LiveData是如何感知Room数据变化的
一 Room数据变化LiveData如何收到onChanged回调的?
1.1 LiveData是如何创建的
这里讨论的LiveData的创建是特指Dao定义的方法的返回类型,而不是所有的LiveData。
以NoteDao 举例:
@Dao
public interface NoteDao {@Query("select * from note")LiveData<List<EntityNote>> getAll();@Updateint update(EntityNote note);@Deleteint delete(EntityNote note);@Insertvoid insert(EntityNote note);
}
Room会通过APT自动为NoteDao 创建实体类NoteDao_Impl.java
package com.example.sourcecode.jetpack.dao;import android.database.Cursor;
import androidx.lifecycle.LiveData;
import androidx.room.EntityDeletionOrUpdateAdapter;
import androidx.room.EntityInsertionAdapter;
import androidx.room.RoomDatabase;
import androidx.room.RoomSQLiteQuery;
import androidx.room.util.CursorUtil;
import androidx.room.util.DBUtil;
import androidx.sqlite.db.SupportSQLiteStatement;
import com.example.sourcecode.jetpack.entity.EntityNote;
import java.lang.Class;
import java.lang.Exception;
import java.lang.Override;
import java.lang.String;
import java.lang.SuppressWarnings;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "deprecation"})
public final class NoteDao_Impl implements NoteDao {private final RoomDatabase __db;private final EntityInsertionAdapter<EntityNote> __insertionAdapterOfEntityNote;private final EntityDeletionOrUpdateAdapter<EntityNote> __deletionAdapterOfEntityNote;private final EntityDeletionOrUpdateAdapter<EntityNote> __updateAdapterOfEntityNote;public NoteDao_Impl(RoomDatabase __db) {this.__db = __db;this.__insertionAdapterOfEntityNote = new EntityInsertionAdapter<EntityNote>(__db) {@Overridepublic String createQuery() {return "INSERT OR ABORT INTO `note` (`id`,`uuid`,`title`,`content`,`searchContent`) VALUES (nullif(?, 0),?,?,?,?)";}@Overridepublic void bind(SupportSQLiteStatement stmt, EntityNote value) {stmt.bindLong(1, value.id);if (value.uuid == null) {stmt.bindNull(2);} else {stmt.bindString(2, value.uuid);}if (value.title == null) {stmt.bindNull(3);} else {stmt.bindString(3, value.title);}if (value.content == null) {stmt.bindNull(4);} else {stmt.bindString(4, value.content);}if (value.searchContent == null) {stmt.bindNull(5);} else {stmt.bindString(5, value.searchContent);}}};this.__deletionAdapterOfEntityNote = new EntityDeletionOrUpdateAdapter<EntityNote>(__db) {@Overridepublic String createQuery() {return "DELETE FROM `note` WHERE `id` = ?";}@Overridepublic void bind(SupportSQLiteStatement stmt, EntityNote value) {stmt.bindLong(1, value.id);}};this.__updateAdapterOfEntityNote = new EntityDeletionOrUpdateAdapter<EntityNote>(__db) {@Overridepublic String createQuery() {return "UPDATE OR ABORT `note` SET `id` = ?,`uuid` = ?,`title` = ?,`content` = ?,`searchContent` = ? WHERE `id` = ?";}@Overridepublic void bind(SupportSQLiteStatement stmt, EntityNote value) {stmt.bindLong(1, value.id);if (value.uuid == null) {stmt.bindNull(2);} else {stmt.bindString(2, value.uuid);}if (value.title == null) {stmt.bindNull(3);} else {stmt.bindString(3, value.title);}if (value.content == null) {stmt.bindNull(4);} else {stmt.bindString(4, value.content);}if (value.searchContent == null) {stmt.bindNull(5);} else {stmt.bindString(5, value.searchContent);}stmt.bindLong(6, value.id);}};}@Overridepublic void insert(final EntityNote note) {__db.assertNotSuspendingTransaction();__db.beginTransaction();try {__insertionAdapterOfEntityNote.insert(note);__db.setTransactionSuccessful();} finally {__db.endTransaction();}}@Overridepublic int delete(final EntityNote note) {__db.assertNotSuspendingTransaction();int _total = 0;__db.beginTransaction();try {_total +=__deletionAdapterOfEntityNote.handle(note);__db.setTransactionSuccessful();return _total;} finally {__db.endTransaction();}}@Overridepublic int update(final EntityNote note) {__db.assertNotSuspendingTransaction();int _total = 0;__db.beginTransaction();try {_total +=__updateAdapterOfEntityNote.handle(note);__db.setTransactionSuccessful();return _total;} finally {__db.endTransaction();}}@Overridepublic LiveData<List<EntityNote>> getAll() {final String _sql = "select * from note";final RoomSQLiteQuery _statement = RoomSQLiteQuery.acquire(_sql, 0);return __db.getInvalidationTracker().createLiveData(new String[]{"note"}, false, new Callable<List<EntityNote>>() {@Overridepublic List<EntityNote> call() throws Exception {final Cursor _cursor = DBUtil.query(__db, _statement, false, null);try {final int _cursorIndexOfId = CursorUtil.getColumnIndexOrThrow(_cursor, "id");final int _cursorIndexOfUuid = CursorUtil.getColumnIndexOrThrow(_cursor, "uuid");final int _cursorIndexOfTitle = CursorUtil.getColumnIndexOrThrow(_cursor, "title");final int _cursorIndexOfContent = CursorUtil.getColumnIndexOrThrow(_cursor, "content");final int _cursorIndexOfSearchContent = CursorUtil.getColumnIndexOrThrow(_cursor, "searchContent");final List<EntityNote> _result = new ArrayList<EntityNote>(_cursor.getCount());while(_cursor.moveToNext()) {final EntityNote _item;_item = new EntityNote();_item.id = _cursor.getInt(_cursorIndexOfId);if (_cursor.isNull(_cursorIndexOfUuid)) {_item.uuid = null;} else {_item.uuid = _cursor.getString(_cursorIndexOfUuid);}if (_cursor.isNull(_cursorIndexOfTitle)) {_item.title = null;} else {_item.title = _cursor.getString(_cursorIndexOfTitle);}if (_cursor.isNull(_cursorIndexOfContent)) {_item.content = null;} else {_item.content = _cursor.getString(_cursorIndexOfContent);}if (_cursor.isNull(_cursorIndexOfSearchContent)) {_item.searchContent = null;} else {_item.searchContent = _cursor.getString(_cursorIndexOfSearchContent);}_result.add(_item);}return _result;} finally {_cursor.close();}}@Overrideprotected void finalize() {_statement.release();}});}public static List<Class<?>> getRequiredConverters() {return Collections.emptyList();}
}
通过InvalidationTracker#createLiveData方法创建需要返回的LiveData对象。
// InvalidationTracker.javapublic <T> LiveData<T> createLiveData(String[] tableNames, Callable<T> computeFunction) {return createLiveData(tableNames, false, computeFunction);
}public <T> LiveData<T> createLiveData(String[] tableNames, boolean inTransaction,Callable<T> computeFunction) {return mInvalidationLiveDataContainer.create(validateAndResolveTableNames(tableNames), inTransaction, computeFunction);
}// InvalidationLiveDataContainer.java<T> LiveData<T> create(String[] tableNames, boolean inTransaction,Callable<T> computeFunction) {return new RoomTrackingLiveData<>(mDatabase, this, inTransaction, computeFunction,tableNames);
}InvalidationLiveDataContainer的功能比较简单:
- 创建
RoomTrackingLiveData对象; - 维护一个装载
LiveData对象的set集合。
总结:
- room会根据开发者定义的dataBae和各个dao类自动创建各自的对应的实体类;
- DAO_Impl的实体方法会委托InvalidationTracker类创建需要返回的LiveData对象,并将数据库操作方法以参数的形式向下传递。
- InvalidationTracker类委托InvalidationLiveDataContainer类创建RoomTrackingLiveData对象。自此LiveData对象创建成功。
1.2 RoomTrackingLiveData有何作用
class RoomTrackingLiveData<T> extends LiveData<T> {final RoomDatabase mDatabase;final boolean mInTransaction;final Callable<T> mComputeFunction;private final InvalidationLiveDataContainer mContainer;final InvalidationTracker.Observer mObserver;final AtomicBoolean mInvalid = new AtomicBoolean(true);final AtomicBoolean mComputing = new AtomicBoolean(false);final AtomicBoolean mRegisteredObserver = new AtomicBoolean(false);final Runnable mRefreshRunnable = new Runnable() {@WorkerThread@Overridepublic void run() {// 向InvalidationTracker注册一个观察者if (mRegisteredObserver.compareAndSet(false, true)) {mDatabase.getInvalidationTracker().addWeakObserver(mObserver);}boolean computed;do {computed = false;// mComputing 初始值为 falseif (mComputing.compareAndSet(false, true)) {// as long as it is invalid, keep computing.try {T value = null;// mInvalid初始值为 true// 此while循环结束后,computed == false,mInvalid == falsewhile (mInvalid.compareAndSet(true, false)) {computed = true;try {// 执行数据库操作方法,并返回结果value = mComputeFunction.call();} catch (Exception e) {// 如果SQL语句执行有误,会非常粗暴的直接报错,// liveData不能将错误状态上报给开发者。throw new RuntimeException("Exception while computing database"+ " live data.", e);}}if (computed) {// 向当前livedata的观察者们发送数据库查询结果postValue(value);}} finally {// release compute lockmComputing.set(false);}}} while (computed && mInvalid.get());}};@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")final Runnable mInvalidationRunnable = new Runnable() {@MainThread@Overridepublic void run() {// 当前livedata是否有存活的观察者boolean isActive = hasActiveObservers();// 如果 mRefreshRunnable正在运行 mInvalid == true,条件不成立。// 如果 mRefreshRunnable运行结束 mInvalid == false,条件成立,重新开启任务。if (mInvalid.compareAndSet(false, true)) {if (isActive) {getQueryExecutor().execute(mRefreshRunnable);}}}};@SuppressLint("RestrictedApi")RoomTrackingLiveData(RoomDatabase database,InvalidationLiveDataContainer container,boolean inTransaction,Callable<T> computeFunction,String[] tableNames) {mDatabase = database;mInTransaction = inTransaction;mComputeFunction = computeFunction;mContainer = container;mObserver = new InvalidationTracker.Observer(tableNames) {@Overridepublic void onInvalidated(@NonNull Set<String> tables) {ArchTaskExecutor.getInstance().executeOnMainThread(mInvalidationRunnable);}};}@Overrideprotected void onActive() {super.onActive();mContainer.onActive(this);getQueryExecutor().execute(mRefreshRunnable);}@Overrideprotected void onInactive() {super.onInactive();mContainer.onInactive(this);}Executor getQueryExecutor() {if (mInTransaction) {return mDatabase.getTransactionExecutor();} else {return mDatabase.getQueryExecutor();}}
}- 当开发者向
RoomTrackingLiveData注册了观察者后(即调用了livedata.observe方法),会调用onActive方法,在子线程里执行mRefreshRunnable任务。 mRefreshRunnable在初次执行时会向InvalidationTracker注册一个观察者。然后会根据SQL语句循环查询数据库,并向开发者返回查询结果。
a. SQL语句是通过开发者在创建DAO层方法的注解自动生成的,并以方法入参的方式最终传递给RoomTrackingLiveData对象。
b. 这里的循环不是一直执行的。在没有外界干扰情况下(指循环条件的值在没有被其他方法修改的情况),循环体只会执行一次。- 构造函数里创建了
mObserver对象,当mObserver被触发时,会在主线程执行mInvalidationRunnable任务。 mInvalidationRunnable会在子线程里开启mRefreshRunnable任务,重新查询数据库,并返回数据。
总结:
RoomTrackingLiveData有三个比较重要的任务:mRefreshRunnable、mInvalidationRunnable和mObserver。mRefreshRunnable主要负责向数据库查询数据,并将结果返回给开发者注册的观察者。mObserver负责唤醒mInvalidationRunnable。mInvalidationRunnable任务分两种情况:- 当
mRefreshRunnable还在运行时,会要求mRefreshRunnable再执行一次数据库查询任务,并按要求将结果上报。(这个逻辑是在mRefreshRunnable里实现的。) - 当
mRefreshRunnable停止运行时,会在子线程里重新开启mRefreshRunnable任务。
- 当
由上可知,room配合livedata使用时,之所以livedata能够自动感知数据库数据变化,是由
mObserver、mInvalidationRunnable、mRefreshRunnable三方共同配合的结果。
1.3 数据库变化时,是如何通知RoomTrackingLiveData
由上文可以推断出,当数据库发生变化时,是通过mObserver来启动数据库查询任务,并将结果通过RoomTrackingLiveData#postValue方法传递给订阅者。接下来就要研究一下mObserver的调用链。
