我的第一个CUDA程序
MatAdd算法
实现两个矩阵对应元素相加

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>// 矩阵加法函数
void MatAdd(int height, int width)
{// 在主机内存中为 A、B 和 C 分配内存float* A = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));float* B = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));float* C = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));// 初始化输入矩阵 A 和 Bfor (int i = 0; i < height; i++){for (int j = 0; j < width; j++){// 例如,初始化为 i+j 的和*(A + i * width + j) = i + j;*(B + i * width + j) = i - j;}}// 执行矩阵加法运算,将结果存储在矩阵 C 中for (int i = 0; i < height; i++){for (int j = 0; j < width; j++){*(C + i * width + j) = *(A + i * width + j) + *(B + i * width + j);}}// 输出结果矩阵 Cprintf("Matrix C (result of A + B):\n");for (int i = 0; i < height; i++){for (int j = 0; j < width; j++){printf("%f ", *(C + i * width + j));}printf("\n");}// 释放分配的内存free(A);free(B);free(C);
}int main()
{int height = 3; // 矩阵的高度int width = 3; // 矩阵的宽度// 执行矩阵加法MatAdd(height, width);return 0;
}
输出:
Matrix C (result of A + B):
0.000000 0.000000 0.000000
2.000000 2.000000 2.000000
4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 MatAdd算法的GPU实现
MatAdd算法的GPU实现
- CPU端为输入矩阵A和B、输出矩阵C分配空间,并进行初始化
- CPU端分配设备端内存,并将A和B传输到GPU上
- 定义数据和线程的映射关系,并确定线程的开启数量和组织方式
- 每个线程负责输出矩阵C的一个元素的计算,全局ID为(i,j)的线程计算索引为(i,j)的矩阵元素
- 当矩阵规模为width*height时,共开启width * height个线程
- 每个block包含256个线程,采用(16,16)的组织形式
- 编写计算kernel,完成计算任务
- CPU端将计算结果从Device内存拷贝到Host内存

内存分配 数据传输

开启线程 启动kernel 结果返回

GPU kernel
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>// CUDA 核函数,用于矩阵加法
__global__ void MatAddKernel(float* A, float* B, float* C, int height, int width) {// 获取线程的全局IDint i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; // 计算全局行索引int j = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y; // 计算全局列索引// 确保索引在矩阵范围内if (i < width && j < height) {// 计算当前线程对应的元素索引int index = j * width + i;// 从矩阵 A 和 B 中读取数据float src_data_A = A[index];float src_data_B = B[index];// 执行加法运算float result = src_data_A + src_data_B;// 将结果写入矩阵 CC[index] = result;}
}void MatAdd(int height, int width) {// 在主机内存中分配 A、B 和 Cfloat* A = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));float* B = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));float* C = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));// 初始化输入矩阵 A 和 Bfor (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) {A[i * width + j] = i + j; // 简单初始化,A的元素为行索引+列索引B[i * width + j] = i - j; // 简单初始化,B的元素为行索引-列索引}}// 第一步:在设备内存中为矩阵 A、B 和 C 分配内存float* d_A;cudaMalloc(&d_A, height * width * sizeof(float)); // 分配矩阵 A 的设备内存float* d_B;cudaMalloc(&d_B, height * width * sizeof(float)); // 分配矩阵 B 的设备内存float* d_C;cudaMalloc(&d_C, height * width * sizeof(float)); // 分配矩阵 C 的设备内存// 第二步:将矩阵 A 和 B 从主机内存复制到设备内存cudaMemcpy(d_A, A, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); // 复制 AcudaMemcpy(d_B, B, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); // 复制 B// 第三步:调用 CUDA 核函数dim3 threadsPerBlock(16, 16); // 定义每个块中的线程数dim3 numBlocks((width + threadsPerBlock.x - 1) / threadsPerBlock.x, (height + threadsPerBlock.y - 1) / threadsPerBlock.y); // 计算网格中的块数MatAddKernel<<<numBlocks, threadsPerBlock>>>(d_A, d_B, d_C, height, width); // 启动 CUDA 核函数// 第四步:将结果从设备内存复制回主机内存cudaMemcpy(C, d_C, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);// 输出结果矩阵 Cprintf("Matrix C (result of A + B):\n");for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) {printf("%f ", C[i * width + j]);}printf("\n");}// 释放设备内存cudaFree(d_A);cudaFree(d_B);cudaFree(d_C);// 释放主机内存free(A);free(B);free(C);
}int main() {int height = 3; // 矩阵的高度int width = 3; // 矩阵的宽度// 调用矩阵加法函数MatAdd(height, width);return 0;
}
输出:
Matrix C (result of A + B):
0.000000 0.000000 0.000000
2.000000 2.000000 2.000000
4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 CUDA程序编译



