GNU/Linux - 系统启动流程及rcS脚本介绍
Linux系统启动流程
在 Linux 系统启动过程中,会按特定顺序执行多个脚本和初始化例程,以使系统进入可用状态。虽然具体顺序可能因 Linux 发行版和版本而异,但以下是典型执行顺序的概括性概述:
1. BIOS/UEFI: 系统开机后,BIOS(或 UEFI 固件)会执行开机自检(POST),然后加载引导加载程序。
对于嵌入式 Linux,它们可能是芯片中的特殊引导 ROM。
2. 引导加载程序: 引导加载器,如 GRUB(Grand Unified Bootloader,统一引导加载器)或 LILO(Linux Loader,Linux 加载器),将 Linux 内核加载到内存中并开始执行,同时按需要初始化重要的硬件组件。
嵌入式系统常用的引导加载器包括 U-Boot、Das U-Boot 和 Barebox。
3. Linux 内核初始化: 一旦引导加载器将内核映像加载到内存中,Linux 内核就会开始控制。Linux 内核会初始化基本硬件组件或设备、设置内存管理、挂载初始 ramdisk(initramfs)、挂载根文件系统、配置其他基本系统参数,并开始初始化根文件系统的过程。
4. 初始化进程: 内核初始化完成后,会启动初始进程。传统上,这是 System V init(SysVinit),但现在许多现代发行版都使用 systemd 或 Upstart 作为 init 系统。
在嵌入式系统中,内核初始化完成后,init 进程(通常为 /sbin/init)就会启动。init 进程负责初始化用户空间环境和启动系统服务。对于嵌入式系统,init 进程可以是一个简单的 shell 脚本,也可以是一个最小的 init 系统(如 BusyBox)。
5. 用户空间初始化和初始脚本:
init 进程运行后,会执行启动脚本或其他初始化任务来设置用户空间环境。
init 进程会读取配置文件并执行启动脚本,这些脚本负责初始化各种系统服务和配置。这些脚本通常位于 /etc/init.d 等目录中,或定义为 /etc/systemd/system 中的 systemd 单元文件。
这可能包括加载额外的文件系统、配置网络接口、设置系统日志以及初始化其他系统服务。
6. 运行级别或目标单元: 根据系统的运行级别(在 SysVinit 中)或目标单元(在 systemd 中),会执行不同的启动脚本或单元文件集。运行级别/目标单元定义了不同的系统状态,如单用户模式、多用户模式或图形模式。
7. 应用程序启动:
系统完全初始化后,将启动配置为自动启动的任何用户应用程序或服务。
这些应用程序可能包括针对嵌入式系统功能的定制软件,以及系统监控或管理工具。
8. 服务管理: 系统服务根据其依赖关系和配置启动。这包括联网、文件系统挂载和系统日志等基本系统服务。
9. 用户会话: 如果系统支持图形用户界面,则启动显示管理器(如 GDM、LightDM),并初始化用户会话。
10. 用户交互或登录提示:
最后,系统显示登录提示(文本或图形),允许用户登录并与系统交互。
根据嵌入式系统的设计,它可能会提供一个用户交互界面,如命令行界面或图形用户界面。
用户可以与系统交互,执行任务或监控系统运行。
本序列提供了 Linux 系统启动过程的高级概览。实际细节和具体步骤可能因发行版、init 系统和配置而异。
英文版:
During the startup process on a Linux system, several scripts and initialization routines are executed in a specific sequence to bring the system to a usable state. While the exact sequence may vary depending on the distribution and version of Linux, here's a generalized overview of the typical execution sequence:
1. BIOS/UEFI: When the system is powered on, the BIOS (or UEFI firmware) performs Power-On Self Test (POST) and then loads the bootloader.
For embedded linux, they may be special boot ROM in the chip.
2. Bootloader: The bootloader, such as GRUB (Grand Unified Bootloader) or LILO (Linux Loader), loads the Linux kernel into memory and starts its execution, and initialize required essential hardware components.
Common bootloaders for embedded systems include U-Boot, Das U-Boot, and Barebox.
3. Linux Kernel Initialization: Once the bootloader has loaded the kernel image into memory, the Linux kernel takes control. The Linux kernel initializes essential hardware components or devices, sets up memory management, mounts the initial ramdisk (initramfs), mounts the root filesystem, configures other essential system parameters, and begins the process of initializing the root filesystem.
4. Init Process: Once the kernel has initialized, it starts the init process. Traditionally, this was System V init (SysVinit), but many modern distributions now use systemd or Upstart as the init system.
In embedded system, after the kernel initialization, the init process (typically /sbin/init) is started. The init process is responsible for initializing the user space environment and launching system services. For embedded systems, the init process may be a simple shell script or a minimal init system like BusyBox.
5. User Space Initialization and Init Scripts:
Once the init process is running, it executes startup scripts or other initialization tasks to set up the user space environment.
The init process reads configuration files and executes startup scripts, which are responsible for initializing various system services and configurations. These scripts are typically located in directories like /etc/init.d or defined as systemd unit files in /etc/systemd/system.
