GO goroutine状态流转
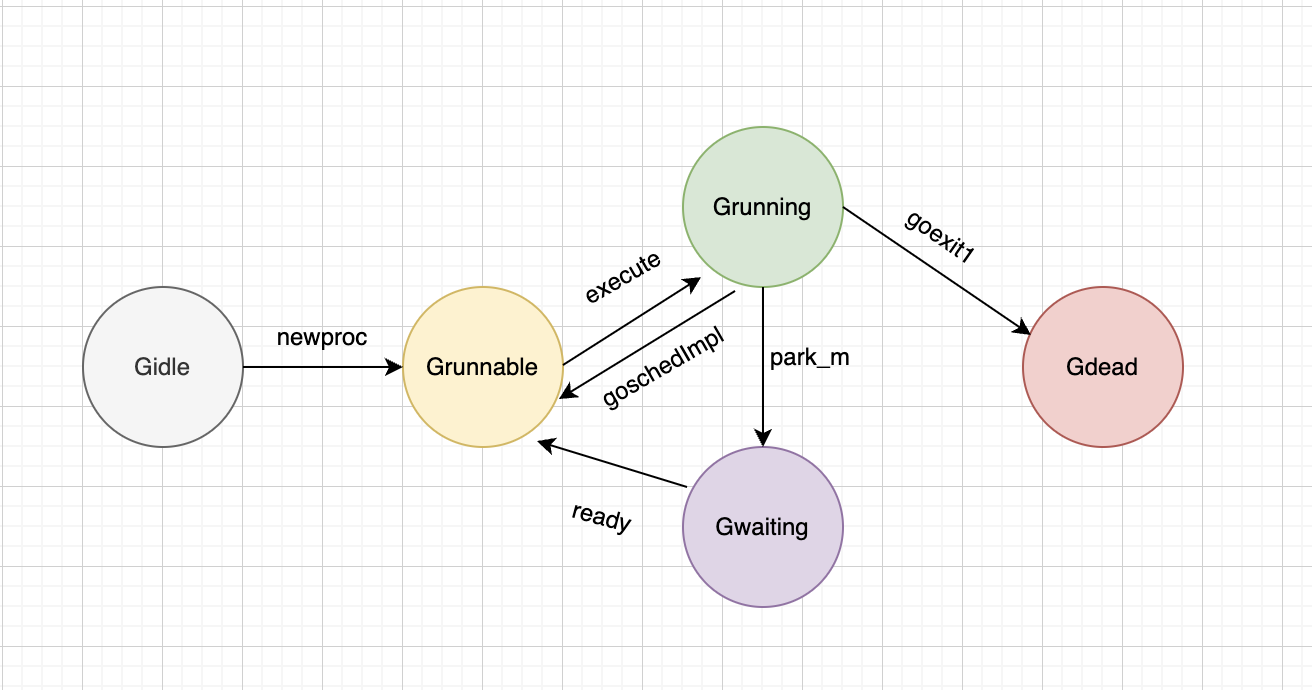
Gidle -> Grunnable
newproc获取新的goroutine,并放置到P运行队列中
这也是go关键字之后实际编译调用的方法
func newproc(fn *funcval) {// 获取当前正在运行中的goroutinegp := getg()// 获取调用者的程序计数器地址,用于调试和跟踪pc := getcallerpc()systemstack(func() {// 创建一个新的 goroutine 并返回新创建的 goroutine 结构 newgnewg := newproc1(fn, gp, pc)// 获取当前P,并将新创建的goroutine放到P的运行队列中pp := getg().m.p.ptr()runqput(pp, newg, true)// 如果主 goroutine 已经启动(mainStarted 为 true),则调用 wakep() 唤醒或启动一个处理器以执行运行队列中的 goroutineif mainStarted {wakep()}})
}
newproc1用于获取新的goroutine
// Create a new g in state _Grunnable, starting at fn. callerpc is the
// address of the go statement that created this. The caller is responsible
// for adding the new g to the scheduler.
func newproc1(fn *funcval, callergp *g, callerpc uintptr) *g {if fn == nil {fatal("go of nil func value")}mp := acquirem() // disable preemption because we hold M and P in local vars.pp := mp.p.ptr()// 首先从P的gfree获取回收的g,如果没有,那么再从全局调度器sched中gfree窃取给P,再不然就只能调用malg()新建gnewg := gfget(pp)if newg == nil {newg = malg(stackMin)casgstatus(newg, _Gidle, _Gdead)allgadd(newg) // publishes with a g->status of Gdead so GC scanner doesn't look at uninitialized stack.}if newg.stack.hi == 0 {throw("newproc1: newg missing stack")}if readgstatus(newg) != _Gdead {throw("newproc1: new g is not Gdead")}// 计算和分配堆栈指针totalSize := uintptr(4*goarch.PtrSize + sys.MinFrameSize) // extra space in case of reads slightly beyond frametotalSize = alignUp(totalSize, sys.StackAlign)sp := newg.stack.hi - totalSizeif usesLR {// caller's LR*(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(sp)) = 0prepGoExitFrame(sp)}if GOARCH == "arm64" {// caller's FP*(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(sp - goarch.PtrSize)) = 0}// 初始化调用帧memclrNoHeapPointers(unsafe.Pointer(&newg.sched), unsafe.Sizeof(newg.sched))newg.sched.sp = spnewg.stktopsp = spnewg.sched.pc = abi.FuncPCABI0(goexit) + sys.PCQuantum // +PCQuantum so that previous instruction is in same functionnewg.sched.g = guintptr(unsafe.Pointer(newg))gostartcallfn(&newg.sched, fn)// 设置新G元数据newg.parentGoid = callergp.goidnewg.gopc = callerpcnewg.ancestors = saveAncestors(callergp)newg.startpc = fn.fnif isSystemGoroutine(newg, false) {sched.ngsys.Add(1)} else {// Only user goroutines inherit pprof labels.if mp.curg != nil {newg.labels = mp.curg.labels}if goroutineProfile.active {// A concurrent goroutine profile is running. It should include// exactly the set of goroutines that were alive when the goroutine// profiler first stopped the world. That does not include newg, so// mark it as not needing a profile before transitioning it from// _Gdead.newg.goroutineProfiled.Store(goroutineProfileSatisfied)}}// Track initial transition?newg.trackingSeq = uint8(cheaprand())if newg.trackingSeq%gTrackingPeriod == 0 {newg.tracking = true}gcController.addScannableStack(pp, int64(newg.stack.hi-newg.stack.lo))// Get a goid and switch to runnable. Make all this atomic to the tracer.// 分配gid,并更新状态为_Grunnabletrace := traceAcquire()casgstatus(newg, _Gdead, _Grunnable)if pp.goidcache == pp.goidcacheend {// Sched.goidgen is the last allocated id,// this batch must be [sched.goidgen+1, sched.goidgen+GoidCacheBatch].// At startup sched.goidgen=0, so main goroutine receives goid=1.pp.goidcache = sched.goidgen.Add(_GoidCacheBatch)pp.goidcache -= _GoidCacheBatch - 1pp.goidcacheend = pp.goidcache + _GoidCacheBatch}newg.goid = pp.goidcachepp.goidcache++newg.trace.reset()if trace.ok() {trace.GoCreate(newg, newg.startpc)traceRelease(trace)}// Set up race context.if raceenabled {newg.racectx = racegostart(callerpc)newg.raceignore = 0if newg.labels != nil {// See note in proflabel.go on labelSync's role in synchronizing// with the reads in the signal handler.racereleasemergeg(newg, unsafe.Pointer(&labelSync))}}releasem(mp)return newg
}
malg 创建新goroutine
主要就是分配了goroutine栈空间
// Allocate a new g, with a stack big enough for stacksize bytes.
