算法-3-基本的数据结构
单双链表
1.单链表双链表如何反转
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;public class Code01_ReverseList {public static class Node {public int value;public Node next;public Node(int data) {value = data;}}public static class DoubleNode {public int value;public DoubleNode last;public DoubleNode next;public DoubleNode(int data) {value = data;}}// head// a -> b -> c -> null// c -> b -> a -> nullpublic static Node reverseLinkedList(Node head) {Node pre = null;Node next = null;while (head != null) {next = head.next;head.next = pre;pre = head;head = next;}return pre;}public static DoubleNode reverseDoubleList(DoubleNode head) {DoubleNode pre = null;DoubleNode next = null;while (head != null) {next = head.next;head.next = pre;head.last = next;pre = head;head = next;}return pre;}public static Node testReverseLinkedList(Node head) {if (head == null) {return null;}ArrayList<Node> list = new ArrayList<>();while (head != null) {list.add(head);head = head.next;}list.get(0).next = null;int N = list.size();for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {list.get(i).next = list.get(i - 1);}return list.get(N - 1);}public static DoubleNode testReverseDoubleList(DoubleNode head) {if (head == null) {return null;}ArrayList<DoubleNode> list = new ArrayList<>();while (head != null) {list.add(head);head = head.next;}list.get(0).next = null;DoubleNode pre = list.get(0);int N = list.size();for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {DoubleNode cur = list.get(i);cur.last = null;cur.next = pre;pre.last = cur;pre = cur;}return list.get(N - 1);}// for testpublic static Node generateRandomLinkedList(int len, int value) {int size = (int) (Math.random() * (len + 1));if (size == 0) {return null;}size--;Node head = new Node((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));Node pre = head;while (size != 0) {Node cur = new Node((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));pre.next = cur;pre = cur;size--;}return head;}// for testpublic static DoubleNode generateRandomDoubleList(int len, int value) {int size = (int) (Math.random() * (len + 1));if (size == 0) {return null;}size--;DoubleNode head = new DoubleNode((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));DoubleNode pre = head;while (size != 0) {DoubleNode cur = new DoubleNode((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));pre.next = cur;cur.last = pre;pre = cur;size--;}return head;}// for testpublic static List<Integer> getLinkedListOriginOrder(Node head) {List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();while (head != null) {ans.add(head.value);head = head.next;}return ans;}// for testpublic static boolean checkLinkedListReverse(List<Integer> origin, Node head) {for (int i = origin.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {if (!origin.get(i).equals(head.value)) {return false;}head = head.next;}return true;}// for testpublic static List<Integer> getDoubleListOriginOrder(DoubleNode head) {List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();while (head != null) {ans.add(head.value);head = head.next;}return ans;}// for testpublic static boolean checkDoubleListReverse(List<Integer> origin, DoubleNode head) {DoubleNode end = null;for (int i = origin.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {if (!origin.get(i).equals(head.value)) {return false;}end = head;head = head.next;}for (int i = 0; i < origin.size(); i++) {if (!origin.get(i).equals(end.value)) {return false;}end = end.last;}return true;}// for testpublic static void main(String[] args) {int len = 50;int value = 100;int testTime = 100000;System.out.println("test begin!");for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {Node node1 = generateRandomLinkedList(len, value);List<Integer> list1 = getLinkedListOriginOrder(node1);node1 = reverseLinkedList(node1);if (!checkLinkedListReverse(list1, node1)) {System.out.println("Oops1!");}Node node2 = generateRandomLinkedList(len, value);List<Integer> list2 = getLinkedListOriginOrder(node2);node2 = testReverseLinkedList(node2);if (!checkLinkedListReverse(list2, node2)) {System.out.println("Oops2!");}DoubleNode node3 = generateRandomDoubleList(len, value);List<Integer> list3 = getDoubleListOriginOrder(node3);node3 = reverseDoubleList(node3);if (!checkDoubleListReverse(list3, node3)) {System.out.println("Oops3!");}DoubleNode node4 = generateRandomDoubleList(len, value);List<Integer> list4 = getDoubleListOriginOrder(node4);node4 = reverseDoubleList(node4);if (!checkDoubleListReverse(list4, node4)) {System.out.println("Oops4!");}}System.out.println("test finish!");}}2.把定值都删除掉
是n就跳过,不是n next指向
public class Code02_DeleteGivenValue {public static class Node {public int value;public Node next;public Node(int data) {this.value = data;}}// head = removeValue(head, 2);public static Node removeValue(Node head, int num) {// head来到第一个不需要删的位置while (head != null) {if (head.value != num) {break;}head = head.next;}// 1 ) head == null// 2 ) head != nullNode pre = head;Node cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.value == num) {pre.next = cur.next;} else {pre = cur;}cur = cur.next;}return head;}}
队列跟栈
双链表实现
