C++ 几何计算库
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_tree.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_traits.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_segment_primitive.h>
#include <CGAL/Polygon_2.h>typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double> K;// custom point type
struct My_point {double m_x;double m_y;double m_z;My_point(const double x,const double y,const double z): m_x(x), m_y(y), m_z(z) {}
};// custom triangle type with
// three pointers to points
struct My_triangle {My_point* m_pa;My_point* m_pb;My_point* m_pc;My_triangle(My_point* pa,My_point* pb,My_point* pc): m_pa(pa), m_pb(pb), m_pc(pc) {}
};// the custom triangles are stored into a vector
typedef std::vector<My_triangle>::const_iterator Iterator;// The following primitive provides the conversion facilities between
// the custom triangle and point types and the CGAL ones
struct My_triangle_primitive {
public:// this is the type of data that the queries returns. For this example// we imagine that, for some reasons, we do not want to store the iterators// of the vector, but raw pointers. This is to show that the Id type// does not have to be the same as the one of the input parameter of the// constructor.typedef const My_triangle* Id;// CGAL types returnedtypedef K::Point_3 Point; // CGAL 3D point typetypedef K::Triangle_3 Datum; // CGAL 3D triangle typeprivate:Id m_pt; // this is what the AABB tree stores internallypublic:My_triangle_primitive() {} // default constructor needed// the following constructor is the one that receives the iterators from the// iterator range given as input to the AABB_treeMy_triangle_primitive(Iterator it): m_pt(&(*it)) {}const Id& id() const { return m_pt; }// utility function to convert a custom// point type to CGAL point type.Point convert(const My_point* p) const{return Point(p->m_x, p->m_y, p->m_z);}// on the fly conversion from the internal data to the CGAL typesDatum datum() const{return Datum(convert(m_pt->m_pa),convert(m_pt->m_pb),convert(m_pt->m_pc));}// returns a reference point which must be on the primitivePoint reference_point() const{return convert(m_pt->m_pa);}
};/*
自定义KDTree测试,点相交
*/
int testKDTree()
{typedef CGAL::AABB_traits<K, My_triangle_primitive> My_AABB_traits;typedef CGAL::AABB_tree<My_AABB_traits> MyTree;typedef K::FT FT;My_point a(1.0, 0.0, 0.0);My_point b(0.0, 1.0, 0.0);My_point c(0.0, 0.0, 1.0);My_point d(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);std::vector<My_triangle> triangles;triangles.push_back(My_triangle(&a, &b, &c));triangles.push_back(My_triangle(&a, &b, &d));triangles.push_back(My_triangle(&a, &d, &c));// constructs AABB treeMyTree tree(triangles.begin(), triangles.end());// counts #intersectionsK::Ray_3 ray_query(K::Point_3(1.0, 0.0, 0.0), K::Point_3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0));std::cout << tree.number_of_intersected_primitives(ray_query)<< " intersections(s) with ray query" << std::endl;// computes closest pointK::Point_3 point_query(2.0, 2.0, 2.0);K::Point_3 closest_point = tree.closest_point(point_query);std::cerr << "closest point is: " << closest_point << std::endl;FT sqd = tree.squared_distance(point_query);std::cout << "squared distance: " << sqd << std::endl;return EXIT_SUCCESS;/* 输出
3 intersections(s) with ray query
closest point is: 0.333333 0.333333 0.333333
*/
}/*
光线追踪,面相交
*/
