Numba 的 CUDA 示例 (2/4):穿针引线
本教程为 Numba CUDA 示例 第 2 部分。
按照本系列从头开始使用 Python 学习 CUDA 编程
介绍
在本系列的第一部分中,我们讨论了如何使用 GPU 运行高度并行算法。高度并行任务是指任务完全相互独立的任务,例如对两个数组求和或应用任何元素函数。

在本教程中
许多任务虽然不是高度并行的,但仍可从并行化中获益。在本期的CUDA by Numba Examples中,我们将介绍一些允许线程协作进行计算的常用技术。本部分的 Google colab 代码:https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1hproEOKvQyBNNxvjr0qM2LPjJWNDfyp9?usp=sharing
入门
导入并加载库,确保您有 GPU。
from time import perf_counter
import numpy as np
import numba
from numba import cudaprint(np.__version__)
print(numba.__version__)---
1.25.2
0.59.1cuda.detect()---
Found 1 CUDA devices
id 0 b'Tesla T4' [SUPPORTED]Compute Capability: 7.5PCI Device ID: 4PCI Bus ID: 0UUID: GPU-0f022a60-18f8-5de0-1f24-ad861dcd84aeWatchdog: DisabledFP32/FP64 Performance Ratio: 32
Summary:1/1 devices are supported
True
线程合作
简单并行缩减算法
我们将从一个非常简单的问题开始本节:对数组的所有元素求和。从本质上讲,这个算法非常简单。如果不借助 NumPy,我们可以将其实现为:
def sum_cpu(array):s = 0.0for i in range(array.size):s += array[i]return s
我知道,这看起来不太符合 Python 风格。但它确实强调了s跟踪数组中的所有元素。如果依赖于数组的每个元素,我们如何并行化该算法s?首先,我们需要重写算法以允许某种并行化。如果有些部分我们无法并行化,我们应该允许线程相互通信。
然而,到目前为止,我们还没有学会如何让线程相互通信……事实上,我们之前说过,不同块中的线程不会通信。我们可以考虑只启动一个块,但请记住,大多数 GPU 中的块只能有 1024 个线程!
我们如何克服这个问题?好吧,如果我们将数组拆分成 1024 个块(或适当数量的threads_per_block),然后分别对每个块求和,结果会怎样?最后,我们可以将每个块的总和结果相加。图 2.1 显示了 2 个块拆分的一个非常简单的示例。
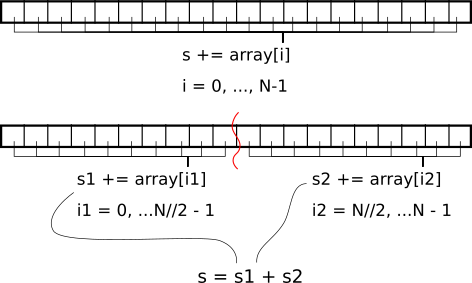
我们如何在 GPU 上做到这一点?首先,我们需要将数组拆分成块。每个块只对应一个块,具有固定数量的线程。在每个块中,每个线程可以对多个数组元素求和(网格步长循环)。然后,我们必须在整个块上计算这些每个线程的值。这部分需要线程进行通信。我们将在下一个示例中介绍如何做到这一点。
由于我们是在块上并行化,因此内核的输出应为块大小。为了完成缩减,我们将其复制到 CPU 并在那里完成作业。
threads_per_block = 1024 # Why not!
blocks_per_grid = 32 * 80 # Use 32 * multiple of streaming multiprocessors# Example 2.1: Naive reduction
@cuda.jit
def reduce_naive(array, partial_reduction):i_start = cuda.grid(1)threads_per_grid = cuda.blockDim.x * cuda.gridDim.xs_thread = 0.0for i_arr in range(i_start, array.size, threads_per_grid):s_thread += array[i_arr]# We need to create a special *shared* array which will be able to be read# from and written to by every thread in the block. Each block will have its# own shared array. See the warning below!s_block = cuda.shared.array((threads_per_block,), numba.float32)# We now store the local temporary sum of a single the thread into the# shared array. Since the shared array is sized# threads_per_block == blockDim.x# (1024 in this example), we should index it with `threadIdx.x`.tid = cuda.threadIdx.xs_block[tid] = s_thread# The next line synchronizes the threads in a block. It ensures that after# that line, all values have been written to `s_block`.cuda.syncthreads()# Finally, we need to sum the values from all threads to yield a single# value per block. We only need one thread for this.if tid == 0:# We store the sum of the elements of the shared array in its first# coordinatefor i in range(1, threads_per_block):s_block[0] += s_block[i]# Move this partial sum to the output. Only one thread is writing here.partial_reduction[cuda.blockIdx.x] = s_block[0]
⚠️ 注意 :共享数组必须
- 尽量“小”。具体大小取决于 GPU 的计算能力,通常在 48 KB 到 163 KB 之间。请参阅本表:https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-c-programming-guide/index.html#features-and-technical-specifications__technical-specifications-per-compute-capability 中的“Maximum amount of shared memory per thread block”项。
- 在编译时有一个已知的大小(这就是为什么我们要设置共享数组
