C++11标准模板(STL)- 算法库 - 类似 std::accumulate,但不依序执行 -(std::reduce)
算法库
算法库提供大量用途的函数(例如查找、排序、计数、操作),它们在元素范围上操作。注意范围定义为 [first, last) ,其中 last 指代要查询或修改的最后元素的后一个元素。
类似 std::accumulate,但不依序执行
std::reduce| template<class InputIt> typename std::iterator_traits<InputIt>::value_type reduce( InputIt first, InputIt last); | (1) | (C++17 起) |
| template<class ExecutionPolicy, class ForwardIt> typename std::iterator_traits<ForwardIt>::value_type reduce( | (2) | (C++17 起) |
| template<class InputIt, class T> | (3) | (C++17 起) |
| template<class ExecutionPolicy, class ForwardIt, class T> T reduce(ExecutionPolicy&& policy, ForwardIt first, ForwardIt last, T init); | (4) | (C++17 起) |
| template<class InputIt, class T, class BinaryOp> | (5) | (C++17 起) |
| template<class ExecutionPolicy, class ForwardIt, class T, class BinaryOp> T reduce(ExecutionPolicy&& policy, ForwardIt first, ForwardIt last, T init, BinaryOp binary_op); | (6) | (C++17 起) |
1) 同 reduce(first, last, typename std::iterator_traits<InputIt>::value_type{})
3) 同 reduce(first, last, init, std::plus<>())
5) 在 binary_op 上以初值 init 规约范围 [first; last) ,可能以未指定方式排序聚合。
2,4,6) 同 (1,3,5) ,但按照 policy 执行。此重载仅若std::is_execution_policy_v<std::decay_t<ExecutionPolicy>> 为 true才参与重载决议
若 binary_op 非结合或非交换,则行为非确定。
若 binary_op 修改 [first; last] 中任何元素或非法化范围中任何迭代器,含尾迭代器,则行为未定义。
参数
| first, last | - | 要应用算法的元素范围 |
| init | - | 广义和的初值 |
| policy | - | 使用的执行策略。细节见执行策略。 |
| binary_op | - | 将以未指定顺序应用于解引用输入迭代器结果、其他 binary_op 结果及 init 上的二元函数对象 (FunctionObject) 。 |
| 类型要求 | ||
- InputIt 必须满足遗留输入迭代器 (LegacyInputIterator) 的要求。 | ||
- ForwardIt 必须满足遗留向前迭代器 (LegacyForwardIterator) 的要求。 | ||
- T 必须满足可移动构造 (MoveConstructible) 的要求。而且 binary_op(init, *first) 、 binary_op(*first, init) 、 binary_op(init, init) 及 binary_op(*first, *first) 必须可转换到 T 。 | ||
返回值
init 及 *first 、 *(first+1) 、…… *(last-1) 在 binary_op 上的广义和,
其中广义和 GSUM(op, a
1, ..., a
N) 定义如下:
- 若 N=1 ,则为 a
1 - 若 N > 1 ,则为 op(GSUM(op, b
1, ..., b
K), GSUM(op, b
M, ..., b
N)) ,其中
- b
1, ..., b
N 可以是任何 a1, ..., aN 的排列,且 - 1 < K+1 = M ≤ N
换言之, reduce 表现类似 std::accumulate ,除了范围中的元素可能以任意顺序分组并重排。
复杂度
O(last - first) 次应用 binary_op.
异常
拥有名为 ExecutionPolicy 的模板形参的重载按下列方式报告错误:
- 若作为算法一部分调用的函数的执行抛出异常,且
ExecutionPolicy为标准策略之一,则调用 std::terminate 。对于任何其他ExecutionPolicy,行为是实现定义的。 - 若算法无法分配内存,则抛出 std::bad_alloc 。
注意
若为空,则返回不修改的 init
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <time.h>
#include <random>
#include <vector>
#include <cassert>struct Cell
{int x;int y;Cell() = default;Cell(int a, int b): x(a), y(b) {}Cell &operator +=(const Cell &cell){x += cell.x;y += cell.y;return *this;}Cell &operator +(const Cell &cell){x += cell.x;y += cell.y;return *this;}Cell &operator *(const Cell &cell){x *= cell.x;y *= cell.y;return *this;}Cell &operator ++(){x += 1;y += 1;return *this;}bool operator <(const Cell &cell) const{if (x == cell.x){return y < cell.y;}else{return x < cell.x;}}bool operator >(const Cell &cell) const{if (x == cell.x){return y > cell.y;}else{return x > cell.x;}}bool operator ==(const Cell &cell) const{return x == cell.x && y == cell.y;}friend Cell operator+(const Cell &lcell, const Cell &rcell){Cell cell = lcell;cell.x += rcell.x;cell.y += rcell.y;return cell;}friend Cell operator-(const Cell &lcell, const Cell &rcell){Cell cell = lcell;cell.x -= rcell.x;cell.y -= rcell.y;return cell;}friend Cell operator*(const Cell &lcell, const Cell &rcell){Cell cell = lcell;cell.x *= rcell.x;cell.y *= rcell.y;return cell;}friend Cell operator/(const Cell &lcell, const Cell &rcell){Cell cell = lcell;cell.x /= rcell.x;cell.y /= rcell.y;return cell;}friend Cell operator%(const Cell &lcell, const Cell &rcell){Cell cell = lcell;cell.x %= rcell.x;cell.y %= rcell.y;return cell;}
