模拟实现c++中的list模版
☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺ 点击 进入杀马特的主页☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺

目录
一·list简述:
二·库内常用接口函数使用:
1·reverse():
2.sort():
3.merge():
4.unique():
5.splice():
三·list的模拟实现相关函数接口:
1.创建头结点和无参构造:
2·有参构造:
3·拷贝构造:
4·赋值重载的现代版本实现:
5.析构函数:
6·list的迭代器类模版内接口函数的实现:
7.insert的接口函数的实现:
8.push_back和push_front的实现:
9·erase的接口函数的实现:
10·pop_front和pop_back的实现:
11·size和empty的实现:
12·front和back的实现:
13·不同容器利用迭代器打印数据:
一·list简述:
即相当于一个放入任意类型的一个容器,底层就是链表。即是与vector的区别。
二·库内常用接口函数使用:
这里简单介绍一下除了下面要实现的接口函数还有些其他接口函数:
1·reverse():
对于以前的vector和string,它们用的是算法库里的,故括号里还要传迭代器区间,而list库自己实现了,可以不传参:
list<int> lt;
lt.emplace_back(1);
lt.emplace_back(2);
lt.emplace_back(3);
lt.emplace_back(4);lt.reverse();
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end()) {cout << *it << " ";it++;
}
2.sort():
对于list库里的sort()是默认升序。
list<int> ltt;
ltt.emplace_back(5);
ltt.emplace_back(3);
ltt.emplace_back(7);
ltt.emplace_back(10);
ltt.sort();
list<int>::iterator itt = ltt.begin();
while (itt != ltt.end()) {cout << *itt << " ";itt++;
}
当然也可以也可以这样完成升降序:


同理,这里其实也可以不创建对象,直接匿名对象也可以。
3.merge():
即把两个list对象按升序拼接起来(前提是两个对象都是有序的,不是的话要提前给它sort一下),最后拼到前者对象,后者对象清空,如:
list<int> lt;
lt.emplace_back(1);
lt.emplace_back(2);
lt.emplace_back(3);
lt.emplace_back(4);
list<int> ltt;
ltt.emplace_back(5);
ltt.emplace_back(3);
ltt.emplace_back(7);
ltt.emplace_back(10);
ltt.sort();
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
lt.merge(ltt);
it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end()) {cout << *it << " ";it++;
}
cout << endl;
4.unique():
去重复操作,但是要求list对象要有序:
///去重操作:
list<int> lt;
lt.emplace_back(1);
lt.emplace_back(1);
lt.emplace_back(1);
lt.emplace_back(2);
lt.unique();
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end()) {cout << *it << "";it++;
}
cout << endl;
5·remove():
删除链表中值为val的节点:
//删除指定元素,只删除找到一个即可:
list<int> lt;
lt.emplace_back(5);
lt.emplace_back(2);
lt.emplace_back(4);
lt.emplace_back(2);
lt.remove(2);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end()) {cout << *it << "";it++;
}
5.splice():
本意是粘连的意思,可以给某个位置前面粘连一个对象的链表也可以给某个位置前粘连任意一个对象的迭代器区间:
一个对象给另一个对象粘:
list<int> lt;
lt.emplace_back(5);
lt.emplace_back(2);
lt.emplace_back(4);
lt.emplace_back(2);
list<int> ltt;
ltt.emplace_back(5);
ltt.emplace_back(3);
ltt.emplace_back(7);
ltt.emplace_back(10);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
lt.splice(++lt.begin(), ltt);
it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end()) {cout << *it << " ";it++;
}
给pos位置前粘一个迭代器区间:
list<int> lt;
lt.emplace_back(5);
lt.emplace_back(2);
lt.emplace_back(4);
lt.emplace_back(2);
list<int> ltt;
ltt.emplace_back(5);
ltt.emplace_back(3);
ltt.emplace_back(7);
ltt.emplace_back(10);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
lt.splice(it, lt, ++lt.begin(), lt.end());
it = lt.begin();//这里会把242转移粘在5的前面,故要重新给begin赋值
while (it != lt.end()) {cout << *it << " ";it++;}
粘连别人的迭代器区间:
list<int> lt;
lt.emplace_back(5);
lt.emplace_back(2);
lt.emplace_back(4);
lt.emplace_back(2);
list<int> ltt;
ltt.emplace_back(5);
ltt.emplace_back(3);
ltt.emplace_back(7);
ltt.emplace_back(10);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
lt.splice(++lt.begin(), ltt, ++ltt.begin(), ltt.end());
it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end()) {cout << *it << " ";it++;}
三·list的模拟实现相关函数接口:
框架构造:list是吧每个节点连接起来,故首先把节点封装成一个类,接着由于迭代器相当于节点指针,即双向迭代器,只能是++或者--无-,+即还要对迭代器去遍历链表,可以把迭代器封装也成一个类。如:
节点类:
namespace li {template<class T>struct list_node {list_node* _pre;list_node* _next;T _val;list_node(const T _val = T()):_val(_val), _pre(nullptr), _next(nullptr) { }};迭代器 类:
template<class T,class ref,class ptr >struct list_iterator {typedef list_node<T> Node;Node* _node;list_iterator( Node* node):_node(node){}
};它们没有资源产生和释放,故只用写所需要的构造函数即可。
这里的template<class T,class ref,class ptr >是为了少写一次const迭代器的类,而多加了对原来的类的模版参数可以实例化出const和普通的迭代器类。
list框架:
template<class T>class list {public:typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;
private:Node* _head;int _size;};
1.创建头结点和无参构造:
void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_pre = _head;_size = 0;}list() {empty_init();}由于后面等有参构造list的时候也是需要构造出头结点,故可以把它封装成一个empty_init函数。
2·有参构造:
list( initializer_list<T> m)//这个模版化出的m对象可以想象成一个数组{empty_init();for (auto& e : m){push_back(e);}}initializer_list<int> il = { 10, 20, 30 };li::list<int> llt(il);//拷贝构造:li::list<int>lt1({ 1,22,223 });//先是隐式类型转换生成的临时对象再拷贝构造给lt1//隐式类型转换:const li::list<int><2={ 1,22,223 };//直接隐式类型转换生成临时对象,由于是给临时对象引用(起别名)故临时对象只能读不能写,故用const
这里可以用 initializer_list这个模版来进行{}的初始化。
3·拷贝构造:
list(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();//创建链表的头结点for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}4·赋值重载的现代版本实现:
void swap(list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);}list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)//不是引用传参故不会改变lt;{swap(lt);return *this;}5.析构函数:
void clear(){auto it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}//利用迭代器遍历链表删除各个节点~list() {clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}6·list的迭代器类模版内接口函数的实现:
ref operator*() {return _node->_val;}ptr operator->() {return &(_node->_val) ;}list_iterator<T,ref, ptr> &operator++(int) {list_iterator<T,ref,ptr> tmp = *this;++*this;return tmp;}list_iterator<T,ref, ptr>&operator--(int) {list_iterator<T,ref,ptr> tmp = *this;--*this;return tmp;}list_iterator<T,ref, ptr>& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}list_iterator<T,ref, ptr>& operator--(){_node = _node->_pre;return *this;}bool operator!=(const list_iterator<T,ref,ptr>& s) const{return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const list_iterator<T,ref,ptr>& s) const{return _node == s._node;}这里需要说的也就是里面对->的重载运算符函数的实现,这样返回节点内数据的地址作用在哪?
其实是为了:如果这里面的val放的自定义类型如:
struct AA {int a1 = 1;int a2 = 2;
};这时候这个操作就可以直接访问到val里的a1,a2,而不用再有通过AA的对象再去访问a1和a2。
