C++ list【常用接口、模拟实现等】
1. list的介绍及使用
1.1 list的介绍
1.list是可以在常数范围内在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代。
2.list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向其前一个元素和后一个元素。
3.list与forward_list非常相似,最主要的不同在于forward_list是单链表,只能朝前迭代,让其更简单高效。
4.与其他的序列式容器相比(array,_vector,deque),list通常在任意位置进行插入、移除元素的执行效率更好。
5.与其他序列式容器相比,list和forward_list最大的缺陷是不支持任意位置的随机访问,比如:要访问list的第六个元素,必须从已知的位置(比如头部或尾部)迭代到该位置,在这段位置上迭代器需要线性的时间开销;list还需要一些额外的空间,以保存每个节点的相关联信息。

1.2 list的使用
1.2.1 list的构造
析构函数(constructor) | 接口说明 |
| list (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type()) | 构造的list中包含n个值为val的元素 |
| list() | 构造空的list |
| list (const list& x) | 拷贝构造函数 |
| list (InputIterator first, InputIterator last) | 用[first, last)区间中的元素构造list |
(若为手机阅读,表格可左右移动)

1.2.2 list iterato的使用
此处,大家可暂时将迭代器理解成一个指针,该指针指向list中的某个节点。
函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| begin+end | 返回第一个元素的迭代器+返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器 |
| rbegin+rend | 返回第一个元素的reverse_iterator,即end位置,返回最后一个元素下一个位置的reverse_iterator,即beign位置 |
(若为手机阅读,表格可左右移动)
【注意】
1. begin与end为正向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向后移动
2. rbegin(end)与rend(begin)为反向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向前移动


1.2.3 list capacity
函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| empty | 检测list是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false |
| size | 返回list中有效节点的个数 |
(若为手机阅读,表格可左右移动)

1.2.4 list element access
函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| front | 返回list的第一个节点中值的引用 |
| back | 返回list的最后一个节点中值的引用 |
(若为手机阅读,表格可左右移动)

1.2.5 list modifiers
函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| push_front | 在list首元素前插入值为val的元素 |
| pop_front | 删除list中的第一个元素 |
| push_back | 在list尾部插入值为val的元素 |
| pop_back | 删除list中最后一个元素 |
| insert | 在list position位置中插入值为val的元素 |
| erase | 删除list position位置的元素 |
| swap | 交换两个list中的元素 |
| clear | 清空list中的有效元素 |
(若为手机阅读,表格可左右移动)


1.2.6 list的迭代器失效
前面说过,此处大家可将迭代器暂时理解成类似于指针,迭代器失效即迭代器所指向的节点的无效,即该节点被删除了。因为list的底层结构为带头结点的双向循环链表,因此在list中进行插入时是不会导致list的迭代器失效的,只有在删除时才会失效,并且失效的只是指向被删除节点的迭代器,其他迭代器不会受到影响。
错误:

改正:

2. list的模拟实现
实现节点类
template<class T> struct ListNode {ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prev;T _data;ListNode(const T& data = T()):_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _data(data){} };
实现正向迭代器
迭代器不用实现析构函数和深拷贝。因为迭代器本身就是为了访问链表的节点,节点属于链表,不属于迭代器,如果需要析构和深拷贝,应该在控制链表的类中实现。
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct ListIterator{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;Node* _node;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}bool operator!=(const self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it){return _node == it._node;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}};
实现反向迭代器
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr> struct RListIterator {typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef RListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;Node* _node;RListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}self& operator++(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}bool operator!=(const self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it){return _node == it._node;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;} };
实现控制list的类
template<class T> class list {typedef ListNode<T> Node;public:typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef RListIterator<T, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;void empty_init(){_head = new Node();_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}list(){empty_init();}list(const list<T>& it){empty_init();for (const auto& e : it) //在范围for上加上引用,如果it内的元素体积很大的话可以减小代价,引用并不会导致浅拷贝//eg:int a=1;int& a1=a;int b=a1;变量b只是和a的值一样并没有指向同一块空间(int b=a;){push_back(e);}}list(initializer_list<T> il){empty_init();for (const auto& e : il){push_back(e);}}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void clear(){auto it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}list<T>& operator=(list<T> it){std::swap(_head, it._head);return *this;}iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}reverse_iterator rbegin(){return reverse_iterator(_head->_prev);}reverse_iterator rend(){return reverse_iterator(_head);}void push_back(const T& x){//Node* newnode = new Node(x);//Node* tail = _head->_prev;//tail->_next = newnode;//newnode->_prev = tail;//newnode->_next = _head;//_head->_prev = newnode;insert(end(), x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* prev = cur->_prev;prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;return iterator(newnode);}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;return iterator(next);}private:Node* _head; };
完整list.h
#pragma once
#include <assert.h>
namespace wmm
{template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prev;T _data;ListNode(const T& data = T()):_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _data(data){}};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct RListIterator{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef RListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;Node* _node;RListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}self& operator++(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}bool operator!=(const self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it){return _node == it._node;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct ListIterator{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;Node* _node;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}bool operator!=(const self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it){return _node == it._node;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}};template<class T>class list{typedef ListNode<T> Node;public:typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef RListIterator<T, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;void empty_init(){_head = new Node();_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}list(){empty_init();}list(const list<T>& it){empty_init();for (const auto& e : it) //在范围for上加上引用,如果it内的元素体积很大的话可以减小代价,引用并不会导致浅拷贝//eg:int a=1;int& a1=a;int b=a1;变量b只是和a的值一样并没有指向同一块空间(int b=a;){push_back(e);}}list(initializer_list<T> il){empty_init();for (const auto& e : il){push_back(e);}}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void clear(){auto it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}list<T>& operator=(list<T> it){std::swap(_head, it._head);return *this;}iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}reverse_iterator rbegin(){return reverse_iterator(_head->_prev);}reverse_iterator rend(){return reverse_iterator(_head);}void push_back(const T& x){//Node* newnode = new Node(x);//Node* tail = _head->_prev;//tail->_next = newnode;//newnode->_prev = tail;//newnode->_next = _head;//_head->_prev = newnode;insert(end(), x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* prev = cur->_prev;prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;return iterator(newnode);}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;return iterator(next);}private:Node* _head;};//遍历测试void test(){list<int> l;l.push_back(1);l.push_back(2);l.push_back(3);l.push_back(4);list<int>::iterator it = l.begin();while (it != l.end()){cout << *it << endl;++it;}}//结构体数据,重载符号->测试struct pos{int _x;int _y;pos(int x = 0, int y = 0):_x(x), _y(y){}};void test2(){list<pos> l;struct pos* a = (struct pos*)malloc(sizeof(struct pos));a->_x = 200;a->_y = 200;struct pos b;b._x = 300;b._y = 300;l.push_back(pos(100, 100));l.push_back(*a);l.push_back(b);list<pos>::iterator it = l.begin();while (it != l.end()){cout << (*it)._x << endl;cout << (*it)._y << endl;cout << it._node->_data._x << endl;cout << it._node->_data._y << endl;cout << it->_x << endl;cout << it->_y << endl;//想让迭代器it像结构体指针一样访问数据,重载了一个->符号++it;}}//erase insert 测试void test3(){list<int> l;l.push_back(1);l.push_back(2);l.push_back(3);l.push_back(4);list<int>::iterator it = l.begin();it=l.erase(it);//注意迭代器失效问题for (auto e : l){cout << e << endl;}cout << endl;//it=l.begin();l.insert(it, 1);for (auto& e : l){cout << e << endl;e = 3;}}//拷贝构造测试void test4(){list<int> l;l.push_back(1);l.push_back(2);l.push_back(3);l.push_back(4);for (auto e : l){cout << e << endl;}cout << endl;list<int> l1(l);for (auto e : l1){cout << e << endl;}cout << endl;list<int>::iterator it = l1.begin();*it = 0;for (auto e : l){cout << e << endl;}cout << endl;for (auto e : l1){cout << e << endl;}cout << endl;}//operator=测试void test5(){list<int> l({ 1,2,3,4,5 });list<int> l1 = { 1,2,3,4,6 };l1 = l;for (const auto& e : l){cout << e << endl;}cout << endl;for (const auto& e : l1){cout << e << endl;}cout << endl;list<int>::iterator it = l1.begin();*it = 0;for (const auto& e : l){cout << e << endl;}cout << endl;for (const auto& e : l1){cout << e << endl;}cout << endl;}//反向迭代器测试void test6(){list<int> l({ 1,2,3,4,5 });list<int>::iterator it = l.begin();while (it != l.end()){cout << *it << endl;++it;}list<int> l2({ 1,2,3,4,5 });list<int>::reverse_iterator it1 = l2.rbegin();while (it1 != l2.rend()){cout << *it1 << endl;++it1;}}
}3. list与vector的对比
vector与list都是STL中非常重要的序列式容器,由于两个容器的底层结构不同,导致其特性以及应用场景不 同,其主要不同如下:

下次再见~~很高兴帮助到你~~
如果有问题欢迎指正批评~~
相关文章:

C++ list【常用接口、模拟实现等】
1. list的介绍及使用 1.1 list的介绍 1.list是可以在常数范围内在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代。 2.list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向其前…...

12.面试题——Spring Boot
1.Spring Boot是什么? Spring Boot 是 Spring 开源组织下的子项目,是 Spring 组件一站式解决方案,主要是简化了使用 Spring 的难度,简省了繁重的配置,提供了各种启动器,开发者能快速上手。 2.为什么要用 …...

【前端VUE】npm i 出现版本错误等报错 简单直接解决命令
前端vue npm i 安装时出现 报错原因 在新版本的npm中,默认情况下,npm install遇到冲突的peerDependencies时将失败。 解决办法 使用--force或--legacy-peer-deps可解决这种情况。 --force 会无视冲突,并强制获取远端npm库资源࿰…...

精彩回顾 | 风丘科技亮相2024名古屋汽车工程博览会
2024年7月17日-19日,风丘科技联合德国IPETRONIK亮相日本名古屋汽车工程博览会。该展会面向汽车行业不同应用场景,包括新的eAxle、FCEV、ADAS、测试测量系统和ECU测试等相关技术,是一个专为活跃在汽车行业前线的工程师和研究人员举办的汽车技术…...

设计模式21-组合模式
设计模式21-组合模式(Composite Pattern) 写在前面 动机定义与结构定义结构主要类及其关系 C代码推导优缺点应用场景总结补充叶子节点不重载这三个方法叶子节点重载这三个方法结论 写在前面 数据结构模式 常常有一些组件在内部具有特定的数据结构。如何…...

如何选择深度学习的损失函数和激活函数
一概述 在深度学习中,损失函数(Loss Function)和激活函数(Activation Function)是两个至关重要的组件,它们共同影响着模型的训练效果和泛化能力。本文将简要介绍这两个概念,阐述选择它们的重要性…...

DATAX自定义KafkaWriter
因为datax目前不支持写入数据到kafka中,因此本文主要介绍如何基于DataX自定义KafkaWriter,用来同步数据到kafka中。本文偏向实战,datax插件开发理论宝典请参考官方文档: https://github.com/alibaba/DataX/blob/master/dataxPlug…...

Mybatis分页多表多条件查询
个人总结三种方式: Xml、queryWrapper、PageHelper第三方组件这三种方式进行查询; 方式一: xml中联表查询,在mapper中传参IPage<T>和条件Map(这里用map装参数)。 代码示例: Mapper层 M…...

SpringBoot快速入门(手动创建)
目录 案例:需求 步骤 1 创建Maven项目 2 导入SpringBoot起步依赖 3 定义Controller 4 编写引导类 案例:需求 搭建简单的SpringBoot工程,创建hello的类定义h1的方法,返回Hello SpringBoot! 步骤 1 创建Maven项目 大家&…...

