C++之运算符重载
1、运算符重载

//Complex.h
#ifndef _COMPLEX_H_
#define _COMPLEX_H_class Complex
{
public:Complex(int real_, int imag_);Complex();~Complex();Complex& Add(const Complex& other); void Display() const;Complex operator+(const Complex& other);private:int real_;int imag_;
};
#endif // _COMPLEX_H_// Complex.cpp
#include "Complex.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;Complex::Complex(int real, int imag) : real_(real), imag_(imag)
{}Complex::Complex()
{}Complex::~Complex()
{}Complex& Complex::Add(const Complex& other)
{real_ += other.real_;imag_ += other.imag_;return *this; // 因为是引用,所以返回的时候不会调用拷贝构造函数
}void Complex::Display() const
{cout << real_ << "+" << imag_ << endl;
}Complex Complex::operator+(const Complex& other)
{int r = real_ + other.real_;int i = imag_ + other.imag_;return Complex(r, i);
}// main.cpp
#include "Complex.h"int main(void)
{Complex c1(3, 5);Complex c2(4, 6);//c1.Add(c2); // 但是这样就修改到了c1对象,我们希望是Complex c3 = c1 + c2;这个时候我们就需要运算符的重载//c1.Display();Complex c3 = c1 + c2; // 这边其实就是函数调用,相当于c1.operator(c2);// Complex c3 = c1.operator(c2);c1.Display();c2.Display();c3.Display();return 0;
}其实运算符的重载,在这边也就是成员函数的重载。

2、非成员函数重载(友元的方式重载)

在vs2008中友元函数的运算符重载能和成员函数的运算符重载共存,有些编译器不行。如果共存,那么优先调用成员函数的运算符重载。
//Complex.h
#ifndef _COMPLEX_H_
#define _COMPLEX_H_class Complex
{
public:Complex(int real_, int imag_);Complex();~Complex();Complex& Add(const Complex& other); void Display() const;Complex operator+(const Complex& other);friend Complex operator+(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2);private:int real_;int imag_;
};
#endif // _COMPLEX_H_// Complex.cpp
#include "Complex.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;Complex::Complex(int real, int imag) : real_(real), imag_(imag)
{}Complex::Complex()
{}Complex::~Complex()
{}Complex& Complex::Add(const Complex& other)
{real_ += other.real_;imag_ += other.imag_;return *this; // 因为是引用,所以返回的时候不会调用拷贝构造函数
}void Complex::Display() const
{cout << real_ << "+" << imag_ << endl;
}Complex Complex::operator+(const Complex& other)
{int r = real_ + other.real_;int i = imag_ + other.imag_;return Complex(r, i);
}Complex operator+(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2)
{int r = c1.real_ + c2.real_;int i = c1.imag_ + c2.imag_;return Complex(r, i);
}// main.cpp
#include "Complex.h"int main(void)
{Complex c1(3, 5);Complex c2(4, 6);//c1.Add(c2); // 但是这样就修改到了c1对象,我们希望是Complex c3 = c1 + c2;这个时候我们就需要运算符的重载//c1.Display();Complex c3 = c1 + c2; // 这边其实就是函数调用,相当于c1.operator(c2);// Complex c3 = c1.operator(c2);c1.Display();c2.Display();c3.Display();return 0;
}3、运算符重载的规则
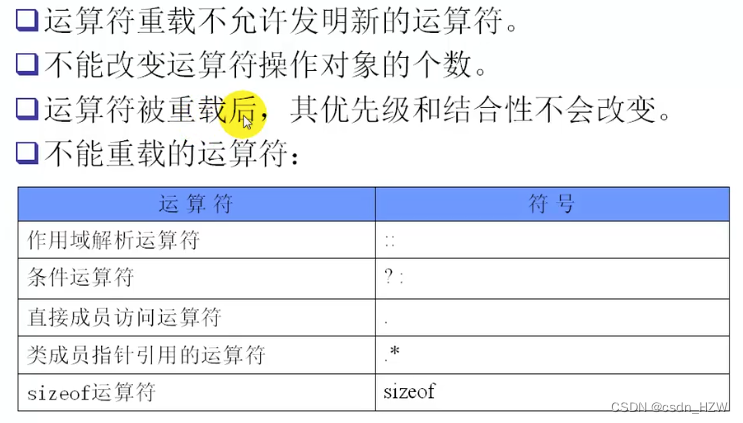
不能重载的运算符:因为如果开放了这些运算符的重载,那么语法就会变得混乱不可控制。