void testGlyph() {typedef K::FT FT;typedef K::Segment_3 Segment;typedef K::Point_3 Point;typedef std::list<Segment> SegmentRange;typedef SegmentRange::const_iterator Iterator;typedef CGAL::AABB_segment_primitive<K, Iterator> Primitive;typedef CGAL::AABB_traits<K, Primitive> Traits;typedef CGAL::AABB_tree<Traits> Tree;typedef Tree::Point_and_primitive_id Point_and_primitive_id;Point a(0.0, 0.0, 1);Point b(2.0, 1.0, 1);Point c(3.0, 4.0, 1);Point d(1.0, 6.0, 1);Point e(-1.0, 3.0, 1);std::list<Segment> seg;seg.push_back(Segment(a, b));seg.push_back(Segment(b, c));seg.push_back(Segment(c, d));seg.push_back(Segment(d, e));seg.push_back(Segment(e, a));// constructs the AABB tree and the internal search tree for// efficient distance computations.Tree tree(seg.begin(), seg.end());tree.build();tree.accelerate_distance_queries();// counts #intersections with a segment querySegment segment_query(Point(1.0, 0.0, 1), Point(0.0, 7.0, 1));std::cout << tree.number_of_intersected_primitives(segment_query)<< " intersections(s) with segment" << std::endl;// computes the closest point from a point queryPoint point_query(1.5, 3.0, 1);Point closest = tree.closest_point(point_query);std::cerr << "closest point is: " << closest << std::endl;Point_and_primitive_id id = tree.closest_point_and_primitive(point_query);std::cout << id.second->source() << " " << id.second->target() << std::endl;
}/*
测试布尔运算
*/#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_exact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Polygon_2.h>
#include <CGAL/Polygon_with_holes_2.h>
#include <CGAL/Polygon_set_2.h>
#include <CGAL/Boolean_set_operations_2.h>
#include <CGAL/Intersections_3/Line_3_Line_3.h>
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Pretty-print a CGAL polygon.
//
template<class Kernel, class Container>
void print_polygon(const CGAL::Polygon_2<Kernel, Container>& P)
{typename CGAL::Polygon_2<Kernel, Container>::Vertex_const_iterator vit;std::cout << "[ " << P.size() << " vertices:";for (vit = P.vertices_begin(); vit != P.vertices_end(); ++vit)std::cout << " (" << *vit << ')';std::cout << " ]" << std::endl;return;
}//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Pretty-print a polygon with holes.
//
template<class Kernel, class Container>
void print_polygon_with_holes
(const CGAL::Polygon_with_holes_2<Kernel, Container>& pwh)
{if (!pwh.is_unbounded()){std::cout << "{ Outer boundary = ";print_polygon(pwh.outer_boundary());}elsestd::cout << "{ Unbounded polygon." << std::endl;typename CGAL::Polygon_with_holes_2<Kernel, Container>::Hole_const_iterator hit;unsigned int k = 1;std::cout << " " << pwh.number_of_holes() << " holes:" << std::endl;for (hit = pwh.holes_begin(); hit != pwh.holes_end(); ++hit, ++k){std::cout << " Hole #" << k << " = ";print_polygon(*hit);}std::cout << " }" << std::endl;return;
}void testBoolOpeation() {typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_exact_constructions_kernel Kernel;typedef Kernel::Point_2 Point_2;typedef CGAL::Polygon_2<Kernel> Polygon_2;typedef CGAL::Polygon_with_holes_2<Kernel> Polygon_with_holes_2;typedef CGAL::Polygon_set_2<Kernel> Polygon_set_2;typedef std::list<Polygon_with_holes_2> Pwh_list_2;typedef CGAL::Line_3<K> Line;typedef CGAL::Point_3<K> Point;// Construct the two initial polygons and the clipping rectangle.Polygon_2 P;P.push_back(Point_2(0, 1));P.push_back(Point_2(2, 0));P.push_back(Point_2(1, 1));P.push_back(Point_2(2, 2));Polygon_2 Q;Q.push_back(Point_2(3, 1));Q.push_back(Point_2(1, 2));Q.push_back(Point_2(2, 1));Q.push_back(Point_2(1, 0));Polygon_2 rect;rect.push_back(Point_2(0, 0));rect.push_back(Point_2(3, 0));rect.push_back(Point_2(3, 2));rect.push_back(Point_2(0, 2));// Perform a sequence of operations.Polygon_set_2 S;S.insert(P);S.join(Q); // Compute the union of P and Q.S.complement(); // Compute the complement.S.intersection(rect); // Intersect with the clipping rectangle.