This may include mounting additional filesystems, configuring network interfaces, setting up system logging, and initializing other system services.
6. Runlevels or Target Units: Depending on the system's runlevel (in SysVinit) or target unit (in systemd), different sets of startup scripts or unit files are executed. Runlevels/target units define different system states, such as single-user mode, multi-user mode, or graphical mode.
7. Application Launch:
Once the system is fully initialized, any user applications or services configured to start automatically are launched.
These applications may include custom software specific to the embedded system's functionality, as well as system monitoring or management tools.
8. Service Management: System services are started according to their dependencies and configuration. This includes essential system services like networking, filesystem mounting, and system logging.
9. User Sessions: If the system supports graphical user interfaces, the display manager (e.g., GDM, LightDM) is started, and user sessions are initialized.
10. User Interaction or Login Prompt:
Finally, the system displays a login prompt (either text-based or graphical), allowing users to log in and interact with the system.
Depending on the embedded system's design, it may provide a user interface for interaction, such as a command-line interface or a graphical user interface.
Users can interact with the system to perform tasks or monitor its operation.
This sequence provides a high-level overview of the startup process on a Linux system. The actual details and specific steps may vary based on the distribution, init system, and configuration.
===== 分割线 =====
rcS脚本介绍
在 Linux 中,rcS 脚本文件是启动过程中使用的初始化脚本之一。该脚本通常位于 /etc/init.d 目录中,由系统在启动过程中执行。
一种说法,"rcS "通常指 "启动时运行命令 "脚本。在包括 Linux 在内的类 Unix 操作系统中,"rcS "脚本通常是系统启动过程中最先执行的脚本之一。它设置初始环境并运行各种系统初始化任务。
还一种说法,"rcS "代表 "单用户模式运行命令"。它是 System V(SysV)init 系统的一部分,是启动类 Unix 操作系统的传统方法。
rcS "脚本在系统启动过程中执行,特别是当系统启动到单用户模式时。单用户模式是一种故障诊断模式,只有单个用户(通常是 root 用户)可以访问系统。它通常用于系统恢复或修复系统问题等维护任务。
rcS "脚本负责初始化启动过程早期所需的基本系统服务和配置,这些服务和配置是单用户模式运行所必需的。这包括挂载基本文件系统、设置基本网络、初始化系统时钟、挂载基本文件系统、配置系统环境以及执行其他必要的设置任务,以使系统达到最低功能状态。
它之所以重要,是因为它为启动过程的其他部分奠定了基础,确保系统在其他服务和应用程序启动前处于正常运行状态。rcS 脚本的内容因 Linux 发行版而异,但其主要目的在大多数发行版中都是一致的。
总的来说,"rcS "脚本在准备系统进入单用户模式时起着至关重要的作用,它能确保基本服务和配置就位,以便进行故障排除和维护。
英文版:
In Linux, the rcS script file is one of the initialization scripts used during the boot process. This script is typically found in the /etc/init.d directory, and it's executed by the system during the boot sequence.
For one explanation, "rcS" typically refers to the "run commands at startup" script. In Unix-like operating systems, including Linux, the "rcS" script is often one of the first scripts executed during the system boot process. It sets up the initial environment and runs various system initialization tasks.
And another explanation, "rcS" stands for "run commands for Single-user mode." It's part of the System V (SysV) init system, which is a traditional method for booting Unix-like operating systems.
The "rcS" script is executed during the system startup process, specifically when the system boots into single-user mode. Single-user mode is a troubleshooting mode where only a single user (typically the root user) has access to the system. It's often used for maintenance tasks such as system recovery or repairing system issues.