C 408—《数据结构》算法题基础篇—数组(通俗易懂)
目录 Δ前言 一、数组的合并 0.题目: 1.算法设计思想: 2.C语言描述: 3.算法的时间和空间复杂度 : 二、数组元素的倒置 0.题目 : 1.算法设计思想 : 2.C语言描述 : 3.算法的时间和空间复杂度 : 三、数组中特定值元素的删除 0.题目 : …...
)
AI秘境-墨小黑奇遇记 - 初体验(一)
“怎么可能!”墨小黑盯着屏幕上的代码,整个人都不好了。调试了三遍,翻了几遍书,结果还是不对。就像你以为自己早起赶车,结果发现闹钟根本没响一样崩溃。 这是他第一次真正接触人工智能实战任务——实现一个简单的感知…...

文件IO813
标准IO文件定位: fseek函数: 功能:将stream流文件中的文件指针从whence位置开始偏移offset个字节的长度。 int fseek(FILE *stream , long offset, int whence); FILE *stream 指的是所需要定位的文件(文化定位前提是文件要被打…...

STP(生成树)的概述和工作原理
💝💝💝欢迎来到我的博客,很高兴能够在这里和您见面!希望您在这里可以感受到一份轻松愉快的氛围,不仅可以获得有趣的内容和知识,也可以畅所欲言、分享您的想法和见解。 推荐:Linux运维老纪的首页…...

从AGV到立库,物流自动化的更迭与未来
AGV叉车 随着柔性制造系统的广泛应用,小批量、多批次的生产需求不断增强,“订单导向”生产已经成为趋势。这也让越来越多的企业认识到,产线的智能设备导入只是第一步,要想达到生产效率的最优解,物流系统的再优化必须提…...

阴阳脚数码管
1.小故事 最近,我接到了一个既“清肺”又“烧脑”的新任务,设计一个低功耗蓝牙肺活量计。在这个项目中我们借鉴了一款蓝牙跳绳的硬件设计方案,特别是它的显示方案——数码管。 在电子工程领域,初学者往往从操作LED开始ÿ…...

【Vue3-Typescript】<script setup lang=“ts“> 使用 ref标签 怎么获取 refs子组件呢
注意:请确保子组件已经正确挂载,并且通过 defineExpose 暴露了您想要在父组件中访问的属性或方法 parent.vue <template><child ref"childRef"></child><button click"fun">点击父组件</button> &l…...

npm 超详细使用教程
文章目录 一、简介二、npm安装三、npm 的使用3.1 npm初始化项目3.2 安装包3.3 安装不同版本包3.4 避免系统权限3.5 更新包3.6 卸载包3.7 执行脚本3.8 pre- 和 post- 脚本3.9 npm link3.10 发布和卸载发布的包3.11 使用npm版本控制3.22 npm资源 四、总结 一、简介 npmÿ…...

TypeScript函数
函数 函数:复用代码块 函数可以不写返回值 调用函数-----函数名() function a(){console.log(无参函数); } a();需要再函数后,写上返回值类型 没有返回值 使用void function e():string{return 可乐 } console.log(我得到了e()); function d():void{console.l…...
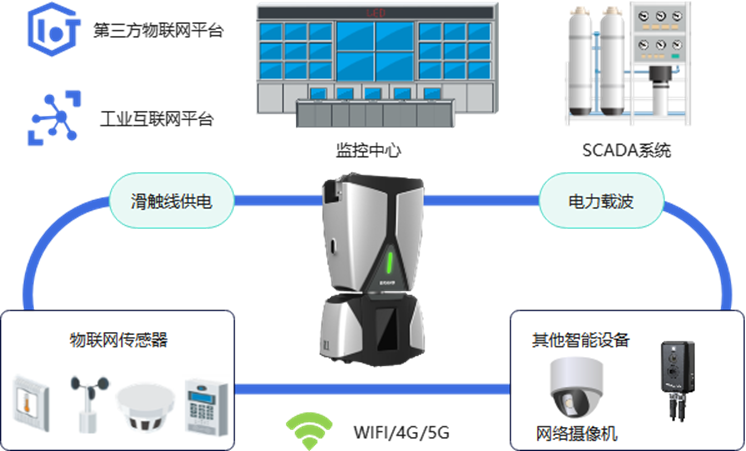
中海油某海上平台轨道巡检机器人解决方案
配电房作为能源传输和分配的核心枢纽,其安全运行直接影响到企业的生产稳定性和安全性。对于中海油这样的大型能源企业,配电房的运行状况至关重要。然而,传统的人工巡检方式存在效率低、作业风险高、巡检误差大等问题。为提升巡检效率、降低安…...

