【Android】使用EventBus进行线程间通讯
EventBus
简介
EventBus:github
EventBus是Android和Java的发布/订阅事件总线。
- 简化组件之间的通信
-
解耦事件发送者和接收者
-
在 Activities, Fragments, background threads中表现良好
-
避免复杂且容易出错的依赖关系和生命周期问题
-
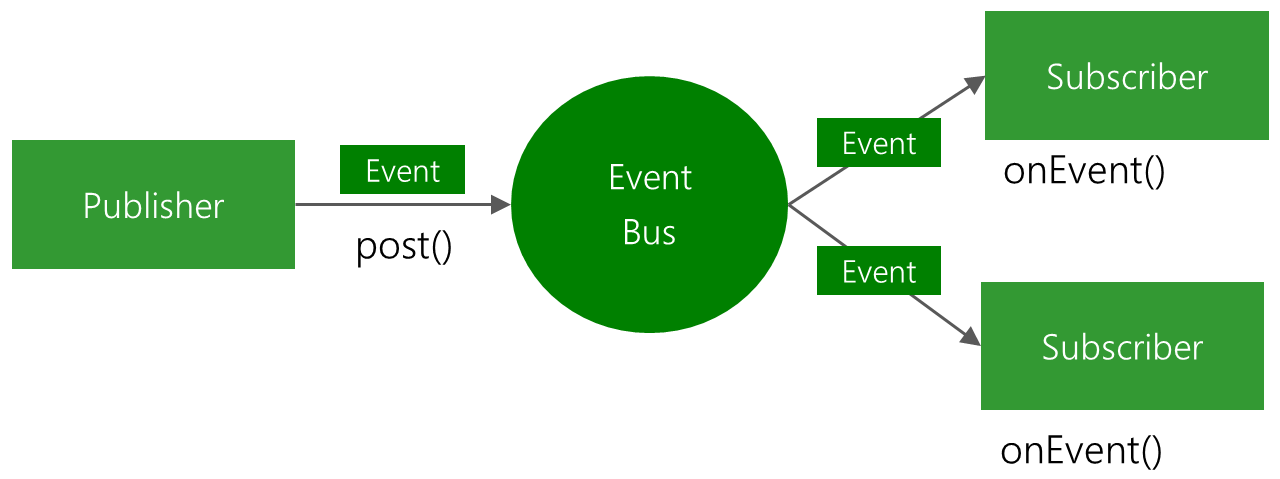
Publisher使用post发出一个Event事件,Subscriber在onEvent()函数中接收事件。
EventBus 是一款在 Android 开发中使用的发布/订阅事件总线框架,基于观察者模式,将事件的接收者和发送者分开,简化了组件之间的通信,使用简单、效率高、体积小!下边是官方的 EventBus 原理图:
导入
Android Projects:
implementation("org.greenrobot:eventbus:3.2.0")
Java Projects:
implementation("org.greenrobot:eventbus-java:3.2.0")
<dependency><groupId>org.greenrobot</groupId><artifactId>eventbus-java</artifactId><version>3.2.0</version>
</dependency>
配置
配置混淆文件
-keepattributes *Annotation*
-keepclassmembers class * {@org.greenrobot.eventbus.Subscribe <methods>;
}
-keep enum org.greenrobot.eventbus.ThreadMode { *; }# If using AsyncExecutord, keep required constructor of default event used.
# Adjust the class name if a custom failure event type is used.
-keepclassmembers class org.greenrobot.eventbus.util.ThrowableFailureEvent {<init>(java.lang.Throwable);
}# Accessed via reflection, avoid renaming or removal
-keep class org.greenrobot.eventbus.android.AndroidComponentsImpl
使用
简单流程
- 创建事件类
public static class MessageEvent { /* Additional fields if needed */ }
- 在需要订阅事件的地方,声明订阅方法并注册EventBus。
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN)
public void onMessageEvent(MessageEvent event) {// Do something
}
public class EventBusActivity extends AppCompatActivity {@Overrideprotected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);}@Overrideprotected void onStart() {super.onStart();//注册EventBusEventBus.getDefault().register(this);}//接收事件@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.POSTING, sticky = true, priority = 1)public void onReceiveMsg(MessageEvent message){Log.e("EventBus_Subscriber", "onReceiveMsg_POSTING: " + message.toString());}//接收事件@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN, sticky = true, priority = 1)public void onReceiveMsg1(MessageEvent message){Log.e("EventBus_Subscriber", "onReceiveMsg_MAIN: " + message.toString());}//接收事件@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN_ORDERED, sticky = true, priority = 1)public void onReceiveMsg2(MessageEvent message){Log.e("EventBus_Subscriber", "onReceiveMsg_MAIN_ORDERED: " + message.toString());}@Overrideprotected void onDestroy() {super.onDestroy();//取消事件EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);}
}
- 提交订阅事件
@OnClick(R2.id.send_event_common)
public void clickCommon(){MessageEvent message = new MessageEvent(1, "这是一条普通事件");EventBus.getDefault().post(message);
}@OnClick(R2.id.send_event_sticky)
public void clickSticky(){MessageEvent message = new MessageEvent(1, "这是一条黏性事件");EventBus.getDefault().postSticky(message);
}
Subcribe注解
Subscribe是EventBus自定义的注解,共有三个参数(可选):threadMode、boolean sticky、int priority。 完整的写法如下:
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN,sticky = true,priority = 1)
public void onReceiveMsg(MessageEvent message) {Log.e(TAG, "onReceiveMsg: " + message.toString());
}
priority
priority是优先级,是一个int类型,默认值为0。值越大,优先级越高,越优先接收到事件。
值得注意的是,只有在post事件和事件接收处理,处于同一个线程环境的时候,才有意义。
sticky
sticky是一个boolean类型,默认值为false,默认不开启黏性sticky特性,那么什么是sticky特性呢?