// RoomTrackingLiveData.javafinal Runnable mRefreshRunnable = new Runnable() {@WorkerThread@Overridepublic void run() {// 1. 向InvalidationTracker注册一个观察者if (mRegisteredObserver.compareAndSet(false, true)) {mDatabase.getInvalidationTracker().addWeakObserver(mObserver);}....}};// InvalidationTracker.javapublic void addWeakObserver(Observer observer) {// 2addObserver(new WeakObserver(this, observer));
}public void addObserver(@NonNull Observer observer) {final String[] tableNames = resolveViews(observer.mTables); int[] tableIds = new int[tableNames.length]; final int size = tableNames.length; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { Integer tableId = mTableIdLookup.get(tableNames[i].toLowerCase(Locale.US)); if (tableId == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("There is no table with name " + tableNames[i]); } tableIds[i] = tableId; } ObserverWrapper wrapper = new ObserverWrapper(observer, tableIds, tableNames); ObserverWrapper currentObserver; synchronized (mObserverMap) { // 3 currentObserver = mObserverMap.putIfAbsent(observer, wrapper); } if (currentObserver == null && mObservedTableTracker.onAdded(tableIds)) { syncTriggers(); }
}RoomTrackingLiveData创建mObserver对象,并一步步将mObserver进行包装,并存放在InvalidationTracker的mObserverMap中。- 接下来则需要调查源码里在哪些情况下会遍历
mObserverMap,并去调用mObserverMap里item的方法。
// InvalidationTracker.javaRunnable mRefreshRunnable = new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {......if (invalidatedTableIds != null && !invalidatedTableIds.isEmpty()) {synchronized (mObserverMap) {// 1. 遍历了 mObserverMapfor (Map.Entry<Observer, ObserverWrapper> entry : mObserverMap) {entry.getValue().notifyByTableInvalidStatus(invalidatedTableIds);}}}}......
};public void notifyObserversByTableNames(String... tables) {synchronized (mObserverMap) {// 2. 遍历了 mObserverMapfor (Map.Entry<Observer, ObserverWrapper> entry : mObserverMap) {if (!entry.getKey().isRemote()) {entry.getValue().notifyByTableNames(tables);}}}
}由源码可知,共有两处遍历了mObserverMap,我们先研究一下mRefreshRunnable的调用链。
/*** Enqueues a task to refresh the list of updated tables.* <p>* This method is automatically called when {@link RoomDatabase#endTransaction()} is called but* if you have another connection to the database or directly use {@link* SupportSQLiteDatabase}, you may need to call this manually.*/
public void refreshVersionsAsync() {// TODO we should consider doing this sync instead of async.if (mPendingRefresh.compareAndSet(false, true)) {if (mAutoCloser != null) {mAutoCloser.incrementCountAndEnsureDbIsOpen();}// 启动 mRefreshRunnable 任务mDatabase.getQueryExecutor().execute(mRefreshRunnable);}
}- 从方法说明上可以看出,当
RoomDatabase#endTransaction()被调用时,会启动mRefreshRunnable任务。继续跟踪refreshVersionsAsync的调用链也能发现这点。 - 接下来让我们回头研究一下room框架自动为开发者定义的dao类自动生成的
xxxDAO_Impl.java。仔细研究一下各个方法的实现会发现,只要涉及到对数据库进行增、删、改的操作,都会调用到__db.endTransaction()。这里的__db就是RoomDatabase的对象。例如:
@Overridepublic void insert(final EntityNote note) {__db.assertNotSuspendingTransaction();__db.beginTransaction();try {__insertionAdapterOfEntityNote.insert(note);__db.setTransactionSuccessful();} finally {__db.endTransaction();}}@Overridepublic int delete(final EntityNote note) {__db.assertNotSuspendingTransaction();int _total = 0;__db.beginTransaction();try {_total +=__deletionAdapterOfEntityNote.handle(note);__db.setTransactionSuccessful();return _total;} finally {__db.endTransaction();}}@Overridepublic int update(final EntityNote note) {__db.assertNotSuspendingTransaction();int _total = 0;__db.beginTransaction();try {_total +=__updateAdapterOfEntityNote.handle(note);__db.setTransactionSuccessful();return _total;} finally {__db.endTransaction();}}1.3.1 __db.endTransaction()中调用internalEndTransaction()
public void endTransaction() {if (mAutoCloser == null) {internalEndTransaction();} else {mAutoCloser.executeRefCountingFunction(db -> {internalEndTransaction();return null;});}}1.3.2 mInvalidationTracker.refreshVersionsAsync()
private void internalEndTransaction() {mOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase().endTransaction();if (!inTransaction()) {// enqueue refresh only if we are NOT in a transaction. Otherwise, wait for the last// endTransaction call to do it.mInvalidationTracker.refreshVersionsAsync();}}1.3.3 mDatabase.getQueryExecutor().execute(mRefreshRunnable)
public void refreshVersionsAsync() {// TODO we should consider doing this sync instead of async.if (mPendingRefresh.compareAndSet(false, true)) {if (mAutoCloser != null) {// refreshVersionsAsync is called with the ref count incremented from// RoomDatabase, so the db can't be closed here, but we need to be sure that our// db isn't closed until refresh is completed. This increment call must be// matched with a corresponding call in mRefreshRunnable.mAutoCloser.incrementCountAndEnsureDbIsOpen();}mDatabase.getQueryExecutor().execute(mRefreshRunnable);}} Runnable mRefreshRunnable = new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {final Lock closeLock = mDatabase.getCloseLock();Set<Integer> invalidatedTableIds = null;closeLock.lock();try {if (!ensureInitialization()) {return;}if (!mPendingRefresh.compareAndSet(true, false)) {// no pending refreshreturn;}if (mDatabase.inTransaction()) {// current thread is in a transaction. when it ends, it will invoke// refreshRunnable again. mPendingRefresh is left as false on purpose// so that the last transaction can flip it on again.return;}// This transaction has to be on the underlying DB rather than the RoomDatabase// in order to avoid a recursive loop after endTransaction.SupportSQLiteDatabase db = mDatabase.getOpenHelper().getWritableDatabase();db.beginTransactionNonExclusive();try {invalidatedTableIds = checkUpdatedTable();db.setTransactionSuccessful();} finally {db.endTransaction();}} catch (IllegalStateException | SQLiteException exception) {// may happen if db is closed. just log.Log.e(Room.LOG_TAG, "Cannot run invalidation tracker. Is the db closed?",exception);} finally {closeLock.unlock();if (mAutoCloser != null) {mAutoCloser.decrementCountAndScheduleClose();}}if (invalidatedTableIds != null && !invalidatedTableIds.isEmpty()) {synchronized (mObserverMap) {for (Map.Entry<Observer, ObserverWrapper> entry : mObserverMap) {entry.getValue().notifyByTableInvalidStatus(invalidatedTableIds);}}}}private Set<Integer> checkUpdatedTable() {HashSet<Integer> invalidatedTableIds = new HashSet<>();Cursor cursor = mDatabase.query(new SimpleSQLiteQuery(SELECT_UPDATED_TABLES_SQL));//noinspection TryFinallyCanBeTryWithResourcestry {while (cursor.moveToNext()) {final int tableId = cursor.getInt(0);invalidatedTableIds.add(tableId);}} finally {cursor.close();}if (!invalidatedTableIds.isEmpty()) {mCleanupStatement.executeUpdateDelete();}return invalidatedTableIds;}};1.3.4 entry.getValue().notifyByTableInvalidStatus(invalidatedTableIds)
void notifyByTableInvalidStatus(Set<Integer> invalidatedTablesIds) {Set<String> invalidatedTables = null;final int size = mTableIds.length;for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) {final int tableId = mTableIds[index];if (invalidatedTablesIds.contains(tableId)) {if (size == 1) {// Optimization for a single-table observerinvalidatedTables = mSingleTableSet;} else {if (invalidatedTables == null) {invalidatedTables = new HashSet<>(size);}invalidatedTables.add(mTableNames[index]);}}}if (invalidatedTables != null) {mObserver.onInvalidated(invalidatedTables);}}1.3.5 mObserver.onInvalidated(invalidatedTables)
RoomTrackingLiveData(RoomDatabase database,InvalidationLiveDataContainer container,boolean inTransaction,Callable<T> computeFunction,String[] tableNames) {mDatabase = database;mInTransaction = inTransaction;mComputeFunction = computeFunction;mContainer = container;mObserver = new InvalidationTracker.Observer(tableNames) {@Overridepublic void onInvalidated(@NonNull Set<String> tables) {ArchTaskExecutor.getInstance().executeOnMainThread(mInvalidationRunnable);}};}1.3.6 ArchTaskExecutor.getInstance().executeOnMainThread(mInvalidationRunnable)
final Runnable mInvalidationRunnable = new Runnable() {@MainThread@Overridepublic void run() {boolean isActive = hasActiveObservers();if (mInvalid.compareAndSet(false, true)) {if (isActive) {getQueryExecutor().execute(mRefreshRunnable);}}}}1.3.7 mRefreshRunnable.run postValue(value)
final Runnable mRefreshRunnable = new Runnable() {@WorkerThread@Overridepublic void run() {// 向InvalidationTracker注册一个观察者if (mRegisteredObserver.compareAndSet(false, true)) {mDatabase.getInvalidationTracker().addWeakObserver(mObserver);}boolean computed;do {computed = false;// mComputing 初始值为 falseif (mComputing.compareAndSet(false, true)) {// as long as it is invalid, keep computing.try {T value = null;// mInvalid初始值为 true// 此while循环结束后,computed == false,mInvalid == falsewhile (mInvalid.compareAndSet(true, false)) {computed = true;try {// 执行数据库操作方法,并返回结果value = mComputeFunction.call();} catch (Exception e) {// 如果SQL语句执行有误,会非常粗暴的直接报错,// liveData不能将错误状态上报给开发者。throw new RuntimeException("Exception while computing database"+ " live data.", e);}}if (computed) {// 向当前livedata的观察者们发送数据库查询结果postValue(value);}} finally {// release compute lockmComputing.set(false);}}} while (computed && mInvalid.get());}};
1.3.8 observer收到onChanged回调
LiveData<List<EntityNote>> EntityNoteLiveData = AppDatabase.getInstance().noteDao().getAll()注册的RoomLiveData的observer会回调onChanged
// 继承AndroidViewModel,带有Application环境
public class NoteViewModel extends AndroidViewModel {private MediatorLiveData<List<EntityNote >> mMediatorLiveData;public NoteViewModel(@NonNull Application application) {super(application);mMediatorLiveData = new MediatorLiveData<>();LiveData<List<EntityNote>> EntityNoteLiveData = AppDatabase.getInstance().noteDao().getAll();mMediatorLiveData.addSource(EntityNoteLiveData, new Observer<List<EntityNote>>() {private List<EntityNote> mLastEntityNoteList;@Overridepublic void onChanged(List<EntityNote> entityNotes) {if (mLastEntityNoteList == null) {mLastEntityNoteList = entityNotes;return;}if (entityNotes == null) {setValue(new ArrayList<>());return;}int lastSize = mLastEntityNoteList.size();int size = entityNotes.size();if (lastSize != size) {setValue(entityNotes);return;}for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {EntityNote lastNote = mLastEntityNoteList.get(i);EntityNote note = entityNotes.get(i);if (!isSameNote(lastNote, note)) {setValue(entityNotes);break;}}// 没有变化不setValue不触发onChangedmLastEntityNoteList = entityNotes;}private void setValue(List<EntityNote> entityNotes) {mMediatorLiveData.setValue(entityNotes);mLastEntityNoteList = entityNotes;}private boolean isSameNote(EntityNote first, EntityNote second) {if (first == null || second == null) {return false;}return first.uuid.equals(second.uuid) && first.title.equals(second.title)&& first.id == second.id && first.content.equals(second.content);}});}//查(所有)public MediatorLiveData<List<EntityNote>> getNoteListLiveData() {return mMediatorLiveData;}
