【Linux】第四十一站:线程控制
一、Linux线程VS进程
1.进程和线程
- 进程是资源分配的基本单位
- 线程是调度的基本单位
- 线程共享进程数据,但也拥有自己的一部分数据:
- 线程ID
- 一组寄存器(上下文)
- 栈
- errno
- 信号屏蔽字
- 调度优先级
2.进程的多个线程共享
同一地址空间,因此Text Segment、Data Segment都是共享的,如果定义一个函数,在各线程中都可以调用,如果定义一个全局变量,在各线程中都可以访问到,除此之外,各线程还共享以下进程资源和环境:
- 文件描述符表
- 每种信号的处理方式(SIG_ IGN、SIG_ DFL或者自定义的信号处理函数)
- 当前工作目录
- 用户id和组id
进程和线程的关系如下图:
3.关于进程线程的问题
如何看待之前学习的单进程?具有一个线程执行流的进程
二、线程控制
1.POSIX线程库
内核中有没有很明确的线程的概念呢?没有的。它只有轻量级进程的概念。
所以它就一定无法给我们提供线程的系统调用,只会给我们提供轻量级进程系统调用!
可是我们用户,需要的是线程的接口!**所以我们的应用层就有了一个pthread线程库。它是将轻量级进程接口进行了封装。为用户提供直接线程的接口。**对于这个pthread线程库,几乎所有的linux平台,都是默认自带这个库的!在Linux中编写多线程代码,需要使用第三方pthread库!
- 与线程有关的函数构成了一个完整的系列,绝大多数函数的名字都是以“pthread_”打头的
- 要使用这些函数库,要通过引入头文<pthread.h>
- 链接这些线程函数库时要使用编译器命令的“-lpthread”选项
2.快速使用一些常见的接口
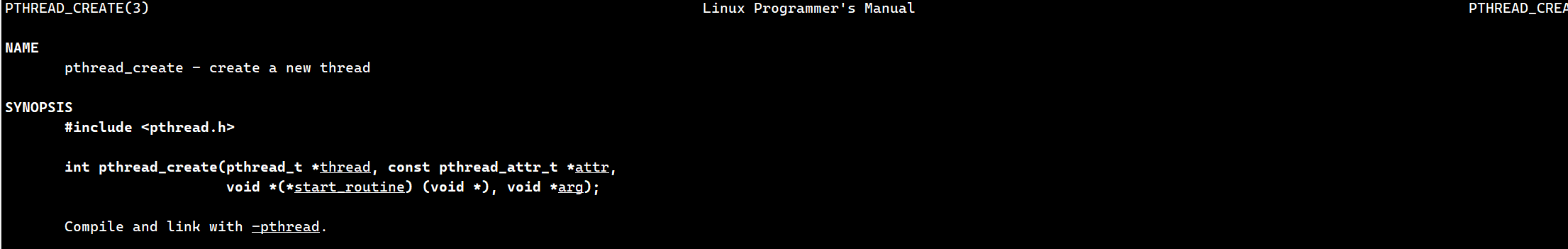
2.1 创建线程
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
- thread:返回线程ID,是一个输出型参数
- attr:设置线程的属性,大部分情况下,attr为NULL表示使用默认属性
- start_routine:是个函数地址,线程启动后要执行的函数,返回值为void*,参数也是void*,他是新线程所执行的入口函数。void*可以接收或返回任意指针类型,因为C语言没有模板,但是想用泛型。注意在linux平台下,指针是8字节,因为是64位机器,并且void的大小是1,且不可以形如void x这样定义变量
- arg:传给线程启动函数的参数。创建线程成功,新线程回调线程函数的时候,需要参数,这个参数就是给线程函数传递的。没有就设置位nullptr
- 返回值:成功返回0;失败返回错误码。
然后我们用如下代码来进行验证
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;void* threadRountine(void* args)
{while(true){cout << "new thread, pid" << getpid() << endl;sleep(2);}
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRountine, nullptr);while(true){cout << "main thread, pid" << getpid() << endl;sleep(1);}return 0;
}
运行结果为
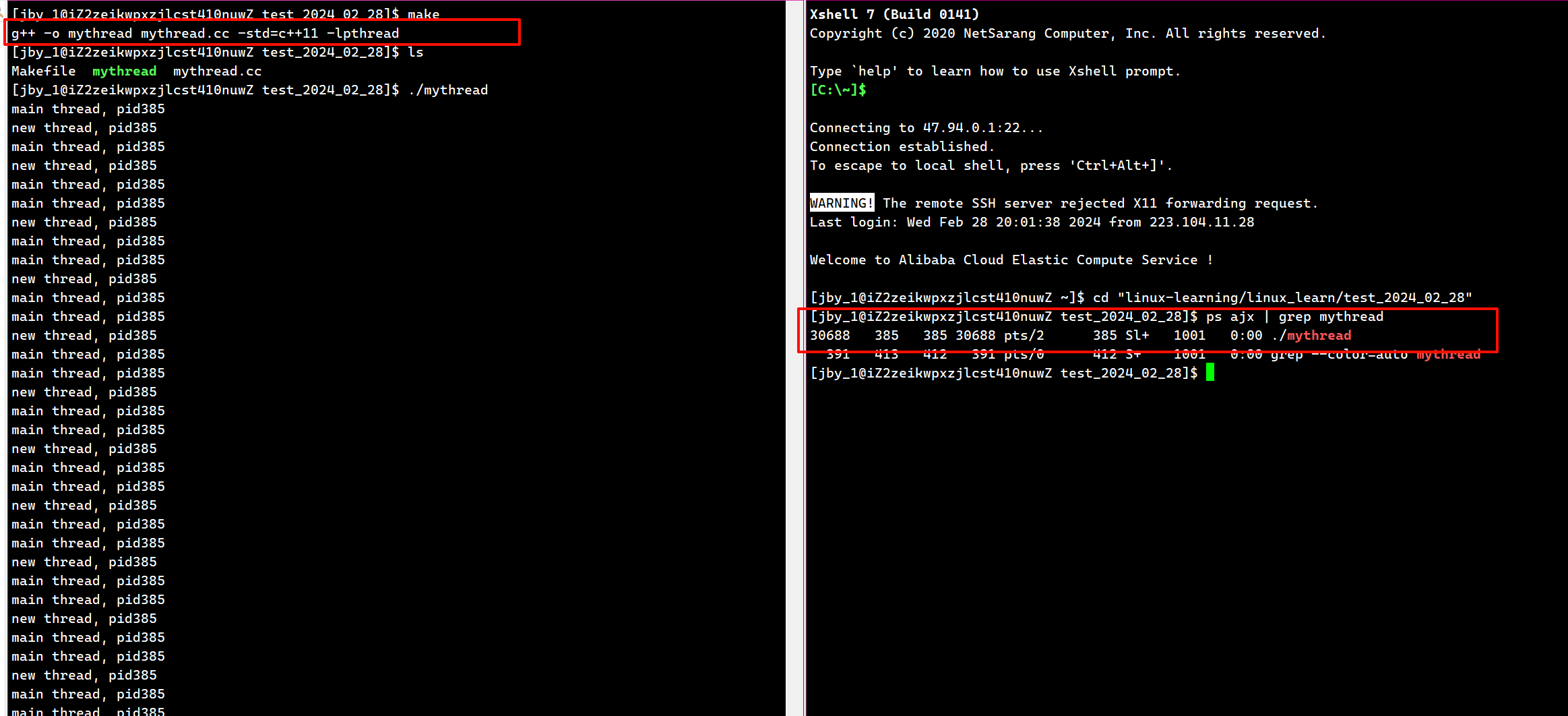
注意我们可以发现,它只有一个pid,说明它确实是一个进程,只不过一个进程里有两个执行流
可是如果我们就想查到两个该怎么办呢?我们可以用如下命令
ps -aL #这里的L我们可以理解为light轻的意思,也就是轻量级进程
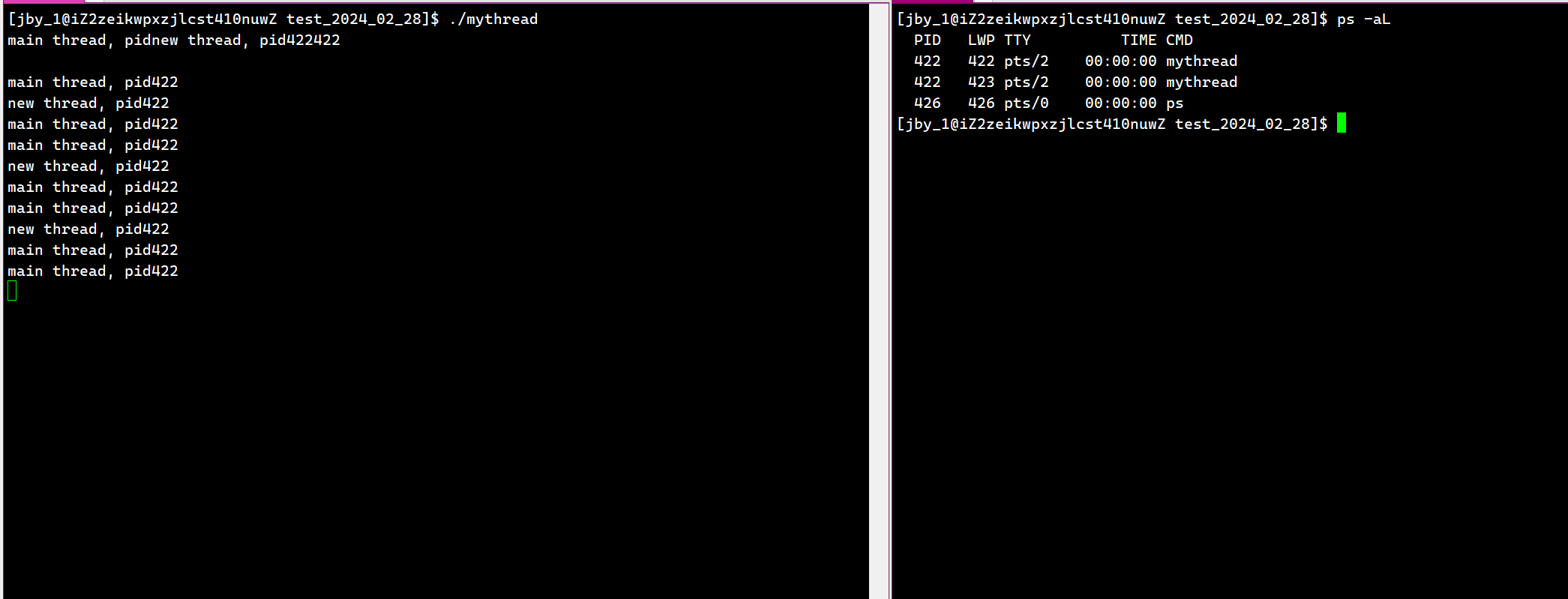
其中第二个LWP(light weight process)其实就是轻量级进程的意思。因为轻量级进程也需要有一个编号
其中有一个PID等于LWP,这里说明了这个线程是主线程,剩下的是被创建出来的线程
像我们以前写的单线程代码,其实就是PID永远等于LWP的。
除此之外,一个进程中的任何一个线程被干掉了,那么整个进程都会被干掉
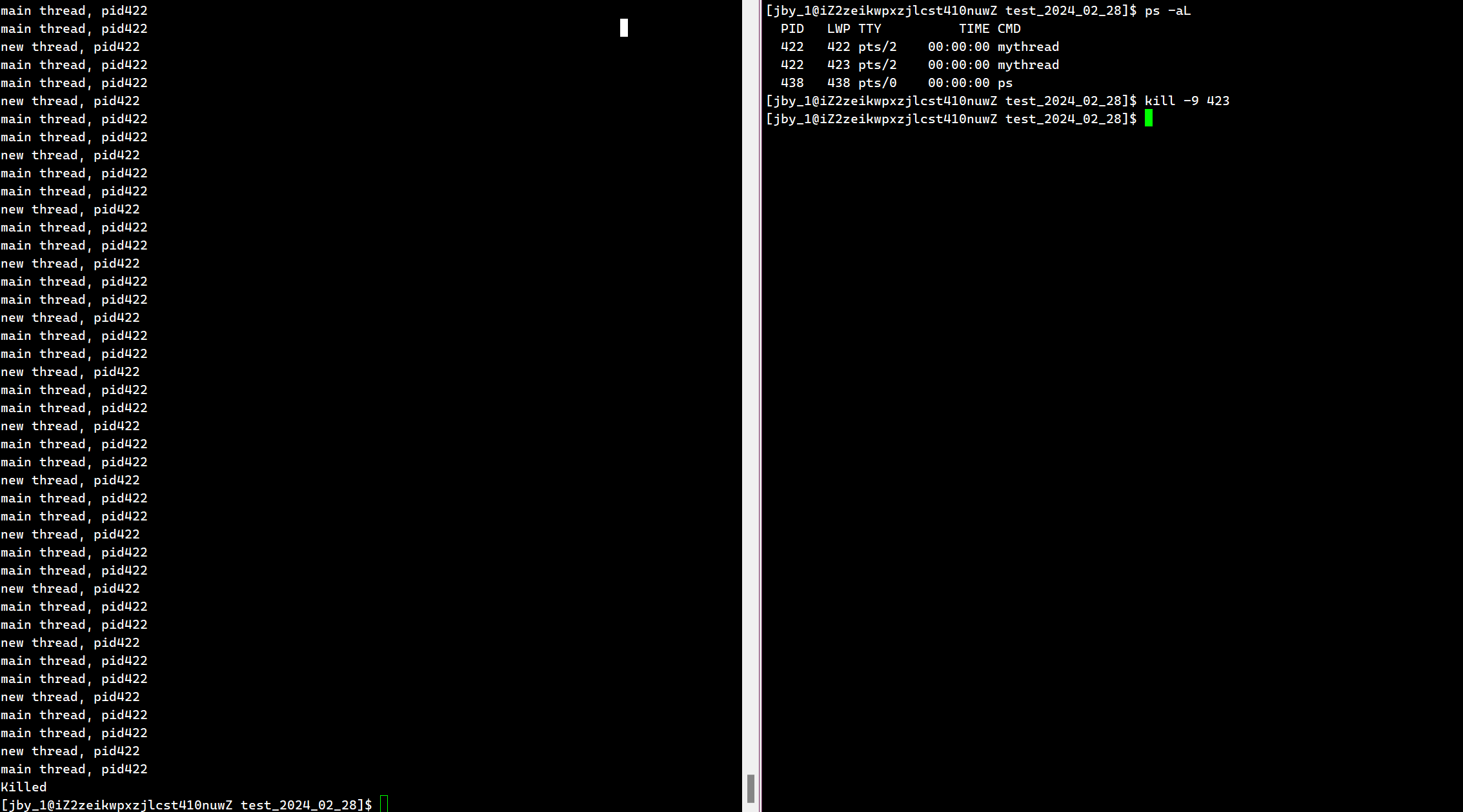
那么这个信号是发给进程还是线程的呢?,其实是发给进程的。因为线程只是进程的一个执行分支。这也就是为什么线程的健壮性很差,因为一个线程被干掉了,其他线程也会被干掉。
我们在看一下下面的代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;void show(const string& name)
{cout << name << "say# " << "hello thread" << endl;
}void* threadRountine(void* args)
{while(true){cout << "new thread, pid" << getpid() << endl;show("[new thread]");sleep(2);}
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRountine, nullptr);while(true){cout << "main thread, pid" << getpid() << endl;show("[main thread]");sleep(1);}return 0;
}
运行结果为
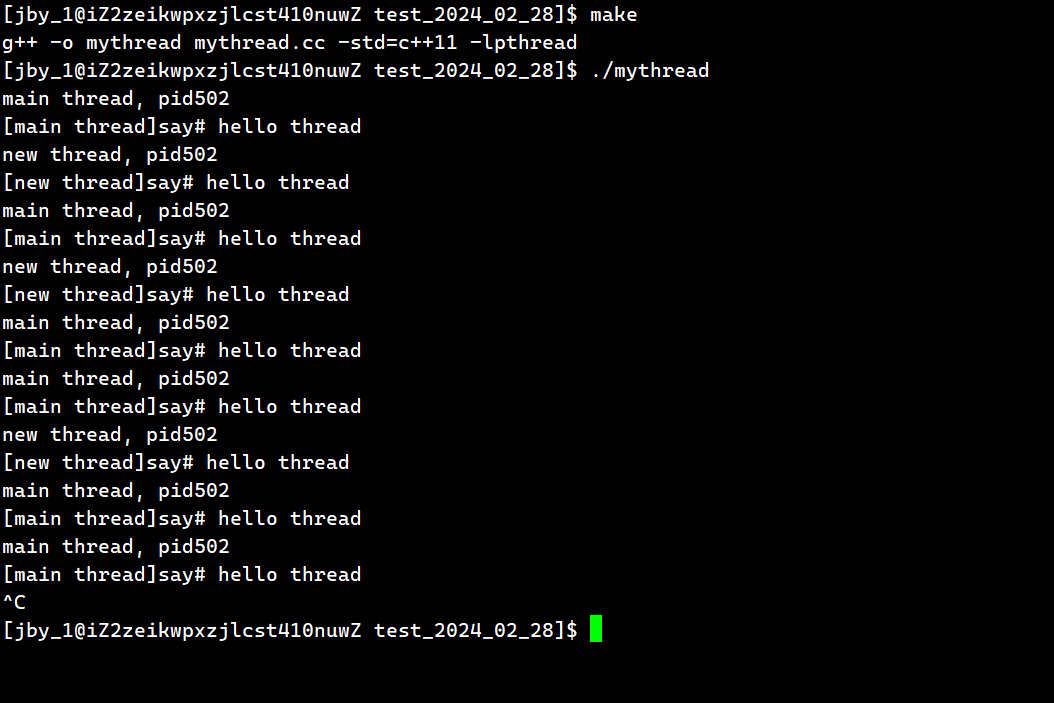
我们可以看到主线程和新线程都调用了这个方法,说明这个函数可以被多个执行流同时执行。即show函数被重入!
我们还可以看下面的代码
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int g_val = 100;void show(const string& name)
{cout << name << "say# " << "hello thread" << endl;
}void* threadRountine(void* args)
{while(true){printf("new thread, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p\n", getpid(), g_val, &g_val);// cout << "new thread, pid" << getpid() << endl;//show("[new thread]");sleep(2);}