};std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Cell &cell)
{os << "{" << cell.x << "," << cell.y << "}";return os;
}namespace std
{
template <typename InputIt, typename T, typename BinaryOperation>
T reduce(InputIt first, InputIt last, T init, BinaryOperation op)
{for (; first != last; ++first){init = op(std::move(init), *first);}return init;
}
}int main()
{std::cout << std::boolalpha;std::mt19937 g{std::random_device{}()};srand((unsigned)time(NULL));auto generate = [](){int n = std::rand() % 10 + 110;Cell cell{n, n};return cell;};//3) 构造拥有 count 个有值 value 的元素的容器。std::vector<Cell> vector1(8, generate());std::generate(vector1.begin(), vector1.end(), generate);std::sort(vector1.begin(), vector1.end());std::cout << "vector1: ";std::copy(vector1.begin(), vector1.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));std::cout << std::endl;std::vector<Cell> vector2(vector1.size(), generate());std::generate(vector2.begin(), vector2.end(), generate);std::sort(vector2.begin(), vector2.end());std::cout << "vector2: ";std::copy(vector2.begin(), vector2.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));std::cout << std::endl;for (size_t index = 0; index < vector1.size(); ++index){std::cout << "std::reduce(vector1.begin(), " << index << ", Cell{0, 0} std::plus<Cell>() ): ";std::cout << std::reduce(vector1.begin(), vector1.begin() + index, Cell{0, 0}, std::plus<Cell>());std::cout << std::endl;}std::cout << std::endl;for (size_t index = 0; index < vector1.size(); ++index){std::cout << "std::reduce(vector1.begin(), " << index << ", Cell{0, 0} std::minus<Cell>() ): ";std::cout << std::reduce(vector1.begin(), vector1.begin() + index, Cell{0, 0}, std::minus<Cell>());std::cout << std::endl;}std::cout << std::endl;for (size_t index = 0; index < vector2.size(); ++index){std::cout << "std::reduce(vector2.begin(), " << index << ", Cell{1, 1} std::multiplies<Cell>() ): ";std::cout << std::reduce(vector2.begin(), vector2.begin() + index, Cell{1, 1}, std::multiplies<Cell>());std::cout << std::endl;}std::cout << std::endl;for (size_t index = 0; index < vector2.size(); ++index){std::cout << "std::reduce(vector2.begin(), " << index << ", Cell{1024, 1024} std::divides<Cell>() ): ";std::cout << std::reduce(vector2.begin(), vector2.begin() + index, Cell{1024, 1024}, std::divides<Cell>());std::cout << std::endl;}std::cout << std::endl;for (size_t index = 0; index < vector2.size(); ++index){std::cout << "std::reduce(vector2.begin(), " << index << ", Cell{1024, 1024} std::modulus<Cell>() ): ";std::cout << std::reduce(vector2.begin(), vector2.begin() + index, Cell{1024, 1024}, std::modulus<Cell>());std::cout << std::endl;}std::cout << std::endl;return 0;
}
输出
vector1: {111,111} {112,112} {113,113} {115,115} {116,116} {116,116} {117,117} {119,119}
vector2: {110,110} {112,112} {112,112} {114,114} {117,117} {117,117} {119,119} {119,119}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 0, Cell{0, 0} std::plus<Cell>() ): {0,0}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 1, Cell{0, 0} std::plus<Cell>() ): {111,111}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 2, Cell{0, 0} std::plus<Cell>() ): {223,223}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 3, Cell{0, 0} std::plus<Cell>() ): {336,336}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 4, Cell{0, 0} std::plus<Cell>() ): {451,451}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 5, Cell{0, 0} std::plus<Cell>() ): {567,567}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 6, Cell{0, 0} std::plus<Cell>() ): {683,683}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 