The "rcS" script is responsible for initializing essential system services and configurations that are required early in the boot process and are needed for single-user mode operation. This includes tasks like mounting essential filesystems, setting up basic networking, initializing the system clock, mounting essential filesystems, configuring the system environment, and performing other necessary setup tasks to bring the system to a minimal functional state.
It's important because it lays the groundwork for the rest of the boot process, ensuring that the system is in a functional state before other services and applications start up. The contents of the rcS script can vary depending on the Linux distribution, but its primary purpose is consistent across most distributions.
Overall, the "rcS" script plays a crucial role in preparing the system for single-user mode, ensuring that essential services and configurations are in place for troubleshooting and maintenance purposes.
====== 分割线 ======
嵌入式系统执行的启动脚本
通常嵌入式系统启动和重启前执行的脚本是rcS和rcK。
# ls /etc/init.d/rc*
rcK rcS
启动和重启时调用rcS和rcK脚本,这个是在/etc/inittab 文件里设置的。Linux系统启动进程会读取这个文件。
# cat /etc/inittab# This is run first except when booting in single-user mode.# Startup the system::sysinit:echo "<< inittab >>"::sysinit:/bin/mount -t proc proc /proc::sysinit:/bin/mount -t sysfs sysfs /sys::sysinit:/bin/mount -t devtmpfs devtmpfs /dev::sysinit:/bin/mount -o remount,rw /::sysinit:/bin/mkdir -p /dev/pts::sysinit:/bin/mount -t devpts devpts /dev/pts::sysinit:/bin/mount -a::sysinit:/sbin/swapon -anull::sysinit:/bin/ln -sf /proc/self/fd /dev/fdnull::sysinit:/bin/ln -sf /proc/self/fd/0 /dev/stdinnull::sysinit:/bin/ln -sf /proc/self/fd/1 /dev/stdoutnull::sysinit:/bin/ln -sf /proc/self/fd/2 /dev/stderr# set hostnamenull::sysinit:/bin/busybox hostname -F /etc/hostname::sysinit:/etc/init.d/rcS# Stuff to do before rebooting#::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/reboot::shutdown:/etc/init.d/rcK::shutdown:/sbin/swapoff -a::shutdown:/bin/umount -a -r# Stuff to do when restarting the init process::restart:/sbin/initttyLP0::respawn:/sbin/getty 115200 ttyLP0# /sbin/getty invocations for the runlevels.## The "id" field MUST be the same as the last# characters of the device (after "tty").## Format:# <id>:<runlevels>:<action>:<process>#tty1:12345:respawn:/sbin/getty 38400 tty1
启动进程就是系统启动后第一个执行的进程:
# ps
PID USER VSZ STAT COMMAND
1 root 3500 S /sbin/init
...
...
具体步骤如下:
1. 初始进程:
* 内核执行指定的初始进程,通常是 /sbin/init 或其符号链接。
* 在使用 BusyBox 的嵌入式系统中,/sbin/init 可能是指向 BusyBox 二进制文件的符号链接。
2. 执行初始化脚本
* 初始进程会读取配置文件(如 /etc/inittab 或 /etc/init/rcS.conf),以确定要执行的脚本。
* 通常,init 进程会生成配置文件中指定的多个脚本,这些脚本通常位于 /etc/init.d/ 或 /etc/rc.d/ 等目录中。
* 这些脚本处理各种系统初始化任务,如加载文件系统、配置网络接口、启动基本服务和设置硬件外设。
1. Init Process:
* The kernel executes the designated init process, which is typically /sbin/init or a symbolic link to it.
* In embedded systems using BusyBox, /sbin/init may be a symbolic link to the BusyBox binary.
2. Init Script Execution:
* The init process reads its configuration file (e.g., /etc/inittab or /etc/init/rcS.conf) to determine which scripts to execute.
* Commonly, the init process spawns multiple scripts specified in the configuration file, usually located in directories like /etc/init.d/ or /etc/rc.d/.
* These scripts handle various system initialization tasks, such as mounting filesystems, configuring network interfaces, starting essential services, and setting up hardware peripherals.
相关文章:

GNU/Linux - 系统启动流程及rcS脚本介绍
Linux系统启动流程 在 Linux 系统启动过程中,会按特定顺序执行多个脚本和初始化例程,以使系统进入可用状态。虽然具体顺序可能因 Linux 发行版和版本而异,但以下是典型执行顺序的概括性概述: 1. BIOS/UEFI: 系统开机后…...

对象,字符串的解构赋值
大家想了解更多,可以去看阮一峰的ECMAScript6(ES6)标准入门课程 对象 简介 解构不仅可以用于数组,还可以用于对象。 let { foo, bar } { foo: aaa, bar: bbb }; foo // "aaa" bar // "bbb" 对象的解构与数组有一个重要的不同。…...

Django 静态文件管理与部署指南
title: Django 静态文件管理与部署指南 date: 2024/5/10 17:38:36 updated: 2024/5/10 17:38:36 categories: 后端开发 tags: WebOptCDN加速DjangoCompressWebpackStaticDeployCICD-ToolsSecStatic 第一章:介绍 Django 静态文件的概念和重要性 在 Web 开发中&a…...

ORACLE ODAX9-2的一个误告警Affects: /SYS/MB的分析处理
在运维的多套ORACLE ODAX9-2版本,都遇到了一个计算节点的告警:Description: The service Processor poweron selftest has deteced a problem. Probabity;:100, UulD:cd1ebbdf-f099-61de-ca44-ef646defe034, Resource:/SYS/MB,;此告警从描述上…...

