【Android】常用基础布局
布局是一种可用于放置很多控件的容器,它可以按照一定的规律调整内部控件的位置,从而编写出精美的界面,布局内不单单可以放控件,也可以嵌套布局,这样可以完成一些复杂的界面,下面就来认识一些常用的布局吧。
线性布局
-
名称:LinearLayout,这个布局会将它所包含的控件在线性方向上依次排列
-
属性:
android:orientation这个属性就规定了是在竖直方向上还是水平方向上,当为vertical时,规定的排列方向就为竖直方向;当为horizontal时,控件就会在水平方向上排列 -
设置一个主活动,并修改其xml中的代码,在这个活动里面加入三个按钮控件,此时设置为竖直方向:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/main"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:orientation="vertical"tools:context=".MainActivity"><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_1"android:text="Button1"/><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_2"android:text="Button2"/><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_3"android:text="Button3"/></LinearLayout>
此时使用的是android:orientation="vertical"即竖直方向,因此运行结果为:

但如果改为android:orientation="horizontal"即为水平方向,即三个按钮水平排列在第一行
注意:如果排列方式为horizontal,内部控件绝不能将宽度设置为match_parent,同样的道理,如果排列方式为vertical,内部控件绝不能将高度设置为match_parent,当不指定orietation属性时,则默认为水平方向排列
重要属性:通过android:layout_gravity来设置控件与上级视图(即布局)的对齐方式,当这三个控件仍然会坚持以布局所规定的方向排列
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/main"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:orientation="horizontal"tools:context=".MainActivity"><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_1"android:layout_gravity="top"android:text="Button1"/><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_2"android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"android:text="Button2"/><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_gravity="bottom"android:id="@+id/Button_3"android:text="Button3"/></LinearLayout>
因此运行结果为:

重要属性:android:layout_weight:允许我们使用比例的方式指定控件的大小,即将控件的宽或者高其中一个设置为0dp,则会根据你所设置的数值计算所占的权重,从而规划大小:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/main"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:orientation="horizontal"tools:context=".MainActivity"><EditTextandroid:layout_width="0dp"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_weight="1"android:id="@+id/editText"android:hint="Type Something"/><Buttonandroid:layout_width="0dp"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_1"android:layout_gravity="top"android:layout_weight="1"android:text="Button1"/></LinearLayout>
此时,我们将一个两个控件的宽度都设置为0dp,权重设置为1,此时权重就管的是宽度,它们两个来分配,都占二分之一,运行程序:

相对布局
- 名称:RelativeLayout
- 作用:可以通过相对定位的方式让控件出现在布局的任何位置
- 对于父布局的定位示例:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/main"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"tools:context=".MainActivity"><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_1"android:layout_alignParentTop="true"android:layout_alignParentStart="true"android:text="Button1"/><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_2"android:layout_alignParentTop="true"android:layout_alignParentEnd="true"android:text="Button2"/><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_3"android:layout_centerInParent="true"android:text="Button3"/><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_4"android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"android:layout_alignParentStart="true"android:text="Button4"/><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_5"android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"android:layout_alignParentEnd="true"android:text="Button5"/></RelativeLayout>
运行结果:

以上是对于父布局进行定位,控件还可以以控件进行定位:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/main"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"tools:context=".MainActivity"><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_1"android:layout_above="@id/Button_3"android:layout_toStartOf="@id/Button_3"android:text="Button1"/><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_2"android:layout_above="@id/Button_3"android:layout_toEndOf="@id/Button_3"android:text="Button2"/><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_3"android:layout_centerInParent="true"android:text="Button3"/><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_4"android:layout_below="@id/Button_3"android:layout_toStartOf="@id/Button_3"android:text="Button4"/><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/Button_5"android:layout_below="@id/Button_3"android:layout_toEndOf="@id/Button_3"android:text="Button5"/>
android:layout_above:可以让一个控件位于另一个控件的上方
android:layout_below:可以让一个控件位于另一个控件的下方
android:layout_toStartOf:可以让一个控件位于另一个控件的左侧
android:layout_toEndOf:可以让一个控件位于另一个控件的右侧
android:layout_alignBottom:一个控件和另一个控件的下边缘对齐
android:layout_alignTop:一个控件和另一个控件的上边缘对齐
android:layout_alignEnd:一个控件和另一个控件的右边缘对齐
android:layout_alignStart:一个控件和另一个控件的左边缘对齐
上面代码运行结果:

帧布局
-
名称:FrameLayout
-
作用:没有方便的定位方式,所有的控件都会默认放在布局的左上角,控件堆叠在一起,通常用于覆盖或弹出窗口。
-
示例:
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/main"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"tools:context=".MainActivity"><TextViewandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="This is TextView"/><ImageViewandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher"/></FrameLayout>
由于都位于左上角,因此文本会被图片遮盖一部分,因此运行结果为:

除了默认的效果还可以通过android:layout_gravity来指定控件在布局里的对齐方式
网格布局
-
名称:GridLayout
-
支持多行多列的表格排列
-
网格布局默认从左向右、从上到下排列,它新增了两个属性:
- columnCount属性,它指定了网格的列数,即每行能放多少个视图
- rowCount属性:它指定了网格的行数,即每列能放多少个视图
-
示例:
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/main"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:columnCount="2"android:rowCount="2"tools:context=".MainActivity"><TextViewandroid:layout_width="0dp"android:layout_height="60dp"android:background="#ffcccc"android:gravity="center"android:layout_columnWeight="1"android:text="aa"/><TextViewandroid:layout_width="0dp"android:layout_height="60dp"android:background="#00ffff"android:gravity="center"android:layout_columnWeight="1"android:text="aa"/><TextViewandroid:layout_width="0dp"android:layout_height="60dp"android:background="#ff00cc"android:gravity="center"android:layout_columnWeight="1"android:text="aa"/><TextViewandroid:layout_width="0dp"android:layout_height="60dp"android:background="#ffcc00"android:gravity="center"android:layout_columnWeight="1"android:text="aa"/></GridLayout>
定义了一个2行2列的网格布局,并注意其中对于宽度进行了权重的赋值,有代码在网格布局当中权重的设置方式是与前面不一样的,运行界面:

约束布局
ConstraintLayout:是一种灵活的布局管理器,它允许开发者在Android应用中创建复杂的布局,同时保持性能和灵活性。
相对定位
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| layout_constraintTop_toTopOf | 将控件的顶部与另一个控件的顶部对齐。 |
| layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf | 将控件的顶部与另一个控件的底部对齐。 |
| layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf | 将控件的底部与另一个控件的底部对齐。 |
| layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf | 将控件的底部与另一个控件的顶部对齐。 |
| layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf | 将控件的左边与另一个控件的左边对齐。 |
| layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf | 将控件的左边与另一个控件的右边对齐。 |
| layout_constraintRight_toRightOf | 将控件的右边与另一个控件的右边对齐。 |
| layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf | 将控件的右边与另一个控件的左边对齐。 |
| layout_constraintStart_toStartOf | 将控件的开始边与另一个控件的开始边对齐。 |
| layout_constraintStart_toEndOf | 将控件的开始边与另一个控件的结束边对齐。 |
| layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf: | 将控件的结束边与另一个控件的结束边对齐。 |
| layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf | 将控件的结束边与另一个控件的开始边对齐。 |
| layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf | 将一个控件的基线(baseline)与另一个控件的基线对齐 |
注意:当出现顶部与底部之间的对齐时这意味着当你将这个属性应用到一个视图上时,它会将视图的顶部放置在另一个所要对其的底部,从而在垂直方向上将它们连接起来。
示例:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/main"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"tools:context=".MainActivity"><Buttonandroid:id="@+id/button1"android:layout_width="100dp"android:layout_height="100dp"android:background="#ff2200"android:text="button1"app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/button2" /><Buttonandroid:id="@+id/buttoncenter"android:layout_width="100dp"android:layout_height="100dp"android:background="@color/teal_200"android:text="button center"app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /><Buttonandroid:id="@+id/button2"android:layout_width="100dp"android:layout_height="100dp"android:layout_marginRight="4dp"android:background="#ff4400"android:text="button2"app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/button1" /><Buttonandroid:id="@+id/button3"android:layout_width="100dp"android:layout_height="100dp"android:background="#ff8825"android:text="button3"app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@+id/button1" /><Buttonandroid:id="@+id/button4"android:layout_width="100dp"android:layout_height="100dp"android:background="#ff6677"android:text="button4"app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"app:layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf="@id/button2" /></androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
运行结果:

角度定位
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| layout_constraintCircle | 指定控件相对于另一个控件的圆形路径进行定位。 |
| layout_constraintCircleAngle | 指定控件在圆形路径上的角度位置。 |
| layout_constraintCircleRadius | 指定控件相对于圆形路径的半径。 |
示例:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/main"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"tools:context=".MainActivity"><TextViewandroid:layout_width="100dp"android:layout_height="100dp"android:id="@+id/TextView1"android:background="#00ff00"android:text="TextView1"android:visibility="visible"app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"/><TextViewandroid:layout_width="100dp"android:layout_height="100dp"android:id="@+id/TextView2"android:background="#ff0033"android:text="TextView2"android:visibility="visible"app:layout_constraintCircle="@id/TextView1"app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="120"app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="150dp"app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"app:layout_goneMarginLeft="50dp"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"/></androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
运行结果:

边距示例:
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| android:layout_marginStart | 设置控件在其起始边(左边或右边,取决于布局方向)的外边距。 |
| android:layout_marginEnd | 设置控件在其结束边(右边或左边,取决于布局方向)的外边距。 |
| android:layout_marginLeft | 设置控件在其左边的外边距。 |
| android:layout_marginTop | 设置控件在其顶部的外边距。 |
| android:layout_marginRight | 设置控件在其右边的外边距。 |
| android:layout_marginBottom | 设置控件在其底部的外边距。 |
当给marginBottom前面加上gone时就代表控件在不可用时相对应位置的外边距
示例:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/main"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"tools:context=".MainActivity"><TextViewandroid:layout_width="100dp"android:layout_height="100dp"android:id="@+id/TextView1"android:background="#00ff00"android:text="TextView1"android:visibility="visible"app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"/><TextViewandroid:layout_width="100dp"android:layout_height="100dp"android:id="@+id/TextView2"android:background="#ff0033"android:text="TextView2"android:visibility="visible"app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@id/TextView1"app:layout_goneMarginLeft="50dp"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"/></androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
运行结果:

当我们将第一个控件的可见性属性进行改变:android:visibility="gone",由于设置,此时运行结果为:

居中和偏移:
居中:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/main"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"tools:context=".MainActivity"><TextViewandroid:layout_width="100dp"android:layout_height="100dp"android:id="@+id/TextView1"android:background="#00ff00"android:text="TextView1"android:visibility="visible"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"/></androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
运行之后,此时就会有一个TextView位于屏幕的中间:

偏移:
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| layout_constraintHorizontal_bias | 水平偏移 |
| layout_constraintVertical_bias | 垂直偏移 |
偏移量的设置范围为0~1,当设置偏移量为1时,当为水平偏移时就会位于最右端,当为垂直偏移时,就会位于最下端。当为0.5就会位于中间,以此类推。
尺寸约束
-
当我们使用wrap_content,即让控件自己确定大小,此时我们可以设立属性来规定它的最大最小宽度与高度:
android:minWidth 最小的宽度 android:minHeight 最小的高度 android:maxWidth 最大的宽度 android:maxHeight 最大的高度 -
使用0dp:
match_parent是一个布局参数,它可以使视图的尺寸与父容器的尺寸相匹配。然而,ConstraintLayout推荐使用MATCH_CONSTRAINT(在XML中表示为0dp)来代替match_parent,因为它提供了更多的灵活性和控制。使用
MATCH_CONSTRAINT时,可以通过设置视图的约束来控制其尺寸。例如,你可以让视图的宽度或高度匹配父容器,或者根据其他视图的尺寸来调整自己的尺寸。这样做的好处是,它允许视图在不同屏幕尺寸和方向下保持更好的适应性。
示例:
<TextViewandroid:layout_width="0dp"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/TextView1"android:background="#00ff00"android:text="TextView1"android:visibility="visible"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent" />
在一般情况下,当我们设置了android:layout_width="0dp"时,这个视图就看不到了,但在约束布局当中由于我们设立了左右要与父视图对齐,因此运行结果如下:

- 宽高比:当宽或高至少有一个尺寸被设置为0dp时,可以通过属性layout_constraintDimensionRatio设置宽高比
示例:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/main"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"tools:context=".MainActivity"><TextViewandroid:layout_width="0dp"android:layout_height="100dp"android:id="@+id/TextView1"android:background="#00ff00"android:text="TextView2"android:visibility="visible"app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="1:1"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent" /><TextViewandroid:layout_width="0dp"android:layout_height="100dp"android:id="@+id/TextView2"android:background="#00ff00"android:text="TextView2"android:visibility="visible"app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="H,2:3"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent" /><TextViewandroid:layout_width="0dp"android:layout_height="100dp"android:id="@+id/TextView3"android:background="#00ff00"android:text="TextView1"android:visibility="visible"app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="W,2:3"app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent" /></androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
运行结果:

一般没有特殊声明时,指的为高比宽,也可在前面加上比例的限制,例如上面的示例文本控件2与文本控件3就加了限制,当前面为H时代表的是高比宽,当前面为W时,代表的是宽比高。
链
在约束布局中,链(Chains)是一种用于定义一组相关控件之间关系的方法,可以控制它们的排列方式和行为。
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle | 定义水平链的样式,可以设置为 spread(均匀分布)、spread_inside(均匀分布,但不包括边缘控件)或 packed(靠拢排列)。 |
| app:layout_constraintVertical_chainStyle | 定义垂直链的样式,可以设置为 spread、spread_inside或 packed。 |
| app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias | 设置水平链中每个控件的偏移量,取值范围为 0.0(左边)到 1.0(右边)。 |
| app:layout_constraintVertical_bias | 设置垂直链中每个控件的偏移量 |
| app:layout_constraintHorizontal_weight | 定义水平链中每个控件的权重,用于均匀分配额外空间。 |
| app:layout_constraintVertical_weight | 定义垂直链中每个控件的权重。 |
示例:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/main"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"tools:context=".MainActivity"><TextViewandroid:layout_width="50dp"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/TextView1"android:background="#00ff00"android:text="TextView2"android:visibility="visible"app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="spread_inside"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"app:layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf="@id/TextView2" /><TextViewandroid:layout_width="50dp"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/TextView2"android:background="#ff0011"android:text="TextView2"android:visibility="visible"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@id/TextView1"app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"app:layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf="@id/TextView3" /><TextViewandroid:layout_width="50dp"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/TextView3"android:background="#1100ff"android:text="TextView1"android:visibility="visible"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@id/TextView2" /></androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
运行程序,此时结果为:

当我们将第一个的属性改变:app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="spread"

app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="packed",此时三个TextView为挨在一起的
到这里就结束了!
相关文章:

【Android】常用基础布局
布局是一种可用于放置很多控件的容器,它可以按照一定的规律调整内部控件的位置,从而编写出精美的界面,布局内不单单可以放控件,也可以嵌套布局,这样可以完成一些复杂的界面,下面就来认识一些常用的布局吧。…...

