Hazelcast 分布式缓存 在Seatunnel中的使用
1、背景
最近在调研seatunnel的时候,发现新版的seatunnel提供了一个web服务,可以用于图形化的创建数据同步任务,然后管理任务。这里面有个日志模块,可以查看任务的执行状态。其中有个取读数据条数和同步数据条数。很好奇这个数据是怎么来的。跟踪源码发现Hazelcast。所以对Hazelcast进行了研究。
2、Hazelcast是什么
Hazelcast是一个开源的分布式内存数据网格(In-Memory Data Grid,简称IMDG)解决方案,主要用于分布式计算和缓存
- 分布式数据结构:Hazelcast提供了一系列分布式数据结构,如Map、List、Set、Queue等,可以在集群中进行分布式存储和访问。
- 缓存:Hazelcast提供了分布式缓存功能,可以将数据存储在内存中,以提供快速的访问速度。它支持多种缓存策略,如LRU(Least Recently Used)、LFU(Least Frequently Used)和TTL(Time to Live)等。
- 分布式计算:Hazelcast支持将计算任务分布到集群中的多个节点上进行并行处理,提高应用程序的处理能力。
- 高可靠性:Hazelcast使用分布式复制和故障转移机制,确保数据的可靠性和高可用性。它具有自动故障检测和恢复机制,可以在节点故障时自动迁移数据和任务。
- 扩展性:Hazelcast可以方便地进行水平扩展,通过添加更多的节点来增加集群的处理能力。它支持动态添加和移除节点,而无需停止应用程序。
- 集成性:Hazelcast提供了与各种应用程序和框架的集成,如Spring、Hibernate、JCache等。它还支持与其他分布式系统的集成,如Apache Kafka、Apache Ignite等。
- 多语言支持:Hazelcast提供了对多种编程语言的支持,包括Java、C#、C++、Python和Node.js等
3、应用场景
- 缓存:Hazelcast可以作为高性能的分布式缓存解决方案,用于缓存应用程序中的热点数据。
- 分布式计算:Hazelcast提供了分布式计算框架,可以将计算任务分布到集群中的多个节点上进行并行处理,适用于金融、电信、电子商务等行业。
- 实时数据处理:Hazelcast可以处理实时数据流,支持数据的实时处理和分析,适用于构建实时应用,如实时监控系统、实时推荐系统等。
- 分布式会话管理:Hazelcast可以用于管理分布式会话,实现会话的共享和负载均衡。
- 分布式数据存储:Hazelcast可以作为分布式数据存储解决方案,用于在多个节点间共享数据。
4、与Redis对比
可以看到Hazelcast可以理解为一个NoSQL,那就不得不说我们用的最多的Redis了。两者都提供了丰富的数据接口,比如map、list等等。那为什么不直接用Redis呢。我理解有下边几个方面的原因:
- 使用Redis需要额外的环境搭建,而Hazelcast如果使用内嵌的方式,则不需要额外的组件引入,做到了开箱即用。
- Hazelcast用的是应用服务器自身的内存,扩展性强,不需要外部内存(有点类似Caffeine)。
- Hazelcast对过期时间的支持没有Redis那么灵活。
- Hazelcast可以进行分布式计算。我们将数据存入到多个节点,通过分布式计算的api,从多个节点上读取数据,然后计算并返回。这也算是相较Redis的一个优势。
- Redis可以供多个应用使用共享数据,与应用解耦。Hazelcast一般使用需要嵌入应用。
如果不考虑分布式计算等场景,完全可以看那个方便。如果公司没有基础架构,并且是自己业务线的产品。那完全可以使用Hazelcast。免去了Redis的搭建、运维、管理等环境。否则还是老老实实的用Redis吧。
但是如果存在实时流式处理,那么使用Hazelcast的分布式特性是个不错的选择。比如咱们做一个监控系统,需要处理很多业务系统的数据,总不能单纯在Redis或者Mysql或者单机内存中处理吧。可以考虑试试Hazelcast。
5、怎么用
上边说了一堆的理论,说到底怎么用呢,这里以SpringBoot嵌入式为例。
- maven中添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>com.hazelcast</groupId> <artifactId>hazelcast</artifactId> <version>你的Hazelcast版本号</version> </dependency> <!-- Hazelcast Spring Boot 集成(如果需要) --> <dependency> <groupId>com.hazelcast</groupId> <artifactId>hazelcast-spring-boot</artifactId> <version>你的Hazelcast Spring Boot集成版本号</version> </dependency> - 代码
import com.hazelcast.core.HazelcastInstance; import com.hazelcast.map.IMap; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class HazelcastService { @Autowired private HazelcastInstance hazelcastInstance; public void putData() { IMap<String, String> map = hazelcastInstance.getMap("my-map"); map.put("key1", "value1"); } public String getData(String key) { IMap<String, String> map = hazelcastInstance.getMap("my-map"); return map.get(key); } } - 启动成功
分别启动两个服务,可以看到有两个Hazelcast节点组成的集群