上面的例子都是对订阅者 (接收事件) 先进行注册,然后在进行post事件。
那么sticky的作用就是:订阅者可以先不进行注册,如果post事件已经发出,再注册订阅者,同样可以接收到事件,并进行处理。
ThreadMode 模式
POSITING:订阅者将在发布事件的同一线程中被直接调用。这是默认值。事件交付意味着最少的开销,因为它完全避免了线程切换。因此,对于已知可以在很短时间内完成而不需要主线程的简单任务,推荐使用这种模式。使用此模式的事件处理程序必须快速返回,以避免阻塞发布线程(可能是主线程)。
MAIN:在Android上,订阅者将在Android的主线程(UI线程)中被调用。如果发布线程是主线程,将直接调用订阅者方法,阻塞发布线程。否则,事件将排队等待交付(非阻塞)。使用此模式的订阅者必须快速返回以避免阻塞主线程。如果不是在Android上,行为与POSITING相同。
MAIN_ORDERED:在Android上,订阅者将在Android的主线程(UI线程)中被调用。与MAIN不同的是,事件将始终排队等待交付。这确保了post调用是非阻塞的。
BACKGROUND:在Android上,订阅者将在后台线程中被调用。如果发布线程不是主线程,订阅者方法将在发布线程中直接调用。如果发布线程是主线程,EventBus使用一个后台线程,它将按顺序传递所有事件。使用此模式的订阅者应尽量快速返回,以避免阻塞后台线程。如果不是在Android上,总是使用一个后台线程。
ASYNC:订阅服务器将在单独的线程中调用。这始终独立于发布线程和主线程。使用此模式发布事件从不等待订阅者方法。如果订阅者方法的执行可能需要一些时间,例如网络访问,则应该使用此模式。避免同时触发大量长时间运行的异步订阅者方法,以限制并发线程的数量。EventBus使用线程池来有效地重用已完成的异步订阅者通知中的线程。
/*** Each subscriber method has a thread mode, which determines in which thread the method is to be called by EventBus.* EventBus takes care of threading independently from the posting thread.* * @see EventBus#register(Object)* @author Markus*/
public enum ThreadMode {/*** Subscriber will be called directly in the same thread, which is posting the event. This is the default. Event delivery* implies the least overhead because it avoids thread switching completely. Thus this is the recommended mode for* simple tasks that are known to complete in a very short time without requiring the main thread. Event handlers* using this mode must return quickly to avoid blocking the posting thread, which may be the main thread.*/POSTING,/*** On Android, subscriber will be called in Android's main thread (UI thread). If the posting thread is* the main thread, subscriber methods will be called directly, blocking the posting thread. Otherwise the event* is queued for delivery (non-blocking). Subscribers using this mode must return quickly to avoid blocking the main thread.* If not on Android, behaves the same as {@link #POSTING}.*/MAIN,/*** On Android, subscriber will be called in Android's main thread (UI thread). Different from {@link #MAIN},* the event will always be queued for delivery. This ensures that the post call is non-blocking.*/MAIN_ORDERED,/*** On Android, subscriber will be called in a background thread. If posting thread is not the main thread, subscriber methods* will be called directly in the posting thread. If the posting thread is the main thread, EventBus uses a single* background thread, that will deliver all its events sequentially. Subscribers using this mode should try to* return quickly to avoid blocking the background thread. If not on Android, always uses a background thread.*/BACKGROUND,/*** Subscriber will be called in a separate thread. This is always independent from the posting thread and the* main thread. Posting events never wait for subscriber methods using this mode. Subscriber methods should* use this mode if their execution might take some time, e.g. for network access. Avoid triggering a large number* of long running asynchronous subscriber methods at the same time to limit the number of concurrent threads. EventBus* uses a thread pool to efficiently reuse threads from completed asynchronous subscriber notifications.*/ASYNC
}
相关文档
- EventBus详解 (详解 + 原理)
- 三幅图弄懂EventBus核心原理
相关文章:

