深度学习部署笔记(十五): CUDA_Run_Time_API_parallel_多流并行,以及多流之间互相同步等待的操作方式
// CUDA运行时头文件
#include <cuda_runtime.h>#include <chrono>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>using namespace std;#define checkRuntime(op) __check_cuda_runtime((op), #op, __FILE__, __LINE__)bool __check_cuda_runtime(cudaError_t code, const char* op, const char* file, int line){if(code != cudaSuccess){ const char* err_name = cudaGetErrorName(code); const char* err_message = cudaGetErrorString(code); printf("runtime error %s:%d %s failed. \n code = %s, message = %s\n", file, line, op, err_name, err_message); return false;}return true;
}__global__ void add_vector(const float* a, const float* b, float* c, int count){int index = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x;if(index >= count) return;c[index] = a[index] + b[index];
}__global__ void mul_vector(const float* a, const float* b, float* c, int count){int index = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x;if(index >= count) return;c[index] = a[index] * b[index];
}cudaStream_t stream1, stream2;
float *a, *b, *c1, *c2;
const int num_element = 100000;
const size_t bytes = sizeof(float) * num_element;
const int blocks = 512;
const int grids = (num_element + blocks - 1) / blocks;
const int ntry = 1000;// 多个流异步
void async(){cudaEvent_t event_start1, event_stop1;cudaEvent_t event_start2, event_stop2;checkRuntime(cudaEventCreate(&event_start1));checkRuntime(cudaEventCreate(&event_stop1));checkRuntime(cudaEventCreate(&event_start2));checkRuntime(cudaEventCreate(&event_stop2));auto tic = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count() / 1000.0;checkRuntime(cudaEventRecord(event_start1, stream1));for(int i = 0; i < ntry; ++i)add_vector<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream1>>>(a, b, c1, num_element);checkRuntime(cudaEventRecord(event_stop1, stream1));checkRuntime(cudaEventRecord(event_start2, stream2));for(int i = 0; i < ntry; ++i)add_vector<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream2>>>(a, b, c2, num_element);checkRuntime(cudaEventRecord(event_stop2, stream2));checkRuntime(cudaStreamSynchronize(stream1));checkRuntime(cudaStreamSynchronize(stream2));auto toc = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count() / 1000.0;float time1, time2;checkRuntime(cudaEventElapsedTime(&time1, event_start1, event_stop1));checkRuntime(cudaEventElapsedTime(&time2, event_start2, event_stop2));printf("async: time1 = %.2f ms, time2 = %.2f ms, count = %.2f ms\n", time1, time2, toc - tic);
}// 单个流串行
void sync(){cudaEvent_t event_start1, event_stop1;checkRuntime(cudaEventCreate(&event_start1));checkRuntime(cudaEventCreate(&event_stop1));auto tic = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count() / 1000.0;checkRuntime(cudaEventRecord(event_start1, stream1));for(int i = 0; i < ntry; ++i)add_vector<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream1>>>(a, b, c1, num_element);for(int i = 0; i < ntry; ++i)add_vector<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream1>>>(a, b, c2, num_element);checkRuntime(cudaEventRecord(event_stop1, stream1));checkRuntime(cudaStreamSynchronize(stream1));auto toc = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count() / 1000.0;float time1;checkRuntime(cudaEventElapsedTime(&time1, event_start1, event_stop1));printf("sync: time1 = %.2f ms, count = %.2f ms\n", time1, toc - tic);
