C++默认构造函数(二)
目录
构造函数补充
构造函数初始化列表的使用
赋值运算符重载函数
运算符重载函数介绍
运算符重载函数的使用
赋值运算符重载函数
赋值运算符重载函数的使用
拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符重载函数
重载前置++和后置++
前置++
后置++
重载流插入<<与流提取>>
流插入运算符<<重载
流提取运算符>>重载
const成员函数
取地址操作符重载与const成员取地址操作符重载
实现日期类练习
声明:本篇为C++默认构造函数最后一篇
构造函数补充
在C++中,可以在构造函数的函数体中为变量进行初始化,但是实际上该过程并不是初始化,可以理解为赋值,因为对象还没有真正创建,并且初始化只能初始化一次,但是赋值可以执行多次,而当对象创建时,所有成员变量就是当成整体创建,那么每一个变量在和何处被初始化变成了一个问题,为了解决这个问题,C++标准中引入构造函数初始化列表,只要是本类的成员变量都是在初始化列表处初始化,具体初始化的内容由程序员自己决定
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 23):_year(year), _month(month), _day(day){}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}
};int main()
{Date d;d.print();return 0;
}
输出结果:
2024/3/23构造函数初始化列表的使用
初始化列表:以一个冒号开始,接着是一个以逗号分隔的数据成员列表,每个"成员变量"后面跟一个放在括号中的初始值或表达式,语法如下
类名(参数列表)
:成员变量(值)
,成员变量(值)
,成员变量(值)
{}📌
注意,并不是所有成员变量都需要写进初始化列表,没写入初始化列表的成员变量也会像写入初始化列表中的成员变量一样走一遍初始化列表,只是没有显式
1. 每个成员变量在初始化列表中只能出现一次(初始化只能初始化一次)
2. 类中包含以下成员,必须放在初始化列表位置进行初始化:
- 引用成员变量
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;class Array
{
private:int* _arr;int _size;int& ref;
public:Array():_arr(nullptr), _size(4), ref(_size)//引用类型必须初始化{_arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * _size);assert(_arr);}Array(const Array& data):ref(_size)//拷贝构造中,引用类型也必须初始化{_arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * data._size);assert(_arr);for (int i = 0; i < data._size; i++){_arr[i] = data[i];}}//重载[]int& operator[](int i){return _arr[i];}//const类型的引用,不可以通过返回的引用改变数组中的值const int& operator[](int i) const{return _arr[i];}
};int main()
{Array a;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){a[i] = i + 1;}const Array p(a);for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){cout << p[i] << " ";}return 0;
}
输出结果:
1 2 3 4const成员变量- 自定义类型成员(且该类没有默认构造函数时)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Time
{
private:int _time;
public:Time(int time){}
};class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;Time _t;
public:Date():_year(2023),_month(3),_day(21){}
};int main()
{Date d;return 0;
}
报错信息:
类 "Time" 不存在默认构造函数在C++11标准规范中,可以在成员变量创建的同时给缺省值,此时如果给了这个缺省值,想使用缺省值时就不需要再将该成员变量写入初始化列表中,如果不想使用缺省值,则将成员变量写入初始化列表中并给定初始值,否则默认初始值为0
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;//构造函数初始化列表
class Date
{
private:int _year = 2023;int _month = 2;int _day = 28;
public:Date()//_year没有写入初始化列表,使用缺省值: _month(3)//写入初始化列表中,给了初始值为3,使用初始值, _day()//写入初始化列表中,但是没给初始值,默认初始值为0{}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}
};int main()
{Date d;d.print();return 0;
}
输出结果:
2023/3/0在初始化列表中无法处理例如动态申请内存的行为,此时可以在函数体内完成,例如
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;class Array
{
private:int* _arr;int _size;
public:Array():_arr(nullptr),_size(4){_arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * _size);//在构造函数体中分配空间assert(_arr);}Array(const Array& data){_arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * data._size);assert(_arr);for (int i = 0; i < data._size; i++){_arr[i] = data[i];}}//重载[]int& operator[](int i){return _arr[i];}const int& operator[](int i) const{return _arr[i];}
};int main()
{Array a;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){a[i] = i + 1;}const Array& p(a);for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){cout << p[i] << " ";}return 0;
}
输出结果:
1 2 3 4所以,如果不使用缺省值,尽量使用初始化列表初始化,因为不管是否使用初始化列表,对于自定义类型的成员变量,一定会先使用初始化列表初始化
📌
注意:成员变量在类中声明次序就是其在初始化列表中的初始化顺序,与其在初始化列表中的先后次序无关
class A
{
public:A(int a):_a1(a),_a2(_a1){}void Print() {cout<<_a1<<" "<<_a2<<endl;}
private:int _a2;int _a1;
};
int main() {A aa(1);aa.Print();
}
输出结果:
1 -858993460在上面的代码中,因为成员变量_a2比_a1先声明,所以在初始化时先走_a2(_a1),所以_a2被初始化为随机值,接着再初始化_a1,所以_a1为1
赋值运算符重载函数
运算符重载函数介绍
在C++中,为了增强代码的可读性引入了运算符重载,运算符重载是具有特殊函数名的函数,也具有其返回值类型,函数名字以及参数列表,其返回值类型与参数列表与普通的函数类似
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}
};int main()
{Date d1;Date d2(d1);cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;//自定义类型无法使用内置的关系运算符进行比较return 0;
}
报错信息:
二进制“==”:“Date”不定义该运算符或到预定义运算符可接收的类型的转换为了自定义类型的对象之间可以进行关系运算,可以使用运算符重载,如下面代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}int getYear(){return _year;}int getMonth(){return _month;}int getDay(){return _day;}
};bool operator==(Date& d1, Date& d2)
{return d1.getYear() == d2.getYear() && d1.getMonth() == d2.getMonth() && d1.getDay() == d1.getDay();
}int main()
{Date d1;Date d2(d1);cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;//有重载==的函数时可以比较return 0;
}
输出结果:
1运算符重载函数的使用
对于运算符重载函数来说,其函数名为:operator+需要重载的运算符,而该函数的原型如下:
函数返回类型 operator运算符(参数列表)定义运算符重载函数时,需要注意下面的问题
- 不能通过连接其他符号来创建新的操作符:比如
operator@ - 重载操作符必须有一个类类型参数
- 用于内置类型的运算符,其含义不能改变,例如:内置的整型
+,不 能改变其含义 - 作为类成员函数重载时,其形参看起来比操作数数目少1,因为成员函数的第一个参数为隐藏的
this .* :: sizeof ?: .:注意以上5个运算符不能重载
对于下面的代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}int getYear(){return _year;}int getMonth(){return _month;}int getDay(){return _day;}
};//全局运算符重载函数
bool operator==(Date& d1, Date& d2)
{return d1.getYear() == d2.getYear() && d1.getMonth() == d2.getMonth() && d1.getDay() == d1.getDay();
}int main()
{Date d1;Date d2(d1);cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;//有重载==的函数时可以比较return 0;