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;public class Code03_DoubleEndsQueueToStackAndQueue {public static class Node<T> {public T value;public Node<T> last;public Node<T> next;public Node(T data) {value = data;}}public static class DoubleEndsQueue<T> {public Node<T> head;public Node<T> tail;public void addFromHead(T value) {Node<T> cur = new Node<T>(value);if (head == null) {head = cur;tail = cur;} else {cur.next = head;head.last = cur;head = cur;}}public void addFromBottom(T value) {Node<T> cur = new Node<T>(value);if (head == null) {head = cur;tail = cur;} else {cur.last = tail;tail.next = cur;tail = cur;}}public T popFromHead() {if (head == null) {return null;}Node<T> cur = head;if (head == tail) {head = null;tail = null;} else {head = head.next;cur.next = null;head.last = null;}return cur.value;}public T popFromBottom() {if (head == null) {return null;}Node<T> cur = tail;if (head == tail) {head = null;tail = null;} else {tail = tail.last;tail.next = null;cur.last = null;}return cur.value;}public boolean isEmpty() {return head == null;}}public static class MyStack<T> {private DoubleEndsQueue<T> queue;public MyStack() {queue = new DoubleEndsQueue<T>();}public void push(T value) {queue.addFromHead(value);}public T pop() {return queue.popFromHead();}public boolean isEmpty() {return queue.isEmpty();}}public static class MyQueue<T> {private DoubleEndsQueue<T> queue;public MyQueue() {queue = new DoubleEndsQueue<T>();}public void push(T value) {queue.addFromHead(value);}public T poll() {return queue.popFromBottom();}public boolean isEmpty() {return queue.isEmpty();}}public static boolean isEqual(Integer o1, Integer o2) {if (o1 == null && o2 != null) {return false;}if (o1 != null && o2 == null) {return false;}if (o1 == null && o2 == null) {return true;}return o1.equals(o2);}public static void main(String[] args) {int oneTestDataNum = 100;int value = 10000;int testTimes = 100000;for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {MyStack<Integer> myStack = new MyStack<>();MyQueue<Integer> myQueue = new MyQueue<>();Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();for (int j = 0; j < oneTestDataNum; j++) {int nums = (int) (Math.random() * value);if (stack.isEmpty()) {myStack.push(nums);stack.push(nums);} else {if (Math.random() < 0.5) {myStack.push(nums);stack.push(nums);} else {if (!isEqual(myStack.pop(), stack.pop())) {System.out.println("oops!");}}}int numq = (int) (Math.random() * value);if (stack.isEmpty()) {myQueue.push(numq);queue.offer(numq);} else {if (Math.random() < 0.5) {myQueue.push(numq);queue.offer(numq);} else {if (!isEqual(myQueue.poll(), queue.poll())) {System.out.println("oops!");}}}}}System.out.println("finish!");}}
数组实现
public class Code04_RingArray {public static class MyQueue {private int[] arr;private int pushi;// endprivate int polli;// beginprivate int size;private final int limit;public MyQueue(int limit) {arr = new int[limit];pushi = 0;polli = 0;size = 0;this.limit = limit;}public void push(int value) {if (size == limit) {throw new RuntimeException("队列满了,不能再加了");}size++;arr[pushi] = value;pushi = nextIndex(pushi);}public int pop() {if (size == 0) {throw new RuntimeException("队列空了,不能再拿了");}size--;int ans = arr[polli];polli = nextIndex(polli);return ans;}public boolean isEmpty() {return size == 0;}// 如果现在的下标是i,返回下一个位置private int nextIndex(int i) {return i < limit - 1 ? i + 1 : 0;}}}
实现一个特殊的栈,在基本功能基础上,再实现返回栈中最小元素的功能
1.pop,push,getMin,操作的时间复杂度都是O(1)
2.设计的栈类型可以使用现成的栈结构
同步压入,同步弹出
import java.util.Stack;public class Code05_GetMinStack {public static class MyStack1 {private Stack<Integer> stackData;private Stack<Integer> stackMin;public MyStack1() {this.stackData = new Stack<Integer>();this.stackMin = new Stack<Integer>();}public void push(int newNum) {if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {this.stackMin.push(newNum);} else if (newNum <= this.getmin()) {this.stackMin.push(newNum);}this.stackData.push(newNum);}public int pop() {if (this.stackData.isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");}int value = this.stackData.pop();if (value == this.getmin()) {this.stackMin.pop();}return value;}public int getmin() {if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");}return this.stackMin.peek();}}public static class MyStack2 {private Stack<Integer> stackData;private Stack<Integer> stackMin;public MyStack2() {this.stackData = new Stack<Integer>();this.stackMin = new Stack<Integer>();}public void push(int newNum) {if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {this.stackMin.push(newNum);} else if (newNum < this.getmin()) {this.stackMin.push(newNum);} else {int newMin = this.stackMin.peek();this.stackMin.push(newMin);}this.stackData.push(newNum);}public int pop() {if (this.stackData.isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");}this.stackMin.pop();return this.stackData.pop();}public int getmin() {if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");}return this.stackMin.peek();}}public static void main(String[] args) {MyStack1 stack1 = new MyStack1();stack1.push(3);System.out.println(stack1.getmin());stack1.push(4);System.out.println(stack1.getmin());stack1.push(1);System.out.println(stack1.getmin());System.out.println(stack1.pop());System.out.println(stack1.getmin());System.out.println("=============");MyStack1 stack2 = new MyStack1();stack2.push(3);System.out.println(stack2.getmin());stack2.push(4);System.out.println(stack2.getmin());stack2.push(1);System.out.println(stack2.getmin());System.out.println(stack2.pop());System.out.println(stack2.getmin());}}
如何使用栈结构实现队列结构