6、源码
源码我想从两个方面去看
1、seatunnel-web提供的查看监控
- 找到查看日志接口
@RequestMapping("/seatunnel/api/v1/task")
@RestController
public class TaskInstanceController {@Autowired ITaskInstanceService<SeaTunnelJobInstanceDto> taskInstanceService;@GetMapping("/jobMetrics")@ApiOperation(value = "get the jobMetrics list ", httpMethod = "GET")public Result<PageInfo<SeaTunnelJobInstanceDto>> getTaskInstanceList(@RequestAttribute(name = "userId") Integer userId,@RequestParam(name = "jobDefineName", required = false) String jobDefineName,@RequestParam(name = "executorName", required = false) String executorName,@RequestParam(name = "stateType", required = false) String stateType,@RequestParam(name = "startDate", required = false) String startTime,@RequestParam(name = "endDate", required = false) String endTime,@RequestParam("syncTaskType") String syncTaskType,@RequestParam("pageNo") Integer pageNo,@RequestParam("pageSize") Integer pageSize) {return taskInstanceService.getSyncTaskInstancePaging(userId,jobDefineName,executorName,stateType,startTime,endTime,syncTaskType,pageNo,pageSize);}
}- 进入getSyncTaskInstancePaging方法
public Result<PageInfo<SeaTunnelJobInstanceDto>> getSyncTaskInstancePaging(Integer userId,String jobDefineName,String executorName,String stateType,String startTime,String endTime,String syncTaskType,Integer pageNo,Integer pageSize) {JobDefinition jobDefinition = null;IPage<SeaTunnelJobInstanceDto> jobInstanceIPage;if (jobDefineName != null) {jobDefinition = jobDefinitionDao.getJobByName(jobDefineName);}Result<PageInfo<SeaTunnelJobInstanceDto>> result = new Result<>();PageInfo<SeaTunnelJobInstanceDto> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(pageNo, pageSize);result.setData(pageInfo);baseService.putMsg(result, Status.SUCCESS);Date startDate = dateConverter(startTime);Date endDate = dateConverter(endTime);if (jobDefinition != null) {jobInstanceIPage =jobInstanceDao.queryJobInstanceListPaging(new Page<>(pageNo, pageSize),startDate,endDate,jobDefinition.getId(),syncTaskType);} else {jobInstanceIPage =jobInstanceDao.queryJobInstanceListPaging(new Page<>(pageNo, pageSize), startDate, endDate, null, syncTaskType);}List<SeaTunnelJobInstanceDto> records = jobInstanceIPage.getRecords();if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(records)) {return result;}addJobDefineNameToResult(records);addRunningTimeToResult(records);// 关键代码,上边都是从本地数据库中获取的,这里会去Hazelcast中获取数据,并更新本地数据jobPipelineSummaryMetrics(records, syncTaskType, userId);pageInfo.setTotal((int) jobInstanceIPage.getTotal());pageInfo.setTotalList(records);result.setData(pageInfo);return result;}- 进入代码jobPipelineSummaryMetrics(records, syncTaskType, userId);
private void jobPipelineSummaryMetrics(List<SeaTunnelJobInstanceDto> records, String syncTaskType, Integer userId) {try {ArrayList<Long> jobInstanceIdList = new ArrayList<>();HashMap<Long, Long> jobInstanceIdAndJobEngineIdMap = new HashMap<>();for (SeaTunnelJobInstanceDto jobInstance : records) {if (jobInstance.getId() != null && jobInstance.getJobEngineId() != null) {jobInstanceIdList.add(jobInstance.getId());jobInstanceIdAndJobEngineIdMap.put(jobInstance.getId(), Long.valueOf(jobInstance.getJobEngineId()));}}Map<Long, JobSummaryMetricsRes> jobSummaryMetrics =// 获取每条日志数据的监控数据jobMetricsService.getALLJobSummaryMetrics(userId,jobInstanceIdAndJobEngineIdMap,jobInstanceIdList,syncTaskType);for (SeaTunnelJobInstanceDto taskInstance : records) {if (jobSummaryMetrics.get(taskInstance.getId()) != null) {taskInstance.setWriteRowCount(jobSummaryMetrics.get(taskInstance.getId()).getWriteRowCount());taskInstance.setReadRowCount(jobSummaryMetrics.get(taskInstance.getId()).getReadRowCount());}}} catch (Exception e) {for (SeaTunnelJobInstanceDto taskInstance : records) {log.error("instance {} {} set instance and engine id error", taskInstance.getId(), e);}}}- 进入jobMetricsService.getALLJobSummaryMetrics( userId,jobInstanceIdAndJobEngineIdMap, jobInstanceIdList, syncTaskType);
@Overridepublic Map<Long, JobSummaryMetricsRes> getALLJobSummaryMetrics(@NonNull Integer userId,@NonNull Map<Long, Long> jobInstanceIdAndJobEngineIdMap,@NonNull List<Long> jobInstanceIdList,@NonNull String syncTaskType) {log.info("jobInstanceIdAndJobEngineIdMap={}", jobInstanceIdAndJobEngineIdMap);funcPermissionCheck(SeatunnelFuncPermissionKeyConstant.JOB_METRICS_SUMMARY, userId);List<JobInstance> allJobInstance = jobInstanceDao.getAllJobInstance(jobInstanceIdList);if (allJobInstance.isEmpty()) {log.warn("getALLJobSummaryMetrics : allJobInstance is empty, task id list is {}",jobInstanceIdList);return new HashMap<>();}Map<Long, JobSummaryMetricsRes> result = null;Map<Long, HashMap<Integer, JobMetrics>> allRunningJobMetricsFromEngine =// 从Hazelcast集群节点中获取监控数据getAllRunningJobMetricsFromEngine(allJobInstance.get(0).getEngineName(),allJobInstance.get(0).getEngineVersion());// 通过不同的方式获取数据if (syncTaskType.equals("BATCH")) {result =getMatricsListIfTaskTypeIsBatch(allJobInstance,userId,allRunningJobMetricsFromEngine,jobInstanceIdAndJobEngineIdMap);} else if (syncTaskType.equals("STREAMING")) {result =getMatricsListIfTaskTypeIsStreaming(allJobInstance,userId,allRunningJobMetricsFromEngine,jobInstanceIdAndJobEngineIdMap);}log.info("result is {}", result == null ? "null" : result.toString());return result;}- 进入方法getAllRunningJobMetricsFromEngine(allJobInstance.get(0).getEngineName(),allJobInstance.get(0).getEngineVersion());
private Map<Long, HashMap<Integer, JobMetrics>> getAllRunningJobMetricsFromEngine(String engineName, String engineVersion) {Engine engine = new Engine(engineName, engineVersion);IEngineMetricsExtractor engineMetricsExtractor =(new EngineMetricsExtractorFactory(engine)).getEngineMetricsExtractor();// 看名字就知道这个是获取任务的监控数据的return engineMetricsExtractor.getAllRunningJobMetrics();}- 进入engineMetricsExtractor.getAllRunningJobMetrics();
@Overridepublic Map<Long, HashMap<Integer, JobMetrics>> getAllRunningJobMetrics() {HashMap<Long, HashMap<Integer, JobMetrics>> allRunningJobMetricsHashMap = new HashMap<>();try {
// 是不是很熟悉。seatunnelproxy,一看就是从这里开始真正和Hazelcast交互,获取数据了String allJobMetricsContent = seaTunnelEngineProxy.getAllRunningJobMetricsContent();if (StringUtils.isEmpty(allJobMetricsContent)) {return new HashMap<>();}JsonNode jsonNode = JsonUtils.stringToJsonNode(allJobMetricsContent);Iterator<JsonNode> iterator = jsonNode.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {LinkedHashMap<Integer, JobMetrics> metricsMap = new LinkedHashMap();JsonNode next = iterator.next();JsonNode sourceReceivedCount = next.get("metrics").get("SourceReceivedCount");Long jobEngineId = 0L;if (sourceReceivedCount != null && sourceReceivedCount.isArray()) {for (JsonNode node : sourceReceivedCount) {jobEngineId = node.get("tags").get("jobId").asLong();Integer pipelineId = node.get("tags").get("pipelineId").asInt();JobMetrics currPipelineMetrics =getOrCreatePipelineMetricsMapStatusRunning(metricsMap, pipelineId);currPipelineMetrics.setReadRowCount(currPipelineMetrics.getReadRowCount() + node.get("value").asLong());}}JsonNode sinkWriteCount = next.get("metrics").get("SinkWriteCount");if (sinkWriteCount != null && sinkWriteCount.isArray()) {for (JsonNode node : sinkWriteCount) {jobEngineId = node.get("tags").get("jobId").asLong();Integer pipelineId = node.get("tags").get("pipelineId").asInt();JobMetrics currPipelineMetrics =getOrCreatePipelineMetricsMapStatusRunning(metricsMap, pipelineId);currPipelineMetrics.setWriteRowCount(currPipelineMetrics.getWriteRowCount()+ node.get("value").asLong());}}JsonNode sinkWriteQPS = next.get("metrics").get("SinkWriteQPS");if (sinkWriteQPS != null && sinkWriteQPS.isArray()) {for (JsonNode node : sinkWriteQPS) {Integer pipelineId = node.get("tags").get("pipelineId").asInt();JobMetrics currPipelineMetrics =getOrCreatePipelineMetricsMapStatusRunning(metricsMap, pipelineId);currPipelineMetrics.setWriteQps(currPipelineMetrics.getWriteQps()+ (new Double(node.get("value").asDouble())).longValue());}}JsonNode sourceReceivedQPS = next.get("metrics").get("SourceReceivedQPS");if (sourceReceivedQPS != null && sourceReceivedQPS.isArray()) {for (JsonNode node : sourceReceivedQPS) {Integer pipelineId = node.get("tags").get("pipelineId").asInt();JobMetrics currPipelineMetrics =getOrCreatePipelineMetricsMapStatusRunning(metricsMap, pipelineId);currPipelineMetrics.setReadQps(currPipelineMetrics.getReadQps()+ (new Double(node.get("value").asDouble())).longValue());}}JsonNode cdcRecordEmitDelay = next.get("metrics").get("CDCRecordEmitDelay");if (cdcRecordEmitDelay != null && cdcRecordEmitDelay.isArray()) {Map<Integer, List<Long>> dataMap = new HashMap<>();for (JsonNode node : cdcRecordEmitDelay) {Integer pipelineId = node.get("tags").get("pipelineId").asInt();long value = node.get("value").asLong();dataMap.computeIfAbsent(pipelineId, n -> new ArrayList<>()).add(value);}dataMap.forEach((key, value) -> {JobMetrics currPipelineMetrics =getOrCreatePipelineMetricsMapStatusRunning(metricsMap, key);OptionalDouble average =value.stream().mapToDouble(a -> a).average();currPipelineMetrics.setRecordDelay(Double.valueOf(average.isPresent()? average.getAsDouble(): 0).longValue());});}log.info("jobEngineId={},metricsMap={}", jobEngineId, metricsMap);allRunningJobMetricsHashMap.put(jobEngineId, metricsMap);}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}return allRunningJobMetricsHashMap;}- 到这里如果有实际操作过seatunnel-web界面的同学们肯定知道,这个基本就已经触及监控数据的来源了。