4、++运算符重载

推荐用成员函数进行重载,因为友元重载是全局的。
// Integer.h
#ifndef _INTEGER_H
#define _INTEGER_Hclass Integer
{
public:Integer (int n);~Integer();void Display();Integer& operator++(); // 前置++成员函数重载//friend Integer& operator++(Integer &i); // 前置++友元重载// 友元不能共存// 后置中的参数int i没什么用,只是为了区分是否是前置还是后置Integer operator++(int i); // 后置++成员函数重载//friend Integer& operator++(Integer &i, int i); // 前置++友元重载
private:int n_;
};#endif //_INTEGER_H// Integer.cpp
#include "Integer.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;Integer::Integer(int n) : n_(n)
{}Integer::~Integer()
{}void Integer::Display()
{cout << "n_ = " << n_ << endl;
}//Integer& Integer::operator++()
//{
// cout << "Integer& Integer::operator++()" << endl;
// ++n_;
// return *this;
//}Integer& operator++(Integer &i)
{cout << "Integer& operator++(Integer &i)" << endl;++i.n_;return i; // 因为返回的是引用不是对象,所以不会调用拷贝构造函数
}//Integer Integer::operator++(int i)
//{
// cout << "Integer& Integer::operator++(int i)" << endl;
// //n++,
// Integer tmp(n_);
// n_++;
// return tmp;
//}Integer& operator++(Integer &i, int j)
{cout << "Integer& operator++(Integer &i, int i)" << endl;//n++,Integer tmp(i.n_);i.n_++;return tmp;
}
// main.cpp
#include "Integer.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main(void)
{Integer n(10);n.Display();Integer n2 = ++n;n.Display();n2.Display();Integer n3 = n++;n.Display();n3.Display();return 0;
}5、=赋值运算符重载
//String.h
#ifndef _STRING_H
#define _STRING_Hclass String
{
public:String(const char* str = "");String(const String& other); // 拷贝构造// 当你使用obj1 = obj2的时候,也是浅拷贝,即obj1.str_ = obj2.str_,所以要重载等号运算符,在里面进行深拷贝String& operator=(const String& other);String& operator=(const char* str);void Display() const;~String(void);private:char* AllocAndCopy(const char* str);char* str_;
};#endif //_STRING_H// String.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;String::String(const char* str)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);
}String::String(const String& other)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);
}String& String::operator=(const String& other)
{if (this == &other)return *this;delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);return *this;
}char* String::AllocAndCopy(const char* str)
{int len= strlen(str)+ 1;char* newStr= new char[len];memset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, str);return newStr;
}
String& String::operator=(const char* str)
{delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);return *this;
}void String::Display() const
{cout << str_ << endl;
}String::~String()
{delete[] str_;
}// main.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main(void)
{String s1("abc");String s2(s1);String s3;s3 = s1;s3.Display();s3 = "xxxx"; // 如果没有去重载String& operator=(const char* str);那么先调用转换构造函数String(const char* str)将字符串构造成一个对象,然后再调用String& operator=(const String& other);重载等号运算符进行赋值。s3.Display();return 0;
}其实主要是内存释放的问题,因为如果直接=,就是浅拷贝,如果有用malloc的话,释放的时候,一块内存会被释放两次。还有就是写法中调用的问题,s1("abc")调用构造函数;s1(s2)调用拷贝构造,当在构造函数中有开辟空间,则在拷贝构造里面也要开辟空间,避免重复释放。
6、!运算符重载
当字符串是空的,那就是假的,当字符串不为空,那就是真。
//String.h
#ifndef _STRING_H
#define _STRING_Hclass String
{
public:String(const char* str = "");String(const String& other); // 拷贝构造// 当你使用obj1 = obj2的时候,也是浅拷贝,即obj1.str_ = obj2.str_,所以要重载等号运算符,在里面进行深拷贝String& operator=(const String& other);String& operator=(const char* str);bool operator!() const;void Display() const;~String(void);private:char* AllocAndCopy(const char* str);char* str_;
};#endif //_STRING_H// String.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;String::String(const char* str)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);
}String::String(const String& other)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str);
}String& String::operator=(const String& other)
{if (this == other)return *this;delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);return *this;
}char* String::AllocAndCopy(const char* str)
{int len= strlen(str)+ 1;char* newStr= new char[len];menset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, str);return newStr;
}
String& String::operator=(const char* str)
{delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str);return *this;
}bool String::operator!() const
{return strlen(str_) != 0;
}void String::Display() const
{cout << str_ << endl;
}String::~String()
{delete[] str_;
}// main.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main(void)
{String s1("abc");String s2(s1);String s3;s3 = s1;s3.Display();s3 = "xxxx"; // 如果没有去重载String& operator=(const char* str);那么先调用转换构造函数String(const char* str)将字符串构造成一个对象,然后再调用String& operator=(const String& other);重载等号运算符进行赋值。s3.Display();String s4;bool notEmpty;notEmpty = !s4;cout << notEmpty << endl;s4 = "aaaa";notEmpty = !s4;cout << notEmpty << endl;return 0;
}7、[]运算符重载
//String.h
#ifndef _STRING_H
#define _STRING_Hclass String
{