import java.util.Stack;public class Code06_TwoStacksImplementQueue {public static class TwoStacksQueue {public Stack<Integer> stackPush;public Stack<Integer> stackPop;public TwoStacksQueue() {stackPush = new Stack<Integer>();stackPop = new Stack<Integer>();}// push栈向pop栈倒入数据private void pushToPop() {if (stackPop.empty()) {while (!stackPush.empty()) {stackPop.push(stackPush.pop());}}}public void add(int pushInt) {stackPush.push(pushInt);pushToPop();}public int poll() {if (stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");}pushToPop();return stackPop.pop();}public int peek() {if (stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");}pushToPop();return stackPop.peek();}}public static void main(String[] args) {TwoStacksQueue test = new TwoStacksQueue();test.add(1);test.add(2);test.add(3);System.out.println(test.peek());System.out.println(test.poll());System.out.println(test.peek());System.out.println(test.poll());System.out.println(test.peek());System.out.println(test.poll());}}
如何使用队列结构实现栈结构
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;public class Code07_TwoQueueImplementStack {public static class TwoQueueStack<T> {public Queue<T> queue;public Queue<T> help;public TwoQueueStack() {queue = new LinkedList<>();help = new LinkedList<>();}public void push(T value) {queue.offer(value);}public T poll() {while (queue.size() > 1) {help.offer(queue.poll());}T ans = queue.poll();Queue<T> tmp = queue;queue = help;help = tmp;return ans;}public T peek() {while (queue.size() > 1) {help.offer(queue.poll());}T ans = queue.poll();help.offer(ans);Queue<T> tmp = queue;queue = help;help = tmp;return ans;}public boolean isEmpty() {return queue.isEmpty();}}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("test begin");TwoQueueStack<Integer> myStack = new TwoQueueStack<>();Stack<Integer> test = new Stack<>();int testTime = 1000000;int max = 1000000;for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {if (myStack.isEmpty()) {if (!test.isEmpty()) {System.out.println("Oops");}int num = (int) (Math.random() * max);myStack.push(num);test.push(num);} else {if (Math.random() < 0.25) {int num = (int) (Math.random() * max);myStack.push(num);test.push(num);} else if (Math.random() < 0.5) {if (!myStack.peek().equals(test.peek())) {System.out.println("Oops");}} else if (Math.random() < 0.75) {if (!myStack.poll().equals(test.pop())) {System.out.println("Oops");}} else {if (myStack.isEmpty() != test.isEmpty()) {System.out.println("Oops");}}}}System.out.println("test finish!");}}
Master 公式求递推的时间复杂度
前提,子问题规模一致,(比如,子问题是分两个二分之N区间分别求最大值,可以Master,若分为三分之N那就不行)
公式:T(N)=a*T(N/b)+O(N的d次方)
得到abd之后
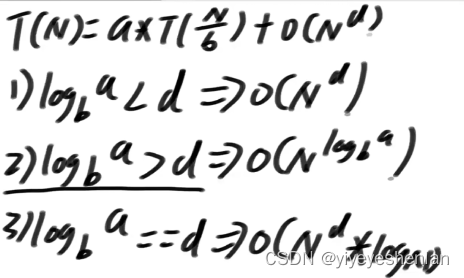
求最大值
public class Code08_GetMax {// 求arr中的最大值public static int getMax(int[] arr) {return process(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);}// arr[L..R]范围上求最大值 L ... R Npublic static int process(int[] arr, int L, int R) {// arr[L..R]范围上只有一个数,直接返回,base caseif (L == R) { return arr[L];}// L...R 不只一个数// mid = (L + R) / 2int mid = L + ((R - L) >> 1); // 中点 1int leftMax = process(arr, L, mid);int rightMax = process(arr, mid + 1, R);return Math.max(leftMax, rightMax);}}
哈希
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.TreeMap;public class HashMapAndSortedMap {public static class Node {public int value;public Node(int v) {value = v;}}public static class Zuo {public int value;public Zuo(int v) {value = v;}}public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap<Integer, String> test = new HashMap<>();Integer a = 19000000;Integer b = 19000000;System.out.println(a == b);test.put(a, "我是3");System.out.println(test.containsKey(b));Zuo z1 = new Zuo(1);Zuo z2 = new Zuo(1);HashMap<Zuo, String> test2 = new HashMap<>();test2.put(z1, "我是z1");System.out.println(test2.containsKey(z2));// UnSortedMapHashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put(1000000, "我是1000000");map.put(2, "我是2");map.put(3, "我是3");map.put(4, "我是4");map.put(5, "我是5");map.put(6, "我是6");map.put(1000000, "我是1000001");System.out.println(map.containsKey(1));System.out.println(map.containsKey(10));System.out.println(map.get(4));System.out.println(map.get(10));map.put(4, "他是4");System.out.println(map.get(4));map.remove(4);System.out.println(map.get(4));// keyHashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();set.add("abc");set.contains("abc");set.remove("abc");// 哈希表,增、删、改、查,在使用时,O(1)System.out.println("=====================");Integer c = 100000;Integer d = 100000;System.out.println(c.equals(d));Integer e = 127; // - 128 ~ 127Integer f = 127;System.out.println(e == f);HashMap<Node, String> map2 = new HashMap<>();Node node1 = new Node(1);Node node2 = node1;map2.put(node1, "我是node1");map2.put(node2, "我是node1");System.out.println(map2.size());System.out.println("======================");// TreeMap 有序表:接口名// 红黑树、avl、sb树、跳表// O(logN)System.out.println("有序表测试开始");TreeMap<Integer, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();treeMap.put(3, "我是3");treeMap.put(4, "我是4");treeMap.put(8, "我是8");treeMap.put(5, "我是5");treeMap.put(7, "我是7");treeMap.put(1, "我是1");treeMap.put(2, "我是2");System.out.println(treeMap.containsKey(1));System.out.println(treeMap.containsKey(10));System.out.println(treeMap.get(4));System.out.println(treeMap.get(10));treeMap.put(4, "他是4");System.out.println(treeMap.get(4));// treeMap.remove(4);System.out.println(treeMap.get(4));System.out.println("新鲜:");System.out.println(treeMap.firstKey());System.out.println(treeMap.lastKey());// <= 4System.out.println(treeMap.floorKey(4));// >= 4System.out.println(treeMap.ceilingKey(4));// O(logN)}}
相关文章:
算法-3-基本的数据结构
单双链表 1.单链表双链表如何反转 import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;public class Code01_ReverseList {public static class Node {public int value;public Node next;public Node(int data) {value data;}}public static class DoubleNode {public int…...