CUDA程序性能测试
使用 CUDA GPU Timers 实际要循环100次求平均值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>// CUDA 核函数,用于矩阵加法
__global__ void MatAddKernel(float* A, float* B, float* C, int height, int width) {// 获取线程的全局IDint i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; // 计算全局行索引int j = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y; // 计算全局列索引// 确保索引在矩阵范围内if (i < width && j < height) {// 计算当前线程对应的元素索引int index = j * width + i;// 从矩阵 A 和 B 中读取数据float src_data_A = A[index];float src_data_B = B[index];// 执行加法运算float result = src_data_A + src_data_B;// 将结果写入矩阵 CC[index] = result;}
}void MatAdd(int height, int width) {// 在主机内存中分配 A、B 和 Cfloat* A = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));float* B = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));float* C = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));// 初始化输入矩阵 A 和 Bfor (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) {A[i * width + j] = i + j; // 简单初始化,A的元素为行索引+列索引B[i * width + j] = i - j; // 简单初始化,B的元素为行索引-列索引}}// 第一步:在设备内存中为矩阵 A、B 和 C 分配内存float* d_A;cudaMalloc(&d_A, height * width * sizeof(float)); // 分配矩阵 A 的设备内存float* d_B;cudaMalloc(&d_B, height * width * sizeof(float)); // 分配矩阵 B 的设备内存float* d_C;cudaMalloc(&d_C, height * width * sizeof(float)); // 分配矩阵 C 的设备内存// 第二步:将矩阵 A 和 B 从主机内存复制到设备内存cudaMemcpy(d_A, A, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); // 复制 AcudaMemcpy(d_B, B, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); // 复制 B// 第三步:定义事件变量,用于测量核函数执行时间cudaEvent_t start, stop;float time;cudaEventCreate(&start); // 创建开始事件cudaEventCreate(&stop); // 创建停止事件// 第四步:调用 CUDA 核函数dim3 threadsPerBlock(16, 16); // 定义每个块中的线程数dim3 numBlocks((width + threadsPerBlock.x - 1) / threadsPerBlock.x, (height + threadsPerBlock.y - 1) / threadsPerBlock.y); // 计算网格中的块数cudaEventRecord(start, 0); // 记录开始时间MatAddKernel<<<numBlocks, threadsPerBlock>>>(d_A, d_B, d_C, height, width); // 启动 CUDA 核函数cudaEventRecord(stop, 0); // 记录结束时间cudaEventSynchronize(stop); // 等待事件完成cudaEventElapsedTime(&time, start, stop); // 计算核函数执行时间printf("Kernel execution time: %f ms\n", time); // 输出核函数执行时间// 销毁事件cudaEventDestroy(start);cudaEventDestroy(stop);// 第五步:将结果从设备内存复制回主机内存cudaMemcpy(C, d_C, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);// 输出结果矩阵 Cprintf("Matrix C (result of A + B):\n");for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) {printf("%f ", C[i * width + j]);}printf("\n");}// 释放设备内存cudaFree(d_A);cudaFree(d_B);cudaFree(d_C);// 释放主机内存free(A);free(B);free(C);
}int main() {int height = 3; // 矩阵的高度int width = 3; // 矩阵的宽度// 调用矩阵加法函数MatAdd(height, width);return 0;
}
输出:
Kernel execution time: 0.086016 ms
Matrix C (result of A + B):
0.000000 0.000000 0.000000
2.000000 2.000000 2.000000
4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 使用 CPU Timers 实际要循环100次求平均值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/time.h> // 包含 gettimeofday 的头文件
#include <cuda_runtime.h>// CUDA 核函数,用于矩阵加法
__global__ void MatAddKernel(float* A, float* B, float* C, int height, int width) {// 获取线程的全局IDint i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; // 计算全局行索引int j = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y; // 计算全局列索引// 确保索引在矩阵范围内if (i < width && j < height) {// 计算当前线程对应的元素索引int index = j * width + i;// 从矩阵 A 和 B 中读取数据float src_data_A = A[index];float src_data_B = B[index];// 执行加法运算float result = src_data_A + src_data_B;// 将结果写入矩阵 CC[index] = result;}
}void MatAdd(int height, int width) {// 在主机内存中分配 A、B 和 Cfloat* A = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));float* B = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));float* C = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));// 初始化输入矩阵 A 和 Bfor (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) {A[i * width + j] = i + j; // 简单初始化,A的元素为行索引+列索引B[i * width + j] = i - j; // 简单初始化,B的元素为行索引-列索引}}// 第一步:在设备内存中为矩阵 A、B 和 C 分配内存float* d_A;cudaMalloc(&d_A, height * width * sizeof(float)); // 分配矩阵 A 的设备内存float* d_B;cudaMalloc(&d_B, height * width * sizeof(float)); // 分配矩阵 B 的设备内存float* d_C;cudaMalloc(&d_C, height * width * sizeof(float)); // 分配矩阵 C 的设备内存// 第二步:将矩阵 A 和 B 从主机内存复制到设备内存cudaMemcpy(d_A, A, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); // 复制 AcudaMemcpy(d_B, B, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); // 复制 B// 第三步:定义时间测量变量struct timeval start, end;double elapsedTime;// 记录开始时间gettimeofday(&start, NULL);// 启动 CUDA 核函数dim3 threadsPerBlock(16, 16); // 定义每个块中的线程数dim3 numBlocks((width + threadsPerBlock.x - 1) / threadsPerBlock.x, (height + threadsPerBlock.y - 1) / threadsPerBlock.y); // 计算网格中的块数MatAddKernel<<<numBlocks, threadsPerBlock>>>(d_A, d_B, d_C, height, width); // 启动 CUDA 核函数cudaDeviceSynchronize(); // 等待核函数完成// 记录结束时间gettimeofday(&end, NULL);// 计算时间差elapsedTime = (end.tv_sec - start.tv_sec) * 1000.0; // 秒转毫秒elapsedTime += (end.tv_usec - start.tv_usec) / 1000.0; // 微秒转毫秒// 输出核函数执行时间printf("Kernel execution time: %f ms\n", elapsedTime);// 第四步:将结果从设备内存复制回主机内存cudaMemcpy(C, d_C, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);// 输出结果矩阵 Cprintf("Matrix C (result of A + B):\n");for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) {printf("%f ", C[i * width + j]);}printf("\n");}// 释放设备内存cudaFree(d_A);cudaFree(d_B);cudaFree(d_C);// 释放主机内存free(A);free(B);free(C);
}int main() {int height = 3; // 矩阵的高度int width = 3; // 矩阵的宽度// 调用矩阵加法函数MatAdd(height, width);return 0;
}
输出:
Kernel execution time: 0.101000 ms
Matrix C (result of A + B):
0.000000 0.000000 0.000000
2.000000 2.000000 2.000000
4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 MatAdd程序之变一:每个线程处理4个元素
- CPU端为输入矩阵A和B、输出矩阵C分配空间,并进行初始化
- CPU端分配设备端内存,并将A和B传输到GPU上
- 定义数据和线程的映射关系,并确定线程的开启数量和组织方式
- 每个线程负责输出矩阵C的四个元素的计算,全局ID为(i,j)的线程计算索引为(i,4*j~4*j+3)的矩阵元素
- 当矩阵规模为width*height时,共开启width/4 * height个线程
- 每个block包含256个线程,采用(16,16)的组织形式
- 编写计算kernel,完成计算任务
- CPU端将计算结果从Device内存拷贝到Host内存