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRountine, nullptr);while(true){printf("main thread, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p\n", getpid(), g_val, &g_val);// cout << "main thread, pid" << getpid() << ", g_val" << g_val << "&g_val" << &g_val << endl;//show("[main thread]");g_val++;sleep(1);}return 0;
}运行结果为
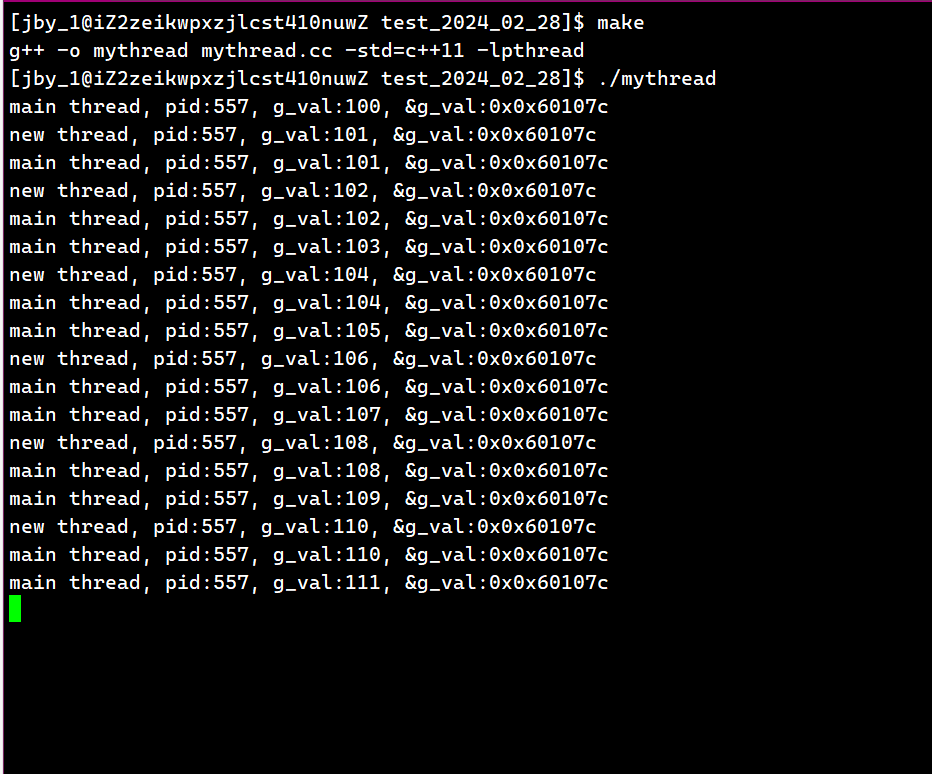
我们可以看到,主线程和新线程都可以看到这个变量被修改了。说明两个线程共享这个变量。
所以两个线程想要进行通信实在是太容易了
我们再用下面的代码进行测试
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int g_val = 100;void show(const string& name)
{cout << name << "say# " << "hello thread" << endl;
}void* threadRountine(void* args)
{while(true){printf("new thread, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p\n", getpid(), g_val, &g_val);// cout << "new thread, pid" << getpid() << endl;//show("[new thread]");sleep(5);int a = 10;a = a / 0;}
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRountine, nullptr);while(true){printf("main thread, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p\n", getpid(), g_val, &g_val);// cout << "main thread, pid" << getpid() << ", g_val" << g_val << "&g_val" << &g_val << endl;//show("[main thread]");g_val++;sleep(1);}return 0;
}
运行结果为:
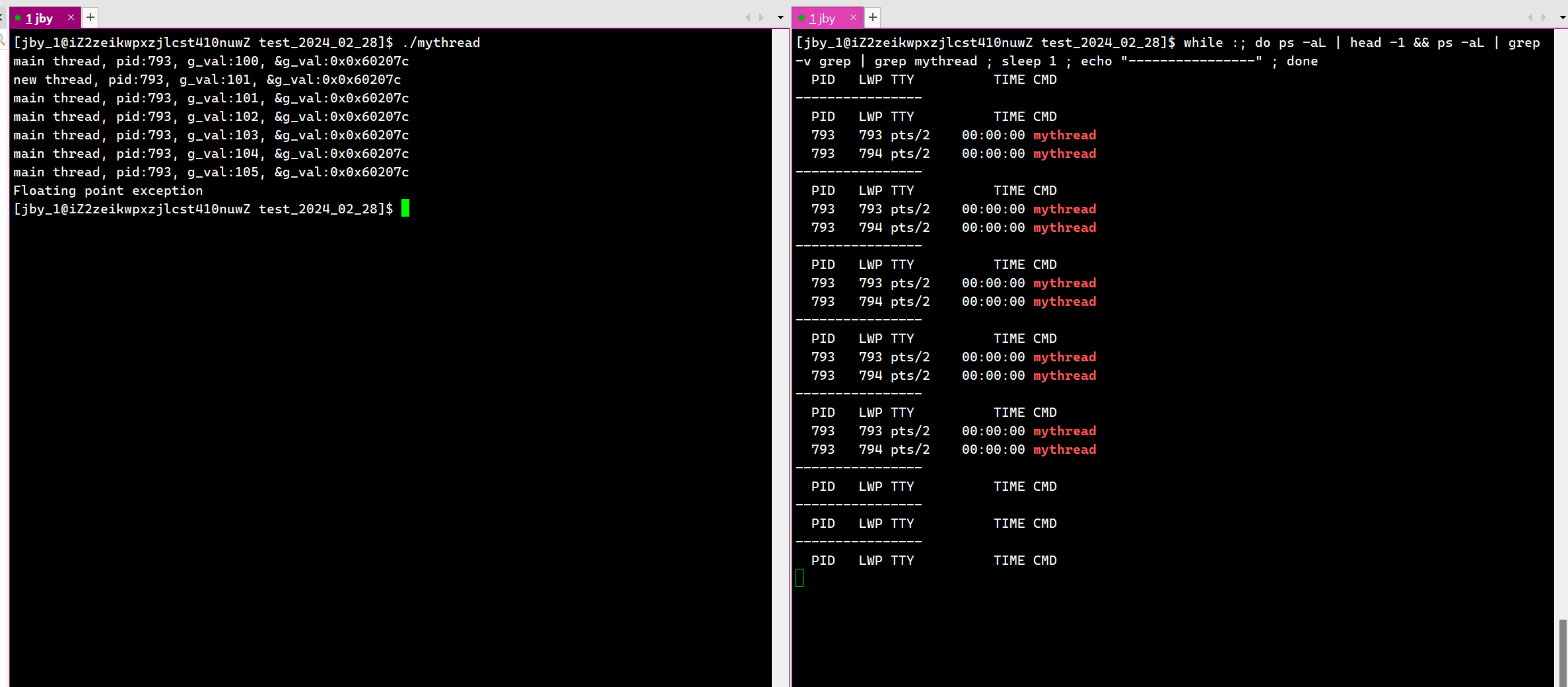
这就是因为一个线程出现异常了,所以导致整个进程挂掉了
我们接下来在看一下这个tid是什么
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int g_val = 100;void show(const string& name)
{cout << name << "say# " << "hello thread" << endl;
}void* threadRountine(void* args)
{while(true){printf("new thread, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p\n", getpid(), g_val, &g_val);// cout << "new thread, pid" << getpid() << endl;//show("[new thread]");sleep(1);// int a = 10;// a = a / 0;}
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRountine, nullptr);while(true){printf("main thread, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p, creat new thread tid:%p\n", getpid(), g_val, &g_val, tid);// cout << "main thread, pid" << getpid() << ", g_val" << g_val << "&g_val" << &g_val << endl;//show("[main thread]");g_val++;sleep(1);}return 0;
}运行结果为
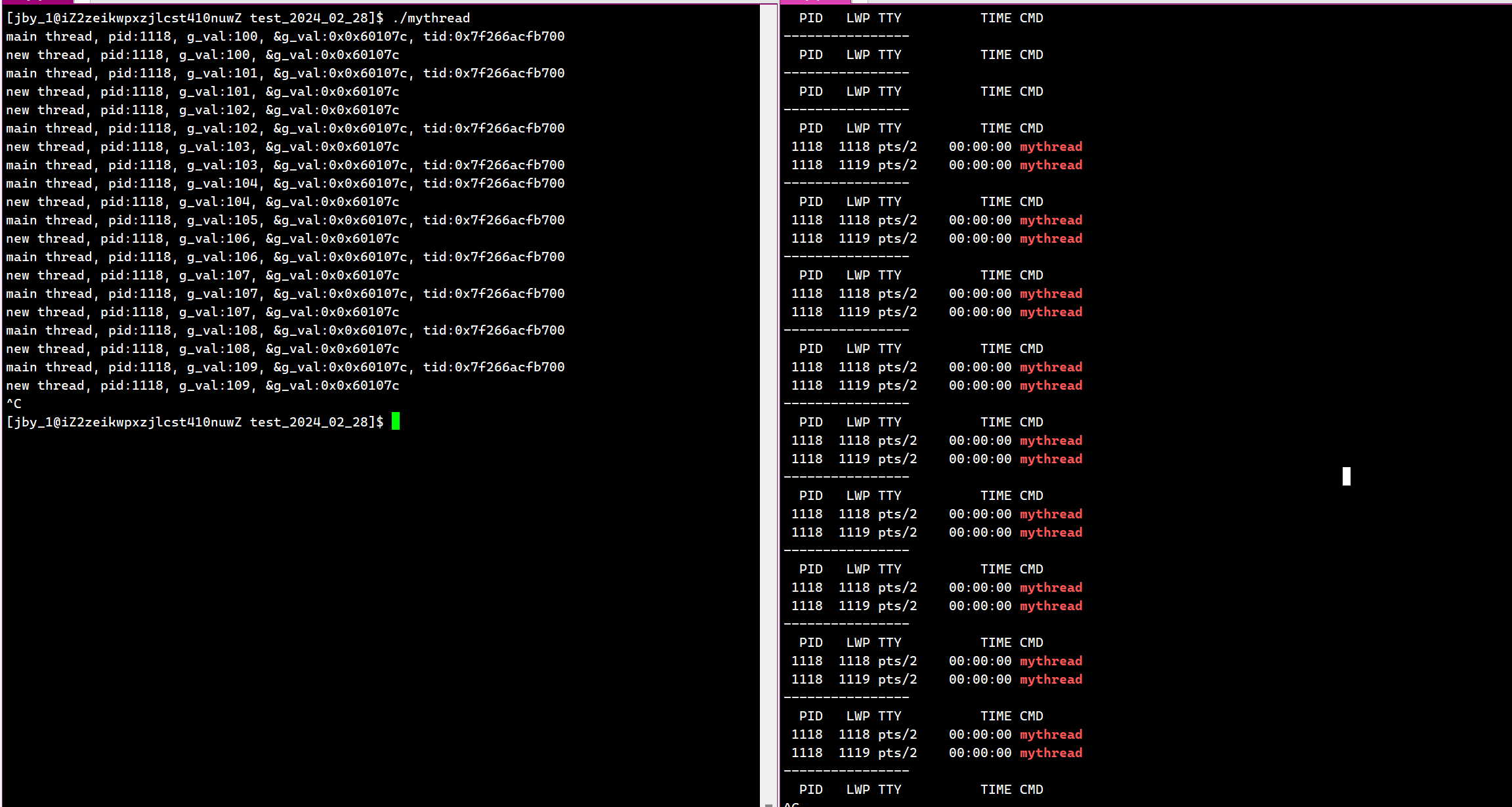
其实这个tid显然不是这个LWP,因为LWP是操作系统认识的就可以了,这tid是我们用户所使用的。至于它的具体使用,我们稍后再谈。
我们再来看看第四个参数,这个第四个参数是给第三个函数进行传参的。
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int g_val = 100;void show(const string& name)
{cout << name << "say# " << "hello thread" << endl;
}void* threadRountine(void* args)
{const char* name = (const char*)args;while(true){printf("%s, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p\n", name, getpid(), g_val, &g_val);// cout << "new thread, pid" << getpid() << endl;//show("[new thread]");sleep(1);// int a = 10;// a = a / 0;}
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRountine, (void*)"thread 1");while(true){printf("main thread, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p, creat new thread tid:%p\n", getpid(), g_val, &g_val, tid);// cout << "main thread, pid" << getpid() << ", g_val" << g_val << "&g_val" << &g_val << endl;//show("[main thread]");g_val++;sleep(1);}return 0;
}
运行结果为
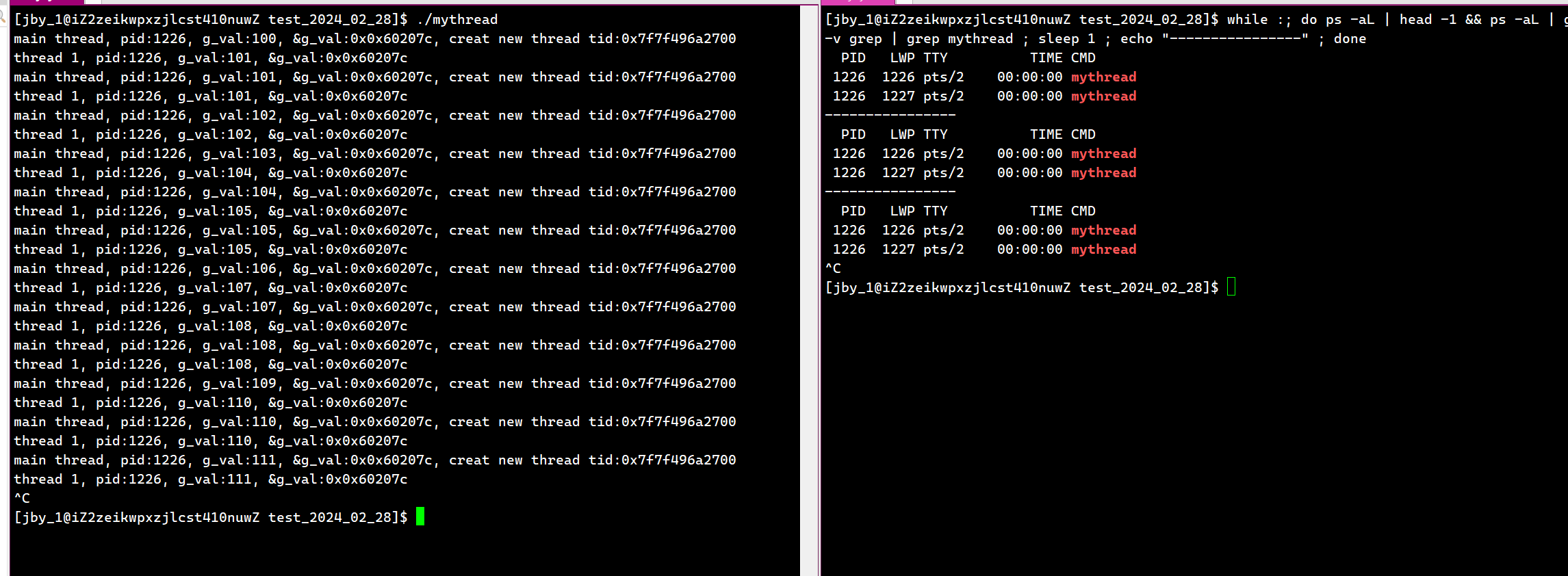
我们果然看到这个第四个参数被传入了进去
2.2 线程等待