探秘Java反射:灵活编程的利器
前言 大家好,我是chowley,不知道大家在学习Java的过程中有没有听过反射的概念,今天我来总结一下我心中的Java反射。 在Java编程中,反射是一种强大的工具,它允许程序在运行时检查和操作类、方法、属性等,而…...

记录 | ubuntu pyqt5 pycharm配置
Ubuntu16.04pycharmpyqt5安装与配置_ubuntu pycharm pyqt5-CSDN博客pycharm激活码 6ZUMD7WWWU-eyJsaWNlbnNlSWQiOiI2WlVNRDdXV1dVIiwibGljZW5zZWVOYW1lIjoiSmV0cyBHcm91cCIsImFzc2lnbmVlTmFtZSI6IiIsImFzc2lnbmVlRW1haWwiOiIiLCJsaWNlbnNlUmVzdHJpY3Rpb24iOiIiLCJjaGVja0NvbmN…...
ESP32学习(1)——环境搭建
使用的ESP32板子如下图所示 它可以用Arduino 软件,基于C语言开发。但是,在这里,我是用Thonny软件,基于micro_python对其进行开发。 1.安装Thonny Thonny的软件安装包,可以去它官网上下载。Thonny, Python IDE for begi…...

Attention Is All Your Need论文笔记
论文解决了什么问题? 提出了一个新的简单网络架构——transformer,仅仅是基于注意力机制,完全免去递推和卷积,使得神经网络训练地速度极大地提高。 We propose a new simple network architecture, the Transformer, based sole…...
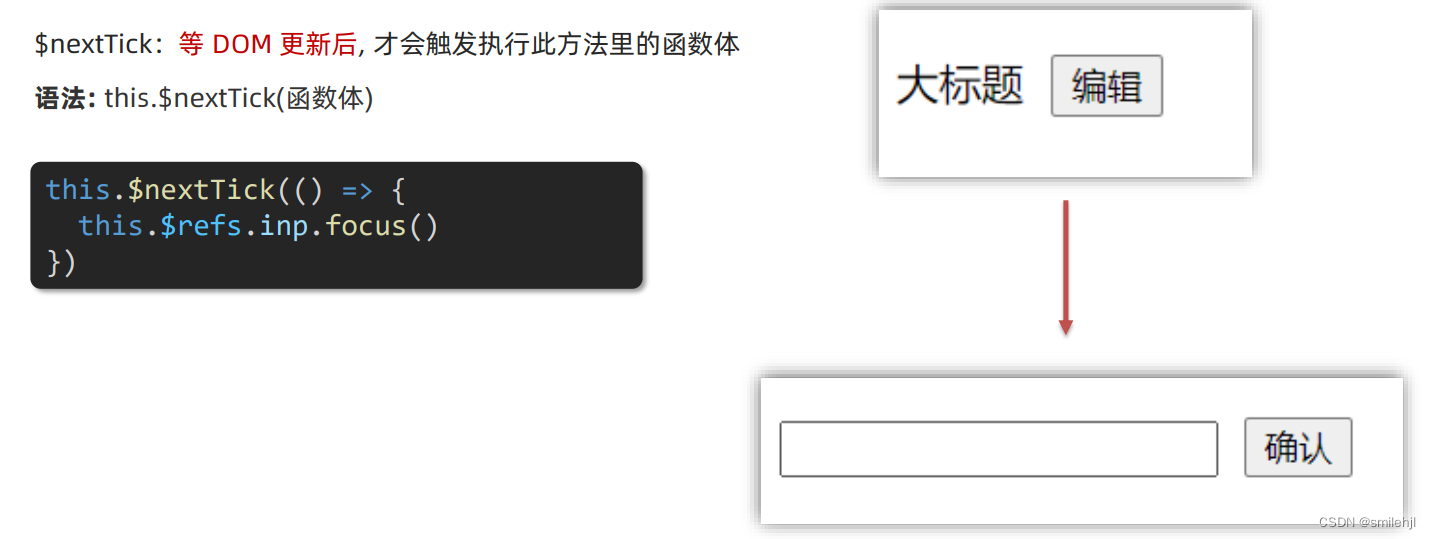
vue-进阶语法(四)
目录 v-model原理 v-model应用于组件 sync修饰符 ref 和 $refs(重点) $nextTick v-model原理 原理:v-model本质上是一个语法糖。例如应用在输入框上,就是 value属性 和 input事件 的合写。 作用:提供数据的双向…...
CGAL::2D Arrangements-7
7 几何Traits 几何Traits封装了几何实体的定义以及处理这些几何实体的几何predicates和构造的实现,供Arrangement_on_surface_2类模板和其他周边模块使用。应用于Arrangement的各种算法所确定的最小要求被组织在精细几何特征概念的层次中。每个概念列出的需求只包括…...