}// 多个流之间并行
void multi_stream_async(){// 这个案例主要实现多个流之间互相等待,使用event控制实现// 存在step1 -> step2 \ // -> step3 -> step4// stepa / //// 这个案例中,存在流程1:step1 -> step2的流程// 存在流程2:stepa// 存在流程3:step3 -> step4,step3要求step2与stepa作为输入// 此时,可以让流程1使用stream1,流程2使用stream2,而流程3继续使用stream1,仅仅在stream1中加入等待(event的等待)// step1 = add_vector// step2 = mul_vector// step3 = add_vector// step4 = mul_vector// stepa = add_vector#define step1 add_vector#define step2 mul_vector#define step3 add_vector#define step4 mul_vector#define stepa add_vectorcudaEvent_t event_async;checkRuntime(cudaEventCreate(&event_async));// stream1的执行流程step1<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream1>>>(a, b, c1, num_element);step2<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream1>>>(a, b, c1, num_element);// 等待event_async有事件checkRuntime(cudaStreamWaitEvent(stream1, event_async));step3<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream1>>>(a, b, c2, num_element);step4<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream1>>>(a, b, c2, num_element);// stream2的执行流程stepa<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream2>>>(a, b, c2, num_element);// 为event_async触发事件,通知cudaStreamWaitEvent函数可以继续了checkRuntime(cudaEventRecord(event_async, stream2));checkRuntime(cudaStreamSynchronize(stream1));printf("multi_stream_async done.\n");
}int main(){// 本程序实现两个核函数的并行,通过多个流实现checkRuntime(cudaStreamCreate(&stream1));checkRuntime(cudaStreamCreate(&stream2));checkRuntime(cudaMalloc(&a, bytes));checkRuntime(cudaMalloc(&b, bytes));checkRuntime(cudaMalloc(&c1, bytes));checkRuntime(cudaMalloc(&c2, bytes));// 演示多流之间的异步执行async();// 演示单个流内的同步执行sync();// 演示多个流之间互相等待的操作multi_stream_async();return 0;
}
2. 单个流串行
void sync(){cudaEvent_t event_start1, event_stop1;checkRuntime(cudaEventCreate(&event_start1));checkRuntime(cudaEventCreate(&event_stop1));auto tic = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count() / 1000.0;checkRuntime(cudaEventRecord(event_start1, stream1));for(int i = 0; i < ntry; ++i)add_vector<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream1>>>(a, b, c1, num_element);for(int i = 0; i < ntry; ++i)add_vector<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream1>>>(a, b, c2, num_element);checkRuntime(cudaEventRecord(event_stop1, stream1));checkRuntime(cudaStreamSynchronize(stream1));auto toc = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count() / 1000.0;float time1;checkRuntime(cudaEventElapsedTime(&time1, event_start1, event_stop1));printf("sync: time1 = %.2f ms, count = %.2f ms\n", time1, toc - tic);
}
cuda count time: 12.26, cpp count time: 12.28
这个函数演示了单个流中的同步执行,具体解释如下:
cudaEvent_t 是 CUDA Runtime API 中的一个结构体,定义在 cuda_runtime_api.h 中。它用于表示一个 CUDA 事件对象,用于记录 GPU 上某个时间点的状态。
CUDA 事件可以用于两种目的:
记录一个时间点(如开始时间点或结束时间点)。
记录一个时间间隔(即时间差)。
通常情况下,CUDA 事件被用于在主机和设备之间进行同步,或在设备内部进行同步。例如,可以在主机代码中调用 cudaEventRecord() 来记录一个事件,然后在设备代码中使用 cudaStreamWaitEvent() 等待该事件,以确保某些设备操作发生在之前记录的事件之后。又或者,可以在设备代码中记录两个事件,然后在主机代码中使用 cudaEventElapsedTime() 计算它们之间的时间差。
首先创建两个事件 event_start1 和 event_stop1,用于记录同步执行的时间;
使用 cudaEventRecord 将 event_start1 记录在 stream1 中,表示从这个时间点开始,将会执行在 stream1 中的操作;
使用 for 循环调用 add_vector 核函数,在 stream1 中执行 ntry 次,计算向量 a 和 b 的加和,存储在向量 c1 和 c2 中;
使用 cudaEventRecord 将 event_stop1 记录在 stream1 中,表示到达这个时间点,stream1 中的操作都已经完成;
使用 cudaStreamSynchronize 等待 stream1 中的所有操作执行完毕;
计算同步执行的时间 time1,并输出时间和整个操作的时间。
可以看到,这个函数中只使用了一个流,因此 add_vector 的计算是按照顺序执行的,不能充分发挥 GPU 的并行计算能力。因此,这个函数的计算时间会比异步执行的 async 函数要长
这段代码中使用了两种方法来计算代码执行的时间。
第一种方法是使用了C++标准库中的chrono库来计算代码执行的起始时间和终止时间,通过计算时间差得到代码执行的时间,这个方法在计算异步执行时比较方便,因为我们需要分别记录多个异步操作的起始时间和终止时间。
第二种方法是使用了CUDA提供的API cudaEventElapsedTime,这个API可以计算CUDA事件的时间差,用于计算CUDA事件执行的时间。在这个例子中,我们使用了这个API来计算在单个流上串行执行的时间。
3. 向量相加相乘的kernel function
__global__ void add_vector(const float* a, const float* b, float* c, int count){int index = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x;if(index >= count) return;c[index] = a[index] + b[index];
}__global__ void mul_vector(const float* a, const float* b, float* c, int count){int index = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x;if(index >= count) return;c[index] = a[index] * b[index];
}
count 是用来限制线程不要访问到超出数组的地址,因为数组的长度在我们开辟的时候就已经定义好了
checkRuntime(cudaMalloc(&a, bytes));
count是num_element, byte是num_element * sizeof(float), 超出地址会访问到虚拟地址
4. 多个流的异步
void async(){cudaEvent_t event_start1, event_stop1;cudaEvent_t event_start2, event_stop2;checkRuntime(cudaEventCreate(&event_start1));checkRuntime(cudaEventCreate(&event_stop1));checkRuntime(cudaEventCreate(&event_start2));checkRuntime(cudaEventCreate(&event_stop2));auto tic = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count() / 1000.0;checkRuntime(cudaEventRecord(event_start1, stream1));for(int i = 0; i < ntry; ++i)add_vector<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream1>>>(a, b, c1, num_element);checkRuntime(cudaEventRecord(event_stop1, stream1));checkRuntime(cudaEventRecord(event_start2, stream2));for(int i = 0; i < ntry; ++i)add_vector<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream2>>>(a, b, c2, num_element);checkRuntime(cudaEventRecord(event_stop2, stream2));checkRuntime(cudaStreamSynchronize(stream1));checkRuntime(cudaStreamSynchronize(stream2));auto toc = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count() / 1000.0;float time1, time2;checkRuntime(cudaEventElapsedTime(&time1, event_start1, event_stop1));checkRuntime(cudaEventElapsedTime(&time2, event_start2, event_stop2));printf("async: time1 = %.2f ms, time2 = %.2f ms, count = %.2f ms\n", time1, time2, toc - tic);
}
async: time1 = 6.97 ms, time2 = 6.94 ms, count = 9.32 ms
输出的内容中包含了在两个流上异步执行的两个内核函数的时间,分别为time1和time2,它们的值应该是相当接近的。同时,输出中还包含了整个函数执行的总时间count,可以看出相比于同步执行的情况,异步执行使得程序的总执行时间更短,效率更高。
