Kafka 之 AdminClient API
目录
一. 前言
二. KafkaAdminClient API
2.1. API 总览
2.2. Topic 操作
2.2.1. 创建 Topic
2.2.2. Topic 列表
2.2.3. 删除 Topic
2.2.4. 描述 Topic 详细信息
2.3. 分区 Partition 操作
2.3.1. 增加分区
2.3.2. 分区副本重新分配
2.3.3. 查询分区副本列表
2.4. Config 配置信息
2.4.1. 描述配置详细信息
2.4.2. 修改配置信息
2.4.3. incrementalAlterConfigs
2.5. Scram 账户操作
2.5.1. 创建 Scram 账户
2.5.2. 删除 Scram 账户
2.5.3. 查询 Scram 账户信息
2.6. Acl 操作
2.6.1. 创建 Acl
2.6.2. 删除 Acl
一. 前言
自0.11.0.0版本起,Kafka 社区推出了 AdminClient 和 KafkaAdminClient,意在统一所有的集群管理 API。使用 0.11.0.0 及以后版本的用户应该始终使用这个类来管理集群。虽然和原先服务器端的 AdminClient 类同名,但这个工具是属于客户端的,因此只需要在管理程序项目中添加 kafka-clients 依赖即可:
<dependency><groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId><artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId><version>3.6.1</version>
</dependency>Kafka 的管理 Java 客户端,支持管理和检查 Topic、Broker、配置和 ACL。所需的最小 Broker版本是 0.10.0.0。有更严格要求的方法将指定所需的最小 Broker 版本。这个客户端是在 0.11.0.0中引入的,API 还在不断发展。我们将尝试以兼容的方式演进 API,但我们保留在必要时在次要版本中进行破坏性更改的权利。一旦 API 被认为是稳定的,我们将更新 InterfaceStability 注解和本通知。
二. KafkaAdminClient API
2.1. API 总览
| 方法名称 | 方法说明 |
|---|---|
| createTopics | 创建一批新主题。此操作不是事务性的,因此它对于某些主题可能成功,而对于其他主题则可能失败。此方法返回成功后,可能需要几秒钟的时间,所有代理才能知道主题已创建。在这段时间内,listTopics()和describeTopics(Collection)可能不会返回有关新主题的信息。版本0.10.1.0或更高版本的代理支持此操作。版本0.10.2.0支持validateOnly选项。 |
| deleteTopics | 删除一批主题。此操作不是事务性的,因此它对于某些主题可能成功,而对于其他主题则可能失败。AdminClient#deleteTopics返回成功后,可能需要几秒钟,所有代理才能意识到主题已消失。在此期间,AdminClient#listTopics和AdminClient#describeTopics可能会继续返回有关已删除主题的信息。如果代理上的delete.topic.enable为false,则deleteTopics将标记主题为删除,但实际上不会删除它们。在这种情况下,期货将成功返回。版本0.10.1.0或更高版本的代理支持此操作。 |
| listTopics | 查询Topic列表 |
| describeTopics | 描述Topic的详情信息 |
| describeCluster | 描述Cluster的详情信息 |
| describeAcls | 根据提供的过滤器列出访问控制列表(ACL)。注意:createAcls或deleteAcls所做的更改可能需要一些时间才能反映到describeAcls的输出中。版本0.11.0.0或更高版本的代理支持此操作。 |
| createAcls | 创建绑定到特定资源的访问控制列表(ACL)。此操作不是事务性的,因此对于某些ACL可能成功,而对于其他ACL则可能失败。如果您尝试添加与现有ACL复制的ACL,则不会引发任何错误,但不会进行任何更改。版本0.11.0.0或更高版本的代理支持此操作。 |
| deleteAcls | 根据提供的过滤器删除访问控制列表(ACL)。此操作不是事务性的,因此对于某些ACL可能成功,而对于其他ACL则可能失败。版本0.11.0.0或更高版本的代理支持此操作。 |
| describeConfigs | 获取指定资源的配置。返回的配置包括默认值,isDefault()方法可用于将其与用户提供的值区分开。isSensitive()为true的配置条目的值始终为null,因此不会公开敏感信息。isReadOnly()为true的配置条目无法更新。版本0.11.0.0或更高版本的代理支持此操作。 |
|
| 使用默认选项更新指定资源的配置。更新不是事务性的,因此更新可能会为某些资源成功而为其他资源失败。特定资源的配置会自动更新。版本0.11.0.0或更高版本的代理支持此操作。 |
| incrementalAlterConfigs | 新版本中是使用incrementalAlterConfigs方法来修改Topic的配置项,该方法使用起来相对于alterConfigs要略微复杂一些,但因此功能更多、更灵活。 |
| alterReplicaLogDirs | 更改指定副本的日志目录。当前仅当在代理上创建副本之前使用此API时,此API才有用。它将支持在完全实施KIP-113之后已经创建的移动副本。此操作不是事务性的,因此它可能对某些副本成功而对其他副本失败。版本1.0.0或更高版本的代理支持此操作。 |
| describeLogDirs | 查询给定代理集上所有日志目录的信息版本1.0.0或更高版本的代理支持此操作。 |
| describeReplicaLogDirs | 查询副本日志目录信息中的指定副本。版本1.0.0或更高版本的代理支持此操作。 |
| createPartitions | 根据相应的值,增加作为newPartitions关键字指定的主题的分区数。如果为具有关键字的主题增加了分区,则分区逻辑或消息的顺序将受到影响。 |
| deleteRecords | 删除消息 |
| createDelegationToken | 创建DelegationToken |
| renewDelegationToken | 更新DelegationToken |
| expireDelegationToken | 过期DelegationToken |
| describeDelegationToken | 描述DelegationToken的详情信息 |
| describeConsumerGroups | 描述消费组的详情信息 |
| listConsumerGroups | 查询消费组列表 |
| listConsumerGroupOffsets | 查询消费组的offset列表 |
| deleteConsumerGroups | 删除消费组,只能是闲置的消费组 |
| deleteConsumerGroupOffsets | 删除消费组中某些分区的已提交偏移量。只有当组没有主动订阅相应的Topic时,才会成功。 |
| electLeaders | 选举Leader |
| alterPartitionReassignments | 修改分区副本 |
| listPartitionReassignments | 查询分区副本列表 |
| removeMembersFromConsumerGroup | 从消费组中移除消费者成员 |
| alterConsumerGroupOffsets | 修改消费组的offset |
| listOffsets | 查询Topic分区的offset列表 |
| describeClientQuotas | 描述客户端配额配置详细信息 |
| alterClientQuotas | 修改客户端配额 |
| describeUserScramCredentials | 描述Scram账户详细信息 |
| alterUserScramCredentials | 修改Scram账户 |
| describeFeatures | 描述已完成的功能以及支持的功能 |
| updateFeatures | 将指定的更新应用于最终确定的功能 |
| describeMetadataQuorum | 描述元数据数量的状态 |
| unregisterBroker | 注销Broker |
| describeProducers | 描述生产者详细信息 |
| describeTransactions | 描述事务的详细信息 |
| abortTransaction | 终止事务 |
| listTransactions | 查询事务列表 |
| fenceProducers | 隔离使用任何提供的事务ID的所有活动生产者 |
| metrics | 获取adminClient保存的度量值 |
2.2. Topic 操作
2.2.1. 创建 Topic
// bootstrapServers 如 localhost:9092
private void createTopics(String bootstrapServers) {Properties properties = new Properties();properties.put("bootstrap.servers", bootstrapServers);properties.put("connections.max.idle.ms", 10000);properties.put("request.timeout.ms", 5000);try (AdminClient client = AdminClient.create(properties)) {CreateTopicsResult result = client.createTopics(Arrays.asList(new NewTopic("topic1", 1, (short) 1),new NewTopic("topic2", 1, (short) 1),new NewTopic("topic3", 1, (short) 1)));try {result.all().get();} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {throw new IllegalStateException(e);}}
}2.2.2. Topic 列表
private void listTopics(String bootstrapServers) {Properties properties = new Properties();properties.put("bootstrap.servers", bootstrapServers);properties.put("connections.max.idle.ms", 10000);properties.put("request.timeout.ms", 5000);try (AdminClient client = AdminClient.create(properties)) {ListTopicsResult result = client.listTopics();try {result.listings().get().forEach(topic -> {System.out.println(topic);});} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {throw new IllegalStateException(e);}}
}// 运行结果
(name=topic1, internal=false)
(name=topic2, internal=false)
(name=topic3, internal=false)
...2.2.3. 删除 Topic
public static void deleteTopics(AdminClient adminClient, String topicName) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {DeleteTopicsResult ret = adminClient.deleteTopics(Arrays.asList(topicName));ret.all().get();
}2.2.4. 描述 Topic 详细信息
一个 Topic 会有自身的描述信息,例如:partition 的数量,副本集的数量,是否为 internal等等。AdminClient 中提供了 describeTopics 方法来查询这些描述信息。代码示例:
public static void describeTopics(AdminClient adminClient, String topicName) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {DescribeTopicsResult ret = adminClient.describeTopics(Arrays.asList(topicName, "__consumer_offsets"));//等待返回结果完成Map<String, TopicDescription> topics = ret.all().get();for (Map.Entry<String, TopicDescription> entry : topics.entrySet()) {System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "---->" + entry.getValue());}}// 运行结果:
testTopic---->(name=testTopic, internal=false, partitions=(partition=0, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)), authorizedOperations=null)
