Gazebo之MyRobot建立
Gazebo之MyRobot建立
- 1. 源由
- 2. 示例
- Step 1: 新建一个简单世界
- Step 2: 新建一个模型(model)
- Step 3: 机器人组成链接(Links)
- Step 3.1: 新增底盘(Links/Chassis)
- Step 3.1.1: 惯性属性(Inertial properties)
- Step 3.1.2: 视觉(Visual)
- Step 3.1.3: 碰撞(Collision)
- Step 3.2: 新增左轮(Links/Left wheel)
- Step 3.2.1: 惯性属性(Inertial properties)
- Step 3.2.2: 视觉(Visual)
- Step 3.2.3: 碰撞(Collision)
- Step 3.3: 新增右轮(Links/Right wheel)
- Step 3.3.1: 惯性属性(Inertial properties)
- Step 3.3.2: 视觉(Visual)
- Step 3.3.3: 碰撞(Collision)
- Step 3.4: 添加任意框架
- Step 3.5: 添加滑轮
- Step 3.5.1 惯性属性(Inertial properties)
- Step 3.5.2 视觉(Visual)
- Step 3.5.3 碰撞(Collision)
- Step 4: 链接关节(links)
- Step 4.1: 添加 Left wheel joint
- Step 4.1.1: 链接连接
- Step 4.1.2: 定义旋转轴
- Step 4.2: 添加 Right wheel joint
- Step 4.3: 添加 Caster wheel joint
- Step 5: 简单验证
- Step 6: 移动机器人
- Step 6.1: 添加 Diff_drive plugin
- Step 6.2: 测试键值
- Step 6.3: 添加 Triggered publisher plugin
- Step 7: 简单测试
- 3. 参考资料
1. 源由
在本章中,将学习如何在 SDFormat 中构建一个简单的两轮机器人。
注:SDFormat(Simulation Description Format),有时简称为 SDF,是一种 XML 格式,用于描述机器人模拟器、可视化和控制的对象和环境。
2. 示例
Step 1: 新建一个简单世界
从构建一个简单的世界开始,然后在其中构建我们的机器人。打开一个名为 empty_world.sdf 的新文件,并将以下代码复制到其中。
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<sdf version="1.10"><world name="car_world"><physics name="1ms" type="ignored"><max_step_size>0.001</max_step_size><real_time_factor>1.0</real_time_factor></physics><pluginfilename="gz-sim-physics-system"name="gz::sim::systems::Physics"></plugin><pluginfilename="gz-sim-user-commands-system"name="gz::sim::systems::UserCommands"></plugin><pluginfilename="gz-sim-scene-broadcaster-system"name="gz::sim::systems::SceneBroadcaster"></plugin><light type="directional" name="sun"><cast_shadows>true</cast_shadows><pose>0 0 10 0 0 0</pose><diffuse>0.8 0.8 0.8 1</diffuse><specular>0.2 0.2 0.2 1</specular><attenuation><range>1000</range><constant>0.9</constant><linear>0.01</linear><quadratic>0.001</quadratic></attenuation><direction>-0.5 0.1 -0.9</direction></light><model name="ground_plane"><static>true</static><link name="link"><collision name="collision"><geometry><plane><normal>0 0 1</normal></plane></geometry></collision><visual name="visual"><geometry><plane><normal>0 0 1</normal><size>100 100</size></plane></geometry><material><ambient>0.8 0.8 0.8 1</ambient><diffuse>0.8 0.8 0.8 1</diffuse><specular>0.8 0.8 0.8 1</specular></material></visual></link></model></world>
</sdf>
保存文件,导航到保存文件的目录并启动模拟器:
$ gz sim empty_world.sdf
注:一个只有地面和阳光的空世界。
Step 2: 新建一个模型(model)
- 定义了模型的名称 vehicle_blue,它应该在其同级(其他标签或同级模型)中是唯一的。
- 每个模型可以有一个链接被指定为 canonical_link,模型的隐式框架附加到这个链接上。
- 如果未定义,则第一个
<link>将被选择为 canonical_link。 <pose>标签用于定义模型的位置和方向,relative_to属性用于定义模型相对于任何其他框架的姿态。- 如果未定义
relative_to,则模型的<pose>将相对于世界。 <pose>标签内的值如下:<pose>X Y Z R P Y</pose>,其中 X Y Z 表示框架的位置,R P Y 表示横滚、俯仰、偏航的方向。我们将它们设置为零,使两个框架(模型和世界)相同。
<model name='vehicle_blue' canonical_link='chassis'><pose relative_to='world'>0 0 0 0 0 0</pose>
Step 3: 机器人组成链接(Links)
Step 3.1: 新增底盘(Links/Chassis)
定义第一个链接,即我们汽车的底盘,以及它相对于模型的姿态。
<link name='chassis'><pose relative_to='__model__'>0.5 0 0.4 0 0 0</pose>
Step 3.1.1: 惯性属性(Inertial properties)
在这里,定义了底盘的惯性属性,如 <mass> 和 <inertia> 矩阵。使用此工具可以计算基本形状的惯性矩阵的值。
<inertial> <!--inertial properties of the link mass, inertia matix--><mass>1.14395</mass><inertia><ixx>0.095329</ixx><ixy>0</ixy><ixz>0</ixz><iyy>0.381317</iyy><iyz>0</iyz><izz>0.476646</izz></inertia></inertial>
Step 3.1.2: 视觉(Visual)
- 顾名思义,
<visual>标签负责定义链接的外观。 - 首先,在
<geometry>标签内将链接的形状定义为一个<box>(长方体),然后在<size>标签内指定这个盒子的三个维度(以米为单位)。 - 接着,在
<material>标签内定义链接的材质。- 定义了
<ambient>、<diffuse>和<specular>颜色,每个颜色用一组四个数字表示,分别为红色/绿色/蓝色/透明度,范围在 [0, 1] 之间。
- 定义了
<visual name='visual'><geometry><box><size>2.0 1.0 0.5</size></box></geometry><!--let's add color to our link--><material><ambient>0.0 0.0 1.0 1</ambient><diffuse>0.0 0.0 1.0 1</diffuse><specular>0.0 0.0 1.0 1</specular></material></visual>
Step 3.1.3: 碰撞(Collision)
<collision> 标签定义了链接的碰撞属性,即链接如何与其他物体发生碰撞以及物理引擎对其的影响。
<collision name='collision'><geometry><box><size>2.0 1.0 0.5</size></box></geometry></collision></link>
</model>
注:<collision> 可以与视觉属性不同,例如,通常使用更简单的碰撞模型来减少计算时间。
Step 3.2: 新增左轮(Links/Left wheel)
- 为机器人添加左轮。
- 以下代码应放在 标签之后和 标签之前。所有属于同一模型的链接和关节应在 之前定义。
- 定义链接的名称为 left_wheel,然后将其