5. 多个流之间互相等待的操作
// 这个案例主要实现多个流之间互相等待,使用event控制实现// 存在step1 -> step2 \ // -> step3 -> step4// stepa / //// 这个案例中,存在流程1:step1 -> step2的流程// 存在流程2:stepa// 存在流程3:step3 -> step4,step3要求step2与stepa作为输入// 此时,可以让流程1使用stream1,流程2使用stream2,而流程3继续使用stream1,仅仅在stream1中加入等待(event的等待)// step1 = add_vector// step2 = mul_vector// step3 = add_vector// step4 = mul_vector// stepa = add_vector#define step1 add_vector#define step2 mul_vector#define step3 add_vector#define step4 mul_vector#define stepa add_vectorcudaEvent_t event_async;checkRuntime(cudaEventCreate(&event_async));// stream1的执行流程step1<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream1>>>(a, b, c1, num_element);step2<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream1>>>(a, b, c1, num_element);// 等待event_async有事件checkRuntime(cudaStreamWaitEvent(stream1, event_async));step3<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream1>>>(a, b, c2, num_element);step4<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream1>>>(a, b, c2, num_element);// stream2的执行流程stepa<<<grids, blocks, 0, stream2>>>(a, b, c2, num_element);// 为event_async触发事件,通知cudaStreamWaitEvent函数可以继续了checkRuntime(cudaEventRecord(event_async, stream2));checkRuntime(cudaStreamSynchronize(stream1));printf("multi_stream_async done.\n");
具体流程如下:
在stream1中先执行step1,然后执行step2,这两个步骤是串行执行的;
在stream1中调用cudaStreamWaitEvent函数等待event_async事件,此时流程3(step3和step4)还不能开始执行;
在stream2中执行stepa,此时stepa和之前的步骤是并行执行的;
在stream2中调用cudaEventRecord函数触发event_async事件,通知stream1可以开始执行流程3;
在stream1中执行step3和step4,这两个步骤是串行执行的;
在stream1中调用cudaStreamSynchronize函数等待所有在该流中的操作执行完毕,程序结束。
总结起来,这个多流程的示例展示了如何使用事件来控制不同流之间的顺序和同步,从而实现流程之间的依赖关系和并行执行。
相关文章:
: CUDA_Run_Time_API_parallel_多流并行,以及多流之间互相同步等待的操作方式)
深度学习部署笔记(十五): CUDA_Run_Time_API_parallel_多流并行,以及多流之间互相同步等待的操作方式
// CUDA运行时头文件 #include <cuda_runtime.h>#include <chrono> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h>using namespace std;#define checkRuntime(op) __check_cuda_runtime((op), #op, __FILE__, __LINE__)bool __check_cuda_runtime(cudaErro…...
【Spring】spring框架简介
一、框架 1.框架的基本特点: 框架(Framework),是基于基础技术之上,从众多业务中抽取出的通用解决方案;框架是一个半成品,使用框架规定的语法开发可以提高开发效率,可以用简单的代码就能完成复杂的基础业务;框架内部使用大量的设…...

WuThreat身份安全云-TVD每日漏洞情报-2023-03-17
漏洞名称:TP-LINK Archer AX21 命令注入漏洞 漏洞级别:严重 漏洞编号:CVE-2023-1389,CNNVD-202303-1280 相关涉及:TP-LINK Archer AX21 1.1.4 Build 20230219之前的固件版本 漏洞状态:POC 参考链接:https://tvd.wuthreat.com/#/listDetail?TVD_IDTVD-2023-06347 漏洞名称:D-L…...
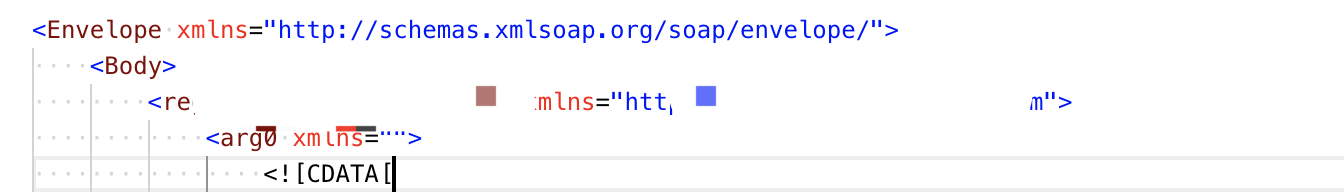
postman 调用webservice
有个外部接口需要提供古老的webservice 格式接口。1 设置格式按照xml 格式设置。2 消息体xml 封装不加envelope:<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap"" target"_blank">http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"><soap:Body><soap:Fault&…...
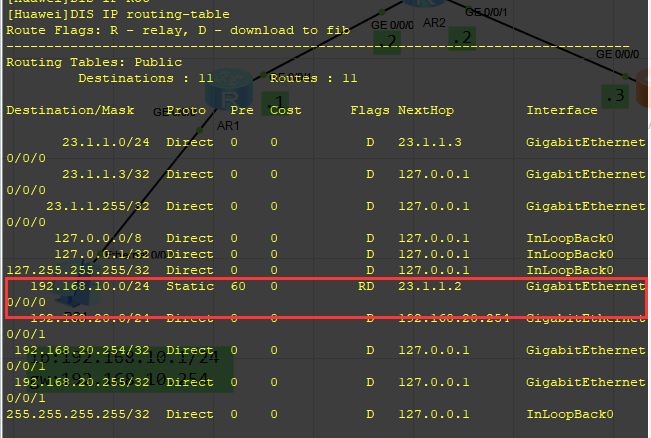
基于华为模拟器(ensp)的静态路由配置实验
一 实验需求静态路由实验,建立拓扑pc1>>R1>>R2>>R3>>pc2,使pc1与pc2能相互通信。二 实验拓扑三 ip地址规划设备接口ip地址AR1G0/0/0192.168.10.254/24G0/0/112.1.1.1/24AR2G0/0/012.1.1.2/24G0/0/123.1.1.2/24 AR3G0/0/023.1.1.…...
