《C++ Primer Plus》(第6版)第13章编程练习
《C++ Primer Plus》(第6版)第13章编程练习
- 《C++ Primer Plus》(第6版)第13章编程练习
- 1. Cd类
- 2. 使用动态内存分配重做练习1
- 3. baseDMA、lacksDMA、hasDMA类
- 4. Port类和VintagePort类
《C++ Primer Plus》(第6版)第13章编程练习
1. Cd类
以下面的类声明为基础:
class Cd { //represents a CD disk
private:char performers[50];char label[20];int selections; //number of selectionsdouble playtime; //playing time in minute
public:Cd(char* s1, char* s2, int n, double x);Cd(const Cd& d);Cd();~Cd();void Report() const; //reports all CD dataCd& operator=(const Cd& d);
};
派生出一个Classic类,并添加一组char成员,用于存储指出CD中主要作品的字符串。修改上述声明,使基类的搜有函数都是虚的。如果上述定义声明的某个方法并不需要,则请删除它。使用下面的程序测试您的产品:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include"classic.h"void Bravo(const Cd& disk);int main()
{Cd c1("beatles", "Capitol", 14, 35.5);Classic c2 = Classic("Piano Sonata in B flat, Fantasia in C", "Alfred Brendel", "Philips", 2, 57.17);Cd* pcd = &c1;cout << "Using object directly:\n";c1.Report(); //use Cd methodc2.Report(); //use Classic methodcout << "Using type cd *pointer to objects:\n";pcd->Report(); //use Cd method for cd objectpcd = &c2;pcd->Report(); //use Classic method for classic objectcout << "Calling a function with a Cd reference argument:\n";Bravo(c1);Bravo(c2);cout << "Testing assignment: ";Classic copy;copy = c2;copy.Report();return 0;
}void Bravo(const Cd& disk)
{disk.Report();
}
代码:
cd.h:
#ifndef CD_H_
#define CD_H_class Cd
{ // represents a CD disk
private:char performers[50];char label[20];int selections; // number of selectionsdouble playtime; // playing time in minutepublic:Cd(char *s1, char *s2, int n, double x);Cd(const Cd &d);Cd();virtual ~Cd();virtual void Report() const; // reports all CD datavirtual Cd &operator=(const Cd &d);
};#endif
cd.cpp:
#include "cd.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>Cd::Cd(char *s1, char *s2, int n, double x)
{strncpy(performers, s1, 49);performers[49] = '\0';strncpy(label, s2, 19);label[19] = '\0';selections = n;playtime = x;
}
Cd::Cd(const Cd &d)
{strncpy(performers, d.performers, 49);performers[49] = '\0';strncpy(label, d.label, 19);label[19] = '\0';selections = d.selections;playtime = d.playtime;
}
Cd::Cd()
{performers[0] = '\0';label[0] = '\0';selections = 0;playtime = 0.0;
}
Cd::~Cd()
{
}
void Cd::Report() const
{using std::cout;using std::endl;cout << "Information:\n";cout << "Performers: " << performers << endl;cout << "Label: " << label << endl;cout << "Selections: " << selections << endl;cout << "Playtime: " << playtime << endl;
}
Cd &Cd::operator=(const Cd &d)
{if (this == &d)return *this;strncpy(performers, d.performers, 49);performers[49] = '\0';strncpy(label, d.label, 19);label[19] = '\0';selections = d.selections;playtime = d.playtime;return *this;
}
classic.h:
#ifndef CLASSIC_H_
#define CLASSIC_H_#include "cd.h"class Classic : public Cd
{
private:char majorWorks[50];public:Classic(char *m, char *s1, char *s2, int n, double x);Classic(char *m, const Cd &cd);Classic();virtual ~Classic();virtual void Report() const;virtual Classic &operator=(const Classic &c);
};#endif
classic.cpp:
#include "classic.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>Classic::Classic(char *m, char *s1, char *s2, int n, double x) : Cd(s1, s2, n, x)
{strncpy(majorWorks, m, 49);majorWorks[49] = '\0';
}
Classic::Classic(char *m, const Cd &cd) : Cd(cd)
{strncpy(majorWorks, m, 49);majorWorks[49] = '\0';
}
Classic::Classic() : Cd()
{majorWorks[0] = '\0';
}
Classic::~Classic()
{
}
void Classic::Report() const
{using std::cout;using std::endl;Cd::Report();cout << "Major works: " << majorWorks << endl;
}
Classic &Classic::operator=(const Classic &c)
{if (this == &c)return *this;Cd::operator=(c);strncpy(majorWorks, c.majorWorks, 49);majorWorks[49] = '\0';return *this;
}
main.cpp:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "classic.h"void Bravo(const Cd &disk);int main()
{Cd c1("beatles", "Capitol", 14, 35.5);Classic c2 = Classic("Piano Sonata in B flat, Fantasia in C", "Alfred Brendel", "Philips", 2, 57.17);Cd *pcd = &c1;cout << "Using object directly:\n";c1.Report(); // use Cd methodc2.Report(); // use Classic methodcout << "Using type cd *pointer to objects:\n";pcd->Report(); // use Cd method for cd objectpcd = &c2;pcd->Report(); // use Classic method for classic objectcout << "Calling a function with a Cd reference argument:\n";Bravo(c1);Bravo(c2);cout << "Testing assignment: ";Classic copy;copy = c2;copy.Report();system("pause");return 0;
}void Bravo(const Cd &disk)
{disk.Report();
}
运行结果:
Microsoft Windows [版本 10.0.19044.2728]
(c) Microsoft Corporation。保留所有权利。C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter13\13.1>g++ cd.cpp classic.cpp main.cpp -o main
main.cpp: In function 'int main()':
main.cpp:9:41: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to 'char*' [-Wwrite-strings]Cd c1("beatles", "Capitol", 14, 35.5);^
main.cpp:9:41: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to 'char*' [-Wwrite-strings]
main.cpp:10:104: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to 'char*' [-Wwrite-strings]Classic c2 = Classic("Piano Sonata in B flat, Fantasia in C", "Alfred Brendel", "Philips", 2, 57.17);^
main.cpp:10:104: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to 'char*' [-Wwrite-strings]
main.cpp:10:104: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to 'char*' [-Wwrite-strings]C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter13\13.1>main