threads_per_block的大小,而不是blockDim.x)。的确,我们可以为任意大小的共享数组定义一个factory function…但要注意这些内核的编译时间- 用 Numba 类型指定 dtype,而不是 Numpy 类型(别问我为什么!)。
N = 1_000_000_000
a = np.arange(N, dtype=np.float32)
a /= a.sum() # a will have sum = 1 (to float32 precision)s_cpu = a.sum()# Highly-optimized NumPy CPU code
timing_cpu = np.empty(21)
for i in range(timing_cpu.size):tic = perf_counter()a.sum()toc = perf_counter()timing_cpu[i] = toc - tic
timing_cpu *= 1e3 # convert to msprint(f"Elapsed time CPU: {timing_cpu.mean():.0f} ± {timing_cpu.std():.0f} ms")---
Elapsed time CPU: 557 ± 307 ms
dev_a = cuda.to_device(a)
dev_partial_reduction = cuda.device_array((blocks_per_grid,), dtype=a.dtype)reduce_naive[blocks_per_grid, threads_per_block](dev_a, dev_partial_reduction)
s = dev_partial_reduction.copy_to_host().sum() # Final reduction in CPUnp.isclose(s, s_cpu) # Ensure we have the right number---
True
timing_naive = np.empty(21)
for i in range(timing_naive.size):tic = perf_counter()reduce_naive[blocks_per_grid, threads_per_block](dev_a, dev_partial_reduction)s = dev_partial_reduction.copy_to_host().sum()cuda.synchronize()toc = perf_counter()assert np.isclose(s, s_cpu) timing_naive[i] = toc - tic
timing_naive *= 1e3 # convert to msprint(f"Elapsed time naive: {timing_naive.mean():.0f} ± {timing_naive.std():.0f} ms")---
Elapsed time naive: 30 ± 11 ms
我在 Google Colab 上运行了这个程序,速度提高了将近 20 倍。非常棒!
一种更好的并行缩减算法
您可能想知道为什么我们将所有内容都命名为“简单”。这意味着有一些非简单的方式来执行相同的功能。事实上,有很多技巧可以加速这种代码(请参阅 Optimizing Parallel Reduction in CUDA 演示以获取基准)。
在我们展示更好的方法之前,让我们回顾一下内核的最后一部分:
if tid == 0: # Single thread taking care of businessfor i in range(1, threads_per_block):s_block[0] += s_block[i]partial_reduction[cuda.blockIdx.x] = s_block[0]
我们几乎把所有事情都并行化了,但在内核末尾,我们让一个线程负责对共享数组 s_block 的所有 threads_per_block 元素求和。我们为什么不把这个总和也并行化呢?
听起来不错,怎么做呢?图 2.2 显示了如何实现 threads_per_block 大小为 16 的函数。我们首先运行 8 个线程,第一个线程将对 s_block[0] 和 s_block[8] 中的值求和。第二个线程对 s_block[1] 和 s_block[9] 中的值求和,直到最后一个线程将对s_block[7] 和 s_block[15] 中的值求和。
下一步,只需要前 4 个线程工作。第一个线程将计算 s_block[0] 和 s_block[4] 的总和;第二个线程将计算 s_block[1] 和 s_block[5] 的总和;第三个线程将计算 s_block[2] 和 s_block[6] 的总和;第四个线程和最后一个线程将计算 s_block[3] 和 s_block[7] 的总和。
在第三步中,我们现在只需要 2 个线程来处理 s_block的前 4 个元素。第四步也是最后一步将使用一个线程来对 2 个元素求和。
由于工作已在线程之间分配,因此它是并行的。当然,它不是由每个线程均等分配的,但这是一种改进。从计算上讲,此算法是 O(log2( threads_per_block)),而第一个算法是 O( threads_per_block)。在我们的示例中,原始算法需要 1024 次操作,而改进算法只需要 10 次!
最后还有一个细节。在每一步中,我们都需要确保所有线程都已写入共享数组。所以我们必须调用cuda.syncthreads()。
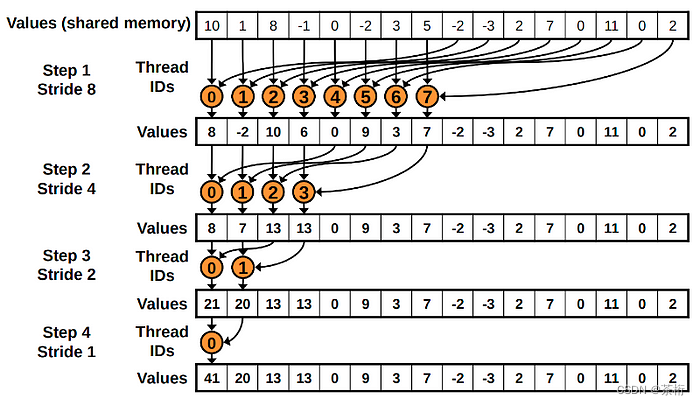
来源:Mark Harris,Optimizing Parallel Reduction in CUDA.
# Example 2.2: Better reduction
@cuda.jit
def reduce_better(array, partial_reduction):i_start = cuda.grid(1)threads_per_grid = cuda.blockDim.x * cuda.gridDim.xs_thread = 0.0for i_arr in range(i_start, array.size, threads_per_grid):s_thread += array[i_arr]# We need to create a special *shared* array which will be able to be read# from and written to by every thread in the block. Each block will have its# own shared array. See the warning below!s_block = cuda.shared.array((threads_per_block,), numba.float32)# We now store the local temporary sum of the thread into the shared array.# Since the shared array is sized threads_per_block == blockDim.x,# we should index it with `threadIdx.x`.tid = cuda.threadIdx.xs_block[tid] = s_thread# The next line synchronizes the threads in a block. It ensures that after# that line, all values have been written to `s_block`.cuda.syncthreads()i = cuda.blockDim.x // 2while (i > 0):if (tid < i):s_block[tid] += s_block[tid + i]cuda.syncthreads()i //= 2if tid == 0:partial_reduction[cuda.blockIdx.x] = s_block[0]reduce_better[blocks_per_grid, threads_per_block](dev_a, dev_partial_reduction)
