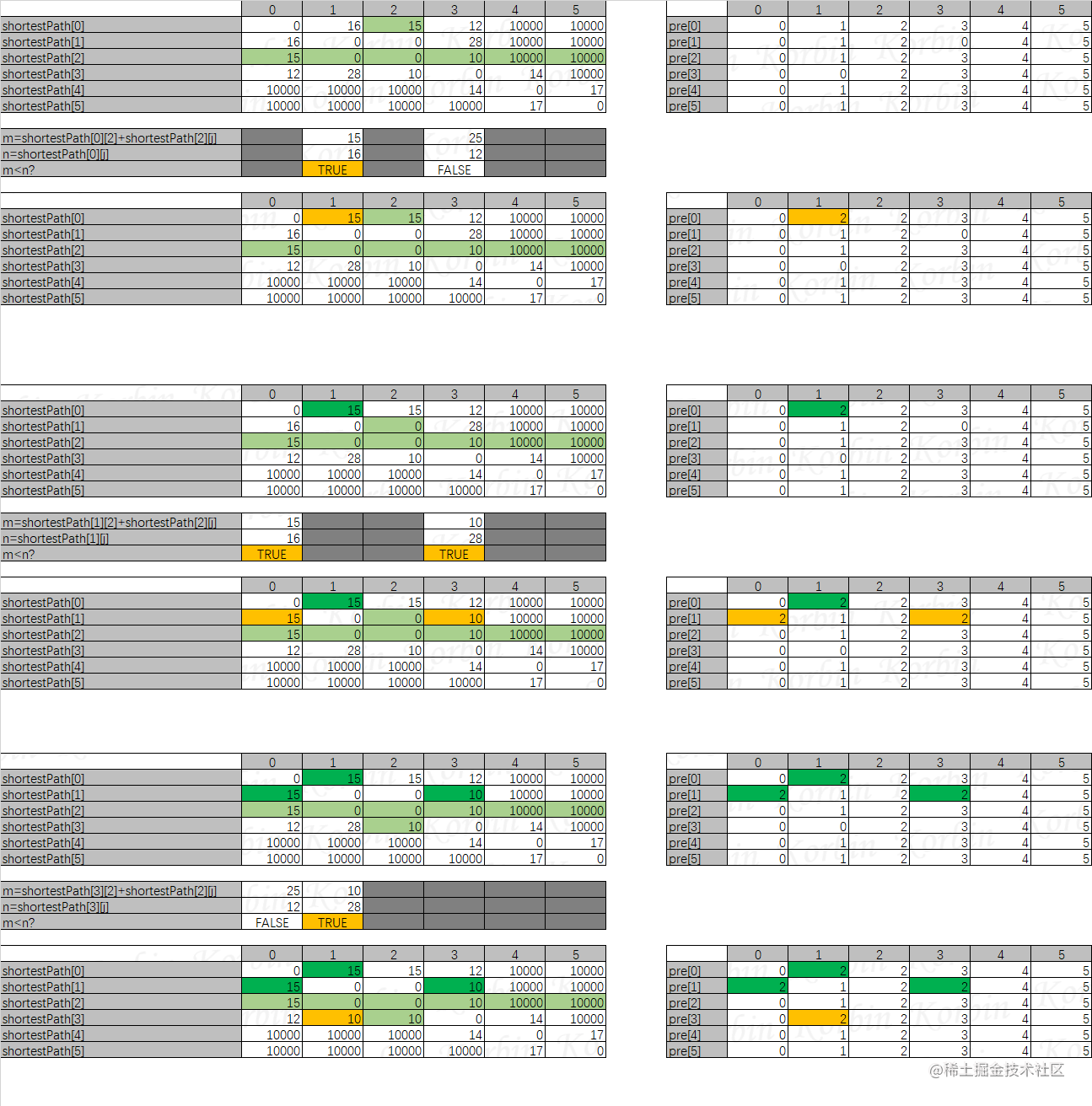
然后是所有顶点通过顶点3连通其他顶点的情况,然后是所有顶点通过顶点4连通其他顶点的情况,依此类推,得到以下最终结果:
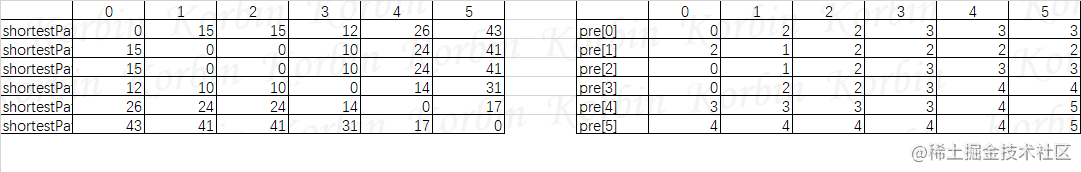
我们再来总结一下规则:
(1) 设有图G(V,E),令shortestPath[][]=arc[][],新建二维数组pre[][],令pre[i][j]=j;
(2) 计算所有顶点通过顶点x(0≤x≤vertexNum0 \leq x \leq vertexNum0≤x≤vertexNum)连通到其他顶点,计算shortestPath[i][j]与shortestPath[i][x]+shortestPath[x][j],如果shortestPath[i][x]+shortestPath[x][j]<shortestPath[i][j],则表示i->x->j的代价比i->j小,于是令shortestPath[i][j]=shortestPath[i][x]+shortestPath[x][j],令pre[i][j]=pre[i][x];
(3) 迭代以上变量,其中0≤i≤vertexNum0 \leq i \leq vertexNum0≤i≤vertexNum、0≤j≤vertexNum0 \leq j \leq vertexNum0≤j≤vertexNum、0≤x≤vertexNum0 \leq x \leq vertexNum0≤x≤vertexNum;
(4) 迭代过程中,若shortestPath[i][x]或者shortestPath[x][j]为无穷大则跳过;当i=x或x=j或j=i时也跳过;
现在我们已经得到了以下结果:
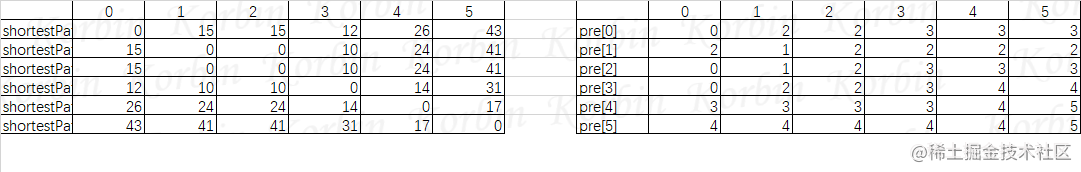
如何计算出顶点i到顶点j的最短路径了,方法如下:
(1) 顶点i到顶点j的最小代价为shortestPath[i][j];
(2) 取出pre[i][j],若pre[i][j]=a,则表示顶点i到顶点j要先经过顶点a,再取出pre[a][j],若pre[a][j]=b,则表示顶点i到顶点a要先经过顶点b,依此类推,直到pre[x][j]=j,于是得到顶点i到顶点j的最短路径为i->a->b…->x->j;
我们来看顶点1到顶点5的最短路径,按照上述规则,我们知道顶点1到顶点5的最小代价为shortestPath[1][5]=2。然后因pre[2][5]=3,pre[3][5]=4,pre[4][5]=5,因此顶点1到顶点5的最短路径为1->2->3->4->5。
于是,在邻接矩阵中,弗洛伊德算法的最短路径代码实现如下所示:
/*** 使用弗洛伊德算法生成的最短路径,只需要计算一次,因此保留计算结果**/
private W[][] shortestPath;/*** 使用弗洛伊德算法生成的最短路径中,各顶点的前驱顶点信息,只需要计算一次,因此保留计算结果**/