#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <iostream>// 自定义向上取整除法函数
int div_up(int a, int b) {return (a + b - 1) / b;
}
// CUDA核函数,执行矩阵加法
__global__ void MatAdd(float *A, float *B, float *C, int height, int width)
{// 获取线程的全局IDint i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;int j = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;// 检查线程是否在有效的计算范围内// 每个线程处理4个连续的元素,因此检查4*i是否在宽度范围内if ((4 * i) < width && j < height){// 获取线程与数据之间的映射关系int index = j * width + 4 * i;// 从源矩阵读取数据float4 src_data_A = *((float4 *)(A + index));float4 src_data_B = *((float4 *)(B + index));// 执行加法运算// 执行加法运算,逐个对float4的分量进行加法float4 result;result.x = src_data_A.x + src_data_B.x;result.y = src_data_A.y + src_data_B.y;result.z = src_data_A.z + src_data_B.z;result.w = src_data_A.w + src_data_B.w;// 将结果写回结果矩阵*((float4 *)(C + index)) = result;}
}// 矩阵加法函数,处理矩阵的加法运算
void MatAdd(int height, int width)
{float *A, *B, *C; // 主机内存指针float *d_A, *d_B, *d_C; // 设备内存指针// 分配主机内存A = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));B = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));C = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));// 初始化矩阵A和B(这里省略具体的初始化代码)// 初始化输入矩阵 A 和 Bfor (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) {A[i * width + j] = i + j; // 简单初始化,A的元素为行索引+列索引B[i * width + j] = i - j; // 简单初始化,B的元素为行索引-列索引}}// 分配设备内存cudaMalloc((void**)&d_A, height * width * sizeof(float));cudaMalloc((void**)&d_B, height * width * sizeof(float));cudaMalloc((void**)&d_C, height * width * sizeof(float));// 将数据从主机内存复制到设备内存cudaMemcpy(d_A, A, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);cudaMemcpy(d_B, B, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);// 设置线程块的大小,每个块中有16x16个线程dim3 threadsPerBlock(16, 16);// 计算需要多少个线程块来覆盖整个矩阵区域// 宽度除以4是因为每个线程处理4个元素dim3 numBlocks(div_up(width / 4, threadsPerBlock.x), div_up(height, threadsPerBlock.y));// 调用核函数,执行矩阵加法运算MatAdd<<<numBlocks, threadsPerBlock>>>(d_A, d_B, d_C, height, width);// 将计算结果从设备内存复制到主机内存cudaMemcpy(C, d_C, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// 输出结果矩阵 Cprintf("Matrix C (result of A + B):\n");for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) {printf("%f ", C[i * width + j]);}printf("\n");}// 释放设备内存cudaFree(d_A);cudaFree(d_B);cudaFree(d_C);// 释放主机内存free(A);free(B);free(C);
}int main() {int height = 8; // 示例矩阵的高度int width = 8; // 示例矩阵的宽度// 调用矩阵加法函数MatAdd(height, width);return 0;
}
输出:
Matrix C (result of A + B):
0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000
2.000000 2.000000 2.000000 2.000000 2.000000 2.000000 2.000000 2.000000
4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000
6.000000 6.000000 6.000000 6.000000 6.000000 6.000000 6.000000 6.000000
8.000000 8.000000 8.000000 8.000000 8.000000 8.000000 8.000000 8.000000
10.000000 10.000000 10.000000 10.000000 10.000000 10.000000 10.000000 10.000000
12.000000 12.000000 12.000000 12.000000 12.000000 12.000000 12.000000 12.000000
14.000000 14.000000 14.000000 14.000000 14.000000 14.000000 14.000000 14.000000 MatAdd程序之变二
矩阵A、B、C都为NxN的方阵,A和B为已知矩阵,C[i][j] = A[i][j] + B[j][i]。