<pose>相对于底盘链接进行定义。 - 由于轮子需要放置在底盘的左后方,因此我们选择了
<pose>的值为 -0.5 0.6 0。 - 轮子是一个圆柱体,但它侧放着。因此我们将方向值定义为 -1.5707 0 0,这是绕 x 轴旋转 -90 度(角度以弧度为单位)。
<link name='left_wheel'><pose relative_to="chassis">-0.5 0.6 0 -1.5707 0 0</pose>
Step 3.2.1: 惯性属性(Inertial properties)
<inertial><mass>1</mass><inertia><ixx>0.043333</ixx><ixy>0</ixy><ixz>0</ixz><iyy>0.043333</iyy><iyz>0</iyz><izz>0.08</izz></inertia></inertial>
Step 3.2.2: 视觉(Visual)
<visual name='visual'><geometry><cylinder><radius>0.4</radius><length>0.2</length></cylinder></geometry><material><ambient>1.0 0.0 0.0 1</ambient><diffuse>1.0 0.0 0.0 1</diffuse><specular>1.0 0.0 0.0 1</specular></material></visual>
Step 3.2.3: 碰撞(Collision)
<collision name='collision'><geometry><cylinder><radius>0.4</radius><length>0.2</length></cylinder></geometry></collision>
Step 3.3: 新增右轮(Links/Right wheel)
- 为机器人添加右轮。
- 以下代码应放在 标签之后和 标签之前。所有属于同一模型的链接和关节应在 之前定义。
- 定义链接的名称为 left_wheel,然后将其
<pose>相对于底盘链接进行定义。 - 由于轮子需要放置在底盘的右后方,因此我们选择了
<pose>的值为 -0.5 -0.6 0。 - 轮子是一个圆柱体,但它侧放着。因此我们将方向值定义为 -1.5707 0 0,这是绕 x 轴旋转 -90 度(角度以弧度为单位)。
<!--The same as left wheel but with different position-->
<link name='right_wheel'><pose relative_to="chassis">-0.5 -0.6 0 -1.5707 0 0</pose> <!--angles are in radian-->
Step 3.3.1: 惯性属性(Inertial properties)
<inertial><mass>1</mass><inertia><ixx>0.043333</ixx><ixy>0</ixy><ixz>0</ixz><iyy>0.043333</iyy><iyz>0</iyz><izz>0.08</izz></inertia></inertial>
Step 3.3.2: 视觉(Visual)
<visual name='visual'><geometry><cylinder><radius>0.4</radius><length>0.2</length></cylinder></geometry><material><ambient>1.0 0.0 0.0 1</ambient><diffuse>1.0 0.0 0.0 1</diffuse><specular>1.0 0.0 0.0 1</specular></material></visual>
Step 3.3.3: 碰撞(Collision)
<collision name='collision'><geometry><cylinder><radius>0.4</radius><length>0.2</length></cylinder></geometry></collision>
Step 3.4: 添加任意框架
任意框架需要两个属性:
name: 框架的名称attached_to: 该框架附加到的框架或链接的名称
给框架命名为 caster_frame,并将其附加到底盘链接上,然后使用 <pose> 标签来定义框架的位置和方向。
注:没有使用 relative_to 属性,因此姿态是相对于 attached_to 属性中指定的框架,即在我们这个例子中是底盘。
<frame name="caster_frame" attached_to='chassis'><pose>0.8 0 -0.2 0 0 0</pose>
</frame>
Step 3.5: 添加滑轮
其姿态是相对于我们上面定义的 caster_frame 框架。
<pose>标签而没有定义位置或方向;在这种情况下,链接的姿态与relative_to框架的姿态相同(即为单位姿态)。
<!--caster wheel-->
<link name='caster'><pose relative_to='caster_frame'/>
Step 3.5.1 惯性属性(Inertial properties)
<inertial><mass>1</mass><inertia><ixx>0.016</ixx><ixy>0</ixy><ixz>0</ixz><iyy>0.016</iyy><iyz>0</iyz><izz>0.016</izz></inertia></inertial>
Step 3.5.2 视觉(Visual)
<visual name='visual'><geometry><sphere><radius>0.2</radius></sphere></geometry><material><ambient>0.0 1 0.0 1</ambient><diffuse>0.0 1 0.0 1</diffuse><specular>0.0 1 0.0 1</specular></material></visual>
Step 3.5.3 碰撞(Collision)
<collision name='collision'><geometry><sphere><radius>0.2</radius></sphere></geometry></collision>
Step 4: 链接关节(links)
最后需要将这些链接连接在一起,这就需要用到 标签。 标签将两个链接连接在一起,并定义它们相互之间的运动方式。在 标签内,我们需要定义要连接的两个链接及其关系(运动方式)。
Step 4.1: 添加 Left wheel joint
第一个关节是 left_wheel_joint。它有两个属性:name='left_wheel_joint' 和 type='revolute'。revolute 类型提供一个具有关节限制的旋转自由度。关节的姿态与子链接框架相同,即 left_wheel 框架。
<joint name='left_wheel_joint' type='revolute'><pose relative_to='left_wheel'/>
Step 4.1.1: 链接连接
将两个链接(实体)连接在一起。在这里,我们将底盘与左轮连接。底盘是父链接,左轮是子链接。
<parent>chassis</parent><child>left_wheel</child>
Step 4.1.2: 定义旋转轴
- 旋转轴可以是任何框架,不仅仅是父链接或子链接。
- 我们选择相对于模型框架的 y 轴,因此我们在 y 元素中放置 1,在其他元素中放置 0。对于旋转关节,我们需要在
<lower>和<upper>标签中定义旋转角度的<limits>。
<axis><xyz expressed_in='__model__'>0 1 0</xyz> <!--can be defined as any frame or even arbitrary frames--><limit><lower>-1.79769e+308</lower> <!--negative infinity--><upper>1.79769e+308</upper> <!--positive infinity--></limit></axis>
</joint>
Step 4.2: 添加 Right wheel joint
right_wheel_joint 非常相似,不同之处在于关节的姿态。这个关节将右轮与底盘连接在一起。
<joint name='right_wheel_joint' type='revolute'><pose relative_to='right_wheel'/><parent>chassis</parent><child>right_wheel</child><axis><xyz expressed_in='__model__'>0 1 0</xyz><limit><lower>-1.79769e+308</lower> <!--negative infinity--><upper>1.79769e+308</upper> <!--positive infinity--></limit></axis>
</joint>
Step 4.3: 添加 Caster wheel joint
对于万向轮,需要不同类型的关节(连接)。这里使用了 type='ball',它提供三个旋转自由度。
<joint name='caster_wheel' type='ball'><parent>chassis</parent><child>caster</child>
</joint>
Step 5: 简单验证
$ gz sim building_robot.sdf