linux系统下vscode portable版本的rust环境搭建004:rust
目的:希望在获得一个新的系统之后,以最简便快速的方式搭配一个rust的编程环境命令在线安装只执行这句就行了 :curl --proto https --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh,因为是要portable安装所以按照以下的方式执行。 下载…...

从汇编角度解释线程间互斥-mutex互斥锁与lock_guard的使用
多线程并发的竞态问题 我们创建三个线程同时进行购票,代码如下 #include<iostream> #include<thread> #include<list> using namespace std; //总票数 int ticketCount100; //售票线程 void sellTicket(int idx) {while(ticketCount>0){cou…...
)
高程 | 多态性(c++)
文章目录 📚多态📚运算符重载🐇定义🐇规则🐇友元运算符重载函数🐇成员运算符重载函数 📚虚函数📚纯虚函数和抽象类 📚多态 多态:同样的消息被不同类型的对象…...
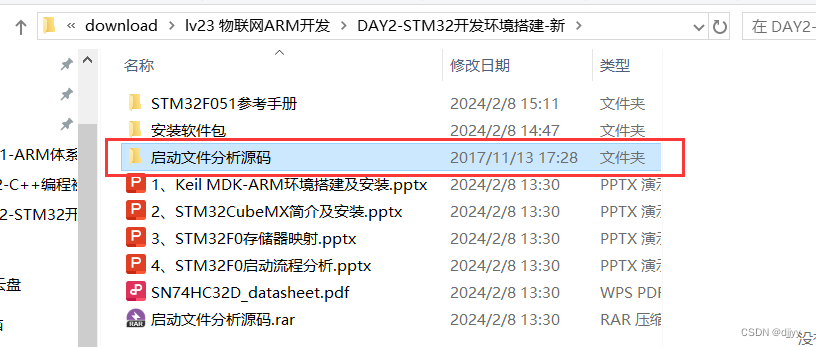
LV.23 D2 开发环境搭建及平台介绍 学习笔记
一、Keil MDK-ARM简介及安装 Keil MDK,也称MDK-ARM,Realview MDK (Microcontroller Development Kit)等。目前Keil MDK 由三家国内代理商提供技术支持和相关服务。 MDK-ARM软件为基于Cortex-M、Cortex-R4、ARM7、ARM9处理器设备…...

[uniapp生命周期]详细讲解uniapp中那些属于vue生命周期,那些属于uniapp独有的生命周期,以及这中间的区别 相关的内容和api 代码注释
目录 1. Vue.js生命周期函数2.Vue生命周期函数代码beforeCreatecreatedbeforeMountmountedbeforeUpdateupdatedbeforeDestroydestroyed$nextTick$forceUpdate$destroy 3. UniApp独有的生命周期函数onLaunchonShowonHideonError 4.总结 在UniApp中,除了Vue.js的生命周…...

【动态规划】【记忆化搜索】【状态压缩】1681. 最小不兼容性
作者推荐 【数位dp】【动态规划】【状态压缩】【推荐】1012. 至少有 1 位重复的数字 本文涉及知识点 动态规划汇总 状态压缩 记忆化搜索 1681. 最小不兼容性 给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k 。你需要将这个数组划分到 k 个相同大小的子集中,使得同一…...
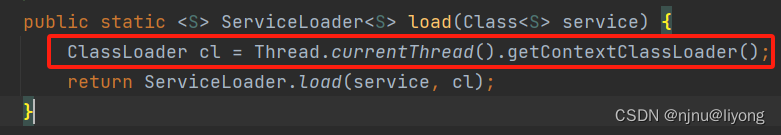
JVM-类加载器 双亲委派机制
申明:文章内容是本人学习极客时间课程所写,文字和图片基本来源于课程资料,在某些地方会插入一点自己的理解,未用于商业用途,侵删。 什么是JVM JVM是Java Virtual Machine(Java虚拟机)的缩写&a…...

vue axios 请求后端无法传参问题
vue请求后端无法传参问题 问题描述处理过程总结 问题描述 在学习vue时,使用axios调用后端,发现无法把参数正确传到后端,现象如下: 使用vue发起请求,浏览器上已经有传参,但是后端没接收到对应的用户名密码&…...

打印最小公倍数
打印最小公倍数 题目描述: 输入2个整数m和n,计算m和n的最小公倍数,并打印出结果 测试1: 输入:18 24 输出:72 测试2: 输入:18 6 输出:18解法思路: 最小公倍数是指两个…...