func malg(stacksize int32) *g {newg := new(g)if stacksize >= 0 {stacksize = round2(stackSystem + stacksize)systemstack(func() {newg.stack = stackalloc(uint32(stacksize))})newg.stackguard0 = newg.stack.lo + stackGuardnewg.stackguard1 = ^uintptr(0)// Clear the bottom word of the stack. We record g// there on gsignal stack during VDSO on ARM and ARM64.*(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(newg.stack.lo)) = 0}return newg
}runqput g置P中
先尝试放高优先的runnext槽中,然后放P本地队列,实在不行就放全局队列
// runqput tries to put g on the local runnable queue.
// If next is false, runqput adds g to the tail of the runnable queue.
// If next is true, runqput puts g in the pp.runnext slot.
// If the run queue is full, runnext puts g on the global queue.
// Executed only by the owner P.
func runqput(pp *p, gp *g, next bool) {if randomizeScheduler && next && randn(2) == 0 {next = false}// 如果next为真,则尝试将gp发到pp.runnext中,如果有正在操作的,再进行尝试if next {retryNext:oldnext := pp.runnextif !pp.runnext.cas(oldnext, guintptr(unsafe.Pointer(gp))) {goto retryNext}if oldnext == 0 {return}// Kick the old runnext out to the regular run queue.// 如果已经有goroutine,则踢出并放入常规运行队列gp = oldnext.ptr()}// 加入常规运行队列
retry:// 加载运行队列的头指针和尾指针h := atomic.LoadAcq(&pp.runqhead) // load-acquire, synchronize with consumerst := pp.runqtail// 如果队列未满,则将gp直接放入队列中if t-h < uint32(len(pp.runq)) {pp.runq[t%uint32(len(pp.runq))].set(gp)atomic.StoreRel(&pp.runqtail, t+1) // store-release, makes the item available for consumptionreturn}// 如果队列已满,则尝试慢策略if runqputslow(pp, gp, h, t) {return}// the queue is not full, now the put above must succeedgoto retry
}runqputslow将一次性将本地队列中的多个g放入到全局队列中
// Put g and a batch of work from local runnable queue on global queue.
// Executed only by the owner P.
func runqputslow(pp *p, gp *g, h, t uint32) bool {var batch [len(pp.runq)/2 + 1]*g// First, grab a batch from local queue.// 先从本地队列中抓取一批gn := t - hn = n / 2if n != uint32(len(pp.runq)/2) {throw("runqputslow: queue is not full")}for i := uint32(0); i < n; i++ {batch[i] = pp.runq[(h+i)%uint32(len(pp.runq))].ptr()}// 如果cas失败,说明已经有其它工作线程从_p_的本地运行队列偷走了一些goroutine,所以直接返回if !atomic.CasRel(&pp.runqhead, h, h+n) { // cas-release, commits consumereturn false}batch[n] = gpif randomizeScheduler {for i := uint32(1); i <= n; i++ {j := cheaprandn(i + 1)batch[i], batch[j] = batch[j], batch[i]}}// 将需要放入全局运行队列的g连起来,减少后面对全局链表的锁住时间,从而降低锁冲突// Link the goroutines.for i := uint32(0); i < n; i++ {batch[i].schedlink.set(batch[i+1])}var q gQueueq.head.set(batch[0])q.tail.set(batch[n])// Now put the batch on global queue.// 将链表放入全局队列中lock(&sched.lock)globrunqputbatch(&q, int32(n+1))unlock(&sched.lock)return true
}Grunnable -> Gruning
将指定的goroutine绑定到当前M上,其状态设置为运行,然后运行实际代码
func execute(gp *g, inheritTime bool) {// 获取当前正在运行的Mmp := getg().m// 如果goroutine是活跃的,那么尝试记录当前goroutine的堆栈信息if goroutineProfile.active {tryRecordGoroutineProfile(gp, osyield)}// goroutine与M相互绑定,并更新goroutine为运行态mp.curg = gpgp.m = mpcasgstatus(gp, _Grunnable, _Grunning)// 初始化goroutine其他信息gp.waitsince = 0gp.preempt = falsegp.stackguard0 = gp.stack.lo + stackGuardif !inheritTime {mp.p.ptr().schedtick++}// Check whether the profiler needs to be turned on or off.hz := sched.profilehzif mp.profilehz != hz {setThreadCPUProfiler(hz)}trace := traceAcquire()if trace.ok() {// GoSysExit has to happen when we have a P, but before GoStart.// So we emit it here.if !goexperiment.ExecTracer2 && gp.syscallsp != 0 {trace.GoSysExit(true)}trace.GoStart()traceRelease(trace)}// 切换到goroutine调度上下文,实际执行goroutine代码// 就是从g0切换到g栈空间,并执行g的用户代码gogo(&gp.sched)
}Gruning -> Gdead
对普通M(不是M0)而言,执行完任务之后,会进行到goexit,并等待重新调度
// Finishes execution of the current goroutine.
func goexit1() {if raceenabled {racegoend()}trace := traceAcquire()if trace.ok() {trace.GoEnd()traceRelease(trace)}mcall(goexit0)
}// goexit continuation on g0.
func goexit0(gp *g) {// 销毁gdestroy(gp)// 调度:查找一个可运行的goroutine并执行schedule()
}
gdestroy 销毁goroutine
销毁其实就是更新状态为Gdead,清除goroutine数据,重新放回P空闲池中