__consumer_offsets---->(name=__consumer_offsets, internal=true, partitions=(partition=0, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=1, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=2, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=3, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=4, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=5, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=6, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=7, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=8, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=9, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=10, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=11, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=12, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=13, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=14, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=15, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=16, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=17, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=18, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=19, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=20, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=21, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=22, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=23, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=24, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=25, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=26, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=27, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=28, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=29, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=30, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=31, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=32, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=33, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=34, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=35, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=36, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=37, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=38, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=39, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=40, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=41, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=42, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=43, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=44, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=45, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=46, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=47, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=48, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)),(partition=49, leader=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), replicas=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null), isr=localhost:9092 (id: 0 rack: null)), authorizedOperations=null)2.3. 分区 Partition 操作
2.3.1. 增加分区
在创建 Topic 时我们需要设定 Partition 的数量,但如果觉得初始设置的 Partition 数量太少了,那么就可以使用 createPartitions 方法来调整 Topic 的 Partition 数量,但是需要注意在 Kafka 中Partition 只能增加不能减少。代码示例:
public static void incrPartitions(AdminClient adminClient, String topicName) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {Map<String, NewPartitions> newPartitions = new HashMap<>();//将Partition数量调整为2newPartitions.put(topicName, NewPartitions.increaseTo(2));CreatePartitionsResult ret = adminClient.createPartitions(newPartitions);ret.all().get();
}2.3.2. 分区副本重新分配
public void alterPartitionReassignments() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 构造要修改的topic和对应的partition idTopicPartition topicPartition = new TopicPartition("java_kafka_tst1", 1);//构造目标副本的partition id,其实就是broker idList<Integer> targetReplicas = new ArrayList<>();//把partition id添加进去targetReplicas.add(1);//使用targetReplicas构造newPartitionReassignmentNewPartitionReassignment newPartitionReassignment=new NewPartitionReassignment(targetReplicas);//构造重新分配的MapMap<TopicPartition, Optional<NewPartitionReassignment>> reassignments = new HashMap<>();//传入构造好的参数topicPartition和newPartitionReassignmentreassignments.put(topicPartition, Optional.of(newPartitionReassignment));//调用重新分配方法AlterPartitionReassignmentsResult result = adminClient.alterPartitionReassignments(reassignments);// 执行方法result.all().get();// 等待结果if (result.all().isDone()) {System.out.println("done");} else {System.out.println("not done");}
}2.3.3. 查询分区副本列表
public static void listPartitionReassignments(AdminClient adminClient, String topicName) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {Set<TopicPartition> tpSet = new HashSet<>();tpSet.add(new TopicPartition("t-test", 0));ListPartitionReassignmentsResult ret = adminClient.listPartitionReassignments(tpSet);ret.reassignments().get();
}2.4. Config 配置信息
2.4.1. 描述配置详细信息
public static void describeConfig(AdminClient adminClient, String topicName) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {DescribeConfigsResult ret = adminClient.describeConfigs(Collections.singleton(new ConfigResource(ConfigResource.Type.TOPIC, topicName)));Map<ConfigResource, Config> configMap = ret.all().get();for (Map.Entry<ConfigResource, Config> entry : configMap.entrySet()) {ConfigResource key = entry.getKey();Config value = entry.getValue();System.out.println(String.format("Resource type: %s, resource name: %s", key.type(), key.name()));Collection<ConfigEntry> configEntries = value.entries();for (ConfigEntry each : configEntries) {System.out.println(each.name() + " = " + each.value());}}
}// 运行结果:
Resource type: TOPIC, resource name: testTopic
compression.type = producer
leader.replication.throttled.replicas =
message.downconversion.enable = true
min.insync.replicas = 1
segment.jitter.ms = 0
cleanup.policy = delete
flush.ms = 9223372036854775807
follower.replication.throttled.replicas =
segment.bytes = 1073741824
retention.ms = 604800000
flush.messages = 9223372036854775807
message.format.version = 3.0-IV1
file.delete.delay.ms = 60000
max.compaction.lag.ms = 9223372036854775807