[AIGC] Java 和 Kotlin 的区别
好的,我还是以“萌萌哒小码农”的身份继续回答您的问题。 Java 和 Kotlin 是两种不同的编程语言,它们有许多共同点,但也有一些重要的区别。以下是一些常见的 Java 和 Kotlin 的区别: 语法 Kotlin 的语法比 Java 简洁得多&#…...
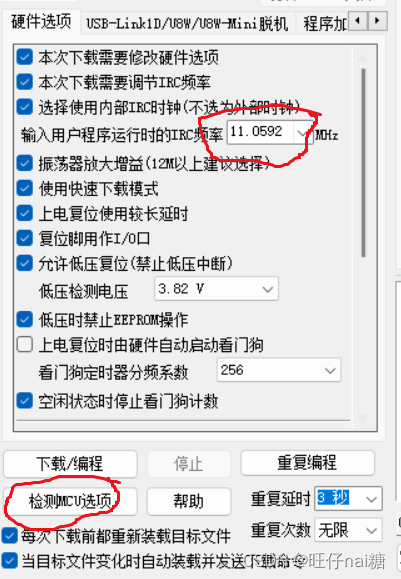
蓝桥杯电子类单片机提升一——超声波测距
前言 单片机资源数据包_2023 一、超声波测距原理 二、超声波测距的应用 1.超声波的发射 2.单片机知识补充:定时器 3.超声波的接收与计时 4.距离的计算 1)定时器1为16位自动重载+1T11.0592MHz 2)定时器1为16位自动重载&am…...

前端架构: 脚手架开发流程中的难点梳理
脚手架的开发流程 1 )开发流程 创建 npm 项目创建脚手架入口文件,最上方添加: #!/usr/bin/env node 配置 package.json, 添加 bin 属性编写脚手架代码将脚手架发布到 npm 2 )使用流程 安装脚手架 npm install -g your-own-cli …...

django中配置使用websocket
Django 默认情况下并不支持 WebSocket,但你可以通过集成第三方库如 channels 来实现 WebSocket 功能。channels 是一个 Django 应用,它提供了对 WebSocket、HTTP2 和其他协议的支持。 下面是如何在 Django 项目中使用 WebSocket 的基本步骤:…...
:爬虫完整流程)
Python爬虫(二):爬虫完整流程
爬虫完整流程详解(7大核心步骤实战技巧) 一、爬虫完整工作流程 以下是爬虫开发的完整流程,我将结合具体技术点和实战经验展开说明: 1. 目标分析与前期准备 网站技术分析: 使用浏览器开发者工具(F12&…...

关于 WASM:1. WASM 基础原理
一、WASM 简介 1.1 WebAssembly 是什么? WebAssembly(WASM) 是一种能在现代浏览器中高效运行的二进制指令格式,它不是传统的编程语言,而是一种 低级字节码格式,可由高级语言(如 C、C、Rust&am…...
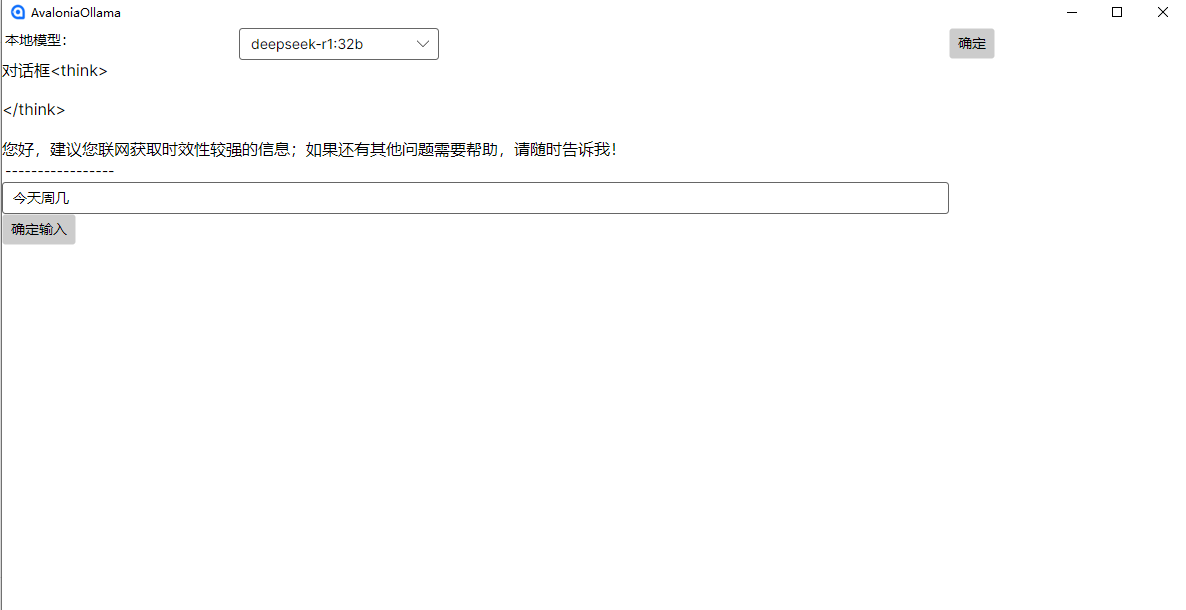
c#开发AI模型对话
AI模型 前面已经介绍了一般AI模型本地部署,直接调用现成的模型数据。这里主要讲述讲接口集成到我们自己的程序中使用方式。 微软提供了ML.NET来开发和使用AI模型,但是目前国内可能使用不多,至少实践例子很少看见。开发训练模型就不介绍了&am…...
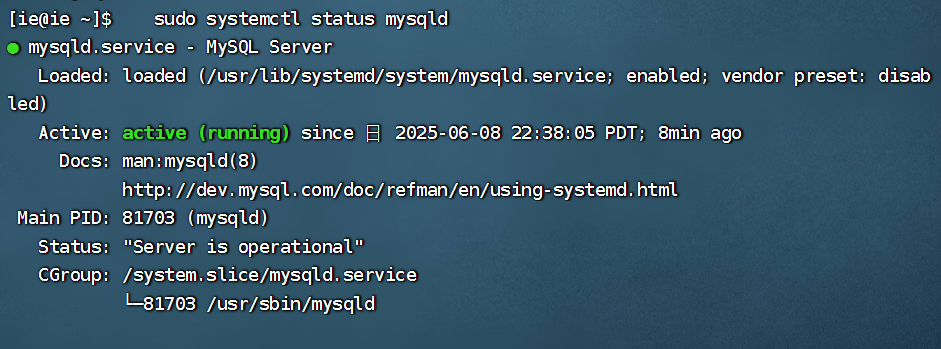
项目部署到Linux上时遇到的错误(Redis,MySQL,无法正确连接,地址占用问题)
Redis无法正确连接 在运行jar包时出现了这样的错误 查询得知问题核心在于Redis连接失败,具体原因是客户端发送了密码认证请求,但Redis服务器未设置密码 1.为Redis设置密码(匹配客户端配置) 步骤: 1).修…...

