北邮22信通:你是不是在looking for……那串代码?(2)第三章单链表
相信有了第二章顺序表的基础,小伙伴们学习第三章链表应该会轻松一点吧
目录
类模板下的单链表
1.1书上干净完整代码(无增改、适合自己动手实验)
1.2对书上代码的完善和对一些问题的验证和解释代码
1.补全一个函数:
2.this指针:
3.关于printlist函数的一点说明:(增改后代码第117行)
4.getlength函数最后一步为什么是--cnt(增改后代码第136行):
5.增改后代码:
6.增改后代码效果图:
7.增改后代码运行效果:
类模板下的单链表
1.1书上干净完整代码(无增改、适合自己动手实验)
下面是书上单链表实现通信录的干净完整代码,基本一字不差~ 有需要的友友可以拿走~
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class phonebook
{
private:int ID;string name;string phone;string group;
public:phonebook() {};phonebook(int ID, string name, string phone, string group){this->ID = ID;this->name = name;this->phone = phone;this->group = group;}void print(){cout << this->ID << " " << this->name << " "<< this->phone << " " << this->group << endl;}bool operator==(phonebook& p){return (p.ID == this->ID) ? true : false;}
};template<class temp>
struct node
{temp data;node* next;
};template <class temp>
class linklist
{
private:node<temp>* front;
public:linklist(){this->front = new node<temp>;this->front->next = nullptr;}linklist(temp a[], int n);~linklist();void printlist();int getlengh() {};node<temp>* get(int i);int locate(temp x);void insert(int i, temp x);temp del(int i);
};//头插法
template<class temp>
linklist<temp>::linklist(temp a[], int n)
{this->front = new node<temp>;this->front->next = NULL;for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--){node<temp>* s = new node<temp>;s->data = a[i];s->next = this->front->next;this->front->next = s;}
}//尾插法
/*
template<class temp>
linklist<temp>::linklist(temp a[], int n)
{this->front = new node<temp>;node<temp>* r = this->front();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){node<temp>* s = new node<temp>;s->data = a[i];r->next = s;r = s;}r->next = NULL;
}
*/template<class temp>
linklist<temp>::~linklist()
{node<temp>* p = this->front;while (p != NULL){this->front = p;p = p->next;delete front;}
}template<class temp>
void linklist<temp>::printlist()
{node<temp>* p = this->front->next;while (p != NULL){p->data.print();//数据域中的print方法(需要用户自定义)p = p->next;}cout << endl;
}//按位置查找,返回地址
template<class temp>
node<temp>* linklist<temp>::get(int i)
{node<temp>* p = this->front->next;int j = 1;while (p != NULL && j != i){p = p->next;j++;}return p;
}//按值查找,返回位置
template<class temp>
int linklist<temp>::locate(temp x)
{node<temp>* p = this->front->next;int j = 1;while (p != NULL){if (p->data == x)return j;p = p->next;j++;}return -1;//如果没有找到,返回无效值
}template <class temp>
void linklist<temp>::insert(int i, temp x)
{node<temp>* p = this->front;if (i != 1)p = get(i - 1);//get(i - 1)表示要插入的位置的前一个结点地址if (p != NULL){node<temp>* s = new node<temp>;s->data = x;s->next = p->next;p->next = s;}else{cout << "插入位置错误:" << endl;exit(0);}
}template<class temp>
temp linklist<temp>::del(int i)
{node<temp>* p = this->front;if (i != 1)p = get(i - 1);node<temp>* q = p->next;p->next = q->next;temp x = q->data;delete q;return x;
}int main()
{phonebook pbook[4] ={{20181208,"mary","13011221827","classmates"},{20181127,"tom","13934621123","family"},{20181156,"john","1324579880","classmates"},{20181133,"lisa","1378001822","teacher"}};phonebook record(20181209, "phoenix", "1590209020", "teacher");linklist<phonebook>list(pbook, 4);cout << "通信录内容列表:" << endl;list.printlist();list.insert(1, record);cout << "通信录内容列表:" << endl;list.printlist();phonebook x = list.del(3);cout << "删除元素:" << endl;x.print();cout << "通信录内容列表:" << endl;list.printlist();int p = list.locate(record);cout << "phoenix的位置是:" << p << endl;return 0;
}代码效果图:
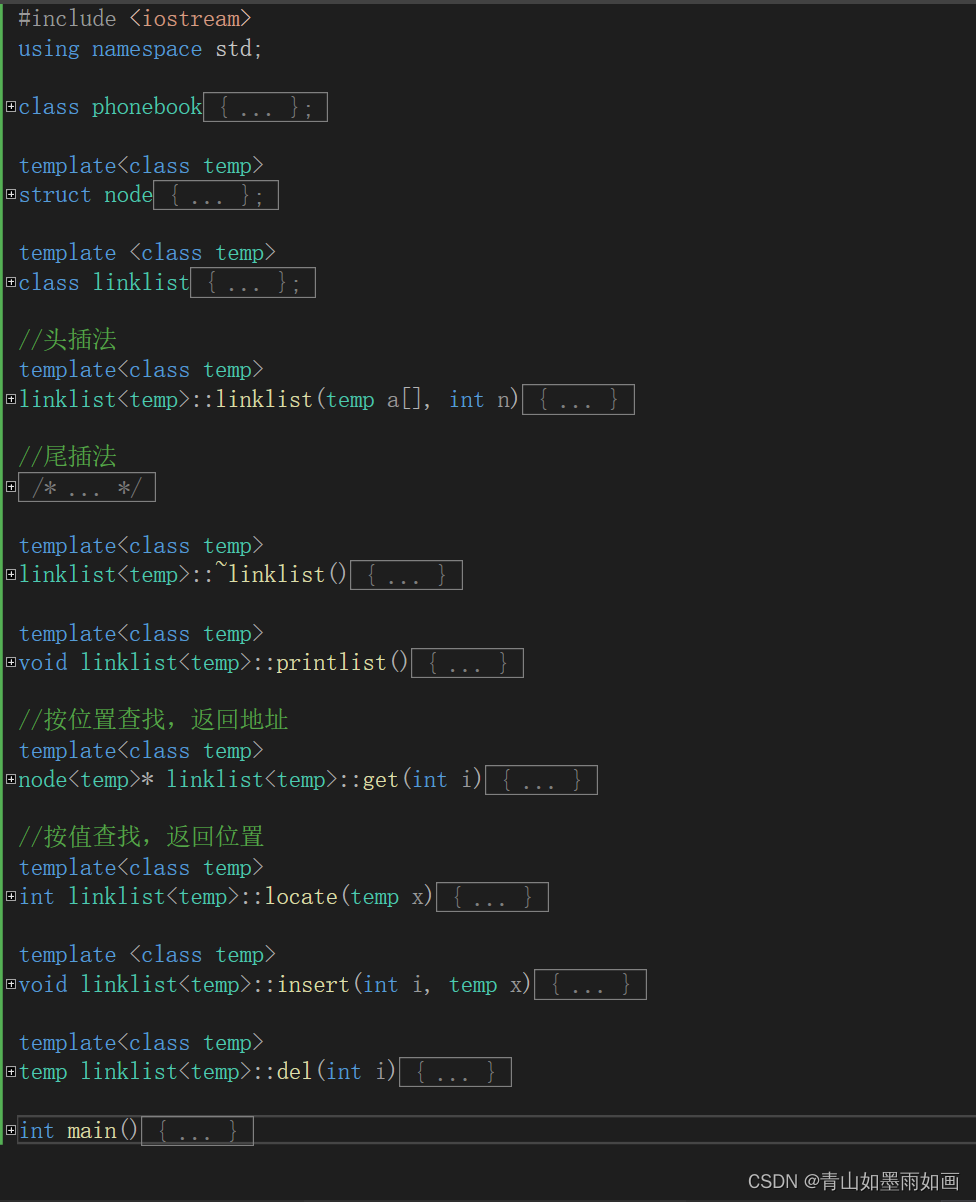
运行效果图:

1.2对书上代码的完善和对一些问题的验证和解释代码
(自己增改部分已经在代码中标明,有助于友友们对问题的理解)
1.补全一个函数:
书上没有对getlength函数做定义,本代码已经补全;
2.this指针:
“this->”,是个指针,p用没有,就是本人觉得写着顺手,看代码的时候直接忽略即可~
3.关于printlist函数的一点说明:(增改后代码第117行)
为什么printlist函数是从this->front->next开始打印数据,而不是this->front呢?
因为无论在显示构造函数还是隐式构造函数中,都没有对头结点的数据域赋值。
如果我们将this->front->next改成this->front:程序不会报错,但是会在头结点数据域输出的位置输出一串乱码。这代表头结点的存储地址。
为了便于验证,我们在linklist中添加了getfront函数,用来输出头结点的数据域。
(见增改后代码第51行函数声明)验证结果已在运行框中显示。
4.getlength函数最后一步为什么是--cnt(增改后代码第136行):
其实有了说明3的解释,相信大家应该都能大概明白,这个顺序表的实际长度确实是cnt的,但是因为头结点默认不存放有效数据,所以考虑有效长度时不将其算在内。
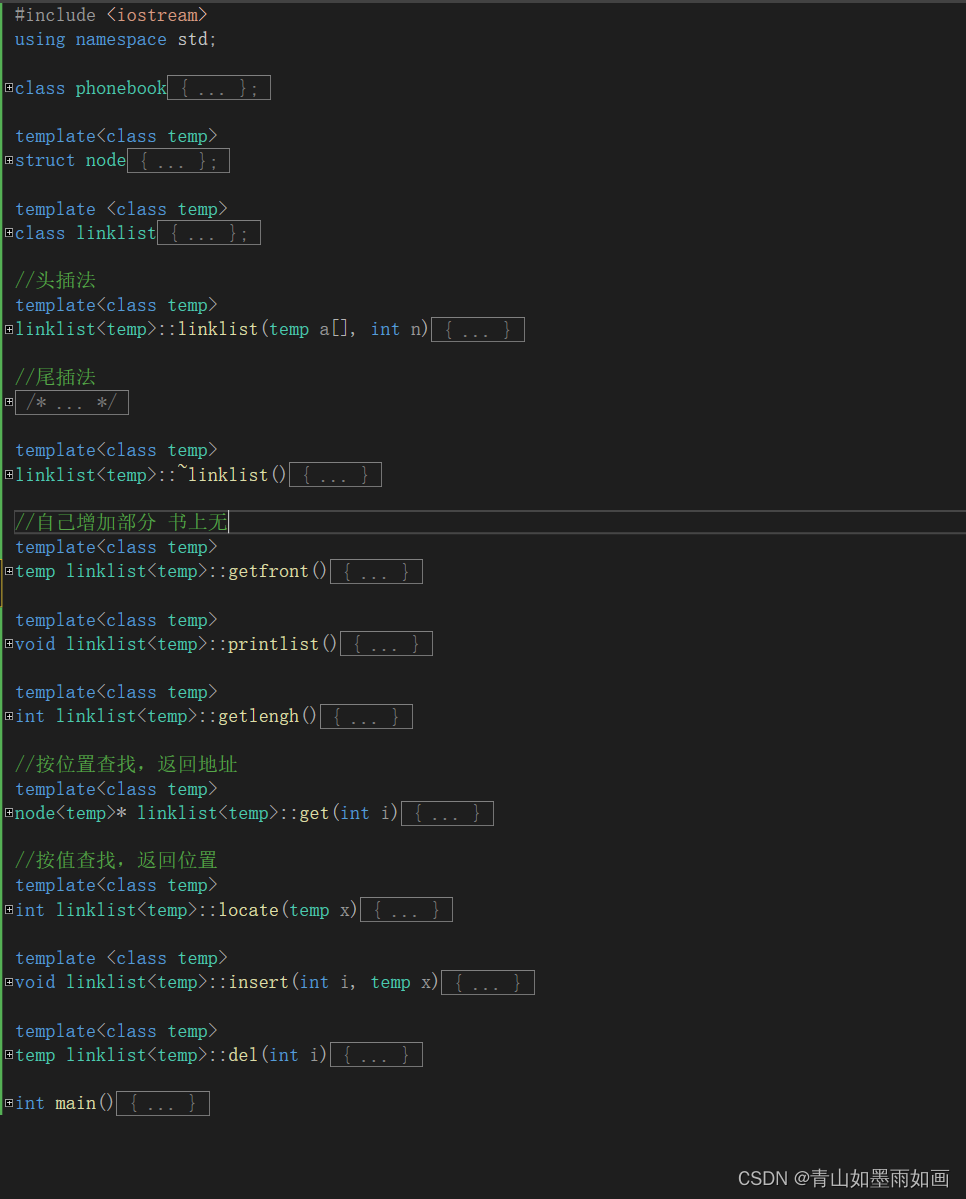
5.增改后代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class phonebook
{
private:int ID;string name;string phone;string group;
public:phonebook() {};phonebook(int ID, string name, string phone, string group){this->ID = ID;this->name = name;this->phone = phone;this->group = group;}void print(){cout << this->ID << " " << this->name << " "<< this->phone << " " << this->group << endl;}bool operator==(phonebook& p){return (p.ID == this->ID) ? true : false;}
};template<class temp>
struct node
{temp data;node* next;
};template <class temp>
class linklist
{
private:node<temp>* front;
public:linklist(){this->front = new node<temp>;this->front->next = nullptr;}linklist(temp a[], int n);~linklist();temp getfront();//自己增加部分 书上无void printlist();int getlengh();node<temp>* get(int i);int locate(temp x);void insert(int i, temp x);temp del(int i);
};//头插法
template<class temp>
linklist<temp>::linklist(temp a[], int n)
{this->front = new node<temp>;this->front->next = NULL;for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--){node<temp>* s = new node<temp>;s->data = a[i];s->next = this->front->next;this->front->next = s;}
}//尾插法
/*
template<class temp>
linklist<temp>::linklist(temp a[], int n)
{this->front = new node<temp>;node<temp>* r = this->front();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){node<temp>* s = new node<temp>;s->data = a[i];r->next = s;r = s;}r->next = NULL;
}
*/template<class temp>
linklist<temp>::~linklist()
{node<temp>* p = this->front;while (p != NULL){this->front = p;p = p->next;delete front;}
}//自己增加部分 书上无
template<class temp>
temp linklist<temp>::getfront()