s = dev_partial_reduction.copy_to_host().sum() # Final reduction in CPUnp.isclose(s, s_cpu)---
True
timing_naive = np.empty(21)
for i in range(timing_naive.size):tic = perf_counter()reduce_better[blocks_per_grid, threads_per_block](dev_a, dev_partial_reduction)s = dev_partial_reduction.copy_to_host().sum()cuda.synchronize()toc = perf_counter()assert np.isclose(s, s_cpu) timing_naive[i] = toc - tic
timing_naive *= 1e3 # convert to msprint(f"Elapsed time better: {timing_naive.mean():.0f} ± {timing_naive.std():.0f} ms")---
Elapsed time better: 23 ± 1 ms
在 Google Colab 上,这比简单方法快约 30%。
⚠️ 注意:你可能会想把
syncthreads移到if块内部,因为每一步之后,超过当前线程数一半的内核将不会被使用。但是,这样做会让调用syncthreads的 CUDA 线程停止并等待其他线程,而其他线程则会继续运行。因此,停止的线程将永远等待永远不会停止同步的线程。这给我们的启示是:如果要同步线程,请确保所有线程都调用了cuda.syncthreads()。
i = cuda.blockDim.x // 2
while (i > 0): if (tid < i): s_block[tid] += s_block[tid + i] cuda.syncthreads() # 不要放在这里cuda.syncthreads() # 而不是这里i //= 2
减少 Numba
由于上述缩减算法并不简单,Numba 提供了一个便捷cuda.reduce装饰器,可将二元函数转换为缩减算法。上面的长而复杂的算法可以用以下方法替代:
# Example 2.3: Numba reduction
@cuda.reduce
def reduce_numba(a, b):return a + b# Compile and check
s = reduce_numba(dev_a)np.isclose(s, s_cpu)---
True
# Time
timing_numba = np.empty(21)
for i in range(timing_numba.size):tic = perf_counter()s = reduce_numba(dev_a)toc = perf_counter()assert np.isclose(s, s_cpu) timing_numba[i] = toc - tic
timing_numba *= 1e3 # convert to msprint(f"Elapsed time better: {timing_numba.mean():.0f} ± {timing_numba.std():.0f} ms")---
Elapsed time better: 20 ± 0 ms
就我个人而言,我发现手写缩减通常要快得多(至少快 2 倍),但 Numba 递归非常容易使用。话虽如此,我还是鼓励大家阅读 reduction code in the Numba source code.
还需要注意的是,默认情况下,reduction 会复制到主机,这会强制同步。为了避免这种情况,您可以使用设备数组作为输出来调用 Reduce:
dev_s = cuda.device_array((1,), dtype=s)reduce_numba(dev_a, res=dev_s)s = dev_s.copy_to_host()[0]
np.isclose(s, s_cpu)---
True
2D 缩减示例
并行缩减技术很棒,但如何将其扩展到更高维度并不明显。虽然我们总是可以使用解开的数组 ( array2d.ravel()) 来调用 Numba 缩减,但了解如何手动缩减多维数组非常重要。
在这个例子中,我们将结合所学的关于 2D 内核的知识和所学的关于 1D 缩减的知识来计算 2D 缩减。
threads_per_block_2d = (16, 16) # 256 threads total
blocks_per_grid_2d = (64, 64)# Total number of threads in a 2D block (has to be an int)
shared_array_len = int(np.prod(threads_per_block_2d))# Example 2.4: 2D reduction with 1D shared array
@cuda.jit
def reduce2d(array2d, partial_reduction2d):ix, iy = cuda.grid(2)threads_per_grid_x, threads_per_grid_y = cuda.gridsize(2)s_thread = 0.0for i0 in range(iy, array2d.shape[0], threads_per_grid_x):for i1 in range(ix, array2d.shape[1], threads_per_grid_y):s_thread += array2d[i0, i1]# Allocate shared arrays_block = cuda.shared.array(shared_array_len, numba.float32)# Index the threads linearly: each tid identifies a unique thread in the# 2D grid.tid = cuda.threadIdx.x + cuda.blockDim.x * cuda.threadIdx.ys_block[tid] = s_threadcuda.syncthreads()# We can use the same smart reduction algorithm by remembering that# shared_array_len == blockDim.x * cuda.blockDim.y# So we just need to start our indexing accordingly.i = (cuda.blockDim.x * cuda.blockDim.y) // 2while (i != 0):if (tid < i):s_block[tid] += s_block[tid + i]cuda.syncthreads()i //= 2# Store reduction in a 2D array the same size as the 2D blocksif tid == 0:partial_reduction2d[cuda.blockIdx.x, cuda.blockIdx.y] = s_block[0]N_2D = (20_000, 20_000)
