beautifulsoup的简单使用
文章目录
- beautifulsoup
- 一. beautifulsoup的简单使用
- 1、安装
- 2、如何使用
- 3、对象的种类
- 二、beautifulsoup的遍历文档树
- 2.1 子节点
- .contents 和 .children
- descendants
- 2.2 节点内容
- .string
- .text
- 2.3 多个内容
- .strings
- **.stripped_strings**
- 2.4 父节点
- .parent
- .parents
- 三、beautiful的搜索文档树
- 3.1 find_all
- name 参数
- keyword 参数
- text 参数
- limit 参数
- 3.3 find()
- 3.4 find_parents() 和 find_parent()
- 四、beautifulsoup的css选择器
- 4.1 通过标签名查找
- 4.2 通过类名查找
- 4.3 id名查找
- 4.4 组合查找
- 4.5 属性查找
- 五.真实案例
- 1、使用 bs4提取豆瓣图书信息
- 2、匹配三国演义中的回合 并写入html文本中
- 3、匹配天气信息 城市与温度
- 4、匹配广州二手房 房源信息
beautifulsoup
一. beautifulsoup的简单使用
1、安装
Beautiful Soup支持Python标准库中的HTML解析器,还支持一些第三方的解析器,如果我们不安装它,则 Python 会使用 Python默认的解析器,lxml 解析器更加强大,速度更快,推荐安装。
pip install beautifulsoup4
2、如何使用
这是一个html的简单页面
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p><p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p><p class="story">...</p>
"""
使用BeautifulSoup解析这段代码,能够得到一个 BeautifulSoup 的对象,并能按照标准的缩进格式的结构输出:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'lxml')
# html进行美化
print(soup.prettify())

