LeetCode 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
LeetCode 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
1、题目
题目链接:106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
示例 1:
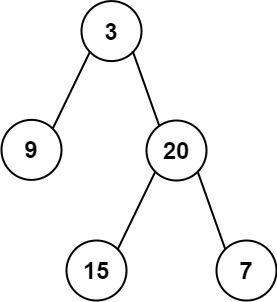
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
输入:inorder = [-1], postorder = [-1]
输出:[-1]
提示:
- 1 <= inorder.length <= 3000
- postorder.length == inorder.length
- -3000 <= inorder[i], postorder[i] <= 3000
- inorder 和 postorder 都由 不同 的值组成
- postorder 中每一个值都在 inorder 中
- inorder 保证是树的中序遍历
- postorder 保证是树的后序遍历
2、递归
思路
首先解决这道题我们需要明确给定一棵二叉树,我们是如何对其进行中序遍历与后序遍历的:
中序遍历的顺序是每次遍历左孩子,再遍历根节点,最后遍历右孩子。
后序遍历的顺序是每次遍历左孩子,再遍历右孩子,最后遍历根节点。
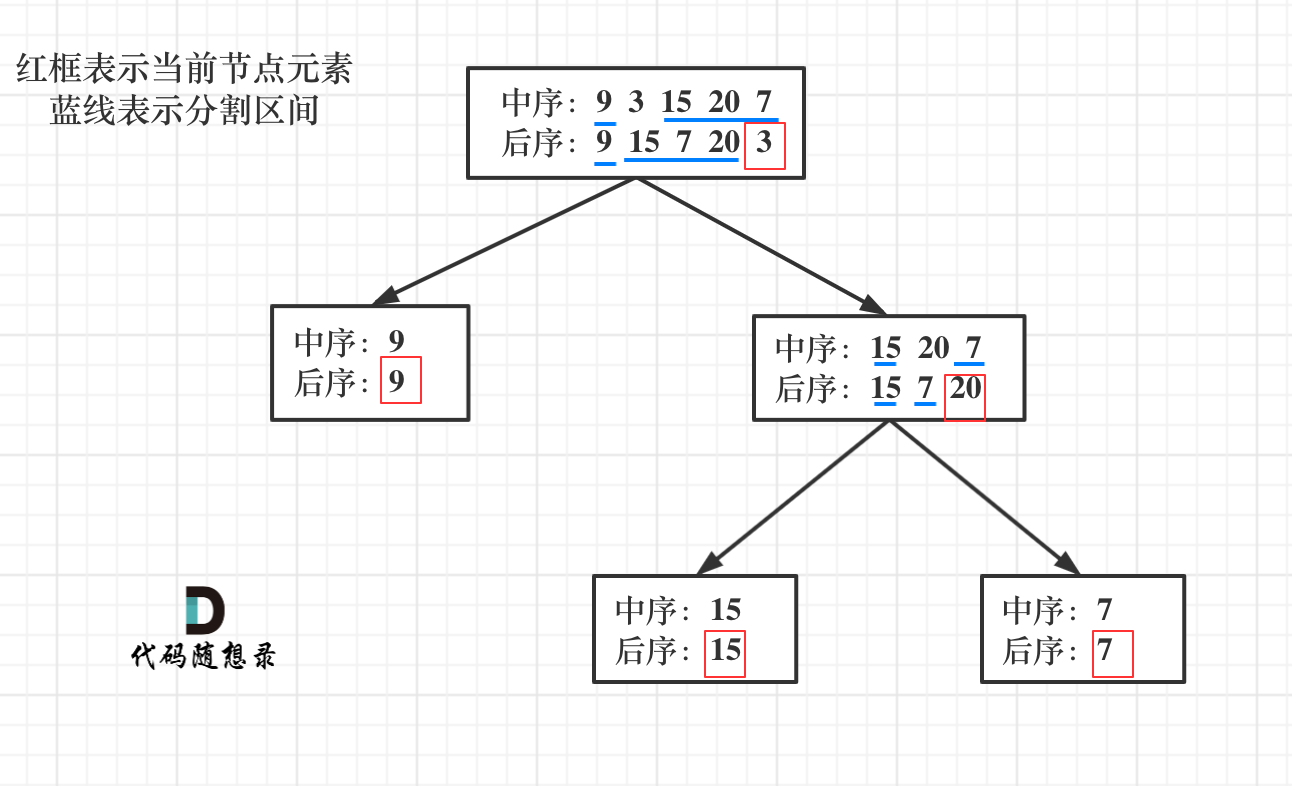
那么如何根据两个顺序构造一个唯一的二叉树,就是以后序数组的最后一个元素为切割点,先切中序数组,根据中序数组,反过来再切后序数组。一层一层切下去,每次后序数组最后一个元素就是节点元素。
流程如图:
那么代码应该怎么写呢?
说到一层一层切割,就应该想到了递归。
来看一下一共分几步:
- 第一步:如果数组大小为零的话,说明是空节点了。
- 第二步:如果不为空,那么取后序数组最后一个元素作为节点元素。
- 第三步:找到后序数组最后一个元素在中序数组的位置,作为切割点
- 第四步:切割中序数组,切成中序左数组和中序右数组 (顺序别搞反了,一定是先切中序数组)
- 第五步:切割后序数组,切成后序左数组和后序右数组
- 第六步:递归处理左区间和右区间
不难写出如下代码:(先把框架写出来)
TreeNode* traversal (vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {// 第一步if (postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;// 第二步:后序遍历数组最后一个元素,就是当前的中间节点int rootValue = postorder[postorder.size() - 1];TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue);// 叶子节点if (postorder.size() == 1) return root;// 第三步:找切割点int delimiterIndex;for (delimiterIndex = 0; delimiterIndex < inorder.size(); delimiterIndex++) {if (inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue) break;}// 第四步:切割中序数组,得到 中序左数组和中序右数组// 第五步:切割后序数组,得到 后序左数组和后序右数组// 第六步root->left = traversal(中序左数组, 后序左数组);root->right = traversal(中序右数组, 后序右数组);return root;
}
难点大家应该发现了,就是如何切割,以及边界值找不好很容易乱套。
此时应该注意确定切割的标准,是左闭右开,还有左开右闭,还是左闭右闭,这个就是不变量,要在递归中保持这个不变量。
首先要切割中序数组,为什么先切割中序数组呢?
切割点在后序数组的最后一个元素,就是用这个元素来切割中序数组的,所以必要先切割中序数组。
中序数组相对比较好切,找到切割点(后序数组的最后一个元素)在中序数组的位置,然后切割,如下代码中我坚持左闭右开的原则:
// 找到中序遍历的切割点
int delimiterIndex;
for (delimiterIndex = 0; delimiterIndex < inorder.size(); delimiterIndex++) {if (inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue) break;
}// 左闭右开区间:[0, delimiterIndex)
vector<int> leftInorder(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex);
// [delimiterIndex + 1, end)
vector<int> rightInorder(inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex + 1, inorder.end() );
接下来就要切割后序数组了。
首先后序数组的最后一个元素指定不能要了,这是切割点 也是 当前二叉树中间节点的元素,已经用了。
后序数组的切割点怎么找?
后序数组没有明确的切割元素来进行左右切割,不像中序数组有明确的切割点,切割点左右分开就可以了。
此时有一个很重的点,就是中序数组大小一定是和后序数组的大小相同的(这是必然)。
中序数组我们都切成了左中序数组和右中序数组了,那么后序数组就可以按照左中序数组的大小来切割,切成左后序数组和右后序数组。
代码如下:
// postorder 舍弃末尾元素,因为这个元素就是中间节点,已经用过了
postorder.resize(postorder.size() - 1);// 左闭右开,注意这里使用了左中序数组大小作为切割点:[0, leftInorder.size)
vector<int> leftPostorder(postorder.begin(), postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size());
// [leftInorder.size(), end)
vector<int> rightPostorder(postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size(), postorder.end());
此时,中序数组切成了左中序数组和右中序数组,后序数组切割成左后序数组和右后序数组。
接下来可以递归了,代码如下:
root->left = traversal(leftInorder, leftPostorder);
root->right = traversal(rightInorder, rightPostorder);
代码
完整代码如下:
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* traversal(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if (postorder.size() == 0) {return nullptr;}// 后序遍历的最后一个元素为根节点的值int rootValue = postorder[postorder.size() - 1];// 创建根节点TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue);if (postorder.size() == 1) {// 如果后序遍历数组只有一个元素,则直接返回根节点return root;}int delimiterIndex;// 在中序遍历数组中找到根节点的位置for (delimiterIndex = 0; delimiterIndex < postorder.size(); delimiterIndex++) {if (inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue) {break;}}// 切割中序遍历数组,得到左子树和右子树的中序遍历数组// 左闭右开区间:[0, delimiterIndex)vector<int> leftInorder(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex);// 左闭右开区间:[delimiterIndex + 1, end)vector<int> rightInorder(inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex + 1, inorder.end());// postorder 舍弃末尾元素postorder.resize(postorder.size() - 1);// 切割后序遍历数组,得到左子树和右子树的后序遍历数组// 依然左闭右开,注意这里使用了左中序数组大小作为切割点// 左闭右开区间:[0, leftInorder.size())vector<int> leftPostorder(postorder.begin(), postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size());// 左闭右开区间:[leftInorder.size(), end)vector<int> rightPostorder(postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size(), postorder.end());// 递归构建左子树和右子树,并连接到根节点上root->left = traversal(leftInorder, leftPostorder);root->right = traversal(rightInorder, rightPostorder);return root;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if (inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) {// 如果中序遍历或后序遍历的数组为空,则返回空指针return nullptr;}// 调用traversal函数构建树return traversal(inorder, postorder);}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
3、递归(带日志)
思路
相信大家自己就算是思路清晰, 代码写出来一定是各种问题,所以一定要加日志来调试,看看是不是按照自己思路来切割的,不要大脑模拟,那样越想越糊涂。
加了日志的代码如下:(加了日志的代码不要在leetcode上提交,容易超时)
代码
class Solution {
private:TreeNode* traversal (vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if (postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;int rootValue = postorder[postorder.size() - 1];TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue);if (postorder.size() == 1) return root;int delimiterIndex;for (delimiterIndex = 0; delimiterIndex < inorder.size(); delimiterIndex++) {if (inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue) break;}vector<int> leftInorder(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex);vector<int> rightInorder(inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex + 1, inorder.end() );postorder.resize(postorder.size() - 1);vector<int> leftPostorder(postorder.begin(), postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size());vector<int> rightPostorder(postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size(), postorder.end());// 以下为日志cout << "----------" << endl;cout << "leftInorder :";for (int i : leftInorder) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;cout << "rightInorder :";for (int i : rightInorder) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;cout << "leftPostorder :";for (int i : leftPostorder) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;cout << "rightPostorder :";for (int i : rightPostorder) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;root->left = traversal(leftInorder, leftPostorder);root->right = traversal(rightInorder, rightPostorder);return root;}
public:TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if (inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;return traversal(inorder, postorder);}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
4、递归(索引)
思路
此时应该发现了,如上的代码性能并不好,因为每层递归定义了新的vector(就是数组),既耗时又耗空间,但上面的代码是最好理解的,为了方便读者理解,所以用如上的代码来讲解。
下面给出用下标索引写出的代码版本:(思路是一样的,只不过不用重复定义vector了,每次用下标索引来分割)
代码
class Solution {
private:// 中序区间:[inorderBegin, inorderEnd),后序区间[postorderBegin, postorderEnd)TreeNode* traversal (vector<int>& inorder, int inorderBegin, int inorderEnd, vector<int>& postorder, int postorderBegin, int postorderEnd) {if (postorderBegin == postorderEnd) return NULL;int rootValue = postorder[postorderEnd - 1];TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue);if (postorderEnd - postorderBegin == 1) return root;int delimiterIndex;for (delimiterIndex = inorderBegin; delimiterIndex < inorderEnd; delimiterIndex++) {if (inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue) break;}// 切割中序数组// 左中序区间,左闭右开[leftInorderBegin, leftInorderEnd)int leftInorderBegin = inorderBegin;int leftInorderEnd = delimiterIndex;// 右中序区间,左闭右开[rightInorderBegin, rightInorderEnd)int rightInorderBegin = delimiterIndex + 1;int rightInorderEnd = inorderEnd;// 切割后序数组// 左后序区间,左闭右开[leftPostorderBegin, leftPostorderEnd)int leftPostorderBegin = postorderBegin;int leftPostorderEnd = postorderBegin + delimiterIndex - inorderBegin; // 终止位置是 需要加上 中序区间的大小size// 右后序区间,左闭右开[rightPostorderBegin, rightPostorderEnd)int rightPostorderBegin = postorderBegin + (delimiterIndex - inorderBegin);int rightPostorderEnd = postorderEnd - 1; // 排除最后一个元素,已经作为节点了root->left = traversal(inorder, leftInorderBegin, leftInorderEnd, postorder, leftPostorderBegin, leftPostorderEnd);root->right = traversal(inorder, rightInorderBegin, rightInorderEnd, postorder, rightPostorderBegin, rightPostorderEnd);return root;}
public:TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if (inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;// 左闭右开的原则return traversal(inorder, 0, inorder.size(), postorder, 0, postorder.size());}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
5、递归(索引带日志)
思路
那么这个版本写出来依然要打日志进行调试,打日志的版本如下:(该版本不要在leetcode上提交,容易超时)
代码
class Solution {
private:TreeNode* traversal (vector<int>& inorder, int inorderBegin, int inorderEnd, vector<int>& postorder, int postorderBegin, int postorderEnd) {if (postorderBegin == postorderEnd) return NULL;int rootValue = postorder[postorderEnd - 1];TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue);if (postorderEnd - postorderBegin == 1) return root;int delimiterIndex;for (delimiterIndex = inorderBegin; delimiterIndex < inorderEnd; delimiterIndex++) {if (inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue) break;}// 切割中序数组// 左中序区间,左闭右开[leftInorderBegin, leftInorderEnd)int leftInorderBegin = inorderBegin;int leftInorderEnd = delimiterIndex;// 右中序区间,左闭右开[rightInorderBegin, rightInorderEnd)int rightInorderBegin = delimiterIndex + 1;int rightInorderEnd = inorderEnd;// 切割后序数组// 左后序区间,左闭右开[leftPostorderBegin, leftPostorderEnd)int leftPostorderBegin = postorderBegin;int leftPostorderEnd = postorderBegin + delimiterIndex - inorderBegin; // 终止位置是 需要加上 中序区间的大小size// 右后序区间,左闭右开[rightPostorderBegin, rightPostorderEnd)int