a_2d = np.arange(np.prod(N_2D), dtype=np.float32).reshape(N_2D)
a_2d /= a_2d.sum() # a_2d will have sum = 1 (to float32 precision)s_2d_cpu = a_2d.sum()dev_a_2d = cuda.to_device(a_2d)
dev_partial_reduction_2d = cuda.device_array(blocks_per_grid_2d, dtype=a.dtype)reduce2d[blocks_per_grid_2d, threads_per_block_2d](dev_a_2d, dev_partial_reduction_2d)
s_2d = dev_partial_reduction_2d.copy_to_host().sum() # Final reduction in CPUnp.isclose(s_2d, s_2d_cpu) # Ensure we have the right number---
True
timing_2d = np.empty(21)
for i in range(timing_2d.size):tic = perf_counter()reduce2d[blocks_per_grid_2d, threads_per_block_2d](dev_a_2d, dev_partial_reduction_2d)s_2d = dev_partial_reduction_2d.copy_to_host().sum()cuda.synchronize()toc = perf_counter()assert np.isclose(s_2d, s_2d_cpu) timing_2d[i] = toc - tic
timing_2d *= 1e3 # convert to msprint(f"Elapsed time better: {timing_2d.mean():.0f} ± {timing_2d.std():.0f} ms")---
Elapsed time better: 11 ± 0 ms
设备功能
到目前为止,我们只讨论了内核,它们是启动线程的特殊 GPU 函数。内核通常依赖于在 GPU 中定义的较小函数,这些函数只能访问 GPU 数组。这些被称为设备函数。与内核不同的是,它们可以返回值。
为了结束本部分教程,我们将展示一个跨不同内核使用设备函数的示例。该示例还将强调在使用共享数组时同步线程的重要性。
注意:在较新版本的 CUDA 中,内核可以启动其他内核。这称为动态并行,Numba CUDA 尚不支持。*
2D 共享数组示例
在此示例中,我们将在固定大小的数组中创建波纹图案。我们首先需要声明将使用的线程数,因为这是共享数组所需的。
threads_16 = 16import math@cuda.jit(device=True, inline=True) # inlining can speed up execution
def amplitude(ix, iy):return (1 + math.sin(2 * math.pi * (ix - 64) / 256)) * (1 + math.sin(2 * math.pi * (iy - 64) / 256))# Example 2.5a: 2D Shared Array
@cuda.jit
def blobs_2d(array2d):ix, iy = cuda.grid(2)tix, tiy = cuda.threadIdx.x, cuda.threadIdx.yshared = cuda.shared.array((threads_16, threads_16), numba.float32)shared[tiy, tix] = amplitude(iy, ix)cuda.syncthreads()array2d[iy, ix] = shared[15 - tiy, 15 - tix]# Example 2.5b: 2D Shared Array without synchronize
@cuda.jit
def blobs_2d_wrong(array2d):ix, iy = cuda.grid(2)tix, tiy = cuda.threadIdx.x, cuda.threadIdx.yshared = cuda.shared.array((threads_16, threads_16), numba.float32)shared[tiy, tix] = amplitude(iy, ix)# When we don't sync threads, we may have not written to shared# yet, or even have overwritten it by the time we write to array2darray2d[iy, ix] = shared[15 - tiy, 15 - tix]N_img = 1024
blocks = (N_img // threads_16, N_img // threads_16)
threads = (threads_16, threads_16)dev_image = cuda.device_array((N_img, N_img), dtype=np.float32)
dev_image_wrong = cuda.device_array((N_img, N_img), dtype=np.float32)blobs_2d[blocks, threads](dev_image)
blobs_2d_wrong[blocks, threads](dev_image_wrong)image = dev_image.copy_to_host()
image_wrong = dev_image_wrong.copy_to_host()import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax1.imshow(image.T, cmap="nipy_spectral")
ax2.imshow(image_wrong.T, cmap="nipy_spectral")
for ax in (ax1, ax2):ax.set_xticks([])ax.set_yticks([])ax.set_xticklabels([])ax.set_yticklabels([])
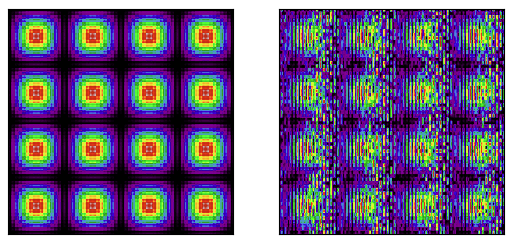
结论
在本教程中,您学习了如何开发需要缩减模式来处理一维和二维数组的内核。在此过程中,我们学习了如何利用共享数组和设备功能。
相关文章:

Numba 的 CUDA 示例 (2/4):穿针引线
本教程为 Numba CUDA 示例 第 2 部分。 按照本系列从头开始使用 Python 学习 CUDA 编程 介绍 在本系列的第一部分中,我们讨论了如何使用 GPU 运行高度并行算法。高度并行任务是指任务完全相互独立的任务,例如对两个数组求和或应用任何元素函数。 在本教…...

项目的各个阶段如何编写标准的Git commit消息
标准提交消息格式 一个标准的提交消息应包括三部分:标题(summary)、正文(description)和脚注(footer)。 1. 标题(Summary) 简洁明了,不超过50个字符。使用…...
Python课设-学生信息管理系统
一、效果展示图 二、前端代码 1、HTML代码 <1>index.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang"en"><head><meta charset"UTF-8"><meta name"viewport" content"widthdevice-width, initial-scale1.0">…...

openssl 常用命令demo
RSA Private Key的结构(ASN.1) RSAPrivateKey :: SEQUENCE { version Version, modulus INTEGER, -- n publicExponent INTEGER, -- e privateExponent INTEGER, -- d prime1 INTEGER, -- …...

【Linux】Linux基本指令2
目录 1.man指令(重要): 2.echo指令 3.cp指令(重要): 4.mv指令 5.cat指令/echo指令重定向 6.more指令 7.less指令(重要) 8.head指令 9.tail指令 我们接着上一篇:h…...

springboot+vue+mybatis博物馆售票系统+PPT+论文+讲解+售后
如今社会上各行各业,都喜欢用自己行业的专属软件工作,互联网发展到这个时候,人们已经发现离不开了互联网。新技术的产生,往往能解决一些老技术的弊端问题。因为传统博物馆售票系统信息管理难度大,容错率低,…...
java—MyBatis框架
简介 什么是 MyBatis? MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持自定义 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 免除了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码以及设置参数和获取结果集的工作。MyBatis 可以通过简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原始类型、接口和 Java POJO&…...

如何使用Spring Cache优化后端接口?
Spring Cache是Spring框架提供的一种缓存抽象,它可以很方便地集成到应用程序中,用于提高接口的性能和响应速度。使用Spring Cache可以避免重复执行耗时的方法,并且还可以提供一个统一的缓存管理机制,简化缓存的配置和管理。 本文将详细介绍如何使用Spring Cache来优化接口,…...

大话C语言:第21篇 数组
1 数组概述 数组是若干个相同类型的变量在内存中有序存储的集合。 数组是 C 语言中的一种数据结构,用于存储一组具有相同数据类型的数据。 数组在内存中会开辟一块连续的空间 数组中的每个元素可以通过一个索引(下标)来访问,索…...

transfomer中attention为什么要除以根号d_k
简介 得到矩阵 Q, K, V之后就可以计算出 Self-Attention 的输出了,计算的公式如下: A t t e n t i o n ( Q , K , V ) S o f t m a x ( Q K T d k ) V Attention(Q,K,V)Softmax(\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d_k}})V Attention(Q,K,V)Softmax(dk QKT)V 好处 除以维…...
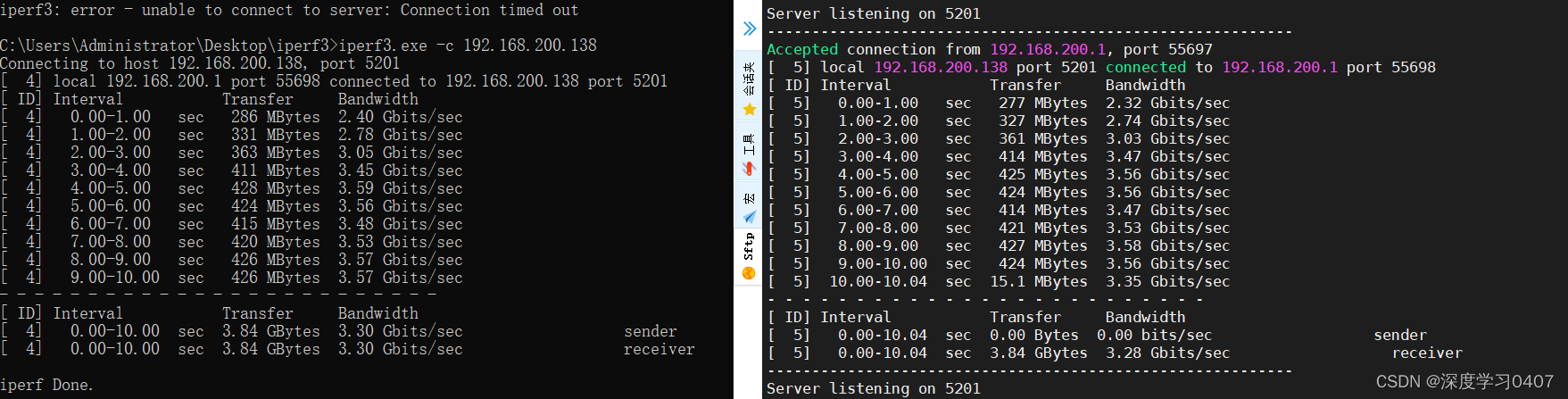
iperf3带宽压测工具使用
iperf3带宽压测工具使用 安装下载地址:[下载入口](https://iperf.fr/iperf-download.php)测试结果:时长测试(压测使用):并行测试反向测试UDP 带宽测试 iPerf3 是用于主动测试 IP 网络上最大可用带宽的工具 安装 下载地址&#x…...