}
输出结果:
1在上面的代码中,因为运算符重载函数不在类中,并且因为类的成员变量为private,所以需要调用获取函数来得到当前对象的成员变量中的值,并且因为在全局中,并不存在哪一个对象调用函数,所以没有this指针,此时形参的个数对应运算符的操作数的个数
📌
注意上面的全局运算符重载函数中形参不可以使用const修饰,因为如果使用了const修饰,那么就是d1和d2都是const修饰的对象,而this只是*const,而不是const*,本来是d1和d2被const修饰不可以修改引用的对象的值,但是如果传递给了this可能会出现通过this改变d1和d2引用的对象的值,所以此处涉及到将引用的权限放大
考虑到如果将运算符重载函数写在类外需要额外写三个函数来获取到指定的值,所以可以将运算符重载函数写进类中
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}//类中的运算符重载函数bool operator==(const Date& d){return _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day;}
};int main()
{Date d1;Date d2(d1);cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;//直接调用类中实现的运算符重载函数//上面的代码相当于:cout << d1.operator==(d2) << endl;return 0;
}
输出结果:
1在上面的代码中,因为运算符重载函数在类中,所以存在this指针,所以只需要传递一个参数(加上this指针参数和额外的参数一共两个参数对应==操作符的操作数个数),并且形参对象引用d指的是第二个操作数,因为d1 == d2等价于d1.operator==(d2),因为是d1在调用运算符重载函数,所以this指针指向的对象即为d1
赋值运算符重载函数
赋值运算符重载函数也是运算符重载函数中的一种,因为重载的运算符为赋值运算符=,重载赋值运算符时,首先不能改变赋值运算符的特性,包括连续赋值
赋值运算符重载函数的使用
赋值运算符重载函数的格式
- 参数类型:
const T&,传递引用可以提高传参效率(T为类名) - 返回值类型:
T&,返回引用可以提高返回的效率,有返回值目的是为了支持连续赋值,并且需要检测是否自己给自己赋值,以减少赋值次数 - 返回
*this:要复合连续赋值的含义
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}void operator=(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}
};int main()
{Date d(2024, 2, 28);Date d1;d1 = d;d1.print();return 0;
}
输出结果:
2024/2/28在上面的代码中,类Date中对赋值运算符进行了重载,将引用指向的对象中的值给调用该运算符重载函数的对象,但是上面的代码无法实现赋值运算符的连续赋值,因为没有返回值
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}void operator=(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}
};int main()
{Date d(2024, 2, 28);Date d1;Date d2;d1 = d;d1.print();d2 = d1 = d;return 0;
}
报错信息:
二元“=”: 没有找到接受“void”类型的右操作数的运算符(或没有可接受的转换)所以,为了解决这个问题,赋值运算符重载函数需要给定返回值为类类型
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}Date& operator=(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;return *this;}
};int main()
{Date d(2024, 2, 28);Date d1;Date d2;d2 = d1 = d;d1.print();d2.print();return 0;
}
输出结果:
2024/2/28
2024/2/28在上面的代码中,赋值运算符重载函数给了返回值为Date类型的引用,此时可以使用连续赋值,因为赋值运算符从右往左结合,所以具体过程为d对象赋值给d1,d1对象的值赋值给d2,从函数调用的角度理解为d2.operator=(d1.operator=(d));(注意不是d2.operator=(d1).operator=(d);,本句理解为d2被赋值为d1中的内容,然后再被赋值为d中的内容,相当于d2 = d1; d2 = d;)
📌
赋值运算符重载函数的返回值也可以不用引用,但是此时在返回时会调用拷贝构造函数将返回值的内容拷贝给调用赋值运算符重载函数的对象,为了减少调用拷贝构造的次数,更推荐使用引用,该解释同样适用于形参
另外,还有一个小问题,如果两个相同的对象进行赋值,那么将产生额外的一次赋值,对于这个问题,在赋值时需要判断形参引用的对象和this指针指向的对象是否是同一个地址的对象
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;}
};int main()
{Date d(2024, 2, 28);d = d;return 0;
}在上面的代码中,判断this指针指向的对象的地址和引用的对象地址是否相等,如果二者相等,则证明是同一个对象,不需要进行赋值直接返回即可,注意形参的Date &d为创建对象的引用,而if语句中的&d是取引用的地址
注意,赋值运算符重载函数必须作为成员函数,不能作为全局函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:int _year;int _month;int _day;Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}
};
Date& operator=(Date& d1, Date& d)
{ if (&d1 != &d){d1._year = d._year;d1._month = d._month;d1._day = d._day;}return d1;
}
int main()
{Date d(2024, 2, 28);Date d1;d1 = d;return 0;
}
报错信息:
“operator=”必须是成员函数赋值运算符如果不显式实现,编译器会生成一个默认的。此时用户再在类外自己实现一个全局的赋值运算符重载,就和编译器在类中生成的默认赋值运算符重载冲突了,所以赋值运算符重载只能是类的成员函数
拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符重载函数
与拷贝构造函数类似,赋值运算符重载函数如果用户没有实现,编译器会自动实现。默认如果不自主实现还是按照字节拷贝,按照字节方式拷贝也会遇到像拷贝函数一样的问题(指对象中有资源申请时)
- 一个对象改变,另一个对象也会跟着改变,严重者会数据覆盖
- 释放资源时会因为多次释放一个空间导致程序崩溃
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}};int main()
{Date d(2024, 2, 28);Date d1;d1 = d;//编译器自动生成的默认赋值运算符重载函数Date d2(d);//编译器自动生成的拷贝构造函数d1.print();d2.print();return 0;
}
输出结果:
2024/2/28
2024/2/28与拷贝构造函数一样,如果类对象中有涉及到资源申请,那么需要自己实现赋值运算符重载函数,否则直接使用默认的即可
重载前置++和后置++
前置++
对于运算符重载函数的使用规则,那么可以很容易写出++的重载函数,如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 22){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}void operator++(){_day += 1;}
};int main()
{Date d;++d;d.print();return 0;
}
输出结果:
2024/3/23因为前++相当于计算+=1,而因为前面实现过获取X天后的日期的函数GetAfterXDays_plusEqual,所以可以直接用该函数进行复用,从而实现++操作
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 22){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}int GetMonthDays(int year, int month){int monthDays[] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0)) || (year % 400 == 0)){return monthDays[month] + 1;} else{return monthDays[month];}}Date& GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(int days){_day += days;while (_day > GetMonthDays(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDays(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month == 13){_year++;_month = 1;}}return *this;}Date GetAfterXDays_plus(int days){Date tmp(*this);tmp._day += days;while (tmp._day > GetMonthDays(tmp._year, tmp._month)){tmp._day -= GetMonthDays(tmp._year, tmp._month);tmp._month++;if (tmp._month == 13){tmp._year++;tmp._month = 1;}}return tmp;}void operator++(){//因为++相当于+=1,所以可以直接复用GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(1)*this = GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(1);}
};int main()
{Date d;++d;d.print();return 0;
}
输出结果:
2024/3/23注意到上面实现的++是无返回值的++运算符重载函数,但是如果函数没有返回值,将无法将++后的值给另外一个对象