private int[][] pre;/*** 使用弗洛伊德算法计算最短路径** @author Korbin* @date 2023-02-23 12:23:31* @param from 起始顶点* @param to 终止顶点* @return 最短路径及权值**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public String shortestPathFloyd(int from, int to) {if (null == shortestPath) {// 弗洛伊德算法只需要计算一次System.out.println("进行了运算");// 初始化shortestPath = arc;pre = new int[vertexNum][vertexNum];for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i ++) {for (int j = 0;j < vertexNum; j++) {pre[i][j] = j;}}// 生成最短路径矩阵for (int k = 0; k < vertexNum; k++) {for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {if (i != k) {// 所有顶点通过顶点k访问其他顶点for (int j = 0;j < vertexNum; j++) {if (j != k && j != i && !shortestPath[i][k].equals(infinity) && !shortestPath[k][j].equals(infinity)) {if (infinity instanceof Integer) {// 以Integer举例,其他类型类似W directWeight = shortestPath[i][j];W transferWeight = (W)Integer.valueOf((Integer)shortestPath[i][k] + (Integer)shortestPath[k][j]);if (transferWeight.compareTo(directWeight) < 0) {shortestPath[i][j] = transferWeight;pre[i][j] = pre[i][k];}}}}}}}}// 获取最短路径W weight = shortestPath[from][to];StringBuilder pathBuilder = new StringBuilder("path is ").append(vertex[from]).append("->");int index = pre[from][to];while (index != to) {pathBuilder.append(vertex[index]).append("->");index = pre[index][to];}pathBuilder.append(vertex[to]);pathBuilder.append(", weight is ").append(weight);return pathBuilder.toString();
}
其他存储结构也可以使用弗洛伊德算法去尝试实现生成最短路径,本处不再赘述。
6.3 总结
最短路径,对于图来说,是两顶点之间经过的边数最少的路径;对于网来说,是指两顶点之间经过的边上权值之和最小的路径。路径上第一个顶点为源点,最后一个顶点是终点。
迪杰斯特拉算法步骤:
(1) 假设要计算顶点k到其他顶点的最短路径;