public:String(const char* str = "");String(const String& other); // 拷贝构造// 当你使用obj1 = obj2的时候,也是浅拷贝,即obj1.str_ = obj2.str_,所以要重载等号运算符,在里面进行深拷贝String& operator=(const String& other);String& operator=(const char* str);bool operator!() const;char& operator[](unsigned int index);const char& operator[](unsigned int index) const;void Display() const;~String(void);private:char* AllocAndCopy(const char* str);char* str_;
};#endif //_STRING_H// String.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;String::String(const char* str)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);
}String::String(const String& other)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str);
}String& String::operator=(const String& other)
{if (this == other)return *this;delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);return *this;
}char* String::AllocAndCopy(const char* str)
{int len= strlen(str)+ 1;char* newStr= new char[len];menset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, str);return newStr;
}
String& String::operator=(const char* str)
{delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str);return *this;
}bool String::operator!() const
{return strlen(str_) != 0;
}char& String::operator[](unsigned int index)
{return str_[index];// 因为这里面的代码和const的代码一样,所以最好合并成同一份代码// 做法是,non const 版本调用const版本return const_cast<char&>(static_cast<const String&>(*this)[index]);
}const char& String::operator[](unsigned int index) const
{return str_[index];
}void String::Display() const
{cout << str_ << endl;
}String::~String()
{delete[] str_;
}// main.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main(void)
{String s1("abcdefg");char ch = s1[2];cout << ch << endl; // 输出c//为什么[]的返回值是字符串的引用?因为一个函数,如果返回值是引用的话,就可以出现在表达式的左边,这样就能重新赋值。s1[2] = 'A';s1.Display(); // 输出abAdefgconst String s2("xyzabc");s2[2] = 'M'; // 这边会调用char& operator[](unsigned int index) const这个重载。因为是const对象,所以希望这个操作是不允许的;解决方案:前面加上const,变成const char& operator[](unsigned int index) const;这样的话,这句在编译的时候就会报错ch = s2[2]; // 希望这个操作是允许的s2.Display(); // 输出xyMabcreturn 0;
}8、+运算符重载
最好写成友元的方式去重载。
9、+=运算符的重载
// String.h
#ifndef STRING_H
#define STRING_H
class String {
public:String(const char* str = "");String(const String& other); // 拷贝构造// 当你使用obj1 = obj2的时候,也是浅拷贝,即obj1.str_ = obj2.str_,所以要重载等号运算符,在里面进行深拷贝String& operator=(const String& other);String& operator=(const char* str);bool operator!() const;char& operator[](unsigned int index);const char& operator[](unsigned int index) const;//+运算符重载(最好用友元的方式来重载)friend String operator+(const String& s1, const String& s2);//+=运算符重载String& operator+=(const String& other);void Display() const;~String(void);private:static char* AllocAndCopy(const char* str);char* str_;
};#endif //STRING_H
// String.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include "String.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;String::String(const char* str)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);
}String::String(const String& other)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);
}String& String::operator=(const String& other)
{if (this == &other)return *this;delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);return *this;
}char* String::AllocAndCopy(const char* str)
{int len= strlen(str)+ 1;char* newStr= new char[len];memset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, str);return newStr;
}
String& String::operator=(const char* str)
{delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);return *this;
}bool String::operator!() const
{return strlen(str_) != 0;
}char& String::operator[](unsigned int index)
{return str_[index];// 因为这里面的代码和const的代码一样,所以最好合并成同一份代码// 做法是,non const 版本调用const版本return const_cast<char&>(static_cast<const String&>(*this)[index]);
}const char& String::operator[](unsigned int index) const
{return str_[index];
}void String::Display() const
{cout << str_ << endl;
}String::~String()
{delete[] str_;
}String operator+(const String& s1, const String& s2)
{int len = strlen(s1.str_) + strlen(s2.str_);char* newStr = new char[len];memset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, s1.str_);strcat(newStr, s2.str_);String tmp(newStr);delete newStr;return tmp;
}String& String::operator+=(const String& other)
{int len = strlen(str_) + strlen(other.str_);char* newStr = new char[len];memset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, str_);strcat(newStr, other.str_);delete[] str_;str_ = newStr;return *this;
}// main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "String.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {String s1("abcdefg");char ch = s1[2];cout << ch << endl; // 输出c//为什么[]的返回值是字符串的引用?因为一个函数,如果返回值是引用的话,就可以出现在表达式的左边,这样就能重新赋值。s1[2] = 'A';s1.Display(); // 输出abAdefgconst String s2("xyzabc");//s2[2] = 'M'; // 这边会调用char& operator[](unsigned int index) const这个重载。因为是const对象,所以希望这个操作是不允许的;解决方案:前面加上const,变成const char& operator[](unsigned int index) const;这样的话,这句在编译的时候就会报错ch = s2[2]; // 希望这个操作是允许的s2.Display(); // 输出xyMabcString s3 = "xxx";String s4 = "yyy";String s5 = s3 + s4;s5.Display();s3 += s4;s3.Display();return 0;
}
10、<<和>>运算符重载

