【数据结构】实现二叉树的基本操作
目录
1. 二叉树的基本操作
2. 具体实现
2.1 创建BinaryTree类以及简单创建一棵树
2.2 前序遍历
2.3 中序遍历
2.4 后序遍历
2.5 层序遍历
2.6 获取树中节点的个数
2.7 获取叶子节点的个数
2.8 获取第K层节点的个数
2.9 获取二叉树的高度
2.10 检测值为val的元素是否存在
2.11 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
3. 整体代码 + 测试代码
测试结果:
上一篇已经了解了一些二叉树的基本内容,这篇来讲二叉树的基本操作。
1. 二叉树的基本操作
// 前序遍历void preOrder(TreeNode root); // 中序遍历void inOrder(TreeNode root);// 后序遍历void postOrder(TreeNode root);// 获取树中节点的个数:遍历思路public static int nodeSize;void size(TreeNode root);// 获取节点的个数:子问题的思路int size2(TreeNode root);//获取叶子节点的个数:遍历思路public static int leafSize = 0;void getLeafNodeCount1(TreeNode root);// 获取叶子节点的个数:子问题int getLeafNodeCount2(TreeNode root);// 获取第K层节点的个数int getKLevelNodeCount(TreeNode root, int k);// 获取二叉树的高度,时间复杂度:O(N)int getHeight(TreeNode root);// 检测值为value的元素是否存在TreeNode find(TreeNode root, char val);//层序遍历void levelOrder(TreeNode root);// 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root);2. 具体实现
2.1 创建BinaryTree类以及简单创建一棵树

public class MyBinTree {private class TreeNode {char val;TreeNode left;// 左孩子的引用,常常代表左孩子为根的整棵左子树TreeNode right;// 右孩子的引用,常常代表右孩子为根的整棵右子树public TreeNode(char val) {this.val = val;}}public TreeNode createTree() {TreeNode root = new TreeNode('A');TreeNode node1 = new TreeNode('B');TreeNode node2 = new TreeNode('C');TreeNode node3 = new TreeNode('D');TreeNode node4 = new TreeNode('E');TreeNode node5 = new TreeNode('F');TreeNode node6 = new TreeNode('G');TreeNode node7 = new TreeNode('H');TreeNode node8 = new TreeNode('I');root.left = node1;root.right = node2;node1.left = node3;node1.right = node5;node2.right = node6;node3.left = node4;node5.left = node7;node5.right = node8;return root;}
}2.2 前序遍历