测试资料:[SnapLearnGazebo/lesson_02_sensor}(https://github.com/SnapDragonfly/SnapLearnGazebo/tree/main/lesson_02_sensor)
Step 6: 移动机器人
Step 6.1: 添加 Diff_drive plugin
diff_drive插件帮助控制机器人,特别是可以差速驱动的机器人。让我们在机器人上设置这个插件。
在building_robot.sdf文件基础上,新建一个moving_robot.sdf文件,并在vehicle_blue模型标签内添加以下代码。
<pluginfilename="gz-sim-diff-drive-system"name="gz::sim::systems::DiffDrive"><left_joint>left_wheel_joint</left_joint><right_joint>right_wheel_joint</right_joint><wheel_separation>1.2</wheel_separation><wheel_radius>0.4</wheel_radius><odom_publish_frequency>1</odom_publish_frequency><topic>cmd_vel</topic>
</plugin>
<plugin>标签有两个属性:
filename表示库文件的名称name表示插件的名称
在<left_joint>和<right_joint>标签中,我们定义了将左轮和右轮连接到机器人主体的关节,在我们的例子中分别是left_wheel_joint和right_wheel_joint。
<wheel_separation>表示两个轮子之间的距离。我们的机器人左轮位于相对于底盘y轴0.6米处,右轮位于-0.6米处,因此轮间距是1.2米。<wheel_radius>表示轮子的半径,该半径在轮链接下的<radius>标签中定义。<odom_publish_frequency>设置在/model/vehicle_blue/odometry上发布里程计的频率。cmd_vel是DiffDrive插件的输入<topic>。
Step 6.2: 测试键值
- 在一个终端启动机器人仿真环境:
$ gz sim building_robot.sdf
-
在仿真界面右上角查找Key publisher插件;并添加到右侧列表中。
-
在另一个终端打印topic值
$ gz topic -e -t /keyboard/keypress
可以获得按键与键值的对应关系:
- Left ← : 16777234
- Up ↑ : 16777235
- Right → : 16777236
- Down ↓ : 16777237
Step 6.3: 添加 Triggered publisher plugin
将每个箭头键(按键)与所需的消息(运动)进行映射:
- Left ➞ 16777234 ➞ linear: {x: 0.0}, angular: {z: 0.5}
- Up ➞ 16777235 ➞ linear: {x: 0.5}, angular: {z: 0.0}
- Right ➞ 16777236 ➞ linear: {x: 0.0}, angular: {z: -0.5}
- Down ➞ 16777237 ➞ linear: {x: -0.5}, angular: {z: 0.0}
<!-- Moving Forward--><!-- Moving Left--><plugin filename="gz-sim-triggered-publisher-system"name="gz::sim::systems::TriggeredPublisher"><input type="gz.msgs.Int32" topic="/keyboard/keypress"><match field="data">16777234</match></input><output type="gz.msgs.Twist" topic="/cmd_vel">linear: {x: 0.0}, angular: {z: 0.5}</output></plugin><!-- Moving Forward--><plugin filename="gz-sim-triggered-publisher-system"name="gz::sim::systems::TriggeredPublisher"><input type="gz.msgs.Int32" topic="/keyboard/keypress"><match field="data">16777235</match></input><output type="gz.msgs.Twist" topic="/cmd_vel">linear: {x: 0.5}, angular: {z: 0.0}</output></plugin><!-- Moving Right--><plugin filename="gz-sim-triggered-publisher-system"name="gz::sim::systems::TriggeredPublisher"><input type="gz.msgs.Int32" topic="/keyboard/keypress"><match field="data">16777236</match></input><output type="gz.msgs.Twist" topic="/cmd_vel">linear: {x: 0.0}, angular: {z: -0.5}</output></plugin><!-- Moving Backward--><plugin filename="gz-sim-triggered-publisher-system"name="gz::sim::systems::TriggeredPublisher"><input type="gz.msgs.Int32" topic="/keyboard/keypress"><match field="data">16777237</match></input><output type="gz.msgs.Twist" topic="/cmd_vel">linear: {x: -0.5}, angular: {z: 0.0}</output></plugin>
Step 7: 简单测试
$ gz sim moving_robot.sdf
测试资料:[SnapLearnGazebo/lesson_02_sensor}(https://github.com/SnapDragonfly/SnapLearnGazebo/tree/main/lesson_02_sensor)
3. 参考资料
【1】ArduPilot开源代码之ROS2Humble+CartographerSLAM+SITL+Gazebo
【2】ArduPilot飞控之Gazebo + SITL + MP的Jetson Orin环境搭建
【3】ArduPilot飞控之ubuntu22.04-Gazebo模拟
【4】PX4模块设计之七:Ubuntu 20.04搭建Gazebo模拟器
相关文章:

Gazebo之MyRobot建立
Gazebo之MyRobot建立 1. 源由2. 示例Step 1: 新建一个简单世界Step 2: 新建一个模型(model)Step 3: 机器人组成链接(Links)Step 3.1: 新增底盘(Links/Chassis)Step 3.1.1: 惯性属性(Inertial properties)Step 3.1.2: 视觉(Visual)Step 3.1.3: 碰撞(Collision) Step 3.2: 新增左…...
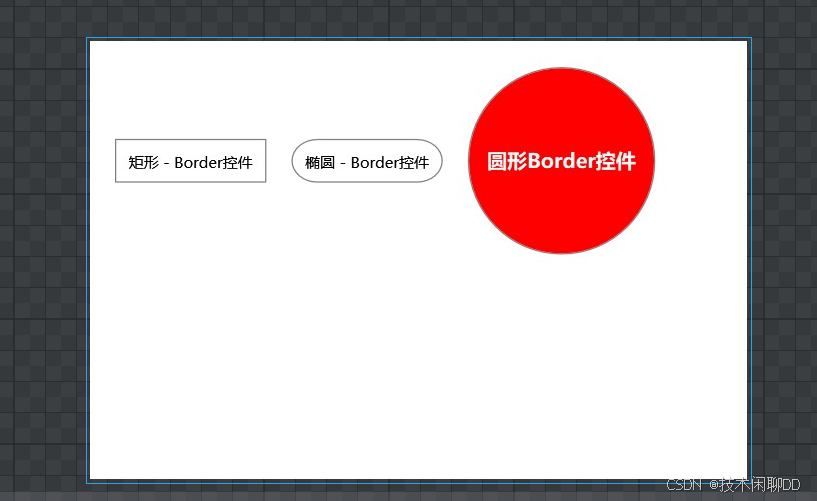
WPF学习(5)- Border控件(边框布局)+GridSplitter分割窗口
严格来说,Border并不是一个布局控件,因为它并不是Panel的子类,而是Decorator装饰器的子类,而Decorator继承于FrameworkElement。我们要先看看它的父类Decorator。 public class Decorator : FrameworkElement, IAddChild {public…...