//String.h
#ifndef STRING_H
#define STRING_H#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class String {
public:String(const char* str = "");String(const String& other); // 拷贝构造// 当你使用obj1 = obj2的时候,也是浅拷贝,即obj1.str_ = obj2.str_,所以要重载等号运算符,在里面进行深拷贝String& operator=(const String& other);String& operator=(const char* str);bool operator!() const;char& operator[](unsigned int index);const char& operator[](unsigned int index) const;//+运算符重载(最好用友元的方式来重载)friend String operator+(const String& s1, const String& s2);//+=运算符重载String& operator+=(const String& other);// << 运算符重载friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const String& str);// >> 运算符重载friend istream& operator>>(istream& is, String& str);void Display() const;~String(void);private:static char* AllocAndCopy(const char* str);char* str_;
};#endif //STRING_H
//String.cpp
include "String.h"
#include "String.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;String::String(const char* str)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);
}String::String(const String& other)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);
}String& String::operator=(const String& other)
{if (this == &other)return *this;delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);return *this;
}char* String::AllocAndCopy(const char* str)
{int len= strlen(str)+ 1;char* newStr= new char[len];memset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, str);return newStr;
}
String& String::operator=(const char* str)
{delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);return *this;
}bool String::operator!() const
{return strlen(str_) != 0;
}char& String::operator[](unsigned int index)
{return str_[index];// 因为这里面的代码和const的代码一样,所以最好合并成同一份代码// 做法是,non const 版本调用const版本return const_cast<char&>(static_cast<const String&>(*this)[index]);
}const char& String::operator[](unsigned int index) const
{return str_[index];
}void String::Display() const
{cout << str_ << endl;
}String::~String()
{delete[] str_;
}String operator+(const String& s1, const String& s2)
{int len = strlen(s1.str_) + strlen(s2.str_);char* newStr = new char[len];memset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, s1.str_);strcat(newStr, s2.str_);String tmp(newStr);delete newStr;return tmp;
}String& String::operator+=(const String& other)
{int len = strlen(str_) + strlen(other.str_);char* newStr = new char[len];memset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, str_);strcat(newStr, other.str_);delete[] str_;str_ = newStr;return *this;
}ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const String& str)
{os << str.str_;return os;
}istream& operator>>(istream& is, String& str)
{char tmp[1024];cin >> tmp;str = tmp;return is;
}
// main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "String.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {String s1("abcdefg");char ch = s1[2];cout << ch << endl; // 输出c//为什么[]的返回值是字符串的引用?因为一个函数,如果返回值是引用的话,就可以出现在表达式的左边,这样就能重新赋值。s1[2] = 'A';s1.Display(); // 输出abAdefgconst String s2("xyzabc");//s2[2] = 'M'; // 这边会调用char& operator[](unsigned int index) const这个重载。因为是const对象,所以希望这个操作是不允许的;解决方案:前面加上const,变成const char& operator[](unsigned int index) const;这样的话,这句在编译的时候就会报错ch = s2[2]; // 希望这个操作是允许的s2.Display(); // 输出xyMabcString s3 = "xxx";String s4 = "yyy";String s5 = s3 + s4;s5.Display();s3 += s4;s3.Display();cout << s3 << endl;String s7;cin >> s7;cout << s7 << endl;return 0;
}
11、类型转换运算符的重载