【Android】使用EventBus进行线程间通讯
EventBus 简介 EventBus:github EventBus是Android和Java的发布/订阅事件总线。 简化组件之间的通信 解耦事件发送者和接收者 在 Activities, Fragments, background threads中表现良好 避免复杂且容易出错的依赖关系和生命周期问题 Publisher使用post发出…...

Leetcode 3179. Find the N-th Value After K Seconds
Leetcode 3179. Find the N-th Value After K Seconds 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3179. Find the N-th Value After K Seconds 1. 解题思路 这一题的话还是一个动态规划的问题,核心递推关系式为: dp(n, k) dp(n-1, k) dp(n, k)我…...
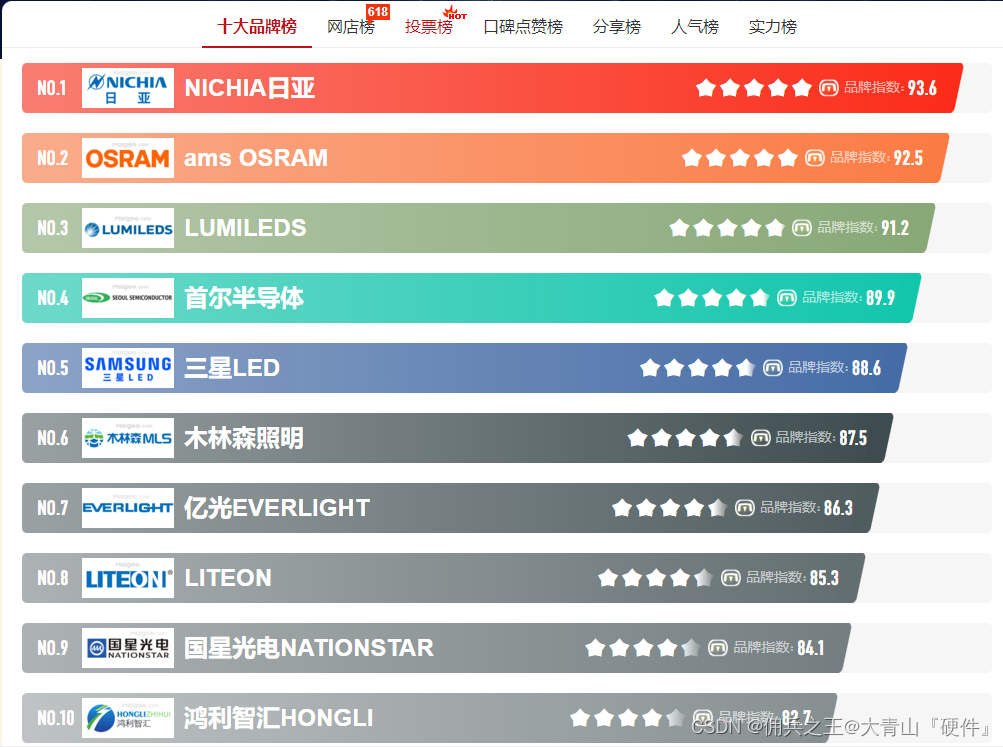
发光二极管十大品牌
日常电路设计中,LED是必用的元器件之一,辅助判定电路异常。 十大发光二极管品牌-LED灯珠生产厂家哪家好-LED发光二极管厂家前十-Maigoo品牌榜...

nginx配置文件
Nginx是一个高性能的HTTP和反向代理服务器,它的配置文件是其灵活性和强大功能的核心。Nginx的配置文件通常位于 /etc/nginx/nginx.conf 或者 /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf,取决于你的操作系统和安装路径。配置文件的结构和语法决定了Nginx如何处理请…...
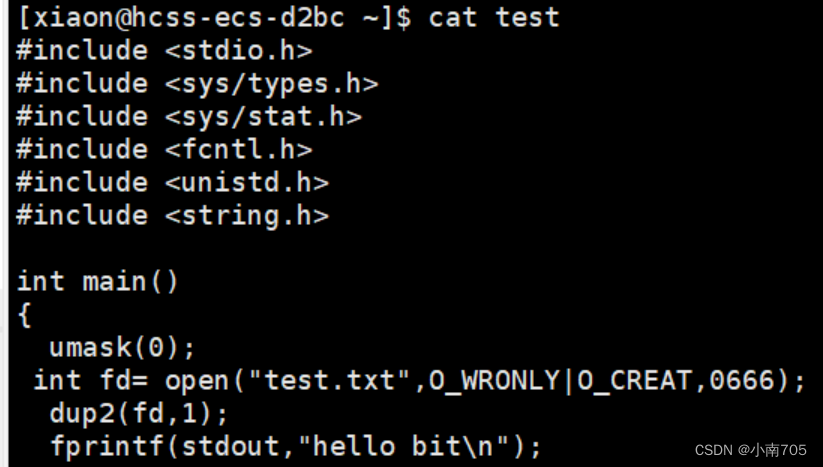
Linux基础I/O
一,系统文件I/O 写文件: #include <stdio.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <string.h> int main() {umask(0);int fd open("myfile", O_WRO…...