rightPostorderBegin = postorderBegin + (delimiterIndex - inorderBegin);int rightPostorderEnd = postorderEnd - 1; // 排除最后一个元素,已经作为节点了cout << "----------" << endl;cout << "leftInorder :";for (int i = leftInorderBegin; i < leftInorderEnd; i++) {cout << inorder[i] << " ";}cout << endl;cout << "rightInorder :";for (int i = rightInorderBegin; i < rightInorderEnd; i++) {cout << inorder[i] << " ";}cout << endl;cout << "leftpostorder :";for (int i = leftPostorderBegin; i < leftPostorderEnd; i++) {cout << postorder[i] << " ";}cout << endl;cout << "rightpostorder :";for (int i = rightPostorderBegin; i < rightPostorderEnd; i++) {cout << postorder[i] << " ";}cout << endl;root->left = traversal(inorder, leftInorderBegin, leftInorderEnd, postorder, leftPostorderBegin, leftPostorderEnd);root->right = traversal(inorder, rightInorderBegin, rightInorderEnd, postorder, rightPostorderBegin, rightPostorderEnd);return root;}
public:TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if (inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;return traversal(inorder, 0, inorder.size(), postorder, 0, postorder.size());}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
6、递归(使用unordered_map)
思路
为了高效查找根节点元素在中序遍历数组中的下标,我们选择创建哈希表来存储中序序列,即建立一个(元素,下标)键值对的哈希表。
代码
class Solution {int post_idx;unordered_map<int, int> idx_map;
public:TreeNode* helper(int in_left, int in_right, vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder){// 如果这里没有节点构造二叉树了,就结束if (in_left > in_right) {return nullptr;}// 选择 post_idx 位置的元素作为当前子树根节点int root_val = postorder[post_idx];TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(root_val);// 根据 root 所在位置分成左右两棵子树int index = idx_map[root_val];// 下标减一post_idx--;// 构造右子树root->right = helper(index + 1, in_right, inorder, postorder);// 构造左子树root->left = helper(in_left, index - 1, inorder, postorder);return root;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {// 从后序遍历的最后一个元素开始post_idx = (int)postorder.size() - 1;// 建立(元素,下标)键值对的哈希表int idx = 0;for (auto& val : inorder) {idx_map[val] = idx++;}return helper(0, (int)inorder.size() - 1, inorder, postorder);}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
7、迭代
思路
为了高效查找根节点元素在中序遍历数组中的下标,我们选择创建哈希表来存储中序序列,即建立一个(元素,下标)键值对的哈希表。
代码
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {// 如果后序遍历数组为空,则返回空指针if (postorder.size() == 0) {return nullptr;}// 创建根节点,其值为后序遍历数组的最后一个元素auto root = new TreeNode(postorder[postorder.size() - 1]);// 创建一个栈,用于存储节点指针auto s = stack<TreeNode*>();// 将根节点入栈s.push(root);// 初始化中序遍历数组的索引int inorderIndex = inorder.size() - 1;// 从后序遍历数组的倒数第二个元素开始遍历for (int i = int(postorder.size()) - 2; i >= 0; i--) {// 当前遍历的后序遍历数组的值int postorderVal = postorder[i];// 获取栈顶节点auto node = s.top();// 如果栈顶节点的值不等于中序遍历数组当前索引的值if (node->val != inorder[inorderIndex]) {// 将当前后序遍历数组的值作为右子节点,并创建新的节点node->right = new TreeNode(postorderVal);// 将右子节点入栈s.push(node->right);} else {// 当栈不为空且栈顶节点的值等于中序遍历数组当前索引的值时while (!s.empty() && s.top()->val == inorder[inorderIndex]) {// 弹出栈顶节点node = s.top();s.pop();// 中序遍历数组索引减一inorderIndex--;}// 将当前后序遍历数组的值作为左子节点,并创建新的节点node->left = new TreeNode(postorderVal);// 将左子节点入栈s.push(node->left);}}// 返回根节点return root;}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
相关文章:

LeetCode 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
LeetCode 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 1、题目 题目链接:106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并…...
函数,动态编译代码的艺术)
Python中的compile()函数,动态编译代码的艺术
关注公众号【一点sir】,领取编程资料。 简介 在Python编程中,compile()函数是一个强大的工具,它允许开发者将字符串形式的Python代码动态编译成字节码。这为执行动态生成或从外部源接收的代码提供了极大的灵活性。这些字节码随后可以被Pytho…...

【考研数学】汤家凤“免单“数学题被吐槽‘太难’,老汤回应「怎么还有脸笑」,网友:这些题有毒!
我看了汤家凤老师出的几道题,实际上对于考研的同学来说,确实是送分题 第一个是三角函数变换中的万能公式;第二个e^x的泰勒展开公式;第三个是第一类重要极限。只要复习过,那基本上都能正常做出来。 至于汤家凤老师说「…...
在另外一个页面,让另外一个页面弹框显示操作(调佣公共的弹框)
大概意思是,登录弹框在另外一个页面中,而当前页面不存在,在当前页面中判断如果token不存在,就弹框出登录的弹框 最后一行 window.location.href … 如果当前用户已登录,则执行后续操作(注意此处,可不要)...

如何利用IPIDEA代理IP优化数据采集效率?
一、 前言二、 IPIDEA介绍三、体验步骤四、实战训练五、结语 一、 前言 在全球化与信息化交织的当代社会,数据已成为驱动商业智慧与技术革新的核心引擎。网络,作为信息汇聚与交流的枢纽,不仅是人们获取知识的窗口,更是商业活动与技…...
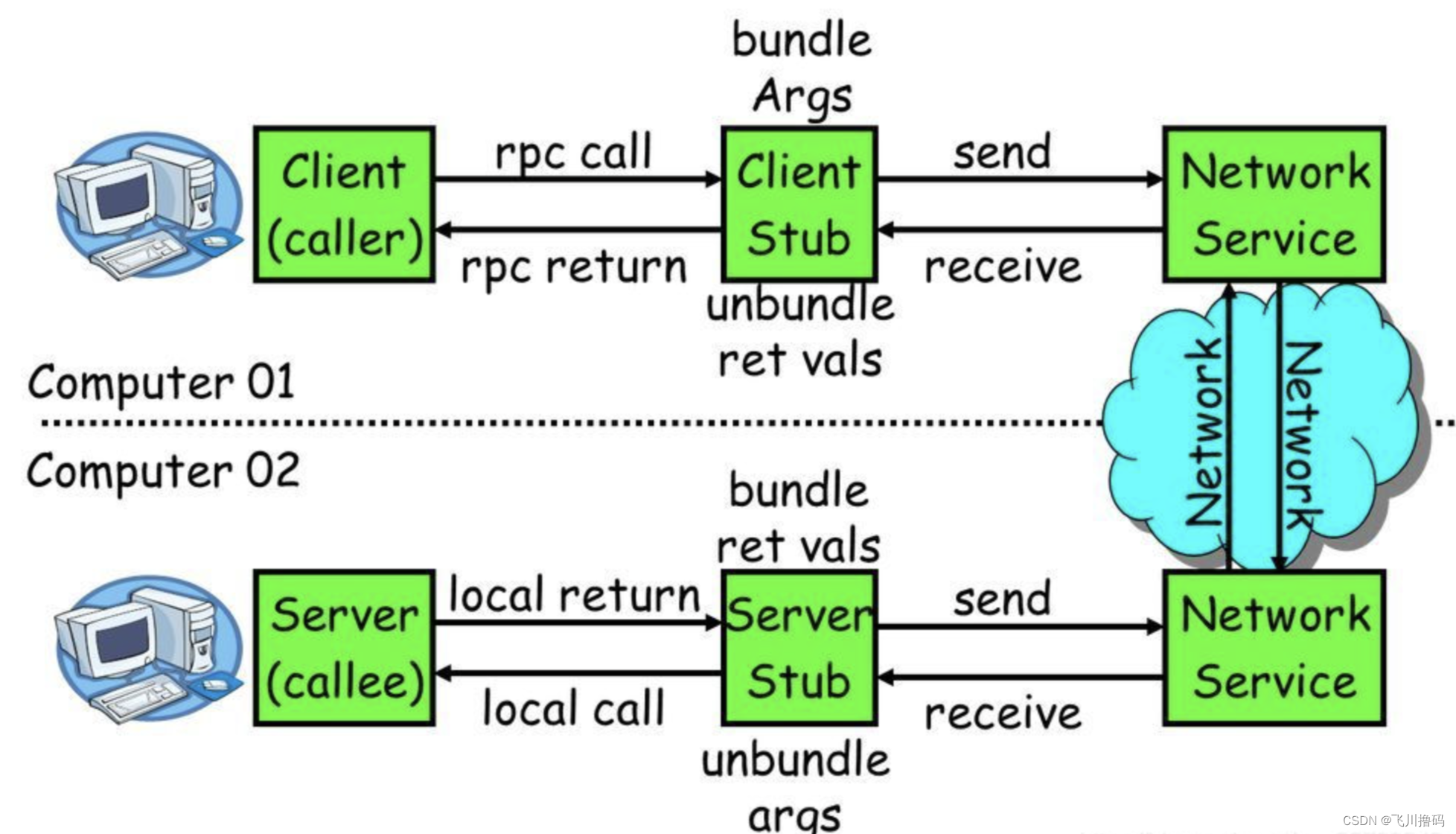
Rpcx (一):详解【介绍、基础示例 demo】
一.rpcx介绍 1.1 rpc是什么 远程过程调用的通信协议。该协议允许运行于一台计算机的程序调用另一台计算机的子程序,而程序员无需额外地为这个交互作用编程。如果涉及的软件采用面向对象编程,那么远程过程调用亦可称作远程调用或远程方法调用。简单地说就是能使应用像调用本地…...
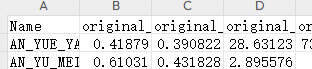
对数据进行标准化和归一化
数据的形式:保存在CSV中,第一列为姓名,第二列之后为特征。 标准化 输入文件的路径,设置保存转化后的文件路径 import pandas as pd from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler# 读取CSV文件 data pd.read_csv(rC:\User…...
【从零开始学架构 架构基础】二 架构设计的复杂度来源:高性能复杂度来源
架构设计的复杂度来源其实就是架构设计要解决的问题,主要有如下几个:高性能、高可用、可扩展、低成本、安全、规模。复杂度的关键,就是新旧技术之间不是完全的替代关系,有交叉,有各自的特点,所以才需要具体…...