func gdestroy(gp *g) {// 获取当前M与Pmp := getg().mpp := mp.p.ptr()// 更新goroutine状态为Gdeadcasgstatus(gp, _Grunning, _Gdead)// 更新GC控制器。减少可扫描的堆栈大小gcController.addScannableStack(pp, -int64(gp.stack.hi-gp.stack.lo))// 如果是系统goroutine,减少计数if isSystemGoroutine(gp, false) {sched.ngsys.Add(-1)}// 清除goroutine状态gp.m = nillocked := gp.lockedm != 0gp.lockedm = 0mp.lockedg = 0gp.preemptStop = falsegp.paniconfault = falsegp._defer = nil // should be true already but just in case.gp._panic = nil // non-nil for Goexit during panic. points at stack-allocated data.gp.writebuf = nilgp.waitreason = waitReasonZerogp.param = nilgp.labels = nilgp.timer = nilif gcBlackenEnabled != 0 && gp.gcAssistBytes > 0 {// Flush assist credit to the global pool. This gives// better information to pacing if the application is// rapidly creating an exiting goroutines.assistWorkPerByte := gcController.assistWorkPerByte.Load()scanCredit := int64(assistWorkPerByte * float64(gp.gcAssistBytes))gcController.bgScanCredit.Add(scanCredit)gp.gcAssistBytes = 0}// 释放当前M的goroutinedropg()if GOARCH == "wasm" { // no threads yet on wasmgfput(pp, gp)return}if mp.lockedInt != 0 {print("invalid m->lockedInt = ", mp.lockedInt, "\n")throw("internal lockOSThread error")}// 将 goroutine 放回空闲池gfput(pp, gp)if locked {// The goroutine may have locked this thread because// it put it in an unusual kernel state. Kill it// rather than returning it to the thread pool.// Return to mstart, which will release the P and exit// the thread.if GOOS != "plan9" { // See golang.org/issue/22227.gogo(&mp.g0.sched)} else {// Clear lockedExt on plan9 since we may end up re-using// this thread.mp.lockedExt = 0}}
}
Grunning -> Gwaiting
park_m主要负责将当前的 goroutine 暂停,切换其状态,并在必要时重新调度执行
// park continuation on g0.
func park_m(gp *g) {mp := getg().mtrace := traceAcquire()// N.B. Not using casGToWaiting here because the waitreason is// set by park_m's caller.// 更改goroutine状态从Grunning到Gwaitingcasgstatus(gp, _Grunning, _Gwaiting)if trace.ok() {trace.GoPark(mp.waitTraceBlockReason, mp.waitTraceSkip)traceRelease(trace)}// 将当前goroutine与M分离dropg()// 确保在某些条件下,安全地将 Goroutine 从等待状态移出,处理失败的解锁操作,并在必要时重新调度该 Goroutine// 调用解锁函数if fn := mp.waitunlockf; fn != nil {ok := fn(gp, mp.waitlock)mp.waitunlockf = nilmp.waitlock = nilif !ok {trace := traceAcquire()casgstatus(gp, _Gwaiting, _Grunnable)if trace.ok() {trace.GoUnpark(gp, 2)traceRelease(trace)}execute(gp, true) // Schedule it back, never returns.}}// 调度,切换到其他 goroutine 执行schedule()
}
Gwaiting -> Grunable
ready将指定的 goroutine 标记为可运行状态,并将其放入运行队列中
// Mark gp ready to run.
func ready(gp *g, traceskip int, next bool) {// 读取 gp 的当前状态status := readgstatus(gp)// 标记为可运行// Mark runnable.mp := acquirem() // disable preemption because it can be holding p in a local varif status&^_Gscan != _Gwaiting {dumpgstatus(gp)throw("bad g->status in ready")}// status is Gwaiting or Gscanwaiting, make Grunnable and put on runqtrace := traceAcquire()casgstatus(gp, _Gwaiting, _Grunnable)if trace.ok() {trace.GoUnpark(gp, traceskip)traceRelease(trace)}// 将 gp 放入当前 P 的运行队列中。如果 next 为 true,表示将 gp 放在队列的前面,否则放在队列的后面runqput(mp.p.ptr(), gp, next)// 确保有一个 P 可以运行 gpwakep()// 重新启用当前M的抢占releasem(mp)
}Grunning -> Grunnable
goschedImpl 函数用于将当前 goroutine 交出 CPU,使其重新排队等待调度执行。它的实现涉及状态检查、状态变更、跟踪信息处理、全局运行队列操作和重新调度
goschedImpl 函数执行的主要步骤包括:
- 获取并验证 gp 的当前状态。
- 将 gp 的状态修改为 _Grunnable,表示它现在是可运行状态。
- 解绑当前 M 和 gp。
- 获取调度器锁并将 gp 放入全局运行队列。
- 如果主 goroutine 已经启动,则唤醒一个 P 以确保运行队列中的 goroutine 被处理。
- 重新进入调度循环,选择下一个可运行的 goroutine 开始执行。
func goschedImpl(gp *g, preempted bool) {trace := traceAcquire()status := readgstatus(gp)if status&^_Gscan != _Grunning {dumpgstatus(gp)throw("bad g status")}casgstatus(gp, _Grunning, _Grunnable)if trace.ok() {if preempted {trace.GoPreempt()} else {trace.GoSched()}traceRelease(trace)}dropg()lock(&sched.lock)globrunqput(gp)unlock(&sched.lock)if mainStarted {wakep()}schedule()
}
大致总结下
go池是所有拥有goroutine的地方,包括P的runnext、P本地队列和全局队列
- Gidle -> Grunnable: 初始化g,放入go池
- Grunnable -> Grunning: 从go池取出,绑定M,执行实际代码
- Grunning
- -> Gdead: 解绑M,重置g,重新放入go池
- -> Gwaiting: 解绑M,等待被唤醒
- -> Grunnable: 解绑M,放入go全局队列
- Gwaiting -> Grunable: 被唤醒后放入go池
- https://github.com/LeoYang90/Golang-Internal-Notes/blob/master/Go%20%E5%8D%8F%E7%A8%8B%E8%B0%83%E5%BA%A6%E2%80%94%E2%80%94%E5%9F%BA%E6%9C%AC%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86%E4%B8%8E%E5%88%9D%E5%A7%8B%E5%8C%96.md
相关文章:

GO goroutine状态流转
Gidle -> Grunnable newproc获取新的goroutine,并放置到P运行队列中 这也是go关键字之后实际编译调用的方法 func newproc(fn *funcval) {// 获取当前正在运行中的goroutinegp : getg()// 获取调用者的程序计数器地址,用于调试和跟踪pc : getcallerp…...
)
DLMS/COSEM中的信息安全:DLMS/COSEM安全概念(上)
DLMS/COSEM中的信息安全描述并规定: ——DLMS/COSEM安全概念; ——选择加密算法; ——安全密钥; ——使用加密算法进行实体认证、xDLMS APDU保护和COSEM数据保护。 1.综述 DLMS/COSEM服务器的资源(COSEM对象属性和方法)可以由在应用连接内的DLMS/COSEM客户机访问。 在AA…...

C语言第九天笔记
数组的概念 什 么是数组 数组是 相同类型, 有序数据的集合。 数 组的特征 数组中的数据被称为数组的 元素,是同构的 数组中的元素存放在内存空间里 (char player_name[6]:申请在内存中开辟6块连续的基于char类 型的变量空间) 衍生概念&…...
智慧环卫可视化:科技赋能城市清洁管理
图扑智慧环卫可视化通过实时监控、数据分析和智能调度,提高环卫作业效率,优化资源配置,提升城市清洁水平,实现城市管理的精细化和现代化。...