ADAS芯片及方案
一 ADAS芯片及方案 1.1 高通SA8775P Snapdragon Ride Flex(SA8775P)舱驾融合平台可通过单颗SoC同时支持数字座舱和智能驾驶功能,在CPU、GPU、NPU的处理能力方面具备强大的性能表现与领先优势,支持实现复杂的智能座舱功能&#x…...

5 mysql 查询语句
1.DML:对数据进行增删改查 提示:Execute执行 Execute and Suppress 执行并且抑制这个警告 person表的结构 /* DML:Data Manipulation Language 数据操作语言,对数据进行 增删改查操作,因为査询的操作太频繁和复杂,将…...

从网络上下载并展示图像数据
一、代码 from PIL import Image import requests from io import BytesIO import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimage_url "https://www.alleycat.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/FELV-cat.jpg" response requests.get(image_url) # response.content 获取 HTTP 响…...

Machine-Learning 机器学习
目录 基本概念与分类 工作原理 应用领域 发展趋势 机器学习中的深度学习是如何工作的,以及它如何影响其他机器学习算法? 在机器学习中,哪些特定的数据预处理技术最有效,特别是在处理大规模数据集时? 强化学习在…...

CSP 2023 普及组第一轮 - CSP/S 2023初试题 基础部分解析
第 1 题 在 C 中,下面哪个关键字用于声明一个变量, 其值不能被修改?(B) A. unsigned B. const C. static D. mutable 【const声明的变量不可修改】 第 2 题 八进制数 12345670(8) 和 07654321(8) 的和为(D) A. 222222…...