- 进入seaTunnelEngineProxy.getAllRunningJobMetricsContent();
public String getAllRunningJobMetricsContent() {SeaTunnelClient seaTunnelClient = new SeaTunnelClient(clientConfig);try {return seaTunnelClient.getJobClient().getRunningJobMetrics();} finally {seaTunnelClient.close();}}- 代码很简单,没啥说的继续跟踪
public String getRunningJobMetrics() {return (String)this.hazelcastClient.requestOnMasterAndDecodeResponse(SeaTunnelGetRunningJobMetricsCodec.encodeRequest(), SeaTunnelGetRunningJobMetricsCodec::decodeResponse);}- hazelcastClient,是不是眼熟。是的,seatunnel对hazelcast的调用,封装了很深。马上就胜利了,继续跟代码
public <S> S requestOnMasterAndDecodeResponse(@NonNull ClientMessage request, @NonNull Function<ClientMessage, Object> decoder) {if (request == null) {throw new NullPointerException("request is marked non-null but is null");} else if (decoder == null) {throw new NullPointerException("decoder is marked non-null but is null");} else {UUID masterUuid = this.hazelcastClient.getClientClusterService().getMasterMember().getUuid();return this.requestAndDecodeResponse(masterUuid, request, decoder);}}- 获取到我们要从那个hazelcast节点获取数据的信息,然后去调用
public <S> S requestAndDecodeResponse(@NonNull UUID uuid, @NonNull ClientMessage request, @NonNull Function<ClientMessage, Object> decoder) {if (uuid == null) {throw new NullPointerException("uuid is marked non-null but is null");} else if (request == null) {throw new NullPointerException("request is marked non-null but is null");} else if (decoder == null) {throw new NullPointerException("decoder is marked non-null but is null");} else {ClientInvocation invocation = new ClientInvocation(this.hazelcastClient, request, (Object)null, uuid);try {ClientMessage response = (ClientMessage)invocation.invoke().get();return this.serializationService.toObject(decoder.apply(response));} catch (InterruptedException var6) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();return null;} catch (Throwable var7) {throw ExceptionUtil.rethrow(var7);}}}- 着重记忆一下ClientInvocation和ClientMessage。因为在跟踪hazelcase-api的代码的时候,就是用的这里。
- 在下边就是调用hazelcast的客户端,发送请求,然后get阻塞,直到数据返回。
2、Hazelcast-api
- hazelcast的api调用,我们以下面这段代码为入口开始看源码。
import com.hazelcast.core.HazelcastInstance;
import com.hazelcast.map.IMap;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
public class HazelcastService { @Autowired private HazelcastInstance hazelcastInstance; public void putData() { IMap<String, String> map = hazelcastInstance.getMap("my-map"); map.put("key1", "value1"); } public String getData(String key) { IMap<String, String> map = hazelcastInstance.getMap("my-map"); return map.get(key); }
}- 可以看到hazelcast的使用基本和java的数据结构使用一样。所以如果我们要使用hazelcast还是很方便入手的。
- 进入hazelcast封装的map的put方法
@Overridepublic V get(@Nonnull Object key) {checkNotNull(key, NULL_KEY_IS_NOT_ALLOWED);return toObject(getInternal(key));}- 进入getInternal方法
protected Object getInternal(Object key) {// TODO: action for read-backup true is not well testedData keyData = toDataWithStrategy(key);if (mapConfig.isReadBackupData()) {Object fromBackup = readBackupDataOrNull(keyData);if (fromBackup != null) {return fromBackup;}}MapOperation operation = operationProvider.createGetOperation(name, keyData);operation.setThreadId(getThreadId());return invokeOperation(keyData, operation);}- 将参数封装为了hazelcast的map数据结构,并调用操作方法
private Object invokeOperation(Data key, MapOperation operation) {int partitionId = partitionService.getPartitionId(key);operation.setThreadId(getThreadId());try {Object result;if (statisticsEnabled) {long startTimeNanos = Timer.nanos();Future future = operationService.createInvocationBuilder(SERVICE_NAME, operation, partitionId).setResultDeserialized(false).invoke();result = future.get();incrementOperationStats(operation, localMapStats, startTimeNanos);} else {Future future = operationService.createInvocationBuilder(SERVICE_NAME, operation, partitionId).setResultDeserialized(false).invoke();result = future.get();}return result;} catch (Throwable t) {throw rethrow(t);}}- 执行方法,并返回了一个InvocationFuture,这个InvocationFuture对象是集成了CompletableFuture的一个future,所以如果需要,也可以使用多线程编排,执行复杂查询的。
@Overridepublic InvocationFuture invoke() {op.setServiceName(serviceName);Invocation invocation;if (target == null) {op.setPartitionId(partitionId).setReplicaIndex(replicaIndex);invocation = new PartitionInvocation(context, op, doneCallback, tryCount, tryPauseMillis, callTimeout, resultDeserialized,failOnIndeterminateOperationState, connectionManager);} else {invocation = new TargetInvocation(context, op, target, doneCallback, tryCount, tryPauseMillis,callTimeout, resultDeserialized, connectionManager);}return async? invocation.invokeAsync(): invocation.invoke();}- 可以看到真正去执行的是不同类型的Invocation。并且可以根据是同步还是异步,调用不同的执行方法,我们直接看invoke方法。
private void invoke0(boolean isAsync) {if (invokeCount > 0) {throw new IllegalStateException("This invocation is already in progress");} else if (isActive()) {throw new IllegalStateException("Attempt to reuse the same operation in multiple invocations. Operation is " + op);}try {setCallTimeout(op, callTimeoutMillis);setCallerAddress(op, context.thisAddress);op.setNodeEngine(context.nodeEngine);boolean isAllowed = context.operationExecutor.isInvocationAllowed(op, isAsync);if (!isAllowed && !isMigrationOperation(op)) {throw new IllegalThreadStateException(Thread.currentThread() + " cannot make remote call: " + op);}doInvoke(isAsync);} catch (Exception e) {handleInvocationException(e);}}- 继续进入doInvoke方法
private void doInvoke(boolean isAsync) {if (!engineActive()) {return;}invokeCount++;setInvocationTime(op, context.clusterClock.getClusterTime());// We'll initialize the invocation before registering it. Invocation monitor iterates over// registered invocations and it must observe completely initialized invocations.Exception initializationFailure = null;try {initInvocationTarget();} catch (Exception e) {// We'll keep initialization failure and notify invocation with this failure// after invocation is registered to the invocation registry.initializationFailure = e;}if (!context.invocationRegistry.register(this)) {return;}if (initializationFailure != null) {notifyError(initializationFailure);return;}if (isLocal()) {doInvokeLocal(isAsync);} else {doInvokeRemote();}}- 如果是本地调用,进入doInvokeLocal。如果是远程调用进入doInvokeRemote。如果是springboot直接引入的情况下,进入本地调用
- 调用远程的hazelcast集群的。进入doInvokeRemote方法。
- 例子中是本地调用,所以进入doInvokeLocal,这里的代码本文就不继续跟进去,如果感兴趣可以debug进去看看,大概的逻辑是调用execute方法,然后将MapOperation(Operation对象)放到一个队列中,线程池异步执行,我们着重看下MapOperation。