【力扣】SQL题库练习5
高级查询和连接 1341.电影评分 表:Movies ------------------------ | Column Name | Type | ------------------------ | movie_id | int | | title | varchar | ------------------------ movie_id 是这个表的主键(具有唯一值的列)。 ti…...

永结无间Ⅸ--你不需要LLM Agent
人们将目光锁定在下一个闪亮的事物上。FOMO 是人性的一部分。这也适用于企业。就像数据科学成为每个企业分析功能的热潮一样,Agentic Architecture 是大多数 AI 雷达上的热门目标。 但您是否考虑过您是否真的需要它? 实际情况是,您不需要 A…...
Simulink|基于粒子群算法的永磁同步电机多参数辨识
目录 主要内容 模型研究 结果一览 下载链接 主要内容 仿真程序参考文献《改进粒子群算法的永磁同步电机多参数辨识》,采用粒子群算法与simulink模型结合的方式,对永磁同步电机进行多参数辨识。程序以定子绕组电阻、d轴电感、q轴电感和永磁…...

程序如何自动点击亚马逊商户后台的“邀请评论”按钮
要在亚马逊上自动点击“邀请评论”按钮,可以使用自动化脚本来实现。由于你希望自动化操作,我提供一个示例代码,使用 Selenium WebDriver 来执行这个任务。Selenium 是一个流行的浏览器自动化工具,能够模拟用户操作,例如…...

大模型算法面试题(十八)
本系列收纳各种大模型面试题及答案。 1、P-tuning v2 思路、优缺点是什么 P-tuning v2是清华大学自然语言处理实验室(THUDM)等研究机构提出的一种新的预训练模型优化方法,主要关注如何通过动态构建任务相关的提示序列来引导预训练模型进行更…...
手机在网状态接口如何对接?(二)
一、什么是手机在网状态? 传入手机号码,查询该手机号的在网状态,返回内容有正常使用、停机、在网但不可用、不在网(销号/未启用/异常)、预销户等多种状态。 二、手机在网状态使用场景? 1.用户验证与联系…...

力扣-3232. 判断是否可以赢得数字游戏
给你一个 正整数 数组 nums。 Alice 和 Bob 正在玩游戏。在游戏中,Alice 可以从 nums 中选择所有个位数 或 所有两位数,剩余的数字归 Bob 所有。如果 Alice 所选数字之和 严格大于 Bob 的数字之和,则 Alice 获胜。 如果 Alice 能赢得这场游…...