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 22){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}int GetMonthDays(int year, int month){int monthDays[] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0)) || (year % 400 == 0)){return monthDays[month] + 1;} else{return monthDays[month];}}Date& GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(int days){_day += days;while (_day > GetMonthDays(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDays(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month == 13){_year++;_month = 1;}}return *this;}Date GetAfterXDays_plus(int days){Date tmp(*this);tmp._day += days;while (tmp._day > GetMonthDays(tmp._year, tmp._month)){tmp._day -= GetMonthDays(tmp._year, tmp._month);tmp._month++;if (tmp._month == 13){tmp._year++;tmp._month = 1;}}return tmp;}void operator++(){//_day += 1;//因为++相当于+=1,所以可以直接复用GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(1)*this = GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(1);//return *this;}Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;}
};int main()
{Date d;++d;d.print();Date d1;d1 = ++d;return 0;
}
报错信息:
二元“=”: 没有找到接受“void”类型的右操作数的运算符(或没有可接受的转换)所以为了解决这种问题将考虑为++运算符重载函数加上返回值为类对象引用类型
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 22){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}int GetMonthDays(int year, int month){int monthDays[] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0)) || (year % 400 == 0)){return monthDays[month] + 1;} else{return monthDays[month];}}Date& GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(int days){_day += days;while (_day > GetMonthDays(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDays(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month == 13){_year++;_month = 1;}}return *this;}Date GetAfterXDays_plus(int days){Date tmp(*this);tmp._day += days;while (tmp._day > GetMonthDays(tmp._year, tmp._month)){tmp._day -= GetMonthDays(tmp._year, tmp._month);tmp._month++;if (tmp._month == 13){tmp._year++;tmp._month = 1;}}return tmp;}Date& operator++(){//_day += 1;//因为++相当于+=1,所以可以直接复用GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(1)*this = GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(1);return *this;}Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;}
};int main()
{Date d;++d;d.print();Date d1;d1 = ++d;return 0;
}
输出结果:
2024/3/23后置++
上面的函数中实现了前置++,但是并没有实现后置++,如果在没有实现后置++时,使用后置++,则会出现下面的情况
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 22){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}int GetMonthDays(int year, int month){int monthDays[] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0)) || (year % 400 == 0)){return monthDays[month] + 1;}else{return monthDays[month];}}Date& GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(int days){_day += days;while (_day > GetMonthDays(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDays(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month == 13){_year++;_month = 1;}}return *this;}Date GetAfterXDays_plus(int days){Date tmp(*this);tmp._day += days;while (tmp._day > GetMonthDays(tmp._year, tmp._month)){tmp._day -= GetMonthDays(tmp._year, tmp._month);tmp._month++;if (tmp._month == 13){tmp._year++;tmp._month = 1;}}return tmp;}Date& operator++(){//_day += 1;//因为++相当于+=1,所以可以直接复用GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(1)*this = GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(1);return *this;}Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;}
};int main()
{Date d;d++;return 0;
}
报错信息:
二进制“++”:“Date”不定义该运算符或到预定义运算符可接收的类型的转换所以有前置++的实现并不能同时应用于后置++,对于后置++来说,编译器为了与前置++作区分,需要在形参位置添加一个整型占位形参,如下
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 22){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}int GetMonthDays(int year, int month){int monthDays[] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0)) || (year % 400 == 0)){return monthDays[month] + 1;}else{return monthDays[month];}}Date& GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(int days){_day += days;while (_day > GetMonthDays(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDays(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month == 13){_year++;_month = 1;}}return *this;}Date GetAfterXDays_plus(int days){Date tmp(*this);tmp._day += days;while (tmp._day > GetMonthDays(tmp._year, tmp._month)){tmp._day -= GetMonthDays(tmp._year, tmp._month);tmp._month++;if (tmp._month == 13){tmp._year++;tmp._month = 1;}}return tmp;}//前置++Date& operator++(){//_day += 1;//因为++相当于+=1,所以可以直接复用GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(1)*this = GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(1);return *this;}//后置++,但是为了不同于前置++,在形参处加入int形参作为占位便于编译器区分Date operator++(int){//后置++满足先使用再++,所以返回值为原值Date tmp(*this);*this = GetAfterXDays_plusEqual(1);return tmp;}Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;}
};int main()
{Date d;d++;d.print();return 0;
}
输出结果:
2024/3/23在上面的代码中,对于后置++重载函数来说,在形参处添加了一个int类型形参作为占位符,这个形参可以不给形参名,因为只是编译器用于区分
重载流插入<<与流提取>>
在C++标准库中,cout和cin是属于iostream中ostream和istream的对象,对于流插入<<运算符,之所以cout输出可以不用指定占位符编译器可以自动匹配的原因是ostream中<<的运算符重载和函数重载,对于内置类型来说,有下面的函数重载