解锁IPython的跨平台魔法:深入探索%%script命令的神秘力量
IPython 的 %%script 魔法命令是一种强大的工具,它允许你在 IPython 环境中执行外部脚本。这个特性特别适用于需要在 IPython Notebook 中直接与 Web 技术交互的场景。下面我将为你详细介绍 %%script 命令的使用方法,并通过代码示例展示其强大功能。 一…...

如何避免项目发布后用户从浏览器WebPack中看到源码
打包前在config->index.js中设置productionSourceMap为false productionSourceMap: false,...

java学习19VUE
VUE NPM npm的全称是Node Package Manager 中文名为Node.js包管理器,是一个NodeJS包管理和分发工具,已经成为了非官方的发布Node模块(包)的标准。NPM可以方便地从一个全球的代码库中获取并安装Node.js模块,这些模块可以用于构建应用程序、…...
哨兵、集群)
Redis7(四)哨兵、集群
哨兵 吹哨人巡查监控后台master主机是否故障,如果故障了根据投票数自动将某一个从库转换为主库,继续对外服务 哨兵的作用: 监控redis运行状态,包括master和slave当master宕机了,能自动将slave转换为master 哨兵的功能…...

校园课程助手【3】-使用枚举类封装异常优雅处理全局异常
接着2中登录模块补充一个点: //可以看到这里返回给前端控制器的是一个类而不是html页面public RespBean doLogin(Valid LoginVo loginVo, HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response){return userService.doLogin(loginVo, request, response);}首先…...

LeetCode面试150——58最后一个单词的长度
题目难度:简单 默认优化目标:最小化平均时间复杂度。 Python默认为Python3。 目录 1 题目描述 2 题目解析 3 算法原理及代码实现 3.1 反向遍历 参考文献 1 题目描述 给你一个字符串 s,由若干单词组成,单词前后用一些空格字…...

MySQL——数据库的操作,数据类型,表的操作
MySQL——数据库的操作,数据类型,表的操作 1. 数据库的操作1.1 显示当前数据库1.2 创建数据库舍弃当前所写的SQL语句查看当前数据库服务全局的默认字符集 1.3 使用数据库1.4 查看当前操作的数据库查看MySQL的帮助 1.5 删除数据库 2. 常见数据类型2.1 数值…...

Go 临界资源 安全问题
临界资源安全的问题: 临界资源: 指并发环境中多个 进程/线程/协程 可以共享(都可以调用)的资源/变量,如果在并发环境中处理不当,就会造成一些 严重、问题 func main() {//临界资源a : 10go func() {a 100f…...

安卓常用控件(上)
文章目录 TextViewButtonEditText TextView textview主要用于在界面上显示一段文本信息。 属性名描述id给当前控件定义一个唯一的标识符。layout_width给控件指定一个宽度。match_parent:控件大小与父布局一样;wrap_content:控件大小刚好够包…...

基于 RabbitMQ 实现延迟消息的订单处理流程
文章目录 订单创建流程1. 商品查询与订单数据初始化2. 总价计算与订单保存3. 扣减库存与购物车清理4. 延迟消息与支付状态检测 订单延迟消息监听器支付成功与订单取消1. 订单支付成功2. 订单取消与库存恢复 总结 在现代电商系统中,订单处理是一个复杂且关键的环节。…...

使用Python将Word文档转换为PNG图片
在这篇博客中,我将介绍一个使用Python编写的小工具,它能够将指定文件夹中的所有Word文档(.doc和.docx格式)转换为PNG图片。这个工具基于wxPython库构建图形用户界面,并结合了win32com和PyMuPDF库实现文档格式的转换。接…...

Qt创建Json对象时浮点数的精度控制
我们在Qt中使用Json都是使用QJsonDocument、QJsonArray、QJsonObject、QJsonValue等类。 当我们在QJsonObject中插入浮点数字段时,会发现浮点数的小数位数很长,如下所示: #include <QJsonDocument> #include <QJsonArray> #incl…...