Table SQL connectors以及FileSystem、JDBC connector
目录 Flink支持的连接器 如何使用连接器 FileSystem SQL Connector 文件格式 分区文件 Source 目录监控 元数据 Streaming Sink 滚动策略 文件合并 JDBC SQL Connector 依赖 如何创建JDBC表 连接器配置 案例 pom依赖 代码 测试 Flink的Table API和SQL…...
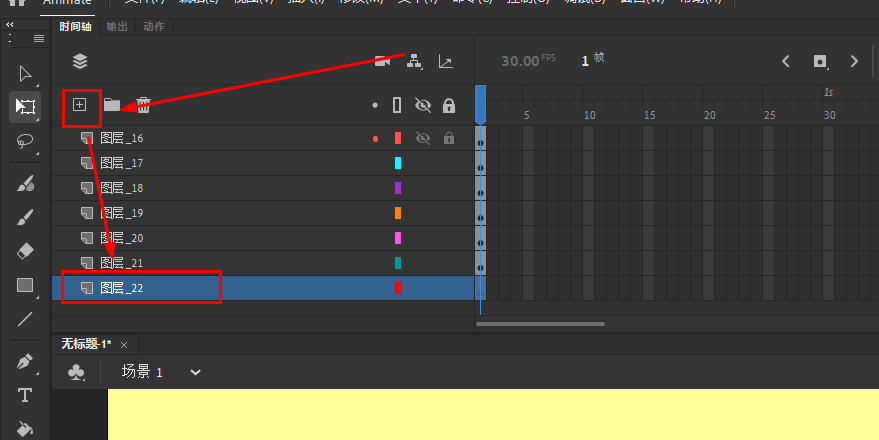
Animate软件基础:“分散到图层”创建的新图层
FlashASer:AdobeAnimate2021软件零基础入门教程https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/633230084 FlashASer:实用的各种Adobe Animate软件教程https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/675680471 FlashASer:Animate教程及作品源文件https://zhuanlan.zhihu.co…...
ffmpeg命令-Windows下常用最全
查询命令 参数 说明 -version 显示版本。 -formats 显示可用的格式(包括设备)。 -demuxers 显示可用的demuxers。 -muxers 显示可用的muxers。 -devices 显示可用的设备。 -codecs 显示libavcodec已知的所有编解码器。 -decoders 显示可用…...
反序列化漏洞靶机实战-serial
一.安装靶机 下载地址为https://download.vulnhub.com/serial/serial.zip,安装好后开启靶机,这里并不需要我们去登录,直接扫描虚拟机nat模式下c网段的ip,看看哪个的80端口开放,然后直接去访问 二.查找cookie 访问靶…...
医疗器械产品没有互联网连接,就不适用于网络安全要求吗?
医疗器械产品是否不适用于网络安全要求,需要考虑产品是否具有网络连接功能以进行电子数据交换或远程控制,以及是否采用储存媒介进行电子数据交换。详细解析如下: 一、医疗器械的网络安全要求不仅限于互联网连接 数据交换接口:医疗…...

可视掏耳勺安全吗?独家揭示六大风险弊病!
很多人习惯在洗漱完顺手拿一根棉签掏耳朵,但是棉签的表面直径大且粗糙,不易将耳朵深处的耳垢挖出,耳垢堆积在耳道深处长时间不清理会导致堵塞耳道,引起耳鸣甚至感染。而可视掏耳勺作为一种新型的挖耳工具,它的安全性也…...

JavaScript 变量声明var、let、const
在 JavaScript 中,var、let和const是用于声明变量的关键字。 let和const是JavaScript里相对较新的变量声明方式。 let用法类似于var,但是所声明的变量,只在let命令所在的代码块内有效。 const声明一个只读的常量。一旦声明,常量的…...