- CPU端为输入矩阵A和B、输出矩阵C分配空间,并进行初始化
- CPU端分配设备端内存,并将A和B传输到GPU上
- 定义数据和线程的映射关系,并确定线程的开启数量和组织方式
- 每个线程负责输出矩阵C的一个元素的计算,全局ID为(i,j)的线程计算索引为(i,j)的矩阵元素
- 当矩阵规模为width*height时,共开启width * height个线程
- 每个block包含256个线程,采用(16,16)的组织形式
- 编写计算kernel,完成计算任务
- CPU端将计算结果从Device内存拷贝到Host内存

#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <iostream>#define N 1024 // 矩阵的大小(N x N)// CUDA核函数,执行矩阵加法运算
__global__ void MatAdd(float *A, float *B, float *C, int height, int width)
{// 获取线程的全局IDint i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;int j = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;// 确保线程在有效的计算范围内if(i < width && j < height){// 获取矩阵元素的索引int index_A = j * width + i;int index_B = i * width + j;int index_C = index_A;// 从矩阵A和B读取数据并计算结果float src_data_A = *(A + index_A);float src_data_B = *(B + index_B);float result = src_data_A + src_data_B;// 将结果写入矩阵C*(C + index_C) = result;}
}// 主函数,处理矩阵的初始化、调用CUDA核函数以及结果输出
void MatAdd(int height, int width)
{// 在主机内存中为A、B和C分配空间float* A = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));float* B = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));float* C = (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));// 初始化矩阵A和Bfor (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) {*(A + i * width + j) = static_cast<float>(i + j); // 示例初始化*(B + i * width + j) = static_cast<float>(i - j); // 示例初始化}}// 分配设备内存float *d_A, *d_B, *d_C;cudaMalloc((void**)&d_A, height * width * sizeof(float));cudaMalloc((void**)&d_B, height * width * sizeof(float));cudaMalloc((void**)&d_C, height * width * sizeof(float));// 将数据从主机内存复制到设备内存cudaMemcpy(d_A, A, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);cudaMemcpy(d_B, B, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);// 配置CUDA网格和线程块大小dim3 threadsPerBlock(16, 16);dim3 numBlocks((width + threadsPerBlock.x - 1) / threadsPerBlock.x,(height + threadsPerBlock.y - 1) / threadsPerBlock.y);// 调用CUDA核函数,执行矩阵加法运算MatAdd<<<numBlocks, threadsPerBlock>>>(d_A, d_B, d_C, height, width);// 将计算结果从设备内存复制回主机内存cudaMemcpy(C, d_C, height * width * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);// 输出部分计算结果用于验证std::cout << "C[0][0] = " << C[0] << std::endl;std::cout << "C[N-1][N-1] = " << C[(N-1) * width + (N-1)] << std::endl;// 释放设备内存cudaFree(d_A);cudaFree(d_B);cudaFree(d_C);// 释放主机内存free(A);free(B);free(C);
}int main() {// 调用矩阵加法函数MatAdd(N, N);return 0;
}
输出:
C[0][0] = 0
C[N-1][N-1] = 2046MatAdd程序之变三
- 矩阵A、B都为MxN的矩阵,矩阵C为(M/2)*(N/2)的矩阵, A和B为已知矩阵,C[i][j] = A[2*i][2*j] *B[2*i][2*j] + A[2*i][2*j+1] *B[2*i][2*j+1] + A[2*i+1][2*j] *B[2*i+1][2*j] + A[2*i+1][2*j +1] *B[2*i+1][2*j+1] 。
 CPU端为输入矩阵A和B、输出矩阵C分配空间,并进行初始化
CPU端为输入矩阵A和B、输出矩阵C分配空间,并进行初始化 - CPU端分配设备端内存,并将A和B传输到GPU上
- 定义数据和线程的映射关系,并确定线程的开启数量和组织方式
- 每个线程负责输出矩阵C的一个元素的计算,全局ID为(i,j)的线程计算索引为(i,j)的矩阵元素
- 当矩阵规模为(M/2)*(N/2)时,共开启(M/2)*(N/2)个线程,每个线程对应A和B的四个元素
- 每个block包含256个线程,采用(16,16)的组织形式
- 编写计算kernel,完成计算任务
- CPU端将计算结果从Device内存拷贝到Host内存