【海贼王航海日志:前端技术探索】CSS你了解多少?(二)
目录 1 -> 字体属性 1.1 -> 设置字体 1.2 -> 字体大小 1.3 -> 字体粗细 1.4 -> 文字样式 2 -> 文本属性 2.1 -> 文本颜色 2.1.1 -> 认识RGB 2.1.2 -> 设置文本颜色 2.2 -> 文本对齐 2.3 -> 文本装饰 2.4 -> 文本缩进 2.5 -&g…...
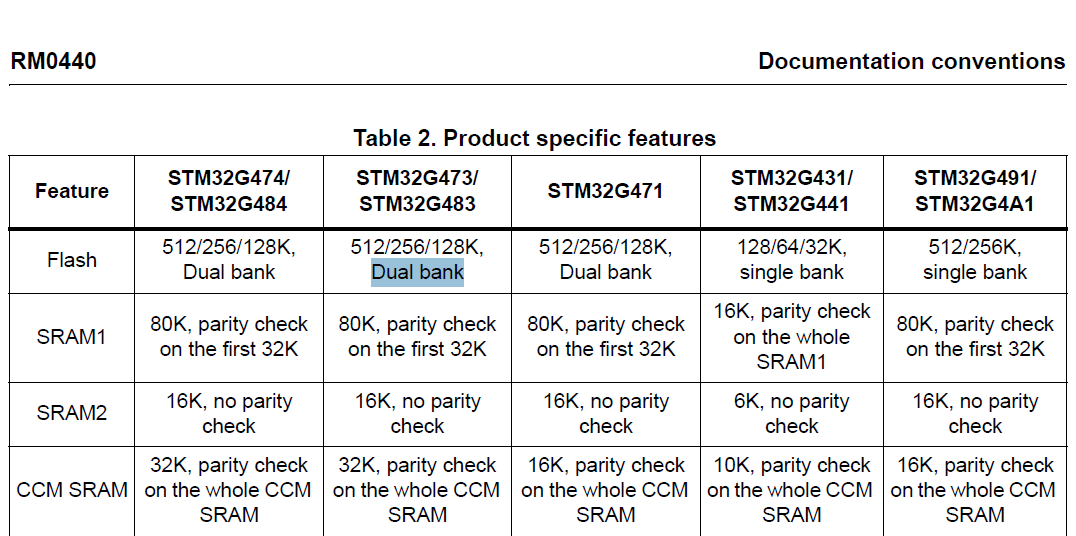
stm32G473的flash模式是单bank还是双bank?
今天突然有人stm32G473的flash模式是单bank还是双bank?由于时间太久,我真忘记了。搜搜发现,还真有人和我一样。见下面的链接:https://shequ.stmicroelectronics.cn/forum.php?modviewthread&tid644563 根据STM32G4系列参考手…...

iPhone密码忘记了办?iPhoneUnlocker,iPhone解锁工具Aiseesoft iPhone Unlocker 高级注册版分享
平时用 iPhone 的时候,难免会碰到解锁的麻烦事。比如密码忘了、人脸识别 / 指纹识别突然不灵,或者买了二手 iPhone 却被原来的 iCloud 账号锁住,这时候就需要靠谱的解锁工具来帮忙了。Aiseesoft iPhone Unlocker 就是专门解决这些问题的软件&…...

蓝牙 BLE 扫描面试题大全(2):进阶面试题与实战演练
前文覆盖了 BLE 扫描的基础概念与经典问题蓝牙 BLE 扫描面试题大全(1):从基础到实战的深度解析-CSDN博客,但实际面试中,企业更关注候选人对复杂场景的应对能力(如多设备并发扫描、低功耗与高发现率的平衡)和前沿技术的…...
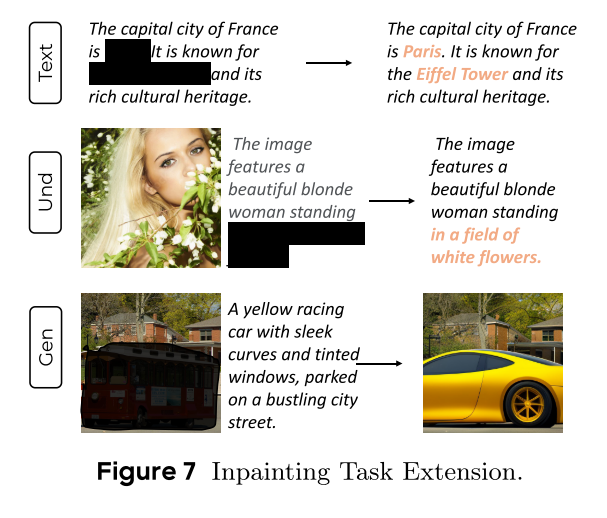
MMaDA: Multimodal Large Diffusion Language Models
CODE : https://github.com/Gen-Verse/MMaDA Abstract 我们介绍了一种新型的多模态扩散基础模型MMaDA,它被设计用于在文本推理、多模态理解和文本到图像生成等不同领域实现卓越的性能。该方法的特点是三个关键创新:(i) MMaDA采用统一的扩散架构…...
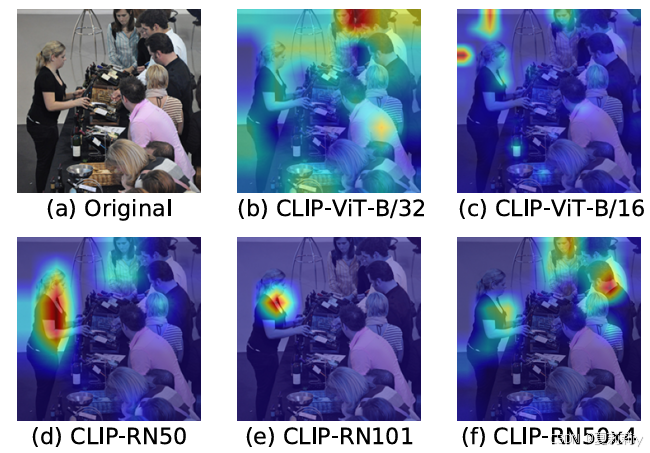