这里介绍几个简单的浏览结构化数据的方法
soup.title # 获取标签title
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title>soup.title.name # 获取标签名称
# 'title'soup.title.string # 获取标签title内的内容
# 'The Dormouse's story'soup.title.parent # 获取父级标签soup.title.parent.name # 获取父级标签名称
# 'head'soup.p
# <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>soup.p['class'] # 获取p的class属性值
# 'title'soup.a
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>soup.find_all('a')
# [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>,
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]soup.find(id="link3") # 获取id为link3的标签
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
3、对象的种类
Beautiful Soup将复杂HTML文档转换成一个复杂的树形结构,每个节点都是Python对象,所有对象可以归纳为种
Tag , NavigableString , BeautifulSoup , Comment .
- Tag
通俗点讲就是 HTML 中的一个个标签,Tag 对象与XML或HTML原生文档中的tag相同:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<b class="boldest">Extremely bold</b>')
tag = soup.b
type(tag)
# <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
- tag的名字
soup对象我以下面的例子为准,操作文档树最简单的方法就是告诉它你想获取的tag的name.如果想获取 标签,只要用 `soup.head
soup.head
# <head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>soup.title
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
- name和attributes属性
Tag有很多方法和属性,现在介绍一下tag中最重要的属性: name和attributes
每个tag都有自己的名字,通过 .name 来获取:
tag.name
# 'b'tag['class']
# 'boldest'tag.attrs
# {'class': 'boldest'}
tag的属性可以被添加,删除或修改. 再说一次, tag的属性操作方法与字典一样(了解)
tag['class'] = 'verybold'
tag['id'] = 1
tag
# <blockquote class="verybold" id="1">Extremely bold</blockquote>del tag['class']
del tag['id']
tag
# <blockquote>Extremely bold</blockquote>tag['class']
# KeyError: 'class'
print(tag.get('class'))
# None
- NavigableString(字符串)
我们既然已经得到了标签的内容,我们想获取具体标签内部的文字怎么办呢?
字符串常被包含在tag内.Beautiful Soup用NavigableString类来包装tag中的字符串。
tag.string
# 'Extremely bold'
type(tag.string)
# <class 'bs4.element.NavigableString'>
- BeautifulSoup
BeautifulSoup对象表示的是一个文档的全部内容.大部分时候,可以把它当作Tag对象,是一个特殊的 Tag,我们可以分别获取它的类型,名称,以及属性。
print(type(soup.name))
# <class 'str'>
print(soup.name)
# [document]
print(soup.attrs)
# {} 空字典
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, ‘html.parser’)
print(soup.a.string) # Elsie
print(type(soup.a.string)) # <class ‘bs4.element.Comment’>
二、beautifulsoup的遍历文档树
我们使用下面的例子,我们来演示下面的几个功能:
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head><body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p><p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p><p class="story">...</p>
"""from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser')
2.1 子节点
一个Tag可能包含多个字符串或其它的Tag,这些都是这个Tag的子节点.Beautiful Soup提供了许多操作和遍历子节点的属性.
.contents 和 .children
tag的 .contents 属性可以将tag的子节点以列表的方式输出:
head_tag = soup.head
head_tag
# <head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>head_tag.contents
[<title>The Dormouse's story</title>]title_tag = head_tag.contents[0]
title_tag
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
title_tag.contents
# [u'The Dormouse's story']
字符串没有 .contents 属性,因为字符串没有子节点:
text = title_tag.contents[0]
text.contents
# AttributeError: 'NavigableString' object has no attribute 'contents'
.children它返回的不是一个 list,不过我们可以通过遍历获取所有子节点。我们打印输出 .children 看一下,可以发现它是一个 list 生成器对象
通过tag的 .children 生成器,可以对tag的子节点进行循环:
print(title_tag.children) # <list_iterator object at 0x101b78860>
print(type(title_tag.children)) # <class 'list_iterator'>for child in title_tag.children:print(child)# The Dormouse's story
descendants
.contents 和 .children 属性仅包含tag的直接子节点.例如,<head>标签只有一个直接子节点<title>
head_tag.contents
# [<title>The Dormouse's story</title>]
但是<title>标签也包含一个子节点:字符串 “The Dormouse’s story”,这种情况下字符串 “The Dormouse’s story”也属于<head>标签的子孙节点.
.descendants 属性可以对所有tag的子孙节点进行递归循环 。
for child in head_tag.descendants:print(child)# <title>The Dormouse's story</title># The Dormouse's story
上面的例子中, <head>标签只有一个子节点,但是有2个子孙节点:<head>节点和<head>的子节点, BeautifulSoup 有一个直接子节点(<html>节点),却有很多子孙节点:
len(list(soup.children))
# 1
len(list(soup.descendants))
# 25
2.2 节点内容
.string
如果tag只有一个 NavigableString 类型子节点,那么这个tag可以使用 .string 得到子节点。如果一个tag仅有一个子节点,那么这个tag也可以使用 .string 方法,输出结果与当前唯一子节点的 .string 结果相同。
通俗点说就是:如果一个标签里面没有标签了,那么 .string 就会返回标签里面的内容。如果标签里面只有唯一的一个标签了,那么 .string 也会返回最里面的内容。例如:
print (soup.head.string)
#The Dormouse's story
# <title><b>The Dormouse's story</b></title>
print (soup.title.string)
#The Dormouse's story
如果tag包含了多个子节点,tag就无法确定,string 方法应该调用哪个子节点的内容, .string 的输出结果是 None
print (soup.html.string)
#None
.text
如果tag包含了多个子节点, text则会返回内部所有文本内容
print (soup.html.text)
注意:
strings和text都可以返回所有文本内容
区别:text返回内容为字符串类型 strings为生成器generator
2.3 多个内容
.strings .stripped_strings 属性
.strings
获取多个内容,不过需要遍历获取,比如下面的例子:
for string in soup.strings:print(repr(string))''''\n'
"The Dormouse's story"
'\n'
'\n'
"The Dormouse's story"
'\n'
'Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\n'
'Elsie'
',\n'
'Lacie'
' and\n'
'Tillie'
';\nand they lived at the bottom of a well.'
'\n'
'...'
'\n' '''
.stripped_strings
输出的字符串中可能包含了很多空格或空行,使用 .stripped_strings 可以去除多余空白内容
for string in soup.stripped_strings:print(repr(string))'''"The Dormouse's story"
"The Dormouse's story"
'Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were'
'Elsie'
','
'Lacie'
'and'
'Tillie'
';\nand they lived at the bottom of a well.'
'...''''
2.4 父节点
.parent
通过 .parent 属性来获取某个元素的父节点.在例子“爱丽丝”的文档中,<head>标签是<title>标签的父节点:
title_tag = soup.title
title_tag
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
title_tag.parent
# <head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
文档的顶层节点比如<html>的父节点是 BeautifulSoup 对象:
html_tag = soup.html
type(html_tag.parent)
# <class 'bs4.BeautifulSoup'>
.parents
通过元素的 .parents 属性可以递归得到元素的所有父辈节点,下面的例子使用了 .parents 方法遍历了<a>标签到根节点的所有节点.
link = soup.a
link
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>
for parent in link.parents:if parent is None:print(parent)else:print(parent.name)
# p
# body
# html
# [document]
# None
三、beautiful的搜索文档树
3.1 find_all
find_all( name , attrs , recursive , string , **kwargs )
-
name: 一个字符串或正则表达式,用于指定要查找的标签名称。如果传入 True,则匹配任何标签。
-
attrs: 一个字典或 None。如果传入字典,字典中的键值对将被用来匹配标签的属性。例如,{‘class’: ‘foo’} 将匹配所有具有 class=“foo” 属性的标签。
-
recursive: 一个布尔值。如果为 True(默认值),则在所有后代中递归搜索匹配的标签;如果为 False,则只在当前标签的直接子标签中搜索。