// Print the result.std::list<Polygon_with_holes_2> res;std::list<Polygon_with_holes_2>::const_iterator it;std::cout << "The result contains " << S.number_of_polygons_with_holes()<< " components:" << std::endl;S.polygons_with_holes(std::back_inserter(res));for (it = res.begin(); it != res.end(); ++it) {std::cout << "--> ";print_polygon_with_holes(*it);}// 交集if ((CGAL::do_intersect(P, Q)))std::cout << "The two polygons intersect in their interior." << std::endl;elsestd::cout << "The two polygons do not intersect." << std::endl;// union// Compute the union of P and Q.Polygon_with_holes_2 unionR;if (CGAL::join(P, Q, unionR)) {std::cout << "The union: ";print_polygon_with_holes(unionR);}elsestd::cout << "P and Q are disjoint and their union is trivial."<< std::endl;// Compute the intersection of P and Q.CGAL::intersection(P, Q, std::back_inserter(res));// Compute the symmetric difference of P and Q.CGAL::symmetric_difference(P, Q, std::back_inserter(res));// 直线相交const Line l = Line(Point(0, 0, 0), Point(1, 2, 3));const Line l_1 = Line(Point(0, 0, 0), Point(-3, -2, -1));const CGAL::Object obj1 = CGAL::intersection(l, l_1);
}/*
凸包检测
*/
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/point_generators_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Delaunay_triangulation_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh.h>
#include <CGAL/algorithm.h>
#include <CGAL/convex_hull_3_to_face_graph.h>
void testConvexHull() {typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel K;typedef K::Point_3 Point_3;typedef CGAL::Delaunay_triangulation_3<K> Delaunay;typedef Delaunay::Vertex_handle Vertex_handle;typedef CGAL::Surface_mesh<Point_3> Surface_mesh;CGAL::Random_points_in_sphere_3<Point_3> gen(100.0);std::list<Point_3> points;// generate 250 points randomly in a sphere of radius 100.0// and insert them into the triangulationstd::copy_n(gen, 250, std::back_inserter(points));Delaunay T;T.insert(points.begin(), points.end());std::list<Vertex_handle> vertices;T.incident_vertices(T.infinite_vertex(), std::back_inserter(vertices));std::cout << "This convex hull of the 250 points has "<< vertices.size() << " points on it." << std::endl;// remove 25 of the input pointsstd::list<Vertex_handle>::iterator v_set_it = vertices.begin();for (int i = 0; i < 25; i++){T.remove(*v_set_it);v_set_it++;}//copy the convex hull of points into a polyhedron and use it//to get the number of points on the convex hullSurface_mesh chull;CGAL::convex_hull_3_to_face_graph(T, chull);std::cout << "After removal of 25 points, there are "<< num_vertices(chull) << " points on the convex hull." << std::endl;
}void test() {testKDTree();testGlyph();testBoolOpeation();testConvexHull();
}
输出
3 intersections(s) with ray query
closest point is: 0.333333 0.333333 0.333333
squared distance: 8.33333
2 intersections(s) with segment
closest point is: 2.55 2.65 1
2 1 1 3 4 1
The result contains 2 components:
--> { Outer boundary = [ 10 vertices: (2 2) (1 2) (0 2) (0 1) (0 0) (1 0) (2 0) (3 0) (3 1) (3 2) ]1 holes:Hole #1 = [ 12 vertices: (3 1) (1.66667 0.333333) (2 0) (1.5 0.25) (1 0) (1.33333 0.333333) (0 1) (1.33333 1.66667) (1 2) (1.5 1.75) (2 2) (1.66667 1.66667) ]}
--> { Outer boundary = [ 4 vertices: (1 1) (1.5 0.5) (2 1) (1.5 1.5) ]0 holes:}
The two polygons intersect in their interior.
The union: { Outer boundary = [ 12 vertices: (1.33333 0.333333) (1 0) (1.5 0.25) (2 0) (1.66667 0.333333) (3 1) (1.66667 1.66667) (2 2) (1.5 1.75) (1 2) (1.33333 1.66667) (0 1) ]1 holes:Hole #1 = [ 4 vertices: (1.5 1.5) (2 1) (1.5 0.5) (1 1) ]}
This convex hull of the 250 points has 88 points on it.
After removal of 25 points, there are 84 points on the convex hull.GitHub - CGAL/cgal: The public CGAL repository, see the README below
创作不易,小小的支持一下吧!