}
1.4 总结:
- 数据库的增、删、改操作会调用
RoomDatabase#endTransaction(); RoomDatabase#endTransaction()会调用InvalidationTracker#refreshVersionsAsync();refreshVersionsAsync()会开启mRefreshRunnable任务。mRefreshRunnable里会遍历mObserverMap,并挨个调用其item的指定方法。RoomTrackingLiveData在构造函数里创建了mObserver对象,并将此对象放置于InvalidationTracker的mObserverMap中。且此对象的方法就是用来唤醒RoomTrackingLiveData的mRefreshRunnable任务。还记得这个任务是干嘛的吗?这个任务就是根据RoomTrackingLiveData持有的数据库查询语句向数据库查询数据,并将查询结果上报给开发者指定的Observer。
至此,RoomTrackingLiveData完美实现了数据库发生变化时,会主动将新的数据上报给开发者的功能。
二 Room是如何通知其他进程的订阅者
如果有两个进程同时关联了同一个数据库,如果一个进程对此数据库的数据进行改变,那么另一个进程的RoomTrackingLiveData依旧能感知到数据变化,这是怎么做到的呢?
还记得上面在调查InvalidationTracker的mObserverMap时,发现有两个方法遍历了这个map吗。其中mRefreshRunnable已经分析过了,接下来分析另一个方法notifyObserversByTableNames。
// InvalidationTracker.javapublic void notifyObserversByTableNames(String... tables) {synchronized (mObserverMap) {// 遍历了 mObserverMapfor (Map.Entry<Observer, ObserverWrapper> entry : mObserverMap) {if (!entry.getKey().isRemote()) {entry.getValue().notifyByTableNames(tables);}}}
}// MultiInstanceInvalidationClient.javafinal IMultiInstanceInvalidationCallback mCallback =new IMultiInstanceInvalidationCallback.Stub() {@Overridepublic void onInvalidation(final String[] tables) {mExecutor.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {//1.调用了 nvalidationTracker#notifyObserversByTableNames()mInvalidationTracker.notifyObserversByTableNames(tables);}});}};final Runnable mSetUpRunnable = new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {final IMultiInstanceInvalidationService service = mService;if (service != null) {//2. 向 service 注册 mCallbackmClientId = service.registerCallback(mCallback, mName);mInvalidationTracker.addObserver(mObserver);}} catch (RemoteException e) {Log.w(Room.LOG_TAG, "Cannot register multi-instance invalidation callback", e);}}
};final ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {@Overridepublic void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {mService = IMultiInstanceInvalidationService.Stub.asInterface(service);// 3. 执行 mSetUpRunnable 任务 mExecutor.execute(mSetUpRunnable);}@Overridepublic void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {mExecutor.execute(mRemoveObserverRunnable);mService = null;}}; - 由上可见,在
MultiInstanceInvalidationClient类里绑定了一个service,并向service注册mCallback。这个mCallback会通过InvalidationTracker#notifyObserversByTableNames()通知RoomTrackingLiveData该干活了(查询和上报数据库新值)。
看到
IMultiInstanceInvalidationService.Stub可以大胆猜测这里涉及到了跨进程通信。
接下来研究MultiInstanceInvalidationService
// MultiInstanceInvalidationService.javapublic class MultiInstanceInvalidationService extends Service {int mMaxClientId = 0;final HashMap<Integer, String> mClientNames = new HashMap<>();// 1. 可以理解成这是一个装载 callBack的集合final RemoteCallbackList<IMultiInstanceInvalidationCallback> mCallbackList =new RemoteCallbackList<IMultiInstanceInvalidationCallback>() {@Overridepublic void onCallbackDied(IMultiInstanceInvalidationCallback callback,Object cookie) {mClientNames.remove((int) cookie);}};private final IMultiInstanceInvalidationService.Stub mBinder =new IMultiInstanceInvalidationService.Stub() {@Overridepublic int registerCallback(IMultiInstanceInvalidationCallback callback,String name) {if (name == null) {return 0;}synchronized (mCallbackList) {int clientId = ++mMaxClientId;// 2. 将 callback 放入 mCallbackList 集合中if (mCallbackList.register(callback, clientId)) {mClientNames.put(clientId, name);return clientId;} else {--mMaxClientId;return 0;}}}@Overridepublic void unregisterCallback(IMultiInstanceInvalidationCallback callback,int clientId) {synchronized (mCallbackList) {mCallbackList.unregister(callback);mClientNames.remove(clientId);}}@Overridepublic void broadcastInvalidation(int clientId, String[] tables) {synchronized (mCallbackList) {String name = mClientNames.get(clientId);if (name == null) {Log.w(Room.LOG_TAG, "Remote invalidation client ID not registered");return;}int count = mCallbackList.beginBroadcast();try {// 这个for循环,可以理解成取出mCallbackList集合中的所有callBack,// 并调用各自的 onInvalidation方法。for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {int targetClientId = (int) mCallbackList.getBroadcastCookie(i);String targetName = mClientNames.get(targetClientId);if (clientId == targetClientId // This is the caller itself.|| !name.equals(targetName)) { // Not the same file.continue;}try {IMultiInstanceInvalidationCallback callback =mCallbackList.getBroadcastItem(i);callback.onInvalidation(tables);} catch (RemoteException e) {Log.w(Room.LOG_TAG, "Error invoking a remote callback", e);}}} finally {mCallbackList.finishBroadcast();}}}};@Nullable@Overridepublic IBinder onBind(@NonNull Intent intent) {return mBinder;}
}- 由以上源码可以推断出这个
service主要做了两件事:- 在内存中维护一个集合,这个集合装载的是所有
client注册的callBack; - 在合适的时机调用所有
client注册的callBack。这个合适的时机,就是调用broadcastInvalidation()的时候。
- 在内存中维护一个集合,这个集合装载的是所有
回到MultiInstanceInvalidationClient,回想一下这个client向service注册了个什么玩意。
// MultiInstanceInvalidationClient.javafinal Runnable mSetUpRunnable = new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {final IMultiInstanceInvalidationService service = mService;if (service != null) {// 1. 向service注册mCallbackmClientId = service.registerCallback(mCallback, mName);mInvalidationTracker.addObserver(mObserver);}} catch (RemoteException e) {Log.w(Room.LOG_TAG, "Cannot register multi-instance invalidation callback", e);}}
};final IMultiInstanceInvalidationCallback mCallback =new IMultiInstanceInvalidationCallback.Stub() {@Overridepublic void onInvalidation(final String[] tables) {mExecutor.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {// 2. 这个方法是干什么的来着?// 是拜托InvalidationTracker通知RoomTrackingLiveData该干活了。// 上文有介绍mInvalidationTracker.notifyObserversByTableNames(tables);}});}};接下来追踪一下MultiInstanceInvalidationService#broadcastInvalidation()
// MultiInstanceInvalidationClient.javaMultiInstanceInvalidationClient(Context context, String name, Intent serviceIntent,InvalidationTracker invalidationTracker, Executor executor) {......mObserver = new InvalidationTracker.Observer(tableNames.toArray(new String[0])) {@Overridepublic void onInvalidated(@NonNull Set<String> tables) {if (mStopped.get()) {return;}try {final IMultiInstanceInvalidationService service = mService;if (service != null) {// 1. 调用了MultiInstanceInvalidationService#broadcastInvalidation()service.broadcastInvalidation(mClientId, tables.toArray(new String[0]));}} catch (RemoteException e) {Log.w(Room.LOG_TAG, "Cannot broadcast invalidation", e);}}@Overrideboolean isRemote() {return true;}};mAppContext.bindService(serviceIntent, mServiceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}final Runnable mSetUpRunnable = new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {final IMultiInstanceInvalidationService service = mService;if (service != null) {mClientId = service.registerCallback(mCallback, mName);// 2. 将mObserver传递给InvalidationTrackermInvalidationTracker.addObserver(mObserver);}} catch (RemoteException e) {Log.w(Room.LOG_TAG, "Cannot register multi-instance invalidation callback", e);}}
};看了以上2个步骤是不是似曾相识?还记得RoomTrackingLiveData的mObserver对象吗?和这里的套路是一模一样。接下来很明显,InvalidationTracker里面会有一个map来装载这个mObserver。然后会有两个方法去遍历这个map。其中一个Runnable方法会在调用数据库的增删改方法时触发,另一个方法notifyObserversByTableNames会在...会在...???
我不是在研究notifyObserversByTableNames的调用链吗?怎么又绕回来了?
这里理解起来有点绕,先明确一下前提:
- 针对不同的进程操作同一个数据库的场景,其实每一个进程都会拥有自己独立的
RoomDatabase实例。相应的MultiInstanceInvalidationClient、InvalidationTracker、RoomTrackingLiveData都是相互独立的。- 只有
MultiInstanceInvalidationService是共同的实例。而这个共同的实例,是保证不同进程能相互感知到数据库操作的关键。InvalidationTracker的mRefreshRunnable是在单进程中调用的。InvalidationTracker的notifyObserversByTableNames是用于跨进程调用的。
下面重新捋一下思路。首先假设现在有两个进程会操作同一个数据库。那么这两个进程都会各自拥有一套自己的独立对象。即都会做一下事情:
- 创建
RoomTrackingLiveData对象,并将mObserver委托给InvalidationTracker管理。 RoomTrackingLiveData里的mRefreshRunnable会在被唤醒时重新查询数据库,并上报结果。- 创建
MultiInstanceInvalidationClient对象,并与唯一的MultiInstanceInvalidationService进行绑定,并将callBack委托给service管理。 callBack里会调用InvalidationTracker#notifyObserversByTableNames()。MultiInstanceInvalidationClient对象将mObserver委托给InvalidationTracker管理。MultiInstanceInvalidationClient的mObserver会通知所有与MultiInstanceInvalidationService进行绑定的MultiInstanceInvalidationClient,告知它们数据库有变化。
针对进程1,我们重点关注3、4、5、6。针对进程2,我们重点关注1、2。现在开始发车:
- 当前用户在进程1操作了数据库的修改操作,那么就会触发进程1的
RoomDatabase#endTransaction(),
进而触发了InvalidationTracker#mRefreshRunnable任务,遍历InvalidationTracker#mObserverMap(在上一节有相关介绍)。此mObserverMap里存在一个MultiInstanceInvalidationClient添加进来的mObserver(上面第5点有提到)。 - 进程1的
MultiInstanceInvalidationClient的mObserver会调用MultiInstanceInvalidationService#broadcastInvalidation()。 MultiInstanceInvalidationService会遍历和执行所有MultiInstanceInvalidationClient注册的callback。这其中的一个callback就是进程2的MultiInstanceInvalidationClient注册的(上面第5点有提到)。- 进程2的
callback会调用进程2的InvalidationTracker#notifyObserversByTableNames()。再回忆一下这个notifyObserversByTableNames()是干嘛的?没错,就是我们研究的第二个遍历InvalidationTracker的mObserverMap的方法。 - 既然进程2已经遍历了
mObserverMap,那么势必会让进程2的RoomTrackingLiveData干活(查询数据库,上报新数据)。
至此,room框架完成了一次完美的跨进程通讯。
要想当前的RoomDataBase具有跨进程通讯的能力,需要在构建databaseBuilder的时候调用enableMultiInstanceInvalidation()。例如:
@Database(entities = {EntityNote.class}, version = 1, exportSchema = false)
public abstract class AppDatabase extends RoomDatabase {private static final String DB_NAME = "note.db";private static volatile AppDatabase instance;//创建单例public static synchronized AppDatabase getInstance() {if (instance == null) {instance = create();}return instance;}/*** 创建数据库*/private static AppDatabase create() {return Room.databaseBuilder(MyApplication.getInstance(), AppDatabase.class, DB_NAME).allowMainThreadQueries().fallbackToDestructiveMigration().enableMultiInstanceInvalidation() // 跨进程通讯的能力.build();}public abstract NoteDao noteDao();
}从源码来看,RoomDataBase正是通过此方法来间接创建MultiInstanceInvalidationClient对象,并与MultiInstanceInvalidationService建立绑定关系。
相关文章:

LiveData是如何感知Room数据变化的
一 Room数据变化LiveData如何收到onChanged回调的? 1.1 LiveData是如何创建的 这里讨论的LiveData的创建是特指Dao定义的方法的返回类型,而不是所有的LiveData。 以NoteDao 举例: Dao public interface NoteDao {Query("select * fr…...

【自动化】WebUI自动化通过读取用户数据的方式启动浏览器实现绕过相关登录验证的方法。
背景说明 我相信做自动化测试或者实现UI自动化相关功能的同学肯定碰到过,每次写好脚本执行时都是默认打开一个 “新”的浏览器,我的意思是就跟刚下载的浏览器一样。而不是平时日常使用着的浏览器的状态,日常使用浏览器时只要近期登录过&…...

信号:干扰类别及特征提取
目录 第一部分:干扰类别 1.压制干扰 1.1噪声调幅瞄准式干扰(单音干扰) 1.2噪声调频阻塞式干扰(宽带噪声干扰) 1.3噪声调频扫频式干扰(线性调频) 2.欺骗干扰 2.1距离欺骗干扰(幅度调制干扰࿰…...
【推荐】用scss循环zoom缩放比例,解决可视化大屏在不同分辨率屏幕下的适配问题
方法1: 指定几种常规屏幕宽度(用这种方式就必须要强制用户全屏查看页面,在固定的宽度下才能达到比较不错的显示效果) // 适配不同分辨率的页面---------------------------------------- html {overflow: hidden;width: 1920px;…...