Spring AOP浅谈
什么是AOP? AOP是Aspect-Oriented Programming的缩写,是一种面向切面的编程方法。 在AOP中,一个切面是一组可以独立于其他代码执行的功能,如日志记录、安全性检查、事务处理等。这些功能通常被称为"通知",并…...
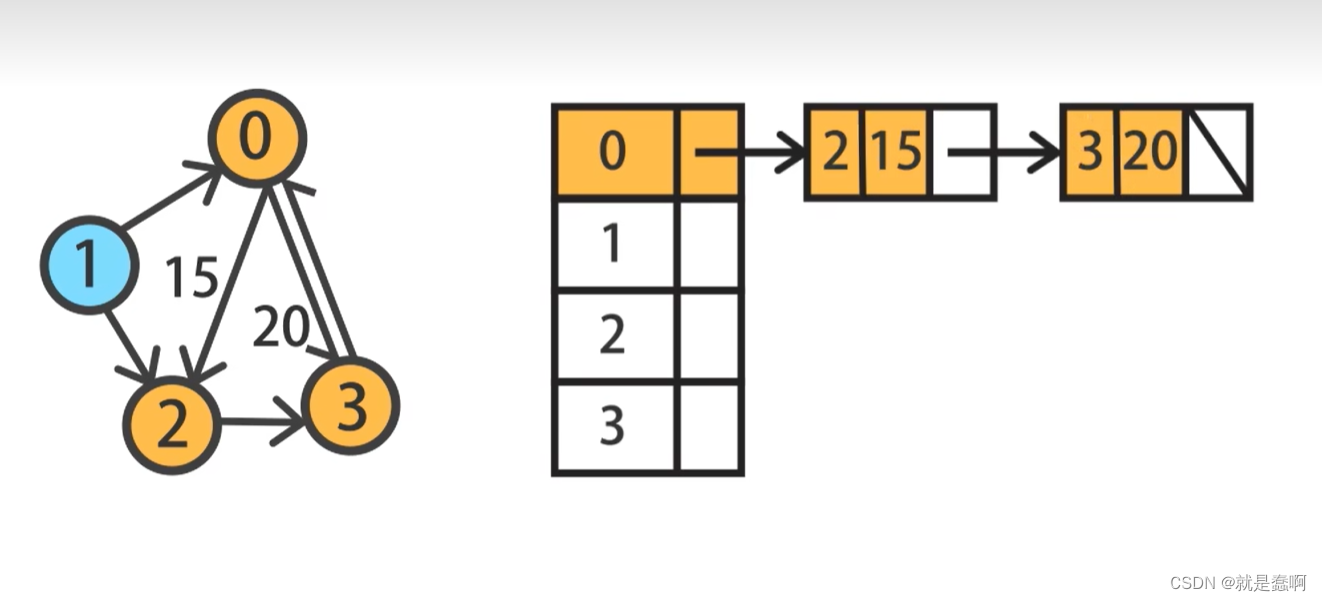
数据结构——图的基础知识与其表示
一:图的定义 由顶点的集合和边的集合组成;常以 G(V,E) 表示,G 代表图,V代表 顶点的集合,E代表边的集合; 如图: 在G1图中,有 0~4 五个顶点,有 0-1,0-2&…...
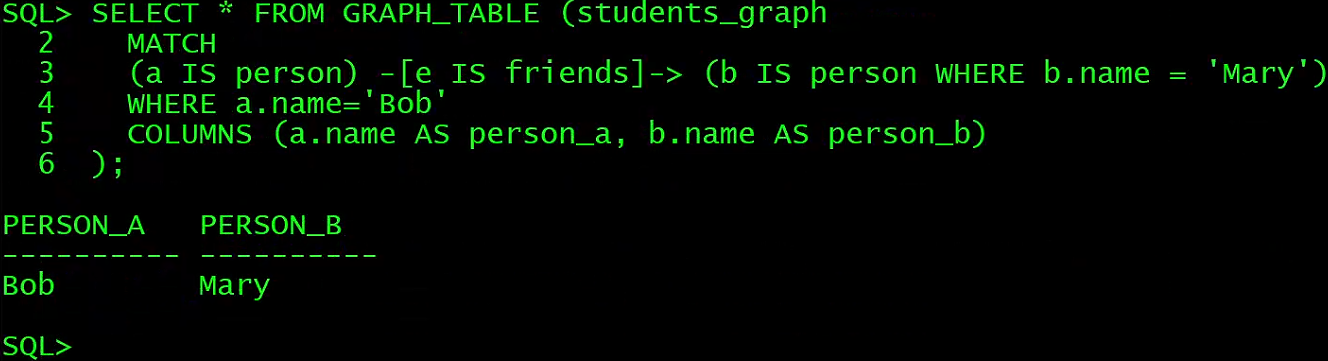
数据库管理-第187期 23ai:怎么用SQL创建图(20240510)
数据库管理187期 2024-05-10 数据库管理-第187期 23ai:怎么用SQL创建图(20240510)1 安装PGX1.1 数据库配置对应用户1.2 使用RPM包安装Graph Server1.3 安装Oracle Graph Client1.4 访问PGX页面 2 SQL Property Graph2.1 创建SQL属性图2.2 关于点和边图元…...
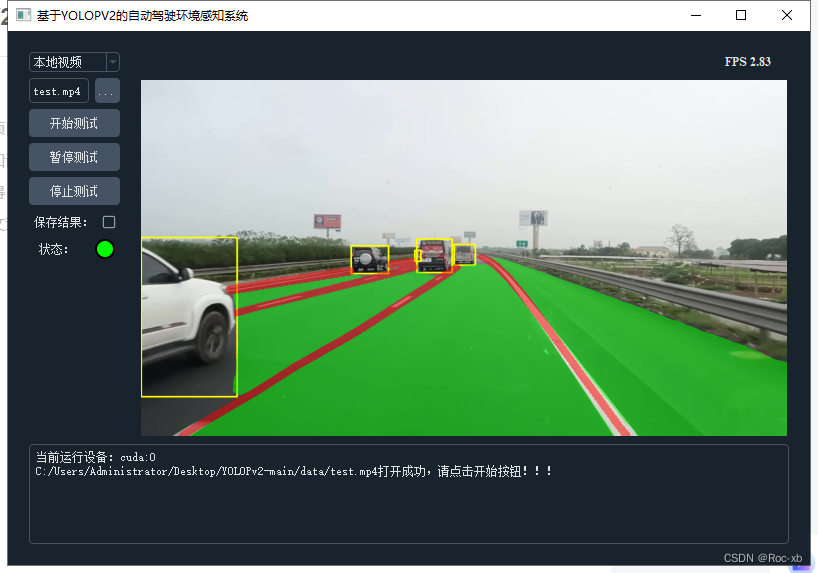
基于VOLOPV2的自动驾驶环境感知系统
基于VOLOPV2的自动驾驶环境感知系统是一个复杂的系统,它主要负责实时检测并识别周围环境中的各种物体和信息,为自动驾驶车辆提供必要的感知数据。以下是对该系统的一个简要介绍: 环境感知是自动驾驶系统中的一个关键部分,它依赖于…...
)
使用Python爬虫会遇到的问题和解决方法(包含案例)
一、HTTP错误(如403 Forbidden) 问题描述: 当使用requests库发起请求时,可能会遇到HTTP 403 Forbidden错误,这通常意味着服务器理解了请求,但是拒绝执行它。 解决方法: 1.设置headers…...