li::list<AA> at;at.push_back(AA());at.push_back(AA());at.push_back(AA());at.push_back(AA());li::list<AA>::iterator ait = at.begin();cout << (ait-> a1 )<<" ";//如果是自定义类型则迭代器(也就是节点的指针)可以直接访问到此自定义类型的变量。//如果没有这个重载:cout << ((ait._node)->_val.a1 )<< " ";//重载后把两个->省略成一个cout << (ait.operator->()->a1) << " ";7·begin()和end()的实现:
这里是list直接访问的,故放在list类模版的函数里。
iterator begin() {return _head->_next;//隐式类型转换,直接传递对应类的构造参数}iterator end() {return _head;}const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const//对应的迭代器实例化出的普通和const类型{return _head;}7.insert的接口函数的实现:
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x) {//在pos和pos前的位置插入数据,故先保存这两个位置。以防后面找不到,然后在连接指针Node* pre = pos._node->_pre ;Node* cur = pos._node;Node* pnode = new Node(x);pnode->_next = cur;cur->_pre = pnode;pre->_next = pnode;pnode->_pre = pre;_size++;return pnode;}这里其实和vector的迭代器不一样,这里插入不会导致迭代器失效,因为它所指向的对象并没有改变,而只是在它前面插入新节点。
8.push_back和push_front的实现:
void push_back(const T& x) {insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x) {insert(begin(), x);}9·erase的接口函数的实现:
这里如果删除了就会导致迭代器失效,故要利用返回值接收再次使用。
iterator erase(iterator pos) {assert(pos != end());Node* pre = pos._node->_pre;Node* next = pos._node->_next;delete pos._node ;pre->_next = next;next->_pre = pre;_size--;return next;}10·pop_front和pop_back的实现:
void pop_front() {erase(begin());}void pop_back() {erase(--end());}11·size和empty的实现:
size_t size() const{return _size;}bool empty() const{return _size == 0;}12·front和back的实现:
T& front() {return begin()._node->_val;}const T& front()const {return begin()._node->_val;}T& back() {return (--end())._node->_val;}const T& back()const {return --end()._node->_val;}//分别是拿到val可修改与不可修改13·不同容器利用迭代器打印数据:
//不同容器的打印
template<class Container>
void con_print(const Container & con) {typename Container::const_iterator it = con.begin();//告诉未实例化的模版是类型//auto it = con.begin();while (it != con.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}14.list实现代码汇总:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
namespace li {template<class T>struct list_node {list_node* _pre;list_node* _next;T _val;list_node(const T _val = T()):_val(_val), _pre(nullptr), _next(nullptr) { }};template<class T,class ref,class ptr >struct list_iterator {typedef list_node<T> Node;Node* _node;list_iterator( Node* node):_node(node){}ref operator*() {return _node->_val;}ptr operator->() {return &(_node->_val) ;}list_iterator<T,ref, ptr> &operator++(int) {list_iterator<T,ref,ptr> tmp = *this;++*this;return tmp;}list_iterator<T,ref, ptr>&operator--(int) {list_iterator<T,ref,ptr> tmp = *this;--*this;return tmp;}list_iterator<T,ref, ptr>& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}list_iterator<T,ref, ptr>& operator--(){_node = _node->_pre;return *this;}bool operator!=(const list_iterator<T,ref,ptr>& s) const{return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const list_iterator<T,ref,ptr>& s) const{return _node == s._node;}};template<class T>class list {public:typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_pre = _head;_size = 0;}list() {empty_init();}list( initializer_list<T> m)//这个模版化出的m对象可以想象成一个数组{empty_init();for (auto& e : m){push_back(e);}}list(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}void swap(list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);}list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)//不是引用传参故不会改变lt:{swap(lt);return *this;}void clear(){auto it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}~list() {clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}iterator begin() {return _head->_next;//隐式类型转换,直接传递对应类的构造参数}iterator end() {return _head;}const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const{return _head;}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x) {//在pos和pos前的位置插入数据,故先保存这两个位置。以防后面找不到,然后在连接指针Node* pre = pos._node->_pre ;Node* cur = pos._node;Node* pnode = new Node(x);pnode->_next = cur;cur->_pre = pnode;pre->_next = pnode;pnode->_pre = pre;_size++;return pnode;}void push_back(const T& x) {insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x) {insert(begin(), x);}iterator erase(iterator pos) {assert(pos != end());Node* pre = pos._node->_pre;Node* next = pos._node->_next;delete pos._node ;pre->_next = next;next->_pre = pre;_size--;return next;}void pop_front() {erase(begin());}void pop_back() {erase(--end());}size_t size() const{return _size;}bool empty() const{return _size == 0;}// List AccessT& front() {return begin()._node->_val;}const T& front()const {return begin()._node->_val;}T& back() {return (--end())._node->_val;}const T& back()const {return --end()._node->_val;}private:Node* _head;int _size;};
}//不同容器的打印
template<class Container>
void con_print(const Container & con) {typename Container::const_iterator it = con.begin();//auto it = con.begin();while (it != con.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}
相关文章:

模拟实现c++中的list模版
☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺ 点击 进入杀马特的主页☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺ 目录 一list简述: 二库内常用接口函数使用: 1reverse(): 2.s…...
从信息论的角度看微博推荐算法
引言 在数字时代,推荐系统已成为社交媒体和其他在线服务平台的核心组成部分。它们通过分析用户行为和偏好,为用户提供个性化的内容,从而提高用户满意度和平台的参与度。推荐系统不仅能够增强用户体验,还能显著提升广告投放的效率…...
与RISC(精简指令集)的区别)
CISC(复杂指令集)与RISC(精简指令集)的区别
RISC(Reduced Instruction Set Computer)和CISC(complex instruction set computer)是当前CPU的两种架构。 它们的区别在于不同的CPU设计理念和方法。 早期的CPU全部是CISC架构,它的设计目的是要用最少的机器语言指令来完成所需的计算任务。比如对于乘法运算&#x…...

自定义数据库连接的艺术:Laravel中配置多数据库连接详解
自定义数据库连接的艺术:Laravel中配置多数据库连接详解 在现代Web应用开发中,经常需要连接到多个数据库。Laravel,作为PHP界最受欢迎的框架之一,提供了强大的数据库抽象层,支持多种数据库系统,并且允许开…...

力扣高频SQL 50题(基础版)第八题
文章目录 力扣高频SQL 50题(基础版)第八题1581. 进店却未进行过交易的顾客题目说明思路分析实现过程准备数据:实现方式:结果截图:总结: 力扣高频SQL 50题(基础版)第八题 1581. 进店…...

【C++20】从0开始自制协程库
文章目录 参考 很多人对协程的理解就是在用户态线程把CPU对线程的调度复制了一遍,减少了线程的数量,也就是说在一个线程内完成对协程的调度,不需要线程切换导致上下文切换的开销。但是线程切换是CPU行为,就算你的程序只有一个线程…...

Docker 深度解析:从入门到精通
引言 在当今的软件开发领域,容器化技术已经成为一种趋势。Docker 作为容器化技术的代表,以其轻量级、可移植性和易用性,被广泛应用于各种场景。本文将从 Docker 的基本概念入手,详细介绍 Docker 的安装、基本操作、网络配置、数据…...

[C++] 模板编程-02 类模板
一 类模板 template <class T或者typename T> class 类名 { .......... } 1.1 两种不同的实现 在以下的两种实现中,其实第一种叫做成员函数模板,并不能称为类模板因为这种实现,我们在调用时,并不需要实例化为Product这个类指定指定特定类型。 // 实现1 clas…...

嵌入式C++、STM32、树莓派4B、OpenCV、TensorFlow/Keras深度学习:基于边缘计算的实时异常行为识别
1. 项目概述 随着物联网和人工智能技术的发展,智能家居安全系统越来越受到人们的关注。本项目旨在设计并实现一套基于边缘计算的智能家居安全系统,利用STM32微控制器和树莓派等边缘设备,实时分析摄像头数据,识别异常行为(如入侵、跌倒等),并及时发出警报,提高家庭安全性。 系…...

C++ //练习 15.30 编写你自己的Basket类,用它计算上一个练习中交易记录的总价格。
C Primer(第5版) 练习 15.30 练习 15.30 编写你自己的Basket类,用它计算上一个练习中交易记录的总价格。 环境:Linux Ubuntu(云服务器) 工具:vim 代码块: /********************…...
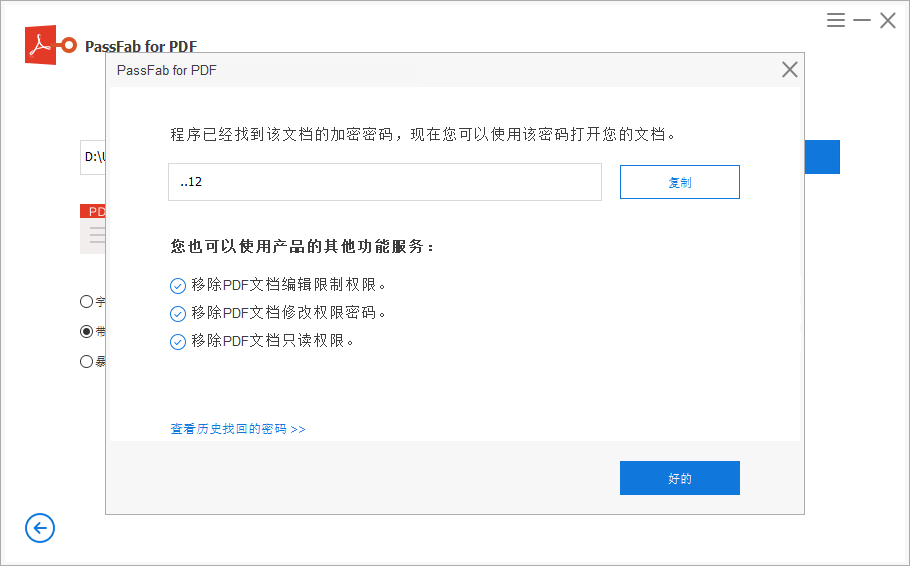
3个方法快速找回忘记的PDF文件密码
为确保PDF文件的重要信息不轻易外泄,很多人都会给PDF文件设置打开密码,但伴随着时间的推移,让我们忘记了原本设置的密码,但这时,我们又非常急需要打开编辑这份文件,这时我们该怎么办呢?下面小编…...