12、指针运算符->
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class DBHelper
{
public:DBHelper(){cout << "DB..." << endl;}~DBHelper(){cout << "~DB..." << endl;}void Open(){cout << "Open..." << endl;}void Close(){cout << "Close..." << endl;}void Query(){cout << "Query..." << endl;}
};class DB
{
public:DB(){db_ = new DBHelper();}~DB(){delete db_;}DBHelper* operator->(){return db_;}private:DBHelper* db_;
};
int main() {// ->指针运算符(一个指针A包装了另一个指针B,利用了A生命周期结束的时候的确定性析构,在析构中销毁B)// 相当于智能指针DB db;db->Open();db->Query();db->Close();return 0;
}
13、operator new、operator delete的重载
new有三种用法
new operator:不能被重载
operator new
placement new

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;//类中operator new、operator delete的重载
class Test
{
public:Test(int n):n_(n){cout << "Test(int n):n_(n)" << endl;}Test(const Test& other){cout << "Test(const Test& other)" << endl;}~Test(){cout << "~Test()" << endl;}// 重载operator newvoid* operator new(size_t size){cout << "void* operator new(size_t size)" << endl;void* p = malloc(size);return p;}// 重载operator deletevoid operator delete (void* p){cout << "void operator delete (void* p)" << endl;free(p);}// 这两个可以共存,看你是调用哪个void operator delete (void* p, size_t size){cout << "void operator delete (void* p, size_t size)" << endl;free(p);}// 不同参数的newvoid* operator new(size_t size, const char* file, long line){cout << "void* operator new(size_t size, const char* file, long line)" << endl;cout << file << ":" << line << endl;void* p = malloc(size);return p;}// 重载operator deletevoid operator delete (void* p, const char* file, long line){cout << "void operator delete (void* p, const char* file, long line)" << endl;cout << file << ":" << line << endl;free(p);}// 重载placement newvoid* operator new(size_t size, void* p){cout << "placement new" << endl;return p;}void operator delete(void*, void*){cout << "placement delete" << endl;}int n_;
};// 全局operator new、operator delete的重载
// 重载operator new
void* operator new(size_t size)
{cout << "global void* operator new(size_t size)" << endl;void* p = malloc(size);return p;
}// 重载operator delete
void operator delete (void* p)
{cout << "global void operator delete (void* p)" << endl;free(p);
}// 重载operator new
void* operator new[](size_t size)
{cout << "global void* operator new[](size_t size)" << endl;void* p = malloc(size);return p;
}// 重载operator delete
void operator delete[](void* p)
{cout << "global void operator delete[] (void* p)" << endl;free(p);
}int main() {Test* p1 = new Test(100); // 这边是调用 new operator这个函数;这个函数相当于调用operator new 然后调用构造函数,两个函数的结合delete p1;char* str = new char;delete str;char* str2 = new char[100];delete []str2;char chunk[10];Test* p2 = new (chunk) Test(200); // 调用placement new,不分配内存,是在chunk这段内存上构造对象的;然后调用operator new 然后调用构造函数cout << p2->n_ << endl;p2->~Test(); // 显示调用析构函数,这边不能用delete,因为是在chunk上面的内存//Test* p3 = (Test*)chunk; // 强制转化Test* p3 = reinterpret_cast<Test*>(chunk);cout << p3->n_ << endl;Test* p4 = new(__FILE__, __LINE__) Test(300);delete p4;return 0;
}相关文章:

C++之运算符重载
1、运算符重载 //Complex.h #ifndef _COMPLEX_H_ #define _COMPLEX_H_class Complex { public:Complex(int real_, int imag_);Complex();~Complex();Complex& Add(const Complex& other); void Display() const;Complex operator(const Complex& other);privat…...

使用springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui后访问swagger-ui/index.html 报错404
按照官网说明,引入 springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui后应该就可以直接访问swagger-ui.html或者swagger-ui/index.html就可以出现swagger页面了,但是我引入后,访问提示报错404. 在我的项目中,有其他依赖间接引入了org.webjars…...