那么这两个线程谁先进行退出呢?一般来说是新线程先退出的,然后主线程才能退出的,因为是主线程创建的它,它要对这个新线程进行管理。
如果我们主线程是一个死循环,而新线程一直不退出,那么也会造成类似于进程中的僵尸进程的问题(当然线程里没有这个说法)。所以新线程被创建出来以后,一般也要被等待,如果不等待,可能会造成类似于僵尸进程的问题。当然这个问题我们是无法验证出来的,因为新线程一退,我们查也就查不到了。但是确确实实会存在这个问题。
更重要的是,我们将新线程创建出来,就是让他就办事的,我们得知道它办的怎么样,结果数据是什么?
所以我们线程等待的两个目的:
- 防止内存泄漏
- 如果需要,我们也可以获取一下子进程的退出结果
下面是线程等待的函数
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);
//Compile and link with -pthread.
如果成功返回0,失败返回错误码。注意:线程里面所有的函数都不用errno错误码,而是直接返回一个错误码。这就保证了所有的线程都可以有一个返回的错误码,不需要去抢占全局的那个变量
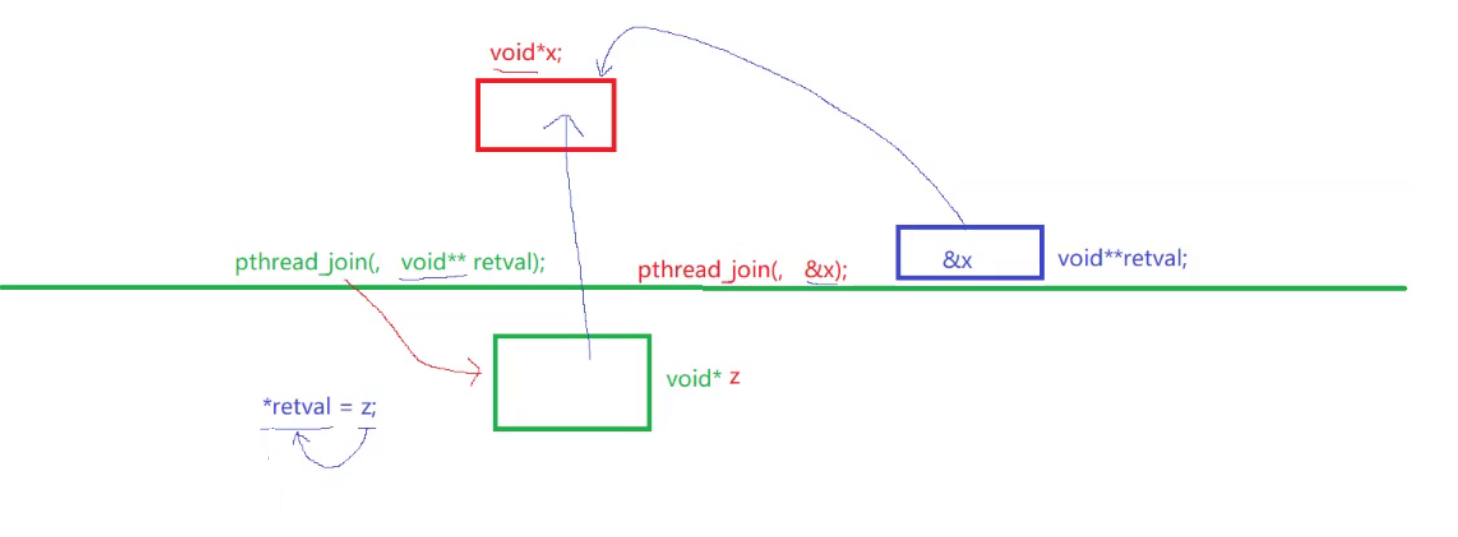
关于参数:
第一个参数是线程的tid
第二个参数是该线程结束时的返回值。注意*retval才是void*类型,也就是*retval才是函数的返回值
如下图所示,当void*通过pthread_join的方式传递的时候,会产生一个临时变量。比如说,我们调用函数的时候传递&x,那么&x其实会被拷贝一份,我们这里暂且记作retavl。然后在pthread_join内部执行,*retval = z这一步。最终就成功的为x赋值了。即x就相当于一个输入型参数。
我们可以用如下代码来进行操作一下
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int g_val = 100;void show(const string& name)
{cout << name << "say# " << "hello thread" << endl;
}void* threadRountine(void* args)
{const char* name = (const char*)args;int cnt = 5;while(true){printf("%s, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p\n", name, getpid(), g_val, &g_val);// cout << "new thread, pid" << getpid() << endl;//show("[new thread]");sleep(1);// int a = 10;// a = a / 0;cnt--;if(cnt == 0){break;}}return nullptr; //走到这里就默认线程退出了。
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRountine, (void*)"thread 1");// while(true)// {// printf("main thread, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p, creat new thread tid:%p\n", getpid(), g_val, &g_val, tid);// // cout << "main thread, pid" << getpid() << ", g_val" << g_val << "&g_val" << &g_val << endl;// //show("[main thread]");// g_val++;// sleep(1);// }sleep(7);pthread_join(tid, nullptr);cout << "main thread quit..." << endl; return 0;
}
运行结果为:
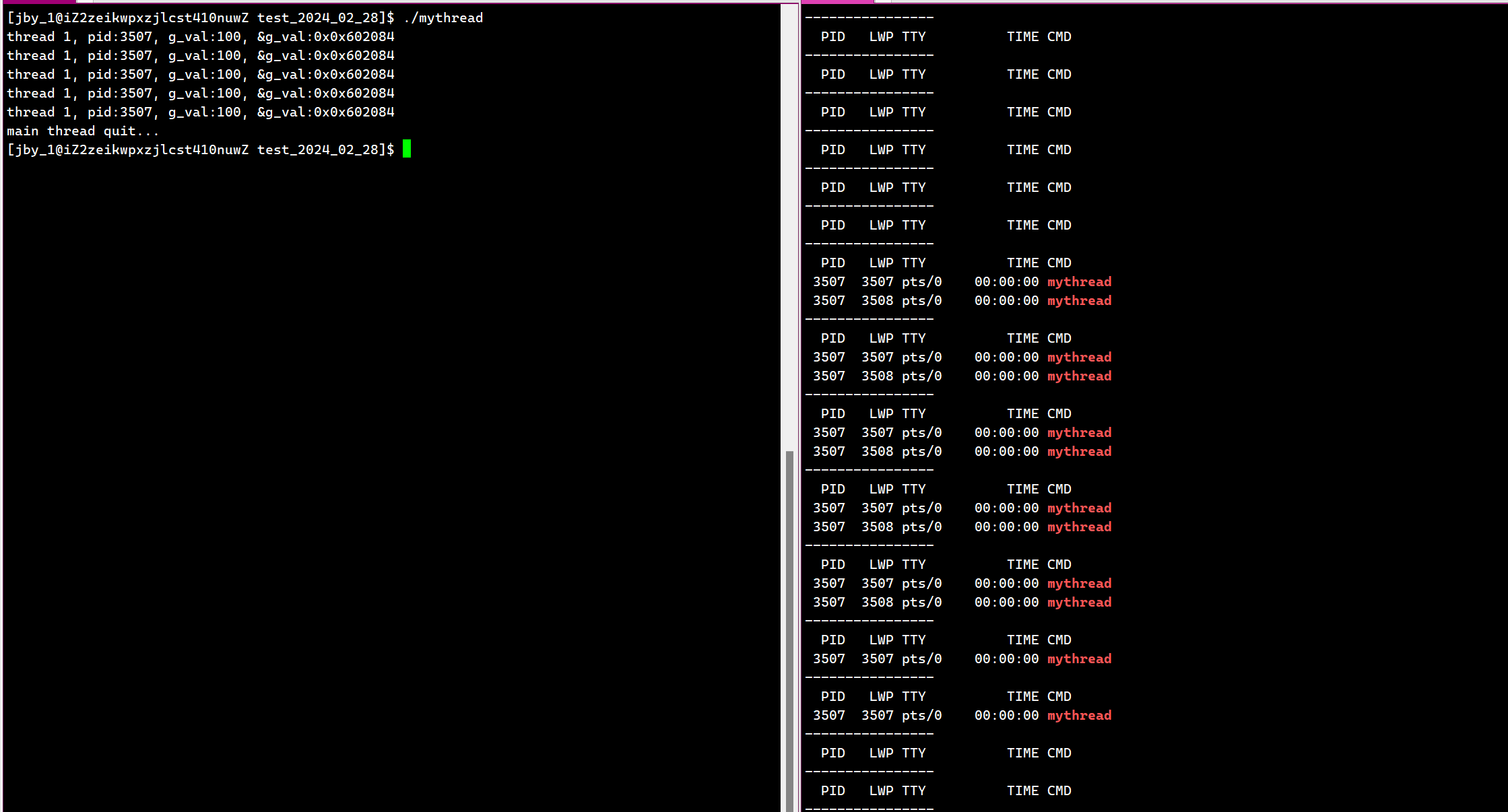
我们可以很明显的看到,新线程先退出了,主线程等两秒之后也就退出了。这里我们观察不到新线程有类似于僵尸的状态,但是确确实实是存在的这个状态
我们现在来使用一下第二个参数retval
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int g_val = 100;void show(const string& name)
{cout << name << "say# " << "hello thread" << endl;
}void* threadRountine(void* args)
{const char* name = (const char*)args;int cnt = 5;while(true){printf("%s, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p\n", name, getpid(), g_val, &g_val);// cout << "new thread, pid" << getpid() << endl;//show("[new thread]");sleep(1);// int a = 10;// a = a / 0;cnt--;if(cnt == 0){break;}}//return nullptr; //走到这里就默认线程退出了。return (void*)1; //走到这里就默认线程退出了。
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRountine, (void*)"thread 1");// while(true)// {// printf("main thread, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p, creat new thread tid:%p\n", getpid(), g_val, &g_val, tid);// // cout << "main thread, pid" << getpid() << ", g_val" << g_val << "&g_val" << &g_val << endl;// //show("[main thread]");// g_val++;// sleep(1);// }//sleep(7);void* retval;pthread_join(tid, &retval); //main thread等待的时候,默认是阻塞等待的cout << "main thread quit..., ret: " << (long long)retval << endl; return 0;
}运行结果为,可以看到我们确实已经拿到了1