{node<temp>* p = front;temp x = p->data;return x;
}template<class temp>
void linklist<temp>::printlist()
{node<temp>* p = this->front->next;//见说明3.while (p != NULL){p->data.print();//数据域中的print方法(需要用户自定义)p = p->next;}cout << endl;
}template<class temp>
int linklist<temp>::getlengh()
{node<temp>* p = this->front;int cnt = 0;while (p != NULL){p = p->next;cnt++;}return --cnt;//见说明4
}//按位置查找,返回地址
template<class temp>
node<temp>* linklist<temp>::get(int i)
{node<temp>* p = this->front->next;int j = 1;while (p != NULL && j != i){p = p->next;j++;}return p;
}//按值查找,返回位置
template<class temp>
int linklist<temp>::locate(temp x)
{node<temp>* p = this->front->next;int j = 1;while (p != NULL){if (p->data == x)return j;p = p->next;j++;}return -1;//如果没有找到,返回无效值
}template <class temp>
void linklist<temp>::insert(int i, temp x)
{node<temp>* p = this->front;if (i != 1)p = get(i - 1);//get(i - 1)表示要插入的位置的前一个结点地址if (p != NULL){node<temp>* s = new node<temp>;s->data = x;s->next = p->next;p->next = s;}else{cout << "插入位置错误:" << endl;exit(0);}
}template<class temp>
temp linklist<temp>::del(int i)
{node<temp>* p = this->front;if (i != 1)p = get(i - 1);node<temp>* q = p->next;p->next = q->next;temp x = q->data;delete q;return x;
}int main()
{phonebook pbook[4] ={{20181208,"mary","13011221827","classmates"},{20181127,"tom","13934621123","family"},{20181156,"john","1324579880","classmates"},{20181133,"lisa","1378001822","teacher"}};phonebook record(20181209, "phoenix", "1590209020", "teacher");linklist<phonebook>list(pbook, 4);cout << "通信录内容列表:" << endl;list.printlist();//自己增加部分 书上无cout << "验证头结点数据无效:" << endl;phonebook y = list.getfront();cout << "头结点数据为:" << endl;y.print();cout << endl;list.insert(1, record);cout << "通信录内容列表:" << endl;list.printlist();phonebook x = list.del(3);cout << "删除元素:" << endl;x.print();cout << "通信录内容列表:" << endl;list.printlist();int p = list.locate(record);cout << "phoenix的位置是:" << p << endl;//自己增加部分 书上无cout << "通信录的长度为:" << endl;cout << list.getlengh();return 0;
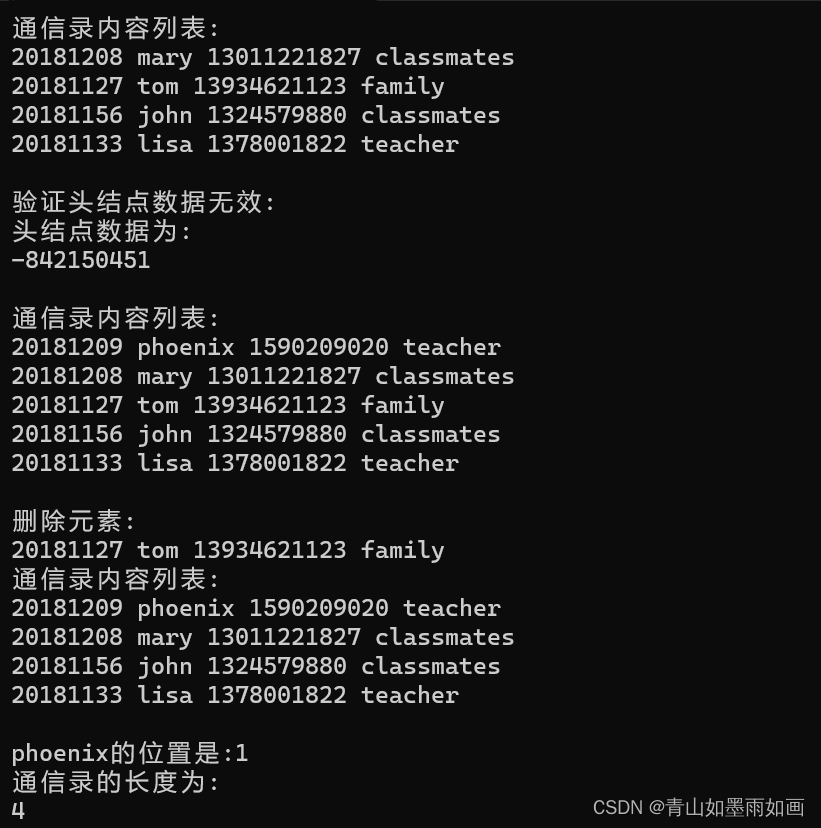
}6.增改后代码效果图:
7.增改后代码运行效果:
上一篇文章:数据结构与算法 第二章 顺序表 请参考以下链接 ~
https://blog.csdn.net/bc202205/article/details/129311232?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
写码不易,关注一下作者再走呗o(╥﹏╥)o
谢谢支持~
相关文章:

北邮22信通:你是不是在looking for……那串代码?(2)第三章单链表
相信有了第二章顺序表的基础,小伙伴们学习第三章链表应该会轻松一点吧 目录 类模板下的单链表 1.1书上干净完整代码(无增改、适合自己动手实验) 1.2对书上代码的完善和对一些问题的验证和解释代码 1.补全一个函数: 2.this指…...

蓝库云|告诉你传统产业该如何进行数字化转型
在后疫情时代下,企业该如何在面临生存危机的情形下,投入「数字化转型」、提升公司竞争力,已成为许多公司的当务之急,但到底什么是数字化转型呢?传统产业又如何着手进行数位转型? 数字化转型是什么…...

121.(leaflet篇)leaflet结合echarts4迁徙图
听老人家说:多看美女会长寿 地图之家总目录(订阅之前建议先查看该博客) 文章末尾处提供保证可运行完整代码包,运行如有问题,可“私信”博主。 效果如下所示: 下面献上完整代码,代码重要位置会做相应解释 <!DOCTYPE html> <html>...
链表及其基本操作
1.单链表:1.1定义/性质:链表是线性表的链式存储方式。单链表通过指针线性遍历,删除/增加节点时间复杂度为O(1),访问节点时间复杂度为O(n)。单链表分为带头结点和不带头结点两种,带头结点是为了方便统一操作(…...