视觉SLAM14精讲——相机与图像3.1
视觉SLAM14精讲 三维空间刚体运动1.0三维空间刚体运动1.1三维空间刚体运动1.2李群与李代数2.1相机与图像3.1 视觉SLAM14精讲——相机与图像3.1 视觉SLAM14精讲简介相机模型内参K 简介 相机是VSLAM中的核心传感器。本章知识点内容涉及到相机相关的知识以及3D计算视觉的一些基础…...
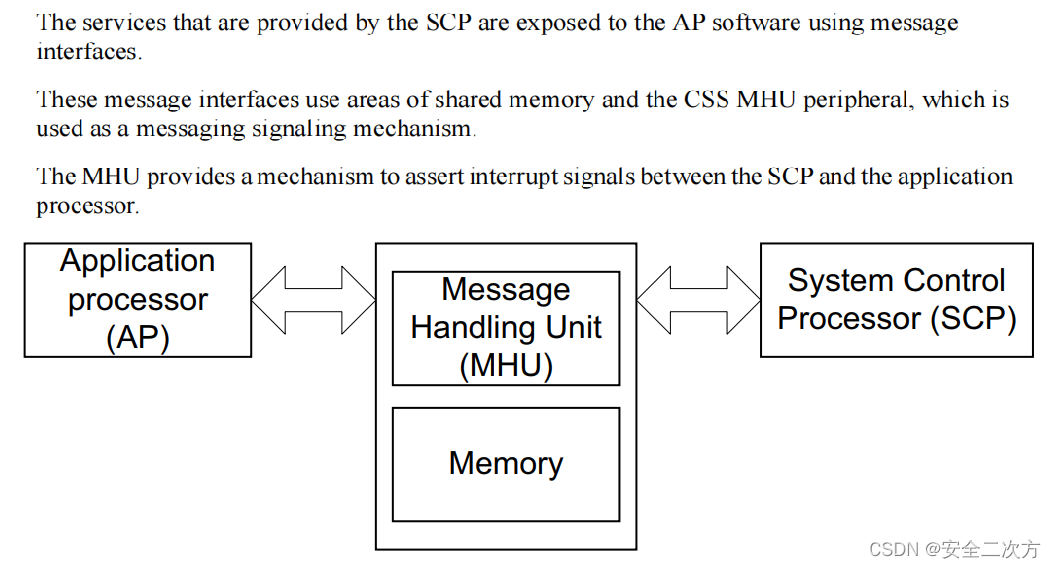
ARM功耗管理框架之SCP
安全之安全(security)博客目录导读 目录 一、功耗管理框架中的SCP 二、SCP的示例 三、SCP固件 四、SCP启动流程 五、SCP的memory map 六、SCP与AP的通信 思考:功耗管理框架?SCP?PPU?LPI?之间的关系?…...

uni-app学习--基础组件使用、页面生命周期、本地存储、网络请求、条件编译、路由跳转
文章目录 1. 基本组件的使用1. text文本组件的使用2. view视图容器组件的使用3. button按钮组件的使用4. image组件的使用5. map组件 2. uni-app中的样式1. uni-app:px2rpx计算 3. uni-app的数据绑定1. 基本的数据绑定2. v-bind,v-for,v-on 4. uni-app的生命周期1. …...

Cweek4+5
C语言学习 十.指针详解 6.有关函数指针的代码 代码1:(*(void (*)())0)(); void(*)()是函数指针类型,0是一个函数的地址 (void(*)())是强制转换 总的是调用0地址处的函数,传入参数为空 代码2:void (*signal(int, void(*)(int))…...

Segment Anything CSharp| 在 C# 中通过 OpenVINO™ 部署 SAM 模型实现万物分割
OpenVINO™ C# API 是一个 OpenVINO™ 的 .Net wrapper,应用最新的 OpenVINO™ 库开发,通过 OpenVINO™ C API 实现 .Net 对 OpenVINO™ Runtime 调用.Segment Anything Model(SAM)是一个基于Transformer的深度学习模型&#x…...

企业应如何选择安全合规的内外网文件摆渡系统?
网络隔离是一种安全措施,旨在将网络划分为不同的部分,以减少安全风险并保护敏感信息。常见的隔离方式像物理隔离、逻辑隔离、防火墙隔离、虚拟隔离、DMZ区隔离等,将网络隔离成内网和外网。内外网文件摆渡通常指在内部网络(内网&am…...

一分钟有60秒,这个有趣的原因你知道吗?
每周跟踪AI热点新闻动向和震撼发展 想要探索生成式人工智能的前沿进展吗?订阅我们的简报,深入解析最新的技术突破、实际应用案例和未来的趋势。与全球数同行一同,从行业内部的深度分析和实用指南中受益。不要错过这个机会,成为AI领…...
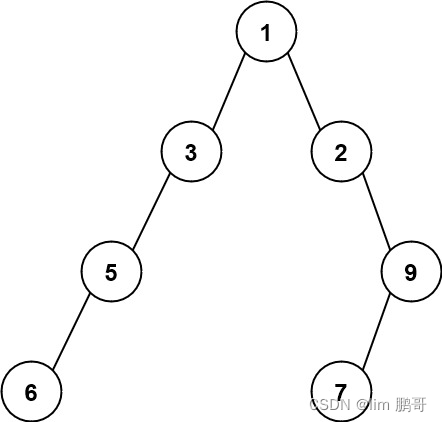
二叉树最大宽度
文章目录 前言二叉树最大宽度1.题目解析2.算法原理3.代码编写 总结 前言 二叉树最大宽度 1.题目解析 给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回树的 最大宽度 。 树的 最大宽度 是所有层中最大的 宽度 。 每一层的 宽度 被定义为该层最左和最右的非空节点(即…...
自定义HOOK)
React@16.x(24)自定义HOOK
目录 1,介绍2,简单举例2.1,获取数据1.2,计时器 2,自定义 HOOK 相比类组件 1,介绍 将一些常用的,跨组件的函数抽离,做成公共函数也就是 HOOK。自定义HOOK需要按照HOOK的规则来实现&a…...

群体优化算法----树蛙优化算法介绍以及应用于资源分配示例
介绍 树蛙优化算法(Tree Frog Optimization Algorithm, TFO)是一种基于群体智能的优化算法,模拟了树蛙在自然环境中的跳跃和觅食行为。该算法通过模拟树蛙在树枝间的跳跃来寻找最优解,属于近年来发展起来的自然启发式算法的一种 …...