不过这里我们会感觉到哪里不对劲,为什么我们在这里join的时候不考虑异常呢??
其实是因为做不到,因为线程一旦出异常了,主线程也就挂了。所以线程这里不用考虑异常,异常这里是进程考虑的。
2.3 线程终止
如果我们想要终止线程,能否像进程终止一样使用exit函数呢?
我们可以用下面代码来验证一下
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int g_val = 100;void show(const string& name)
{cout << name << "say# " << "hello thread" << endl;
}void* threadRountine(void* args)
{const char* name = (const char*)args;int cnt = 5;while(true){printf("%s, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p\n", name, getpid(), g_val, &g_val);// cout << "new thread, pid" << getpid() << endl;//show("[new thread]");sleep(1);// int a = 10;// a = a / 0;cnt--;if(cnt == 0){break;}}exit(11);//return nullptr; //走到这里就默认线程退出了。//return (void*)1; //走到这里就默认线程退出了。
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRountine, (void*)"thread 1");// while(true)// {// printf("main thread, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p, creat new thread tid:%p\n", getpid(), g_val, &g_val, tid);// // cout << "main thread, pid" << getpid() << ", g_val" << g_val << "&g_val" << &g_val << endl;// //show("[main thread]");// g_val++;// sleep(1);// }//sleep(7);void* retval;pthread_join(tid, &retval); //main thread等待的时候,默认是阻塞等待的cout << "main thread quit..., ret: " << (long long)retval << endl; return 0;
}
运行结果为
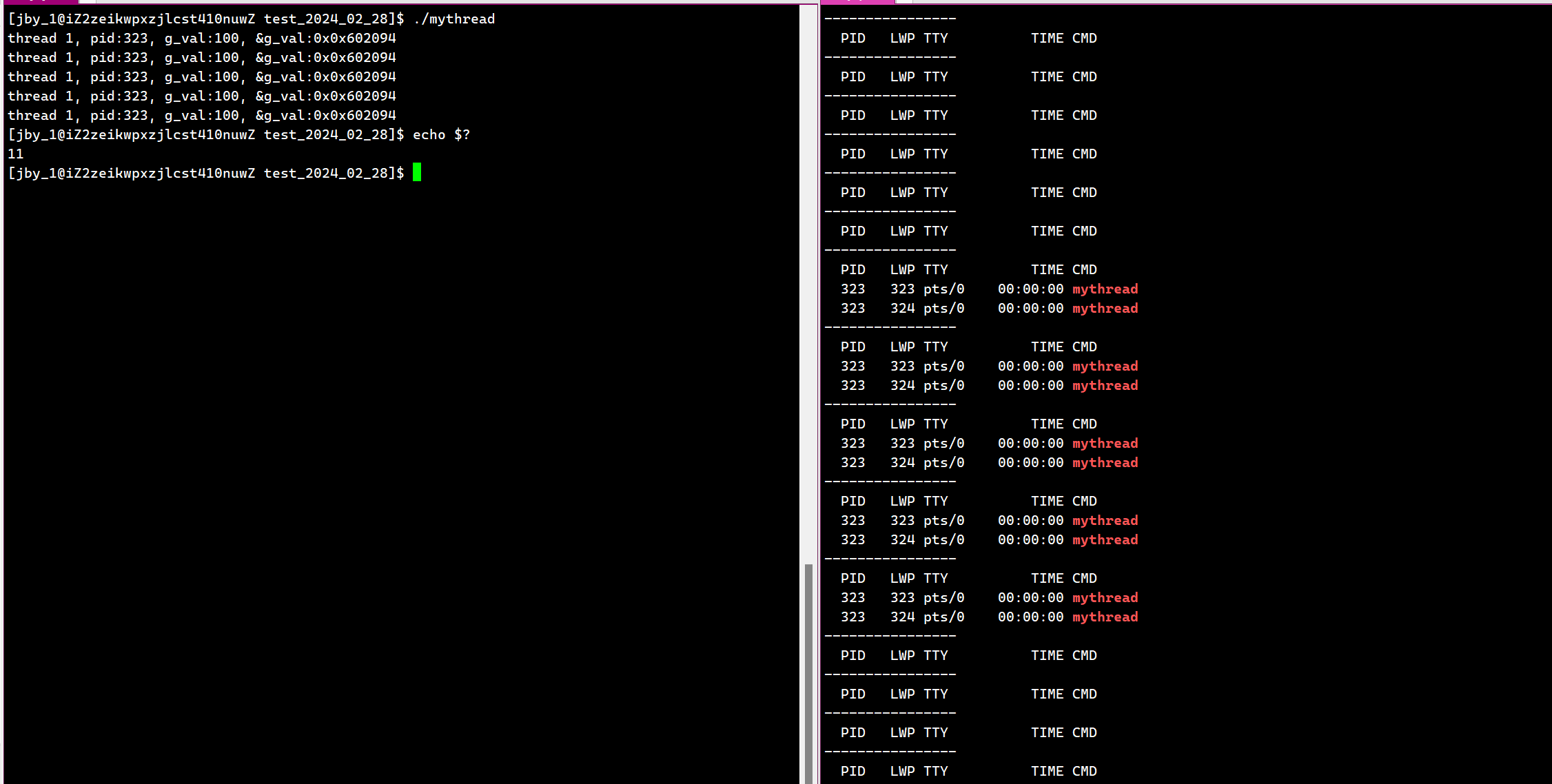
我们可以注意到,主线程并没有打印出对应的main thread quit…。所以说明exit直接将主线程也终止了。
即exit是用来终止进程的!,不能用来直接终止线程
线程终止的接口如下所示:
#include <pthread.h>
void pthread_exit(void *retval);
//Compile and link with -pthread.
它的作用是终止调用这个函数的线程,谁调用它就终止谁。参数是void*,和这个函数的返回值的含义是一样的。
我们用如下代码来进行测试
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int g_val = 100;void show(const string& name)
{cout << name << "say# " << "hello thread" << endl;
}void* threadRountine(void* args)
{const char* name = (const char*)args;int cnt = 5;while(true){printf("%s, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p\n", name, getpid(), g_val, &g_val);// cout << "new thread, pid" << getpid() << endl;//show("[new thread]");sleep(1);// int a = 10;// a = a / 0;cnt--;if(cnt == 0){break;}}pthread_exit((void*)100);//exit(11);//return nullptr; //走到这里就默认线程退出了。//return (void*)1; //走到这里就默认线程退出了。
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRountine, (void*)"thread 1");// while(true)// {// printf("main thread, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p, creat new thread tid:%p\n", getpid(), g_val, &g_val, tid);// // cout << "main thread, pid" << getpid() << ", g_val" << g_val << "&g_val" << &g_val << endl;// //show("[main thread]");// g_val++;// sleep(1);// }//sleep(7);void* retval;pthread_join(tid, &retval); //main thread等待的时候,默认是阻塞等待的cout << "main thread quit..., ret: " << (long long)retval << endl; return 0;
}
运行结果为
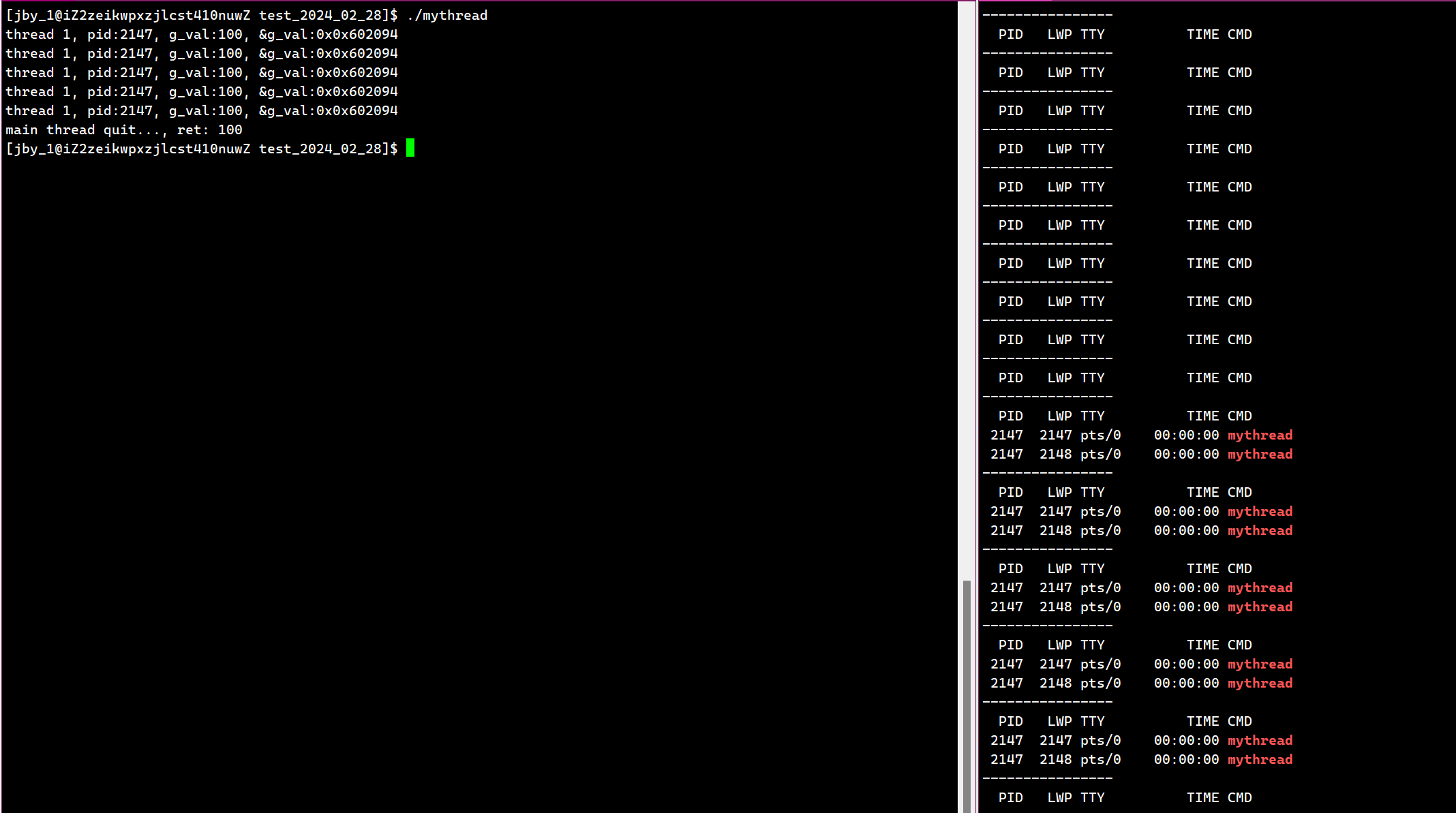
上面是新线程去调用pthread_exit接口,那么只有这个线程会退出,如果主线程去调用这个接口退出的话,那么整个进程都会终止
2.4 线程取消
如下所示,是线程取消的接口。
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);
//Compile and link with -pthread.
我们用如下代码来进行验证
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int g_val = 100;void show(const string& name)
{cout << name << "say# " << "hello thread" << endl;
}void* threadRountine(void* args)
{const char* name = (const char*)args;int cnt = 5;while(true){printf("%s, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p\n", name, getpid(), g_val, &g_val);// cout << "new thread, pid" << getpid() << endl;//show("[new thread]");sleep(1);// int a = 10;// a = a / 0;cnt--;if(cnt == 0){break;}}//pthread_exit((void*)100);//exit(11);//return nullptr; //走到这里就默认线程退出了。//return (void*)1; //走到这里就默认线程退出了。
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRountine, (void*)"thread 1");// while(true)// {// printf("main thread, pid:%d, g_val:%d, &g_val:0x%p, creat new thread tid:%p\n", getpid(), g_val, &g_val, tid);// // cout << "main thread, pid" << getpid() << ", g_val" << g_val << "&g_val" << &g_val << endl;// //show("[main thread]");// g_val++;// sleep(1);// }//sleep(7);sleep(1); //保证新线程已经启动pthread_cancel(tid);void* retval;pthread_join(tid, &retval); //main thread等待的时候,默认是阻塞等待的cout << "main thread quit..., ret: " << (long long)retval << endl; return 0;