[数据集][目标检测]焊接处缺陷检测数据集VOC+YOLO格式3400张8类别
数据集格式:Pascal VOC格式YOLO格式(不包含分割路径的txt文件,仅仅包含jpg图片以及对应的VOC格式xml文件和yolo格式txt文件) 图片数量(jpg文件个数):3400 标注数量(xml文件个数):3400 标注数量(txt文件个数):3400 标注…...
)
2024华为OD机试真题-剩余银饰的重量-C++(C卷D卷)
题目描述 有 N 块二手市场收集的银饰,每块银饰的重量都是正整数,收集到的银饰会被熔化用于打造新的饰品。 每一回合,从中选出三块 最重的 银饰,然后一起熔掉。假设银饰的重量分别为 x 、y 和 z, 且 x <= y <= z。那么熔掉的可能结果如下: 如果x == y == z,那么三…...

糖果促销【百度之星】/思维
糖果促销 思维 大佬的解法: #include<bits/stdc.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; int main() {ll t;cin>>t;for(int i0;i<t;i){ll p,k;cin>>p>>k;if(k0) cout<<0<<endl;else{k-(k-1)/p;cout<<k<…...
【python学习】安装Anaconda后,如何进行环境管理(命令行操作及图形化操作Anaconda Navigator)及包管理
命令行的方式 首先,打开 Anaconda Powershell Prompt 环境查看 使用以下命令查看当前所有环境: conda env list目前只有一个 base环境,就是安装 anaconda的时候选择的。 光标在闪烁,目前已经进入 base 环境模式: …...

HTML大雪纷飞
目录 写在前面 HTML简介 完整代码 代码分析 运行结果 系列文章 写在后面 写在前面 小编又又又出现啦!这次小编给大家带来大雪纷飞HTML版,不需要任何的环境,只要有一个浏览器,就可以随时随地下一场大雪哦! HTM…...

问界新M7 Ultra仅售28.98万元起,上市即交付
5月31日,问界新M7 Ultra正式上市。发布会上,鸿蒙智行旗下多款产品交出最新答卷——问界新M5上市1个月大定突破2万台;智界S7位列30万纯电轿车4月交付量NO.3;问界M9上市5个月大定突破9万台。其中,作为中国高端豪华SUV市场…...
【Java数据结构】详解LinkedList与链表(四)
🔒文章目录: 1.❤️❤️前言~🥳🎉🎉🎉 2.什么是LinkedList 3.LinkedList的使用 3.1LinkedList的构造方法 3.2LinkedList的其他常用方法介绍 addAll方法 subList方法 LinkedList的常用方法总使…...
ssm汉服文化平台网站
博主介绍:✌程序员徐师兄、8年大厂程序员经历。全网粉丝15w、csdn博客专家、掘金/华为云/阿里云/InfoQ等平台优质作者、专注于Java技术领域和毕业项目实战✌ 🍅文末获取源码联系🍅 👇🏻 精彩专栏推荐订阅👇…...

如何让 LightRoom 每次导入照片后不自动弹出 SD 卡 LR
如何让 LightRoom 每次导入照片后不自动弹出 SD 卡 LR 在导入窗口左上角有个选项: 导入后弹出 把这个去掉就可以了...