-
string: 一个字符串或正则表达式,用于匹配标签内的文本。如果传入字符串,Beautiful Soup 将查找包含该字符串的标签;如果传入正则表达式,则使用该正则表达式来匹配标签内的文本。
-
**kwargs: 额外的关键字参数,这些参数将被传递给 find_all 方法的内部实现,用于进一步定制搜索条件。
soup.find_all("title")
# [<title>The Dormouse's story</title>]soup.find_all("p", "title")
# [<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>]soup.find_all("a")
# [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>,
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]soup.find_all(id="link2")
# [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>]import re
# 模糊查询 包含sisters的就可以
soup.find(string=re.compile("sisters"))
# 'Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\n'
有几个方法很相似,还有几个方法是新的,参数中的 string 和 id 是什么含义? 为什么 find_all("p", "title") 返回的是CSS Class为”title”的<p>标签? 我们来仔细看一下 find_all() 的参数.
name 参数
name 参数可以查找所有名字为 name 的tag,字符串对象会被自动忽略掉.
简单的用法如下:
soup.find_all("title")
# [<title>The Dormouse's story</title>]
- <1> 传字符串
最简单的过滤器是字符串.在搜索方法中传入一个字符串参数,Beautiful Soup会查找与字符串完整匹配的内容,下面的例子用于查找文档中所有的标签
soup.find_all('b')
# [<b>The Dormouse's story</b>]
- <2> 传正则表达式
import re
for tag in soup.find_all(re.compile("^b")):print(tag.name)
# body
# b
- <3> 传列表
如果传入列表参数,Beautiful Soup会将与列表中任一元素匹配的内容返回.下面代码找到文档中所有<a>标签和<b>标签
soup.find_all(["a", "b"])
# [<b>The Dormouse's story</b>,
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>,
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
keyword 参数
如果一个指定名字的参数不是搜索内置的参数名,搜索时会把该参数当作指定名字tag的属性来搜索,如果包含一个名字为 id 的参数,Beautiful Soup会搜索每个tag的”id”属性.
soup.find_all(id='link2')
# [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>]import re
# 超链接包含elsie标签
print(soup.find_all(href=re.compile("elsie")))
# [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>]
# 以The作为开头的字符串
print(soup.find_all(text=re.compile("^The")))
# ["The Dormouse's story", "The Dormouse's story"]
# class选择器包含st的节点
print(soup.find_all(class_=re.compile("st")))
搜索指定名字的属性时可以使用的参数值包括 字符串 , 正则表达式 , 列表, True .
下面的例子在文档树中查找所有包含 id 属性的tag,无论 id 的值是什么:
soup.find_all(id=True)
# [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>,
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
使用多个指定名字的参数可以同时过滤tag的多个属性:
soup.find_all(href=re.compile("elsie"), id='link1')
# [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">three</a>]
在这里我们想用 class 过滤,不过 class 是 python 的关键词,这怎么办?加个下划线就可以:
print(soup.find_all("a", class_="sister"))'''
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
]'''
通过 find_all() 方法的 attrs 参数定义一个字典参数来搜索包含特殊属性的tag:
]
data_soup.find_all(attrs={"data-foo": "value"})
# [<div data-foo="value">foo!</div>]
注意:如何查看条件id和class同时存在时的写法
data_soup.find_all(attrs={"data-foo": "value"})
# [<div data-foo="value">foo!</div>]
注意:如何查看条件id和class同时存在时的写法
print(soup.find_all('b', class_="story", id="x"))
print(soup.find_all('b', attrs={"class":"story", "id":"x"}))
text 参数
通过 text 参数可以搜搜文档中的字符串内容.与 name 参数的可选值一样, text 参数接受 字符串 , 正则表达式 , 列表, True.
import reprint(soup.find_all(text="Elsie"))
# ['Elsie']print(soup.find_all(text=["Tillie", "Elsie", "Lacie"]))
# ['Elsie', 'Lacie', 'Tillie']# 只要包含Dormouse就可以
print(soup.find_all(text=re.compile("Dormouse")))
# ["The Dormouse's story", "The Dormouse's story"]
limit 参数
find_all() 方法返回全部的搜索结构,如果文档树很大那么搜索会很慢.如果我们不需要全部结果,可以使用 limit 参数限制返回结果的数量.效果与SQL中的limit关键字类似,当搜索到的结果数量达到 limit 的限制时,就停止搜索返回结果.
print(soup.find_all("a",limit=2))
print(soup.find_all("a")[0:2])'''
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>]
'''
3.3 find()
find(name , attrs , recursive , string , **kwargs )
-
name: 一个字符串或正则表达式,用于指定要查找的标签名称。如果设置为 None 或省略,则匹配任何标签。
-
attrs: 一个字典,用于指定要查找的标签的属性。如果属性字典中的键值对完全匹配一个标签的属性,则该标签会被返回。如果设置为 None 或省略,则不进行属性匹配。
-
recursive: 一个布尔值。如果为 True(默认值),则在所有后代中递归搜索匹配的标签;如果为 False,则只在当前标签的直接子标签中搜索。
-
string: 一个字符串或正则表达式,用于匹配标签内的文本。如果传入字符串,find 将查找包含该字符串的第一个标签;如果传入正则表达式,则使用该正则表达式来匹配标签内的文本。
-
**kwargs: 额外的关键字参数,这些参数可以用于指定其他搜索条件,如 limit(限制返回的结果数量)等。
find_all() 方法将返回文档中符合条件的所有tag,尽管有时候我们只想得到一个结果.比如文档中只有一个<body>标签,那么使用 find_all() 方法来查找<body>标签就不太合适, 使用 find_all 方法并设置 limit=1 参数不如直接使用 find() 方法.下面两行代码是等价的:
soup.find_all('title', limit=1)
# [<title>The Dormouse's story</title>]soup.find('title')
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
唯一的区别是 find_all() 方法的返回结果是值包含一个元素的列表,而 find() 方法直接返回结果.
find_all() 方法没有找到目标是返回空列表, find() 方法找不到目标时,返回 None .
print(soup.find("nosuchtag"))
# None
soup.head.title 是 tag的名字 方法的简写.这个简写的原理就是多次调用当前tag的 find() 方法:
soup.head.title
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title>soup.find("head").find("title")
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
3.4 find_parents() 和 find_parent()
a_string = soup.find(text="Lacie")
print(a_string) # Lacieprint(a_string.find_parent())
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
print(a_string.find_parents())
print(a_string.find_parent("p"))
'''
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>;and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>'''
四、beautifulsoup的css选择器
我们在写 CSS 时,标签名不加任何修饰,类名前加点,id名前加 #,在这里我们也可以利用类似的方法来筛选元素,用到的方法是 **soup.select(),**返回类型是 list
4.1 通过标签名查找
print(soup.select("title")) #[<title>The Dormouse's story</title>]
print(soup.select("b")) #[<b>The Dormouse's story</b>]
4.2 通过类名查找
print(soup.select(".sister")) '''
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]'''
4.3 id名查找
print(soup.select("#link1"))
# [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>]
4.4 组合查找
组合查找即和写 class 文件时,标签名与类名、id名进行的组合原理是一样的,例如查找 p 标签中,id 等于 link1的内容,二者需要用空格分开。
print(soup.select("p #link2"))#[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>]
直接子标签查找
print(soup.select("p > #link2"))
# [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>]
查找既有class也有id选择器的标签
a_string = soup.select(".story#test")
查找有多个class选择器的标签
a_string = soup.select(".story.test")
查找有多个class选择器和一个id选择器的标签
a_string = soup.select(".story.test#book")
4.5 属性查找
查找时还可以加入属性元素,属性需要用中括号括起来,注意属性和标签属于同一节点,所以中间不能加空格,否则会无法匹配到。
print(soup.select("a[href='http://example.com/tillie']"))
#[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
select 方法返回的结果都是列表形式,可以遍历形式输出,然后用 get_text() 方法来获取它的内容:
for title in soup.select('a'):print (title.get_text())'''
Elsie
Lacie
Tillie
'''
五.真实案例
1、使用 bs4提取豆瓣图书信息