排序算法:选择排序,golang实现
目录 前言 选择排序 代码示例 1. 算法包 2. 选择排序代码 3. 模拟排序 4. 运行程序 5. 从大到小排序 循环细节 外层循环 内层循环 总结 选择排序的适用场景 1. 数据规模非常小 2. 稳定性不重要 3. 几乎全部数据已排序 4. 教育目的 前言 在实际场景中…...

【测试】博客系统的测试报告
项目背景 个人博客系统采用了 SSM 框架与 Redis 缓存技术的组合 ,为用户提供了一个功能丰富、性能优越的博客平台。 在技术架构上 ,SSM 框架确保了系统的稳定性和可扩展性。Spring 负责管理项目的各种组件 ,Spring MVC 实现了清晰的请求处理…...

PointCLIP: Point Cloud Understanding by CLIP
Abstract 近年来,基于对比视觉语言预训练(CLIP)的零镜头和少镜头学习在二维视觉识别中表现出了令人鼓舞的效果,该方法在开放词汇设置下学习图像与相应文本的匹配。然而,通过大规模二维图像-文本对预训练的CLIP是否可以推广到三维识别&#x…...

搜索(剪枝)
定义: 剪枝,就是减少搜索树的规模、尽早排除搜索树中不必要分支的一种手段。 在深度优先搜索中,有以下几类常见的剪枝方法: 优化搜索顺序排除等效冗余可行性剪枝最优性剪枝记忆化剪枝 例题1:AcWing 167.木棒 题目:…...
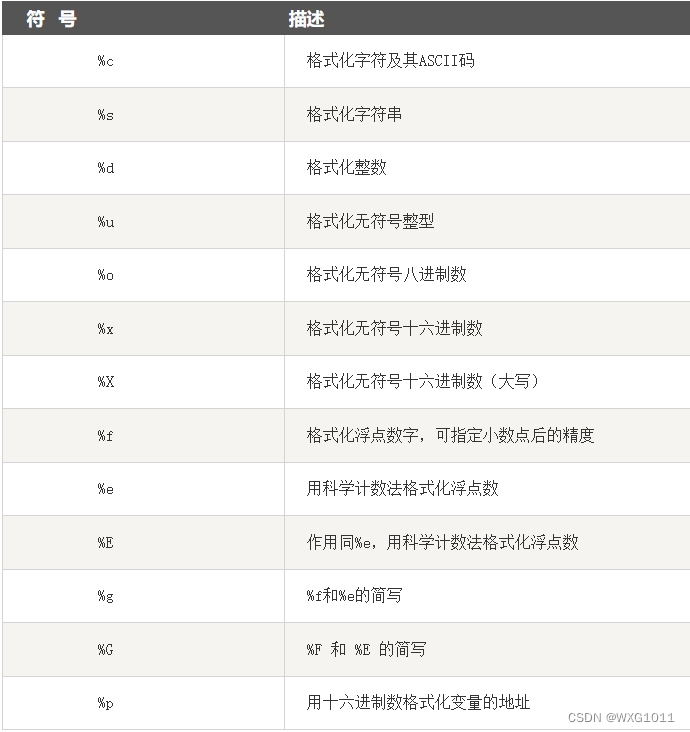
python基础知识点
最近系统温习了一遍python基础语法,把自己不熟知的知识点罗列一遍,便于查阅~~ python教程 Python 基础教程 | 菜鸟教程 1、python标识符 以单下划线开头 _foo 的代表不能直接访问的类属性,需通过类提供的接口进行访问,不能用 f…...
)
Android SurfaceFlinger——GraphicBuffer获取内存信息(三十一)
上一篇文章介绍了 GraphicBuffer 初始化的 initWithSize() 函数中的申请内存流程,这里我们看一下另一个比较重要的函数,GraphicBufferMapper. getTransportSize 获取内存信息。该函数通常在需要了解缓冲区的实际内存占用情况时调用,例如在调试内存使用情况或优化性能时。 一…...