max.message.bytes = 1048588
min.compaction.lag.ms = 0
message.timestamp.type = CreateTime
preallocate = false
min.cleanable.dirty.ratio = 0.5
index.interval.bytes = 4096
unclean.leader.election.enable = false
retention.bytes = -1
delete.retention.ms = 86400000
segment.ms = 604800000
message.timestamp.difference.max.ms = 9223372036854775807
segment.index.bytes = 104857602.4.2. 修改配置信息
在早期版本中,使用 alterConfigs 方法来修改配置项。代码示例:
public static void alterConfigs(AdminClient adminClient, String topicName) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 指定ConfigResource的类型及名称ConfigResource configResource = new ConfigResource(ConfigResource.Type.TOPIC, topicName);// 配置项以ConfigEntry形式存在Config config = new Config(Arrays.asList(new ConfigEntry("cleanup.policy", "compact")));//构建Map<ConfigResource, Config> configMap = new HashMap<>();configMap.put(configResource, config);//执行AlterConfigsResult ret = adminClient.alterConfigs(configMap);ret.all().get();
}2.4.3. incrementalAlterConfigs
在新版本中则是使用 incrementalAlterConfigs 方法来修改配置项,该方法使用起来相对于 alterConfigs 要略微复杂一些,但因此功能更多、更灵活。代码示例:
public static void incrementalAlterConfigs(AdminClient adminClient, String topicName) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 指定ConfigResource的类型及名称ConfigResource configResource = new ConfigResource(ConfigResource.Type.TOPIC, topicName);// 配置项同样以ConfigEntry形式存在,只不过增加了操作类型// 以及能够支持操作多个配置项,相对来说功能更多、更灵活Collection<AlterConfigOp> configs = Arrays.asList(new AlterConfigOp(new ConfigEntry("preallocate", "false"),AlterConfigOp.OpType.SET));Map<ConfigResource, Collection<AlterConfigOp>> configMaps = new HashMap<>();configMaps.put(configResource, configs);AlterConfigsResult result = adminClient.incrementalAlterConfigs(configMaps);result.all().get();
}2.5. Scram 账户操作
2.5.1. 创建 Scram 账户
public void createAccount(String name, String pwd, String salt) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//创建User列表List<UserScramCredentialAlteration> alterations = new ArrayList<>();//构造Scram认证机制信息,这里笔者选择了SCRAM_SHA_512,大家也可以选择 ScramMechanism.SCRAM_SHA_256//alterations.size()此时为0,或许会报错,可以试下传入数字构造,比如下面添加了一个认证信息,那么这里传入数字1。// ScramCredentialInfo info=new ScramCredentialInfo(ScramMechanism.SCRAM_SHA_512, alterations.size()); //这里时间久远,忘记当时写例子的场景了ScramCredentialInfo info=new ScramCredentialInfo(ScramMechanism.SCRAM_SHA_512, 10000);//三个UserScramCredentialAlteration构造方法,三选一笔者选了一个最简单的//UserScramCredentialAlteration userScramCredentialAdd=new UserScramCredentialUpsertion(name,info,pwd.getBytes());//UserScramCredentialAlteration userScramCredentialAdd=new UserScramCredentialUpsertion(name,info,pwd.getBytes(),salt.getBytes());UserScramCredentialAlteration userScramCredentialAdd=new UserScramCredentialUpsertion(name,info,pwd);//添加认证信息到列表alterations.add(userScramCredentialAdd);//执行方法,并拿到返回结果AlterUserScramCredentialsResult result = adminClient.alterUserScramCredentials(alterations);//阻塞等待结果完成result.all().get();
}2.5.2. 删除 Scram 账户
public void deleteAccount(String name) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//创建删除列表List<UserScramCredentialAlteration> alterations = new ArrayList<>();//构建删除用的UserScramCredentialAlterationUserScramCredentialAlteration userScramCredentialDel=new UserScramCredentialDeletion(name,ScramMechanism.SCRAM_SHA_512);//添加认证信息到列表alterations.add(userScramCredentialDel);//执行方法,并拿到返回结果AlterUserScramCredentialsResult result = adminClient.alterUserScramCredentials(alterations);//阻塞等待结果完成result.all().get();
}2.5.3. 查询 Scram 账户信息
public void describeAccount() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//***************************************查询所有用户信息*****************************************************//查询所有的账户,这也是默认方法DescribeUserScramCredentialsResult result = adminClient.describeUserScramCredentials();//执行方法,并拿到返回结果Map<String, UserScramCredentialsDescription> future = result.all().get();//输出future.forEach((name,info)-> System.out.println("[ScramUserName:"+name+"]:[ScramUserInfo:"+info.toString()+"]"));//***************************************这里是分割线*****************************************************//***************************************查询指定的用户信息*****************************************************//构造指定的用户列表List<String> userScramList=new ArrayList<>();//添加两个用户userScramList.add("user1");userScramList.add("user2");//传入特定用户列表执行方法,并拿到返回结果DescribeUserScramCredentialsResult targetResult = adminClient.describeUserScramCredentials(userScramList);//执行方法,并拿到返回结果Map<String, UserScramCredentialsDescription> targetFuture = targetResult.all().get();//输出targetFuture.forEach((name,info)-> System.out.println("[ScramUserName:"+name+"]:[ScramUserInfo:"+info.toString()+"]"));
}2.6. Acl 操作
2.6.1. 创建 Acl
public void createACL() {//创建ResourcePatternResourcePattern resourcePattern = new ResourcePattern(ResourceType.TOPIC, "topicName", PatternType.LITERAL);//创建AccessControlEntryAccessControlEntry accessControlEntry=new AccessControlEntry("User:accountName","*", AclOperation.READ, AclPermissionType.ALLOW);//绑定到AclBinding上AclBinding aclBinding=new AclBinding(resourcePattern,accessControlEntry);Collection<AclBinding> aclBindingCollection= new ArrayList<>();aclBindingCollection.add(aclBinding); //添加到集合CreateAclsResult aclResult = adminClient.createAcls(aclBindingCollection);KafkaFuture<Void> result = aclResult.all();try {result.get(); //执行if (result.isDone()){ //验证是否成功System.out.println(result.toString());}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}2.6.2. 删除 Acl
public void deleteAcls() {ResourcePatternFilter resourcePatternFilter = new ResourcePatternFilter(ResourceType.TOPIC, "topicName", PatternType.LITERAL);AccessControlEntryFilter accessControlEntryFilter=new AccessControlEntryFilter("User:accountName","*", AclOperation.ALL, AclPermissionType.ALLOW);AclBindingFilter aclBinding=new AclBindingFilter(resourcePatternFilter,accessControlEntryFilter);Collection<AclBindingFilter> aclBindingCollection= new ArrayList<>();aclBindingCollection.add(aclBinding);DeleteAclsResult aclResult = adminClient.deleteAcls(aclBindingCollection);KafkaFuture<Collection<AclBinding>> result = aclResult.all();try {result.get();if (result.isDone()){System.out.println(result.toString());}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}相关文章:

Kafka 之 AdminClient API
目录 一. 前言 二. KafkaAdminClient API 2.1. API 总览 2.2. Topic 操作 2.2.1. 创建 Topic 2.2.2. Topic 列表 2.2.3. 删除 Topic 2.2.4. 描述 Topic 详细信息 2.3. 分区 Partition 操作 2.3.1. 增加分区 2.3.2. 分区副本重新分配 2.3.3. 查询分区副本列表 2.4.…...

Flutter run 一直 Running Gradle task ‘assembleDebug’…
发生缘由 Flutter 项目引入 fluttertoast 插件后,执行 Flutter run 一直 Running Gradle task ‘assembleDebug’…,最后发现下载 kotlin-compiler-embeddable-7.1.0.jar 特别的缓慢。 运行环境 电脑系统版本:Windows 10 64bit VS Code&…...
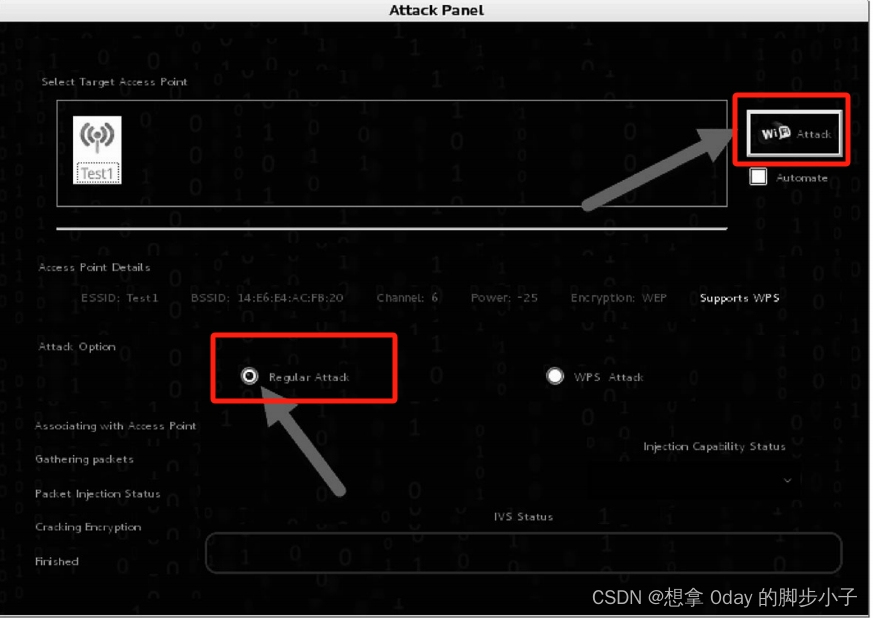
kali无线渗透之用wps加密模式破解出wpa模式的密码12
WPS(Wi-Fi Protected Setup,Wi-Fi保护设置)是由Wi-Fi联盟推出的全新Wi-Fi安全防护设定标准。该标准推出的主要原因是为了解决长久以来无线网络加密认证设定的步骤过于繁杂之弊病,使用者往往会因为步骤太过麻烦,以致干脆不做任何加密安全设定&…...