常见汇编指令
下面是一些包含汇编指令 MOV、PUSH、POP、LEA、LDS、ADD、ADC、INC、SUB、SBB、DEC、CMP、MUL、DIV、AND、OR、XOR、NOT、TEST、SHL、SAL、SHR、SAR、ROL、ROR、RCL、RCR、LODS、MOVS 的例题。这些例题展示了每条指令的用法及其作用。 1. MOV 指令 MOV AX, BX ; 将寄存器 B…...

Mysql学习(七)——约束
文章目录 四、约束4.1 概述4.2 约束演示4.3 外键约束 总结 四、约束 4.1 概述 概念:约束是作用于表中字段上的规则,用于限制存储在表中的数据。目的:保证数据库中数据的正确、有效性和完整性。分类: 4.2 约束演示 根据需求&…...

Redis实战篇02
1.分布式锁Redisson 简单介绍: 使用setnx可能会出现的极端问题: Redisson的简介: 简单的使用: 业务代码的改造: private void handleVoucherOrder(VoucherOrder voucherOrder) {Long userId voucherOrder.getUserI…...
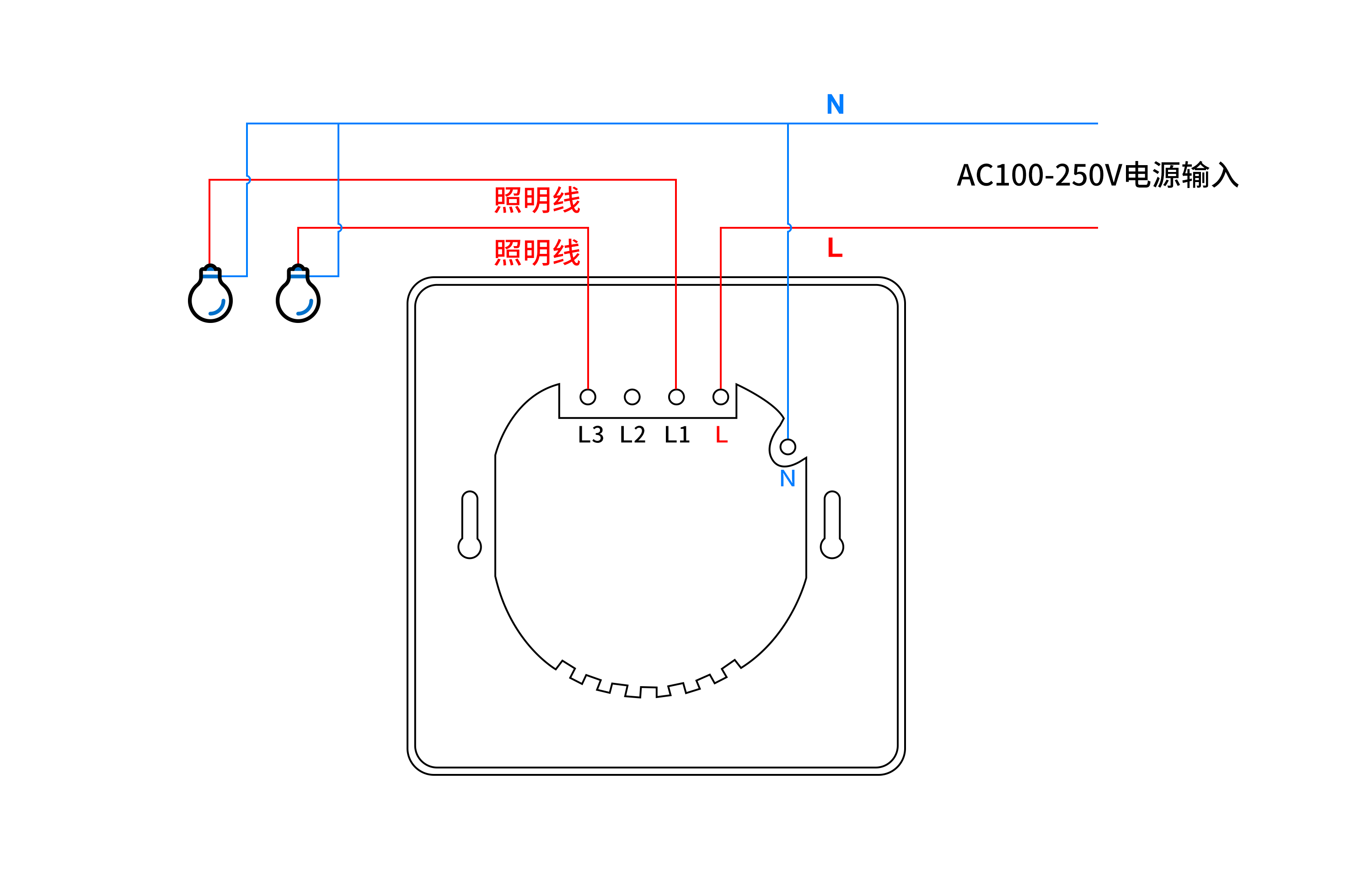
怎么用PHP语言实现远程控制两路照明开关
怎么用PHP语言实现远程控制两路开关呢? 本文描述了使用PHP语言调用HTTP接口,实现控制两路开关,两路开关可控制两路照明、排风扇等电器。 可选用产品:可根据实际场景需求,选择对应的规格 序号设备名称厂商1智能WiFi墙…...