相关文章:

C++ 几何计算库
代码 #include <iostream> #include <list> #include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h> #include <CGAL/AABB_tree.h> #include <CGAL/AABB_traits.h> #include <CGAL/AABB_segment_primitive.h> #include <CGAL/Polygon_2.h>typedef CGAL…...

云动态摘要 2024-07-16
给您带来云厂商的最新动态,最新产品资讯和最新优惠更新。 最新优惠与活动 数据库上云优选 阿里云 2024-07-04 RDS、PolarDB、Redis、MongoDB 全系产品新用户低至首年6折起! [免费体验]智能助手ChatBI上线 腾讯云 2024-07-02 基于混元大模型打造&…...

数仓工具—Hive基础之临时表及示例
Hive基础之临时表及示例 临时表是应用程序自动管理在大型或复杂查询执行期间生成的中间数据的一种便捷方式。Hive 0.14 及更高版本支持临时表。可以在用户会话中像使用普通表一样多次使用它们。在本文中,我们将介绍 Apache Hive 临时表,以及如何创建和使用限制的示例。 Hiv…...

机体坐标系和导航坐标系
目录 机体坐标系(Body Frame)例子:无人机的机体坐标系 导航坐标系(Navigation Frame)例子:地球固定的导航坐标系 具体例子说明机体坐标系描述导航坐标系描述 总结 机体坐标系(Body Frame&#x…...

软件测试——web单功能测试
工作职责: 1.负责产品系统测试,包括功能测试、性能测试、稳定性测试、用户场景测试、可靠性测试等。 2.负责测试相关文档的编写,包括测试计划、测试用例、测试报告等。 3.负责自动化测试框架、用例的维护。 岗位要求: 1.熟练…...

django-ckeditor富文本编辑器
一.安装django-ckeditor 1.安装 pip install django-ckeditor2.注册应用 INSTALLED_APPS [...ckeditor, ]3.配置model from ckeditor.fields import RichTextFieldcontent RichTextField()4.在项目中manage.py文件下重新执行迁移,生成迁移文件 py…...

鸿蒙模拟器(HarmonyOS Emulator)Beta申请审核流程
文 | Promise Sun 一.背景: 鸿蒙项目开发需要使用模拟器进行开发测试,但目前想在DevEco Studio开发工具中使用模拟器就必须到华为官网进行报名申请,参加“鸿蒙模拟器(HarmonyOS Emulator)Beta活动申请”。 申请审核通…...

VUE:跨域配置代理服务器
//在vite.config。js中,同插件配置同级进行配置server:{proxy:{"/myrequest":{//代理域名,可自行修改target:"https://m.wzj.com/",//访问服务器的目标域名changeOrigin:true,//允许跨域configure:(proxy,options) > {proxy.on(&…...

Redis实战—附近商铺、用户签到、UV统计
本博客为个人学习笔记,学习网站与详细见:黑马程序员Redis入门到实战 P88 - P95 目录 附近商铺 数据导入 功能实现 用户签到 签到功能 连续签到统计 UV统计 附近商铺 利用Redis中的GEO数据结构实现附近商铺功能,常见命令如下图所示。…...

小程序里面使用vant ui中的vant-field组件,如何使得输入框自动获取焦点
//.wxml <van-fieldmodel:value"{{ userName }}"placeholder"请输入学号"focus"{{focusUserName}}"/>// .js this.setData({focusUserName: true});vant-field...
)
Html_Css问答集(12)
99、将上例的0%改为30%,会如何变化? none:延迟2秒间无色,3.8秒(0%-30%占1.8秒)前无色,之后变红到5秒绿最后蓝,动画结束时恢复初始(无色)。 forward:延迟2秒间无色&am…...

【C语言】条件运算符详解 - 《 A ? B : C 》
目录 C语言条件运算符详解1. 条件运算符的语法和使用示例 1:基本用法输出 2. 嵌套条件运算符示例 2:嵌套条件运算符输出 3. 条件运算符与 if-else 语句的比较示例 3:使用 if-else 语句示例 4:使用条件运算符 4. 条件运算符的实际应…...
乘积量化pq:将高维向量压缩 97%
向量相似性搜索在处理大规模数据集时,往往面临着内存消耗的挑战。例如,即使是一个包含100万个密集向量的小数据集,其索引也可能需要数GB的内存。随着数据集规模的增长,尤其是高维数据,内存使用量会迅速增加,…...

解决一下git clone失败的问题
1).不开梯子,我们用https克隆 git clone https://github.com 报错: Failed to connect to github.com port 443 after 2091 ms: Couldnt connect to server 解决办法: 开梯子,然后# 注意修改成自己的IP和端口号 gi…...

【 香橙派 AIpro评测】烧系统运行部署LLMS大模型跑开源yolov5物体检测并体验Jupyter Lab AI 应用样例(新手入门)
文章目录 一、引言⭐1.1下载镜像烧系统⭐1.2开发板初始化系统配置远程登陆💖 远程ssh💖查看ubuntu桌面💖 远程向日葵 二、部署LLMS大模型&yolov5物体检测⭐2.1 快速启动LLMS大模型💖拉取代码💖下载mode数据&#x…...

Azure Repos 仓库管理
从远端仓库克隆到本地 前提:本地要安装git,并且登录了账户 1.在要放这个远程仓库的路径下,打git 然后 git clone https://.. 如果要登录验证,那就验证下,点 generate git credentials,复制password 克隆完后,cd 到克隆的路径, 可以用 git branch -a //查看分…...