模拟实现字符串函数(长度受限制的详讲)
上次发布了长度不受限制的字符串函数的模拟实现方法,这次就给大家说说长度受限制的字符串函数。首先,长度受限制和不受限制有什么区别呢?其实从某种意义上来讲,长度受限制的字符串函数比长度不受限制的字符串安全,为什…...

分布式ID生成方案总结
什么是分布式 ID 分布式 ID 是指,在分布式环境下可用于对数据进行标识且易存储的全局唯一的 ID 标识。 为什么需要分布式 ID 对于单体系统来说,主键ID可能会常用主键自动的方式进行设置,这种ID生成方法在单体项目是可行的。 对于分布式系统…...

极智AI | 百度推出文心一言,对标ChatGPT功力几成
欢迎关注我,获取我的更多经验分享,极智传送《极智AI | 百度推出文心一言,对标 ChatGPT 功力几成》 大家好,我是极智视界,本文介绍一下 百度今日推出文心一言,对标ChatGPT功力几成。 邀您加入我的知识星球「极智视界」,星球内有超多好玩的项目实战源码下载,链接:https…...
CleanMyMac X最新版本4.12.6
系统要求macOS 10.12及更高,M1机型及最新macOS 13 CleanMyMac可以为Mac腾出空间,软件已经更新到CleanMyMac X支持最新版Mac系统。CleanMyMac具有一系列巧妙的新功能,可让您安全,智能地扫描和清理整个系统,删除大量未使…...
替代notepad++,notepad--介绍及插件cmake编译
Notepad 是一个文本编辑器小软件,用来替代windows自带的记事本。然而Notepad软件的作者是台湾省人,其具有明显的gd/jd/td倾向,如果你不赞同他的观点,Notepad将会在你的源码里面插入随机字符。推荐一款国产的开源跨平台软件NDD(not…...
Gradient Boosting)
机器学习笔记之集成学习(四)Gradient Boosting
机器学习笔记之集成学习——Gradient Boosting引言回顾:Boosting\text{Boosting}Boosting算法思想与AdaBoost\text{AdaBoost}AdaBoostGradient Boosting\text{Gradient Boosting}Gradient Boosting算法介绍场景构建算法过程迭代过程与梯度下降法之间的关联关系引言 …...
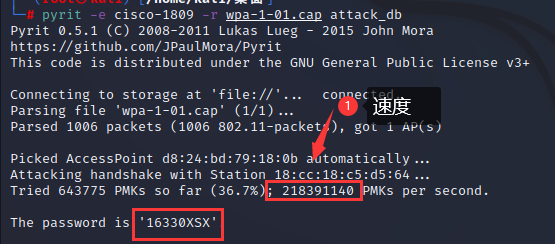
WPA渗透-pyrit:batch-table加速attack_db模块加速_“attack_db”模块加速
WPA渗透-pyrit:batch-table加速attack_db模块加速_“attack_db”模块加速 1.渗透WIFI 1.导入密码字典 pyrit -i 字典文件 import_passwords -i:输入的文件名 import_passwords:从类文件源导入密码。pyrit -i pwd.txt import_passwords2.导…...

kotlin第二部分复习纪要
扩展函数。 例如: fun Context.toast(msg: String, length: Int Toast.LENGTH_SHORT){Toast.makeText(this, msg, length).show() } 使用 val activity: Context? getActivity() activity?.toast("Hello world!") activity?.toast("Hello worl…...