}
运行结果为
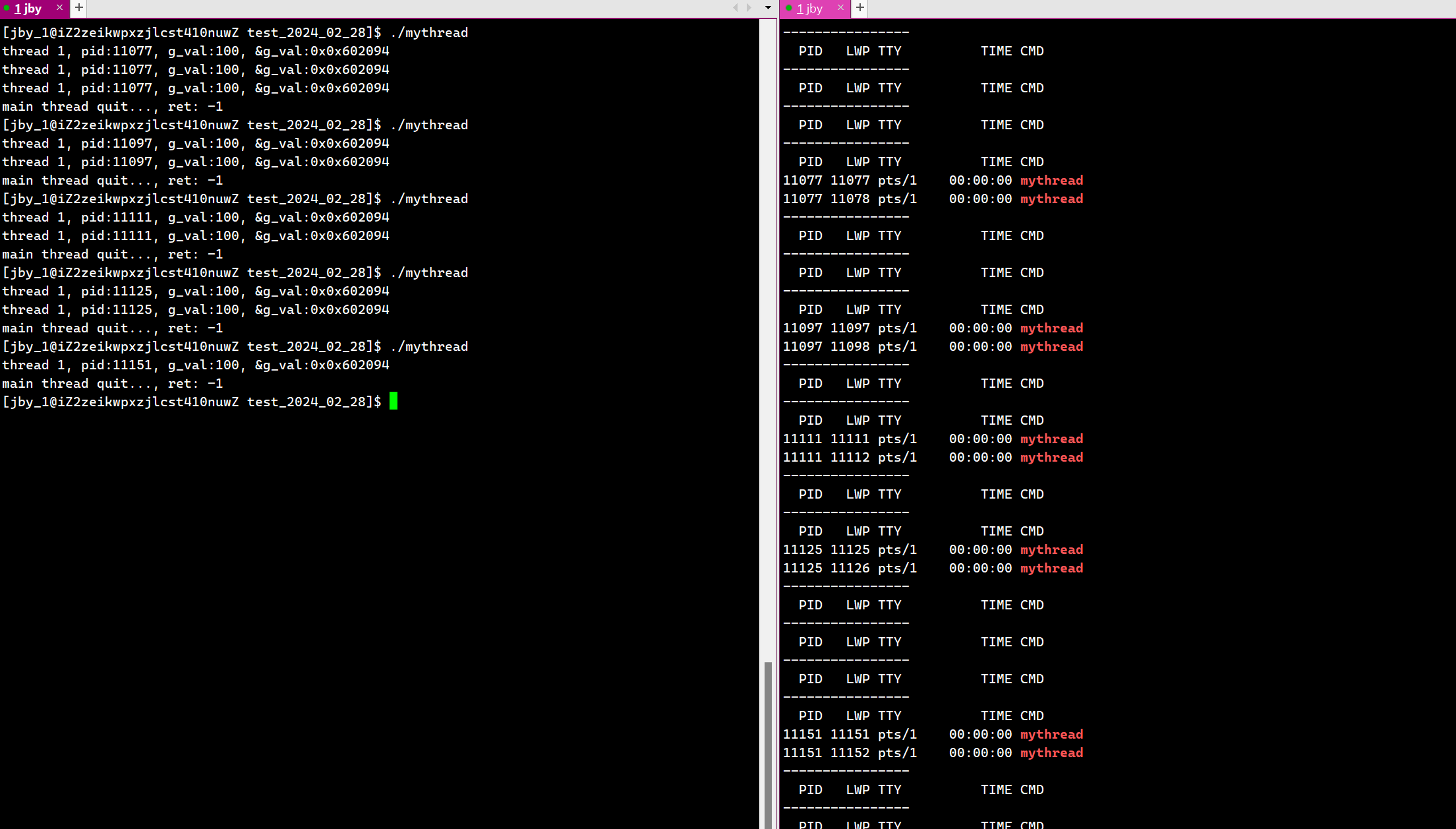
我们可以注意到,此时这个线程等待以后的返回值为-1
其实是因为一个线程如果被取消的话,会有这样一个宏
#define PTHREAD_CANCELED ((void *) -1)
换句话说,如果线程是被取消的,那么它退出时的返回码就是-1,即上面的宏
2.5 综合使用前面的四个接口
其实线程的参数和返回值,不仅仅可以用来传递一般参数,也可以传递对象
我们可以用下面的代码来看
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;class Request
{
public:Request(int start, int end, const string& threadname):_start(start),_end(end),_threadname(threadname){}
public:int _start;int _end;string _threadname;
};
class Response
{
public:Response(int result, int exitcode):_result(result),_exitcode(exitcode){}
public:int _result; //计算结果int _exitcode; //计算结果是否可靠
};void* sumCount(void* args) //线程的参数和返回值,不仅仅可以用来传递一般参数,也可以传递对象
{Request *rq = static_cast<Request*>(args);Response *rsp = new Response(0, 0);for(int i = rq->_start; i <= rq->_end; i++){cout << rq->_threadname << " is runing, caling..., " << i << endl;rsp->_result += i;usleep(100000);}delete rq;return (void*)rsp;
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;Request* rq = new Request(1, 100, "thread 1"); pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, sumCount, rq);void* ret;pthread_join(tid, &ret);Response *rsp = static_cast<Response*>(ret);cout << "rsp->result: " << rsp->_result << ", exitcode: " << rsp->_exitcode << endl; delete rsp;return 0;
}运行结果为
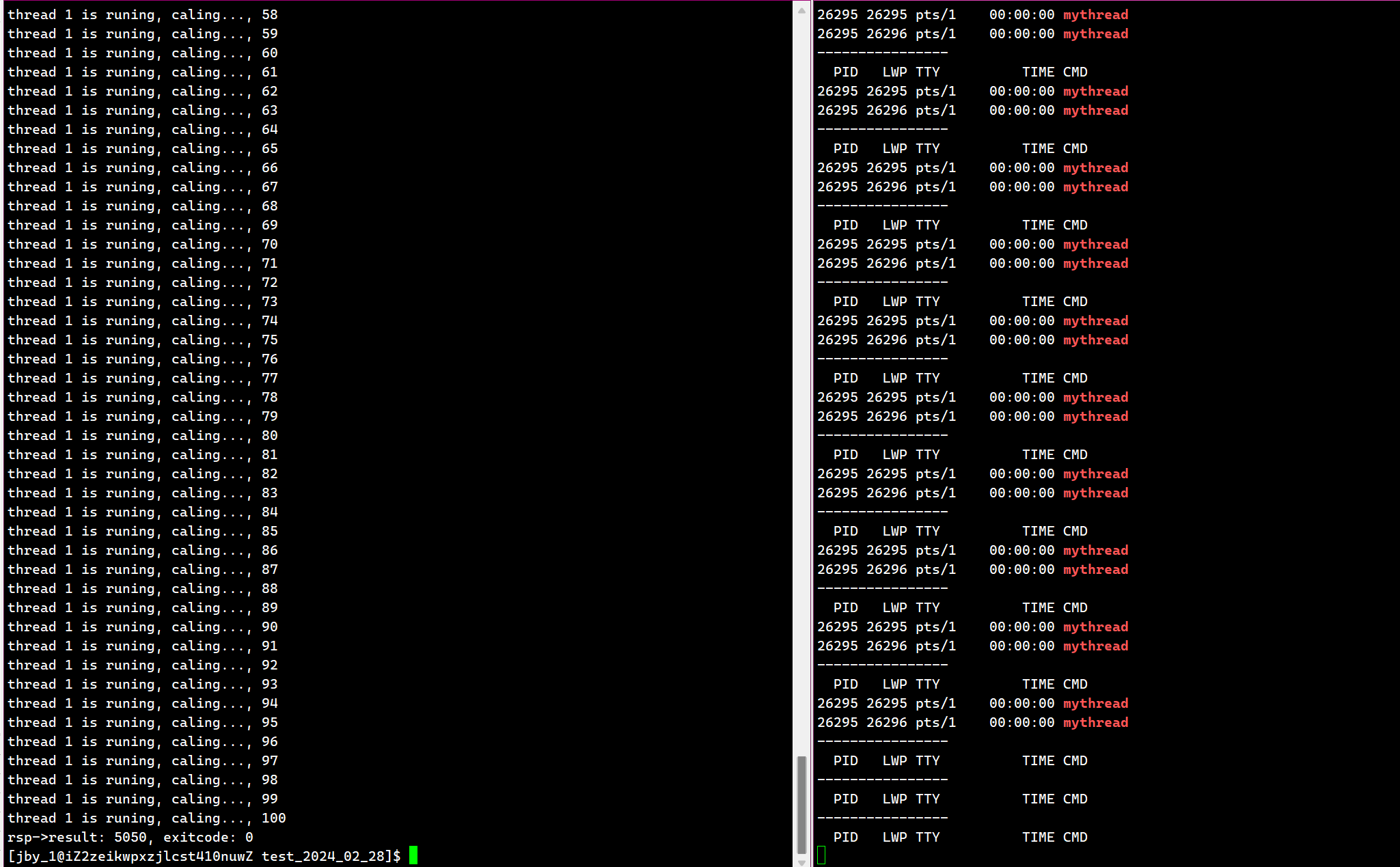
所以它就可以用来求出和。让每一个线程只执行其中的一部分计算,然后我们自己在将这些结果合并起来。
并且我们发现,我们的这些对象都是在堆区创建的。并且我们是交叉使用的,说明堆空间的也是被线程共享使用的
2.6 C++11中的线程
目前,我们使用的是原生线程库(pthread库)
其实C++11 语言本身也已经支持多线程了,它与我们的原生线程库有什么关系呢?
C++11的线程需要用下面的库
#include<thread>
我们看下面的代码
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
void threadrun()
{while(true){cout << "I am a new thread for C++" << endl;sleep(1);}
}int main()
{thread t1(threadrun);t1.join();return 0;
}运行结果为
我们需要注意的是,C++11中的线程库其实底层还是封装了linux提供的系统调用接口,所以我们编译的时候还是需要使用-lpthread选项的。
而C++11其实是有跨平台性的。因为它在不同平台下已经写好了不同版本的库。所以对我们而言,不同的平台写代码是没有感觉的。
我们最好使用C++的多线程。因为具有跨平台性
3.线程ID与进程地址空间布局
我们现在还没有解释这个tid究竟是什么东西,我们先看下面的代码
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;std::string toHex(pthread_t tid)
{char hex[64];snprintf(hex, sizeof(hex), "%p", tid);return hex;
}void *threadRoutine(void *args)
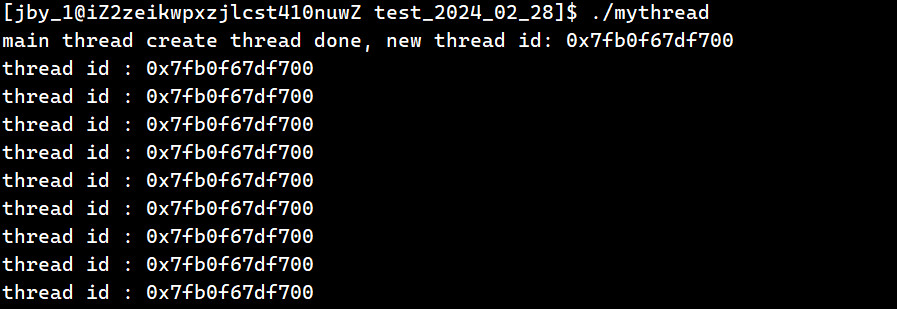
{while(true){cout << "thread id : " << toHex(pthread_self()) << endl; sleep(1);}
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void*)"thread 1");cout << "main thread create thread done, new thread id: " << toHex(tid) << endl;pthread_join(tid, nullptr);return 0;
}
运行结果为
我们知道的是,内核中并没有明确的线程的概念,只有轻量级进程的概念
而轻量级进程接口是这样的
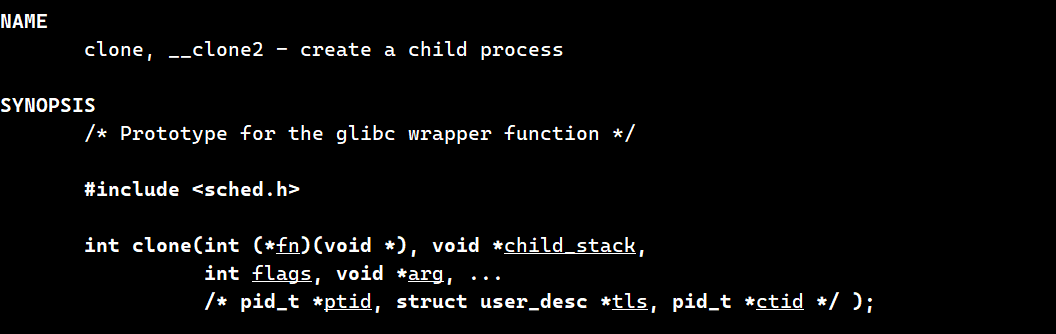
这个接口我们一般是不用的,包括fork的底层其实用的也是这个接口
这个的第一个参数是一个函数指针,第二个参数是自定义的一个栈…
这个接口是被pthread线程库封装了。
所以我们采用的是pthread_create,pthread_join这些接口。
如下图所示,这个clone这个接口它需要提供一个回调函数,独立栈结构等,用它去维护线程。
而这些都是线程库在做的事情,也就是线程的概念是库给我们维护的,我们用的原生线程库,也要加载到内存中,因为都是基于内存的。线程库是一个动态库,经过页表映射后,也要到共享区的。
这些栈都是在共享区创建的。我们的线程库只需要维护线程的概念即可,不用维护线程的执行流,不过线程库注定了要维护多个线程属性集合,线程也要管理这些线程,先描述在组织。
而这个线程控制块它就要可以找到这些回调函数,独立栈,以及在内部的LWP。这个线程控制块就是用户级线程
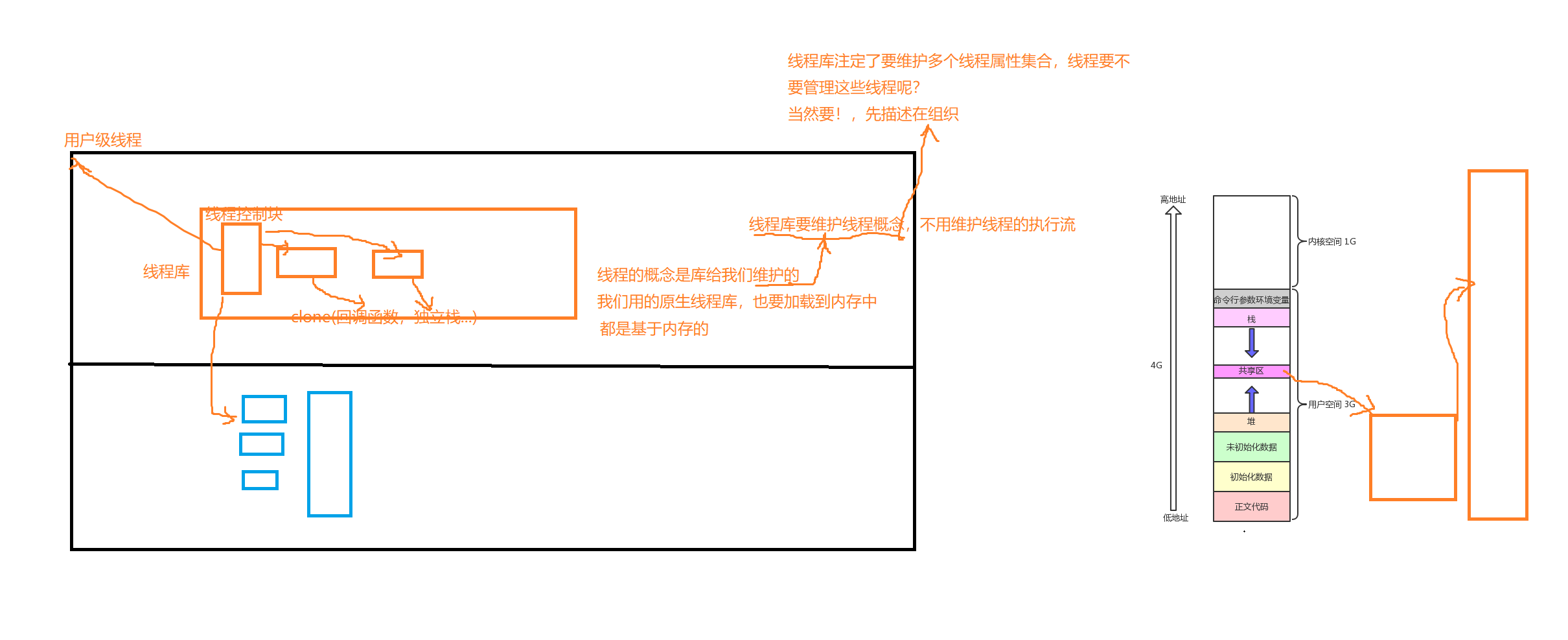
所以我们就将这个下面的这个叫做线程的tcb。而每一个tcb的起始地址,叫做线程的tid
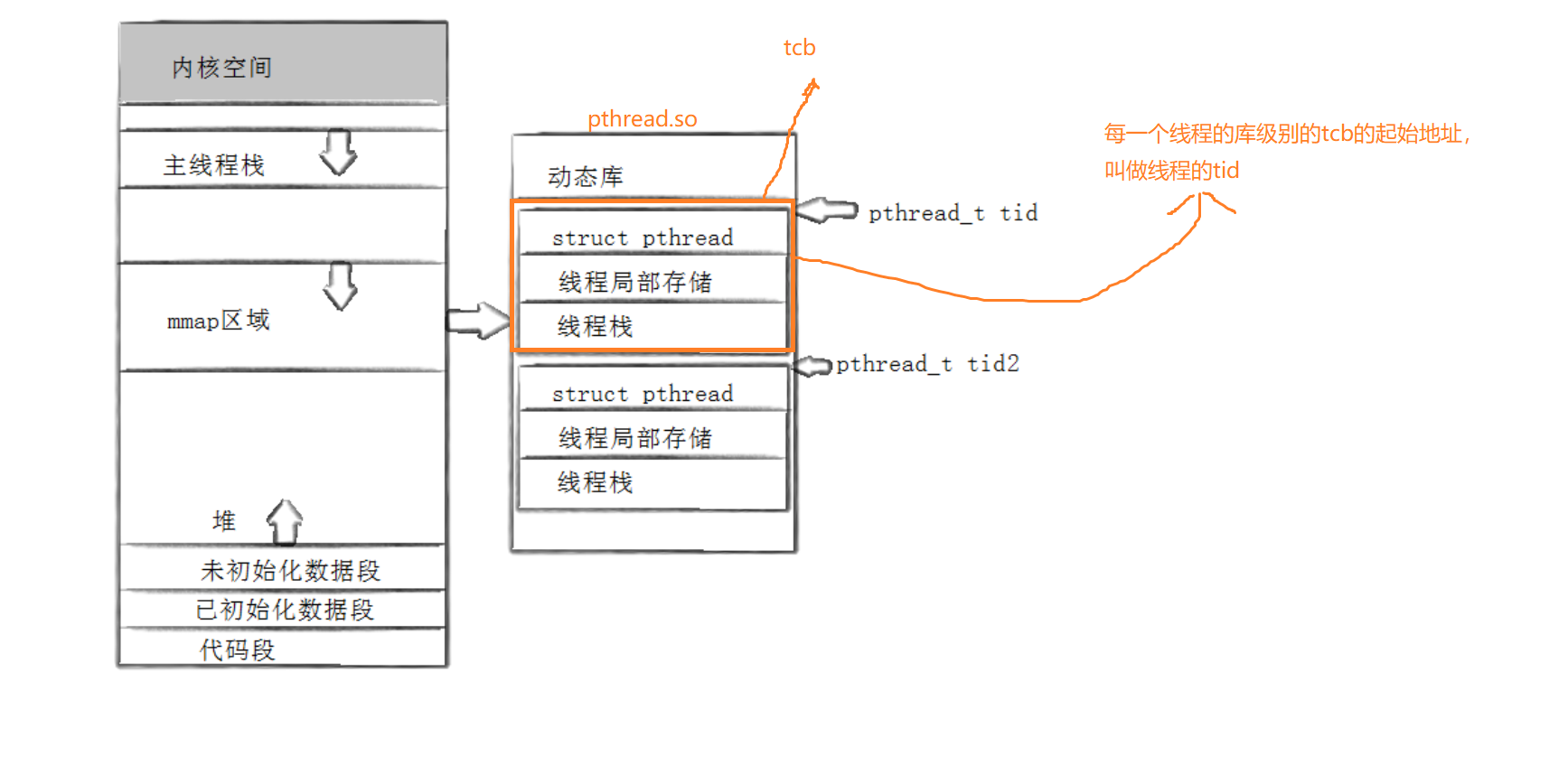
所以拿着这个tid,就可以找到库里面的属性了。
而我们前面打印出来的这个地址,我们也可以看到,它是比较大的,其实它就是介于堆栈之间的共享区
每一个线程都必须要有自己的独立栈结构,因为它有独立的调用链,要进行压栈等操作。其中主线程用的就是地址空间中的这个栈。剩下的轻量级进程在我们创建的时候会先创建一个tcb,它里面的起始地址作为线程tid,它的里面有一个默认大小的空间,叫做线程栈,然后内核中调用clone创建好执行流。在clone中形成的临时数据都会压入到这个线程库中的栈结构中。
即,除了主线程,所有其他线程的独立站,都共享区,具体来讲是在pthread库中,tid指向的用户tcb中
所以其实Linux的线程 = 用户级线程 + 内核的LWP
线程可以分为用户级线程和内核级线程,而linux就属于用户级线程
在linux中, 每一个用户级线程就要对应内核中的一个LWP。用户级执行流:内核LWP = 1 : 1
- pthread_ create函数会产生一个线程ID,存放在第一个参数指向的地址中。该线程ID和前面说的线程ID不是一回事。
- 前面讲的线程ID属于进程调度的范畴。因为线程是轻量级进程,是操作系统调度器的最小单位,所以需要一个数值来唯一表示该线程。
- pthread_ create函数第一个参数指向一个虚拟内存单元,该内存单元的地址即为新创建线程的线程ID,属于NPTL(原生线程库)线程库的范畴。线程库的后续操作,就是根据该线程ID来操作线程的。
- 线程库NPTL(原生线程库)提供了pthread_ self函数,可以获得线程自身的ID
pthread_t pthread_self(void);
相关文章:

【Linux】第四十一站:线程控制
一、Linux线程VS进程 1.进程和线程 进程是资源分配的基本单位线程是调度的基本单位线程共享进程数据,但也拥有自己的一部分数据:线程ID一组寄存器(上下文)栈errno信号屏蔽字调度优先级 2.进程的多个线程共享 同一地址空间,因此Text Segment、…...
ChatGPT提示词工程:prompt和chatbot
ChatGPT Prompt Engineering for Developers 本文是 https://www.deeplearning.ai/short-courses/chatgpt-prompt-engineering-for-developers/ 这门课程的学习笔记。 ChatGPT提示词工程:prompt和chatbot 文章目录 ChatGPT Prompt Engineering for DevelopersWhat …...
java算法
常见的七种查找算法: 数据结构是数据存储的方式,算法是数据计算的方式。所以在开发中,算法和数据结构息息相关。 1. 基本查找 也叫做顺序查找 说明:顺序查找适合于存储结构为数组或者链表。 基本思想:顺序查找也称…...

铭文资产是比特币生态破局者 or 短暂热点?
比特币作为加密货币的鼻祖,一直以来都扮演着数字资产市场的引领者角色。最近几年,随着 BRC20 项目的兴起,我们看到了更多与比特币相互关联的创新。在比特币生态中,BRC20 项目不仅仅是数字资产的代表,更是一种对于区块链…...
Java基础 - 8 - 算法、正则表达式、异常
一. 算法 什么是算法? 解决某个实际问题的过程和方法 学习算法的技巧? 先搞清楚算法的流程,再直接去推敲如何写算法 1.1 排序算法 1.1.1 冒泡排序 每次从数组中找出最大值放在数组的后面去 public class demo {public static void main(S…...