Day71 代码随想录打卡|回溯算法篇---全排列
题目(leecode T46): 给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。 方法:全排列是数学中的基础问题,也是回溯算法能解决的经典问题。全排列因为每个元素都会…...

开源科学工程技术软件
目录 0 参考链接 1 Silx 2 Klampt 3 参数化三维3D软件Dune 3D 4 GPS日志文件查看器GPXSee 5 三维3D软件Chili3D 6 集成电路设计软件XicTools 7 天文学软件Cosmonium 8 计算流体力学软件FluidX3D 9 点云处理软件CloudCompare 10 野外火灾建模软件WindNinja 11 电子设…...

甄选范文“论软件维护方法及其应用”软考高级论文,系统架构设计师论文
论文真题 软件维护是指在软件交付使用后,直至软件被淘汰的整个时间范围内,为了改正错误或满足 新的需求而修改软件的活动。在软件系统运行过程中,软件需要维护的原因是多种多样的, 根据维护的原因不同,可以将软件维护分为改正性维护、适应性维护、完善性维护和预防性 维护…...

【服务器】端口映射
文章目录 1.端口映射的概念1.1 端口映射的类型1.2 端口映射的应用场景1.3 示例 2.为什么要进行端口映射呢?3.原理3.1【大白话】原理解释3.2 原理图 4.代码 1.端口映射的概念 端口映射(Port Mapping),也称为端口转发(P…...
XCTF-web-easyupload
试了试php,php7,pht,phtml等,都没有用 尝试.user.ini 抓包修改将.user.ini修改为jpg图片 在上传一个123.jpg 用蚁剑连接,得到flag...

OpenLayers 可视化之热力图
注:当前使用的是 ol 5.3.0 版本,天地图使用的key请到天地图官网申请,并替换为自己的key 热力图(Heatmap)又叫热点图,是一种通过特殊高亮显示事物密度分布、变化趋势的数据可视化技术。采用颜色的深浅来显示…...
【网络安全产品大调研系列】2. 体验漏洞扫描
前言 2023 年漏洞扫描服务市场规模预计为 3.06(十亿美元)。漏洞扫描服务市场行业预计将从 2024 年的 3.48(十亿美元)增长到 2032 年的 9.54(十亿美元)。预测期内漏洞扫描服务市场 CAGR(增长率&…...

鱼香ros docker配置镜像报错:https://registry-1.docker.io/v2/
使用鱼香ros一件安装docker时的https://registry-1.docker.io/v2/问题 一键安装指令 wget http://fishros.com/install -O fishros && . fishros出现问题:docker pull 失败 网络不同,需要使用镜像源 按照如下步骤操作 sudo vi /etc/docker/dae…...