23中设计模式之一— — — —命令模式的详细介绍
命令模式 Command Pattern讲解 概念描述模式结构主要角色模式的UIM类图模式优点模式缺点应用场景实例演示类图代码演示运行结果 概念 命令模式(别名:动作,事务) 命令模式是一种行为设计模式,将一个请求封装为一个对象…...
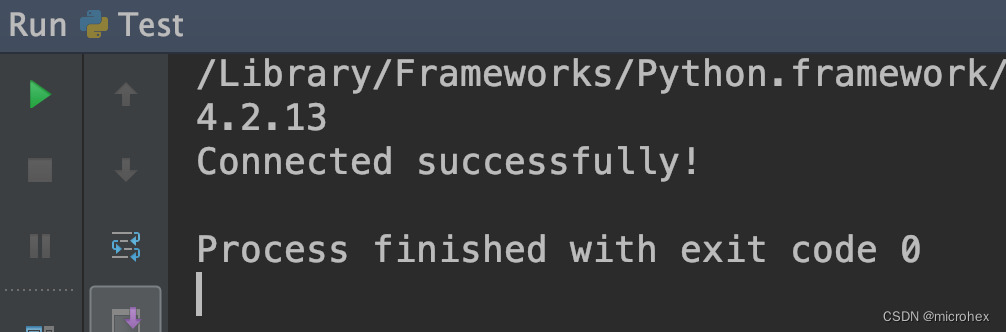
解决 Mac Django 连接Mysql 出现 image not found 问题
最近在使用 Django 框架,因为升级到4.2版本了,对应的本机 Mysql 5.7 就不适用了,于是升级到了 Mysql 8.0,写好代码之后出现如下错误: 仔细分析一下错误的描述: ImportError: dlopen(/Library/Frameworks/P…...