(2) 首先定义三个数组,calculated[i]表示k->i的最短路径是否已计算出来,所有元素初始值均为false;pathVal[i]表示k->i的最短路径,所有元素初始值均为无穷大;pre[i]表示k->i中经历的顶点;
(3) 定义一个变量minWeight,表示“k->上一个顶点的最小权值”,k表示minWeight对应的顶点的下标,定义minWeightIndex表示minWeight对应的下标,初始值为minWeightIndex=k;
(4) 然后把arc[minWeightIndex][i]与现有的pathVal[i]比较,规则是:
1) calculated[i]=true表示已找到最短路径,不进行任何处理;
2) 如果arc[minWeightIndex][i]+minWeight<pathVal[i],则令pathVal[i]=arc[minWeightIndex][i]+minWeight,令pre[i]=minWeightIndex,表示k->i至少要经过顶点minWeightIndex;同时设置calculated[minWeightIndex]=true;
3) 如果arc[minWeightIndex][i]+minWeight>=pathVal[i],则pathVal[i]不变,pre[i]也不变,表示k->i不会经过顶点minWeightIndex;
(5) 然后令minWeight为当前pathVal[i]中的最小值,令minWeightIndex为最小值对应的下标,重复第(4)步,直到所有顶点都已计算出最短路径,即calculated数组的元素值全为true;
费洛伊德算法步骤:
(1) 设有图G(V,E),令shortestPath[][]=arc[][],新建二维数组pre[][],令pre[i][j]=j;
(2) 计算所有顶点通过顶点x(0≤x≤vertexNum0 \leq x \leq vertexNum0≤x≤vertexNum)连通到其他顶点,计算shortestPath[i][j]与shortestPath[i][x]+shortestPath[x][j],如果shortestPath[i][x]+shortestPath[x][j]<shortestPath[i][j],则表示i->x->j的代价比i->j小,于是令shortestPath[i][j]=shortestPath[i][x]+shortestPath[x][j],令pre[i][j]=pre[i][x];
(3) 迭代以上变量,其中0≤i≤vertexNum0 \leq i \leq vertexNum0≤i≤vertexNum、0≤j≤vertexNum0 \leq j \leq vertexNum0≤j≤vertexNum、0≤x≤vertexNum0 \leq x \leq vertexNum0≤x≤vertexNum;
(4) 迭代过程中,若shortestPath[i][x]或者shortestPath[x][j]为无穷大则跳过;当i=x或x=j或j=i时也跳过;
迪杰斯特拉算法的时间复杂度是O(n2),主要用于解决特定顶点到其他顶点的最短路径问题,如果需要计算所有顶点到其他顶点的最短路径,则在迪杰斯特拉算法的基础上把起始顶点全部迭代一遍即可,这时时间复杂度为O(3)。
弗洛伊德算法的时间复杂度也是O(3),通常用于解决需要计算所有顶点到其他顶点最短距离问题。
注:本文为程 杰老师《大话数据结构》的读书笔记,其中一些示例和代码是笔者阅读后自行编制的。
相关文章:

大话数据结构-迪杰斯特拉算法(Dijkstra)和弗洛伊德算法(Floyd)
6 最短路径 最短路径,对于图来说,是两顶点之间经过的边数最少的路径;对于网来说,是指两顶点之间经过的边上权值之和最小的路径。路径上第一个顶点为源点,最后一个顶点是终点。 6.1 迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra&am…...

2023年全国最新食品安全管理员精选真题及答案10
百分百题库提供食品安全管理员考试试题、食品安全员考试预测题、食品安全管理员考试真题、食品安全员证考试题库等,提供在线做题刷题,在线模拟考试,助你考试轻松过关。 91.实施日常检查,如果违反关键项的,应当即作出如…...
Unity常见面试题详解(持续更新...)
一丶声明、定义、实例化、初始化 1、首先我们来讨论在C/C中的声明和定义.. 1)我们先从函数声明和定义说起... 一般我们在C里都会先定义一个函数,然后再Main函数前将函数声明,比如: //函数声明 int Add(int);int Main {} //函数…...
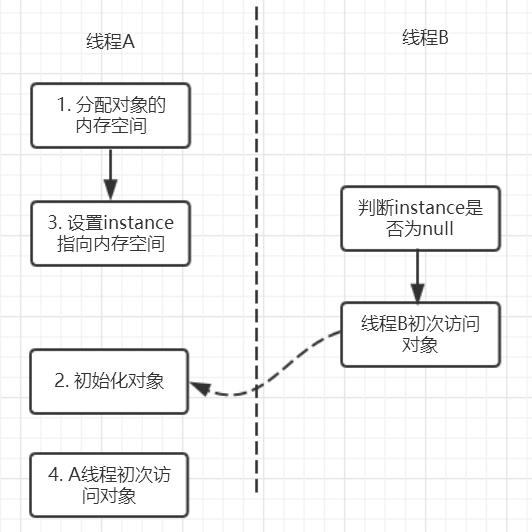
java高级篇之三大性质总结:原子性、可见性以及有序性
1. 三大性质简介 在并发编程中分析线程安全的问题时往往需要切入点,那就是两大核心:JMM抽象内存模型以及happens-before规则(在这篇文章中已经经过了),三条性质:原子性,有序性和可见性。关于sy…...
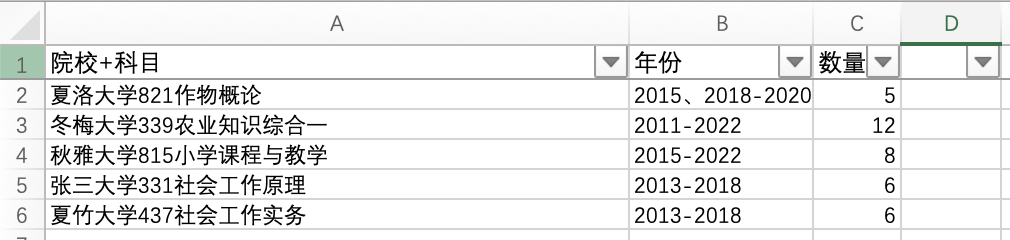
真涨脸,我用 Python 为朋友自动化整理表格
今天,在工作的时候,我的美女同事问我有没有办法自动生成一个这样的表格: 第一列是院校科目,第二列是年份,第三列是数量。 这张表格是基于这一文件夹填充的,之前要一个文件夹一个文件夹打开然后手动填写年份…...
MySQL学习笔记(1.操作数据库与数据的SQL)
1. 下载安装 参照:MySQL8.0下载安装_凯尔萨厮的博客-CSDN博客 2. MySQL启动与停止 方式(1).我的电脑>右键>管理>服务和应用程序>服务>(或在windows搜索栏输入services.msc) 找到MySQL80,右键启动或停止 方式(2…...