基于 SASL/SCRAM 让 Kafka 实现动态授权认证
一、说明 在大数据处理和分析中 Apache Kafka 已经成为了一个核心组件。然而在生产环境中部署 Kafka 时,安全性是一个必须要考虑的重要因素。SASL(简单认证与安全层)和 SCRAM(基于密码的认证机制的盐化挑战响应认证机制ÿ…...
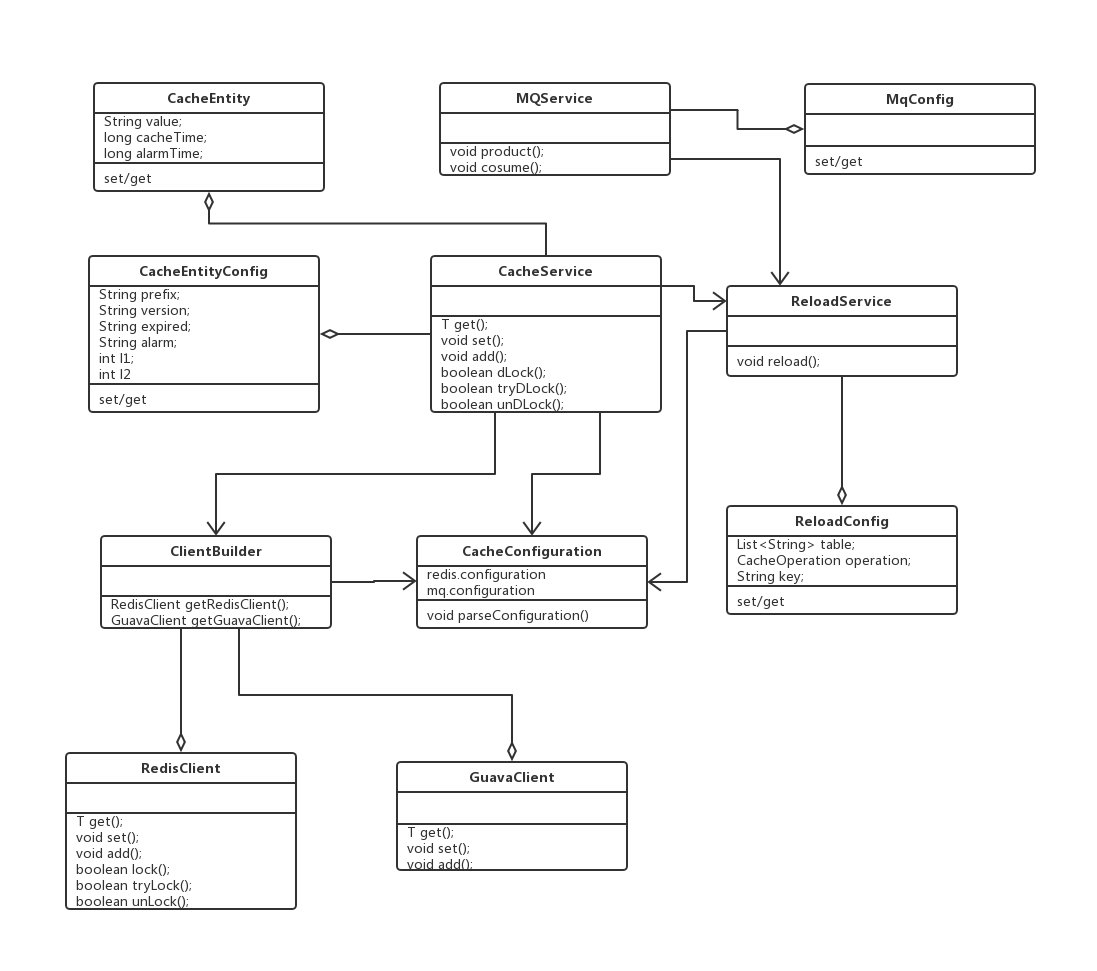
通用多级缓件组件
背景 业界第三方缓存框架一般为redis,本地缓地ehcache或guava,一般通过spring提供的restTemplate操作缓存 然而这样会存在以下问题: 与缓存中间件强耦合需手动整合多级缓存不支持注解数据更新时无法自动刷新缓存存在缓存穿透、缓存击穿、缓…...

MindIE Service服务化集成部署通义千问Qwen模型
一、昇腾开发者平台申请镜像 登录Ascend官网昇腾社区-官网丨昇腾万里 让智能无所不及 二、登录并下载mindie镜像 #登录docker login -u XXX#密码XXX#下载镜像docker pull XXX 三、下载Qwen的镜像 使用wget命令下载Qwen1.5-0.5B-Chat镜像,放在/mnt/Qwen/Qwen1.5-…...

Linux应用开发之网络套接字编程(实例篇)
服务端与客户端单连接 服务端代码 #include <sys/socket.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <pthread.h> …...