Using object directly:
Information:
Performers: beatles
Label: Capitol
Selections: 14
Playtime: 35.5
Information:
Performers: Alfred Brendel
Label: Philips
Selections: 2
Playtime: 57.17
Major works: Piano Sonata in B flat, Fantasia in C
Using type cd *pointer to objects:
Information:
Performers: beatles
Label: Capitol
Selections: 14
Playtime: 35.5
Information:
Performers: Alfred Brendel
Label: Philips
Selections: 2
Playtime: 57.17
Major works: Piano Sonata in B flat, Fantasia in C
Calling a function with a Cd reference argument:
Information:
Performers: beatles
Label: Capitol
Selections: 14
Playtime: 35.5
Information:
Performers: Alfred Brendel
Label: Philips
Selections: 2
Playtime: 57.17
Major works: Piano Sonata in B flat, Fantasia in C
Testing assignment: Information:
Performers: Alfred Brendel
Label: Philips
Selections: 2
Playtime: 57.17
Major works: Piano Sonata in B flat, Fantasia in C
请按任意键继续. . .C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter13\13.1>
2. 使用动态内存分配重做练习1
完成练习1,但让两个类使用动态内存分配而不是长度固定的数组来记录字符串。
代码:
cd.h
#ifndef CD_H_
#define CD_H_class Cd
{ // represents a CD disk
private:char *performers;char *label;int selections; // number of selectionsdouble playtime; // playing time in minutepublic:Cd(char *s1, char *s2, int n, double x);Cd(const Cd &d);Cd();virtual ~Cd();virtual void Report() const; // reports all CD datavirtual Cd &operator=(const Cd &d);
};#endif
cd.cpp:
#include "cd.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using std::strcpy;
using std::strlen;Cd::Cd(char *s1, char *s2, int n, double x)
{performers = new char[strlen(s1) + 1];strcpy(performers, s1);label = new char[strlen(s2) + 1];strcpy(label, s2);selections = n;playtime = x;
}
Cd::Cd(const Cd &d)
{performers = new char[strlen(d.performers) + 1];strcpy(performers, d.performers);label = new char[strlen(d.label) + 1];strcpy(label, d.label);selections = d.selections;playtime = d.playtime;
}
Cd::Cd()
{performers = new char[1];strcpy(performers, "\0");label = new char[1];strcpy(label, "\0");selections = 0;playtime = 0.0;
}
Cd::~Cd()
{delete[] performers;delete[] label;
}
void Cd::Report() const
{using std::cout;using std::endl;cout << "Information:\n";cout << "Performers: " << performers << endl;cout << "Label: " << label << endl;cout << "Selections: " << selections << endl;cout << "Playtime: " << playtime << endl;
}
Cd &Cd::operator=(const Cd &d)
{if (this == &d)return *this;delete[] performers;delete[] label;performers = new char[strlen(d.performers) + 1];strcpy(performers, d.performers);label = new char[strlen(d.label) + 1];strcpy(label, d.label);selections = d.selections;playtime = d.playtime;return *this;
}
classic.h:
#ifndef CLASSIC_H_
#define CLASSIC_H_#include "cd.h"class Classic : public Cd
{
private:char *majorWorks;public:Classic(char *m, char *s1, char *s2, int n, double x);Classic(char *m, const Cd &cd);Classic();virtual ~Classic();virtual void Report() const;virtual Classic &operator=(const Classic &c);
};#endif
classic.cpp:
#include "classic.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using std::strcpy;
using std::strlen;Classic::Classic(char *m, char *s1, char *s2, int n, double x) : Cd(s1, s2, n, x)
{majorWorks = new char[strlen(m) + 1];strcpy(majorWorks, m);
}
Classic::Classic(char *m, const Cd &cd) : Cd(cd)
{majorWorks = new char[strlen(m) + 1];strcpy(majorWorks, m);
}
Classic::Classic() : Cd()
{majorWorks = new char[1];strcpy(majorWorks, "\0");
}
Classic::~Classic()
{delete[] majorWorks;
}
void Classic::Report() const
{using std::cout;using std::endl;Cd::Report();cout << "Major works: " << majorWorks << endl;
}
Classic &Classic::operator=(const Classic &c)
{if (this == &c)return *this;Cd::operator=(c);majorWorks = new char[strlen(c.majorWorks) + 1];strcpy(majorWorks, c.majorWorks);return *this;
}
main.cpp与练习1的main.cpp相同。
运行结果:
C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter13\13.2>g++ cd.cpp classic.cpp main.cpp -o main
main.cpp: In function 'int main()':
main.cpp:9:41: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to 'char*' [-Wwrite-strings]Cd c1("beatles", "Capitol", 14, 35.5);^
main.cpp:9:41: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to 'char*' [-Wwrite-strings]
main.cpp:10:104: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to 'char*' [-Wwrite-strings]Classic c2 = Classic("Piano Sonata in B flat, Fantasia in C", "Alfred Brendel", "Philips", 2, 57.17);^
main.cpp:10:104: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to 'char*' [-Wwrite-strings]
main.cpp:10:104: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to 'char*' [-Wwrite-strings]C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter13\13.2>main
Using object directly:
Information:
Performers: beatles
Label: Capitol
Selections: 14
Playtime: 35.5
Information:
Performers: Alfred Brendel
Label: Philips
Selections: 2
Playtime: 57.17
Major works: Piano Sonata in B flat, Fantasia in C
Using type cd *pointer to objects:
Information:
Performers: beatles
Label: Capitol
Selections: 14
Playtime: 35.5
Information:
Performers: Alfred Brendel
Label: Philips
Selections: 2
Playtime: 57.17
Major works: Piano Sonata in B flat, Fantasia in C
Calling a function with a Cd reference argument:
Information:
Performers: beatles
Label: Capitol
Selections: 14
Playtime: 35.5
Information:
Performers: Alfred Brendel