from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(open('../素材/豆瓣.html', 'r'), 'lxml')# 匹配图片地址
print(soup.find_all('img'))
for i in soup.find_all('img'):print(i.attrs) # 获取图片连接地址# 获取标题 简介 评分等信息h = soup.find_all('div', class_='detail-frame')
for i in h:# print(i.text) # 获取当前节点里所有的文本内容print(i.a.text) # 获取标题 超链接里面的文本内容print(i.find('span', class_='font-small color-lightgray').text) # 获取评分print(i.find('p', 'color-gray').text) # 获取简介print(i.find_all('p')[-1].text) # 获取简介2、匹配三国演义中的回合 并写入html文本中
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup# 进行请求
# 获取页面内容
con = open('../素材/三国演义.html', 'r')
# 参数 页面内容 解析器
soup = BeautifulSoup(con, 'lxml')
title_list = soup.select('.book-mulu>ul>li>a')with open('./爬取三国演义.html', 'w', encoding='GBK') as f:for t in title_list:# 输出文章标题title = t.text# 获取文章地址href = t['href']url = 'https://www.shicimingju.com/'+hrefprint(url)f.write(f"<a href='{url}' target='_blank'>{title}</a>"+'<br />')
3、匹配天气信息 城市与温度
只要城市与气温。