C++——特殊类设计
目录 不能被拷贝的类 只能在堆上创建对象的类 只能在栈上创建对象的类 不能被继承的类 只能创建一个对象的类(单例模式) 饿汉模式 懒汉模式 单例对象释放问题 不能被拷贝的类 C98:将拷贝构造函数与赋值运算符重载只声明不定义,并且将其访问权…...

Scratch少儿编程案例-植物大战僵尸-趣味角色版
专栏分享 点击跳转=>Unity3D特效百例点击跳转=>案例项目实战源码点击跳转=>游戏脚本-辅助自动化点击跳转=>Android控件全解手册点击跳转=>Scratch编程案例👉关于作者...

Vue的路由守卫
对于绝大部分的网站而言,都是有个人主页的,但是你如果没登陆的话,还能访问个人主页吗? 从逻辑上来讲,那肯定是不行的。 所以,要怎么阻止没登录状态下去访问个人主页呢? 就是利用路由守卫&#x…...

【算法】151. 反转字符串中的单词
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string/给你一个字符串 s ,请你反转字符串中 单词 的顺序。单词 是由非空格字符组成的字符串。s 中使用至少一个空格将字符串中的 单词 分隔开。返回 单词 顺序颠倒且 单词 之间用单个空格连接的结…...
-认知服务(2))
Azure AI基础到实战(C#2022)-认知服务(2)
目录 ComputerVisionClient Class定义构造函数属性上一节例子Task.Wait 方法其它部分分析winform调用认知服务代码剖析1、调用参数2、定义ComputerVisionClient对象,准备调用 REST API3、Authenticate4、调用REST API,这是重点和关键(1)Lambda 表达式和匿名函数(2)async(3)…...

并发就一定快吗?答:肯定不是啊
文章目录一、多线程概念1.1 程序的并发与并行1.1.1 程序的并行1.1.2 程序的并发1.2 进程与线程1.2.1 进程1.2.2 线程1.2.3 多线程并发就一定快吗?答案直接戳这里👉:多线程并发就一定快吗? 一、多线程概念 在实际应用中ÿ…...

前端的学习路线和方法
一些前端工程师面临的现状 1.没有系统的的学习基础知识 2.技术上存在短板,说句不好听的话,大多数开发者的上升通道都没有明确的路线,大公司还好,小公司基本都是后端作为开发组组长 3.前端各种技术层出不穷,需要花费…...
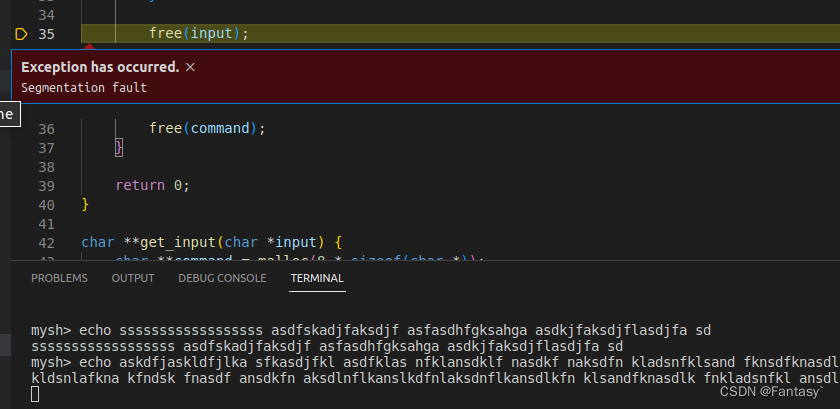
用C语言写一个自己的shell-Part Ⅱ--execute commands
Part Ⅱ–execute commands Exec This brings us to the exec family of functions. Namely, it has the following functions: execlexecvexecleexecveexeclpexecvp For our needs,we will use execvp whose signature looks like this int execvp(const char *file, cha…...