【Python】高级数据类型
🚩 WRITE IN FRONT 🚩 🔎 介绍:"謓泽"正在路上朝着"攻城狮"方向"前进四" 🔎🏅 荣誉:2021|2022年度博客之星物联网与嵌入式开发TOP5|TOP4、2021|2222年获评…...

挑战杯 python区块链实现 - proof of work工作量证明共识算法
文章目录 0 前言1 区块链基础1.1 比特币内部结构1.2 实现的区块链数据结构1.3 注意点1.4 区块链的核心-工作量证明算法1.4.1 拜占庭将军问题1.4.2 解决办法1.4.3 代码实现 2 快速实现一个区块链2.1 什么是区块链2.2 一个完整的快包含什么2.3 什么是挖矿2.4 工作量证明算法&…...

如何给最小化安装的CentOS主机装个远程桌面?
正文共:888 字 18 图,预估阅读时间:1 分钟 前面我们领微软云Azure的免费主机时(白嫖党618福利!来Azure领200美刀!外加云主机免费用一年!),发现“有资格免费试用服务”的主…...

知识图谱:py2neo将csv文件导入neo4j
文章目录 安装py2neo创建节点-连线关系图导入csv文件删除重复节点并连接边 安装py2neo 安装python中的neo4j操作库:pip install py2neo 安装py2neo后我们可以使用其中的函数对neo4j进行操作。 图数据库Neo4j中最重要的就是结点和边(关系)&a…...