public abstract class MapOperation extends AbstractNamedOperationimplements IdentifiedDataSerializable, ServiceNamespaceAware {private static final boolean ASSERTION_ENABLED = MapOperation.class.desiredAssertionStatus();protected transient MapService mapService;protected transient RecordStore<Record> recordStore;protected transient MapContainer mapContainer;protected transient MapServiceContext mapServiceContext;protected transient MapEventPublisher mapEventPublisher;protected transient boolean createRecordStoreOnDemand = true;protected transient boolean disposeDeferredBlocks = true;private transient boolean canPublishWanEvent;public MapOperation() {}public MapOperation(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic final void beforeRun() throws Exception {super.beforeRun();mapService = getService();mapServiceContext = mapService.getMapServiceContext();mapEventPublisher = mapServiceContext.getMapEventPublisher();try {recordStore = getRecordStoreOrNull();if (recordStore == null) {mapContainer = mapServiceContext.getMapContainer(name);} else {mapContainer = recordStore.getMapContainer();}} catch (Throwable t) {disposeDeferredBlocks();throw rethrow(t, Exception.class);}canPublishWanEvent = canPublishWanEvent(mapContainer);assertNativeMapOnPartitionThread();innerBeforeRun();}protected void innerBeforeRun() throws Exception {if (recordStore != null) {recordStore.beforeOperation();}// Concrete classes can override this method.}@Overridepublic final void run() {try {runInternal();} catch (NativeOutOfMemoryError e) {rerunWithForcedEviction();}}protected void runInternal() {// Intentionally empty method body.// Concrete classes can override this method.}private void rerunWithForcedEviction() {try {runWithForcedEvictionStrategies(this);} catch (NativeOutOfMemoryError e) {disposeDeferredBlocks();throw e;}}@Overridepublic final void afterRun() throws Exception {afterRunInternal();disposeDeferredBlocks();super.afterRun();}protected void afterRunInternal() {// Intentionally empty method body.// Concrete classes can override this method.}@Overridepublic void afterRunFinal() {if (recordStore != null) {recordStore.afterOperation();}}protected void assertNativeMapOnPartitionThread() {if (!ASSERTION_ENABLED) {return;}assert mapContainer.getMapConfig().getInMemoryFormat() != NATIVE|| getPartitionId() != GENERIC_PARTITION_ID: "Native memory backed map operations are not allowed to run on GENERIC_PARTITION_ID";}ILogger logger() {return getLogger();}protected final CallerProvenance getCallerProvenance() {return disableWanReplicationEvent() ? CallerProvenance.WAN : CallerProvenance.NOT_WAN;}private RecordStore getRecordStoreOrNull() {int partitionId = getPartitionId();if (partitionId == -1) {return null;}PartitionContainer partitionContainer = mapServiceContext.getPartitionContainer(partitionId);if (createRecordStoreOnDemand) {return partitionContainer.getRecordStore(name);} else {return partitionContainer.getExistingRecordStore(name);}}@Overridepublic void onExecutionFailure(Throwable e) {disposeDeferredBlocks();super.onExecutionFailure(e);}@Overridepublic void logError(Throwable e) {ILogger logger = getLogger();if (e instanceof NativeOutOfMemoryError) {Level level = this instanceof BackupOperation ? Level.FINEST : Level.WARNING;logger.log(level, "Cannot complete operation! -> " + e.getMessage());} else {// we need to introduce a proper method to handle operation failures (at the moment// this is the only place where we can dispose native memory allocations on failure)disposeDeferredBlocks();super.logError(e);}}void disposeDeferredBlocks() {if (!disposeDeferredBlocks|| recordStore == null|| recordStore.getInMemoryFormat() != NATIVE) {return;}recordStore.disposeDeferredBlocks();}private boolean canPublishWanEvent(MapContainer mapContainer) {boolean canPublishWanEvent = mapContainer.isWanReplicationEnabled()&& !disableWanReplicationEvent();if (canPublishWanEvent) {mapContainer.getWanReplicationDelegate().doPrepublicationChecks();}return canPublishWanEvent;}@Overridepublic String getServiceName() {return MapService.SERVICE_NAME;}public boolean isPostProcessing(RecordStore recordStore) {MapDataStore mapDataStore = recordStore.getMapDataStore();return mapDataStore.isPostProcessingMapStore()|| !mapContainer.getInterceptorRegistry().getInterceptors().isEmpty();}public void setThreadId(long threadId) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public long getThreadId() {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}protected final void invalidateNearCache(List<Data> keys) {if (!mapContainer.hasInvalidationListener() || isEmpty(keys)) {return;}Invalidator invalidator = getNearCacheInvalidator();for (Data key : keys) {invalidator.invalidateKey(key, name, getCallerUuid());}}// TODO: improve here it's possible that client cannot manage to attach listenerpublic final void invalidateNearCache(Data key) {if (!mapContainer.hasInvalidationListener() || key == null) {return;}Invalidator invalidator = getNearCacheInvalidator();invalidator.invalidateKey(key, name, getCallerUuid());}/*** This method helps to add clearing Near Cache event only from* one-partition which matches partitionId of the map name.*/protected final void invalidateAllKeysInNearCaches() {if (mapContainer.hasInvalidationListener()) {int partitionId = getPartitionId();Invalidator invalidator = getNearCacheInvalidator();if (partitionId == getNodeEngine().getPartitionService().getPartitionId(name)) {invalidator.invalidateAllKeys(name, getCallerUuid());} else {invalidator.forceIncrementSequence(name, getPartitionId());}}}private Invalidator getNearCacheInvalidator() {MapNearCacheManager mapNearCacheManager = mapServiceContext.getMapNearCacheManager();return mapNearCacheManager.getInvalidator();}protected final void evict(Data justAddedKey) {if (mapContainer.getEvictor() == Evictor.NULL_EVICTOR) {return;}recordStore.evictEntries(justAddedKey);disposeDeferredBlocks();}@Overridepublic int getFactoryId() {return MapDataSerializerHook.F_ID;}@Overridepublic ObjectNamespace getServiceNamespace() {MapContainer container = mapContainer;if (container == null) {MapService service = getService();container = service.getMapServiceContext().getMapContainer(name);}return container.getObjectNamespace();}// for testing onlypublic void setMapService(MapService mapService) {this.mapService = mapService;}// for testing onlypublic void setMapContainer(MapContainer mapContainer) {this.mapContainer = mapContainer;}protected final void publishWanUpdate(Data dataKey, Object value) {publishWanUpdateInternal(dataKey, value, false);}private void publishWanUpdateInternal(Data dataKey, Object value, boolean hasLoadProvenance) {if (!canPublishWanEvent) {return;}Record<Object> record = recordStore.getRecord(dataKey);if (record == null) {return;}Data dataValue = toHeapData(mapServiceContext.toData(value));ExpiryMetadata expiryMetadata = recordStore.getExpirySystem().getExpiryMetadata(dataKey);WanMapEntryView<Object, Object> entryView = createWanEntryView(toHeapData(dataKey), dataValue, record, expiryMetadata,getNodeEngine().getSerializationService());mapEventPublisher.publishWanUpdate(name, entryView, hasLoadProvenance);}protected final void publishLoadAsWanUpdate(Data dataKey, Object value) {publishWanUpdateInternal(dataKey, value, true);}protected final void publishWanRemove(@Nonnull Data dataKey) {if (!canPublishWanEvent) {return;}mapEventPublisher.publishWanRemove(name, toHeapData(dataKey));}protected boolean disableWanReplicationEvent() {return false;}protected final TxnReservedCapacityCounter wbqCapacityCounter() {return recordStore.getMapDataStore().getTxnReservedCapacityCounter();}protected final Data getValueOrPostProcessedValue(Record record, Data dataValue) {if (!isPostProcessing(recordStore)) {return dataValue;}return mapServiceContext.toData(record.getValue());}@Overridepublic TenantControl getTenantControl() {return getNodeEngine().getTenantControlService().getTenantControl(MapService.SERVICE_NAME, name);}@Overridepublic boolean requiresTenantContext() {return true;}
}- 既然要线程异步去执行,所以它肯定要实现run方法,所以找到run方法,进入runInternal。实现方法很多,找到map包相关的类。
@Overrideprotected void runInternal() {Object currentValue = recordStore.get(dataKey, false, getCallerAddress());if (noCopyReadAllowed(currentValue)) {// in case of a 'remote' call (e.g a client call) we prevent making// an on-heap copy of the off-heap dataresult = (Data) currentValue;} else {// in case of a local call, we do make a copy, so we can safely share// it with e.g. near cache invalidationresult = mapService.getMapServiceContext().toData(currentValue);}}- 这里基本就是获取到hazelcast管理的内存中数据的地方,不再一一debug,一路向下找到代码
public V get(Object key) {int hash = hashOf(key);return segmentFor(hash).get(key, hash);}- 怎么样,熟悉吧。java的map调用是不是也是这样,先hash找到位置,在获取数据。其实这里的hash和map的hash有一些区别。这是由于hazelcast的架构决定的,如果对原理架构感兴趣可以百度搜一搜,很多。这里大概提一嘴,有一个分片的概念,put的时候会hash到不同的分区(分片)。这也是hazelcast分布式的原理。
7、结语
本文只是介绍了hazelcast的最基本用法,如果按照案例中的使用,完全可以用redis或者本地缓存。但是如果有了更高级(实际中的使用),那么hazelcast的分布式计算特性还是很好用的。源码也只是分析了本地的调用。如果感兴趣其实可以debug跟进去看下远程调用的方式。其实想想本质还是一样,远程调用就需要1、发现节点;2、注册节点;3、网络调用其他节点。而seatunnel的调用就相对来说更高级一些,它进行了一系列的封装。最后也还是网络调用其他节点。然后返回future阻塞等待返回结果,由于是内存级别的,处理特别快。
对了差点忘记一点,一直在说分布式特性。本文只说了单纯作为缓存使用get、put方法。这里大概介绍下分布式api的使用
IExecutorService executorService = hazelcastInstance.getExecutorService("myExecutor");
Runnable task = () -> { // 这里是任务的逻辑 System.out.println("Executing task on " + hazelcastInstance.getCluster().getLocalMember().getAddress());
};
Future<Void> future = executorService.submit(task);
future.get(); // 等待任务完成这样就可以查询分布式节点上的数据,然后聚合返回。是不是有点像MapReduce。确实,hazelcast也可以使用MapReduce进行复杂运算,想了解的,也可以去搜一搜看看。
相关文章:

Hazelcast 分布式缓存 在Seatunnel中的使用
1、背景 最近在调研seatunnel的时候,发现新版的seatunnel提供了一个web服务,可以用于图形化的创建数据同步任务,然后管理任务。这里面有个日志模块,可以查看任务的执行状态。其中有个取读数据条数和同步数据条数。很好奇这个数据…...

分数限制下,选好专业还是选好学校?
目录 分数限制下,选好专业还是选好学校? 方向一:专业解析 1. 专业选择的重要性 2. 不同专业的优势与挑战 3. 个人专业选择经验分享 4. 实际场景下的“专业VS学校”选择方案 方向二:名校效应分析 1. 名校声誉与品牌效应 2…...
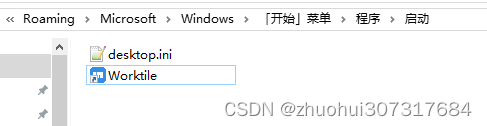
软件改为开机自启动
1.按键 win R,输入“shell:startup”命令, 然后就可以打开启动目录了,如下: 2.然后,把要开机启动的程序的图标拖进去即可。 参考:开机启动项如何设置...
)
集群down机的应急和恢复测试(非重做备机)
1. 集群的两台服务器的状态 实例 正常情况主备 ip 端口 node1 主机 192.168.6.6 9088 node2 备机 192.168.6.7 9088 2. 测试的步骤 down掉node1观察node2的状态在node2未自动切换的时候手动将node2调整为单机状态,模拟紧急使用模拟不紧急时࿰…...
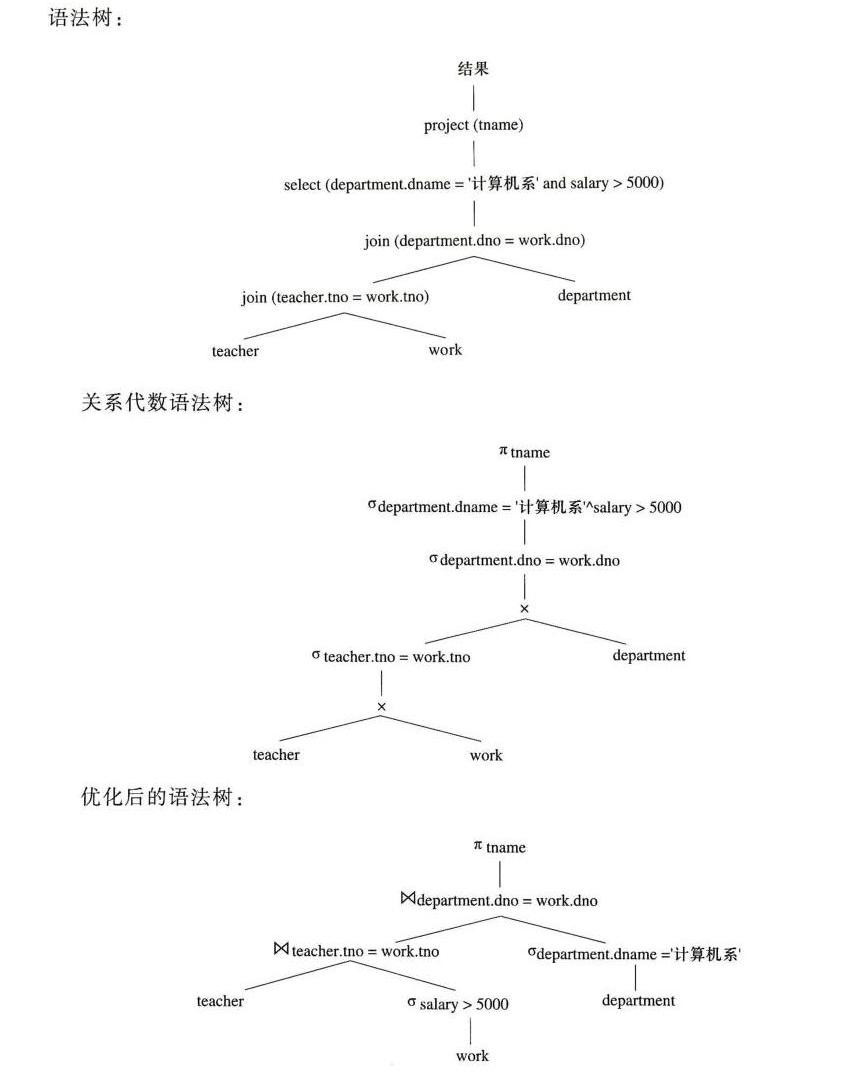
【数据库系统概论复习】关系数据库与关系代数笔记
文章目录 基本概念数据库基本概念关系数据结构完整性约束 关系代数关系代数练习课堂练习 语法树 基本概念 数据库基本概念 DB 数据库, 为了存用户的各种数据,我们要建很多关系(二维表),所以把相关的关系(二…...