EitbaseEX香港业务开展,提升用户友好交易体验
在全球范围内备受瞩目的加密货币交易平台Coinbase,宣布正式入驻香港市场,并命名为EitbaseEX。这一战略性扩展举措,旨在为香港提供先进的加密货币交易技术和服务,同时将香港打造为其在亚太地区的重要枢纽。 作为国际金融中心&#…...
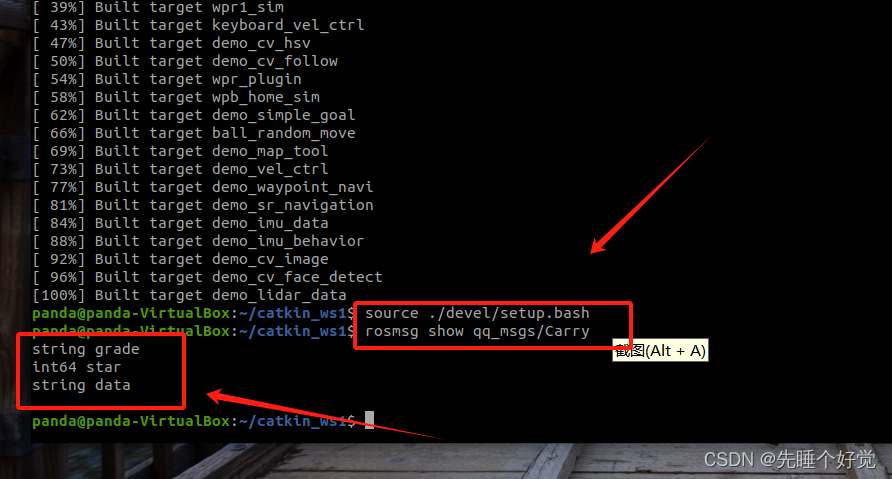
ROS学习记录:自定义消息类型
前言 当我们需要传输一些特殊的数据时,且官方的消息包无法满足需求,我们便可以自己定义一个消息类型。 实验步骤 一、在终端输入cd ~/catkin_ws1/src进入工作空间中src目录 二、输入catkin_create_pkg qq_msgs roscpp rospy std_msgs message_generati…...

创新实训2024.06.06日志:部署web服务
1. 运行web项目前后端服务 首先我们要先在服务器上运行客户端以及服务端的应用程序。随后再考虑如何通过公网/局域网访问的问题。 如何启动服务在仓库对应分支下的Readme文件中已经有详细描述了。 1.1. 启动服务端 对于服务端,即(要求你在服务端子项…...

使用C++实现YOLO图像分类:从环境搭建到性能评估的完整指南
⭐️我叫忆_恒心,一名喜欢书写博客的研究生👨🎓。 如果觉得本文能帮到您,麻烦点个赞👍呗! 近期会不断在专栏里进行更新讲解博客~~~ 有什么问题的小伙伴 欢迎留言提问欧,喜欢的小伙伴给个三连支…...
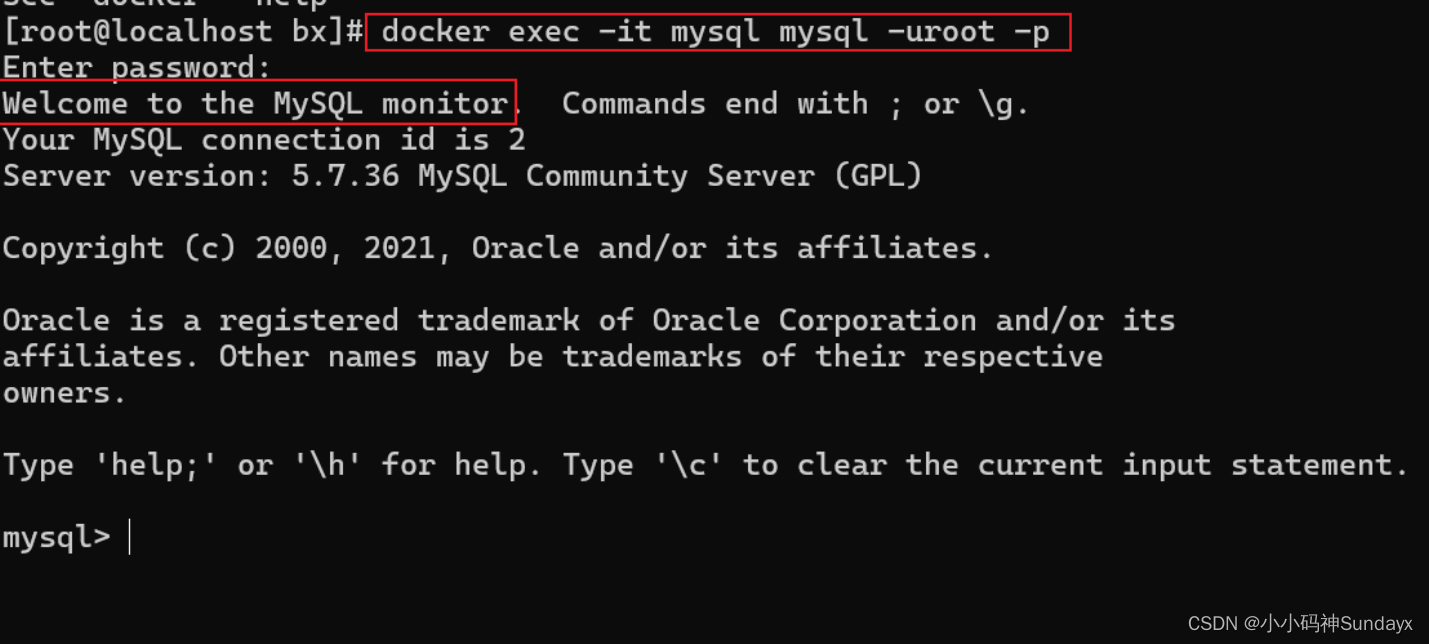
Linux中安装Docker,并使用Docker安装MySQL和Redis
1、安装docker 1卸载系统之前的docker yum remove docker \docker-client \docker-client-latest \docker-common \docker-latest \docker-latest-logrotate \docker-logrotate \docker-engine2、安装Docker-CE #安装必须的依赖 sudo yum install -y yum-utils \device-map…...