备战蓝桥杯---图论之最短路Bellman-Ford算法及优化
目录 上次我们讲到复杂度为(nm)logm(m为边,n为点)的迪杰斯特拉算法,其中有一个明显的不足就是它无法解决包含负权边的图。 于是我们引进Bellman-Ford算法。 核心:枚举所有的点,能松弛就松弛,直…...

C++ //练习 5.19 编写一段程序,使用do while循环重复地执行下述任务:首先提示用户输入两个string对象,然后挑出较短的那个并输出它。
C Primer(第5版) 练习 5.19 练习 5.19 编写一段程序,使用do while循环重复地执行下述任务:首先提示用户输入两个string对象,然后挑出较短的那个并输出它。 环境:Linux Ubuntu(云服务器&#x…...
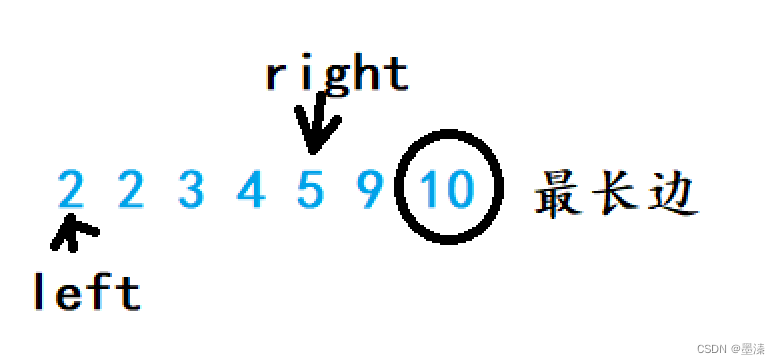
算法刷题:有效三角形个数
有效三角形个数 .题目链接题目详情算法原理补充知识点双指针:对撞指针 我的答案 . 题目链接 有效三角形个数 题目详情 算法原理 补充知识点 有效三角形需要满足的条件: ab>cac>bbc>a 其实在满足1的时候,c是最大的,那么2和3是显然成立的,因此我们可以这样解题: 对…...

python---变量
1.变量就是存储数据的空间,在内存上; 2.变量命名规则:(1)由数字,字母,下划线组成,数字不能开头; (2)不能和关键字冲突; (…...
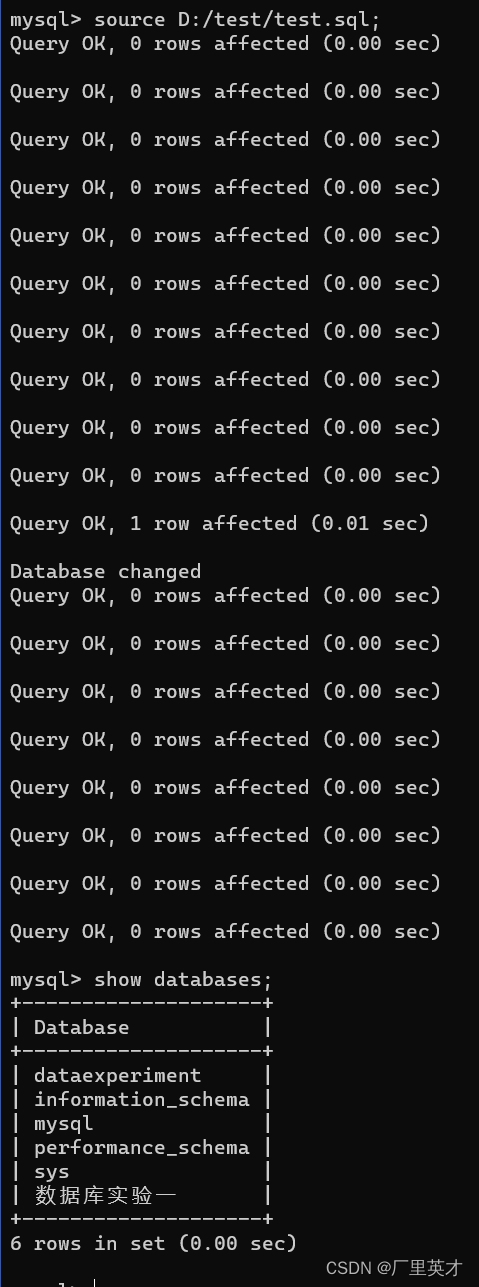
数据库第二次实验
目录 1 实验内容 2 SQL代码及运行截图 2.1 创建表并插入数据 2.1.1 创建表 2.1.2 插入数据 2.1.3 运行截图 2.2 修改表 2.2.1 SQL代码 2.2.2 运行截图 2.3 删除操作 2.3.1 SQL代码 2.3.2 运行截图 2.4 数据库的备份 2.5 数据库的恢复 1 实验内容 实验目的&#…...

容器高级知识:Kubernetes Pod 适配器模式详解
Kubernetes Pod 适配器(Adapter)模式详解 Kubernetes Pod 适配器模式是侧车(Sidecar)模式的一个特例,其中使用专用的 适配器容器 在主应用程序容器和其他服务或客户端之间 翻译 数据或信号。它充当桥梁,调整通信格式或协议以实现…...