#include <iostream>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>#define BLOCK_SIZE 16__global__ void MatAdd(float *A, float *B, float *C, int height, int width)
{// Get thread IDint i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;int j = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;if (i < width / 2 && j < height / 2){// Get the mapping between thread and dataint index_A_1 = 2 * j * width + 2 * i;int index_A_2 = 2 * j * width + 2 * i + 1;int index_A_3 = (2 * j + 1) * width + 2 * i;int index_A_4 = (2 * j + 1) * width + 2 * i + 1;int index_B_1 = index_A_1; // Indexes for matrix B are the same as Aint index_B_2 = index_A_2;int index_B_3 = index_A_3;int index_B_4 = index_A_4;int index_C = j * (width / 2) + i;// Read data from source matricesfloat A1 = A[index_A_1];float A2 = A[index_A_2];float A3 = A[index_A_3];float A4 = A[index_A_4];float B1 = B[index_B_1];float B2 = B[index_B_2];float B3 = B[index_B_3];float B4 = B[index_B_4];// Computefloat result = A1 * B1 + A2 * B2 + A3 * B3 + A4 * B4;// Write resultC[index_C] = result;}
}int main()
{int M = 4; // Example dimensions for the matricesint N = 4;int size_A = M * N * sizeof(float);int size_B = M * N * sizeof(float);int size_C = (M / 2) * (N / 2) * sizeof(float);// Allocate host memoryfloat *h_A = (float*)malloc(size_A);float *h_B = (float*)malloc(size_B);float *h_C = (float*)malloc(size_C);// Initialize matrices A and Bfor (int i = 0; i < M * N; ++i){h_A[i] = i + 1; // Example initializationh_B[i] = i + 1;}// Allocate device memoryfloat *d_A, *d_B, *d_C;cudaMalloc(&d_A, size_A);cudaMalloc(&d_B, size_B);cudaMalloc(&d_C, size_C);// Copy data from host to devicecudaMemcpy(d_A, h_A, size_A, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);cudaMemcpy(d_B, h_B, size_B, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);// Define block and grid sizedim3 blockDim(BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE);dim3 gridDim((N / 2 + BLOCK_SIZE - 1) / BLOCK_SIZE, (M / 2 + BLOCK_SIZE - 1) / BLOCK_SIZE);// Launch kernelMatAdd<<<gridDim, blockDim>>>(d_A, d_B, d_C, M, N);// Copy result from device to hostcudaMemcpy(h_C, d_C, size_C, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);// Print resultfor (int i = 0; i < M / 2; ++i){for (int j = 0; j < N / 2; ++j){std::cout << h_C[i * (N / 2) + j] << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;}// Free device memorycudaFree(d_A);cudaFree(d_B);cudaFree(d_C);// Free host memoryfree(h_A);free(h_B);free(h_C);return 0;
}
输出:
66 138
546 746 - 异构计算整成为当前计算领域的重点方向
- GPGPU是异构计算的主要形式
- GPGPU是一款大规模细粒度并行处理器,并行思维是进行GPGPU编程的重要前提
- NVIDIA是当前GPGPU领域当之无愧的霸主
- GPGPU编程的重点是定义明确的线程和数据间的映射
相关文章:

我的第一个CUDA程序
MatAdd算法 实现两个矩阵对应元素相加 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>// 矩阵加法函数 void MatAdd(int height, int width) {// 在主机内存中为 A、B 和 C 分配内存float* A (float*)malloc(height * width * sizeof(float));float* B (float*)malloc…...

workerman下的webman路由浏览器跨域的一种问题
软件版本 "php": ">7.2", "workerman/webman-framework": "^1.5.0",问题情景 使用“分组路由”做API接口前后端分离跨域,在接口测试工具调试是能正常获取数据的;但在网页浏览器上调试就遇到了CORS、404的错…...