期货短线交易的核心技术是什么
一、市场分析是短线交易的基础: 技术分析在短线交易中尤为重要,包括K线图、均线系统、成交量与持仓量等指标。K线图可以帮助交易者识别关键价格形态和趋势线,从而判断市场走势。均线系统则可以利用短期均线交叉作为买卖信号,如金…...
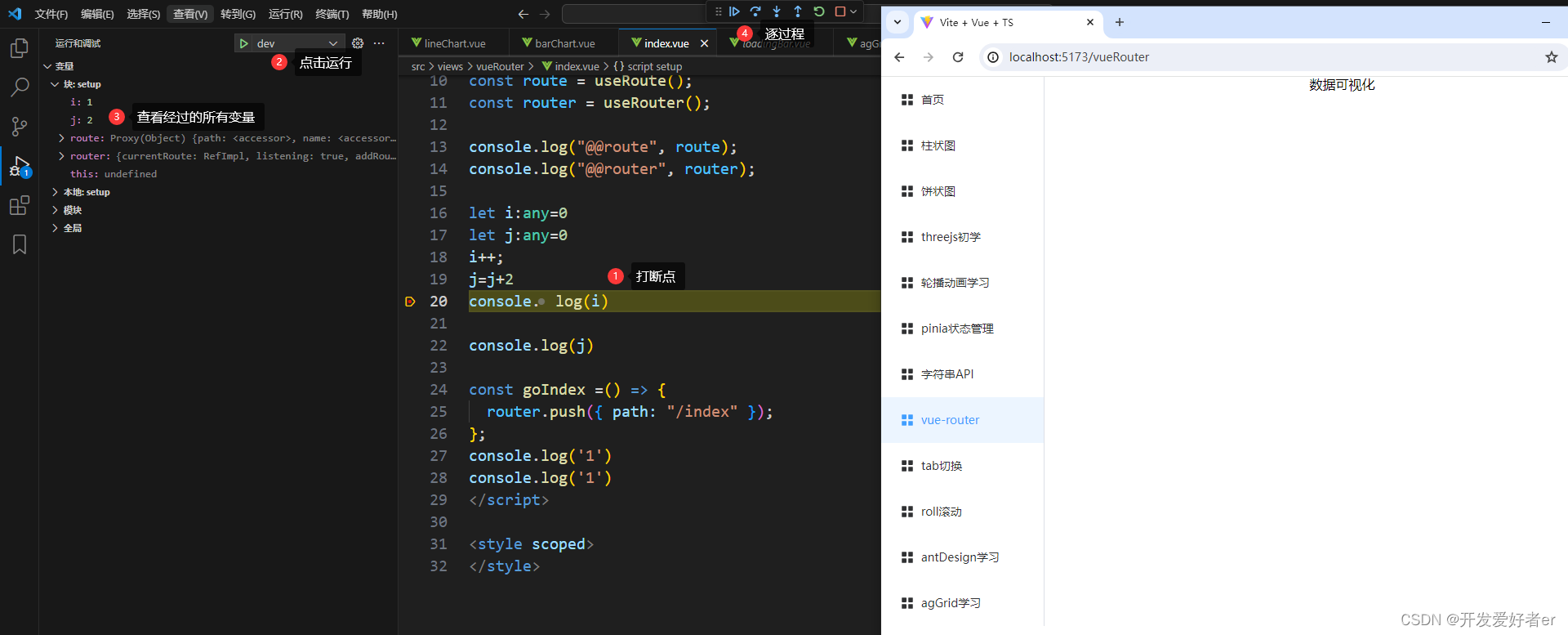
VSCode+Vite+Vue3断点调试
目录 lunch.json创建 vite.config.ts 打断点运行 lunch.json创建 首先,点击VSCode左上角,甲壳虫运行的按钮,然后点击运行与调试,选择chrome浏览器,修改成一下配置。 { // 使用 IntelliSense 了解相关属性。 // 悬停…...
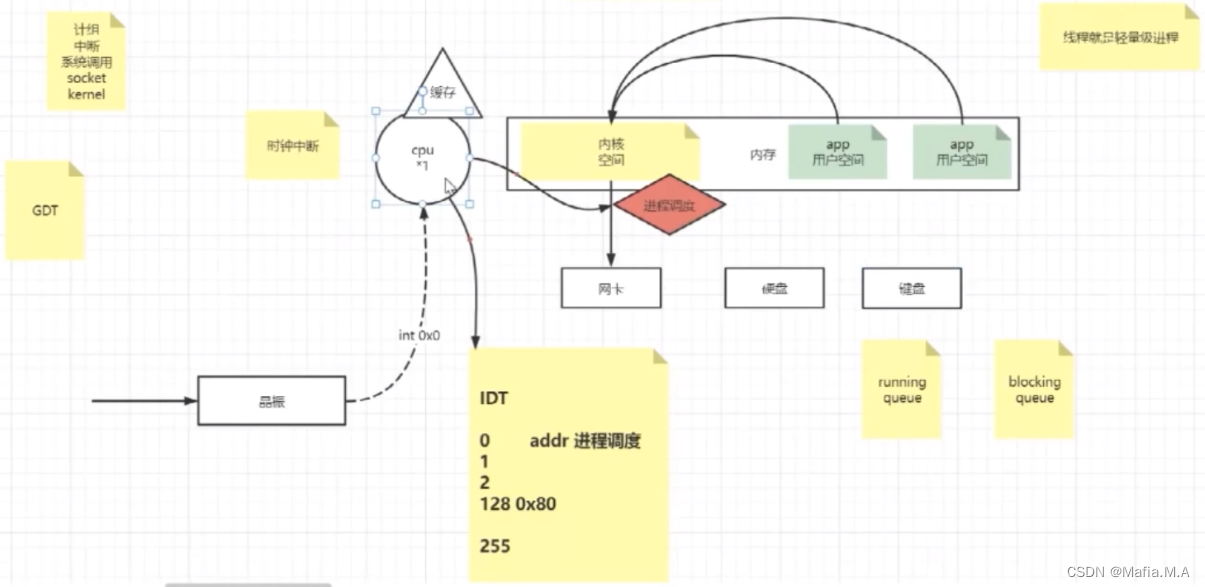
RPC框架原理(一)
RPC框架原理 网络和IO的关系,IO(input和output)面向的是谁?OSI 7层参考模型,TCP/IP协议为什么会出现一个会话层三次握手socket心跳keep alive四次挥手 网络IO(IO模型) IO框架底层 学习顺序&…...
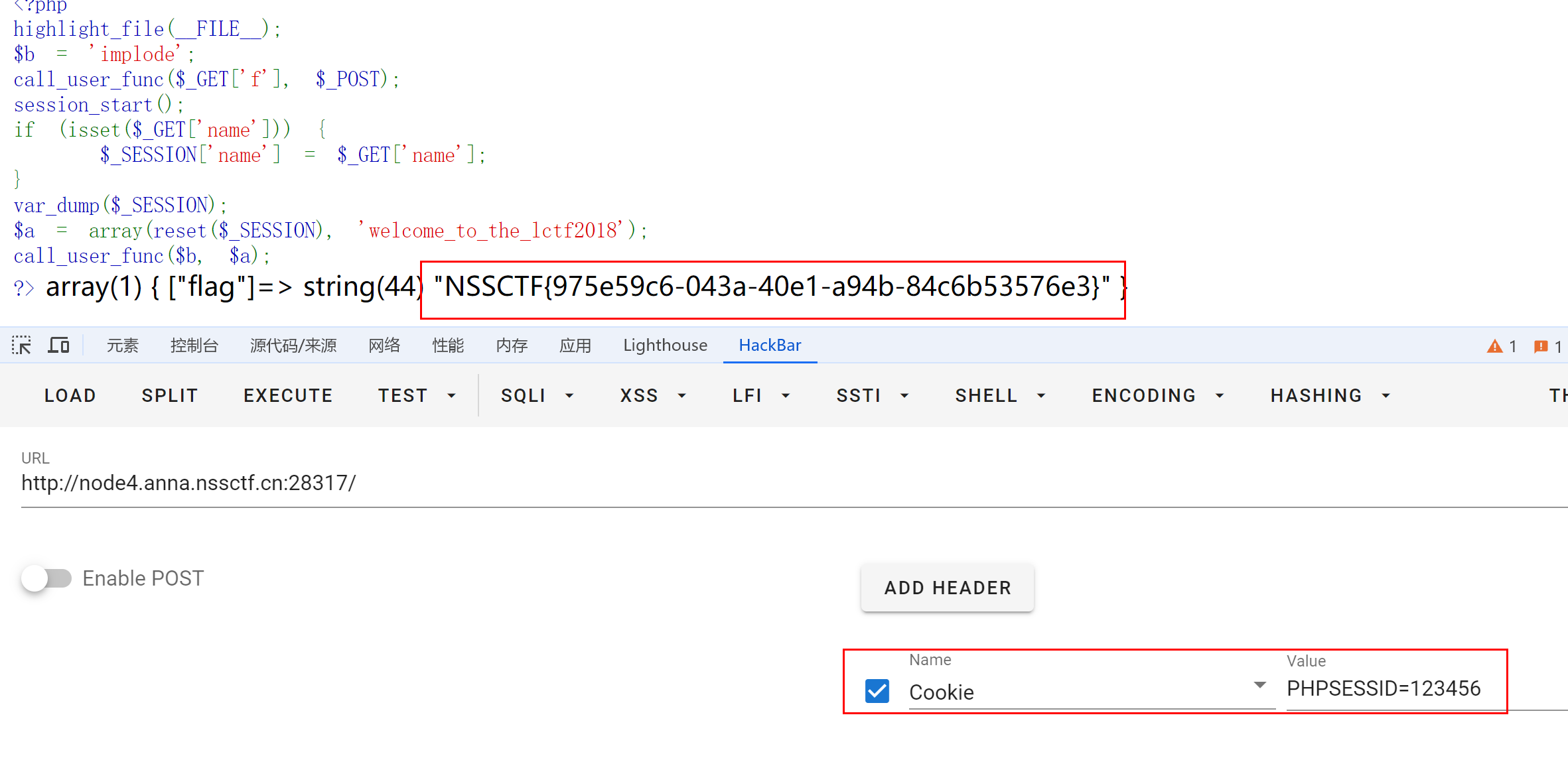
LCTF 2018 bestphp‘s revenge
考点:Soap原生类Session反序列化CRLF注入 <?php highlight_file(__FILE__); $b implode; call_user_func($_GET[f], $_POST); session_start(); if (isset($_GET[name])) { $_SESSION[name] $_GET[name]; } var_dump($_SESSION); $a array(reset($_…...