Spring Boot 读取配置优先级顺序是什么?
在使用 Spring Boot 进行开发时,配置文件是非常重要的一部分,它可以用来配置应用程序的行为、数据源、日志级别等信息。 但是,当配置文件中存在多个配置来源时,Spring Boot 是如何确定读取配置的优先级顺序的呢? 本文…...

数据挖掘(二)数据预处理
前言 基于国防科技大学 丁兆云老师的《数据挖掘》 数据挖掘 数据挖掘(一)数据类型与统计 2、数据预处理 2.1数据清理 缺失值处理: from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer# 创建一个SimpleImputer对象,指定缺失值的处理策略…...
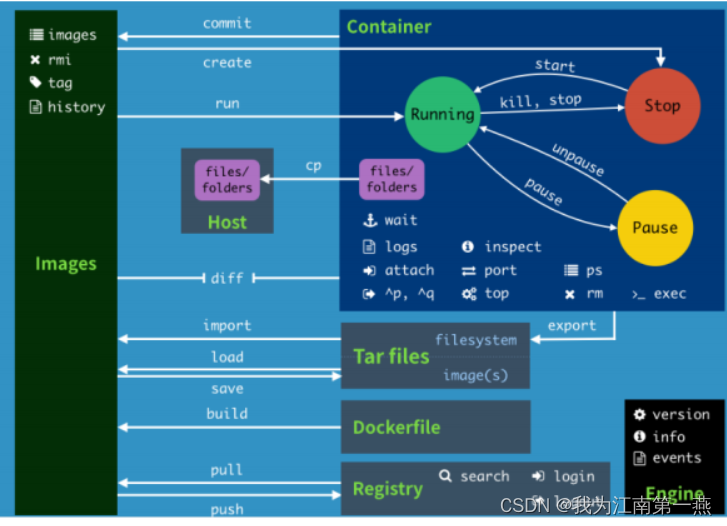
docker学习-docker常用其他命令整理
随便写写,后面有空再更新 镜像命令,容器命令已在之前略有更新,这次不写, 一、后台启动命令 # 命令 docker run -d 容器名 # 例子 docker run -d centos # 启动centos,使用后台方式启动 # 问题: 使用doc…...

【matlab基础知识代码】(十六)代数方程的图解法多项式型方程的准解析解方法
>> ezplot(exp(-3*t)*sin(4*t2)4*exp(-0.5*t)*cos(2*t)-0.5,[0 5]), line([0 5],[0 0]) 验证 >> t0.6738; >> exp(-3*t)*sin(4*t2)4*exp(-0.5*t)*cos(2*t)-0.5 ans -2.9852e-04 >> ezplot(x^2*exp(-x*y^2/2)exp(-x/2)*sin(x*y)) >> hold on; …...

智能奶柜:健康生活新风尚
智能奶柜:健康生活新风尚 在快节奏的都市生活中,健康与便利成为了现代人的双重追求。而在这两者交汇之处,智能奶柜应运而生,它不仅是科技与生活的完美融合,更是日常营养补给的智慧之选。 清晨的第一缕温暖 —— 新鲜…...