from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
ALL_DATA = []
soup = BeautifulSoup(open('../素材/匹配天气.html', 'r'), 'lxml')
conMidtab = soup.find('div',class_='conMidtab')
# 获取所有的天气信息表格
tables = conMidtab.find_all('table')
for table in tables:# 过滤掉标题行trs = table.find_all('tr')[2:]for index, tr in enumerate(trs):tds = tr.find_all('td')# print(index, tds)# 获取城市和天气city_td = tds[0]temp_td = tds[3]# 过滤掉表格左侧的省/直辖市if index == 0:city_td = tds[1]temp_td = tds[4]city_td = list(city_td.stripped_strings)[0]temp_td = list(temp_td.stripped_strings)[0]ALL_DATA.append({'city':city_td,'temp':temp_td})print(ALL_DATA)4、匹配广州二手房 房源信息
from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(open('../素材/二手房详情页.html', 'r'), 'lxml')
# 通过select方式进行获取
# sidefixedbox = soup.select('.sidefixedbox#sidefixedbox')
# print(sidefixedbox[0].text)
# 通过属性
sidefixedbox = soup.find('div', attrs={'class': 'sidefixedbox', 'id': 'sidefixedbox'}).text
print(sidefixedbox)
相关文章:

beautifulsoup的简单使用
文章目录 beautifulsoup一. beautifulsoup的简单使用1、安装2、如何使用3、对象的种类 二、beautifulsoup的遍历文档树2.1 子节点.contents 和 .children descendants2.2 节点内容.string.text 2.3 多个内容.strings**.stripped_strings** 2.4 父节点.parent.parents 三、beaut…...

【Python】Jupyter Notebook的安装及简单使用
Jupyter Notebook的安装及简单使用1、安装2、language设置为中文3、Jupyter Notebook启动4、Jupyter Notebook的常用快捷方式5、将Notebook笔记转为其他文件格式保存 Jupyter Notebook的安装及简单使用 不安装AnaCoda,但需要使用Jupyter Notebook 1、安装 pip inst…...

中国自动驾驶出租车冲击网约车市场
近年来,中国的自动驾驶技术迅速发展,对传统网约车市场构成了越来越大的冲击。随着科技巨头百度旗下的萝卜快跑等公司加速推广无人驾驶出租车,这一趋势引发了广泛的讨论和担忧。 自动驾驶技术的迅猛发展 中国自动驾驶行业正处于快速发展阶段&…...

解决浏览器书签同步问题,极空间部署开源免费的跨平台书签同步工具『xBrowserSync』
解决浏览器书签同步问题,极空间部署开源免费的跨平台书签同步工具『xBrowserSync』 哈喽小伙伴们好,我是Stark-C~ 作为一个喜欢折腾的数码党,我平时上网冲浪使用的浏览器绝不会只限于一种,就比如说我在上班的地方只会用到Edge浏…...

14个SpringBoot优化小妙招
今天我们来分享一下平时用SpringBoot开发时候的一些优化小妙招,用好这些优化小妙招让我们开发的系统架构、系统代码、开发流程、测试流程、运维监控看起来就跟写诗一样优雅,让我们每个人手头负责的代码和工程都要很漂亮~~~ 这里的优化小妙招很多不是说直…...
聚合详解及示例)
Elasticsearch 度量(Metric)聚合详解及示例
Elasticsearch 提供了强大的聚合功能,允许用户对数据进行深入的统计分析。度量(Metric)聚合是其中一种,它用于对数值型数据进行计算,如求和、平均值、最大值、最小值等。本文将详细介绍 Elasticsearch 的度量聚合&…...

基于 jsp 的健身俱乐部会员系统设计与实现
点击下载源码 基于 jsp 的健身俱乐部会员系统设计与实现 摘 要 目前我国虽然己经开发出了应用计算机操作的健身俱乐部管理系统,但管理软件,管理方法和管理思想三者往往相脱节。造成我国健身俱乐部信息管理系统极端化的缺陷。在国外健身俱乐部已经有了一…...

苍穹外卖项目DAY01
苍穹外卖项目Day01 1、软件开发整体介绍 1.1、软件开发流程 1.2、角色分工 项目经理:对整个项目负责,任务分配、把控进度产品经理:进行需求调研,输出需求调研文档、产品原型等UI设计师:根据产品原型输出界面效果图架…...

SpringBoot(Ⅰ)——HelloWorld和基本打包部署+Pom依赖概述+@SpringBootApplication注解+自动装配原理+约定大于配置
前言 如果SSM学的比较好,那么SpringBoot说白了就两件事:约定大于配置和自动装配 SpringBoot不会提供任何的功能拓展,完全依赖我们手动添加 所以SpringBoot的本质是一个依赖脚手架,可以快速集成配置各种依赖 1.1 SpringBoot相关依赖 创建…...

[Unity]关闭URP的SRP,开启GPU Instancing。
1. 对应材质的gpu instancing勾选上。 2. 游戏初始化时动态关闭SRP,或者在Graphics里全局关闭。动态关闭的代码如下: GraphicsSettings.useScriptableRenderPipelineBatching false; 模型合批的一些规则: 1. 模型一致。 2. 材质一致。 …...