Label: Philips
Selections: 2
Playtime: 57.17
Major works: Piano Sonata in B flat, Fantasia in C
Testing assignment: Information:
Performers: Alfred Brendel
Label: Philips
Selections: 2
Playtime: 57.17
Major works: Piano Sonata in B flat, Fantasia in C
请按任意键继续. . .C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter13\13.2>
3. baseDMA、lacksDMA、hasDMA类
修改baseDMA-lacksDMA-hasDMA类层次,让三个类都从一个ABC派生而来,然后使用与程序清单13.10相似的程序对结果进行测试。也就是说,它应使用ABC指针数组,并让用户决定要创建的对象类型。在类定义中添加virtual View()方法以处理数据显示。
代码:
dma.h:
#ifndef DMA_H_
#define DMA_H_#include <iostream>class ABC
{
public:ABC(){};~ABC(){};virtual void View() = 0;
};class baseDMA : public ABC
{
private:char *label;int rating;public:baseDMA(const char *l = "null", int r = 0);baseDMA(const baseDMA &rs);virtual ~baseDMA();baseDMA &operator=(const baseDMA &rs);friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const baseDMA &rs);virtual void View();
};class lacksDMA : public baseDMA
{
private:enum{COL_LEN = 40};char color[COL_LEN];public:lacksDMA(const char *c = "blank", const char *l = "null", int r = 0);lacksDMA(const char *c, const baseDMA &rs);friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const lacksDMA &rs);virtual void View();
};
class hasDMA : public baseDMA
{
private:char *style;public:hasDMA(const char *s = "none", const char *l = "null", int r = 0);hasDMA(const char *s, const baseDMA &rs);hasDMA(const hasDMA &hs);~hasDMA();hasDMA &operator=(const hasDMA &hs);friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const hasDMA &hs);virtual void View();
};#endif
dma.cpp:
#include "dma.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::strcpy;
using std::strlen;
using std::strncpy;// baseDMA methods
baseDMA::baseDMA(const char *l, int r)
{label = new char[strlen(l) + 1];strcpy(label, l);rating = r;
}
baseDMA::baseDMA(const baseDMA &rs)
{label = new char[strlen(rs.label) + 1];strcpy(label, rs.label);rating = rs.rating;
}
baseDMA::~baseDMA()
{delete[] label;
}
baseDMA &baseDMA::operator=(const baseDMA &rs)
{if (this == &rs)return *this;delete[] label;label = new char[strlen(rs.label) + 1];strcpy(label, rs.label);rating = rs.rating;return *this;
}
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const baseDMA &rs)
{os << "Label: " << rs.label << endl;os << "Rating: " << rs.rating << endl;return os;
}
void baseDMA::View()
{cout << "Label: " << label << endl;cout << "Rating: " << rating << endl;
}// lacksDMA methods
lacksDMA::lacksDMA(const char *c, const char *l, int r) : baseDMA(l, r)
{strncpy(color, c, 39);color[39] = '\0';
}
lacksDMA::lacksDMA(const char *c, const baseDMA &rs) : baseDMA(rs)
{strncpy(color, c, COL_LEN - 1);color[COL_LEN - 1] = '\0';
}
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const lacksDMA &ls)
{os << (const baseDMA &)ls;os << "Color: " << ls.color << endl;return os;
}
void lacksDMA::View()
{baseDMA::View();cout << "Color: " << color << endl;
}// hasDMA methods
hasDMA::hasDMA(const char *s, const char *l, int r) : baseDMA(l, r)
{style = new char[strlen(s) + 1];strcpy(style, s);
}
hasDMA::hasDMA(const char *s, const baseDMA &rs) : baseDMA(rs)
{style = new char[strlen(s) + 1];strcpy(style, s);
}
hasDMA::hasDMA(const hasDMA &hs) : baseDMA(hs)
{style = new char[strlen(hs.style) + 1];strcpy(style, hs.style);
}
hasDMA::~hasDMA()
{delete[] style;
}
hasDMA &hasDMA::operator=(const hasDMA &hs)
{if (this == &hs)return *this;baseDMA::operator=(hs);delete[] style;style = new char[strlen(hs.style) + 1];strcpy(style, hs.style);return *this;
}
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const hasDMA &hs)
{os << (const baseDMA &)hs;os << "Style: " << hs.style << endl;return os;
}
void hasDMA::View()
{baseDMA::View();cout << "Style: " << style << endl;
}
main.cpp:
#include "dma.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{int n;cout << "How many DMAs do you have? ";cin >> n;ABC *p_dma[n];char *t_label = new char[50];int t_rating;int kind;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){cout << "Enter label: ";cin.getline(t_label, 50);cout << "Enter rating: ";cin >> t_rating;cout << "Enter 1 for baseDMA or 2 for lacksDMA or 3 for hasDMA: ";while (cin >> kind && kind != 1 && kind != 2 && kind != 3)cout << "Enter either 1 or 2 or 3: ";cin.ignore();switch (kind){case 1:p_dma[i] = new baseDMA(t_label, t_rating);break;case 2:char t_color[40];cout << "Enter color: ";cin.getline(t_color, 40);p_dma[i] = new lacksDMA(t_color, t_label, t_rating);break;case 3:char *t_style = new char[20];cout << "Enter style: ";cin.getline(t_style, 20);p_dma[i] = new hasDMA(t_style, t_label, t_rating);break;}while (cin.get() != '\n')continue;}cout << endl;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){p_dma[i]->View();cout << endl;}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){delete p_dma[i];}cout << "Done.\n"<< endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
运行结果:
Microsoft Windows [版本 10.0.19044.2728]
(c) Microsoft Corporation。保留所有权利。C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter13\13.3>g++ dma.cpp main.cpp -o mainC:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter13\13.3>main
Enter label: Portabelly
Enter rating: 8
Enter 1 for baseDMA or 2 for lacksDMA or 3 for hasDMA: 1Enter label: Blimpo
Enter rating: 4
Enter 1 for baseDMA or 2 for lacksDMA or 3 for hasDMA: 2
Enter color: redEnter label: Buffalo Keys
Enter rating: 5