MySQL主从搭建--保姆级教学
MYSQL主从搭建步骤 主节点 # 进入目录 cd /opt# 下载安装包 wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/MySQL-8.0/mysql-8.0.20-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.xz# 解压 tar -xvf mysql-8.0.20-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.xz# 拷贝到/usr/local mv /opt/mysql-8.0.20-linux-g…...

Modbus通信协议--RTU
一、RTU介绍 MODBUS协议支持多种功能码,不同的功能码对应不同的操作: 0x01读线圈状态0x02读离散输入状态0x03读保持寄存器0x04读输入寄存器0x05写单个线圈0x06写单个保持寄存器0x0F写多个线圈0x10写多个保持寄存器 二、实验 1.0x03功能码读单个保持寄…...

我是大学生,应该选系统运维方向,还是web开发方向?
选择系统运维方向还是Web开发方向取决于你的兴趣、职业目标和个人技能。以下是对这两个方向的详细对比和建议,帮助你做出更明智的选择 双方比较 🤦♀️系统运维方向 优点: 稳定性:系统运维工作通常比较稳定,许多…...
Qt窗口与对话框
目录 Qt窗口 1.菜单栏 2.工具栏 3.状态栏 4.滑动窗口 QT对话框 1.基础对话框QDiaog 创建新的ui文件 模态对话框与非模态对话框 2.消息对话框 QMessageBox 3.QColorDialog 4.QFileDialog文件对话框 5.QFontDialog 6.QInputDialog Qt窗口 前言:之前以上…...
【笔记】Windows 中 一键部署本地私人专属知识库:MaxKB + Docker + MaxKB docker + Ollama
Docker的部署: Docker下载直接进入链接: https://www.docker.com/ Docker使用需要启动Docker,启动Docker以后,会在桌面右下角看到Docker的一个图标: 只有启动了Docker以后,Docker的各种命令才可以使用。 好像还需要…...

变量 varablie 声明- Rust 变量 let mut 声明与 C/C++ 变量声明对比分析
一、变量声明设计:let 与 mut 的哲学解析 Rust 采用 let 声明变量并通过 mut 显式标记可变性,这种设计体现了语言的核心哲学。以下是深度解析: 1.1 设计理念剖析 安全优先原则:默认不可变强制开发者明确声明意图 let x 5; …...

【Linux】shell脚本忽略错误继续执行
在 shell 脚本中,可以使用 set -e 命令来设置脚本在遇到错误时退出执行。如果你希望脚本忽略错误并继续执行,可以在脚本开头添加 set e 命令来取消该设置。 举例1 #!/bin/bash# 取消 set -e 的设置 set e# 执行命令,并忽略错误 rm somefile…...
)
进程地址空间(比特课总结)
一、进程地址空间 1. 环境变量 1 )⽤户级环境变量与系统级环境变量 全局属性:环境变量具有全局属性,会被⼦进程继承。例如当bash启动⼦进程时,环 境变量会⾃动传递给⼦进程。 本地变量限制:本地变量只在当前进程(ba…...
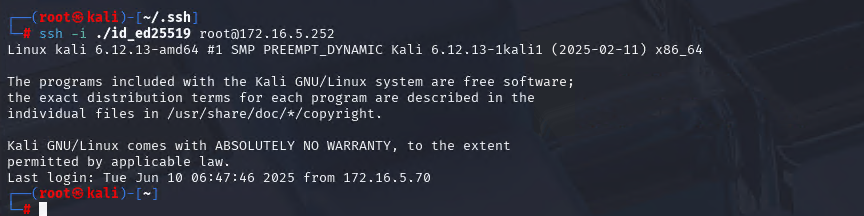
Xshell远程连接Kali(默认 | 私钥)Note版
前言:xshell远程连接,私钥连接和常规默认连接 任务一 开启ssh服务 service ssh status //查看ssh服务状态 service ssh start //开启ssh服务 update-rc.d ssh enable //开启自启动ssh服务 任务二 修改配置文件 vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config //第一…...

【Web 进阶篇】优雅的接口设计:统一响应、全局异常处理与参数校验
系列回顾: 在上一篇中,我们成功地为应用集成了数据库,并使用 Spring Data JPA 实现了基本的 CRUD API。我们的应用现在能“记忆”数据了!但是,如果你仔细审视那些 API,会发现它们还很“粗糙”:有…...

BCS 2025|百度副总裁陈洋:智能体在安全领域的应用实践
6月5日,2025全球数字经济大会数字安全主论坛暨北京网络安全大会在国家会议中心隆重开幕。百度副总裁陈洋受邀出席,并作《智能体在安全领域的应用实践》主题演讲,分享了在智能体在安全领域的突破性实践。他指出,百度通过将安全能力…...

ios苹果系统,js 滑动屏幕、锚定无效
现象:window.addEventListener监听touch无效,划不动屏幕,但是代码逻辑都有执行到。 scrollIntoView也无效。 原因:这是因为 iOS 的触摸事件处理机制和 touch-action: none 的设置有关。ios有太多得交互动作,从而会影响…...

Rapidio门铃消息FIFO溢出机制
关于RapidIO门铃消息FIFO的溢出机制及其与中断抖动的关系,以下是深入解析: 门铃FIFO溢出的本质 在RapidIO系统中,门铃消息FIFO是硬件控制器内部的缓冲区,用于临时存储接收到的门铃消息(Doorbell Message)。…...
企业如何增强终端安全?
在数字化转型加速的今天,企业的业务运行越来越依赖于终端设备。从员工的笔记本电脑、智能手机,到工厂里的物联网设备、智能传感器,这些终端构成了企业与外部世界连接的 “神经末梢”。然而,随着远程办公的常态化和设备接入的爆炸式…...

IP如何挑?2025年海外专线IP如何购买?
你花了时间和预算买了IP,结果IP质量不佳,项目效率低下不说,还可能带来莫名的网络问题,是不是太闹心了?尤其是在面对海外专线IP时,到底怎么才能买到适合自己的呢?所以,挑IP绝对是个技…...