gRPC-第二代rpc服务
在如今云原生技术的大环境下,rpc服务作为最重要的互联网技术,蓬勃发展,诞生了许多知名基于rpc协议的框架,其中就有本文的主角gRPC技术。 一款高性能、开源的通用rpc框架 作者作为一名在JD实习的Cpper,经过一段时间的学…...

Node.js是什么?
概念:Node.js1运行在服务器端的js,用来编写服务器 特点:单线程、异步、非阻塞、统一API 是一个构建在V8引擎之上的js运行环境,它使得js可以运行在浏览器以外的地方,相对于大部分的服务器端语言来说,Node.J…...
java SSM厂房管理系统myeclipse开发mysql数据库springMVC模式java编程计算机网页设计
一、源码特点 java SSM厂房管理系统是一套完善的web设计系统(系统采用SSM框架进行设计开发,springspringMVCmybatis),对理解JSP java编程开发语言有帮助,系统具有完整的源代码和数据库,系统主要采用B/S…...
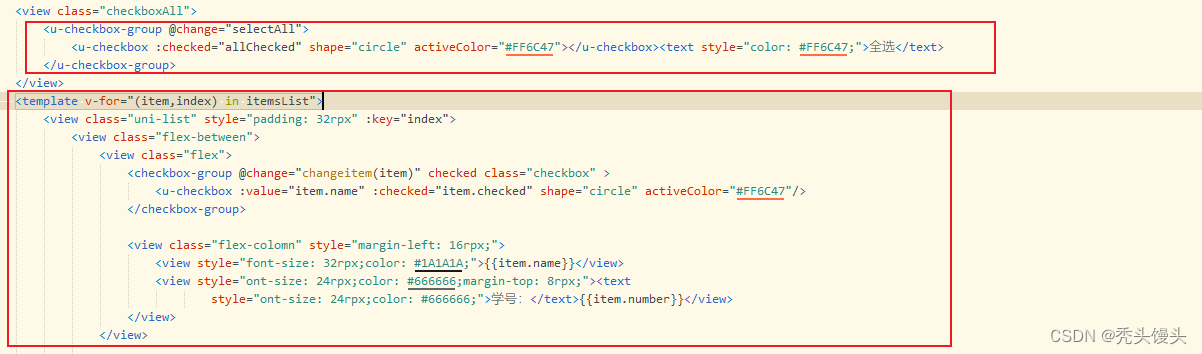
uniapp实现---类似购物车全选
目录 一、实现思路 二、实现步骤 ①view部分展示 ②JavaScript 内容 ③css中样式展示 三、效果展示 四、小结 注意事项 一、实现思路 点击商家复选框,可选中当前商家下的所有商品。点击全选,选中全部商家的商品 添加单个多选框,在将多选…...