【Java基础 下】 031 -- 反射 动态代理
一、什么是反射? 换句话说就是(从类里拿出来) 可以获取到:(利用反射,我们可以获取到类中所有的东西) 获取是先从class字节码文件中获取的 二、获取class对象的三种方式 三种方式也对应了三种阶段…...
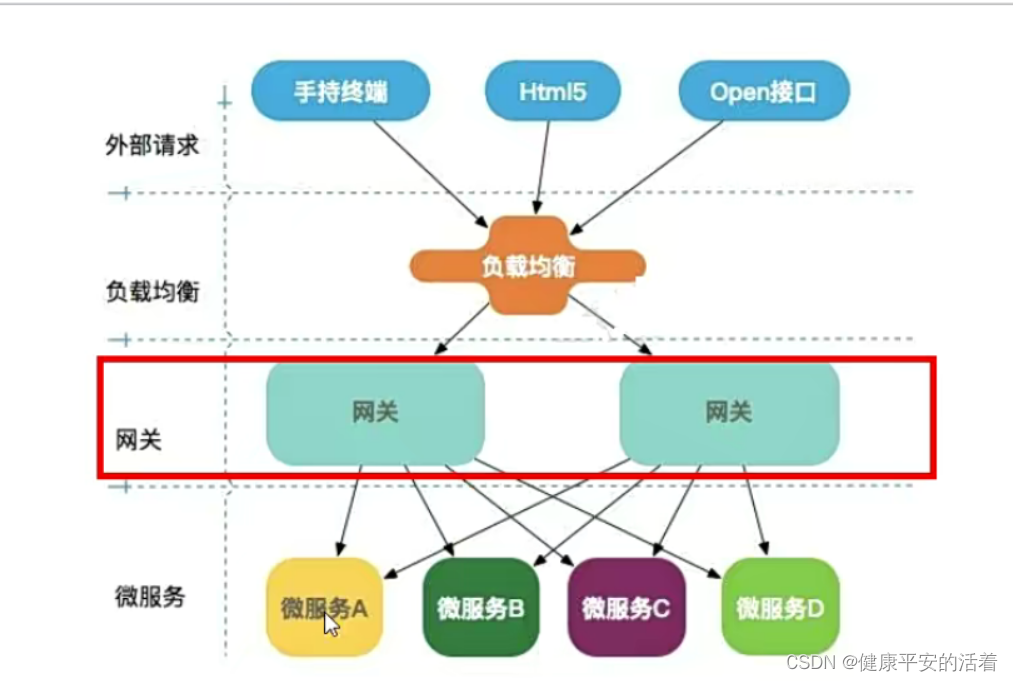
springcloud3 GateWay
一 GateWay 1.1 GateWay的作用 gateway相当于所有服务的门户,将客户端请求与服务端应用相分离,客户端请求通过gateway后由定义的路由和断言进行转发,路由代表需要转发请求的地址,断言相当于请求这些地址时所满足的条件ÿ…...

万字长文:Stable Diffusion 保姆级教程
万字长文:Stable Diffusion 保姆级教程 2022年绝对是人工智能爆发的元年,前有 stability.ai 开源 Stable Diffusion 模型,后有 Open AI 发布 ChatGPT,二者都是里程碑式的节点事件,其重要性不亚于当年苹果发布iPhone&a…...

WAMP搭建靶场
WAMP W:windows A:apache M:mysql,mariadb P:php 1. 下载phpstudy Windows版phpstudy下载 - 小皮面板(phpstudy) 2. 安装phpstudy 默认安装即可 3. 下载DVWA靶场 https://github.com/digininja/DVWA/archive/…...
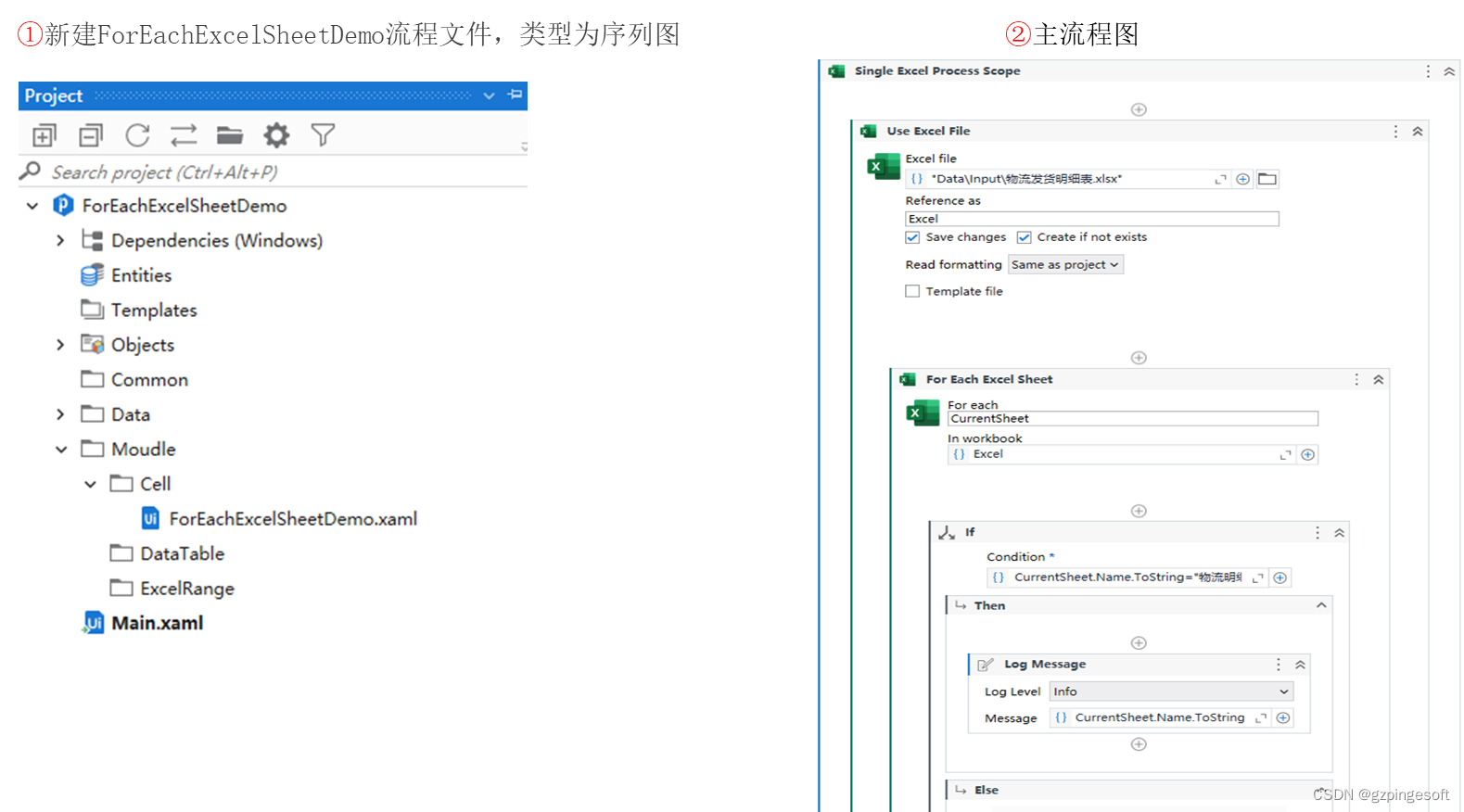
Uipath Excel 自动化系列13-ForEachExcelSheet(遍历Sheet)
活动描述 ForEachExcelSheet(遍历Sheet):遍历Excel中的工作表,可以对 Excel 工作簿中的每个工作表重复一个或多个活动,该活动需与Use Excel File 活动选择的 Excel 文件一起使用。 使用场景:当处理包含多张工作表的 Excel 文件,…...