赛氪网受邀参加上海闵行区翻译协会年会,共探科技翻译创新之路
在科技飞速发展的时代背景下,翻译行业正面临着前所未有的机遇与挑战。作为连接高校、企业与社会的桥梁,赛氪网在推动翻译创新、促进学术交流方面展现出了独特的魅力。2024年6月9日,在华东师范大学外语学院举办的第十三届上海市闵行区翻译协会…...

项目管理进阶之EVM(挣值管理)
前言 项目管理进阶系列,终于有时间更新啦!!!欢迎持续关注哦~ 上一节博主重点讲了一个环:PDCA,无论各行各业,上到航空航天、下到种地种菜,都离不开对质量的监督和改进。这个环既是一…...
PLSQL、Oracle以及客户端远程连接服务器笔记(仅供参考)
1.PLSQL参考链接: 全网最全最细的PLSQL下载、安装、配置、使用指南、问题解答,相关问题已汇总-CSDN博客文章浏览阅读2.9w次,点赞98次,收藏447次。双击之后,这里选择安装目录,你安装目录选的哪里࿰…...

Win快速删除node_modules
在Windows系统上删除 node_modules 文件夹通常是一个缓慢且耗时的过程。这主要是由于几个关键因素导致的: 主要原因 文件数量多且嵌套深: node_modules 文件夹通常包含成千上万的子文件夹和文件。由于其结构复杂,文件和文件夹往往嵌套得非常…...

【机器学习】基于顺序到顺序Transformer机器翻译
引言 1.1 序列到序列模型详解 序列到序列(Seq2Seq)模型是深度学习中处理序列数据转换问题的关键架构。在自然语言处理(NLP)任务中,如机器翻译、文本摘要和聊天机器人等,Seq2Seq模型能够高效地将输入序列转换为期望的输出序列。 模型架构: 编…...

TEA 加密的 Java 实现
import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.ByteOrder;public class TeaUtils {private static final int DELTA 0x9E3779B9;private static final int ROUND 32;private static final String KEY "password";/*** 加密字符串,使用 TEA 加密算法*/p…...
】)
鸿蒙开发电话服务:【@ohos.telephony.data (蜂窝数据)】
蜂窝数据 说明: 本模块首批接口从API version 7开始支持。后续版本的新增接口,采用上角标单独标记接口的起始版本。 导入模块 import data from ohos.telephony.data;data.getDefaultCellularDataSlotId getDefaultCellularDataSlotId(callback: Async…...
Maven认识与学习
1. Maven介绍 1.2 初识Maven 1.2.1 什么是Maven Maven是Apache旗下的一个开源项目,是一款用于管理和构建java项目的工具。 官网:Maven – Welcome to Apache Maven Apache 软件基金会,成立于1999年7月,是目前世界上最大的最受…...
“深入探讨Redis主从复制:原理、配置与优化“
目录 # 概念 1. 配置主从同步步骤 1.1 创建文件夹 1.2 复制配置文件 1.3 配置文件关闭 1.4 查看端口号,发现端口号存在 1.5 连接三个端口号 1.6 查看主机运行情况 1.7 让服务器变成(主机)或(从机) 1.8 实现效…...
HTML初体验
可参考jd.com官网,ctrlu查看当前页面源代码 找到你的项目,在项目中创建html类型的网页文件 标准的HTML正确书写格式 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang"en"> <head><meta charset"UTF-8"><title>Title&…...

全局特征提取netvlad的理解
...

【设计模式-12】代理模式的代码实现及使用场景
&emsp;代理模式是一种应用很广发的结构性设计模式,它的设计初衷就是通过引入新的代理对象,在客户端和目标对象之间起到中介的作用,从而实现控制客户端对目标对象的访问,比如增强或者阉割某些能力。 1. 概述 代理模…...