Enter 1 for baseDMA or 2 for lacksDMA or 3 for hasDMA: 3
Enter style: MercatorEnter label: lable1
Enter rating: 10
Enter 1 for baseDMA or 2 for lacksDMA or 3 for hasDMA: 1Enter label: lable2
Enter rating: 3
Enter 1 for baseDMA or 2 for lacksDMA or 3 for hasDMA: 1Enter label: lable3
Enter rating: 1
Enter 1 for baseDMA or 2 for lacksDMA or 3 for hasDMA: 9
Enter either 1 or 2 or 3: 1Label: Portabelly
Rating: 8Label: Blimpo
Rating: 4
Color: redLabel: Buffalo Keys
Rating: 5
Style: MercatorLabel: lable1
Rating: 10Label: lable2
Rating: 3Label: lable3
Rating: 1Done.请按任意键继续. . .C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter13\13.3>
4. Port类和VintagePort类
Benevolent Order of Programmers用来维护瓶装葡萄酒箱。为描述它,BOP Portmaster设置了一个Port类,并声明如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Port
{
private:char *brand;char style[20]; // i.e., tawny, ruby, vintageint bottles;public:Port(const char *br = "none", const char *st = "none", int b = 0);Port(const Port &p); // copy constructorvirtual ~Port() { delete[] brand; }Port &operator=(const Port &p);Port &operator+=(int b); // add b to bottlesPort &operator-=(int b); // subtracts b from bottles , if availableint BottleCount() const { return bottles; }virtual void Show() const;friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const Port &p);
};
show()方法按下面的格式显示信息:
Brand : Gallo
Kind : tawny
Bottles : 20
operator<<()函数按下面的格式显示信息(末尾没有换行符):
Gallo, tawny, 20
PortMaster完成了Port类的方法定义后派生了VintagePort类,然后被解职——因为不小心将一瓶45度Cockburn泼到了正在准备烤肉调料的人身上,VintagePort类如下显示:
class VintagePort : public Port //style necessarily = "vintage"
{
private:char* nickname; //i.e. , "The Noble" or "Old Velvet", etc.int year; //vintage year
public:VintagePort();VintagePort(const char* br, const char* st, int b, const char* nn, int y);VintagePort(const VintagePort& vp);~VintagePort() { delete[] nickname; }VintagePort& operator = (const VintagePort& vp);void show() const;friend ostream& operator <<(ostream& os, const VintagePort& vp);
};
您被制定指定负责完成VintagePort。
a.第一个任务是重新创建Port方法定义,因为前任被开除时销毁了方法定义。
b.第二个任务是解释为什么有的方法重新定义了,而有些没有重新定义。
c.第三个任务解释为何没有将operator = () 和operator << ()声明为虚的。
d.第四个任务是提供VintagePort中各个方法的定义。
答:
a.第一个任务是重新创建Port方法定义,因为前任被开除时销毁了方法定义。
#include "port.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;Port::Port(const char *br, const char *st, int b)
{brand = new char[strlen(br) + 1];strcpy(brand, br);strcpy(style, st);bottles = b;
}
Port::Port(const Port &p) // copy constructor
{brand = new char[strlen(p.brand) + 1];strcpy(brand, p.brand);strcpy(style, p.style);bottles = p.bottles;
}
Port &Port::operator=(const Port &p)
{if (this == &p)return *this;delete[] brand;brand = new char[strlen(p.brand) + 1];strcpy(brand, p.brand);strcpy(style, p.style);bottles = p.bottles;return *this;
}
Port &Port::operator+=(int b) // add b to bottles
{bottles += b;return *this;
}
Port &Port::operator-=(int b) // subtracts b from bottles , if available
{bottles -= b;return *this;
}
void Port::Show() const
{cout << "Brand: " << brand << endl;cout << "Kind: " << style << endl;cout << "Bottles: " << bottles << endl;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const Port &p)
{os << p.brand << "," << p.style << "," << p.bottles;return os;
}
b.第二个任务是解释为什么有的方法重新定义了,而有些没有重新定义。
当派生类成员函数需要处理派生类独有的成员变量时,需要重新定义方法,如果不需要处理派生类独有的成员变量,直接调用基类的方法即可。
c.第三个任务解释为何没有将operator = () 和operator << ()声明为虚的。
a).如果要在派生类中重新定义基类的方法,则将它设置为虚方法。但是基类的operator = () 和派生类的operator = () 形参不一样,根本不是一个类方法,不存在重新定义的问题,因从也不必声明为虚的。
b).operator<<()函数是友元函数,友元函数不能是虚函数,因为友元不是类成员,而只有类成员才能是虚函数。
d.第四个任务是提供VintagePort中各个方法的定义。
#include "VintagePort.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;VintagePort::VintagePort() : Port()
{
}
VintagePort::VintagePort(const char *br, const char *st, int b, const char *nn, int y) : Port(br, st, b)
{nickname = new char[strlen(nn) + 1];strcpy(nickname, nn);int year = y;
}
VintagePort::VintagePort(const VintagePort &vp) : Port(vp)
{nickname = new char[strlen(vp.nickname) + 1];strcpy(nickname, vp.nickname);int year = vp.year;
}
VintagePort &VintagePort::operator=(const VintagePort &vp)
{if (this == &vp)return *this;Port::operator=(vp);delete[] nickname;nickname = new char[strlen(vp.nickname) + 1];strcpy(nickname, vp.nickname);strcpy(nickname, vp.nickname);year = vp.year;return *this;
}
void VintagePort::show() const
{Port::Show();cout << "Nick Name: " << nickname << endl;cout << "Year: " << year << endl;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const VintagePort &vp)
{os << (const Port &)vp;os << vp.nickname << "," << vp.year;return os;
}
相关文章:
第13章编程练习)
《C++ Primer Plus》(第6版)第13章编程练习
《C Primer Plus》(第6版)第13章编程练习《C Primer Plus》(第6版)第13章编程练习1. Cd类2. 使用动态内存分配重做练习13. baseDMA、lacksDMA、hasDMA类4. Port类和VintagePort类《C Primer Plus》(第6版)第…...
【多线程】多线程案例
✨个人主页:bit me👇 ✨当前专栏:Java EE初阶👇 ✨每日一语:we can not judge the value of a moment until it becomes a memory. 目 录🍝一. 单例模式🍤1. 饿汉模式实现🦪2. 懒汉模…...
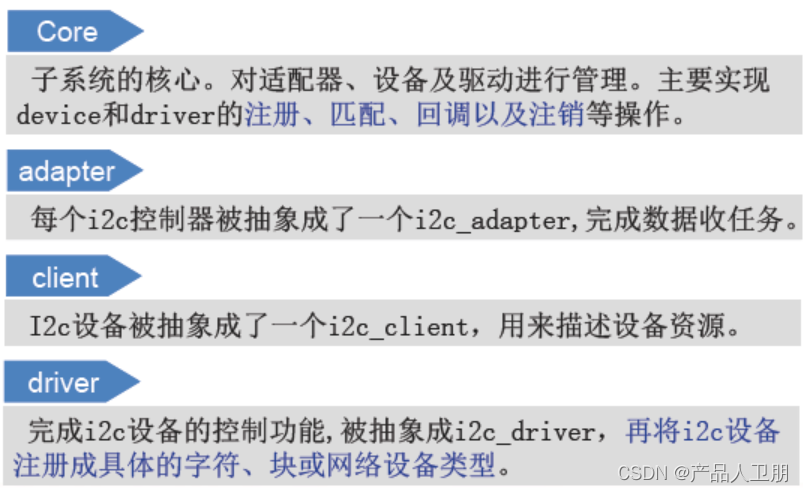
【IoT】嵌入式驱动开发:IIC子系统
IIC有三种接口实现方式 三种时序对比: 图1 IIC子系统组成 图2 图3 IIC操作流程 设备端 1.i2c_get_adapter 2.i2c_new_device(相当于register设备) 3.I2c_put_adapter 驱动端 1.填充i2c_driver 2.i2c_add_driver(相当于register驱动) 3.在probe中建立访问方式 client相…...
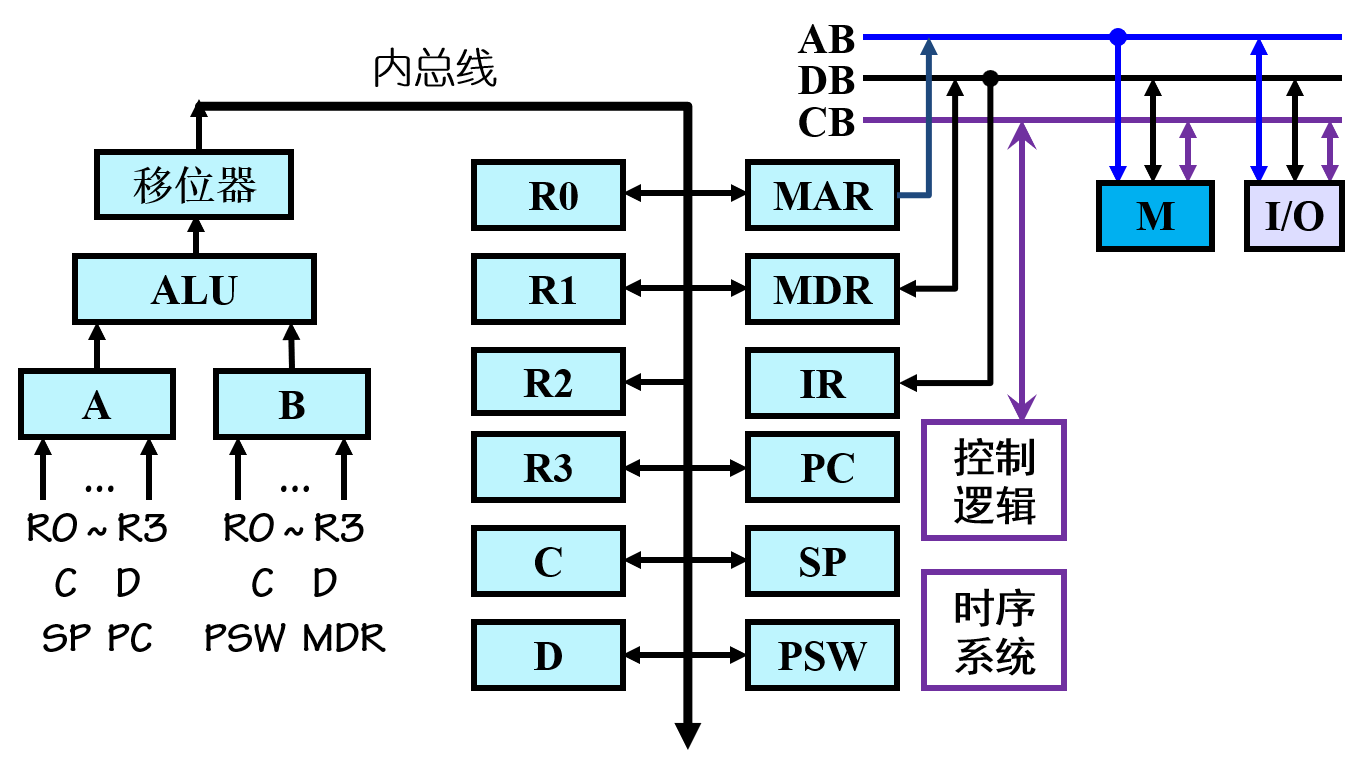
DJ2-4 进程同步(第一节课)
目录 2.4.1 进程同步的基本概念 1. 两种形式的制约关系 2. 临界资源(critical resource) 3. 生产者-消费者问题 4. 临界区(critical section) 5. 同步机制应遵循的规则 2.4.2 硬件同步机制 1. 关中断 2. Test-and-Set …...