JDBC快速入门
🍎道阻且长,行则将至。🍓 目录 一、JDBC入门 1.概述 (1)JDBC本质 (2)JDBC好处 2.快速入门 (1)步骤 (2)实践 (3)两个小问题 一、JDBC入门 1.概述 JDBC就是使用Java语言操作关系型数据库的一套API,全称:( Java…...

蓝桥杯三月刷题 第六天
文章目录💥前言😉解题报告💥星期计算🤔一、思路:😎二、代码:💥考勤刷卡🤔一、思路:😎二、代码:💥卡片🤔一、思路:😎二、代…...
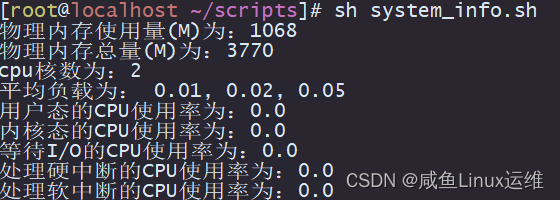
分享几个常用的运维 shell 脚本
今天咸鱼给大家分享几个不错的 Linux 运维脚本,这些脚本中大量使用了 Linux 的文本三剑客: awkgrepsed 建议大家这三个工具都要了解并最好能够较为熟练的使用 根据 PID 显示进程所有信息 根据用户输入的PID,过滤出该PID所有的信息 #! /b…...
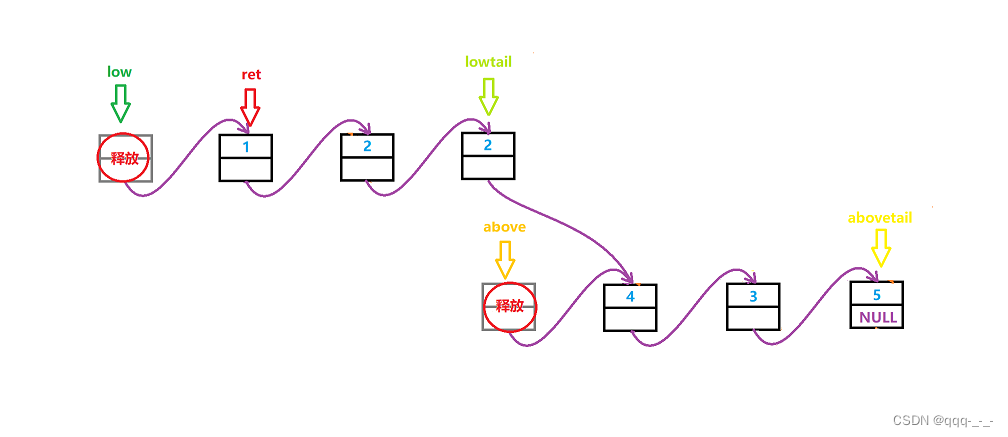
分隔链表(精美图示详解哦)
全文目录引言分隔链表题目描述与思路实现总结引言 前面,我们熟悉了管理链表中的数据的方法,也了解了几道与链表相关的题目: 戳我看单链表详解哦 在本篇文章中,我们将再了解一道题目:分隔链表: 分隔链表OJ…...
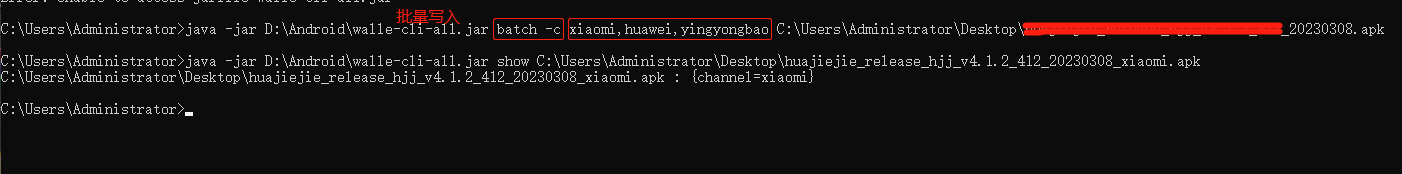
腾讯乐固加固+app签名+多渠道打包
一、腾讯乐固-基础版免费加固-上传未加固的app-下载加固包(加固成功会清除原apk的签名信息和多渠道信息)https://console.cloud.tencent.com/ms/reinforce/list/basic二、使用AndroidStudio自带工具apksigner对apk重新签名找到apksigner.bat文件 路径D:\…...
)
Spring Boot整合Redis缓存(Lettuce)
spring-boot-demo-cache-redis 此 demo 主要演示了 Spring Boot 如何整合 redis,操作redis中的数据,并使用redis缓存数据。连接池使用 Lettuce。 Lettuce官网 pom.xml <!-- data-redis --> <dependency><groupId>org.springframework…...
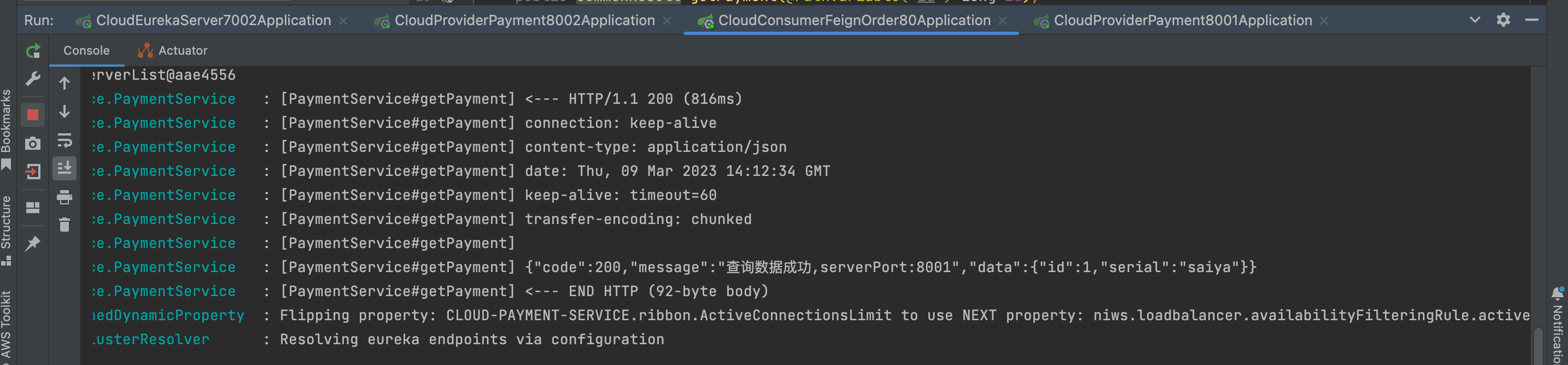
Feign
而Feign则会完全代理HTTP请求,我们只需要像调用方法一样调用它就可以完成服务请求及相关处理。Feign整合了Ribbon和Hystrix,可以让我们不再需要显式地使用这两个组件。 Feign具有如下特性: 支持可插拔的HTTP编码器和解码器; 支持Hystrix和…...