7, Cell{0, 0} std::plus<Cell>() ): {800,800}std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 0, Cell{0, 0} std::minus<Cell>() ): {0,0}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 1, Cell{0, 0} std::minus<Cell>() ): {-111,-111}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 2, Cell{0, 0} std::minus<Cell>() ): {-223,-223}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 3, Cell{0, 0} std::minus<Cell>() ): {-336,-336}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 4, Cell{0, 0} std::minus<Cell>() ): {-451,-451}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 5, Cell{0, 0} std::minus<Cell>() ): {-567,-567}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 6, Cell{0, 0} std::minus<Cell>() ): {-683,-683}
std::reduce(vector1.begin(), 7, Cell{0, 0} std::minus<Cell>() ): {-800,-800}std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 0, Cell{1, 1} std::multiplies<Cell>() ): {1,1}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 1, Cell{1, 1} std::multiplies<Cell>() ): {110,110}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 2, Cell{1, 1} std::multiplies<Cell>() ): {12320,12320}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 3, Cell{1, 1} std::multiplies<Cell>() ): {1379840,1379840}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 4, Cell{1, 1} std::multiplies<Cell>() ): {157301760,157301760}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 5, Cell{1, 1} std::multiplies<Cell>() ): {1224436736,1224436736}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 6, Cell{1, 1} std::multiplies<Cell>() ): {1525177344,1525177344}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 7, Cell{1, 1} std::multiplies<Cell>() ): {1107477504,1107477504}std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 0, Cell{1024, 1024} std::divides<Cell>() ): {1024,1024}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 1, Cell{1024, 1024} std::divides<Cell>() ): {9,9}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 2, Cell{1024, 1024} std::divides<Cell>() ): {0,0}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 3, Cell{1024, 1024} std::divides<Cell>() ): {0,0}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 4, Cell{1024, 1024} std::divides<Cell>() ): {0,0}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 5, Cell{1024, 1024} std::divides<Cell>() ): {0,0}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 6, Cell{1024, 1024} std::divides<Cell>() ): {0,0}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 7, Cell{1024, 1024} std::divides<Cell>() ): {0,0}std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 0, Cell{1024, 1024} std::modulus<Cell>() ): {1024,1024}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 1, Cell{1024, 1024} std::modulus<Cell>() ): {34,34}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 2, Cell{1024, 1024} std::modulus<Cell>() ): {34,34}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 3, Cell{1024, 1024} std::modulus<Cell>() ): {34,34}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 4, Cell{1024, 1024} std::modulus<Cell>() ): {34,34}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 5, Cell{1024, 1024} std::modulus<Cell>() ): {34,34}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 6, Cell{1024, 1024} std::modulus<Cell>() ): {34,34}
std::reduce(vector2.begin(), 7, Cell{1024, 1024} std::modulus<Cell>() ): {34,34}相关文章:
- 算法库 - 类似 std::accumulate,但不依序执行 -(std::reduce))
C++11标准模板(STL)- 算法库 - 类似 std::accumulate,但不依序执行 -(std::reduce)
算法库 算法库提供大量用途的函数(例如查找、排序、计数、操作),它们在元素范围上操作。注意范围定义为 [first, last) ,其中 last 指代要查询或修改的最后元素的后一个元素。 类似 std::accumulate,但不依序执行 std…...