网工内推 | 神州数码、弧聚科技网工,IE认证优先,最高18K
01 神州数码 🔷招聘岗位:高级网络工程师 🔷岗位职责: 1)提供7*24小时一线运维技术服务,如因应急故障处理应15分钟内到达现场。 2)提供设备的告警信息的分析处理及与故障问题定位服务。 3)完成数据中心网络和HPC超算…...
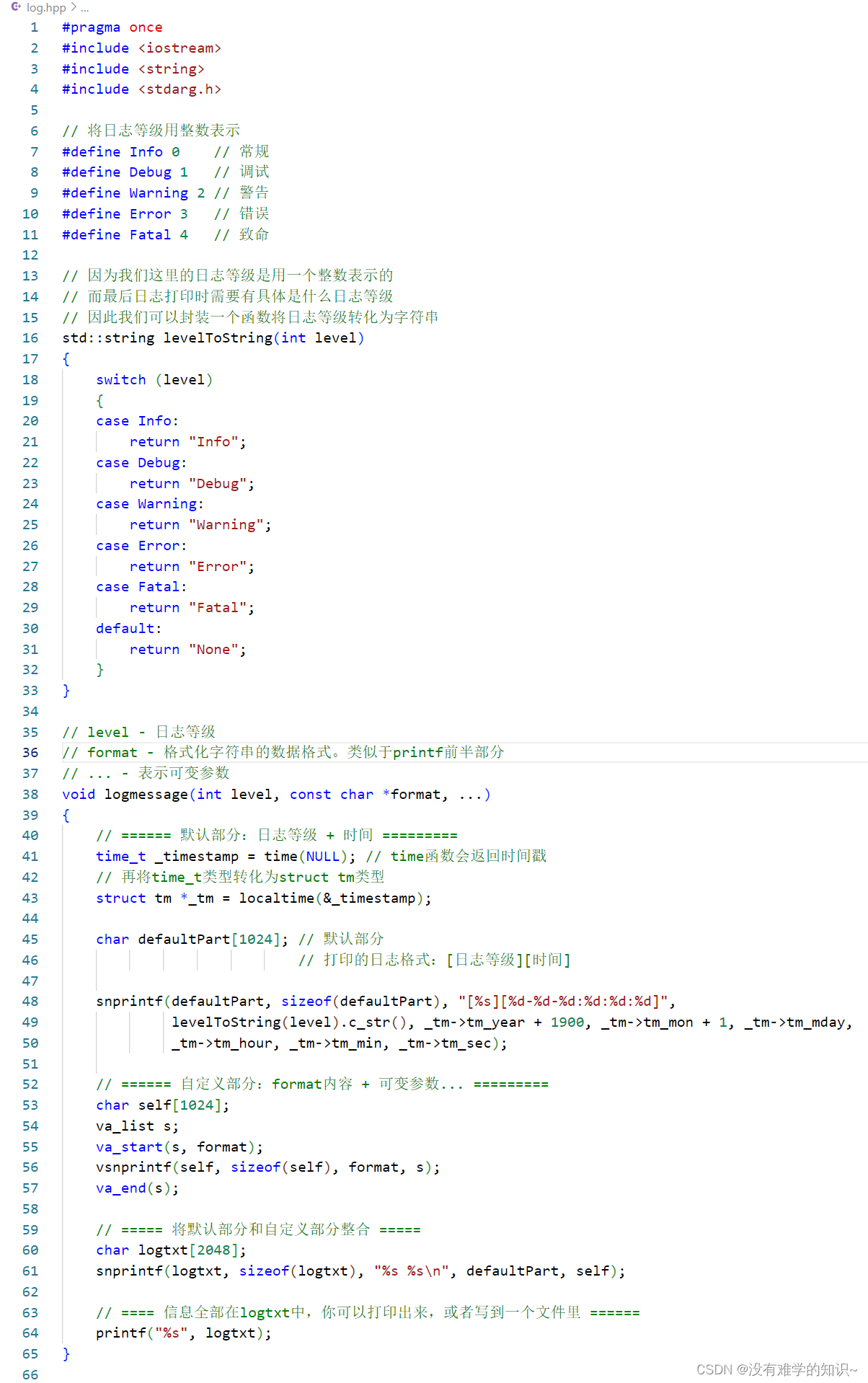
【Linux】模拟实现一个简单的日志系统
👦个人主页:Weraphael ✍🏻作者简介:目前正在学习c和算法 ✈️专栏:Linux 🐋 希望大家多多支持,咱一起进步!😁 如果文章有啥瑕疵,希望大佬指点一二 如果文章对…...
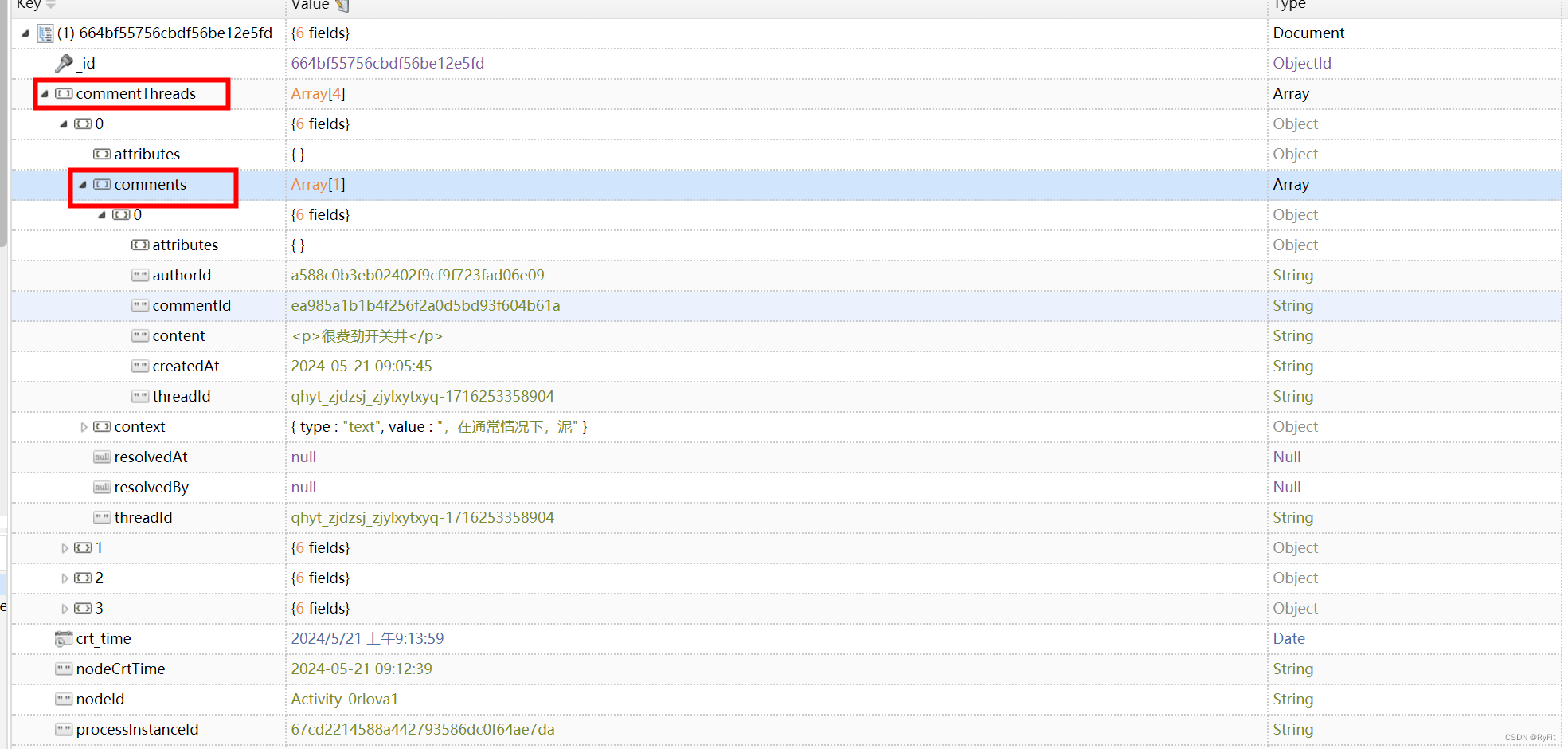
MongoDB 多层级查询
多层级查询 注意:要注意代码顺序 查询层级数据代码放前面,查询条件放后面 if (StringUtils.isBlank(params.getDocType())) {params.setDocType(DOC_TDCTYPE);}String docName mapper.findByDocInfo(params.getDocType());List<ExpertApprovalOpin…...
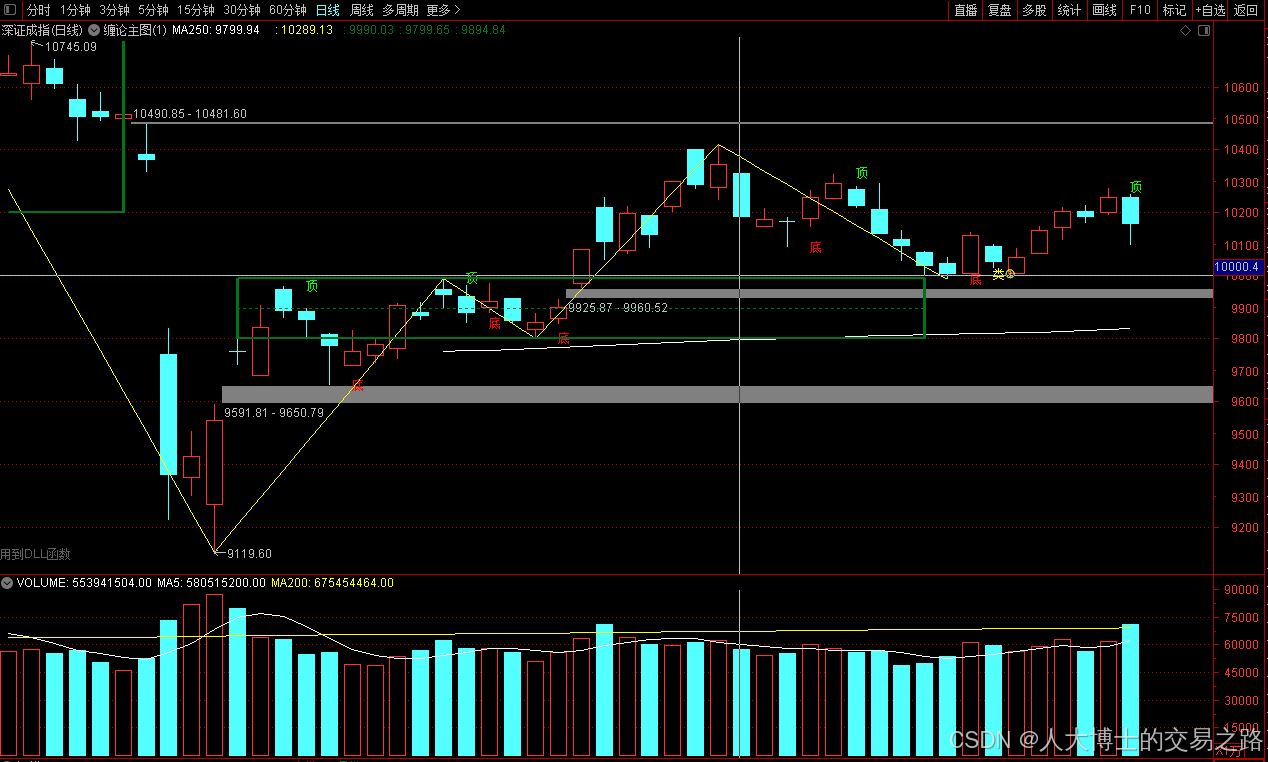
龙虎榜——20250610
上证指数放量收阴线,个股多数下跌,盘中受消息影响大幅波动。 深证指数放量收阴线形成顶分型,指数短线有调整的需求,大概需要一两天。 2025年6月10日龙虎榜行业方向分析 1. 金融科技 代表标的:御银股份、雄帝科技 驱动…...
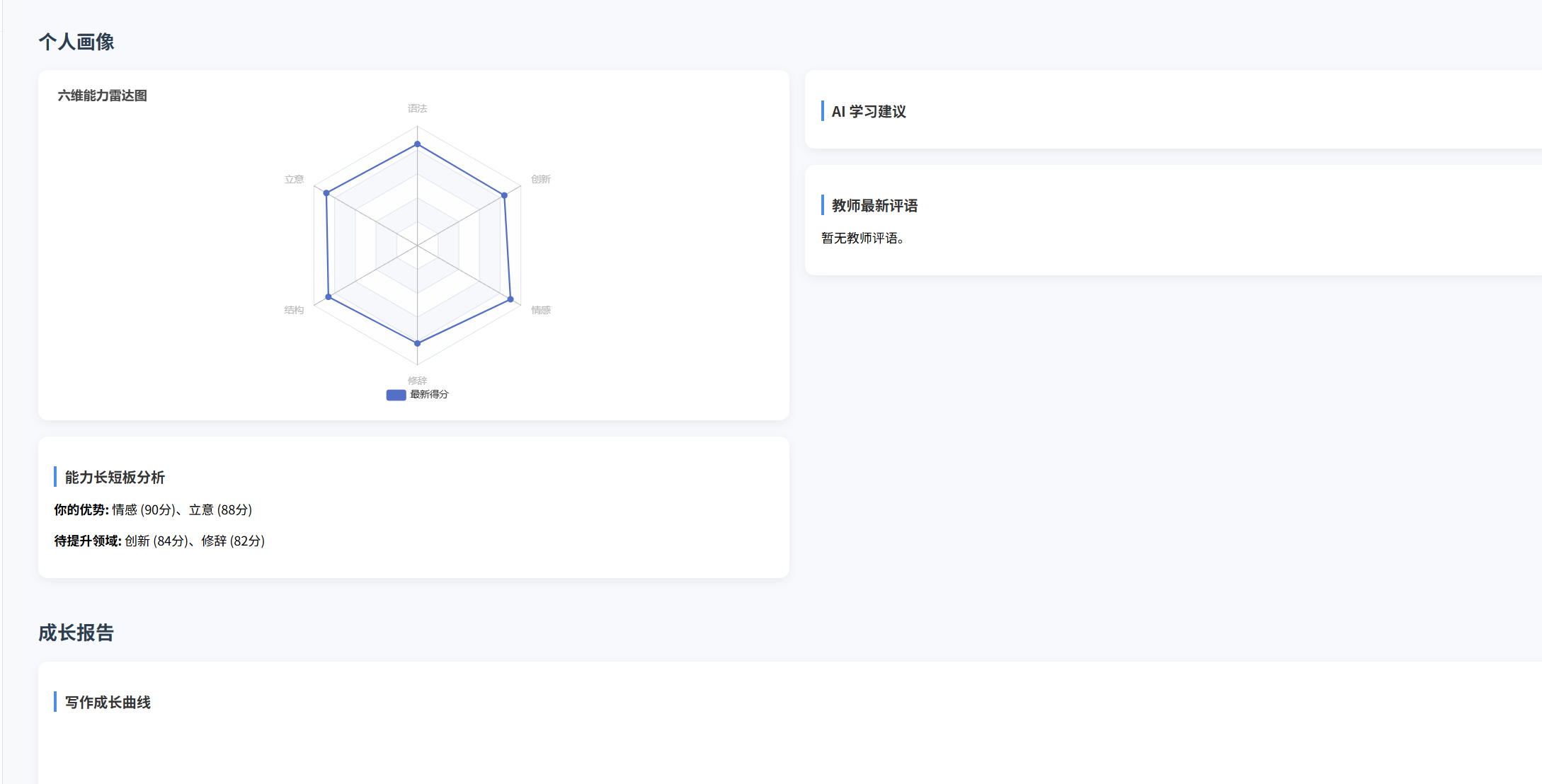
(十)学生端搭建
本次旨在将之前的已完成的部分功能进行拼装到学生端,同时完善学生端的构建。本次工作主要包括: 1.学生端整体界面布局 2.模拟考场与部分个人画像流程的串联 3.整体学生端逻辑 一、学生端 在主界面可以选择自己的用户角色 选择学生则进入学生登录界面…...