Windows11 -MASKRCNN-部署测试
文章目录 Detectron2环境配置搭建python 环境安装Cuda \CUDNN 、PyTorch、 torchvision、cudatoolkit1、Cuda \CUDNN2、 PyTorch、 torchvision、cudatoolkit进入python测试:错误信息 3、detectron2环境在安装detecteron中,遇到报错:编译的时…...

函数(子程序)的常见、易混淆概念详解【对初学者有帮助】
C语⾔中的函数也被称做子程序,意思就是⼀个完成某项特定的任务的⼀小段代码。 C语⾔标准中提供了许多库函数,点击下面的链接可以查看c语言的库函数和头文件。 C/C官⽅的链接:https://zh.cppreference.com/w/c/header 目录 一、函数头与函…...

TiDB-从0到1-DM工具
TiDB从0到1系列 TiDB-从0到1-体系结构TiDB-从0到1-分布式存储TiDB-从0到1-分布式事务TiDB-从0到1-MVCCTiDB-从0到1-部署篇TiDB-从0到1-配置篇TiDB-从0到1-集群扩缩容TiDB-从0到1-数据导出导入TiDB-从0到1-BR工具 一、DM原理 支持全量抽取数据\检测新的数据变化同步到下游实例…...

AppScan——Web 应用安全扫描的得力工具
一、引言 在当今数字化时代,Web 应用成为企业业务的重要支撑,但同时也面临着各种安全威胁。AppScan 作为一款专业的 Web 应用安全扫描工具,为保障 Web 应用的安全性提供了有力的支持。本文将对 AppScan 进行详细介绍,包括其功能、…...

虚幻5|AI行为树,进阶篇
一,打开敌人的角色蓝图,编写以下蓝图,该蓝图只是创建一个敌人并非ai行为树 1.编写蓝图 2.打开主界面,创建一个导航网格体积,上一章都有讲,在添加体积这里面,找到导航网格体积,点击创…...

在 Spring Boot 中配置 Tomcat 监听多个端口
在现代微服务架构中,应用程序可能需要监听多个端口,以支持不同的服务或协议。Spring Boot 提供了灵活的配置选项,使得这一需求变得简单而高效。本文将介绍如何在 Spring Boot 中配置 Tomcat 以监听多个端口,并简要说明其中一些关键…...

stm32f407新建项目工程及烧录
1、新建一个文件夹,打开keil5将项目工程放入文件夹中 2、弹出选择对应型号设备 3、弹出选择对应库 可以看见出现下图:感叹号表示有错 最后如图所示:点击ok就行了 4、创建对应的文件夹存放文件 4、建立main.c 5、添加对应的设置 最后写一个空白…...

c++中加不加const的值传递和引用传递的区别
文章目录 可以修改参数值的比较值传递(int x)和引用传递(int &x)使用const不修改参数值的比较值传递(const int x)和引用传递(const int &x)1. const int x 示例2. const int &x 示例 可以修改参数值的比较值传递(int x)和引用传递(int &x) #include <iost…...

Qt的窗口设置
本文介绍Qt的窗口设置。 采用Qt开发界面程序,会涉及到窗口的设置,如窗口标题栏是否显示,是否有最小,最大化按钮等,窗口当前显示最小化,最大化等。本文简要介绍常用的窗口设置方法。 1.窗口属性 窗口属性…...

51单片机-LCD1602显示屏
简介 是一个液晶显示屏,通过电压对显示区域进行控制,有电就显示。 能够同时显示32个字符,分为两行,一行显示16个字符。可以显示的内容只能是字母、数字或者一些特殊符号。 使用ASCII码来让LCD1602来显示对应的字符。 电路图 …...

多模态分析代理 MAIA:多智能体解决 视觉模型 黑盒问题
多模态分析代理 MAIA:多智能体解决 视觉模型 黑盒问题 论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.14394 代码:https://github.com/multimodal-interpretability/maia 提出背景 神经网络方法提取的特征,没有可解释性。 数据在通过多个层…...