【NXP-MCXA153】SPI驱动移植
介绍 SPI总线由摩托罗拉公司开发,是一种全双工同步串行总线,由四个IO口组成:CS、SCLK、MISO、MOSI;通常用于CPU和外设之间进行通信,常见的SPI总线设备有:TFT LCD、QSPI FLASH、时钟模块、IMU等;…...
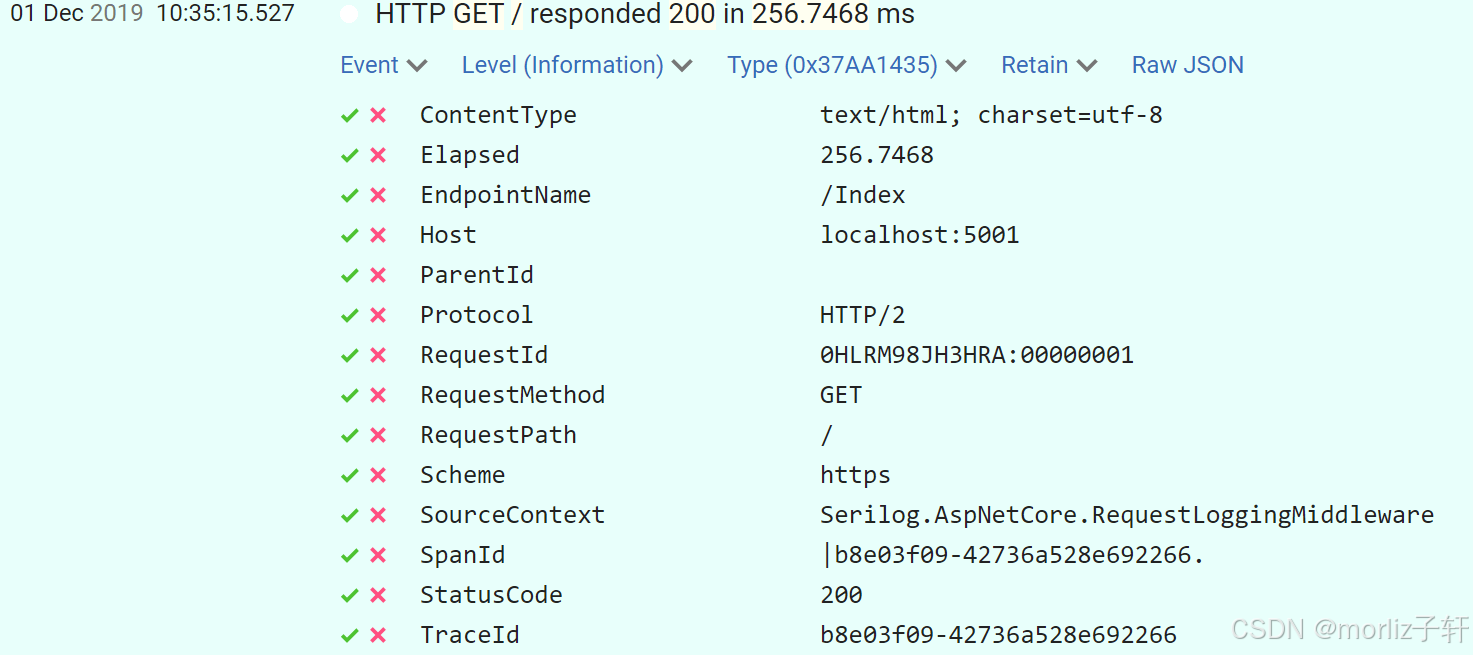
深入浅出Asp.Net Core MVC应用开发系列-AspNetCore中的日志记录
ASP.NET Core 是一个跨平台的开源框架,用于在 Windows、macOS 或 Linux 上生成基于云的新式 Web 应用。 ASP.NET Core 中的日志记录 .NET 通过 ILogger API 支持高性能结构化日志记录,以帮助监视应用程序行为和诊断问题。 可以通过配置不同的记录提供程…...