04创建型设计模式——建造者模式
一、建造者模式简介 建造者模式(Builder Pattern)又被称为生成器模式。它旨在构建一个复杂对象的各个部分,而不需要指定该对象的具体类。该模式特别适用于对象的构建过程复杂且需要多个步骤的情况。建造者模式是一种对象创建型模式之一&…...

前端开发中的代码规范
引言 在前端开发中,遵循良好的代码规范是非常重要的。这不仅能提高代码的可读性和可维护性,还能帮助团队成员更好地协作。本文将介绍一些前端开发中常用的代码规范,并探讨它们的重要性。 1. 代码规范的重要性 1.1 可读性 良好的代码规范可…...

WHAT - 远程控制机制
目录 1. 客户端-服务器架构2. 连接建立3. 数据传输4. 通信协议5. 安全性6. 远程控制软件示例7. 操作流程示例 远程控制别人的电脑涉及到技术和安全多个方面。其基本机制通常包括以下几个方面: 1. 客户端-服务器架构 远程控制软件通常采用客户端-服务器架构&#x…...
苹果手机录音功能在哪里?3招轻松打开手机录音
无论是记录重要的会议内容、捕捉生活中的美好瞬间,还是进行语言学习,苹果手机的录音功能都能提供极大的便利。那么,苹果手机录音功能在哪里呢?本文将为您揭示苹果手机录音功能的藏身之处,并通过3个简单步骤,…...

RCE之突破长度限制
我们在写webshell时通常会遇到过滤,但除了过滤之外还可能会有长度限制,这里就简单说一下关于RCE突破长度限制的技巧 突破16位 例如:PHP Eval函数参数限制在16个字符的情况下 ,如何拿到Webshell? <?php $param …...

Arduino控制带编码器的直流电机速度
Arduino DC Motor Speed Control with Encoder, Arduino DC Motor Encoder 作者 How to control dc motor with encoder:DC Motor with Encoder Arduino, Circuit Diagram:Driving the Motor with Encoder and Arduino:Control DC motor using Encoder feedback loop: How …...

LangChain与Elasticsearch向量数据库的完美结合
在过去的一年中,生成式 AI (Generative AI) 领域取得了显著的进展。许多新的服务和工具应运而生。其中,LangChain 已成为构建大语言模型 (LLM) 应用程序(例如检索增强生成 (RAG) 系统)最受欢迎的框架之一。该框架极大地简化了原型…...

element时间段选择器或时间选择器 只设置默认起始时间或者结束时间,不显示问题
element时间段选择器或时间选择器 只设置默认起始时间或者结束时间,不显示问题 <div v-for"(item,index) in [a,b]":key"item"><el-date-pickerv-if"b"v-model"value1[item]"type"datetimerange"value-…...

Vue 3 中,组件间传值有多种方式
在 Vue 3 中,组件间传值有多种方式,以下是几种常见的方式 父组件向子组件传值(通过 props):以下是几个父组件向子组件传值的示例:示例 1:传递字符串示例 2:传递数字示例 3࿱…...
:npm 和npx异同点)
前置(3):npm 和npx异同点
npm(Node Package Manager)和npx(Node Package Execute)是两个密切相关但用途不同的命令行工具,它们都是Node.js生态系统中的重要组成部分。 npm 用途:npm是Node.js的包管理器,主要用于安装、…...
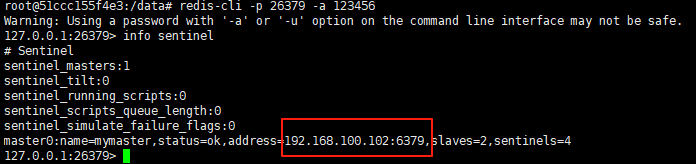
使用docker在3台服务器上搭建基于redis 6.x的一主两从三台均是哨兵模式
一、环境及版本说明 如果服务器已经安装了docker,则忽略此步骤,如果没有安装,则可以按照一下方式安装: 1. 在线安装(有互联网环境): 请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 2. 离线安装(内网环境):请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 说明:假设每台服务器已…...