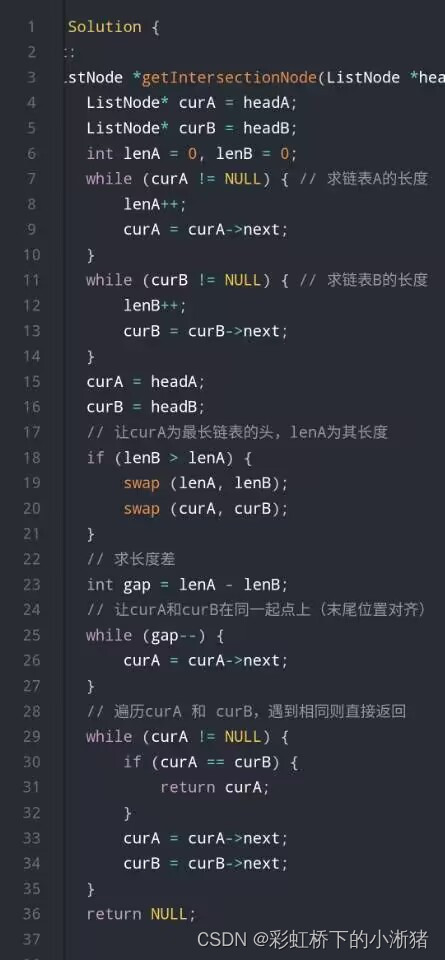
代码随想录--链表--删除链表第n个节点题型、链表相交题型
删除链表第n个节点题型 链表遍历学清楚! | LeetCode:19.删除链表倒数第N个节点 (opens new window) 这道题我一开始想的是,倒数第n个节点,链表不方便往前找,那就从链表头结点开始找链表长度减n,这时候就是…...
一起来学5G终端射频标准(In-band emissions-2)
上一篇我们列出了IBE的测试要求表格,今天我们详细说一下IBE如何测量计算,以及CA/NR-DC/SUL/UL-MIMO/V2X/Tx Diversity模式下的IBE情况。01—IBE如何测量和计算IBE的测试是对落入到未被分配的RB的干扰的测量,为12个子载波的平均发射功率&#…...

硬刚ChatGPT,中国版ChatGPT“狂飙”的机会在哪儿?
整体来讲,个人的态度是积极的。 ChatGPT、文心一言 都是在多重因素及大量 AI 模型/数据 长时间累积的成果,不是一蹴而就,立竿见影的功能产品。两者产生的基础和背景均不相同,各有优劣,不存在强行对比的概念。 以下是 …...

ReactNative——导航器createBottomTabNavigator(底部标签导航器篇)
上一篇有讲到堆栈式导航器的写法,点这里->堆栈式导航器标签导航器官网链接先安装依赖包yarn add react-navigation/bottom-tabs接着在src/navigator文件夹下新建BottomTabs.tsx文件,写法跟堆栈式导航器类似的~import React from react; import { NavigationConta…...
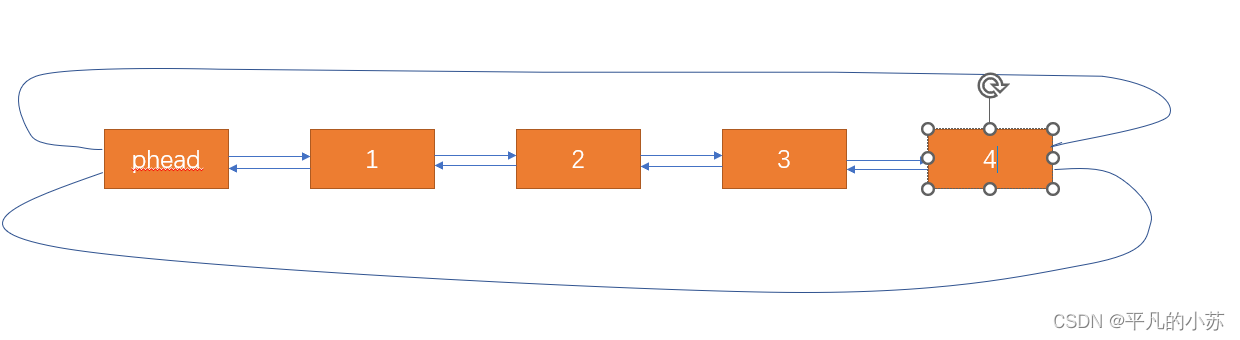
【数据结构】带头双向循环链表的实现
🌇个人主页:平凡的小苏 📚学习格言:别人可以拷贝我的模式,但不能拷贝我不断往前的激情 🛸C语言专栏:https://blog.csdn.net/vhhhbb/category_12174730.html 🚀数据结构专栏ÿ…...