云原生容器化-5 Docker常见操作命令
1.登录和退出docker仓库 使用docker login和docker logout分别用于登录和退出docker仓库。 #登录时携带用户名、密码、仓库地址信息 docker login --username test --password test123 192.168.0.22:8000 docker login --username seong --password 3er4#ER$ 192.168.0.22:8…...

几道简单的题目练一下手感
第 1 题 【 问答题 】 • 找和为K的两个元素 在一个长度为n(n < 1000)的整数序列中,判断是否存在某两个元素之和为k。 时间限制:1000 内存限制:65536 输入 第一行输入序列的长度n和k,用空格分开。 第二行输入序列中的n个整数&a…...
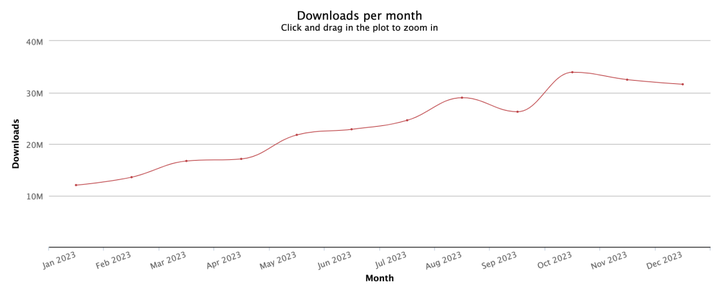
2023年哪个前端框架用的最多?
2023 年,TypeScript 的每月下载量持续稳定增长,年度累计下载量高达2,071,832,110(20.7 亿),展现了强大的市场需求和用户认可。 本文来通过详细的数据(2023 年 npm 累计下载量),看看…...
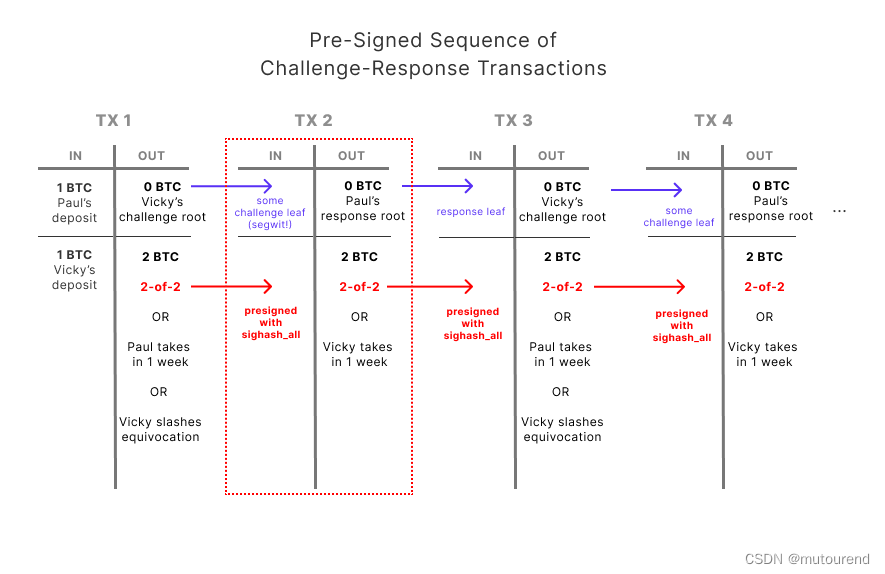
基于BitVM的乐观 BTC bridge
1. 引言 前序博客: 区块链互操作协议Bitcoin Bridge:治愈还是诅咒?BitVM:Bitcoin的链下合约 基于BitVM的乐观 BTC bridge: Trust-minimized two-way peg 机制 BitVM BTC bridge背后的主要思想是: 为比…...
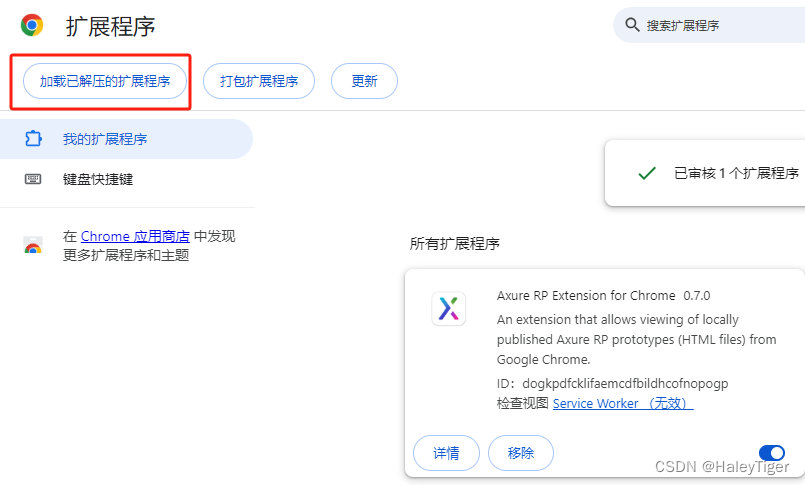
谷歌浏览器安装扩展程序axure-chrome-extension
注: 文末附扩展附件:axure-chrome-extension_v0.7.0.crx 1、安装扩展程序axure-chrome-extension 找到axure-chrome-extension.crx,把axure-chrome-extension.crx后缀改为zip,然后解压,得到一个文件夹 2、打开谷歌浏览…...