Docker面试整理-什么是多阶段构建?它的好处是什么?
多阶段构建是 Docker 在 Dockerfile 中引入的一个功能,允许你在单个 Dockerfile 中使用多个构建阶段,但最终只生成一个轻量级的镜像。这是通过在一个 Dockerfile 中定义多个 FROM 指令来实现的,每个 FROM 指令都可以使用不同的基础镜像,并开始一个新的构建阶段。 多阶段构建…...

React 第五十五节 Router 中 useAsyncError的使用详解
前言 useAsyncError 是 React Router v6.4 引入的一个钩子,用于处理异步操作(如数据加载)中的错误。下面我将详细解释其用途并提供代码示例。 一、useAsyncError 用途 处理异步错误:捕获在 loader 或 action 中发生的异步错误替…...

TDengine 快速体验(Docker 镜像方式)
简介 TDengine 可以通过安装包、Docker 镜像 及云服务快速体验 TDengine 的功能,本节首先介绍如何通过 Docker 快速体验 TDengine,然后介绍如何在 Docker 环境下体验 TDengine 的写入和查询功能。如果你不熟悉 Docker,请使用 安装包的方式快…...

Linux链表操作全解析
Linux C语言链表深度解析与实战技巧 一、链表基础概念与内核链表优势1.1 为什么使用链表?1.2 Linux 内核链表与用户态链表的区别 二、内核链表结构与宏解析常用宏/函数 三、内核链表的优点四、用户态链表示例五、双向循环链表在内核中的实现优势5.1 插入效率5.2 安全…...

k8s从入门到放弃之Ingress七层负载
k8s从入门到放弃之Ingress七层负载 在Kubernetes(简称K8s)中,Ingress是一个API对象,它允许你定义如何从集群外部访问集群内部的服务。Ingress可以提供负载均衡、SSL终结和基于名称的虚拟主机等功能。通过Ingress,你可…...
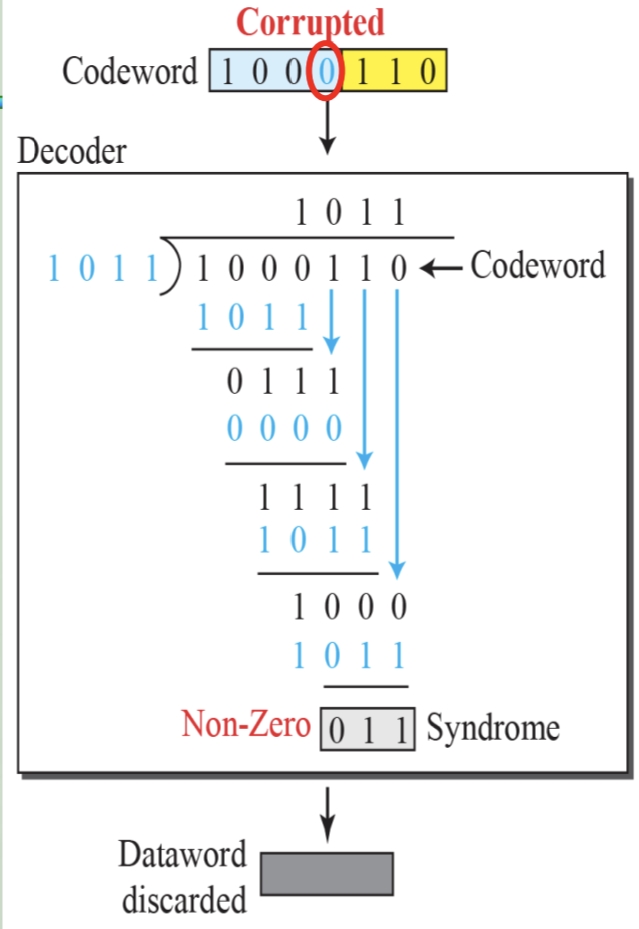
循环冗余码校验CRC码 算法步骤+详细实例计算
通信过程:(白话解释) 我们将原始待发送的消息称为 M M M,依据发送接收消息双方约定的生成多项式 G ( x ) G(x) G(x)(意思就是 G ( x ) G(x) G(x) 是已知的)࿰…...