AI独立开发者:一周涨粉8万赚2W美元;推特#HustleGPT GPT-4创业挑战;即刻#AIHackathon创业者在行动 | ShowMeAI周刊
👀日报&周刊合辑 | 🎡生产力工具与行业应用大全 | 🧡 点赞关注评论拜托啦! 这是ShowMeAI周刊的第7期。聚焦AI领域本周热点,及其在各圈层泛起的涟漪;拆解AI独立开发者的盈利案例,关注中美AIG…...
不要迷信 QUIC
很多人都在强调 QUIC 能解决 HoL blocking 问题,不好意思,我又要泼冷水了。假设大家都懂 QUIC,不再介绍 QUIC 的细节,直接说问题。 和 TCP 一样,QUIC 也是一个基于连接的,保序的可靠传输协议,T…...

【28】Verilog进阶 - RAM的实现
VL53 单端口RAM 1 思路 简简单单,读取存储器单元值操作即可 2 功能猜想版 说明: 下面注释就是我对模块端口信号 自己猜测的理解。 因为题目并没有说清楚,甚至连参考波形都没有给出。 唉,这就完全是让人猜测呢,如果一点学术背景的人来刷题,指定不容易!! 好在,我有较为…...

【MySQL】聚合查询
目录 1、前言 2、插入查询结果 3、聚合查询 3.1 聚合函数 3.1.1 count 3.1.2 sum 3.1.3 avg 3.1.4 max 和 min 4、GROUP BY 子句 5、HAVING 关键字 1、前言 前面的内容已经把基础的增删改查介绍的差不多了,也介绍了表的相关约束, 从本期开始…...
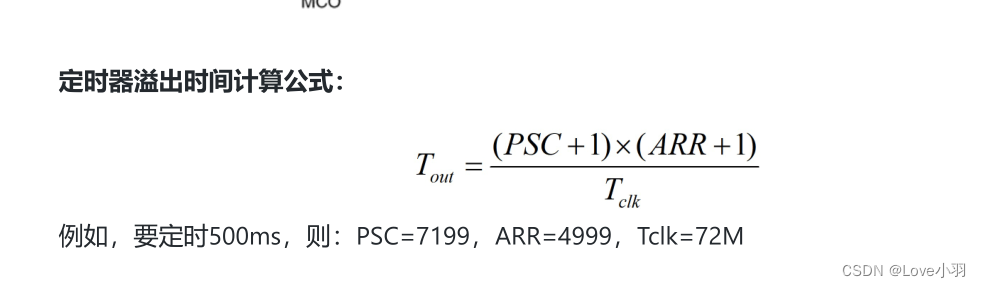
初时STM32单片机
目录 一、单片机基本认知 二、STM系列单片机命名规则 三、标准库与HAL库区别 四、通用输入输出端口GPIO 五、推挽输出与开漏输出 六、复位和时钟控制(RCC) 七、时钟控制 八、中断和事件 九、定时器介绍 一、单片机基本认知 单片机和PC电脑相比…...

debian部署docker(傻瓜式)
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 debian10部署dockerdebian10部署docker(傻瓜式)一、准备工作二、**使用 APT 安装,注意要先配置apt网络源**1.配置网络源2.官方下载三、安装…...
JS判断是否为base64字符串如何转换为图片src格式
需求背景 : 如何判断后端给返回的 字符串 是否为 base-64 位 呢 ? 以及如果判断为是的话,如何给它进行转换为 img 标签可使用的那种 src 格式 呢 ? 1、判断字符串是否为 base64 以下方法,可自行挨个试试,…...

【SpringMVC】SpringMVC方式,向作用域对象共享数据(ModelAndView、Model、map、ModelMap)
个人简介:Java领域新星创作者;阿里云技术博主、星级博主、专家博主;正在Java学习的路上摸爬滚打,记录学习的过程~ 个人主页:.29.的博客 学习社区:进去逛一逛~ 向域对象共享数据一、使用 原生ServletAPI二、…...
】实验3 - Activity及数据存储)
本科课程【移动互联网应用开发(Android开发)】实验3 - Activity及数据存储
大家好,我是【1+1=王】, 热爱java的计算机(人工智能)渣硕研究生在读。 如果你也对java、人工智能等技术感兴趣,欢迎关注,抱团交流进大厂!!! Good better best, never let it rest, until good is better, and better best. 近期会把自己本科阶段的一些课程设计、实验报…...

为何在 node 项目中使用固定版本号,而不使用 ~、^?
以语雀 文档为准 使用 ~、^ 时吃过亏希望版本号掌握在自己手里,作者自己升级(跟随官方进行升级,就算麻烦作者,也不想麻烦使用者)虽然 pnpm 很好用,但是不希望在项目中用到(临时性解决问题可以选…...