[ICLR 2022]How Much Can CLIP Benefit Vision-and-Language Tasks?
论文网址:pdf 英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用 目录 1. 心得 2. 论文逐段精读 2.1. Abstract 2…...
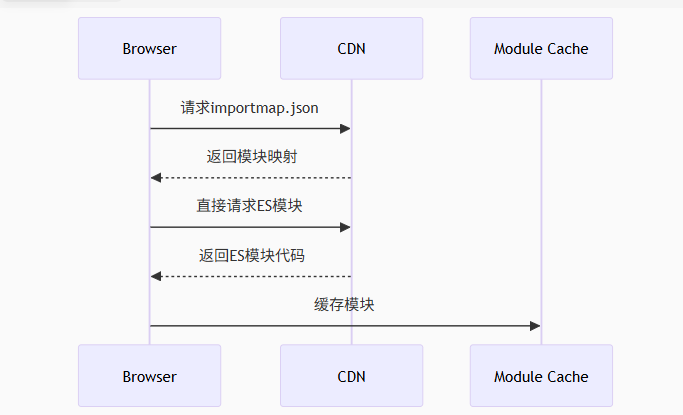
Module Federation 和 Native Federation 的比较
前言 Module Federation 是 Webpack 5 引入的微前端架构方案,允许不同独立构建的应用在运行时动态共享模块。 Native Federation 是 Angular 官方基于 Module Federation 理念实现的专为 Angular 优化的微前端方案。 概念解析 Module Federation (模块联邦) Modul…...

学习STC51单片机32(芯片为STC89C52RCRC)OLED显示屏2
每日一言 今天的每一份坚持,都是在为未来积攒底气。 案例:OLED显示一个A 这边观察到一个点,怎么雪花了就是都是乱七八糟的占满了屏幕。。 解释 : 如果代码里信号切换太快(比如 SDA 刚变,SCL 立刻变&#…...
)
.Net Framework 4/C# 关键字(非常用,持续更新...)
一、is 关键字 is 关键字用于检查对象是否于给定类型兼容,如果兼容将返回 true,如果不兼容则返回 false,在进行类型转换前,可以先使用 is 关键字判断对象是否与指定类型兼容,如果兼容才进行转换,这样的转换是安全的。 例如有:首先创建一个字符串对象,然后将字符串对象隐…...

laravel8+vue3.0+element-plus搭建方法
创建 laravel8 项目 composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel laravel8 8.* 安装 laravel/ui composer require laravel/ui 修改 package.json 文件 "devDependencies": {"vue/compiler-sfc": "^3.0.7","axios": …...
sipsak:SIP瑞士军刀!全参数详细教程!Kali Linux教程!
简介 sipsak 是一个面向会话初始协议 (SIP) 应用程序开发人员和管理员的小型命令行工具。它可以用于对 SIP 应用程序和设备进行一些简单的测试。 sipsak 是一款 SIP 压力和诊断实用程序。它通过 sip-uri 向服务器发送 SIP 请求,并检查收到的响应。它以以下模式之一…...