深入理解计算机系统 家庭作业4.52
练习题4.3 p.254 \sim\seq\seq-full.hcl文件内已经说的很清楚了哪些不能更改,哪些是题目要求更改的控制逻辑块. 依据家庭作业4.51的答案,在seq-full.hcl文件内更改对应的HCL描述即可 以下答案注释了#changed的就是更改部分 #/* $begin seq-all-hcl */ ######################…...
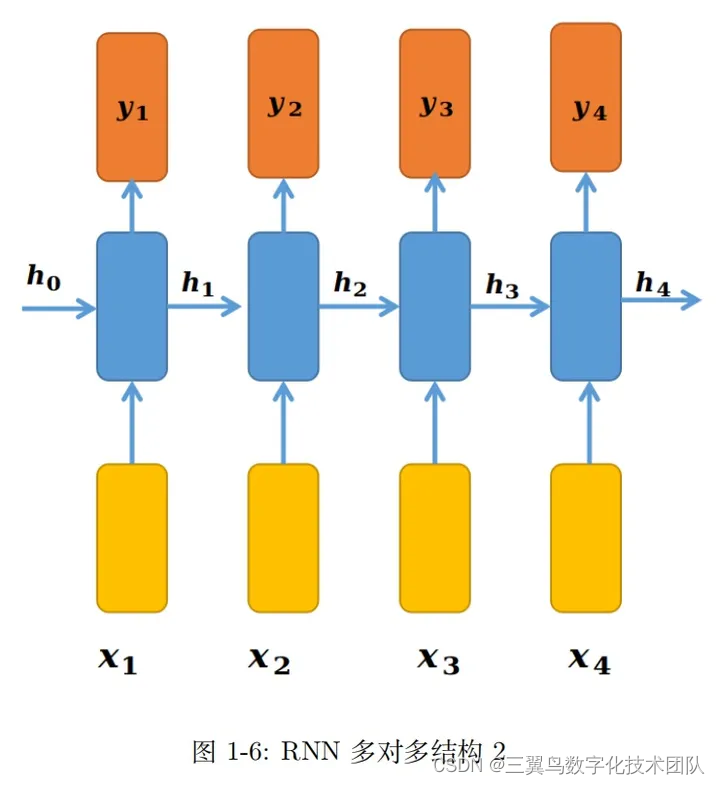
深度学习:手撕 RNN(2)-RNN 的常见模型架构
本文首次发表于知乎,欢迎关注作者。 上一篇文章我们介绍了一个基本的 RNN 模块。有了 这个 RNN 模块后,就像搭积木一样,以 RNN 为基本单元,根据不同的任务或者需求,可以构建不同的模型架构。本节介绍的所有结构&#…...
【Linux进程篇】Linux进程管理——进程创建与终止
W...Y的主页 😊 代码仓库分享💕 目录 进程创建 fork函数初识 写时拷贝 fork常规用法 fork调用失败的原因 进程终止 进程退出场景 _exit函数 exit函数 return退出 进程创建 fork函数初识 在linux中fork函数时非常重要的函数,它从已…...
Python爬虫实战(实战篇)—17获取【CSDN某一专栏】数据转为Markdown列表放入文章中
文章目录 专栏导读背景结果预览1、页面分析2、通过返回数据发现适合利用lxmlxpath3、进行Markdown语言拼接总结 专栏导读 在这里插入图片描述 🔥🔥本文已收录于《Python基础篇爬虫》 🉑🉑本专栏专门针对于有爬虫基础准备的一套基…...

Go语言-big.Int
文章目录 Go 语言 big.Int应用场景:大整数位运算使用举例: go sdk中crypto/ecdsa 椭圆曲线生成私钥相关结构中就有使用 Go 语言 big.Int Go 语言 big.Int 参考URL: https://blog.csdn.net/wzygis/article/details/82867793 math/big 作为 Go 语言提供的…...
); 会导致内存泄露吗?里面有SurfaceView ViewBinding)
getContentView(mBinding.getRoot()); 会导致内存泄露吗?里面有SurfaceView ViewBinding
在上述代码中,ActivityTestingBinding 是一个 Data Binding 库生成的类,用于绑定 XML 布局到 Activity 中。inflate(getLayoutInflater()) 用于将布局文件解析并转换为对应的视图层次结构。然后 getWindow().setFlags() 设置窗口属性,保持屏幕…...
基于transformers框架实践Bert系列6-完形填空
本系列用于Bert模型实践实际场景,分别包括分类器、命名实体识别、选择题、文本摘要等等。(关于Bert的结构和详细这里就不做讲解,但了解Bert的基本结构是做实践的基础,因此看本系列之前,最好了解一下transformers和Bert…...
cesium绘制编辑区域
npm 安装也是可以的 #默认安装最新的 yarn add cesium#卸载插件 yarn remove cesium#安装指定版本的 yarn add cesium1.96.0#安装指定版本到测试环境 yarn add cesium1.96.0 -D yarn install turf/turf token记得换成您自己的!!! <t…...

数据库攻防之MySQL
MySQL 是最流行的关系型数据库,与此同时也是 web 应用中最好的关系型数据库管理应用软件。我们在渗透过程中碰到的 PHP 站点大部分都会搭配 MySQL 数据库,因此它是红队攻防中最常遇到的数据库。 0x01 MySQL简介 MySQL 是典型的关系型数据库,…...
八国多语言微盘微交易所系统源码 单控点控 K线完好
安装环境linux NGMySQL5.6PHP7.2(函数全删)pm2管理器(node版本选择v12.20.0) config/ database.php 修改数据库链接 设置运行目录 public 伪静态thinkphp...