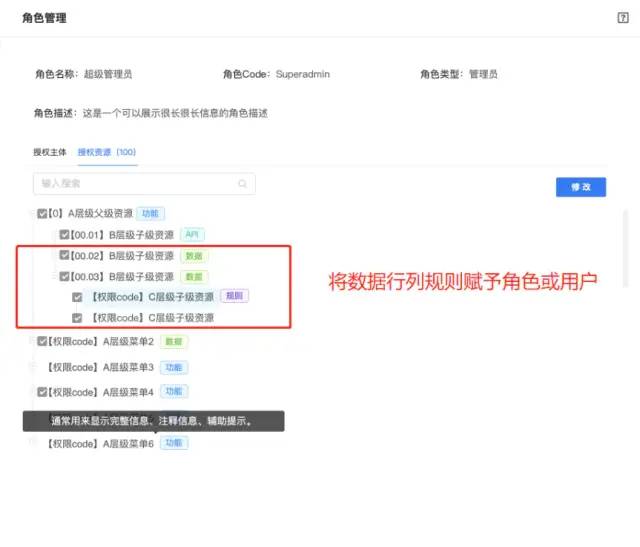
软件开发的权限系统功能模块设计,分享主流的九种常见权限模型
软件系统的权限控制几乎是非常常见且必备的,这篇文章整理下常见的九种模型,几乎基本够你用了,主流的权限模型主要有以下9种: 1、ACL模型 访问控制列表 2、DAC模型 自主访问控制 3、MAC模型 强制访问控制 4、ABAC模型 基于属性的访…...
CSS3-数据可视化
2D动画 - transform CSS3 transform属性允许你旋转,缩放,倾斜或平移给定元素。 Transform是形变的意思(通常也叫变换),transformer就是变形金刚 常见的函数transform function有: 平移:transl…...

[2025CVPR]DeepVideo-R1:基于难度感知回归GRPO的视频强化微调框架详解
突破视频大语言模型推理瓶颈,在多个视频基准上实现SOTA性能 一、核心问题与创新亮点 1.1 GRPO在视频任务中的两大挑战 安全措施依赖问题 GRPO使用min和clip函数限制策略更新幅度,导致: 梯度抑制:当新旧策略差异过大时梯度消失收敛困难:策略无法充分优化# 传统GRPO的梯…...

安宝特方案丨XRSOP人员作业标准化管理平台:AR智慧点检验收套件
在选煤厂、化工厂、钢铁厂等过程生产型企业,其生产设备的运行效率和非计划停机对工业制造效益有较大影响。 随着企业自动化和智能化建设的推进,需提前预防假检、错检、漏检,推动智慧生产运维系统数据的流动和现场赋能应用。同时,…...

1688商品列表API与其他数据源的对接思路
将1688商品列表API与其他数据源对接时,需结合业务场景设计数据流转链路,重点关注数据格式兼容性、接口调用频率控制及数据一致性维护。以下是具体对接思路及关键技术点: 一、核心对接场景与目标 商品数据同步 场景:将1688商品信息…...
【机器视觉】单目测距——运动结构恢复
ps:图是随便找的,为了凑个封面 前言 在前面对光流法进行进一步改进,希望将2D光流推广至3D场景流时,发现2D转3D过程中存在尺度歧义问题,需要补全摄像头拍摄图像中缺失的深度信息,否则解空间不收敛…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个医院查看报告小程序
一、开发环境准备 工具安装: 下载安装DevEco Studio 4.0(支持HarmonyOS 5)配置HarmonyOS SDK 5.0确保Node.js版本≥14 项目初始化: ohpm init harmony/hospital-report-app 二、核心功能模块实现 1. 报告列表…...