Android Wi-Fi 连接失败日志分析
1. Android wifi 关键日志总结 (1) Wi-Fi 断开 (CTRL-EVENT-DISCONNECTED reason3) 日志相关部分: 06-05 10:48:40.987 943 943 I wpa_supplicant: wlan0: CTRL-EVENT-DISCONNECTED bssid44:9b:c1:57:a8:90 reason3 locally_generated1解析: CTR…...

java 实现excel文件转pdf | 无水印 | 无限制
文章目录 目录 文章目录 前言 1.项目远程仓库配置 2.pom文件引入相关依赖 3.代码破解 二、Excel转PDF 1.代码实现 2.Aspose.License.xml 授权文件 总结 前言 java处理excel转pdf一直没找到什么好用的免费jar包工具,自己手写的难度,恐怕高级程序员花费一年的事件,也…...

STM32+rt-thread判断是否联网
一、根据NETDEV_FLAG_INTERNET_UP位判断 static bool is_conncected(void) {struct netdev *dev RT_NULL;dev netdev_get_first_by_flags(NETDEV_FLAG_INTERNET_UP);if (dev RT_NULL){printf("wait netdev internet up...");return false;}else{printf("loc…...
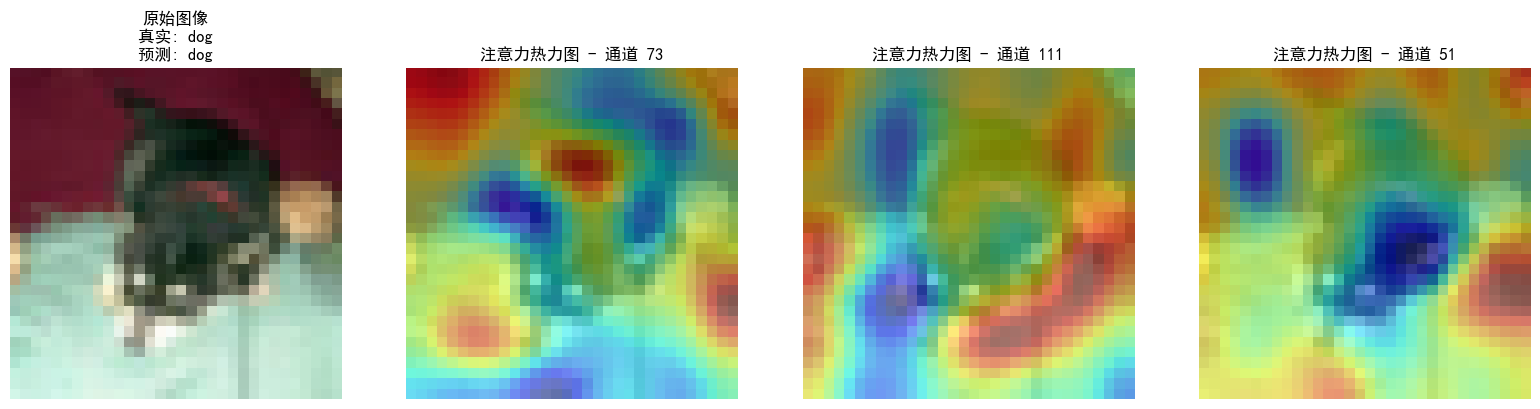
DAY 47
三、通道注意力 3.1 通道注意力的定义 # 新增:通道注意力模块(SE模块) class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):"""通道注意力模块(Squeeze-and-Excitation)"""def __init__(self, in_channels, reduction_rat…...

工程地质软件市场:发展现状、趋势与策略建议
一、引言 在工程建设领域,准确把握地质条件是确保项目顺利推进和安全运营的关键。工程地质软件作为处理、分析、模拟和展示工程地质数据的重要工具,正发挥着日益重要的作用。它凭借强大的数据处理能力、三维建模功能、空间分析工具和可视化展示手段&…...
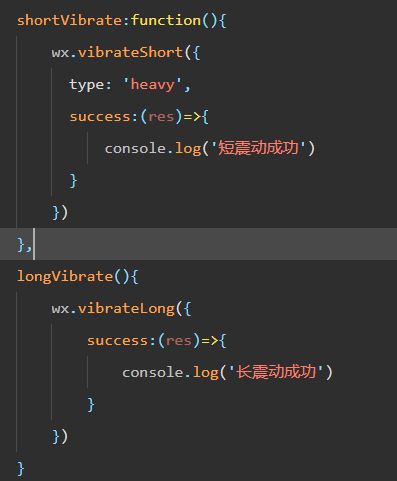
微信小程序 - 手机震动
一、界面 <button type"primary" bindtap"shortVibrate">短震动</button> <button type"primary" bindtap"longVibrate">长震动</button> 二、js逻辑代码 注:文档 https://developers.weixin.qq…...