AT360-6T杭州中科微单频高精度授时模块场景应用
AT360-6T是一款高性能多系统卫星定位授时模块,基于自主研发的北斗多系统SOC芯片,可以同时接收中国的BDS(北斗二号和北斗三号)、美国的GPS、俄罗斯的GLONASS、欧盟的 GALILEO 和日本的QZSS等多个卫星导航系统的GNSS信号来实现多系统联合定位授时ÿ…...

Python酷库之旅-第三方库Pandas(081)
目录 一、用法精讲 336、pandas.Series.str.rpartition方法 336-1、语法 336-2、参数 336-3、功能 336-4、返回值 336-5、说明 336-6、用法 336-6-1、数据准备 336-6-2、代码示例 336-6-3、结果输出 337、pandas.Series.str.slice方法 337-1、语法 337-2、参数 …...

C语言基础⑩——构造类型(结构体)
一、数据类型分类 1、基本类型 整数型 短整型:short(2个字节);整型(默认):int(4个字节);长整型:long(8个字节)…...

宝兰德荣获openEuler项目群青铜捐赠人称号,共筑开源生态繁荣新篇章
近日,开放原子开源基金会正式公布了新增捐赠人名单,宝兰德凭借在开源领域的卓越贡献与深厚实力,被授予openEuler项目群青铜捐赠人称号。 开放原子开源基金会是致力于推动全球开源事业发展的非营利机构,于2020年6月在北京成立。开放…...

【Python单元测试】学习笔记3
文章目录 08.PyTest框架什么是PyTestPyTest的优点PyTest的测试环境PyTest常用参数跳过测试 09.PyTest fixture基础PyTest fixture定义和使用引用多个Fixture 10. conftest.pyconftest.py的用途 11. 参数化测试用例为什么需要参数化测试用例使用parameterizer插件实现使用pytest…...

OpenSSL源码编译及Debug
** 1. 环境 Linux 5.19.0-14-generic 22.04.1-Ubuntu 2. 所需工具 gcc version 11.3.0 (Ubuntu 11.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) cmake version 3.22.1 3. 步骤 3.1 获取openssl源码 方法可以git clone获得源码,或者直接去GitHub上下载压缩包,GitHub网址…...

go之goburrow/modbus 学习
goburrow/modbus 是一个用Go语言实现的Modbus协议库,提供了Modbus主机(Master)和从机(Slave)的实现,支持两种主要的Modbus传输模式:Modbus TCP和Modbus RTU。 功能介绍 1. 支持的传输模式 Mod…...

应用升级/灾备测试时使用guarantee 闪回点迅速回退
1.场景 应用要升级,当升级失败时,数据库回退到升级前. 要测试系统,测试完成后,数据库要回退到测试前。 相对于RMAN恢复需要很长时间, 数据库闪回只需要几分钟。 2.技术实现 数据库设置 2个db_recovery参数 创建guarantee闪回点,不需要开启数据库闪回。…...