日语AI面试高效通关秘籍:专业解读与青柚面试智能助攻
在如今就业市场竞争日益激烈的背景下,越来越多的求职者将目光投向了日本及中日双语岗位。但是,一场日语面试往往让许多人感到步履维艰。你是否也曾因为面试官抛出的“刁钻问题”而心生畏惧?面对生疏的日语交流环境,即便提前恶补了…...
渗透实战PortSwigger靶场-XSS Lab 14:大多数标签和属性被阻止
<script>标签被拦截 我们需要把全部可用的 tag 和 event 进行暴力破解 XSS cheat sheet: https://portswigger.net/web-security/cross-site-scripting/cheat-sheet 通过爆破发现body可以用 再把全部 events 放进去爆破 这些 event 全部可用 <body onres…...

工程地质软件市场:发展现状、趋势与策略建议
一、引言 在工程建设领域,准确把握地质条件是确保项目顺利推进和安全运营的关键。工程地质软件作为处理、分析、模拟和展示工程地质数据的重要工具,正发挥着日益重要的作用。它凭借强大的数据处理能力、三维建模功能、空间分析工具和可视化展示手段&…...
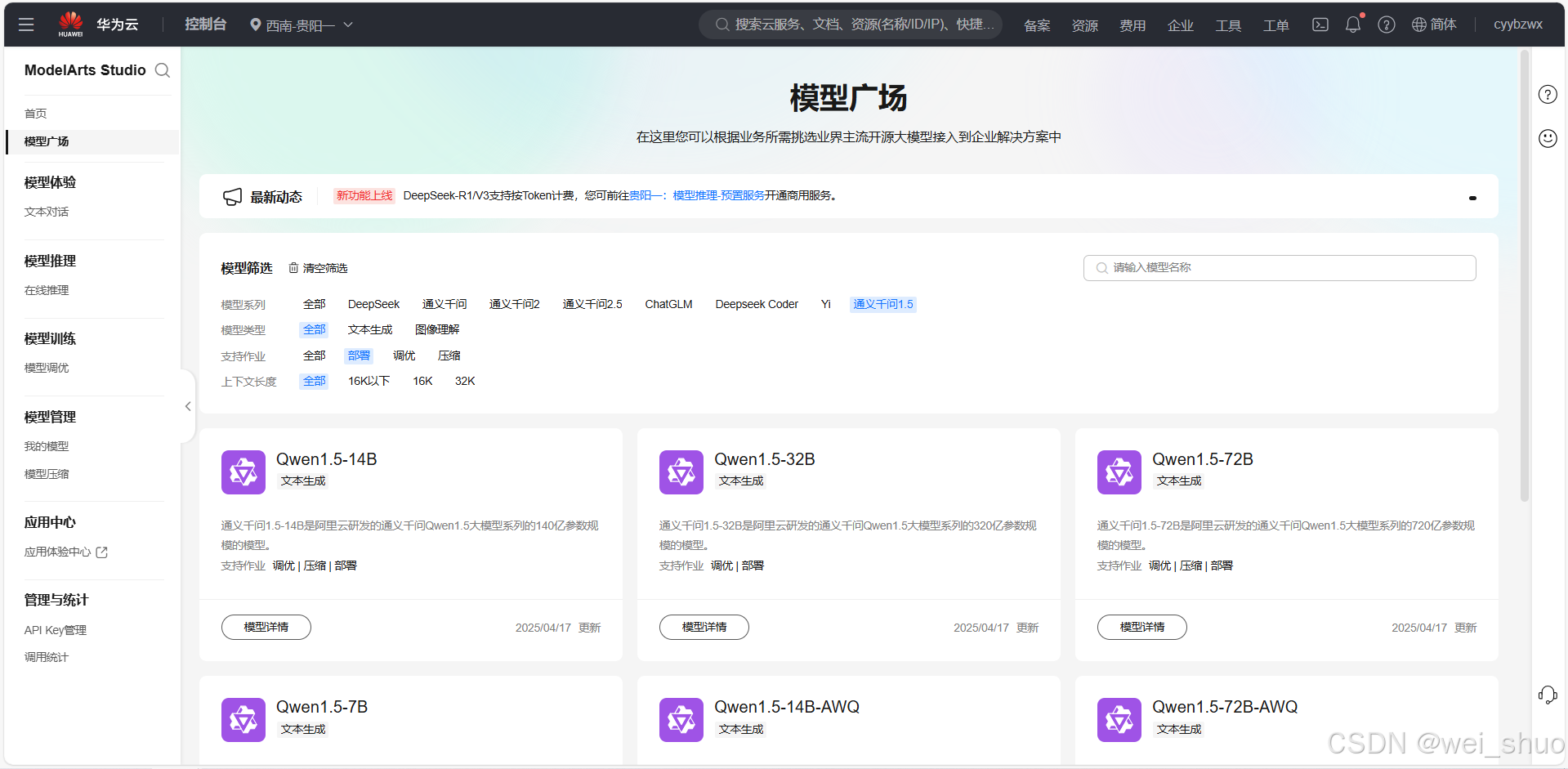
华为云Flexus+DeepSeek征文|DeepSeek-V3/R1 商用服务开通全流程与本地部署搭建
华为云FlexusDeepSeek征文|DeepSeek-V3/R1 商用服务开通全流程与本地部署搭建 前言 如今大模型其性能出色,华为云 ModelArts Studio_MaaS大模型即服务平台华为云内置了大模型,能助力我们轻松驾驭 DeepSeek-V3/R1,本文中将分享如何…...