同样对于流提取运算符>>来说也是如此,如下图所示

但是流插入和流提取运算符并没有对自定义类型有函数重载,所以可以对流提取运算符和流插入运算符进行函数重载
流插入运算符<<重载
按照前面的运算符重载思路可以写出下面的代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 22){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void operator<<(ostream& cout){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}
};int main()
{Date d;cout << d;return 0;
}
报错信息:
二元“<<”: 没有找到接受“Date”类型的右操作数的运算符(或没有可接受的转换)在上面的代码中,虽然重载了<<,但是形参是ostream流的对象,而隐含的形参是this,而在运算符重载函数形参列表的规则中,对于有两个操作数的运算符重载来说,第一个参数为左操作数,第二个参数为右操作数,所以上面的代码调用应该为d << cout
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 22){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void operator<<(ostream& cout){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}
};int main()
{Date d;//cout << d;d << cout;return 0;
}
输出结果:
2024/3/22但是和正常的输出刚好顺序相反,所以这种方法需要改变,但是因为不能改变this在形参的位置,所以考虑到将<<重载放置到全局中,此时可以决定两个操作数的顺序,但是这个方法就不能使用this指针,并且需要考虑到成员变量的private属性,本处给出一种解决方案是使用get函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 22){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}int getYear(){return _year;}int getMonth(){return _month;}int getDay(){return _day;}
};void operator<<(ostream& cout, Date& d)
{cout << d.getYear() << "/" << d.getMonth() << "/" << d.getDay() << endl;
}int main()
{Date d;cout << d;return 0;
}
输出结果:
2024/3/22在上面的代码中,将流插入运算符重载函数放置到全局中可以控制cout和d的顺序,此时即可写为cout << d,但是因为上面的<<并没有返回值,所以不可以连续插入,所以可以改进为如下
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 22){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}int getYear(){return _year;}int getMonth(){return _month;}int getDay(){return _day;}
};ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, Date& d)
{cout << d.getYear() << "/" << d.getMonth() << "/" << d.getDay() << endl;return cout;
}int main()
{Date d;Date d1;cout << d << d1 << endl;return 0;
}
输出结果:
2024/3/22
2024/3/22流提取运算符>>重载
对于流提取运算符>>的重载类似于流插入运算符<<,但是此时不能使用获取函数,所以对于流提取运算符的重载来说,考虑用友元解决,使用友元可以让全局函数中的对象获取到private属性的变量
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 22){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}//友元friend istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Date& d);int getYear(){return _year;}int getMonth(){return _month;}int getDay(){return _day;}
};ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, Date& d)
{cout << d.getYear() << "/" << d.getMonth() << "/" << d.getDay() << endl;return cout;
}istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Date& d)
{cin >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;return cin;
}int main()
{Date d;Date d1;cin >> d >> d1;cout << d << d1 << endl;return 0;
}
输入:
2024 2 28 2024 3 31
输出结果:
2024/2/28
2024/3/31使用友元解决流插入运算符的重载函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 22){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}//友元friend istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Date& d);friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, Date& d);
};ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, Date& d)
{cout << d._year << "/" << d._month << "/" << d._day << endl;return cout;
}istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Date& d)
{cin >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;return cin;
}int main()
{Date d;Date d1;cin >> d >> d1;cout << d << d1 << endl;return 0;
}
输入:
2024 2 23 2022 3 31
输出结果:
2024/2/23
2022/3/31const成员函数
将const修饰的“成员函数”称之为const成员函数,const修饰类成员函数,实际修饰该成员函数隐含的this指针,表明在该成员函数中不能对类的任何成员进行修改
在前面的运算符重载函数中,当运算符重载函数在全局时不可以使用const修饰形式参数,因为const成员变量传递给成员函数时涉及到引用权限放大,那么const成员函数就是用来解决这种权限放大问题,可以将权限保持不变或者缩小,例如在下面的代码中
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}int getYear() const{return _year;}int getMonth() const{return _month;}int getDay() const{return _day;}
};//全局运算符重载函数,const形参
bool operator==(const Date& d1, const Date& d2)
{return d1.getYear() == d2.getYear() && d1.getMonth() == d2.getMonth() && d1.getDay() == d1.getDay();
}int main()
{Date d1;Date d2(d1);cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;//有重载==的函数时可以比较return 0;
}
输出结果:
1在上面的代码中,使用const修饰了==运算符重载函数的两个形式参数,此时d1和d2不可以被修改,当对象d1和d2调用get系列函数时,成员函数的形式参数需要保证获得的权限不被放大,所以需要修饰形式参数,但是因为this指针不可以直接显式做形式参数,所以不可以使用const显式对this指针进行修饰,此时就需要将const放置到函数名后,作为修饰this指针的const以满足指针及引用权限不被放大
但是,如果==运算符重载函数中的两个形式参数并不是const修饰的变量,此时调用const成员函数也不会有错,因为此时是权限的缩小(从可修改到成员函数的不可修改),如下面的代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}int getYear() const{return _year;}int getMonth() const{return _month;}int getDay() const{return _day;}
};//全局运算符重载函数,非const形参
bool operator==(Date& d1, Date& d2)
{return d1.getYear() == d2.getYear() && d1.getMonth() == d2.getMonth() && d1.getDay() == d1.getDay();
}int main()
{Date d1;Date d2(d1);cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;//有重载==的函数时可以比较return 0;
}对于const成员函数和非const成员函数之间也是如此
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}//非const成员函数void printYear(){cout << _year;} int getYear() const{printYear();return _year;}
};int main()
{Date d1;Date d2(d1);return 0;
}
报错信息:
“void Date::printYear(void)”: 不能将“this”指针从“const Date”转换为“Date &”而对于const成员函数和const成员函数之间可以直接调用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}//非const成员函数void printYear() const{cout << _year;} int getYear() const{printYear();return _year;}
};int main()
{Date d1;Date d2(d1);return 0;
}同样非const成员函数可以调用const成员函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}//非const成员函数void printYear() const{cout << _year;} int getYear() {printYear();return _year;}
};int main()
{Date d1;Date d2(d1);return 0;
}取地址操作符重载与const成员取地址操作符重载
在C++中,这两个运算符重载函数可以不用显式定义,编译器会默认生成
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}};int main()
{Date d1;Date d2;const Date d3;cout << &d1 << endl;cout << &d2 << endl;cout << &d3 << endl;return 0;
}
输出结果:
00000031E9FEF628
00000031E9FEF658
00000031E9FEF688也可以显式定义
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}Date* operator&(){return this;}const Date* operator&()const{return this;}};int main()
{Date d1;Date d2;const Date d3;cout << &d1 << endl;cout << &d2 << endl;cout << &d3 << endl;return 0;
}
输出结果:
0000006B086FFC38
0000006B086FFC68
0000006B086FFC98只有特殊情况,才需要重载这两个函数,比如想让别人获取到指定的内容,让其访问非法地址
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 21){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}Date* operator&(){return (Date*)0;}const Date* operator&()const{return (Date*)0;}};int main()
{Date d1;Date d2;const Date d3;cout << &d1 << endl;cout << &d2 << endl;cout << &d3 << endl;return 0;
}
输出结果:
0000000000000000
0000000000000000
0000000000000000实现日期类练习
//头文件
#pragma once#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;public://构造函数Date(int year = 2024, int month = 3, int day = 23):_year(year),_month(month),_day(day){}friend inline istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Date& d);friend inline ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, Date& d);//获取月份日期函数int GetMonthDays(int year, int month);//+=运算符重载Date& operator+=(int days);//+运算符重载Date operator+(int days){Date tmp(*this);//复用+=重载tmp += days;return tmp;}//赋值运算符重载Date& operator=(const Date& d);//前置++运算符重载Date& operator++(){//复用+=重载*this += 1;return *this;}//后置++运算符重载Date operator++(int){//复用+=函数Date tmp(*this);tmp += 1;return tmp;}//>=运算符重载bool operator>=(const Date& d) const;//<=运算符重载bool operator<=(const Date& d) const;//<运算符重载bool operator<(const Date& d) const{//<的对立事件为>=,故直接对>=取反return !(*this >= d);}//>运算符重载bool operator>(const Date& d) const{//>的对立事件为<=,故直接对<=取反return !(*this <= d);}//==运算符重载bool operator==(const Date& d) const{return _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day;}//!=运算符重载bool operator!=(const Date& d) const{//!=的对立事件为==,故直接对==取反return !(*this == d);}//-=运算符重载Date& operator-=(int days);//-运算符重载Date operator-(int days){Date tmp(*this);tmp._day -= days;return tmp;}//前置--运算符重载Date& operator--(){//复用-=重载函数*this -= 1;return *this;}//后置--运算符重载Date operator--(int){//复用-=重载Date tmp(*this);*this -= 1;return tmp;}//日期-日期int operator-(const Date& d);
};inline ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, Date& d)
{cout << d._year << "/" << d._month << "/" << d._day << endl;return cout;
}inline istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Date& d)
{cin >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;return cin;
}//实现文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Date_class.h"//获取月份日期函数
int Date::GetMonthDays(int year, int month)
{int monthDays[] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && (((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0)) || (year % 400 == 0))){return monthDays[month] + 1;}return monthDays[month];
}//+=运算符重载
Date& Date::operator+=(int days)
{_day += days;while (_day > GetMonthDays(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDays(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month == 13){_year++;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}//赋值运算符重载
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d)
{if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;
}//>=运算符重载
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d) const
{//如果年大就直接返回trueif (_year>d._year){return true;}else if(_year == d._year && _month > d._month)//年相等时比较月份,月份大就直接返回true{return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day)//年相等,月份相等时,天大就直接返回true{return true;}else//其他情况均返回false{return false;}
}//<=运算符重载
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d) const
{//如果年小就直接返回trueif (_year < d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month < d._month)//年相等时比较月份,月份小就直接返回true{return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day)//年相等,月份相等时,天小就直接返回true{return true;}else//其他情况均返回false{return false;}
}//-=运算符重载
Date& Date::operator-=(int days)
{_day -= days;while (_day <= 0){_month--;if (_month == 0){_year--;_month = 12;}_day += GetMonthDays(_year, _month);}return *this;
}//日期-日期
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{Date maxYear = *this;Date minYear = d;int flag = 1;if (maxYear < minYear){maxYear = d;minYear = *this;flag = -1;}int count = 0;while (maxYear != minYear){count++;++minYear;}return count * flag;
}//测试文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Date_class.h"int main()
{Date d;Date d1(d);Date d2(2023, 1, 1);d--;cout << d;cout << (d != d1) << endl;cout << (d >= d1) << endl;Date d3;d3 = --d2;cout << d3;Date d4(2023, 2, 7);d4 -= 100;cout << d4;cout << d4 - d1 << endl;Date d5;Date d6;cin >> d5 >> d6;cout << d5 << d6 << endl;return 0;
}
输入:
2024 3 23
2023 2 23
输出结果:
2024/3/22
1
0
2022/12/31
2022/10/30
-510
2024/3/23
2023/2/23相关文章:

C++默认构造函数(二)
目录 构造函数补充 构造函数初始化列表的使用 赋值运算符重载函数 运算符重载函数介绍 运算符重载函数的使用 赋值运算符重载函数 赋值运算符重载函数的使用 拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符重载函数 重载前置和后置 前置 后置 重载流插入<<与流提取>> 流插…...
云原生部署手册02:将本地应用部署至k8s集群
(一)部署集群镜像仓库 1. 集群配置 首先看一下集群配置: (base) ➜ ~ multipass ls Name State IPv4 Image master Running 192.168.64.5 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS1…...

AJAX——JSON
目录 一、JSON概述 二、JSON对象语法 三、JSON序列化方法 四、JSON与XML比较 五、Java对象与Json对象的转换 六、Js解析服务器发送过来的JSON字符串 七、$.getJSON() 一、JSON概述 JSON简介:JSON的全称为JavaScript Object Nation(JavaScript 对象表示语法),…...
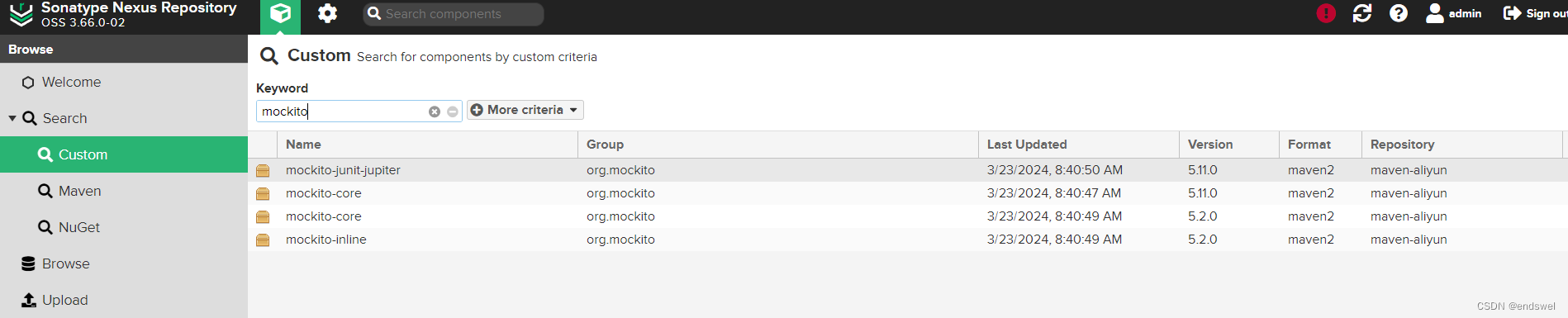
Nexus3 Docker 私有仓库
Nexus3 Docker 私有仓库 安装并部署 Nexus3 $ docker search nexus3$ docker pull sonatype/nexus3$ mkdir /home/tester/data/docker/nexus3/sonatype-work $ sudo chown -R 200 /home/tester/data/docker/nexus3/sonatype-work$ docker run -d --namenexus3 \ --restartalw…...