SpringBoot 集成 FFmpeg 解析音视频
文章目录 1 摘要2 核心 Maven 依赖3 核心代码3.1 FFmpeg 解析音视频工具类3.2 音视频文件信息参数3.3 音视频文件上传Controller3.4 application 配置文件 4 测试数据4.1 视频文件解析4.2 音频文件解析 5 注意事项5.1 文件必须在本地 6 推荐参考文档7 Github 源码 1 摘要 FFmp…...
基于单片机的直流电机测速装置研究与设计
摘要: 基于单片机的直流电机测速装置采用了对直流电机的中枢供电回路串联取样电阻的方式实现对电机转速的精确实时测量。系统由滤波电路、信号放大电路、单片机控制电路以及稳压电源等功能模块电路构成。工作过程中高频磁环作为载体,利用电磁感应的基本原理对直流电…...

【快捷部署】022_ZooKeeper(3.5.8)
📣【快捷部署系列】022期信息 编号选型版本操作系统部署形式部署模式复检时间022ZooKeeper3.5.8Ubuntu 20.04tar包单机2024-05-07 一、快捷部署 #!/bin/bash ################################################################################# # 作者ÿ…...

引领AI数据标注新纪元:景联文科技为智能未来筑基
在人工智能蓬勃发展的今天,数据如同燃料,驱动着每一次技术飞跃。在这场智能革命的浪潮中,景联文科技凭借其深厚的专业实力与前瞻性的战略眼光,正站在行业前沿,为全球的人工智能企业提供坚实的数据支撑。 全国布局&…...

多模态大语言模型和 Apple 的 MM1
原文地址:multimodal-large-language-models-apples-mm1 2024 年 4 月 13 日 抽象是计算机科学中最关键的概念之一,具有一些最强大的影响。从简单的角度来看,抽象就是将某一事物应用于多种不同情况的能力。例如,如果你创造了一种…...
算法day04
第一题 : 209. 长度最小的子数组 有上题可知,我们会采用双指针和单调性的思路来解决 我们本题采用左右双指针从数组的0位置同向前进,所以将此类模型称为滑块; 步骤思路如下: 步骤一: 定义所有双指针都指向…...

深度学习在微纳光子学中的应用
深度学习在微纳光子学中的主要应用方向 深度学习与微纳光子学的结合主要集中在以下几个方向: 逆向设计 通过神经网络快速预测微纳结构的光学响应,替代传统耗时的数值模拟方法。例如设计超表面、光子晶体等结构。 特征提取与优化 从复杂的光学数据中自…...
盘古信息PCB行业解决方案:以全域场景重构,激活智造新未来
一、破局:PCB行业的时代之问 在数字经济蓬勃发展的浪潮中,PCB(印制电路板)作为 “电子产品之母”,其重要性愈发凸显。随着 5G、人工智能等新兴技术的加速渗透,PCB行业面临着前所未有的挑战与机遇。产品迭代…...
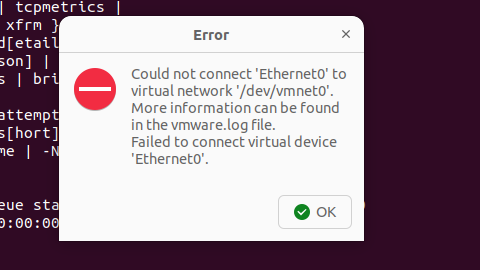
解决Ubuntu22.04 VMware失败的问题 ubuntu入门之二十八
现象1 打开VMware失败 Ubuntu升级之后打开VMware上报需要安装vmmon和vmnet,点击确认后如下提示 最终上报fail 解决方法 内核升级导致,需要在新内核下重新下载编译安装 查看版本 $ vmware -v VMware Workstation 17.5.1 build-23298084$ lsb_release…...

Java - Mysql数据类型对应
Mysql数据类型java数据类型备注整型INT/INTEGERint / java.lang.Integer–BIGINTlong/java.lang.Long–––浮点型FLOATfloat/java.lang.FloatDOUBLEdouble/java.lang.Double–DECIMAL/NUMERICjava.math.BigDecimal字符串型CHARjava.lang.String固定长度字符串VARCHARjava.lang…...