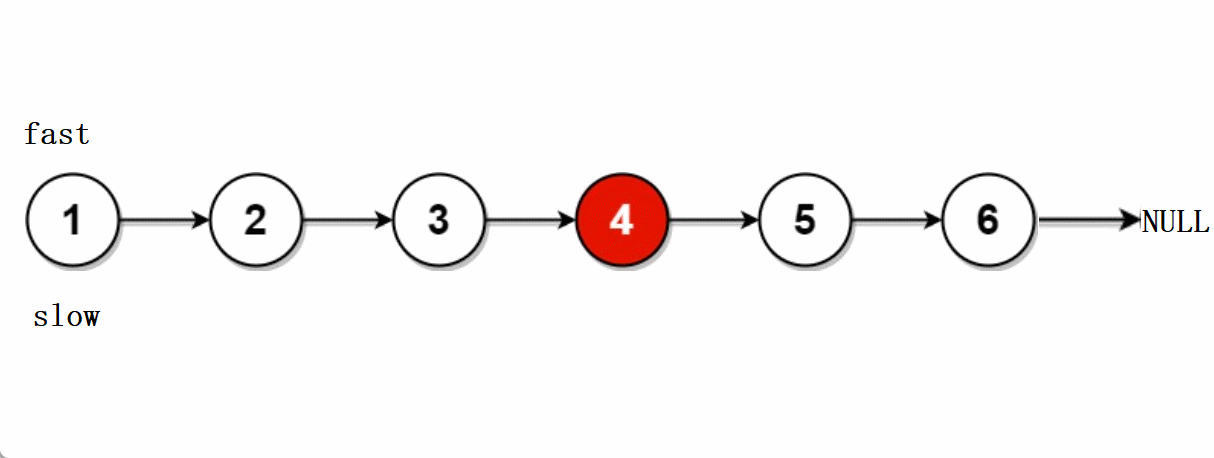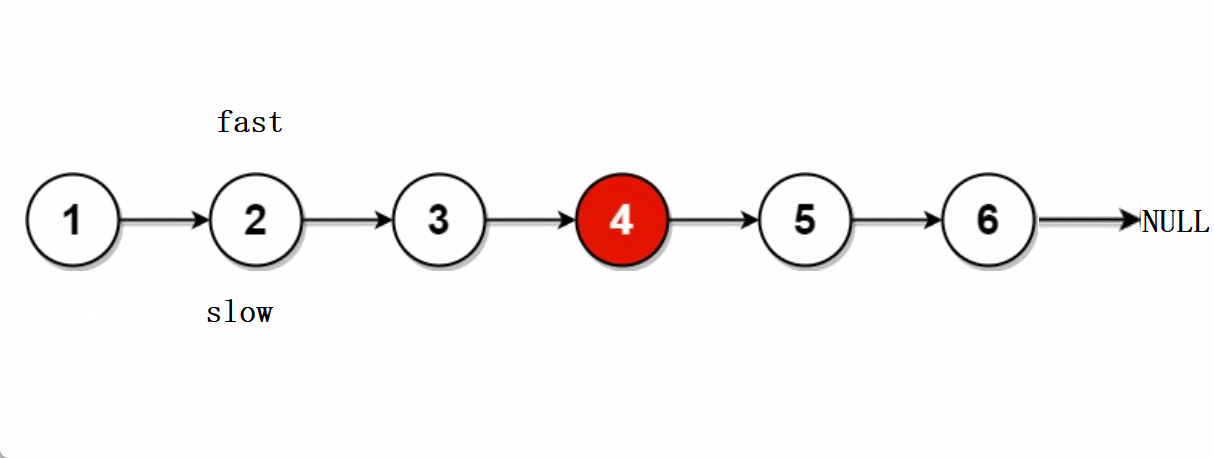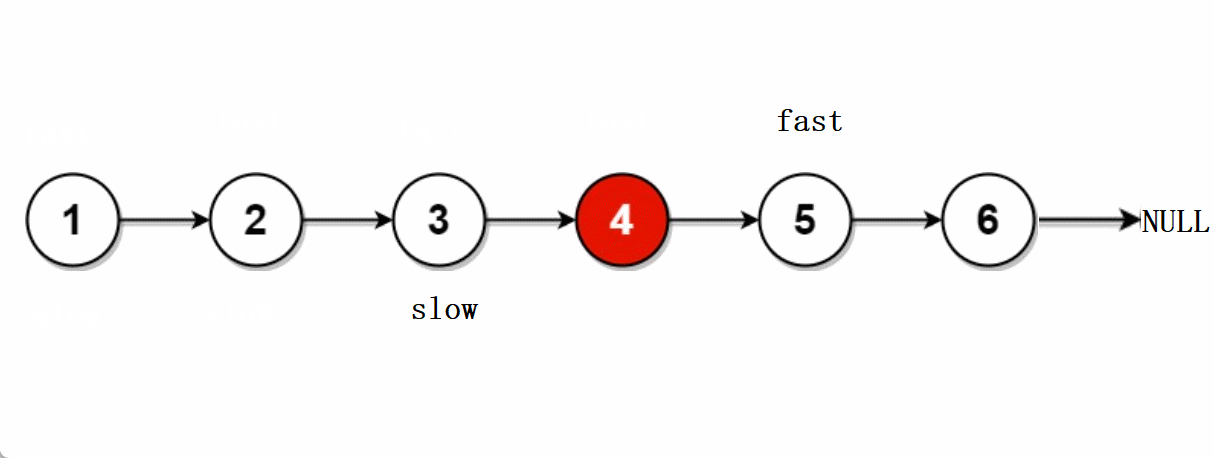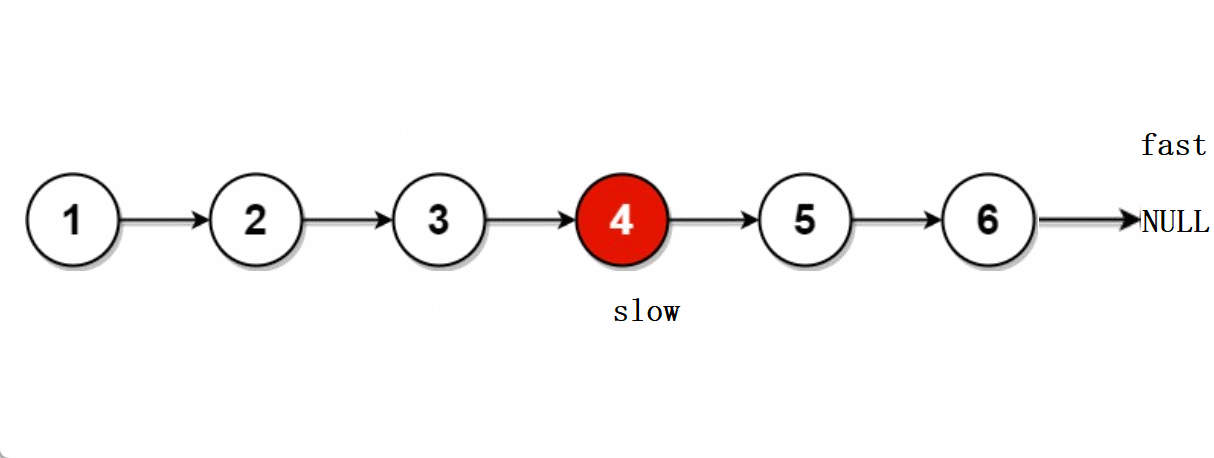
leetcode -- 876.链表的中间节点
文章目录🐨1.题目🐇2. 解法1-两次遍历🍀2.1 思路🍀2.2 代码实现🐁3. 解法2-快慢指针🌾3.1 思路🌾3.2 **代码实现**🐮4. 题目链接🐨1.题目 给你单链表的头结点head&#…...

企业网络安全防御策略需要考虑哪些方面?
随着企业数字化转型的加速,企业网络安全面临越来越多的威胁。企业网络安全不仅仅关乎企业数据的安全,还关系到企业的声誉和利益,因此,建立全面的网络安全防御策略至关重要。 企业网络安全防御策略的实现需要考虑以下几个方面&…...