什么?连接服务器也能可视化显示界面?:基于X11 Forwarding + CentOS + MobaXterm实战指南
文章目录 什么是X11?环境准备实战步骤1️⃣ 服务器端配置(CentOS)2️⃣ 客户端配置(MobaXterm)3️⃣ 验证X11 Forwarding4️⃣ 运行自定义GUI程序(Python示例)5️⃣ 成功效果
全志A40i android7.1 调试信息打印串口由uart0改为uart3
一,概述 1. 目的 将调试信息打印串口由uart0改为uart3。 2. 版本信息 Uboot版本:2014.07; Kernel版本:Linux-3.10; 二,Uboot 1. sys_config.fex改动 使能uart3(TX:PH00 RX:PH01),并让boo…...
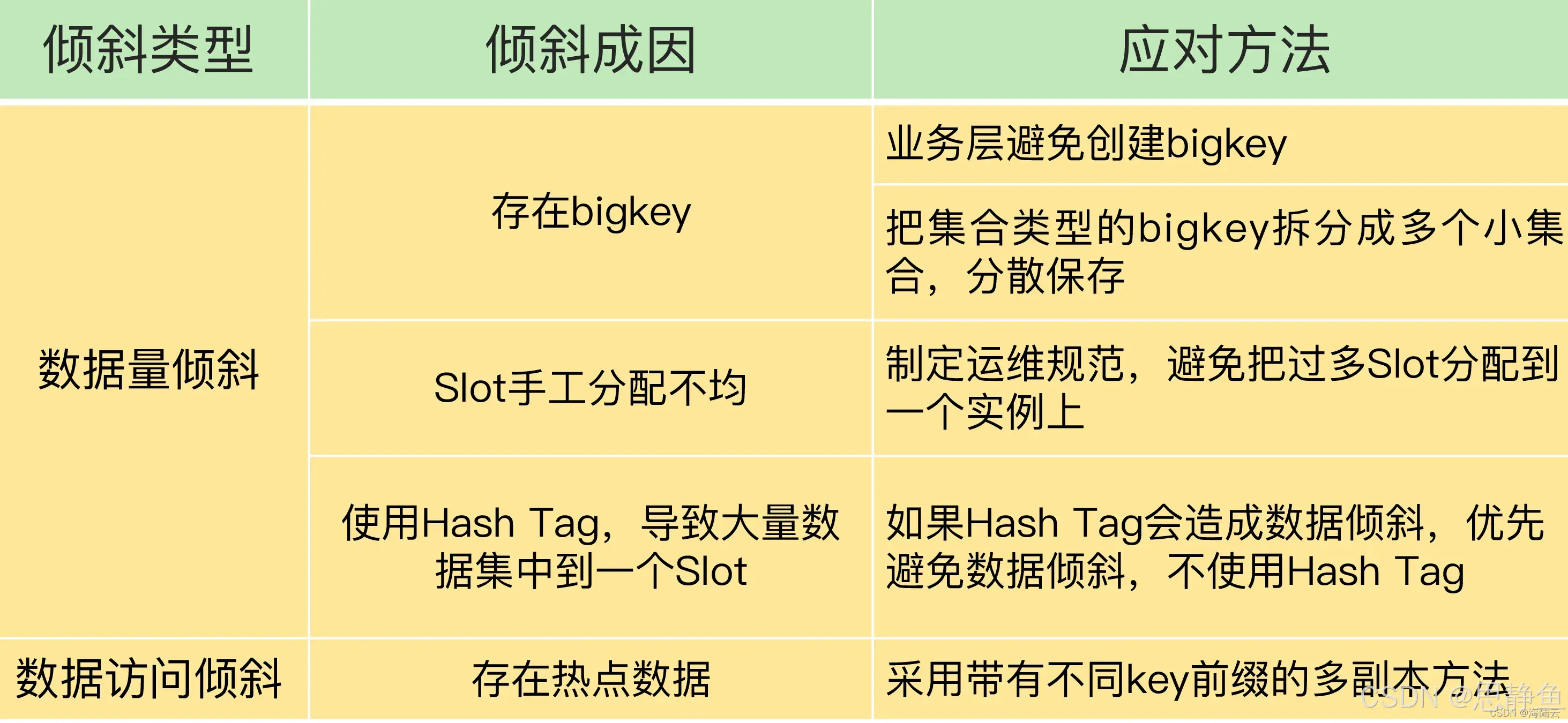
Redis数据倾斜问题解决
Redis 数据倾斜问题解析与解决方案 什么是 Redis 数据倾斜 Redis 数据倾斜指的是在 Redis 集群中,部分节点存储的数据量或访问量远高于其他节点,导致这些节点负载过高,影响整体性能。 数据倾斜的主要表现 部分节点内存使用率远高于其他节…...

零基础在实践中学习网络安全-皮卡丘靶场(第九期-Unsafe Fileupload模块)(yakit方式)
本期内容并不是很难,相信大家会学的很愉快,当然对于有后端基础的朋友来说,本期内容更加容易了解,当然没有基础的也别担心,本期内容会详细解释有关内容 本期用到的软件:yakit(因为经过之前好多期…...

Python ROS2【机器人中间件框架】 简介
销量过万TEEIS德国护膝夏天用薄款 优惠券冠生园 百花蜂蜜428g 挤压瓶纯蜂蜜巨奇严选 鞋子除臭剂360ml 多芬身体磨砂膏280g健70%-75%酒精消毒棉片湿巾1418cm 80片/袋3袋大包清洁食品用消毒 优惠券AIMORNY52朵红玫瑰永生香皂花同城配送非鲜花七夕情人节生日礼物送女友 热卖妙洁棉…...

08. C#入门系列【类的基本概念】:开启编程世界的奇妙冒险
C#入门系列【类的基本概念】:开启编程世界的奇妙冒险 嘿,各位编程小白探险家!欢迎来到 C# 的奇幻大陆!今天咱们要深入探索这片大陆上至关重要的 “建筑”—— 类!别害怕,跟着我,保准让你轻松搞…...