基于数字孪生的水厂可视化平台建设:架构与实践
分享大纲: 1、数字孪生水厂可视化平台建设背景 2、数字孪生水厂可视化平台建设架构 3、数字孪生水厂可视化平台建设成效 近几年,数字孪生水厂的建设开展的如火如荼。作为提升水厂管理效率、优化资源的调度手段,基于数字孪生的水厂可视化平台的…...
新能源汽车智慧充电桩管理方案:新能源充电桩散热问题及消防安全监管方案
随着新能源汽车的快速普及,充电桩作为核心配套设施,其安全性与可靠性备受关注。然而,在高温、高负荷运行环境下,充电桩的散热问题与消防安全隐患日益凸显,成为制约行业发展的关键瓶颈。 如何通过智慧化管理手段优化散…...
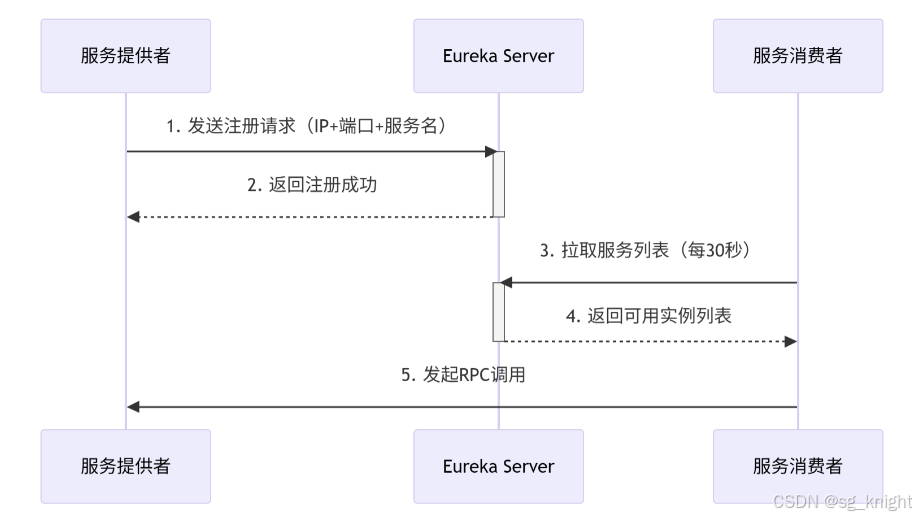
Springcloud:Eureka 高可用集群搭建实战(服务注册与发现的底层原理与避坑指南)
引言:为什么 Eureka 依然是存量系统的核心? 尽管 Nacos 等新注册中心崛起,但金融、电力等保守行业仍有大量系统运行在 Eureka 上。理解其高可用设计与自我保护机制,是保障分布式系统稳定的必修课。本文将手把手带你搭建生产级 Eur…...
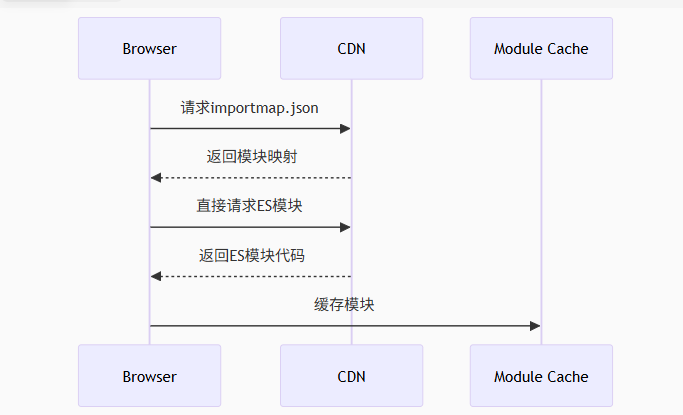
Module Federation 和 Native Federation 的比较
前言 Module Federation 是 Webpack 5 引入的微前端架构方案,允许不同独立构建的应用在运行时动态共享模块。 Native Federation 是 Angular 官方基于 Module Federation 理念实现的专为 Angular 优化的微前端方案。 概念解析 Module Federation (模块联邦) Modul…...

拉力测试cuda pytorch 把 4070显卡拉满
import torch import timedef stress_test_gpu(matrix_size16384, duration300):"""对GPU进行压力测试,通过持续的矩阵乘法来最大化GPU利用率参数:matrix_size: 矩阵维度大小,增大可提高计算复杂度duration: 测试持续时间(秒&…...

力扣-35.搜索插入位置
题目描述 给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。 请必须使用时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法。 class Solution {public int searchInsert(int[] nums, …...