服务攻防-中间件安全(漏洞复现)
一.中间件-IIS-短文件&解析&蓝屏 IIS现在用的也少了,漏洞也基本没啥用 1、短文件:信息收集 2、文件解析:还有点用 3、HTTP.SYS:蓝屏崩溃 没有和权限挂钩 4、CVE-2017-7269 条件过老 windows 2003上面的漏洞 二.中…...

【SD】深入理解Stable Diffusion与ComfyUI的使用
【SD】深入理解Stable Diffusion与ComfyUI的使用 1. Stable Diffusion(SD)原理概述2. 各部件详解3. SD的工作流程4. ComfyUI与SD的结合5. 总结 1. Stable Diffusion(SD)原理概述 整体结构:SD不是单一模型,…...

Linux 12:多线程2
1. 生产者消费者模型 生产者消费者模型有三种关系,两个角色,一个交易场所。 三种关系: 生产者之间是什么关系?竞争 - 互斥 消费者和消费者之间?竞争 - 互斥 消费者和消费者之间?互斥和同步 两个角色: 生产者和消费者 一个交…...

Android RSA 加解密
文章目录 一、RSA简介二、RSA 原理介绍三、RSA 秘钥对生成1. 密钥对生成2. 获取公钥3. 获取私钥 四、PublicKey 和PrivateKey 的保存1. 获取公钥十六进制字符串1. 获取私钥十六进制字符串 五、PublicKey 和 PrivateKey 加载1. 加载公钥2. 加载私钥 六、 RSA加解密1. RSA 支持三…...

类与对象-多态-案例3-电脑组装具体实现
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; //CPU class CPU { public:virtual void calculate() 0; }; //显卡 class GraCard { public:virtual void graphics() 0; }; //存储 class Memory { public:virtual void memory() 0; }; class Compu…...

try-with-resources 语句的用途和优点有哪些,它如何自动管理资源?
在Java编程中,资源管理是一个重要的议题,尤其是当你在代码中使用那些需要显式关闭的资源,比如文件流、数据库连接或者网络套接字等。 如果资源使用完毕后忘记关闭,不仅会导致资源泄露,还可能引起程序性能问题甚至系统…...

GraphRAG参数与使用步骤 | 基于GPT-4o-mini实现更便宜的知识图谱RAG
首先给兄弟朋友们展示一下结论,一个文本18万多字,txt文本大小185K,采用GraphRAG,GPT-4o-mini模型,索引耗时差不多5分钟,消耗API价格0.15美元 GraphRAG介绍 GraphRAG是微软最近开源的一款基于知识图谱技术的框架&#…...

/秋招突击——7/21——复习{堆——数组中的第K大元素}——新作{回溯——全排列、子集、电话号码的字母组合、组合总和、括号生成}
文章目录 引言复习数组中的第K大的最大元素复习实现参考实现 新作回溯模板46 全排列个人实现参考实现 子集个人实现参考实现 电话号码的字母组合复习实现 组合总和个人实现参考实现 括号生成复习实现 总结 引言 昨天的科大讯飞笔试做的稀烂,今天回来好好练习一下&a…...

matlab 异常值检测与处理——Robust Z-score法
目录 一、算法原理1、概述2、主要函数3、参考文献二、代码实现三、结果展示四、相关链接本文由CSDN点云侠翻译,原文链接。如果你不是在点云侠的博客中看到该文章,那么此处便是不要脸的爬虫。 一、算法原理 1、概述 Robust Z-score法也被称为中位数绝对偏差法。它类似于Z-sc…...

Ubuntu 20安装JDK17和MySQL8.0
一.jdk 安装JDK 第一步:更新软件包:sudo apt update 第二步:安装JDK:sudo apt install openjdk-17-jdk 第三步:检测JDK: java -version 卸载JDK: 第一步:移除JDK包:apt-get purg…...