day52 ResNet18 CBAM
在深度学习的旅程中,我们不断探索如何提升模型的性能。今天,我将分享我在 ResNet18 模型中插入 CBAM(Convolutional Block Attention Module)模块,并采用分阶段微调策略的实践过程。通过这个过程,我不仅提升…...

安宝特方案丨XRSOP人员作业标准化管理平台:AR智慧点检验收套件
在选煤厂、化工厂、钢铁厂等过程生产型企业,其生产设备的运行效率和非计划停机对工业制造效益有较大影响。 随着企业自动化和智能化建设的推进,需提前预防假检、错检、漏检,推动智慧生产运维系统数据的流动和现场赋能应用。同时,…...
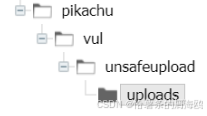
Unsafe Fileupload篇补充-木马的详细教程与木马分享(中国蚁剑方式)
在之前的皮卡丘靶场第九期Unsafe Fileupload篇中我们学习了木马的原理并且学了一个简单的木马文件 本期内容是为了更好的为大家解释木马(服务器方面的)的原理,连接,以及各种木马及连接工具的分享 文件木马:https://w…...
佰力博科技与您探讨热释电测量的几种方法
热释电的测量主要涉及热释电系数的测定,这是表征热释电材料性能的重要参数。热释电系数的测量方法主要包括静态法、动态法和积分电荷法。其中,积分电荷法最为常用,其原理是通过测量在电容器上积累的热释电电荷,从而确定热释电系数…...

回溯算法学习
一、电话号码的字母组合 import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;import javax.management.loading.PrivateClassLoader;public class letterCombinations {private static final String[] KEYPAD {"", //0"", //1"abc", //2"…...

【JavaSE】多线程基础学习笔记
多线程基础 -线程相关概念 程序(Program) 是为完成特定任务、用某种语言编写的一组指令的集合简单的说:就是我们写的代码 进程 进程是指运行中的程序,比如我们使用QQ,就启动了一个进程,操作系统就会为该进程分配内存…...
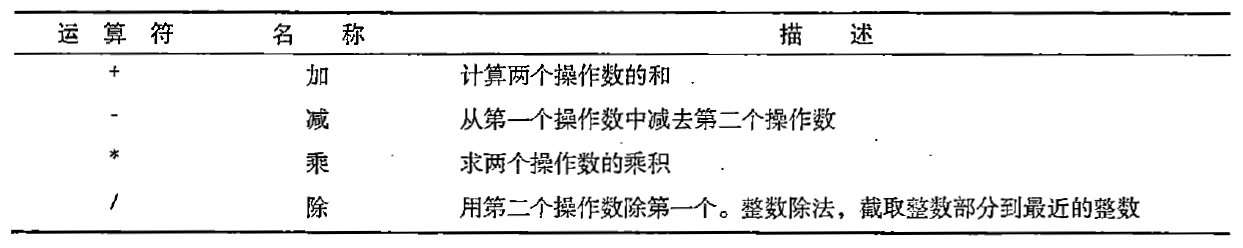
C# 表达式和运算符(求值顺序)
求值顺序 表达式可以由许多嵌套的子表达式构成。子表达式的求值顺序可以使表达式的最终值发生 变化。 例如,已知表达式3*52,依照子表达式的求值顺序,有两种可能的结果,如图9-3所示。 如果乘法先执行,结果是17。如果5…...

深度学习之模型压缩三驾马车:模型剪枝、模型量化、知识蒸馏
一、引言 在深度学习中,我们训练出的神经网络往往非常庞大(比如像 ResNet、YOLOv8、Vision Transformer),虽然精度很高,但“太重”了,运行起来很慢,占用内存大,不适合部署到手机、摄…...