Vim 调用外部命令学习笔记
Vim 外部命令集成完全指南 文章目录 Vim 外部命令集成完全指南核心概念理解命令语法解析语法对比 常用外部命令详解文本排序与去重文本筛选与搜索高级 grep 搜索技巧文本替换与编辑字符处理高级文本处理编程语言处理其他实用命令 范围操作示例指定行范围处理复合命令示例 实用技…...
)
云计算——弹性云计算器(ECS)
弹性云服务器:ECS 概述 云计算重构了ICT系统,云计算平台厂商推出使得厂家能够主要关注应用管理而非平台管理的云平台,包含如下主要概念。 ECS(Elastic Cloud Server):即弹性云服务器,是云计算…...
)
椭圆曲线密码学(ECC)
一、ECC算法概述 椭圆曲线密码学(Elliptic Curve Cryptography)是基于椭圆曲线数学理论的公钥密码系统,由Neal Koblitz和Victor Miller在1985年独立提出。相比RSA,ECC在相同安全强度下密钥更短(256位ECC ≈ 3072位RSA…...
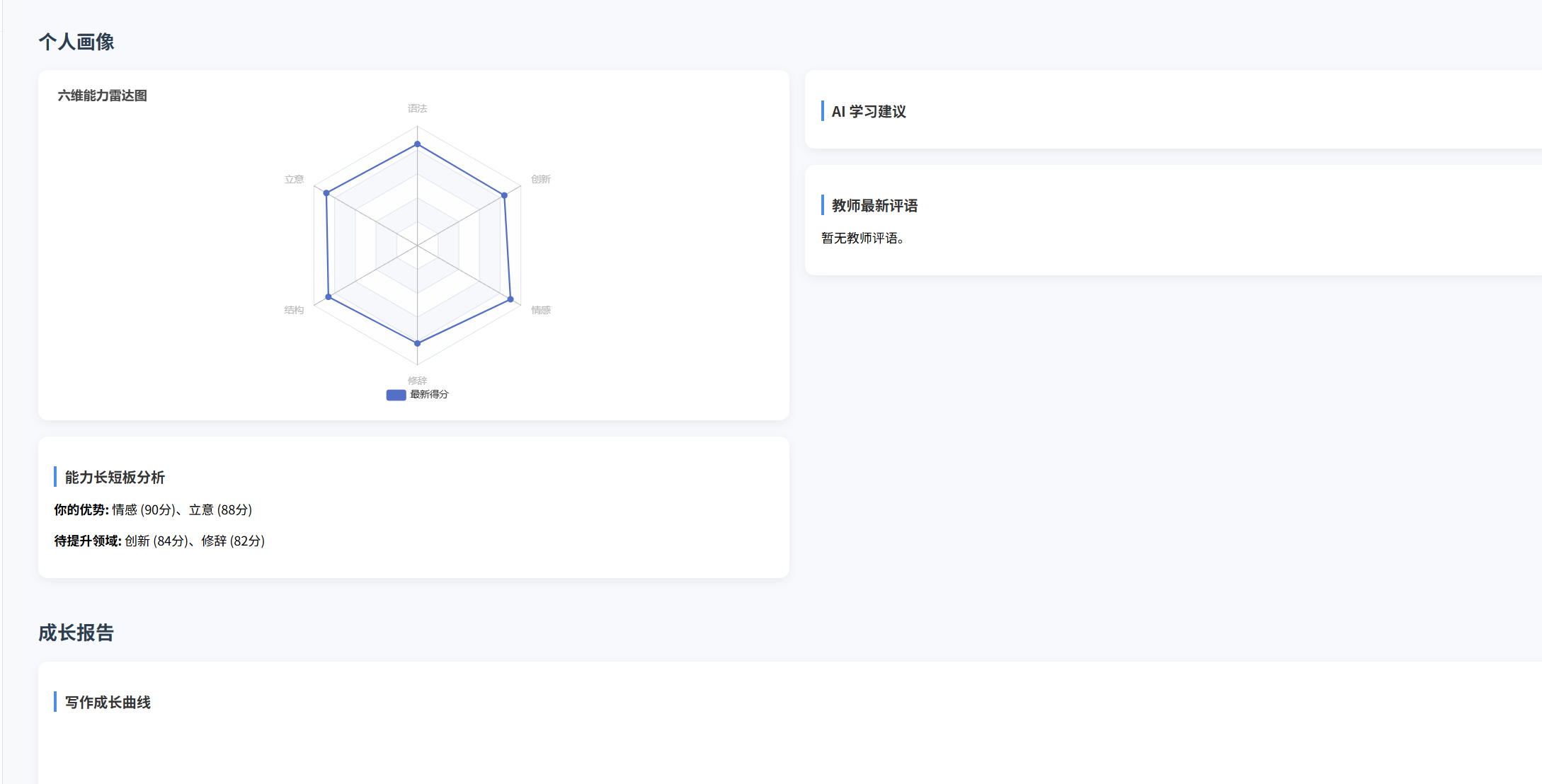
(十)学生端搭建
本次旨在将之前的已完成的部分功能进行拼装到学生端,同时完善学生端的构建。本次工作主要包括: 1.学生端整体界面布局 2.模拟考场与部分个人画像流程的串联 3.整体学生端逻辑 一、学生端 在主界面可以选择自己的用户角色 选择学生则进入学生登录界面…...
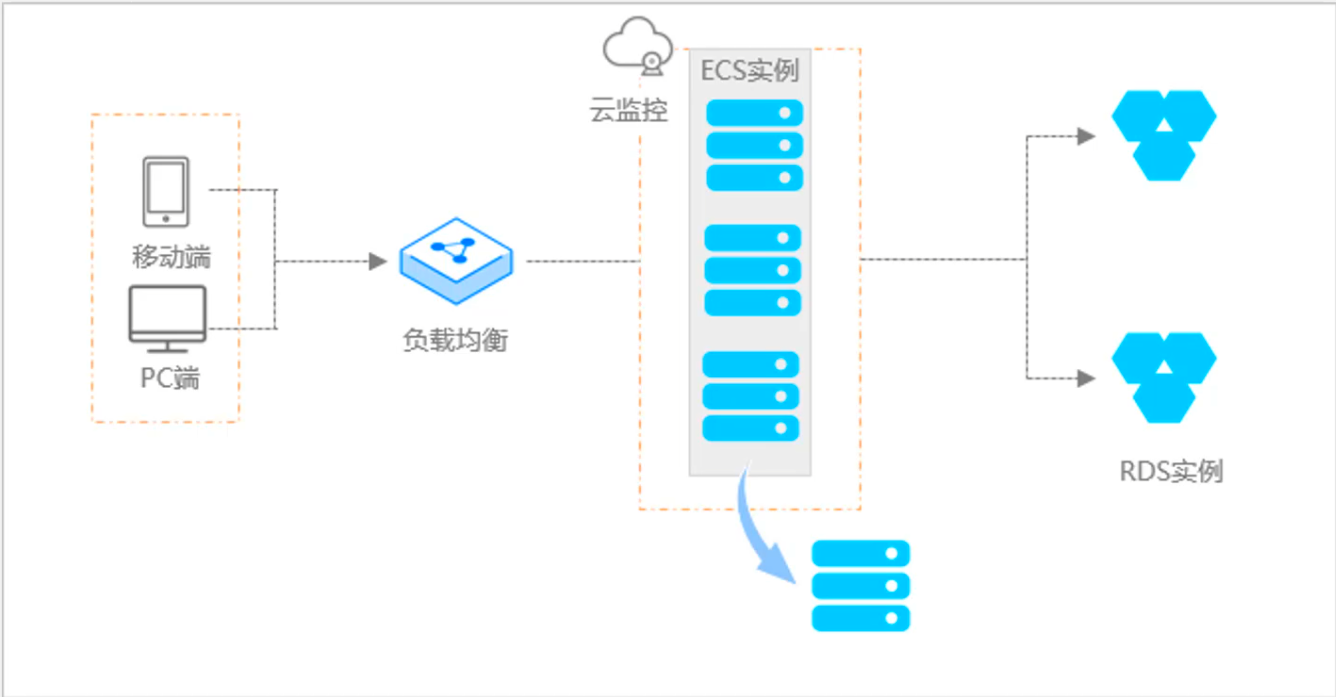
阿里云ACP云计算备考笔记 (5)——弹性伸缩
目录 第一章 概述 第二章 弹性伸缩简介 1、弹性伸缩 2、垂直伸缩 3、优势 4、应用场景 ① 无规律的业务量波动 ② 有规律的业务量波动 ③ 无明显业务量波动 ④ 混合型业务 ⑤ 消息通知 ⑥ 生命周期挂钩 ⑦ 自定义方式 ⑧ 滚的升级 5、使用限制 第三章 主要定义 …...