Element UI el-dialog自由拖动功能
1.创建drag .js文件 /*** 拖拽移动* param {elementObjct} bar 鼠标点击控制拖拽的元素* param {elementObjct} target 移动的元素* param {function} callback 移动后的回调*/ export function startDrag(bar, target, callback) {var params {top: 0,left: 0,currentX: …...

RPC浅析,加密数据解析
个人总结 其实就是HOOK注入wbsocket 链接创建服务端和客户端进行通信,直接调用js代码中的加密方法 将结果通过浏览器客户端传入服务端。一种比较好实用的一种技术 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36759224/article/details/123082574 (搬运记录下ÿ…...
光速论文能用吗 #媒体#知识分享#学习方法
光速论文是一个非常有效的论文写作、查重降重工具,它的使用非常简单方便,而且功能强大,是每个写作者必备的利器。 首先,光速论文具有强大的查重降重功能,能够快速检测论文中的抄袭部分,帮助作者避免不必要的…...
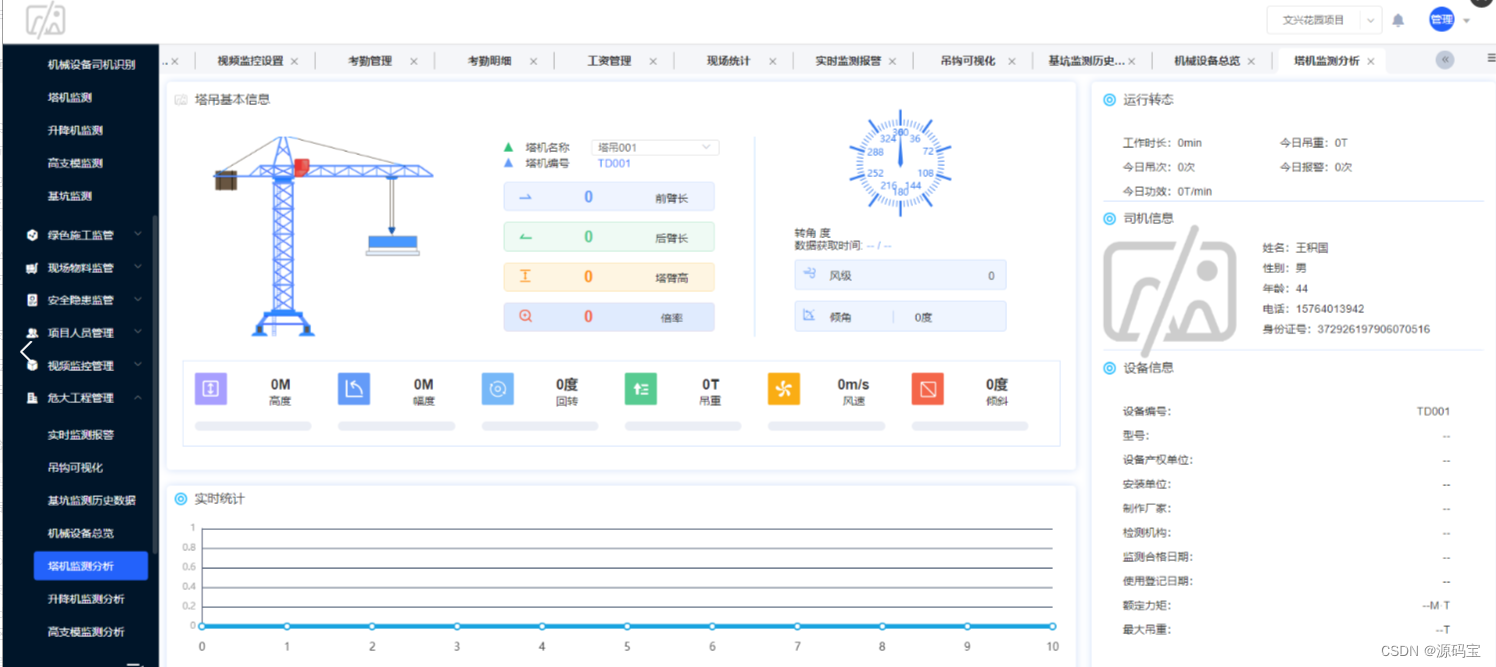
智慧工地解决方案,智慧工地项目管理系统源码,支持大屏端、PC端、手机端、平板端
智慧工地解决方案依托计算机技术、物联网、云计算、大数据、人工智能、VR&AR等技术相结合,为工程项目管理提供先进技术手段,构建工地现场智能监控和控制体系,弥补传统方法在监管中的缺陷,最线实现项目对人、机、料、法、环的全…...

【前端寻宝之路】学习和使用label标签
🌈个人主页: Aileen_0v0 🔥热门专栏: 华为鸿蒙系统学习|计算机网络|数据结构与算法|MySQL| 💫个人格言:“没有罗马,那就自己创造罗马~” #mermaid-svg-2nm9oQQVtSL8hDS1 {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-serif;f…...