OpenHarmony 实战开发——3.1 Release + Linux 原厂内核Launcher起不来问题分析报告
1、关键字 Launcher 无法启动;原厂内核;Access Token ID; 2、问题描述 芯片:rk3566;rk3399 内核版本:Linux 4.19,是 RK 芯片原厂发布的 rk356x 4.19 稳定版内核 OH 版本:OpenHa…...
小猫咪邮件在线发送系统源码,支持添加附件
一款免登录发送邮件,支持发送附件,后台可添加邮箱,前台可选择发送邮箱 网站数据采取本地保存,所以使用前请给网站修改权限,否则很多功能将无法使用 安装教程: 1.上传服务器或者主机 2.登录后台,添加发送…...
是什么?)
Django REST framework(DRF)是什么?
Django REST framework(DRF)是什么? Django REST framework(简称DRF)是一个强大且灵活的工具包,用于构建Web API。它是基于Django(一个高级Python Web框架)构建的,提供了…...

用hMailServer+roundcubemail+宝塔安装配置一个自己的邮箱服务
用hMailServerroundcubemail安装配置一个自己的邮箱服务 1、准备工具与资料: 云服务器一台 基础配置就行 2核4G。域名一个 以下用lizipro.cn示例。hMailServer安装包roundcubemail安装包异常处理插件补丁: libmysql.zip 2、hMailServer服务安装&#…...
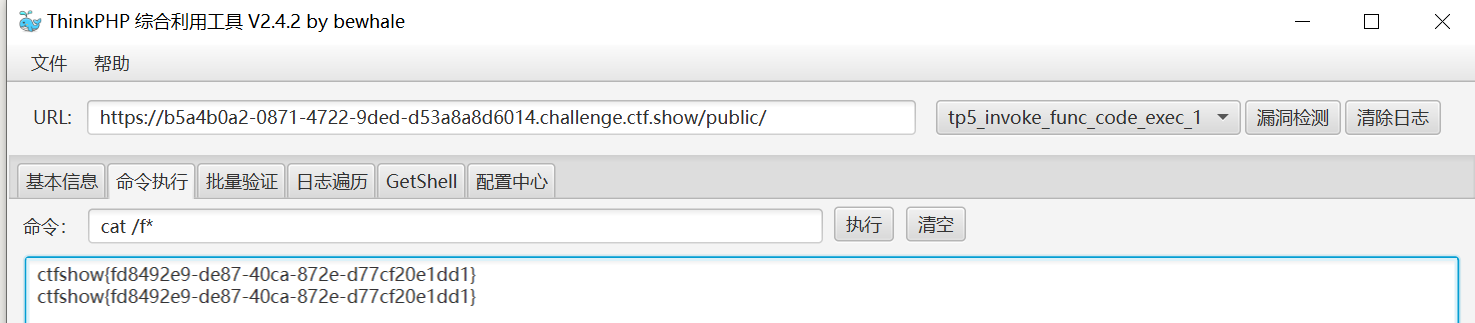
ctfshow 框架复现
文章目录 web 466web 467web 468web469web 470web 471web 472web 473web 474web 475web 476 web 466 Laravel5.4版本 ,提交数据需要base64编码 代码审计学习—Laravel5.4 - 先知社区 (aliyun.com) 用第二条链子 反序列化格式 /admin/序列化串base64<?php na…...
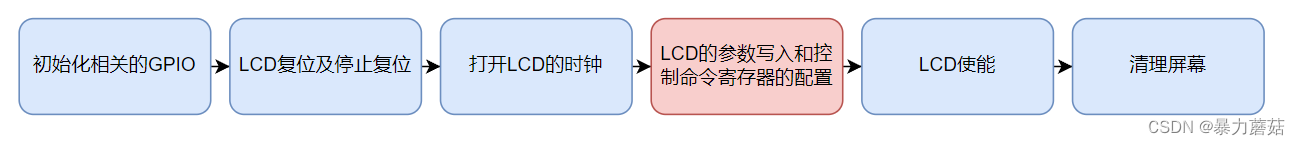
【Linux-IMX6ULL-DDR3简介测试-RGBLCD控制原理】
目录 1. DDR3 简介1.1 前要基本概念RAM & ROM 2. DDR3测试及初始化3. RGBLCD简介及控制原理3.1 RGBLCD简介3.2.1 RGB LCD时序3.2.2 像素时钟(800*400分辨率)3.2.2 显存(800*400分辨率) 3.3 RGBLCD的控制3.3.1 DOTCLK 硬件接口…...