爪哇,我初学乍道
>>上一篇(学校上课,是耽误我学习了。。) 2016年9月,我大二了。 自从我发现上课会耽误我学习,只要我认为不影响我期末学分的,我就逃课了。 绝大多数课都是要签到的,有的是老师突击喊名字…...
-限制)
【MySQL精通之路】全文搜索(5)-限制
主博客:【MySQL精通之路】全文搜索功能-CSDN博客 全文搜索仅支持InnoDB和MyISAM表。 分区表不支持全文搜索。参见“分区的限制和限制”。 全文搜索可用于大多数多字节字符集。 例外的是,对于Unicode,可以使用utf8mb3或utf8mb4字符集ÿ…...
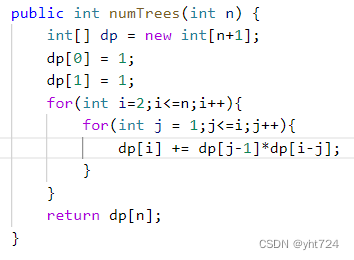
动态规划part03 Day43
LC343整数拆分(未掌握) 未掌握分析:dp数组的含义没有想清楚,dp[i]表示分解i能够达到的最大乘积,i能够如何分解呢,从1开始遍历,直到i-1;每次要不是j和i-j两个数,要不是j和…...

Activity->Activity生命周期和启动模式
<四大组件 android:name"xxx"android:exported"true" // 该组边能够被其他组件启动android:enabled"true" // 该组件能工与用户交互 </四大组件>Activity常用生命周期 启动Activity 2024-05-29 03:53:57.401 21372-21372 yang …...
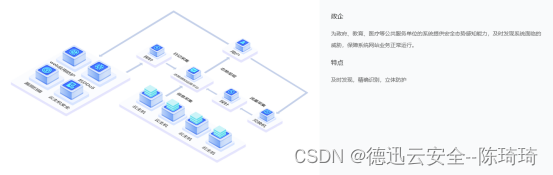
浅谈网络安全态势感知
前言 网络空间环境日趋复杂,随着网络攻击种类和频次的增加,自建强有力的网络安全防御系统成为一个国家发展战略的一部分,而网络态势感知是实现网络安全主动防御的重要基础和前提。 什么是网络安全态势感知? 态势感知一词来源于对…...
cesium本地文档-天空盒-arcgis切片404-服务查询
1.vite-plugin-cesium // vite-plugin-cesium 是一个 Vite 插件,用于在 Vite 项目中轻松集成和使用 Cesium 地图引擎。它简化了在 Vite 项目中使用 Cesium 的配置和引入过程。 // 具体来说,vite-plugin-cesium 主要提供了以下功能: // 自动…...

OpenMv图片预处理
本博客讲述的是获取一张图片首先对图像进行处理,比如畸形矫正,图像滤波等操作。 1.histeq()自适应直方图均衡 # 自适应直方图均衡例子 # # 此示例展示了如何使用自适应直方图均衡来改善图像中的对比度。 #自适应直方图均衡将图像分割成区域,然后均衡这些区域中的直方图,…...
Springboot 实战运用
一,基本配置 1,pom文件配置介绍 1.1继承 <parent><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><version>2.5.2</version><relativePath/> <…...

TDengine 快速体验(Docker 镜像方式)
简介 TDengine 可以通过安装包、Docker 镜像 及云服务快速体验 TDengine 的功能,本节首先介绍如何通过 Docker 快速体验 TDengine,然后介绍如何在 Docker 环境下体验 TDengine 的写入和查询功能。如果你不熟悉 Docker,请使用 安装包的方式快…...

DeepSeek 赋能智慧能源:微电网优化调度的智能革新路径
目录 一、智慧能源微电网优化调度概述1.1 智慧能源微电网概念1.2 优化调度的重要性1.3 目前面临的挑战 二、DeepSeek 技术探秘2.1 DeepSeek 技术原理2.2 DeepSeek 独特优势2.3 DeepSeek 在 AI 领域地位 三、DeepSeek 在微电网优化调度中的应用剖析3.1 数据处理与分析3.2 预测与…...

FFmpeg 低延迟同屏方案
引言 在实时互动需求激增的当下,无论是在线教育中的师生同屏演示、远程办公的屏幕共享协作,还是游戏直播的画面实时传输,低延迟同屏已成为保障用户体验的核心指标。FFmpeg 作为一款功能强大的多媒体框架,凭借其灵活的编解码、数据…...