在Ubuntu24上采用Wine打开SourceInsight
1. 安装wine sudo apt install wine 2. 安装32位库支持,SourceInsight是32位程序 sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386 sudo apt update sudo apt install wine32:i386 3. 验证安装 wine --version 4. 安装必要的字体和库(解决显示问题) sudo apt install fonts-wqy…...
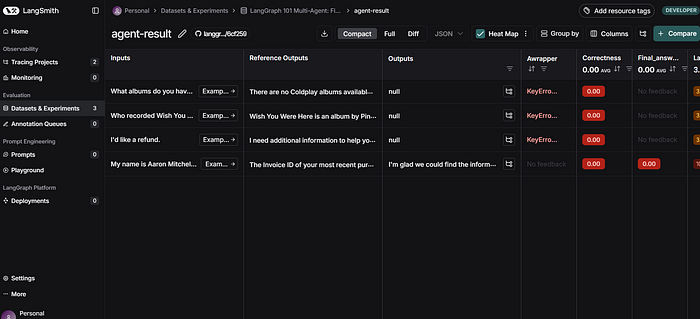
使用LangGraph和LangSmith构建多智能体人工智能系统
现在,通过组合几个较小的子智能体来创建一个强大的人工智能智能体正成为一种趋势。但这也带来了一些挑战,比如减少幻觉、管理对话流程、在测试期间留意智能体的工作方式、允许人工介入以及评估其性能。你需要进行大量的反复试验。 在这篇博客〔原作者&a…...
)
GitHub 趋势日报 (2025年06月06日)
📊 由 TrendForge 系统生成 | 🌐 https://trendforge.devlive.org/ 🌐 本日报中的项目描述已自动翻译为中文 📈 今日获星趋势图 今日获星趋势图 590 cognee 551 onlook 399 project-based-learning 348 build-your-own-x 320 ne…...
)
安卓基础(Java 和 Gradle 版本)
1. 设置项目的 JDK 版本 方法1:通过 Project Structure File → Project Structure... (或按 CtrlAltShiftS) 左侧选择 SDK Location 在 Gradle Settings 部分,设置 Gradle JDK 方法2:通过 Settings File → Settings... (或 CtrlAltS)…...

Kubernetes 网络模型深度解析:Pod IP 与 Service 的负载均衡机制,Service到底是什么?
Pod IP 的本质与特性 Pod IP 的定位 纯端点地址:Pod IP 是分配给 Pod 网络命名空间的真实 IP 地址(如 10.244.1.2)无特殊名称:在 Kubernetes 中,它通常被称为 “Pod IP” 或 “容器 IP”生命周期:与 Pod …...