案例实践|运营腾讯游戏,Proxima Beta 使用 Apache Pulsar 升级团队协作与数据治理...
文章摘要本文整理自 Pulsar Summit Asia 2022 上,Proxima Beta 软件工程师施磊的分享《How to achieve better team integration and data governance by using Apache Pulsar》。本文首先将为大家介绍 CQRS 和 Event Sourcing 概念,便于了解为何 Proxim…...
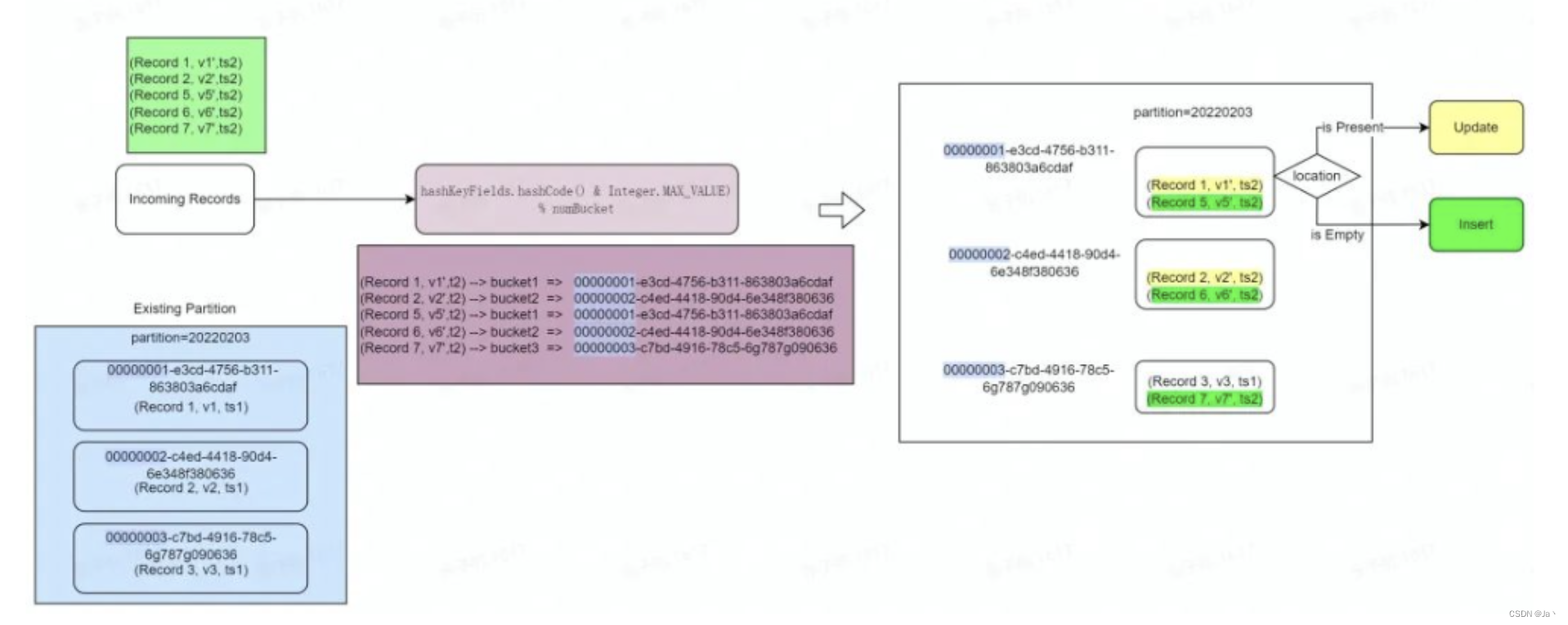
Hudi的7种索引
1、Bloom Index Bloom Index (default) 使用根据记录键构建的bloom过滤器,也可以使用记录键范围修剪候选文件.原理为计算RecordKey的hash值然后将其存储到bitmap中,为避免hash冲突一般选择计算3次 HoodieKey 主键信息:主要包含recordKey 和p…...
系统软中断 software)
Linux内核(十三)系统软中断 software
文章目录中断概述Linux内核中断软中断相关代码解析软中断结构体软中断类型软中断两种触发方式函数__do_softirq解析定时器的软中断实现解析定时器相关代码总结Linux版本:linux-3.18.24.x 中断概述 中断要求 快进快出,提高执行效率,…...
Linux -- 查看进程 PS 命令 详解
我们上篇介绍了, Linux 中的进程等概念,那么,在Linux 中如何查看进程呢 ??我们常用到的有两个命令, PS 和 top 两个命令,今天先来介绍下 PS 命令~!PS 命令 :作用 &#x…...