C++学习:大小写转换
islower/isupper函数 islower和isupper是C标准库中的字符分类函数,用于检查一个字符是否为小写字母或大写字母。 islower和isupper函数需要包含头文件,也可用万能头文<bits/stdc.h>包含。 函数返回值为bool类型。 char ch1 A; char ch2 a;//…...

【王道数据结构】【chapter5树与二叉树】【P159t16】
试设计判断两棵二叉树是否相似的算法。所谓二叉树T1和T2相似,指的是T1和T2都是空的二叉树或都只有一个根节点;或者T1的左子树和T2的左子树是相似的,且T1的右子树和T2的右子树是相似的 #include <iostream> #include <stack> #inc…...
:にする)
日语学习-日语知识点小记-构建基础-JLPT-N4阶段(33):にする
日语学习-日语知识点小记-构建基础-JLPT-N4阶段(33):にする 1、前言(1)情况说明(2)工程师的信仰2、知识点(1) にする1,接续:名词+にする2,接续:疑问词+にする3,(A)は(B)にする。(2)復習:(1)复习句子(2)ために & ように(3)そう(4)にする3、…...

关于iview组件中使用 table , 绑定序号分页后序号从1开始的解决方案
问题描述:iview使用table 中type: "index",分页之后 ,索引还是从1开始,试过绑定后台返回数据的id, 这种方法可行,就是后台返回数据的每个页面id都不完全是按照从1开始的升序,因此百度了下,找到了…...
Vue2 第一节_Vue2上手_插值表达式{{}}_访问数据和修改数据_Vue开发者工具
文章目录 1.Vue2上手-如何创建一个Vue实例,进行初始化渲染2. 插值表达式{{}}3. 访问数据和修改数据4. vue响应式5. Vue开发者工具--方便调试 1.Vue2上手-如何创建一个Vue实例,进行初始化渲染 准备容器引包创建Vue实例 new Vue()指定配置项 ->渲染数据 准备一个容器,例如: …...
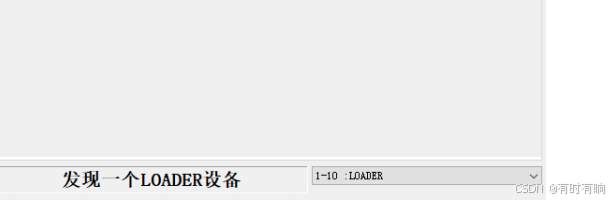
linux arm系统烧录
1、打开瑞芯微程序 2、按住linux arm 的 recover按键 插入电源 3、当瑞芯微检测到有设备 4、松开recover按键 5、选择升级固件 6、点击固件选择本地刷机的linux arm 镜像 7、点击升级 (忘了有没有这步了 估计有) 刷机程序 和 镜像 就不提供了。要刷的时…...
cf2117E
原题链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/2117/problem/E 题目背景: 给定两个数组a,b,可以执行多次以下操作:选择 i (1 < i < n - 1),并设置 或,也可以在执行上述操作前执行一次删除任意 和 。求…...
DIY|Mac 搭建 ESP-IDF 开发环境及编译小智 AI
前一阵子在百度 AI 开发者大会上,看到基于小智 AI DIY 玩具的演示,感觉有点意思,想着自己也来试试。 如果只是想烧录现成的固件,乐鑫官方除了提供了 Windows 版本的 Flash 下载工具 之外,还提供了基于网页版的 ESP LA…...

C# SqlSugar:依赖注入与仓储模式实践
C# SqlSugar:依赖注入与仓储模式实践 在 C# 的应用开发中,数据库操作是必不可少的环节。为了让数据访问层更加简洁、高效且易于维护,许多开发者会选择成熟的 ORM(对象关系映射)框架,SqlSugar 就是其中备受…...

【python异步多线程】异步多线程爬虫代码示例
claude生成的python多线程、异步代码示例,模拟20个网页的爬取,每个网页假设要0.5-2秒完成。 代码 Python多线程爬虫教程 核心概念 多线程:允许程序同时执行多个任务,提高IO密集型任务(如网络请求)的效率…...
JDK 17 序列化是怎么回事
如何序列化?其实很简单,就是根据每个类型,用工厂类调用。逐个完成。 没什么漂亮的代码,只有有效、稳定的代码。 代码中调用toJson toJson 代码 mapper.writeValueAsString ObjectMapper DefaultSerializerProvider 一堆实…...

Java多线程实现之Runnable接口深度解析
Java多线程实现之Runnable接口深度解析 一、Runnable接口概述1.1 接口定义1.2 与Thread类的关系1.3 使用Runnable接口的优势 二、Runnable接口的基本实现方式2.1 传统方式实现Runnable接口2.2 使用匿名内部类实现Runnable接口2.3 使用Lambda表达式实现Runnable接口 三、Runnabl…...