ipvlan: operation not supported 导致的POD不断重启
情况描述 接到反馈有一台虚拟机HA迁移了,需要检查一下上面业务是否正常,由于是K8S node节点,正常情况下重启会自动恢复的,不过抱着严谨的态度,上去看了一眼。 问题:发现docker运行正常,但是业…...
组蛋白乳酸化和RNA甲基化如何联动?请大数据把这个思路推给科研人
在细胞生物学中,基因表达调控是决定细胞功能与命运的核心过程之一。组蛋白作为修饰性蛋白,在调控基因转录中起着至关重要的作用。近年来,科学家们发现,组蛋白的多种化学修饰(如甲基化、乙酰化、磷酸化等)影…...
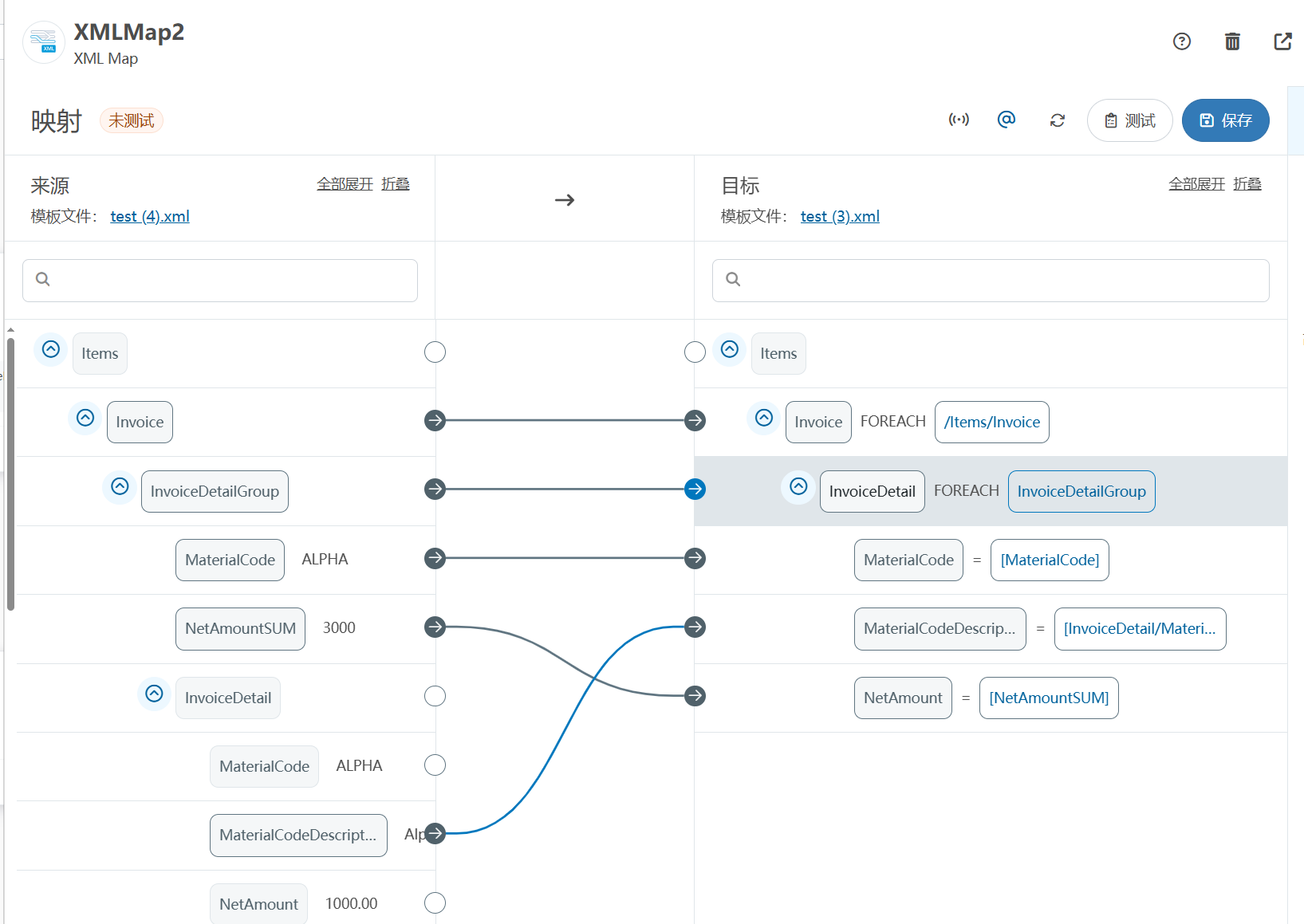
XML Group端口详解
在XML数据映射过程中,经常需要对数据进行分组聚合操作。例如,当处理包含多个物料明细的XML文件时,可能需要将相同物料号的明细归为一组,或对相同物料号的数量进行求和计算。传统实现方式通常需要编写脚本代码,增加了开…...