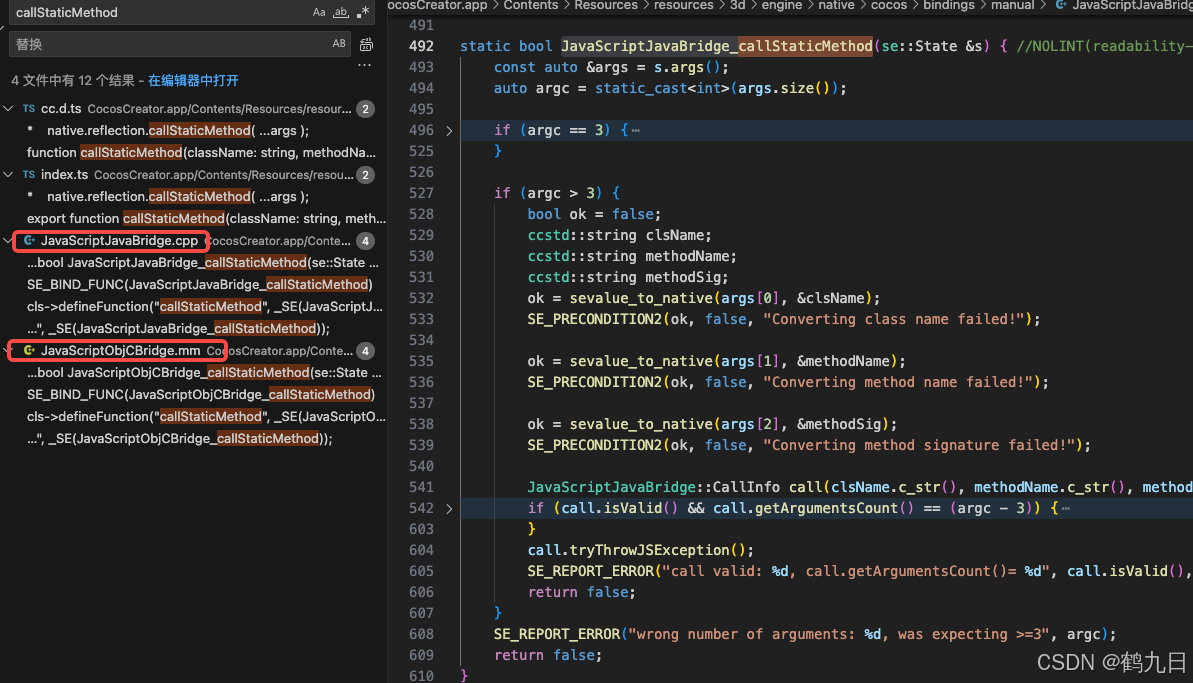
CocosCreator 之 JavaScript/TypeScript和Java的相互交互
引擎版本: 3.8.1 语言: JavaScript/TypeScript、C、Java 环境:Window 参考:Java原生反射机制 您好,我是鹤九日! 回顾 在上篇文章中:CocosCreator Android项目接入UnityAds 广告SDK。 我们简单讲…...

关于 WASM:1. WASM 基础原理
一、WASM 简介 1.1 WebAssembly 是什么? WebAssembly(WASM) 是一种能在现代浏览器中高效运行的二进制指令格式,它不是传统的编程语言,而是一种 低级字节码格式,可由高级语言(如 C、C、Rust&am…...

Unit 1 深度强化学习简介
Deep RL Course ——Unit 1 Introduction 从理论和实践层面深入学习深度强化学习。学会使用知名的深度强化学习库,例如 Stable Baselines3、RL Baselines3 Zoo、Sample Factory 和 CleanRL。在独特的环境中训练智能体,比如 SnowballFight、Huggy the Do…...

AspectJ 在 Android 中的完整使用指南
一、环境配置(Gradle 7.0 适配) 1. 项目级 build.gradle // 注意:沪江插件已停更,推荐官方兼容方案 buildscript {dependencies {classpath org.aspectj:aspectjtools:1.9.9.1 // AspectJ 工具} } 2. 模块级 build.gradle plu…...

算法笔记2
1.字符串拼接最好用StringBuilder,不用String 2.创建List<>类型的数组并创建内存 List arr[] new ArrayList[26]; Arrays.setAll(arr, i -> new ArrayList<>()); 3.去掉首尾空格...