Java 8 Stream API 入门到实践详解
一、告别 for 循环! 传统痛点: Java 8 之前,集合操作离不开冗长的 for 循环和匿名类。例如,过滤列表中的偶数: List<Integer> list Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); List<Integer> evens new ArrayList…...
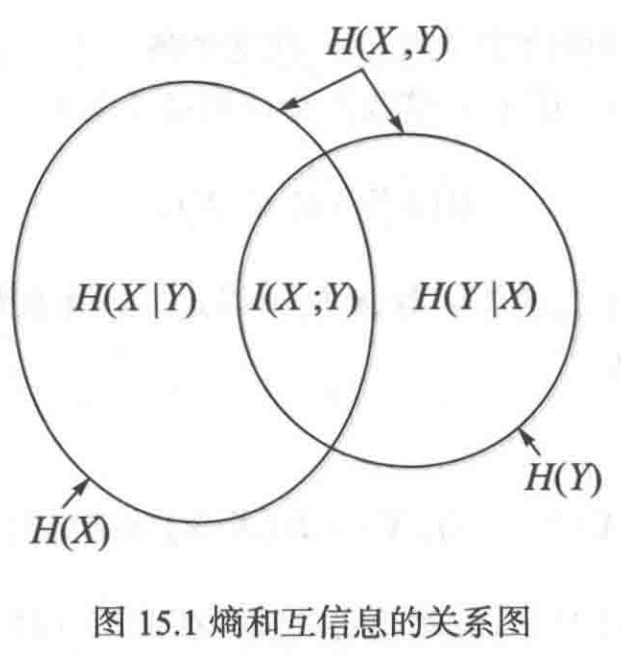
《通信之道——从微积分到 5G》读书总结
第1章 绪 论 1.1 这是一本什么样的书 通信技术,说到底就是数学。 那些最基础、最本质的部分。 1.2 什么是通信 通信 发送方 接收方 承载信息的信号 解调出其中承载的信息 信息在发送方那里被加工成信号(调制) 把信息从信号中抽取出来&am…...
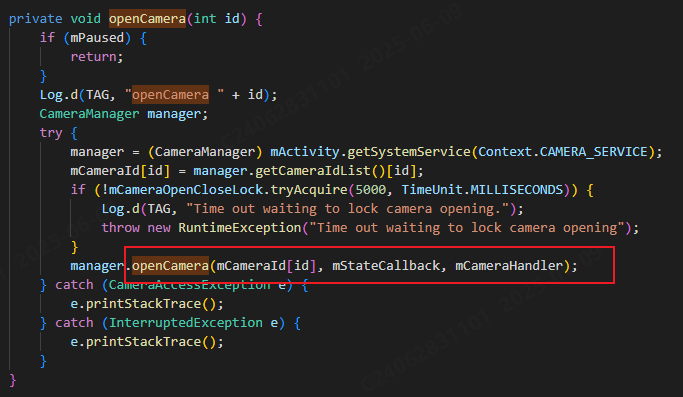
相机从app启动流程
一、流程框架图 二、具体流程分析 1、得到cameralist和对应的静态信息 目录如下: 重点代码分析: 启动相机前,先要通过getCameraIdList获取camera的个数以及id,然后可以通过getCameraCharacteristics获取对应id camera的capabilities(静态信息)进行一些openCamera前的…...

Linux云原生安全:零信任架构与机密计算
Linux云原生安全:零信任架构与机密计算 构建坚不可摧的云原生防御体系 引言:云原生安全的范式革命 随着云原生技术的普及,安全边界正在从传统的网络边界向工作负载内部转移。Gartner预测,到2025年,零信任架构将成为超…...

tree 树组件大数据卡顿问题优化
问题背景 项目中有用到树组件用来做文件目录,但是由于这个树组件的节点越来越多,导致页面在滚动这个树组件的时候浏览器就很容易卡死。这种问题基本上都是因为dom节点太多,导致的浏览器卡顿,这里很明显就需要用到虚拟列表的技术&…...