反射机制的介绍
什么是反射 Java反射机制是Java语言一个很重要的特性,它使得Java具有了“动态性”。在Java程序运行时,对于任意的一个类,我们能不能知道这个类有哪些属性和方法呢?对于任意的一个对象,我们又能不能调用它任意的方法&a…...

AI图文带货,手把手教学,傻瓜操作,轻松日入500+,小白教程
通过自媒体的力量,帮助普通人成为企业家。 建立自己的财富事业,用你的影响力帮助更多的人。 从而实现你更加自由的生活方式。 记住关注我,不要错过每一次分享。 对标账号 作为公司的一个项目实际拆解者,最热门的项目怎么能不拆…...

java:实现简单的验证码功能
效果 实现思路 验证码图片的url由后端的一个Controller生成,前端请求这个Controller接口的时候根据当前时间生成一个uuid,并把这个uuid在前端使用localStorage缓存起来,下一次还是从缓存中获取。 Controller生成验证码之后,把前…...

MybatisPlus使用指南
MybatisPlus 1. 快速入门1.1 入门案例1.2 常见注解1.3 常见配置 2. 核心功能2.1 条件构造器2.2 自定义SQL2.3 Service接口 3. 扩展功能3.1 代码生成3.2 静态工具3.3 逻辑删除 4. 插件功能4.1 分页插件4.2 通用分页实体 1. 快速入门 1.1 入门案例 步骤一:引入Mybat…...

5. MongoDB 集合创建、更新、删除
1. 创建集合 1.1 语法 db.createCollection(name, options) 参数说明: name: 要创建的集合名称。options: 可选参数, 指定有关内存大小及索引的选项。 options 可以是如下参数: 参数名类型描述示例值capped布尔值是否创建一个固定大小的集合。truesize…...

PHP中如何将变量从函数传递给acf_add_filter
在PHP开发中,我们有时需要将变量从函数传递给acf的add_filter钩子。这样做可以让我们在acf字段加载时,对字段值进行动态修改。下面,我将详细介绍如何实现这一功能。 在acf中,我们使用add_filter来添加钩子,对字段的加…...

KNN算法的使用
目录 一、KNN 算法简介 二、KNN算法的使用 1.读取数据 2.处理数据 三、训练模型 1.导入KNN模块 2.训练模型 3.出厂前测试 四、进行测试 1.处理数据 2.进行测试 总结 一、KNN 算法简介 KNN 是一种基于实例的学习算法。它通过比较样本之间的距离来进行预测。算法的核心…...

java文件上传
导入jar包,或者maven <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-fileupload/commons-fileupload --> <dependency><groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId><artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId><version>…...

MySQL 数据库经验总结
一、数据库操作 1. 创建数据库 CREATE DATABASE database_name;例如,创建一个名为 my_database 的数据库: CREATE DATABASE my_database;2. 选择数据库 USE database_name;要使用刚才创建的 my_database 数据库: USE my_database;3. 删除…...
Python环境安装及PIP安装(Mac OS版)
官网 https://www.python.org/downloads/ 安装python python-3.12.1-macos11.pkg下载后,安装一直下一步即可 验证是否安装成功,执行python3命令和pip3命令 配置环境变量 获取python3安装位置并配置在.bash_profile #查看python路径 which python3#…...

2024自动驾驶(多模态)大模型综述:从DriveGPT4、DriveMLM到DriveLM、DriveVLM
前言 由于今年以来,一直在不断深挖具身智能机器人相关,而自动驾驶其实和机器人有着无比密切的联系,甚至可以认为,汽车就是一个带着4个轮子的机器人 加之个人认为,目前大模型落地潜力最大的两个方向,一个是…...

晨控CK-GW08-EC与汇川AC801系列PLC的EtherCAT通讯连接说明手册
晨控CK-GW08-EC与汇川AC801系列PLC的EtherCAT通讯连接说明手册 晨控CK-GW08-EC是一款支持标准工业通讯协议EtherCAT的网关控制器,方便用户集成到PLC等控制系统中。系统还集成了8路读写接口,用户可通过通信接口使用EtherCAT协议对8路读写接口所连接的读卡器进行相对…...

向上or向下调整建堆 的时间复杂度的本质区别的讲解
知识点:(N代表节点数,h代表高度) 1:高度为h的满二叉树节点个数N为 2^(h)-1 即N 2^(h)-1 2:所以h log(N1) 一:向上…...