连锁超市冷库节能解决方案:如何实现超市降本增效
在连锁超市冷库运营中,高能耗、设备损耗快、人工管理低效等问题长期困扰企业。御控冷库节能解决方案通过智能控制化霜、按需化霜、实时监控、故障诊断、自动预警、远程控制开关六大核心技术,实现年省电费15%-60%,且不改动原有装备、安装快捷、…...
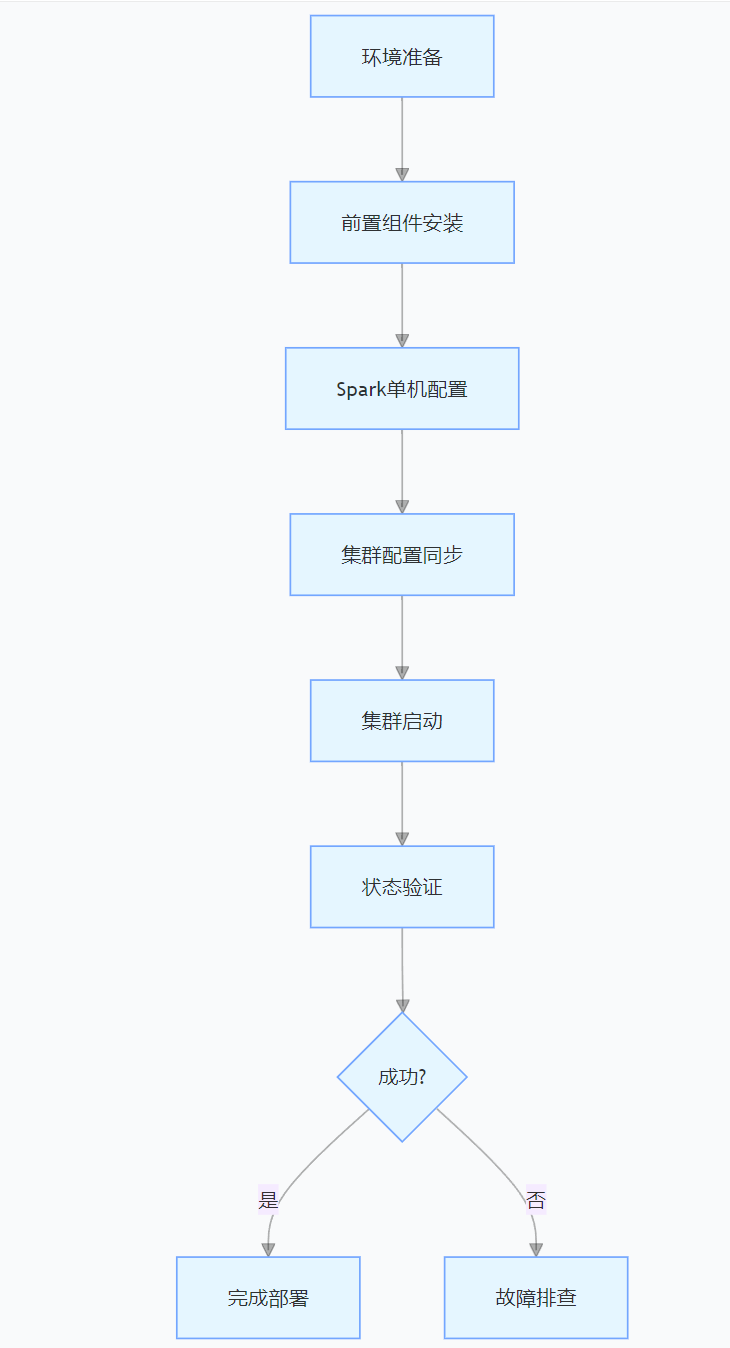
CentOS下的分布式内存计算Spark环境部署
一、Spark 核心架构与应用场景 1.1 分布式计算引擎的核心优势 Spark 是基于内存的分布式计算框架,相比 MapReduce 具有以下核心优势: 内存计算:数据可常驻内存,迭代计算性能提升 10-100 倍(文档段落:3-79…...

PL0语法,分析器实现!
简介 PL/0 是一种简单的编程语言,通常用于教学编译原理。它的语法结构清晰,功能包括常量定义、变量声明、过程(子程序)定义以及基本的控制结构(如条件语句和循环语句)。 PL/0 语法规范 PL/0 是一种教学用的小型编程语言,由 Niklaus Wirth 设计,用于展示编译原理的核…...

OpenPrompt 和直接对提示词的嵌入向量进行训练有什么区别
OpenPrompt 和直接对提示词的嵌入向量进行训练有什么区别 直接训练提示词嵌入向量的核心区别 您提到的代码: prompt_embedding = initial_embedding.clone().requires_grad_(True) optimizer = torch.optim.Adam([prompt_embedding...

06 Deep learning神经网络编程基础 激活函数 --吴恩达
深度学习激活函数详解 一、核心作用 引入非线性:使神经网络可学习复杂模式控制输出范围:如Sigmoid将输出限制在(0,1)梯度传递:影响反向传播的稳定性二、常见类型及数学表达 Sigmoid σ ( x ) = 1 1 +...

DeepSeek 技术赋能无人农场协同作业:用 AI 重构农田管理 “神经网”
目录 一、引言二、DeepSeek 技术大揭秘2.1 核心架构解析2.2 关键技术剖析 三、智能农业无人农场协同作业现状3.1 发展现状概述3.2 协同作业模式介绍 四、DeepSeek 的 “农场奇妙游”4.1 数据处理与分析4.2 作物生长监测与预测4.3 病虫害防治4.4 农机协同作业调度 五、实际案例大…...

《C++ 模板》
目录 函数模板 类模板 非类型模板参数 模板特化 函数模板特化 类模板的特化 模板,就像一个模具,里面可以将不同类型的材料做成一个形状,其分为函数模板和类模板。 函数模板 函数模板可以简化函数重载的代码。格式:templa…...

代码随想录刷题day30
1、零钱兑换II 给你一个整数数组 coins 表示不同面额的硬币,另给一个整数 amount 表示总金额。 请你计算并返回可以凑成总金额的硬币组合数。如果任何硬币组合都无法凑出总金额,返回 0 。 假设每一种面额的硬币有无限个。 题目数据保证结果符合 32 位带…...

AGain DB和倍数增益的关系
我在设置一款索尼CMOS芯片时,Again增益0db变化为6DB,画面的变化只有2倍DN的增益,比如10变为20。 这与dB和线性增益的关系以及传感器处理流程有关。以下是具体原因分析: 1. dB与线性增益的换算关系 6dB对应的理论线性增益应为&…...