Java如何权衡是使用无序的数组还是有序的数组
在 Java 中,选择有序数组还是无序数组取决于具体场景的性能需求与操作特点。以下是关键权衡因素及决策指南: ⚖️ 核心权衡维度 维度有序数组无序数组查询性能二分查找 O(log n) ✅线性扫描 O(n) ❌插入/删除需移位维护顺序 O(n) ❌直接操作尾部 O(1) ✅内存开销与无序数组相…...
python/java环境配置
环境变量放一起 python: 1.首先下载Python Python下载地址:Download Python | Python.org downloads ---windows -- 64 2.安装Python 下面两个,然后自定义,全选 可以把前4个选上 3.环境配置 1)搜高级系统设置 2…...

《Playwright:微软的自动化测试工具详解》
Playwright 简介:声明内容来自网络,将内容拼接整理出来的文档 Playwright 是微软开发的自动化测试工具,支持 Chrome、Firefox、Safari 等主流浏览器,提供多语言 API(Python、JavaScript、Java、.NET)。它的特点包括&a…...

pam_env.so模块配置解析
在PAM(Pluggable Authentication Modules)配置中, /etc/pam.d/su 文件相关配置含义如下: 配置解析 auth required pam_env.so1. 字段分解 字段值说明模块类型auth认证类模块,负责验证用户身份&am…...

生成 Git SSH 证书
🔑 1. 生成 SSH 密钥对 在终端(Windows 使用 Git Bash,Mac/Linux 使用 Terminal)执行命令: ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_emailexample.com" 参数说明: -t rsa&#x…...

【Web 进阶篇】优雅的接口设计:统一响应、全局异常处理与参数校验
系列回顾: 在上一篇中,我们成功地为应用集成了数据库,并使用 Spring Data JPA 实现了基本的 CRUD API。我们的应用现在能“记忆”数据了!但是,如果你仔细审视那些 API,会发现它们还很“粗糙”:有…...
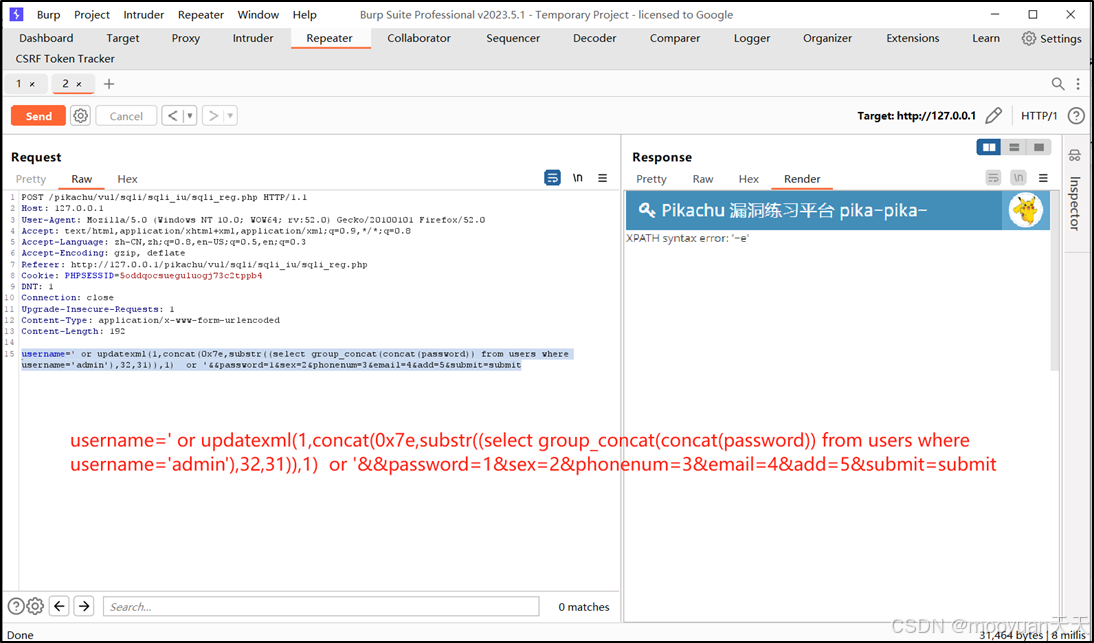
pikachu靶场通关笔记22-1 SQL注入05-1-insert注入(报错法)
目录 一、SQL注入 二、insert注入 三、报错型注入 四、updatexml函数 五、源码审计 六、insert渗透实战 1、渗透准备 2、获取数据库名database 3、获取表名table 4、获取列名column 5、获取字段 本系列为通过《pikachu靶场通关笔记》的SQL注入关卡(共10关࿰…...