阿一网络安全实战演练之利用 REST URL 中的服务器端参数污染
所需知识 要解决这个实验室问题,您需要了解以下内容: 如何确定用户输入是否包含在服务器端的 URL 路径或查询字符串中。如何使用路径遍历序列尝试更改服务器端请求。如何查找 API 文档。 这些内容在我们的 API 测试学院主题中有涵盖。 进入实验室 研…...

[游戏开发] LuaTable转string存读二进制文件
UE5和Unity通用此方案,只不过读写文件的接口略有不同,lua代码的处理是相同的。 下面两个方法是 LuaTable和字符串互相转换的代码 function XUtils.luaTableToString(tab, sp)sp sp or ""local s ""for k,v in pairs(tab) doif t…...

光伏业务管理系统的一些妙用功能
现在信息化流程化基本上每个行业都必须要有的了,光伏业务管理系统软件是一种专门用于光伏产业运营和管理的综合性系统,它结合了信息技术、数据分析、项目管理、客户管理等多个领域的知识,为光伏企业提供了一个全面、高效、智能的管理平台&…...

Java面试八股之请简述消息队列的发布订阅模式
请简述消息队列的发布订阅模式 发布订阅(Publish-Subscribe,简称 Pub/Sub)模型是一种消息传递模式,它在组件之间提供了高度的解耦和灵活性。这种模式广泛应用于分布式系统、事件驱动架构以及消息队列系统中。下面是发布订阅模型的…...

七、2 ADC数模转换器有关函数介绍(Keil5)
函数介绍 (1)ADCCLK的配置函数(在rcc.h中) (2)ADC的库函数(在adc.h中)...
)
了解载波侦听多路访问CSMA(上)
1.CSMA的思想 CSMA的全称是Carrier Sense Multiple Access,在笔者的理解中,其更趋向于一种理论研究的随机接入协议,或者说,基于其思想诞生了比如CSMA/CD与CSMA/CA这样的具体协议。CSMA可以分成以下三种: 1-persistent…...

conda相比python好处
Conda 作为 Python 的环境和包管理工具,相比原生 Python 生态(如 pip 虚拟环境)有许多独特优势,尤其在多项目管理、依赖处理和跨平台兼容性等方面表现更优。以下是 Conda 的核心好处: 一、一站式环境管理:…...

深入剖析AI大模型:大模型时代的 Prompt 工程全解析
今天聊的内容,我认为是AI开发里面非常重要的内容。它在AI开发里无处不在,当你对 AI 助手说 "用李白的风格写一首关于人工智能的诗",或者让翻译模型 "将这段合同翻译成商务日语" 时,输入的这句话就是 Prompt。…...