DC-1靶场打靶第一次!!!!冲冲冲!
今天打了一下DC-1这个靶场,感觉收获比大,我就来记录一下。 我的思路是下面的这个 我们先把靶机导入,然后与我们的liunx(攻击机)在同一个网段中,这也大大的减低难度。 然后我们先对自己这个网段内存活的主机进行操作,我…...

【LeetCode】填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
目录 一、题目二、解法完整代码 一、题目 给定一个二叉树: struct Node { int val; Node *left; Node *right; Node *next; } 填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NUL…...

mac无法清空废纸篓怎么办 mac废纸篓清空了如何找回 cleanmymac误删文件怎么恢复
废纸篓相当于“一颗后悔药”,用于临时存储用户删除的文件。我们从从Mac上删除的文件,一般会进入废纸篓中。如果我们后悔了,可以从废纸篓中找回来。然而,有时我们会发现mac无法清空废纸篓,这是怎么回事?本文将探讨一些…...

树上启发加点分治思想
题目链接 思路: 对于一条链可以组成回文串,意味着最多只有一个奇数字母,比起我们记录路径各个字母的个数和,我们可以发现回文串实际上不在意真正的个数,只在意个数的奇偶。又我们发现字母只有20来个,可以使…...

【iOS】类对象的结构分析
目录 对象的分类object_getClass和class方法isa流程和继承链分析isa流程实例验证类的继承链实例验证 类的结构cache_t结构bits分析实例验证属性properties方法methods协议protocolsro类方法 类结构流程图解 对象的分类 OC中的对象主要可以分为3种:实例对象…...

接口性能优化思路
前言 日常开发中设计接口,响应时间是衡量一个接口质量的重要指标。 接口响应时间这里粗糙地分为三种: 即时响应:毫秒级,小于500毫秒快速响应:秒级,大于500毫秒且小于2秒长时间操作:大于2秒&a…...

PyQt5 多线程编程详细教程
PyQt5 多线程编程详细教程 在 PyQt5 中,多线程编程是提高应用程序性能和响应性的重要手段。本教程将详细介绍如何在 PyQt5 中使用 QThread 进行多线程编程,学习如何避免界面冻结和线程安全问题,并通过丰富的案例来展示如何实现这些功能。 Q…...

uniapp小程序上传pdf文件
<template><view class"mainInnBox"><view class"formBox"><!-- 注意,如果需要兼容微信小程序,最好通过setRules方法设置rules规则 --><u-form :model"form" ref"uForm" :rules&quo…...

Python酷库之旅-第三方库Pandas(036)
目录 一、用法精讲 111、pandas.Series.item方法 111-1、语法 111-2、参数 111-3、功能 111-4、返回值 111-5、说明 111-6、用法 111-6-1、数据准备 111-6-2、代码示例 111-6-3、结果输出 112、pandas.Series.xs方法 112-1、语法 112-2、参数 112-3、功能 112-…...
简易版抽奖活动的设计技术方案
1.前言 本技术方案旨在设计一套完整且可靠的抽奖活动逻辑,确保抽奖活动能够公平、公正、公开地进行,同时满足高并发访问、数据安全存储与高效处理等需求,为用户提供流畅的抽奖体验,助力业务顺利开展。本方案将涵盖抽奖活动的整体架构设计、核心流程逻辑、关键功能实现以及…...