项目————网络聊天室
服务器 #include <myhead.h> typedef struct msg{char flag;char name[20];char cont[128]; }msg_t;typedef struct link{struct sockaddr_in cin;struct link* next; }link_t;void do_login(int sfd,msg_t msg,link_t *L,struct sockaddr_in cin){link_t* pL;if(sendto…...
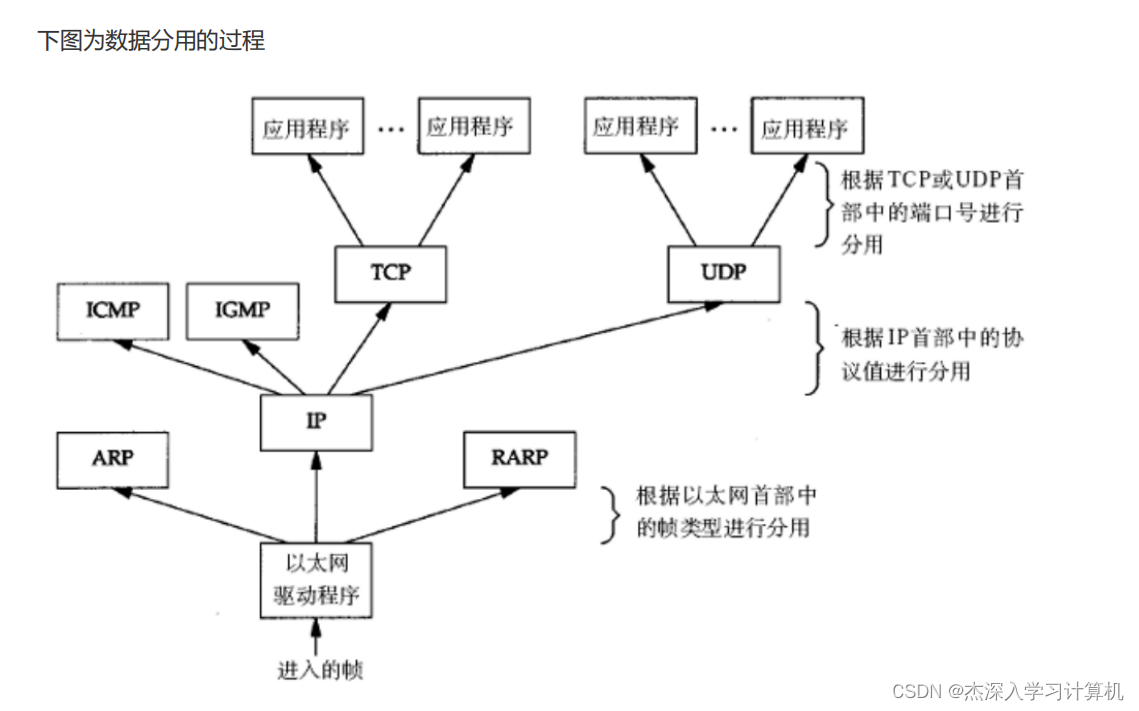
【计算机网络】基本概念
基本概念 IP 地址端口号协议协议分层封装分用客户端服务器请求和响应两台主机之间的网络通信流程 IP 地址 概念:IP 地址主要是用于唯一标识网络主机、其他网络设备(如路由器)的网络地址。简单来说,IP地址用来唯一定位主机。格式&…...
Redis入门到实战-第七弹
Redis实战热身Sets篇 完整命令参考官网 官网地址 声明: 由于操作系统, 版本更新等原因, 文章所列内容不一定100%复现, 还要以官方信息为准 https://redis.io/Redis概述 Redis是一个开源的(采用BSD许可证),用作数据库、缓存、消息代理和流…...
)
图像处理学习笔记(一)
本文主要介绍,以供读者能够理解该技术的定义、原理、应用。 🎬个人简介:一个全栈工程师的升级之路! 📋个人专栏:ISP处理 🎀CSDN主页 发狂的小花 🌄人生秘诀:学习的本质就…...

duckdb学习-1
DuckDB is a fast in-process analytical database DuckDB supports a feature-rich SQL dialect complemented with deep integrations into client APIs 在notebook中使用duckdb 安装 pip install duckdb 示例代码: #> pip install jupysql #> pip install duckdb-en…...

GEE高阶案例——Landsat/Sentinel/MODIS影像进行缨帽变换一行代码实现
本教程的主要目的是利用eemont中的tasseledCap()的函数进行缨帽变换实现。 在 eemont 中,可使用扩展到 ee.Image 和 ee.ImageCollection 对象的 tasseledCap 方法计算缨帽亮度、绿度和湿度组件。只需从支持的平台加载图像,然后使用 tasseledCap 添加分量带即可。 代码: !p…...
)
数独游戏(c++题解)
题目描述 给出一个的表格,部分格子已经填好数。请填完所有空白格子,使得表格每一行、每一列、每个的九宫格,都恰好填满这9个数字。 输入格式 9行9列的方阵状态,0代表空格。 输出格式 输出完成后的方阵状态,每一个…...

【开发方案】Android 应用双卡搜网功能
一、功能简介 需求:开机自动开始搜网并显示网络列表 那么就不能将相关类做成单例,不能将subId、phoneId等卡相关的属性作为UI、服务的全局变量。 二、流程设计 NetworkSelectReceiver:监听开机广播,触发拉起搜网服务 NetworkOperatorService:搜网服务,完成后调起用户…...

图论基础|深度优先dfs、广度优先bfs
dfs 与 bfs 区别 提到深度优先搜索(dfs),就不得不说和广度优先搜索(bfs)有什么区别 先来了解dfs的过程,很多录友可能对dfs(深度优先搜索),bfs(广度优先搜索…...

Python从入门到精通秘籍十七
一、Python的构造方法 在Python中,构造方法是一个特殊的方法,用于创建和初始化类的实例。构造方法的名称是__init__(),它在创建对象时自动调用。 下面是一个示例代码来详细解释Python的构造方法: class Person:def __init__(se…...

Java——抽象类和接口
目录 1.抽象类 1.概念: 2.语法 3.特性 2.接口 1.概念 2.语法 3.特性 1.抽象类 1.概念: 在面向对象的概念中,所有的对象都是通过类来描绘的,但是反过来,并不是所有的类都是用来描绘对象的,如果一个类中没有包含足够的…...

KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南
Linux_k8s篇 欢迎来到Linux的世界,看笔记好好学多敲多打,每个人都是大神! 题目:KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南 版本号: 1.0,0 作者: 老王要学习 日期: 2025.06.05 适用环境: Ubuntu22 文档说…...
【Axure高保真原型】引导弹窗
今天和大家中分享引导弹窗的原型模板,载入页面后,会显示引导弹窗,适用于引导用户使用页面,点击完成后,会显示下一个引导弹窗,直至最后一个引导弹窗完成后进入首页。具体效果可以点击下方视频观看或打开下方…...
Prompt Tuning、P-Tuning、Prefix Tuning的区别
一、Prompt Tuning、P-Tuning、Prefix Tuning的区别 1. Prompt Tuning(提示调优) 核心思想:固定预训练模型参数,仅学习额外的连续提示向量(通常是嵌入层的一部分)。实现方式:在输入文本前添加可训练的连续向量(软提示),模型只更新这些提示参数。优势:参数量少(仅提…...