C2科一考试道路通行规定
目录 低能见度等恶劣环境下的通行规定 驾驶机动车禁止行为 停车规定 通行常识 高速公路限速规定 三观不一样的人,无论重来多少次,结果都一样 他不会懂你的委屈 只是觉得自已没错 两个人真正的可悲连吵架都不在一个点上 有句话说得好 我要是没点自我…...
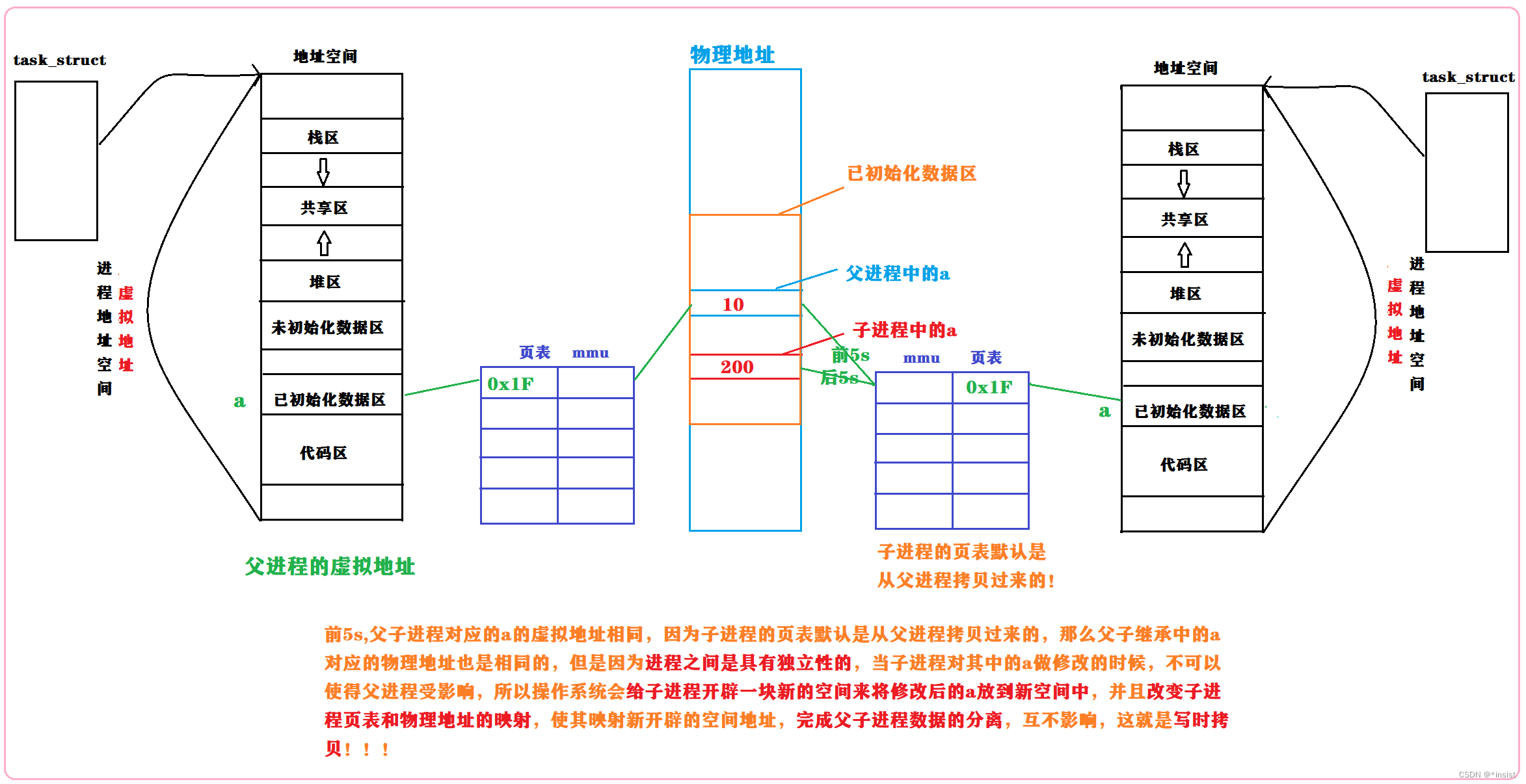
进程概念(详细版)
进程的概念本文主要介绍进程的相关知识 文章目录认识冯诺依曼体系结构操作系统的基本概念操作系统的作用是什么系统调用和库函数相关概念进程基本概念描述进程进程控制块(PCB)task_struct 结构体进程是如何被操作系统管理起来的先描述再组织描述好,组织好࿰…...