Java:List列表去重有序和无序
目录 待去重列表HashSet去重(不保证顺序)TreeSet去重(不保证顺序)LinkedHashSet去重(保证顺序)遍历List去重(保证顺序)Java8中Stream流处理(保证顺序)参考文章 待去重列表 // 列表 …...
Python绘图-12地理数据可视化
Matplotlib 自 带 4 类别 地理投影: Aitoff, Hammer, Mollweide 及 Lambert 投影,可以 结 合以下四 张 不同 的 图 了解四 种 不同投影 区别 。 12.1Aitoff投影 12.1.1图像呈现 12.1.2绘图代码 import numpy as np # 导入numpy库,用于…...

NineData与OceanBase完成产品兼容认证,共筑企业级数据库新生态
近日,云原生智能数据管理平台 NineData 和北京奥星贝斯科技有限公司的 OceanBase 数据库完成产品兼容互认证。经过严格的联合测试,双方软件完全相互兼容、功能完善、整体运行稳定且性能表现优异。 此次 NineData 与 OceanBase 完成产品兼容认证…...

旅游专业VR虚拟仿真情景教学实训
一、生动的情景模拟 VR技术能够创建出高度逼真的虚拟环境,使学生能够身临其境地体验旅游场景。无论是古色古香的古代建筑,还是充满异国情调的热带雨林,亦或是繁华的都市风光,VR都能一一呈现。这种沉浸式的体验,使得学…...

解决方案TypeError: string indices must be integers
文章目录 一、现象:二、解决方案 一、现象: PyTorch深度学习框架,运行bert-mini,本地环境是torch1.4-gpu,发现报错显示:TypeError: string indices must be integers 后面报字符问题,百度过找…...

【论文阅读】Segment Anything论文梳理
Abstract 我们介绍了Segment Anything(SA)项目:新的图像分割任务、模型和数据集。高效的数据循环采集,使我们建立了迄今为止最大的分割数据集,在1100万张图像中,共超过10亿个掩码。 该模型被设计和训练为可…...

接口自动化测试框架搭建:基于python+requests+pytest+allure实现
众所周知,目前市面上大部分的企业实施接口自动化最常用的有两种方式: 1、基于代码类的接口自动化,如: PythonRequestsPytestAllure报告定制 2、基于工具类的接口自动化,如: PostmanNewmanJenkinsGit/svnJme…...
)
蓝桥杯(3.9)
1210. 连号区间数 蓝桥杯暴力过80% import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc new Scanner(System.in);int n sc.nextInt();int[] res new int[n];int[] copy new int[n];for(int i0;i&…...
万物皆可Find My,伦茨科技ST17H6x芯片赋能产品苹果Find My功能
苹果的Find My功能使得用户可以轻松查找iPhone、Mac、AirPods以及Apple Watch等设备。如今Find My还进入了耳机、充电宝、箱包、电动车、保温杯等多个行业。苹果发布AirTag发布以来,大家都更加注重物品的防丢,苹果的 Find My 就可以查找 iPhone、Mac、Ai…...

UHF无线麦克风方案的特点
U段无线麦克风方案是一种基于UHF频段的无线音频传输技术。相比于传统的VHF频段和2.4GHZ频段,U段频谱资源更为宽阔,信号传输更加稳定可靠。 1.广阔的频谱资源:U段频段通常指450MHZ至900MH之间的频谱范围,相比于VHF频段的100MH至30…...
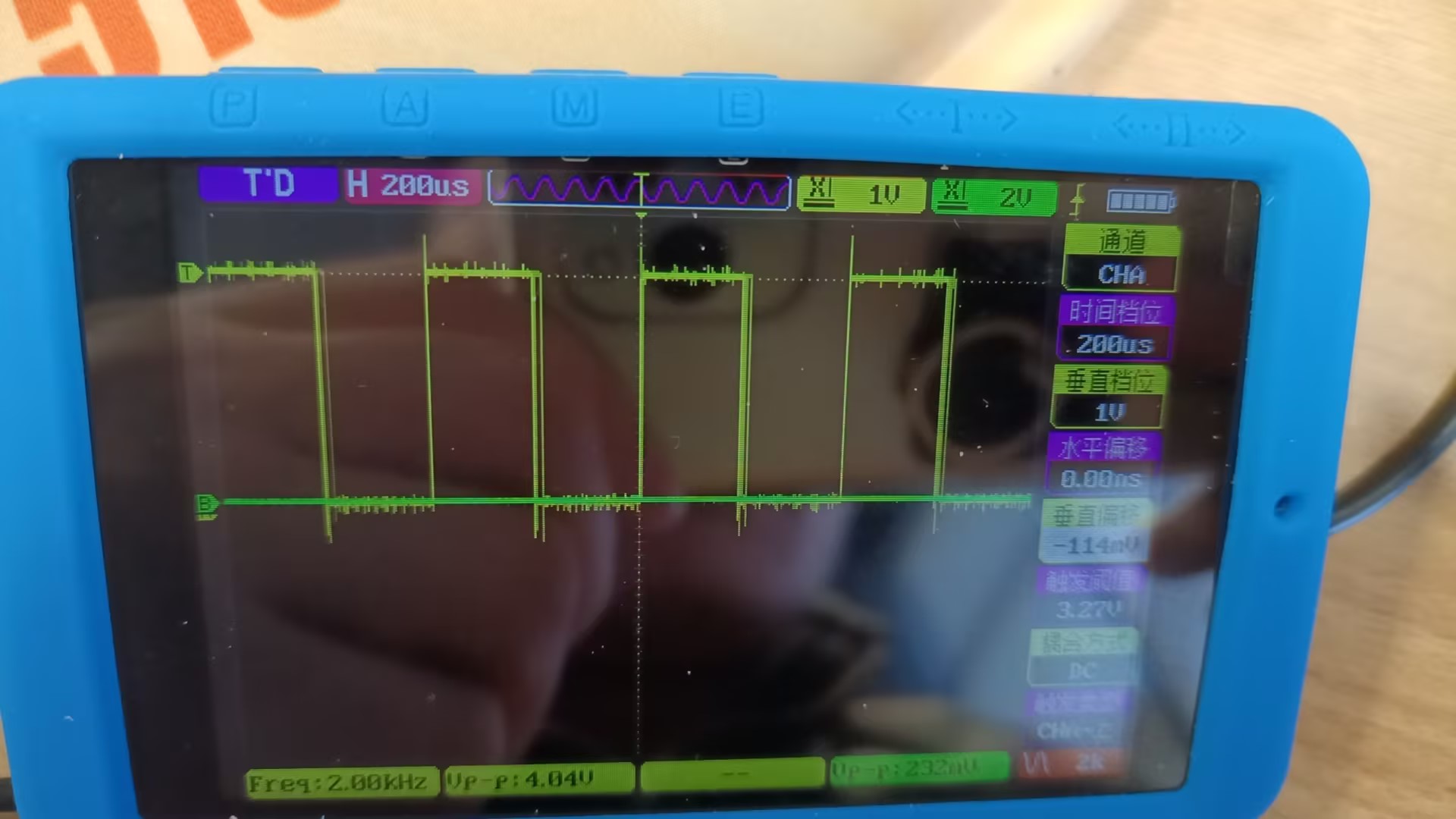
STM32 学习10 PWM输出
STM32 学习10 PWM输出 一、PWM简介1. PWM的概念2. PWM的工作原理3. PWM 常用的应用场景 二、一些概念1. 频率2. 占空比 三、STM32F1 PWM介绍1. 定时器与寄存器(1)**自动重装载寄存器(ARR)**:(2)…...

Docker 离线安装指南
参考文章 1、确认操作系统类型及内核版本 Docker依赖于Linux内核的一些特性,不同版本的Docker对内核版本有不同要求。例如,Docker 17.06及之后的版本通常需要Linux内核3.10及以上版本,Docker17.09及更高版本对应Linux内核4.9.x及更高版本。…...
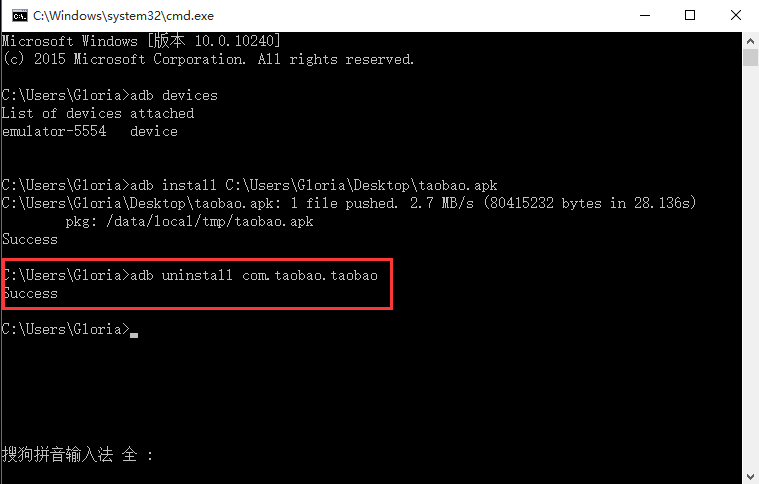
Appium+python自动化(十六)- ADB命令
简介 Android 调试桥(adb)是多种用途的工具,该工具可以帮助你你管理设备或模拟器 的状态。 adb ( Android Debug Bridge)是一个通用命令行工具,其允许您与模拟器实例或连接的 Android 设备进行通信。它可为各种设备操作提供便利,如安装和调试…...

Qt Widget类解析与代码注释
#include "widget.h" #include "ui_widget.h"Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget) {ui->setupUi(this); }Widget::~Widget() {delete ui; }//解释这串代码,写上注释 当然可以!这段代码是 Qt …...

Opencv中的addweighted函数
一.addweighted函数作用 addweighted()是OpenCV库中用于图像处理的函数,主要功能是将两个输入图像(尺寸和类型相同)按照指定的权重进行加权叠加(图像融合),并添加一个标量值&#x…...

Leetcode 3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations
Leetcode 3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations 1. 解题思路 这一题其实就是一个脑筋急转弯,要想要能够将所有的电脑解锁&#x…...

JDK 17 新特性
#JDK 17 新特性 /**************** 文本块 *****************/ python/scala中早就支持,不稀奇 String json “”" { “name”: “Java”, “version”: 17 } “”"; /**************** Switch 语句 -> 表达式 *****************/ 挺好的ÿ…...

MySQL中【正则表达式】用法
MySQL 中正则表达式通过 REGEXP 或 RLIKE 操作符实现(两者等价),用于在 WHERE 子句中进行复杂的字符串模式匹配。以下是核心用法和示例: 一、基础语法 SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name REGEXP pattern; …...

多种风格导航菜单 HTML 实现(附源码)
下面我将为您展示 6 种不同风格的导航菜单实现,每种都包含完整 HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript 代码。 1. 简约水平导航栏 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang"zh-CN"> <head><meta charset"UTF-8"><meta name"viewport&qu…...

基于matlab策略迭代和值迭代法的动态规划
经典的基于策略迭代和值迭代法的动态规划matlab代码,实现机器人的最优运输 Dynamic-Programming-master/Environment.pdf , 104724 Dynamic-Programming-master/README.md , 506 Dynamic-Programming-master/generalizedPolicyIteration.m , 1970 Dynamic-Programm…...

Linux C语言网络编程详细入门教程:如何一步步实现TCP服务端与客户端通信
文章目录 Linux C语言网络编程详细入门教程:如何一步步实现TCP服务端与客户端通信前言一、网络通信基础概念二、服务端与客户端的完整流程图解三、每一步的详细讲解和代码示例1. 创建Socket(服务端和客户端都要)2. 绑定本地地址和端口&#x…...