多场景 OkHttpClient 管理器 - Android 网络通信解决方案
下面是一个完整的 Android 实现,展示如何创建和管理多个 OkHttpClient 实例,分别用于长连接、普通 HTTP 请求和文件下载场景。 <?xml version"1.0" encoding"utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android"http://schemas…...

在rocky linux 9.5上在线安装 docker
前面是指南,后面是日志 sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo sudo dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io -y docker version sudo systemctl start docker sudo systemctl status docker …...

macOS多出来了:Google云端硬盘、YouTube、表格、幻灯片、Gmail、Google文档等应用
文章目录 问题现象问题原因解决办法 问题现象 macOS启动台(Launchpad)多出来了:Google云端硬盘、YouTube、表格、幻灯片、Gmail、Google文档等应用。 问题原因 很明显,都是Google家的办公全家桶。这些应用并不是通过独立安装的…...
k8s业务程序联调工具-KtConnect
概述 原理 工具作用是建立了一个从本地到集群的单向VPN,根据VPN原理,打通两个内网必然需要借助一个公共中继节点,ktconnect工具巧妙的利用k8s原生的portforward能力,简化了建立连接的过程,apiserver间接起到了中继节…...

QT: `long long` 类型转换为 `QString` 2025.6.5
在 Qt 中,将 long long 类型转换为 QString 可以通过以下两种常用方法实现: 方法 1:使用 QString::number() 直接调用 QString 的静态方法 number(),将数值转换为字符串: long long value 1234567890123456789LL; …...
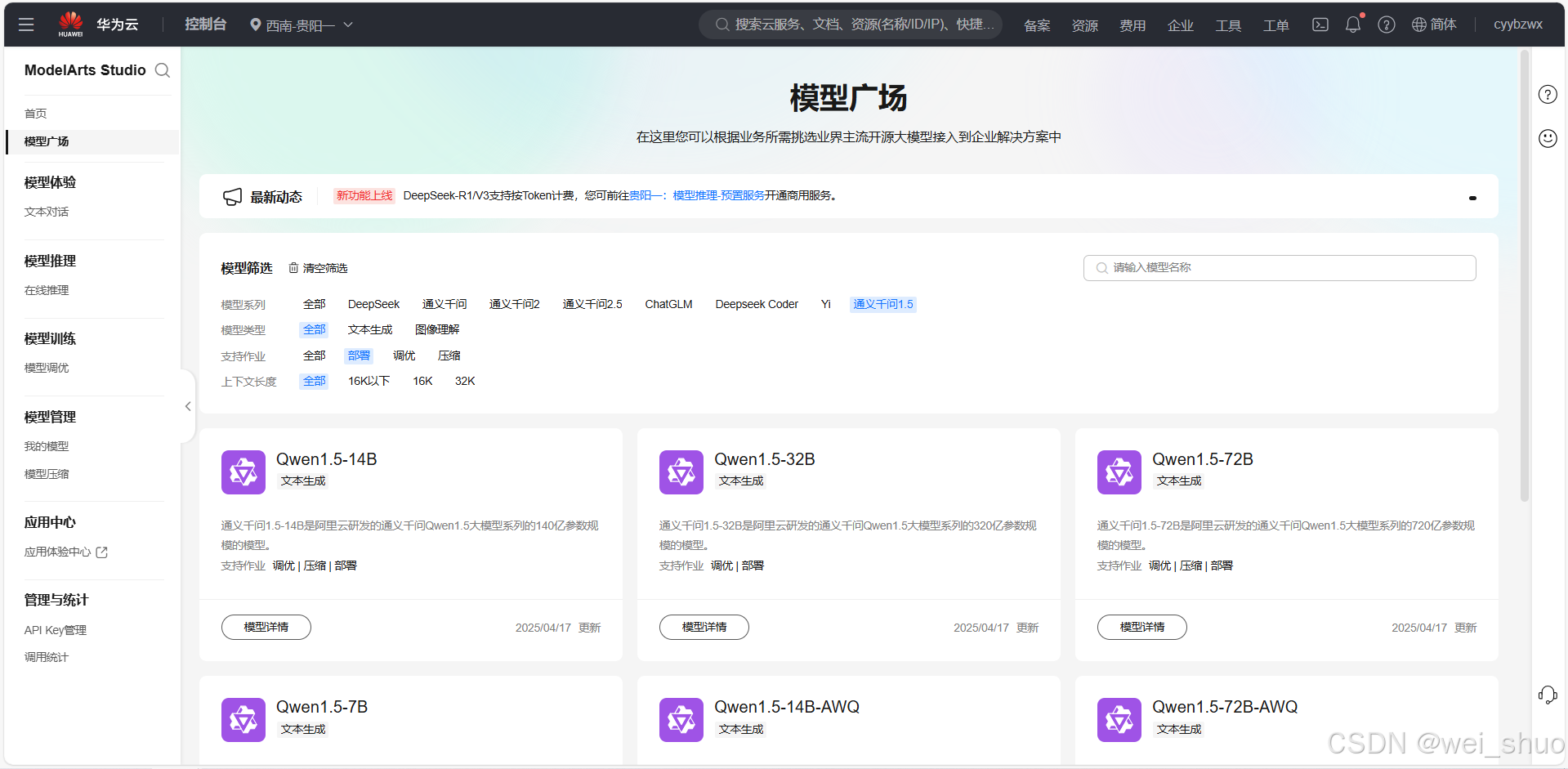
华为云Flexus+DeepSeek征文|DeepSeek-V3/R1 商用服务开通全流程与本地部署搭建
华为云FlexusDeepSeek征文|DeepSeek-V3/R1 商用服务开通全流程与本地部署搭建 前言 如今大模型其性能出色,华为云 ModelArts Studio_MaaS大模型即服务平台华为云内置了大模型,能助力我们轻松驾驭 DeepSeek-V3/R1,本文中将分享如何…...

智能仓储的未来:自动化、AI与数据分析如何重塑物流中心
当仓库学会“思考”,物流的终极形态正在诞生 想象这样的场景: 凌晨3点,某物流中心灯火通明却空无一人。AGV机器人集群根据实时订单动态规划路径;AI视觉系统在0.1秒内扫描包裹信息;数字孪生平台正模拟次日峰值流量压力…...