【代码训练营】day54 | 392.判断子序列 115.不同的子序列
所用代码 java 判断子序列 LeetCode 392 题目链接:判断子序列 LeetCode 392 - 简单 思路 这题和之前求最长公共子序列一样。 dp[i] [j]:以i-1为结尾的字符串s 和 以j-1为结尾的字符串t 组成的相同子序列的长度 递推公式: 相等dp[i][j] d…...
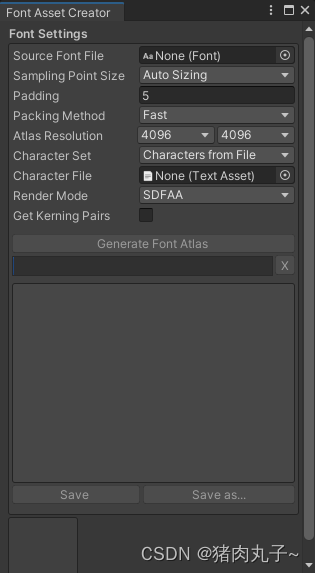
【unity3D】创建TextMeshPro(TMP)中文字体(解决输入中文乱码问题)
💗 未来的游戏开发程序媛,现在的努力学习菜鸡 💦本专栏是我关于游戏开发的学习笔记 🈶本篇是unity的TMP中文输入显示乱码的解决方式 创建 TextMeshPro 中文字体遇到的问题描述解决方式Font Asset Creator 面板扩展中文字体文本遇到…...
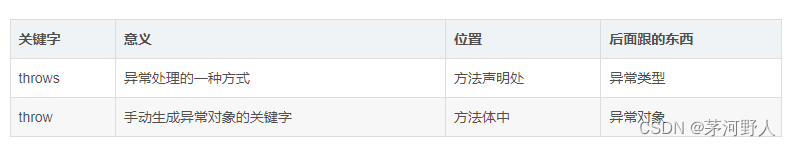
JAVA开发(JAVA中的异常)
在java开发与代码运行过程中,我们经常会遇到需要处理异常的时候。有时候是在用编辑器写代码,点击保存的时候,编辑器就提示我们某块代码有异常,强制需要处理。有时候是我们启动,运行JAVA代码的时候的,日志里…...
lesson8-Linux多线程
Linux线程概念 线程在进程内部执行,是OS调度的基本单位OS是可以做到让进程进行资源的细粒度划分的物理内存是以4kb为单位的我们的.exe可执行程序本来就是按照地址空间的方式进行编译的页表映射 - 详细图 理解线程 线程在进程的地址空间内运行, 进程内部具有多个执行流的,而线程…...

变量 varablie 声明- Rust 变量 let mut 声明与 C/C++ 变量声明对比分析
一、变量声明设计:let 与 mut 的哲学解析 Rust 采用 let 声明变量并通过 mut 显式标记可变性,这种设计体现了语言的核心哲学。以下是深度解析: 1.1 设计理念剖析 安全优先原则:默认不可变强制开发者明确声明意图 let x 5; …...