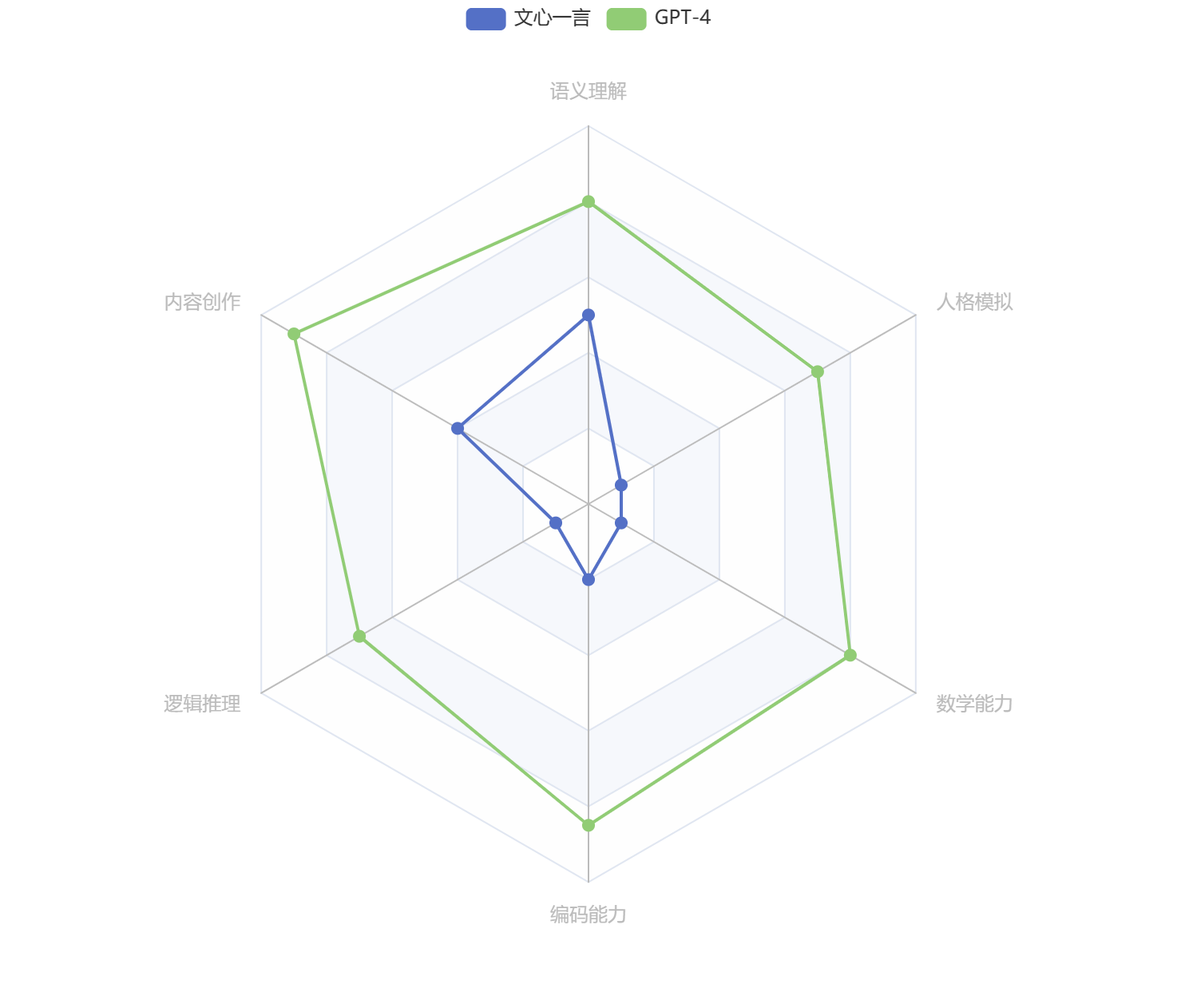
文心一言 vs. GPT-4 —— 全面横向比较
文心一言 vs. GPT-4 —— 全面横向比较 3月15日凌晨,OpenAI发布“迄今为止功能最强大的模型”——GPT-4。我第一时间为大家奉上了体验报告《OpenAI 发布GPT-4——全网抢先体验》。 时隔一日,3月16日下午百度发布大语言模型——文心一言。发布会上&…...
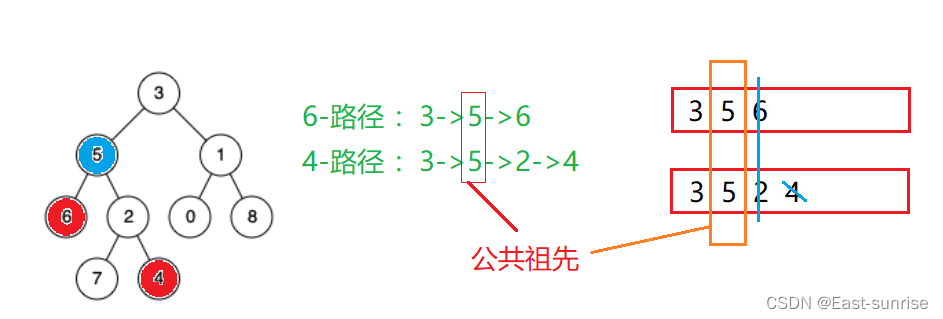
【进阶数据结构】二叉搜索树经典习题讲解
🌈感谢阅读East-sunrise学习分享——[进阶数据结构]二叉搜索树 博主水平有限,如有差错,欢迎斧正🙏感谢有你 码字不易,若有收获,期待你的点赞关注💙我们一起进步 🌈我们在之前已经学习…...
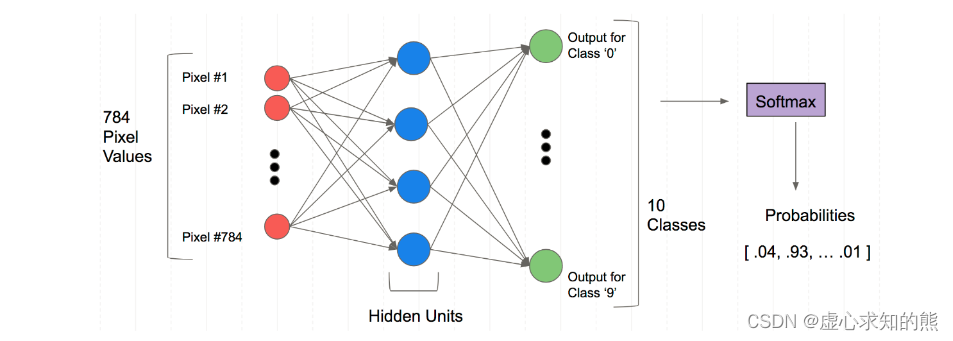
PyTorch 之 神经网络 Mnist 分类任务
文章目录一、Mnist 分类任务简介二、Mnist 数据集的读取三、 Mnist 分类任务实现1. 标签和简单网络架构2. 具体代码实现四、使用 TensorDataset 和 DataLoader 简化本文参加新星计划人工智能(Pytorch)赛道:https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/613989052 一、Mnist 分类任…...

如何实现用pillow库来实现给图片加滤镜?
使用Pillow库可以非常容易地给图片加滤镜。Pillow库是Python图像处理的一个强大库,提供了多种滤镜效果,如模糊、边缘检测、色彩增强等。 下面是使用Pillow库实现给图片加滤镜的简单步骤: 安装Pillow库:首先需要安装Pillow库。可…...

[特殊字符] 智能合约中的数据是如何在区块链中保持一致的?