基于Docker Compose部署Java微服务项目
一. 创建根项目 根项目(父项目)主要用于依赖管理 一些需要注意的点: 打包方式需要为 pom<modules>里需要注册子模块不要引入maven的打包插件,否则打包时会出问题 <?xml version"1.0" encoding"UTF-8…...
python执行测试用例,allure报乱码且未成功生成报告
allure执行测试用例时显示乱码:‘allure’ �����ڲ����ⲿ���Ҳ���ǿ�&am…...
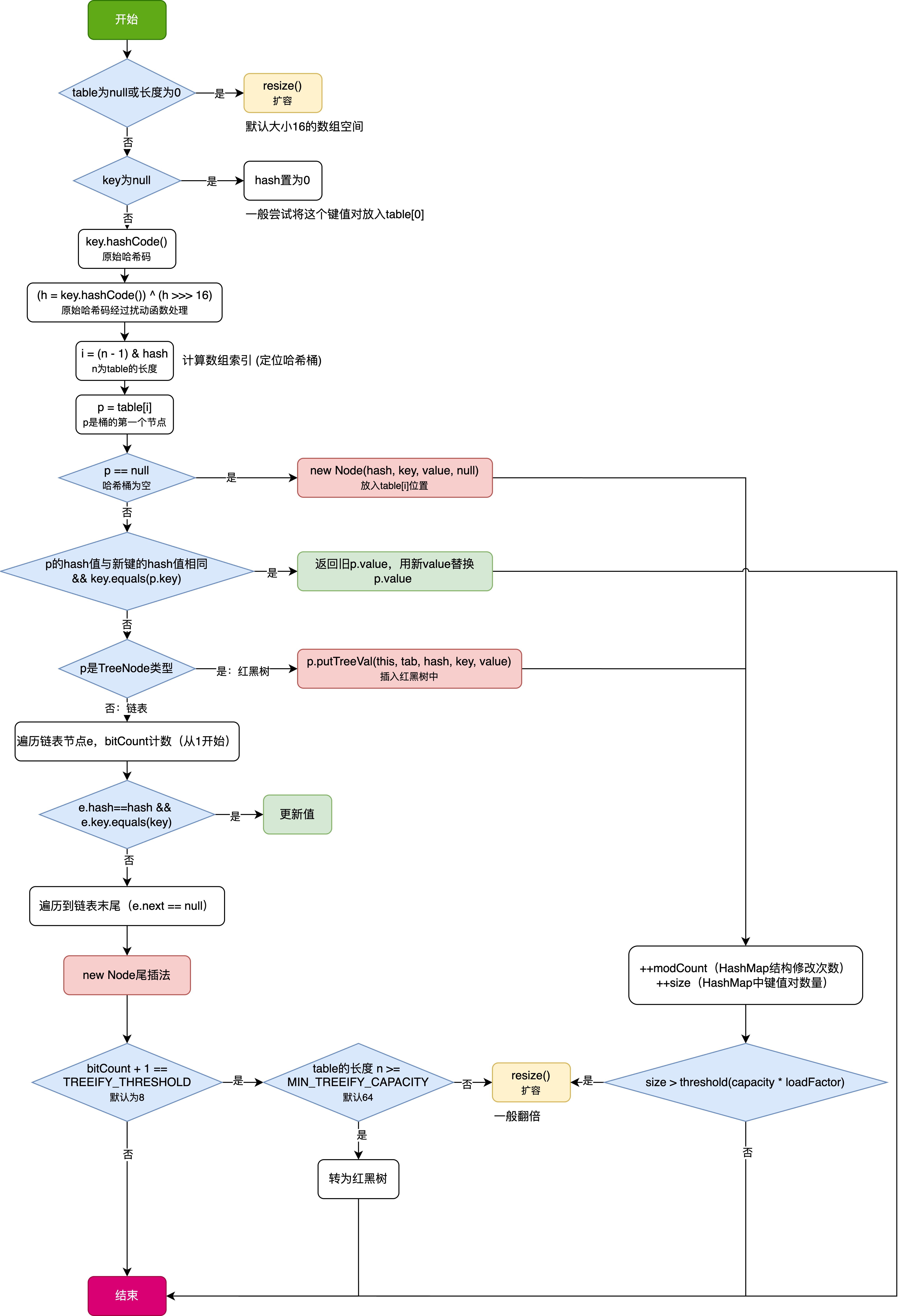
HashMap中的put方法执行流程(流程图)
1 put操作整体流程 HashMap 的 put 操作是其最核心的功能之一。在 JDK 1.8 及以后版本中,其主要逻辑封装在 putVal 这个内部方法中。整个过程大致如下: 初始判断与哈希计算: 首先,putVal 方法会检查当前的 table(也就…...