SkyWalking 10.2.0 SWCK 配置过程
SkyWalking 10.2.0 & SWCK 配置过程 skywalking oap-server & ui 使用Docker安装在K8S集群以外,K8S集群中的微服务使用initContainer按命名空间将skywalking-java-agent注入到业务容器中。 SWCK有整套的解决方案,全安装在K8S群集中。 具体可参…...
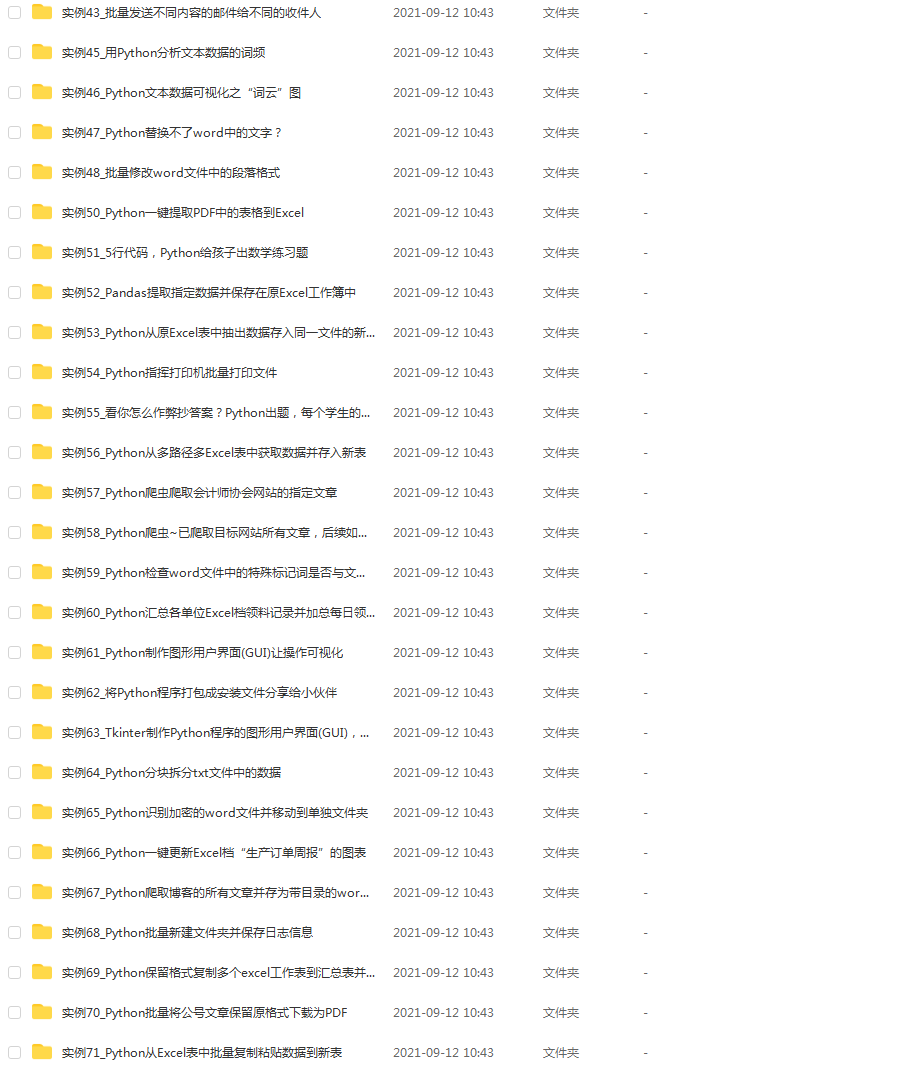
《从零掌握MIPI CSI-2: 协议精解与FPGA摄像头开发实战》-- CSI-2 协议详细解析 (一)
CSI-2 协议详细解析 (一) 1. CSI-2层定义(CSI-2 Layer Definitions) 分层结构 :CSI-2协议分为6层: 物理层(PHY Layer) : 定义电气特性、时钟机制和传输介质(导线&#…...
visual studio 2022更改主题为深色
visual studio 2022更改主题为深色 点击visual studio 上方的 工具-> 选项 在选项窗口中,选择 环境 -> 常规 ,将其中的颜色主题改成深色 点击确定,更改完成...
1.3 VSCode安装与环境配置
进入网址Visual Studio Code - Code Editing. Redefined下载.deb文件,然后打开终端,进入下载文件夹,键入命令 sudo dpkg -i code_1.100.3-1748872405_amd64.deb 在终端键入命令code即启动vscode 需要安装插件列表 1.Chinese简化 2.ros …...

Nginx server_name 配置说明
Nginx 是一个高性能的反向代理和负载均衡服务器,其核心配置之一是 server 块中的 server_name 指令。server_name 决定了 Nginx 如何根据客户端请求的 Host 头匹配对应的虚拟主机(Virtual Host)。 1. 简介 Nginx 使用 server_name 指令来确定…...

拉力测试cuda pytorch 把 4070显卡拉满
import torch import timedef stress_test_gpu(matrix_size16384, duration300):"""对GPU进行压力测试,通过持续的矩阵乘法来最大化GPU利用率参数:matrix_size: 矩阵维度大小,增大可提高计算复杂度duration: 测试持续时间(秒&…...

成都鼎讯硬核科技!雷达目标与干扰模拟器,以卓越性能制胜电磁频谱战
在现代战争中,电磁频谱已成为继陆、海、空、天之后的 “第五维战场”,雷达作为电磁频谱领域的关键装备,其干扰与抗干扰能力的较量,直接影响着战争的胜负走向。由成都鼎讯科技匠心打造的雷达目标与干扰模拟器,凭借数字射…...

爬虫基础学习day2
# 爬虫设计领域 工商:企查查、天眼查短视频:抖音、快手、西瓜 ---> 飞瓜电商:京东、淘宝、聚美优品、亚马逊 ---> 分析店铺经营决策标题、排名航空:抓取所有航空公司价格 ---> 去哪儿自媒体:采集自媒体数据进…...