PHP和Node.js哪个更爽?
先说结论,rust完胜。 php:laravel,swoole,webman,最开始在苏宁的时候写了几年php,当时觉得php真的是世界上最好的语言,因为当初活在舒适圈里,不愿意跳出来,就好比当初活在…...
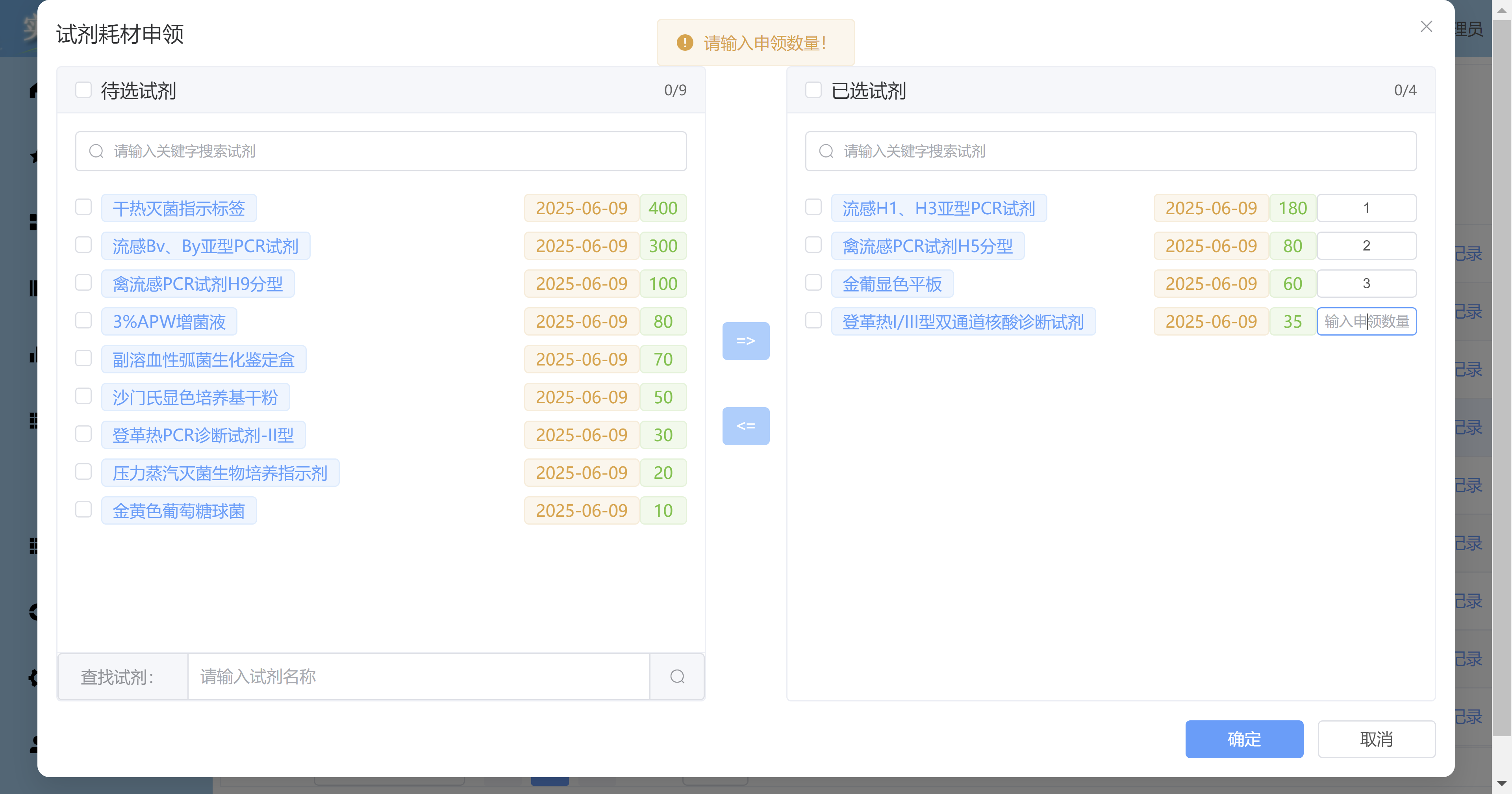
Vue3 + Element Plus + TypeScript中el-transfer穿梭框组件使用详解及示例
使用详解 Element Plus 的 el-transfer 组件是一个强大的穿梭框组件,常用于在两个集合之间进行数据转移,如权限分配、数据选择等场景。下面我将详细介绍其用法并提供一个完整示例。 核心特性与用法 基本属性 v-model:绑定右侧列表的值&…...

对WWDC 2025 Keynote 内容的预测
借助我们以往对苹果公司发展路径的深入研究经验,以及大语言模型的分析能力,我们系统梳理了多年来苹果 WWDC 主题演讲的规律。在 WWDC 2025 即将揭幕之际,我们让 ChatGPT 对今年的 Keynote 内容进行了一个初步预测,聊作存档。等到明…...

C++ 基础特性深度解析
目录 引言 一、命名空间(namespace) C 中的命名空间 与 C 语言的对比 二、缺省参数 C 中的缺省参数 与 C 语言的对比 三、引用(reference) C 中的引用 与 C 语言的对比 四、inline(内联函数…...
SpringBoot+uniapp 的 Champion 俱乐部微信小程序设计与实现,论文初版实现
摘要 本论文旨在设计并实现基于 SpringBoot 和 uniapp 的 Champion 俱乐部微信小程序,以满足俱乐部线上活动推广、会员管理、社交互动等需求。通过 SpringBoot 搭建后端服务,提供稳定高效的数据处理与业务逻辑支持;利用 uniapp 实现跨平台前…...

TRS收益互换:跨境资本流动的金融创新工具与系统化解决方案
一、TRS收益互换的本质与业务逻辑 (一)概念解析 TRS(Total Return Swap)收益互换是一种金融衍生工具,指交易双方约定在未来一定期限内,基于特定资产或指数的表现进行现金流交换的协议。其核心特征包括&am…...

Rust 异步编程
Rust 异步编程 引言 Rust 是一种系统编程语言,以其高性能、安全性以及零成本抽象而著称。在多核处理器成为主流的今天,异步编程成为了一种提高应用性能、优化资源利用的有效手段。本文将深入探讨 Rust 异步编程的核心概念、常用库以及最佳实践。 异步编程基础 什么是异步…...

Axios请求超时重发机制
Axios 超时重新请求实现方案 在 Axios 中实现超时重新请求可以通过以下几种方式: 1. 使用拦截器实现自动重试 import axios from axios;// 创建axios实例 const instance axios.create();// 设置超时时间 instance.defaults.timeout 5000;// 最大重试次数 cons…...

Android Bitmap治理全解析:从加载优化到泄漏防控的全生命周期管理
引言 Bitmap(位图)是Android应用内存占用的“头号杀手”。一张1080P(1920x1080)的图片以ARGB_8888格式加载时,内存占用高达8MB(192010804字节)。据统计,超过60%的应用OOM崩溃与Bitm…...