Java + Spring Boot + Mybatis 实现批量插入
在 Java 中使用 Spring Boot 和 MyBatis 实现批量插入可以通过以下步骤完成。这里提供两种常用方法:使用 MyBatis 的 <foreach> 标签和批处理模式(ExecutorType.BATCH)。 方法一:使用 XML 的 <foreach> 标签ÿ…...
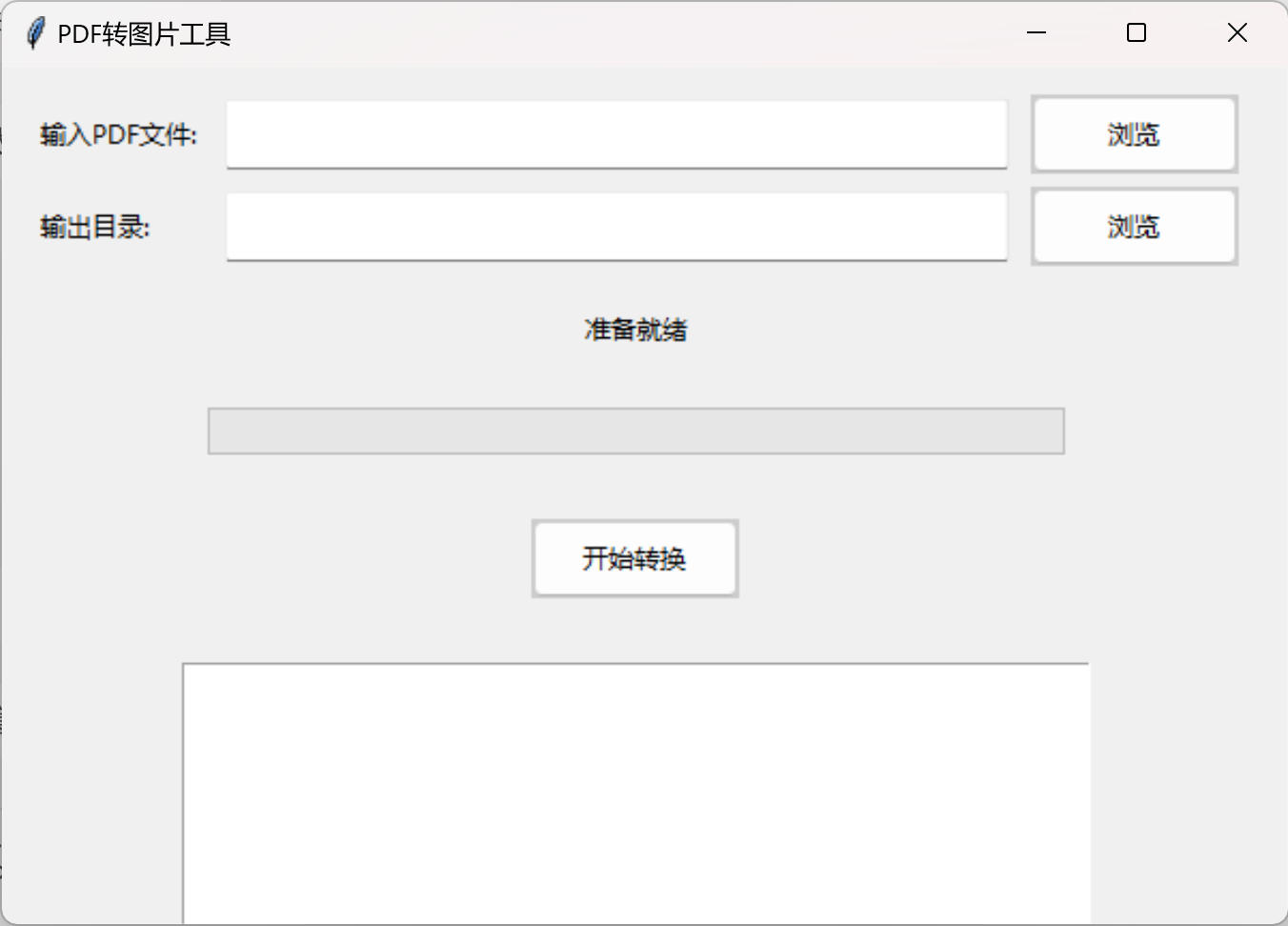
免费PDF转图片工具
免费PDF转图片工具 一款简单易用的PDF转图片工具,可以将PDF文件快速转换为高质量PNG图片。无需安装复杂的软件,也不需要在线上传文件,保护您的隐私。 工具截图 主要特点 🚀 快速转换:本地转换,无需等待上…...
宇树科技,改名了!
提到国内具身智能和机器人领域的代表企业,那宇树科技(Unitree)必须名列其榜。 最近,宇树科技的一项新变动消息在业界引发了不少关注和讨论,即: 宇树向其合作伙伴发布了一封公司名称变更函称,因…...