Golang 面试经典题:map 的 key 可以是什么类型?哪些不可以?
Golang 面试经典题:map 的 key 可以是什么类型?哪些不可以? 在 Golang 的面试中,map 类型的使用是一个常见的考点,其中对 key 类型的合法性 是一道常被提及的基础却很容易被忽视的问题。本文将带你深入理解 Golang 中…...
)
Spring Boot 实现流式响应(兼容 2.7.x)
在实际开发中,我们可能会遇到一些流式数据处理的场景,比如接收来自上游接口的 Server-Sent Events(SSE) 或 流式 JSON 内容,并将其原样中转给前端页面或客户端。这种情况下,传统的 RestTemplate 缓存机制会…...
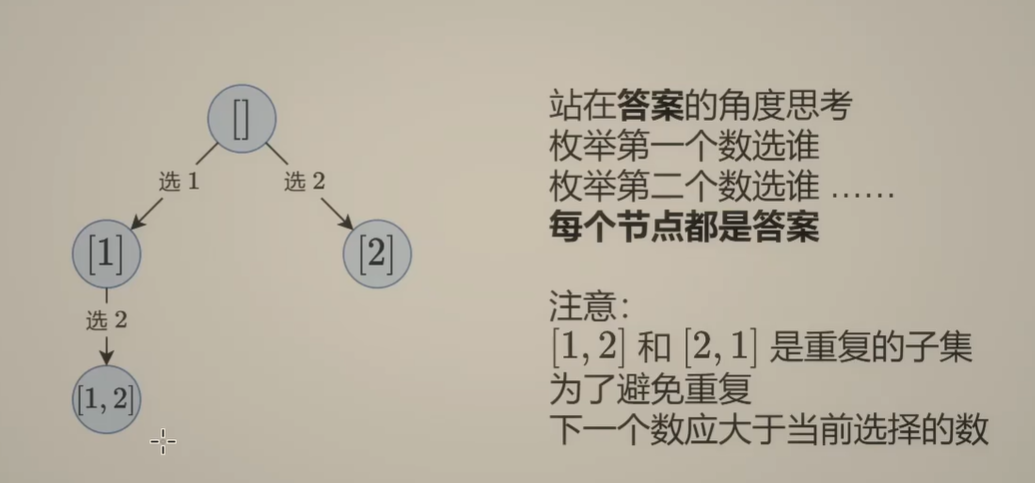
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集 78.子集 78. 子集 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路: 笔者写过很多次这道题了,不想写题解了,大家看灵神讲解吧 回溯算法套路①子集型回溯【基础算法精讲 14】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 完…...

Leetcode 3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations
Leetcode 3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations 1. 解题思路 这一题其实就是一个脑筋急转弯,要想要能够将所有的电脑解锁&#x…...

BCS 2025|百度副总裁陈洋:智能体在安全领域的应用实践
6月5日,2025全球数字经济大会数字安全主论坛暨北京网络安全大会在国家会议中心隆重开幕。百度副总裁陈洋受邀出席,并作《智能体在安全领域的应用实践》主题演讲,分享了在智能体在安全领域的突破性实践。他指出,百度通过将安全能力…...

Spring AI 入门:Java 开发者的生成式 AI 实践之路
一、Spring AI 简介 在人工智能技术快速迭代的今天,Spring AI 作为 Spring 生态系统的新生力量,正在成为 Java 开发者拥抱生成式 AI 的最佳选择。该框架通过模块化设计实现了与主流 AI 服务(如 OpenAI、Anthropic)的无缝对接&…...

Spring AI与Spring Modulith核心技术解析
Spring AI核心架构解析 Spring AI(https://spring.io/projects/spring-ai)作为Spring生态中的AI集成框架,其核心设计理念是通过模块化架构降低AI应用的开发复杂度。与Python生态中的LangChain/LlamaIndex等工具类似,但特别为多语…...
)
安卓基础(aar)
重新设置java21的环境,临时设置 $env:JAVA_HOME "D:\Android Studio\jbr" 查看当前环境变量 JAVA_HOME 的值 echo $env:JAVA_HOME 构建ARR文件 ./gradlew :private-lib:assembleRelease 目录是这样的: MyApp/ ├── app/ …...

AI病理诊断七剑下天山,医疗未来触手可及
一、病理诊断困局:刀尖上的医学艺术 1.1 金标准背后的隐痛 病理诊断被誉为"诊断的诊断",医生需通过显微镜观察组织切片,在细胞迷宫中捕捉癌变信号。某省病理质控报告显示,基层医院误诊率达12%-15%,专家会诊…...