挑战杯推荐项目
“人工智能”创意赛 - 智能艺术创作助手:借助大模型技术,开发能根据用户输入的主题、风格等要求,生成绘画、音乐、文学作品等多种形式艺术创作灵感或初稿的应用,帮助艺术家和创意爱好者激发创意、提高创作效率。 - 个性化梦境…...
深入浅出Asp.Net Core MVC应用开发系列-AspNetCore中的日志记录
ASP.NET Core 是一个跨平台的开源框架,用于在 Windows、macOS 或 Linux 上生成基于云的新式 Web 应用。 ASP.NET Core 中的日志记录 .NET 通过 ILogger API 支持高性能结构化日志记录,以帮助监视应用程序行为和诊断问题。 可以通过配置不同的记录提供程…...

蓝桥杯 2024 15届国赛 A组 儿童节快乐
P10576 [蓝桥杯 2024 国 A] 儿童节快乐 题目描述 五彩斑斓的气球在蓝天下悠然飘荡,轻快的音乐在耳边持续回荡,小朋友们手牵着手一同畅快欢笑。在这样一片安乐祥和的氛围下,六一来了。 今天是六一儿童节,小蓝老师为了让大家在节…...

在 Nginx Stream 层“改写”MQTT ngx_stream_mqtt_filter_module
1、为什么要修改 CONNECT 报文? 多租户隔离:自动为接入设备追加租户前缀,后端按 ClientID 拆分队列。零代码鉴权:将入站用户名替换为 OAuth Access-Token,后端 Broker 统一校验。灰度发布:根据 IP/地理位写…...

BCS 2025|百度副总裁陈洋:智能体在安全领域的应用实践
6月5日,2025全球数字经济大会数字安全主论坛暨北京网络安全大会在国家会议中心隆重开幕。百度副总裁陈洋受邀出席,并作《智能体在安全领域的应用实践》主题演讲,分享了在智能体在安全领域的突破性实践。他指出,百度通过将安全能力…...

工业自动化时代的精准装配革新:迁移科技3D视觉系统如何重塑机器人定位装配
AI3D视觉的工业赋能者 迁移科技成立于2017年,作为行业领先的3D工业相机及视觉系统供应商,累计完成数亿元融资。其核心技术覆盖硬件设计、算法优化及软件集成,通过稳定、易用、高回报的AI3D视觉系统,为汽车、新能源、金属制造等行…...

多种风格导航菜单 HTML 实现(附源码)
下面我将为您展示 6 种不同风格的导航菜单实现,每种都包含完整 HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript 代码。 1. 简约水平导航栏 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang"zh-CN"> <head><meta charset"UTF-8"><meta name"viewport&qu…...
网络编程(UDP编程)
思维导图 UDP基础编程(单播) 1.流程图 服务器:短信的接收方 创建套接字 (socket)-----------------------------------------》有手机指定网络信息-----------------------------------------------》有号码绑定套接字 (bind)--------------…...
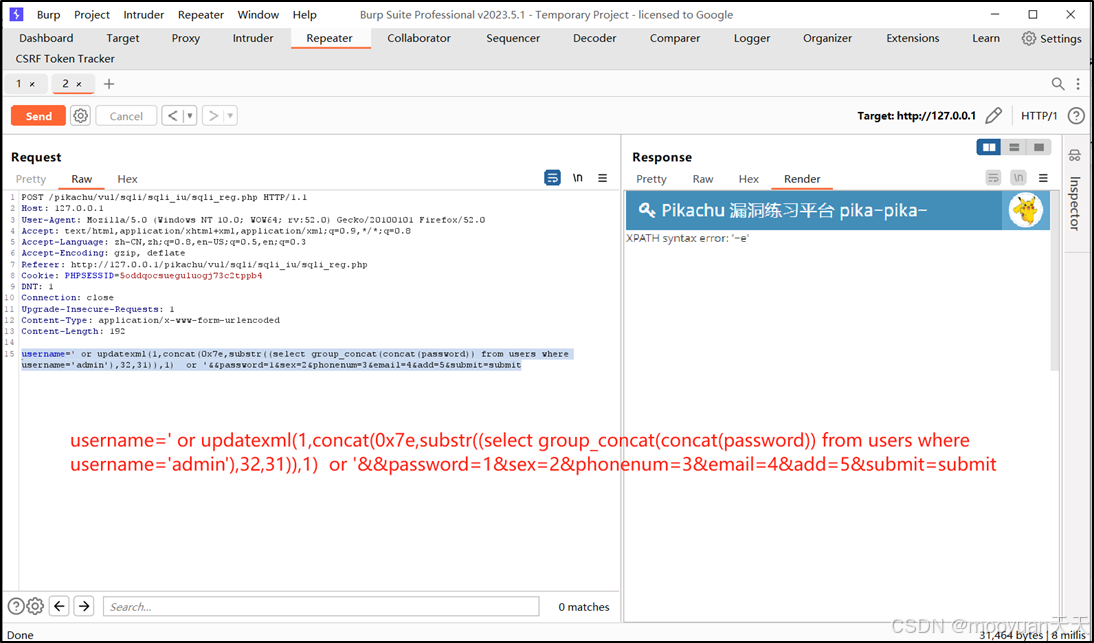
pikachu靶场通关笔记22-1 SQL注入05-1-insert注入(报错法)
目录 一、SQL注入 二、insert注入 三、报错型注入 四、updatexml函数 五、源码审计 六、insert渗透实战 1、渗透准备 2、获取数据库名database 3、获取表名table 4、获取列名column 5、获取字段 本系列为通过《pikachu靶场通关笔记》的SQL注入关卡(共10关࿰…...