从面试角度回答Android中ContentProvider启动原理
Android中ContentProvider原理的面试角度解析,分为已启动和未启动两种场景: 一、ContentProvider已启动的情况 1. 核心流程 触发条件:当其他组件(如Activity、Service)通过ContentR…...
AI语音助手的Python实现
引言 语音助手(如小爱同学、Siri)通过语音识别、自然语言处理(NLP)和语音合成技术,为用户提供直观、高效的交互体验。随着人工智能的普及,Python开发者可以利用开源库和AI模型,快速构建自定义语音助手。本文由浅入深,详细介绍如何使用Python开发AI语音助手,涵盖基础功…...
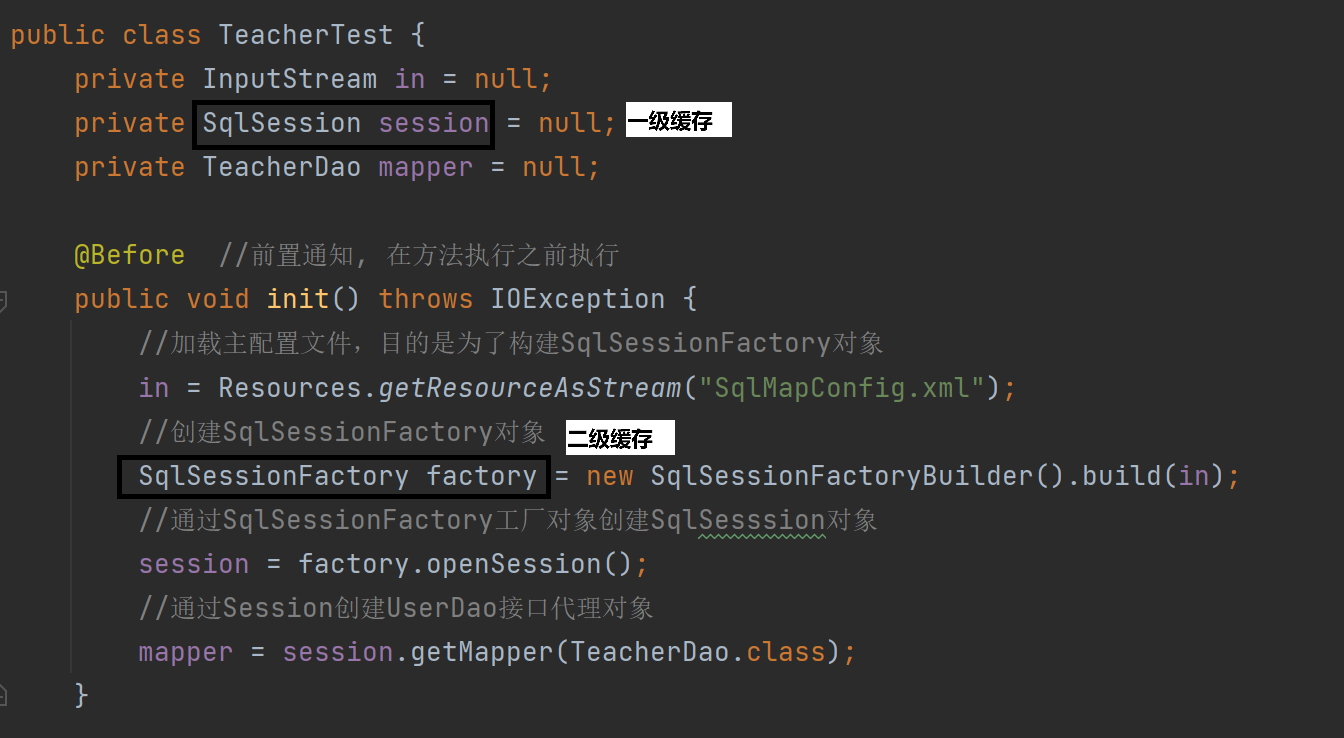
MyBatis中关于缓存的理解
MyBatis缓存 MyBatis系统当中默认定义两级缓存:一级缓存、二级缓存 默认情况下,只有一级缓存开启(sqlSession级别的缓存)二级缓存需要手动开启配置,需要局域namespace级别的缓存 一级缓存(本地缓存&#…...