解锁数据库简洁之道:FastAPI与SQLModel实战指南
在构建现代Web应用程序时,与数据库的交互无疑是核心环节。虽然传统的数据库操作方式(如直接编写SQL语句与psycopg2交互)赋予了我们精细的控制权,但在面对日益复杂的业务逻辑和快速迭代的需求时,这种方式的开发效率和可…...
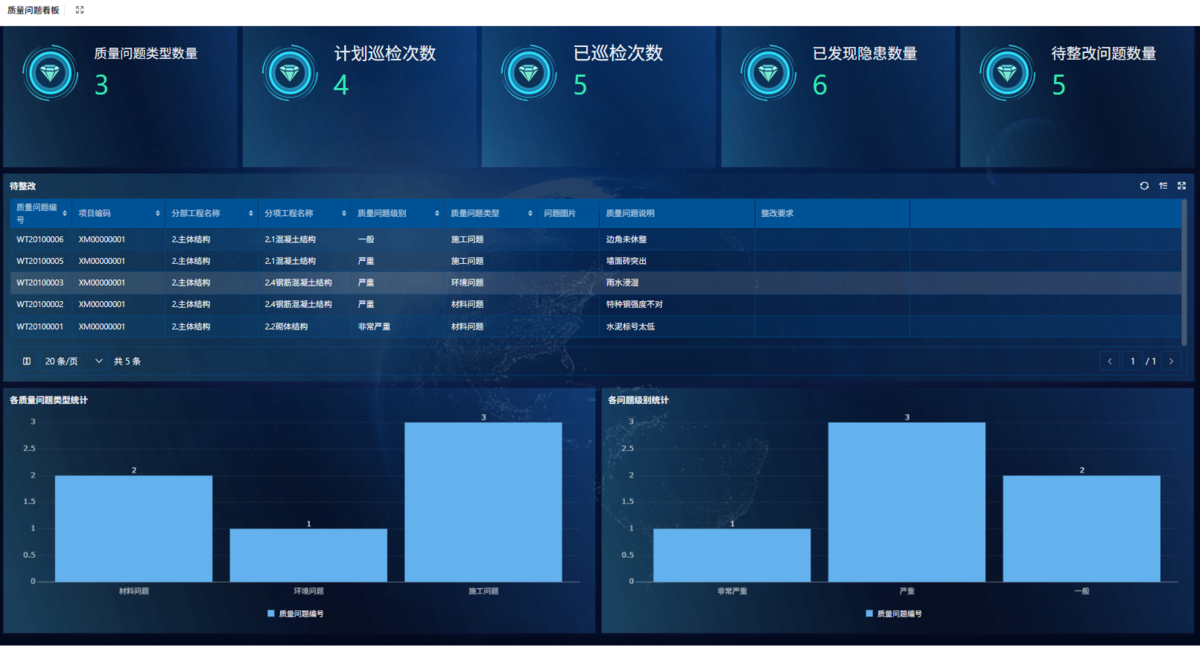
为什么需要建设工程项目管理?工程项目管理有哪些亮点功能?
在建筑行业,项目管理的重要性不言而喻。随着工程规模的扩大、技术复杂度的提升,传统的管理模式已经难以满足现代工程的需求。过去,许多企业依赖手工记录、口头沟通和分散的信息管理,导致效率低下、成本失控、风险频发。例如&#…...