java_网络服务相关_gateway_nacos_feign区别联系
1. spring-cloud-starter-gateway 作用:作为微服务架构的网关,统一入口,处理所有外部请求。 核心能力: 路由转发(基于路径、服务名等)过滤器(鉴权、限流、日志、Header 处理)支持负…...
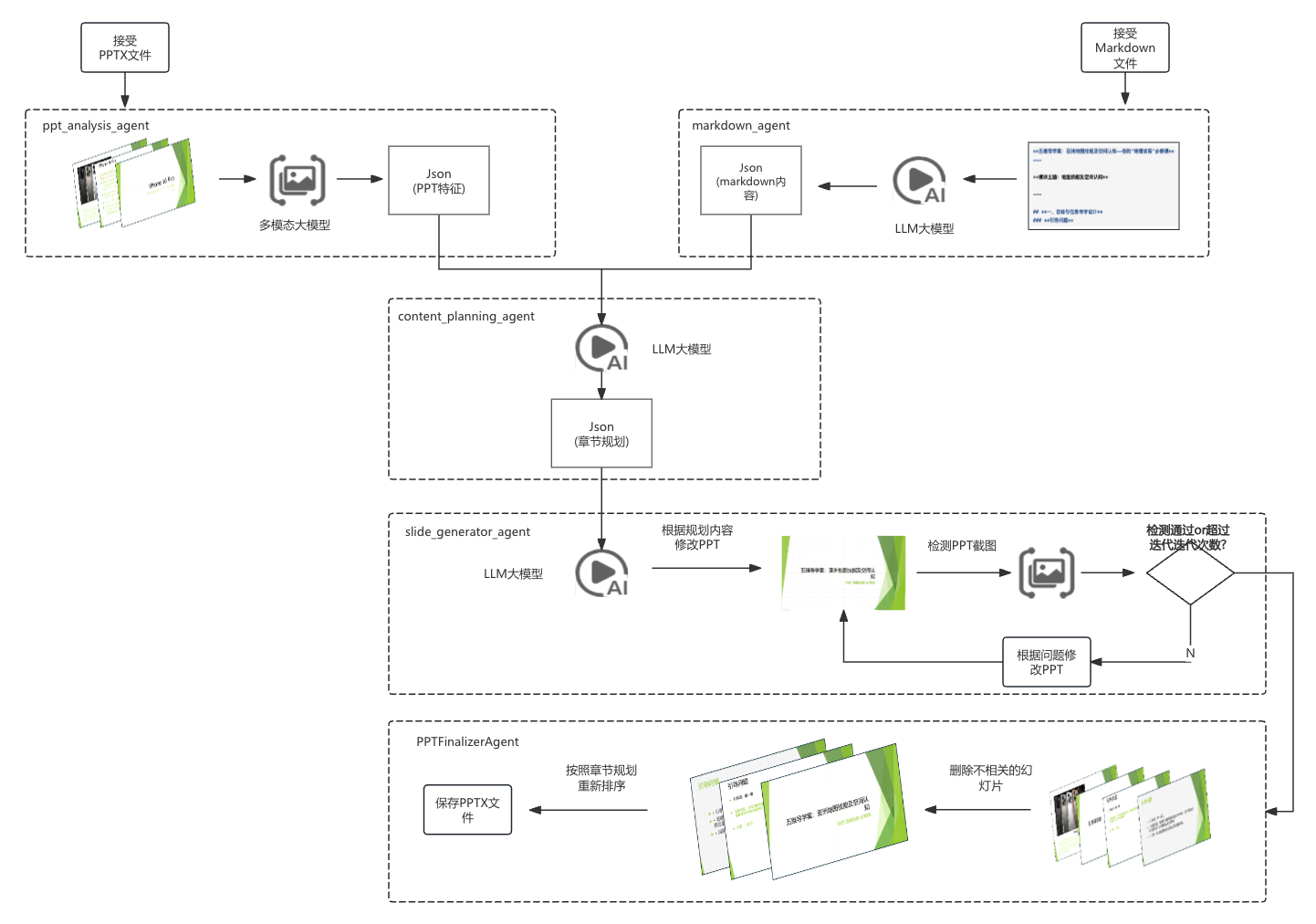
【项目实战】通过多模态+LangGraph实现PPT生成助手
PPT自动生成系统 基于LangGraph的PPT自动生成系统,可以将Markdown文档自动转换为PPT演示文稿。 功能特点 Markdown解析:自动解析Markdown文档结构PPT模板分析:分析PPT模板的布局和风格智能布局决策:匹配内容与合适的PPT布局自动…...