🧠 智能合约中的数据是如何在区块链中保持一致的? 为什么所有区块链节点都能得出相同结果?合约调用这么复杂,状态真能保持一致吗?本篇带你从底层视角理解“状态一致性”的真相。 一、智能合约的数据存储在哪里…...

内存分配函数malloc kmalloc vmalloc
内存分配函数malloc kmalloc vmalloc malloc实现步骤: 1)请求大小调整:首先,malloc 需要调整用户请求的大小,以适应内部数据结构(例如,可能需要存储额外的元数据)。通常,这包括对齐调整,确保分配的内存地址满足特定硬件要求(如对齐到8字节或16字节边界)。 2)空闲…...
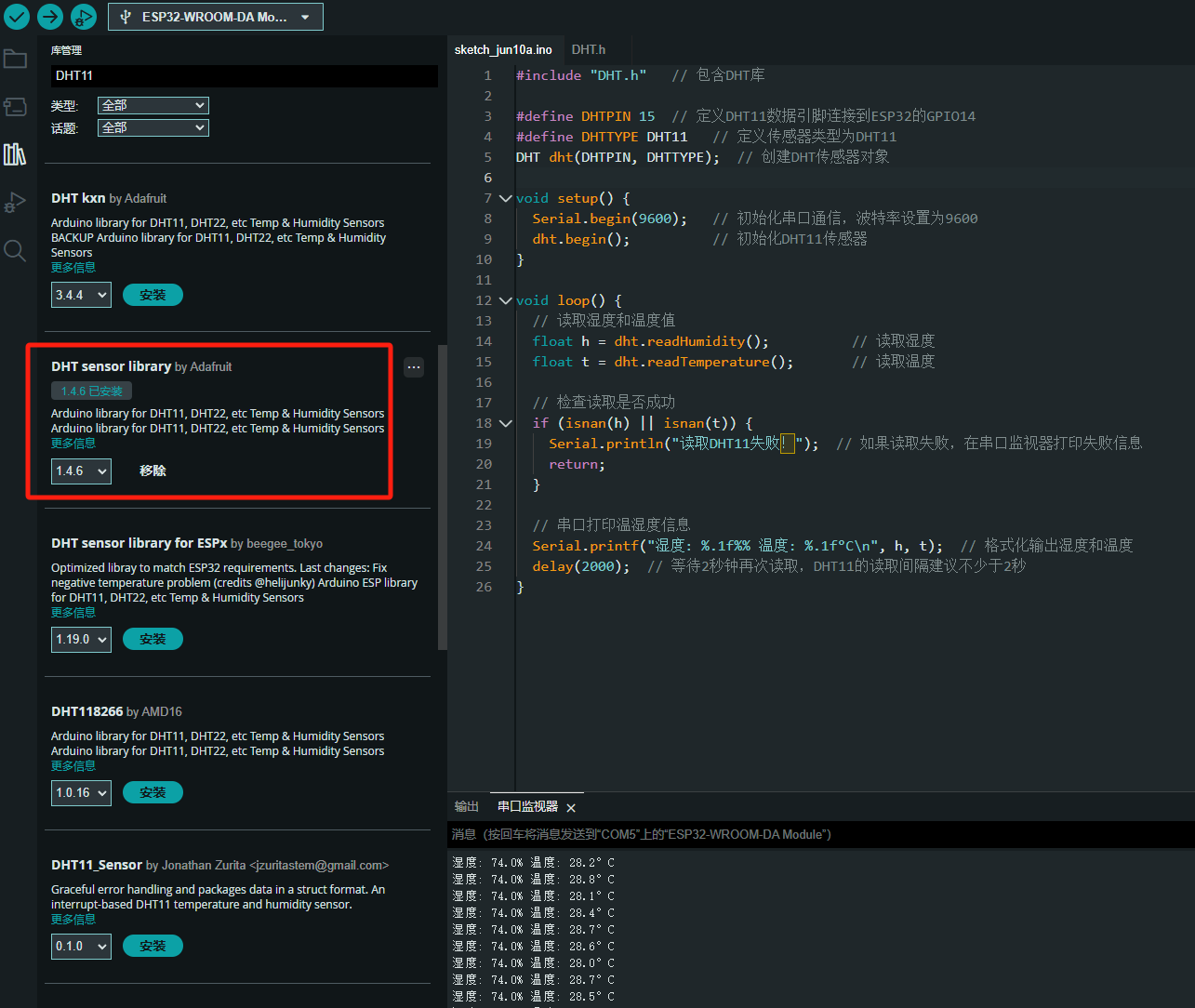
ESP32读取DHT11温湿度数据
芯片:ESP32 环境:Arduino 一、安装DHT11传感器库 红框的库,别安装错了 二、代码 注意,DATA口要连接在D15上 #include "DHT.h" // 包含DHT库#define DHTPIN 15 // 定义DHT11数据引脚连接到ESP32的GPIO15 #define D…...

Unit 1 深度强化学习简介
Deep RL Course ——Unit 1 Introduction 从理论和实践层面深入学习深度强化学习。学会使用知名的深度强化学习库,例如 Stable Baselines3、RL Baselines3 Zoo、Sample Factory 和 CleanRL。在独特的环境中训练智能体,比如 SnowballFight、Huggy the Do…...
使用 SymPy 进行向量和矩阵的高级操作
在科学计算和工程领域,向量和矩阵操作是解决问题的核心技能之一。Python 的 SymPy 库提供了强大的符号计算功能,能够高效地处理向量和矩阵的各种操作。本文将深入探讨如何使用 SymPy 进行向量和矩阵的创建、合并以及维度拓展等操作,并通过具体…...

Pinocchio 库详解及其在足式机器人上的应用
Pinocchio 库详解及其在足式机器人上的应用 Pinocchio (Pinocchio is not only a nose) 是一个开源的 C 库,专门用于快速计算机器人模型的正向运动学、逆向运动学、雅可比矩阵、动力学和动力学导数。它主要关注效率和准确性,并提供了一个通用的框架&…...

Java + Spring Boot + Mybatis 实现批量插入
在 Java 中使用 Spring Boot 和 MyBatis 实现批量插入可以通过以下步骤完成。这里提供两种常用方法:使用 MyBatis 的 <foreach> 标签和批处理模式(ExecutorType.BATCH)。 方法一:使用 XML 的 <foreach> 标签ÿ…...
逻辑回归暴力训练预测金融欺诈
简述 「使用逻辑回归暴力预测金融欺诈,并不断增加特征维度持续测试」的做法,体现了一种逐步建模与迭代验证的实验思路,在金融欺诈检测中非常有价值,本文作为一篇回顾性记录了早年间公司给某行做反欺诈预测用到的技术和思路。百度…...

2025年- H71-Lc179--39.组合总和(回溯,组合)--Java版
1.题目描述 2.思路 当前的元素可以重复使用。 (1)确定回溯算法函数的参数和返回值(一般是void类型) (2)因为是用递归实现的,所以我们要确定终止条件 (3)单层搜索逻辑 二…...
Java中HashMap底层原理深度解析:从数据结构到红黑树优化
一、HashMap概述与核心特性 HashMap作为Java集合框架中最常用的数据结构之一,是基于哈希表的Map接口非同步实现。它允许使用null键和null值(但只能有一个null键),并且不保证映射顺序的恒久不变。与Hashtable相比,Hash…...