Java 加密常用的各种算法及其选择
在数字化时代,数据安全至关重要,Java 作为广泛应用的编程语言,提供了丰富的加密算法来保障数据的保密性、完整性和真实性。了解这些常用加密算法及其适用场景,有助于开发者在不同的业务需求中做出正确的选择。 一、对称加密算法…...
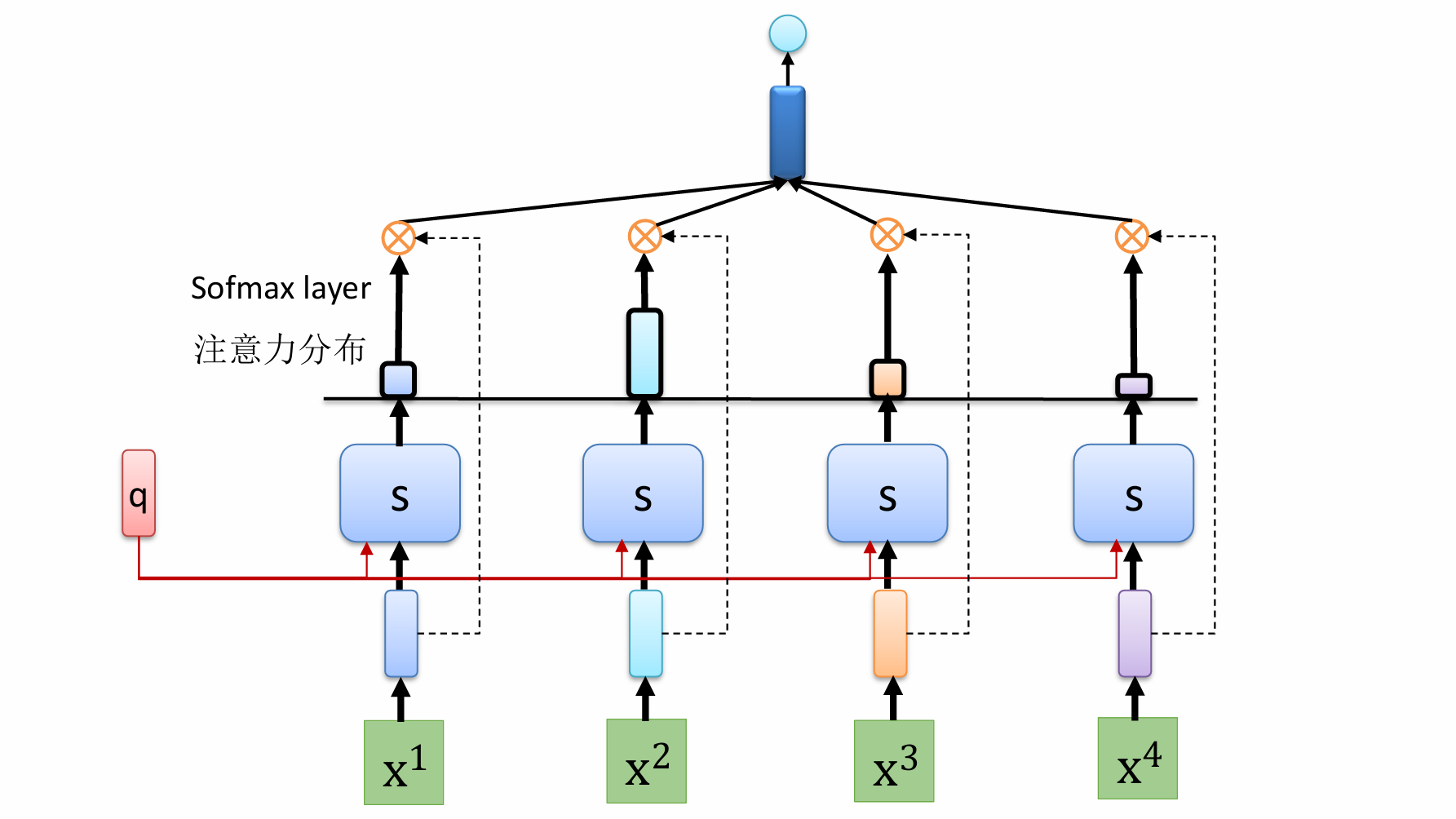
自然语言处理——循环神经网络
自然语言处理——循环神经网络 循环神经网络应用到基于机器学习的自然语言处理任务序列到类别同步的序列到序列模式异步的序列到序列模式 参数学习和长程依赖问题基于门控的循环神经网络门控循环单元(GRU)长短期记忆神经网络(LSTM)…...
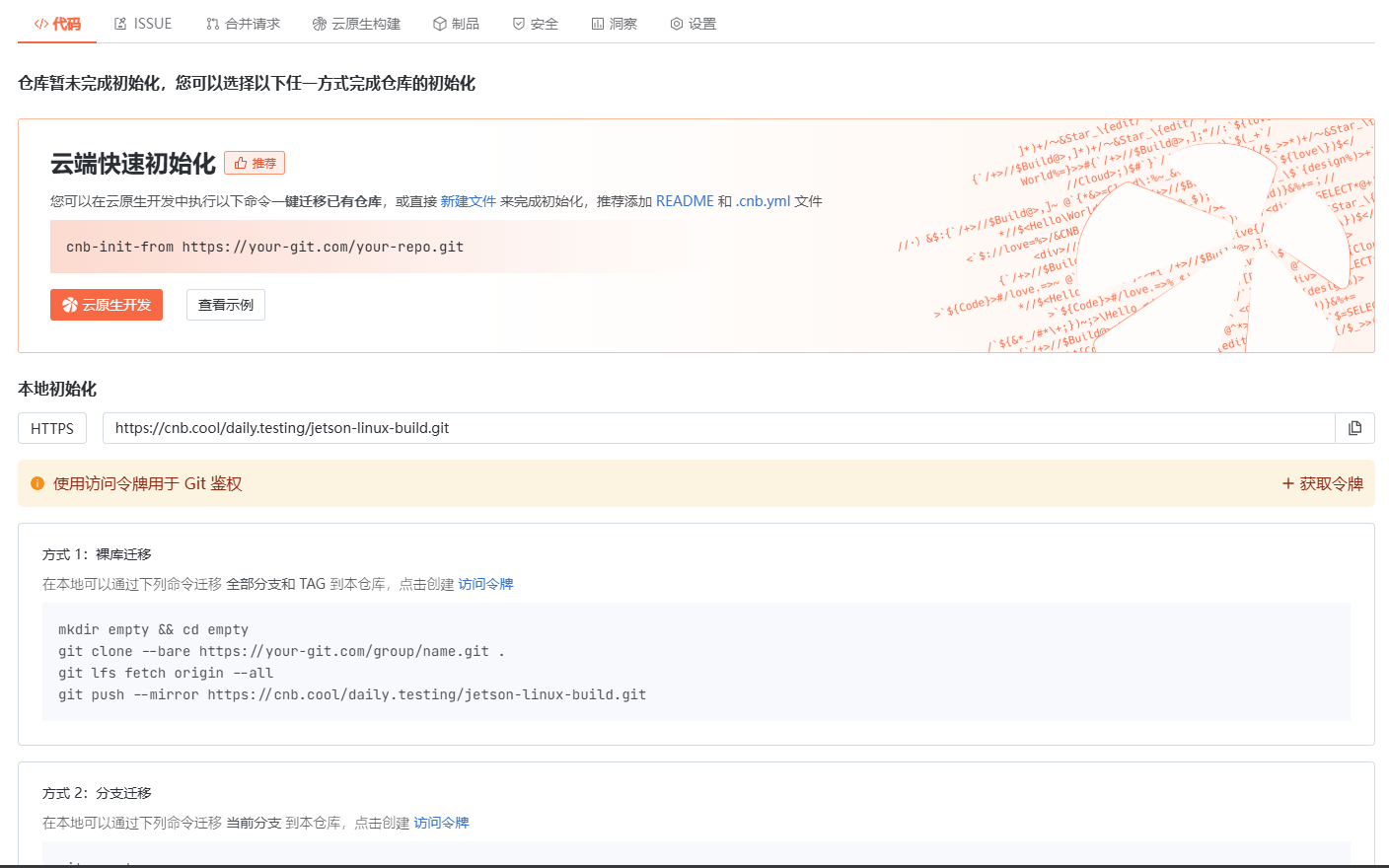
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境 引言 临时运维一个古董项目,无文档,无环境,无交接人,俗称三无。 运行设备的环境老,本地环境版本高,ssh不过去。正好最近对 腾讯出品的云原生 cnb 感兴趣&…...