使用van-uploader 的UI组件,结合vue2如何实现图片上传组件的封装
以下是基于 vant-ui(适配 Vue2 版本 )实现截图中照片上传预览、删除功能,并封装成可复用组件的完整代码,包含样式和逻辑实现,可直接在 Vue2 项目中使用: 1. 封装的图片上传组件 ImageUploader.vue <te…...
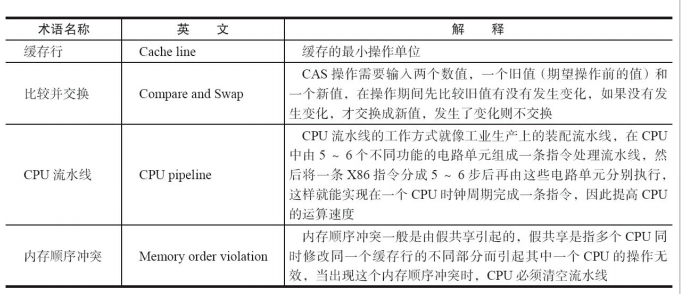
JUC笔记(上)-复习 涉及死锁 volatile synchronized CAS 原子操作
一、上下文切换 即使单核CPU也可以进行多线程执行代码,CPU会给每个线程分配CPU时间片来实现这个机制。时间片非常短,所以CPU会不断地切换线程执行,从而让我们感觉多个线程是同时执行的。时间片一般是十几毫秒(ms)。通过时间片分配算法执行。…...
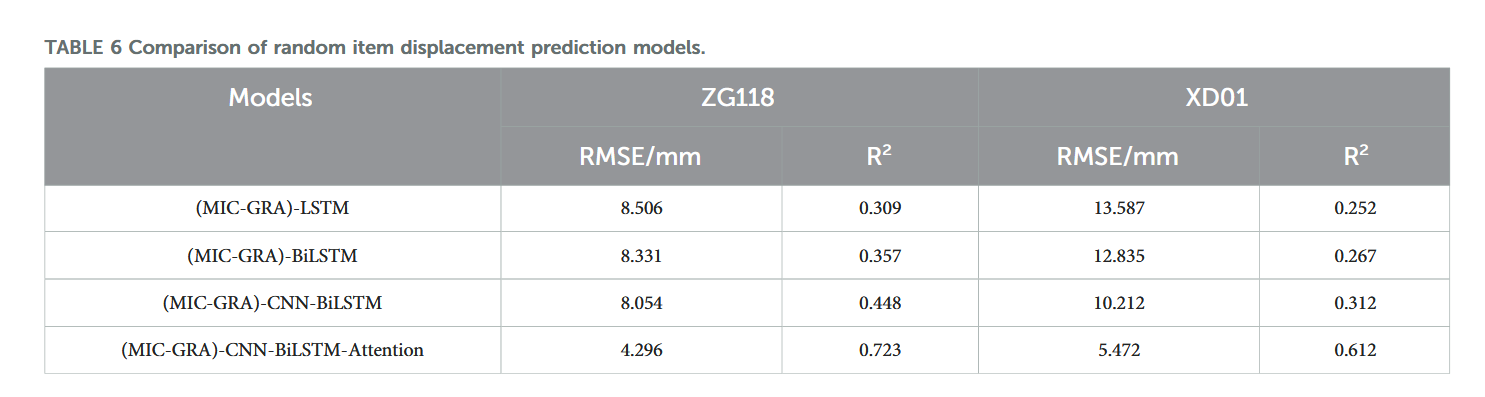
【论文阅读28】-CNN-BiLSTM-Attention-(2024)
本文把滑坡位移序列拆开、筛优质因子,再用 CNN-BiLSTM-Attention 来动态预测每个子序列,最后重构出总位移,预测效果超越传统模型。 文章目录 1 引言2 方法2.1 位移时间序列加性模型2.2 变分模态分解 (VMD) 具体步骤2.3.1 样本熵(S…...

C++八股 —— 单例模式
文章目录 1. 基本概念2. 设计要点3. 实现方式4. 详解懒汉模式 1. 基本概念 线程安全(Thread Safety) 线程安全是指在多线程环境下,某个函数、类或代码片段能够被多个线程同时调用时,仍能保证数据的一致性和逻辑的正确性…...
基于TurtleBot3在Gazebo地图实现机器人远程控制
1. TurtleBot3环境配置 # 下载TurtleBot3核心包 mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src cd ~/catkin_ws/src git clone -b noetic-devel https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/turtlebot3.git git clone -b noetic https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/turtlebot3_msgs.git git clone -b noetic-dev…...
推荐 github 项目:GeminiImageApp(图片生成方向,可以做一定的素材)
推荐 github 项目:GeminiImageApp(图片生成方向,可以做一定的素材) 这个项目能干嘛? 使用 gemini 2.0 的 api 和 google 其他的 api 来做衍生处理 简化和优化了文生图和图生图的行为(我的最主要) 并且有一些目标检测和切割(我用不到) 视频和 imagefx 因为没 a…...
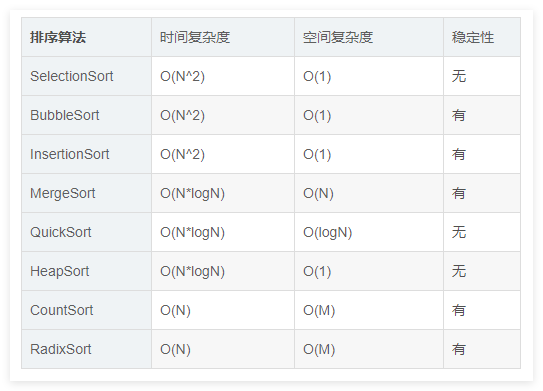
排序算法总结(C++)
目录 一、稳定性二、排序算法选择、冒泡、插入排序归并排序随机快速排序堆排序基数排序计数排序 三、总结 一、稳定性 排序算法的稳定性是指:同样大小的样本 **(同样大小的数据)**在排序之后不会改变原始的相对次序。 稳定性对基础类型对象…...