贪心算法-----柠檬水找零
今日题目:leetcode860 题目链接:点击跳转题目 分析: 顾客只会给三种面值:5、10、20,先分类讨论 当收到5美元时:不用找零,面值5张数1当收到10美元时:找零5美元,面值5张数…...

MySQL技能树学习
在MySQL中,DDL(数据定义语言)用于定义数据库对象(如表、索引、视图等),DML(数据操纵语言)用于操作数据库中的数据(如插入、更新、删除数据),DQL&a…...

java 动态代理详解
cglib 动态代理 介绍 CGLIB是一个功能强大,高性能的代码生成包。它为没有实现接口的类提供代理,为JDK的动态代理提供了很好的补充。通常可以使用Java的动态代理创建代理,但当要代理的类没有实现接口或者为了更好的性能,CGLIB 是一…...

Web路径专题
文章目录 Web路径专题什么是路径?绝对路径相对路径 如何使用路径?使用base标签 注意事项小结 Web路径专题 在Web开发中,路径是一个非常重要的概念。路径用来定位资源的位置,包括文件、目录、网页等。在本文中,我们将介…...

解决vue3项目打包后部署后某些静态资源图片不加载问题
目录 问题 原因 解决方案 问题 开发完项目打包并部署 然后访问时发现导航栏背景图片没加载 打开浏览器控制台发现这张图片报错404 原因 可能是因为在部署后的服务器环境中对中文文件名的支持不完善。服务器在解析 URL 时可能无法正确识别或编码中文字符,导致无…...
传感网应用开发教程--AT指令访问新大陆云平台(ESP8266模块+物联网云+TCP)
实现目标 1、熟悉AT指令 2、熟悉新大陆云平台新建项目 3、具体目标:(1)注册新大陆云平台;(2)新建一个联网方案为WIFI的项目;(3)ESP8266模块,通过AT指令访问…...
。】2022-5-15)
【根据当天日期输出明天的日期(需对闰年做判定)。】2022-5-15
缘由根据当天日期输出明天的日期(需对闰年做判定)。日期类型结构体如下: struct data{ int year; int month; int day;};-编程语言-CSDN问答 struct mdata{ int year; int month; int day; }mdata; int 天数(int year, int month) {switch (month){case 1: case 3:…...

深入剖析AI大模型:大模型时代的 Prompt 工程全解析
今天聊的内容,我认为是AI开发里面非常重要的内容。它在AI开发里无处不在,当你对 AI 助手说 "用李白的风格写一首关于人工智能的诗",或者让翻译模型 "将这段合同翻译成商务日语" 时,输入的这句话就是 Prompt。…...

大型活动交通拥堵治理的视觉算法应用
大型活动下智慧交通的视觉分析应用 一、背景与挑战 大型活动(如演唱会、马拉松赛事、高考中考等)期间,城市交通面临瞬时人流车流激增、传统摄像头模糊、交通拥堵识别滞后等问题。以演唱会为例,暖城商圈曾因观众集中离场导致周边…...

高频面试之3Zookeeper
高频面试之3Zookeeper 文章目录 高频面试之3Zookeeper3.1 常用命令3.2 选举机制3.3 Zookeeper符合法则中哪两个?3.4 Zookeeper脑裂3.5 Zookeeper用来干嘛了 3.1 常用命令 ls、get、create、delete、deleteall3.2 选举机制 半数机制(过半机制࿰…...

测试markdown--肇兴
day1: 1、去程:7:04 --11:32高铁 高铁右转上售票大厅2楼,穿过候车厅下一楼,上大巴车 ¥10/人 **2、到达:**12点多到达寨子,买门票,美团/抖音:¥78人 3、中饭&a…...

基于Docker Compose部署Java微服务项目
一. 创建根项目 根项目(父项目)主要用于依赖管理 一些需要注意的点: 打包方式需要为 pom<modules>里需要注册子模块不要引入maven的打包插件,否则打包时会出问题 <?xml version"1.0" encoding"UTF-8…...

Spring Cloud Gateway 中自定义验证码接口返回 404 的排查与解决
Spring Cloud Gateway 中自定义验证码接口返回 404 的排查与解决 问题背景 在一个基于 Spring Cloud Gateway WebFlux 构建的微服务项目中,新增了一个本地验证码接口 /code,使用函数式路由(RouterFunction)和 Hutool 的 Circle…...

Mysql8 忘记密码重置,以及问题解决
1.使用免密登录 找到配置MySQL文件,我的文件路径是/etc/mysql/my.cnf,有的人的是/etc/mysql/mysql.cnf 在里最后加入 skip-grant-tables重启MySQL服务 service mysql restartShutting down MySQL… SUCCESS! Starting MySQL… SUCCESS! 重启成功 2.登…...

Java数值运算常见陷阱与规避方法
整数除法中的舍入问题 问题现象 当开发者预期进行浮点除法却误用整数除法时,会出现小数部分被截断的情况。典型错误模式如下: void process(int value) {double half = value / 2; // 整数除法导致截断// 使用half变量 }此时...

多模态图像修复系统:基于深度学习的图片修复实现
多模态图像修复系统:基于深度学习的图片修复实现 1. 系统概述 本系统使用多模态大模型(Stable Diffusion Inpainting)实现图像修复功能,结合文本描述和图片输入,对指定区域进行内容修复。系统包含完整的数据处理、模型训练、推理部署流程。 import torch import numpy …...