DeepSeek 赋能智慧能源:微电网优化调度的智能革新路径
目录 一、智慧能源微电网优化调度概述1.1 智慧能源微电网概念1.2 优化调度的重要性1.3 目前面临的挑战 二、DeepSeek 技术探秘2.1 DeepSeek 技术原理2.2 DeepSeek 独特优势2.3 DeepSeek 在 AI 领域地位 三、DeepSeek 在微电网优化调度中的应用剖析3.1 数据处理与分析3.2 预测与…...
UE5 学习系列(三)创建和移动物体
这篇博客是该系列的第三篇,是在之前两篇博客的基础上展开,主要介绍如何在操作界面中创建和拖动物体,这篇博客跟随的视频链接如下: B 站视频:s03-创建和移动物体 如果你不打算开之前的博客并且对UE5 比较熟的话按照以…...

Qwen3-Embedding-0.6B深度解析:多语言语义检索的轻量级利器
第一章 引言:语义表示的新时代挑战与Qwen3的破局之路 1.1 文本嵌入的核心价值与技术演进 在人工智能领域,文本嵌入技术如同连接自然语言与机器理解的“神经突触”——它将人类语言转化为计算机可计算的语义向量,支撑着搜索引擎、推荐系统、…...

成都鼎讯硬核科技!雷达目标与干扰模拟器,以卓越性能制胜电磁频谱战
在现代战争中,电磁频谱已成为继陆、海、空、天之后的 “第五维战场”,雷达作为电磁频谱领域的关键装备,其干扰与抗干扰能力的较量,直接影响着战争的胜负走向。由成都鼎讯科技匠心打造的雷达目标与干扰模拟器,凭借数字射…...

智能分布式爬虫的数据处理流水线优化:基于深度强化学习的数据质量控制
在数字化浪潮席卷全球的今天,数据已成为企业和研究机构的核心资产。智能分布式爬虫作为高效的数据采集工具,在大规模数据获取中发挥着关键作用。然而,传统的数据处理流水线在面对复杂多变的网络环境和海量异构数据时,常出现数据质…...

Linux C语言网络编程详细入门教程:如何一步步实现TCP服务端与客户端通信
文章目录 Linux C语言网络编程详细入门教程:如何一步步实现TCP服务端与客户端通信前言一、网络通信基础概念二、服务端与客户端的完整流程图解三、每一步的详细讲解和代码示例1. 创建Socket(服务端和客户端都要)2. 绑定本地地址和端口&#x…...

NPOI操作EXCEL文件 ——CAD C# 二次开发
缺点:dll.版本容易加载错误。CAD加载插件时,没有加载所有类库。插件运行过程中用到某个类库,会从CAD的安装目录找,找不到就报错了。 【方案2】让CAD在加载过程中把类库加载到内存 【方案3】是发现缺少了哪个库,就用插件程序加载进…...
零知开源——STM32F103RBT6驱动 ICM20948 九轴传感器及 vofa + 上位机可视化教程
STM32F1 本教程使用零知标准板(STM32F103RBT6)通过I2C驱动ICM20948九轴传感器,实现姿态解算,并通过串口将数据实时发送至VOFA上位机进行3D可视化。代码基于开源库修改优化,适合嵌入式及物联网开发者。在基础驱动上新增…...

小木的算法日记-多叉树的递归/层序遍历
🌲 从二叉树到森林:一文彻底搞懂多叉树遍历的艺术 🚀 引言 你好,未来的算法大神! 在数据结构的世界里,“树”无疑是最核心、最迷人的概念之一。我们中的大多数人都是从 二叉树 开始入门的,它…...

拟合问题处理
在机器学习中,核心任务通常围绕模型训练和性能提升展开,但你提到的 “优化训练数据解决过拟合” 和 “提升泛化性能解决欠拟合” 需要结合更准确的概念进行梳理。以下是对机器学习核心任务的系统复习和修正: 一、机器学习的核心任务框架 机…...