"根左右":从树根开始,先遍历根节点,继续递归的遍历左子树,最后再递归的遍历右子树。
public void preOrder(TreeNode root) {// 1.base caseif (root == null) {return;}// 根System.out.print(root.val + " ");// 左preOrder(root.left);//右preOrder(root.right);}2.3 中序遍历
"左根右":先递归的访问左子树,然后访问根节点,最后递归的访问右子树。
// 中序遍历public void inOrder(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return;}// 先左子树的中序inOrder(root.left);// 根System.out.print(root.val + " ");// 再右子树的中序inOrder(root.right);}2.4 后序遍历
"左右根":先递归的访问左子树,然后递归的访问右子树,最后访问根节点。
// 后序遍历public void postOrder(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return;}// 先左子树的后序postOrder(root.left);// 再右子树的后序postOrder(root.right);// 根System.out.print(root.val + " ");}2.5 层序遍历
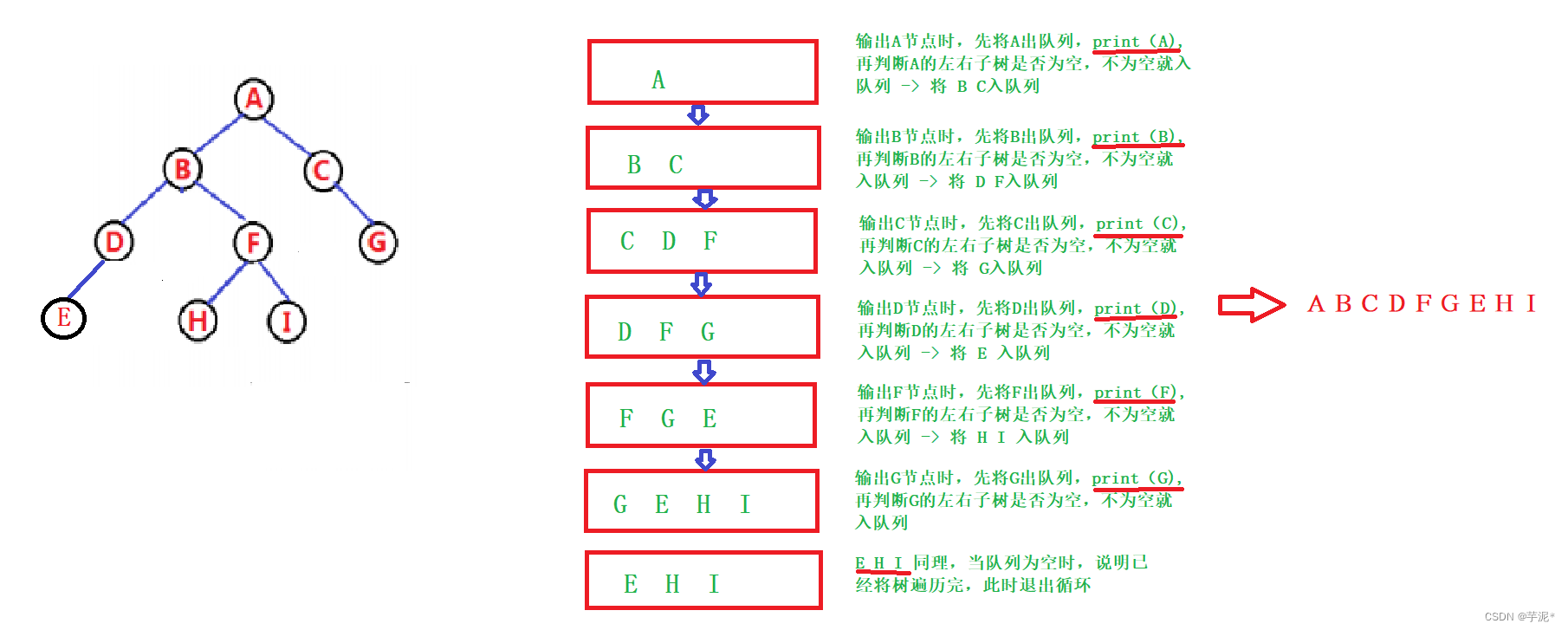
借助队列先进先出的特点来遍历节点:
void levelOrder(TreeNode root) {if (root == null){System.out.println("这是颗空树!!!");return;}// 借助队列来模拟层序遍历的过程Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);// 队列为空,表示所有元素访问完毕while (!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNode cur = queue.pop();System.out.print(cur.val + " ");// 依次将当前节点的左右子树依次入队if (cur.left != null){queue.offer(cur.left);}if (cur.right != null){queue.offer(cur.right);}}}2.6 获取树中节点的个数
将问题拆分成根节点与左右子树的问题,解决根节点的问题再递归调用本方法解决左右子树的问题。
第一种:需要一个全局变量来保存节点的个数,每走到一个节点先判断它是否为空,为空返回,否则加上这个节点即nodeSize+1,然后再递归的访问它的左右子树。
第二种:每走到一个节点先判断它是否为空,为空返回,否则返回1 + 左子树的节点个数 + 右子树的节点个数。
public static int nodeSize;/*** 获取树中节点的个数:遍历思路*/void size(TreeNode root) {if (root == null){return;}nodeSize ++;size(root.left);size(root.right);}/*** 获取节点的个数:子问题的思路*/int size2(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;return size2(root.left) + size2(root.right) + 1;}2.7 获取叶子节点的个数
与上一个的思路类似,也是拆分成根节点与左右子树的问题再递归调用本方法。
第一种:需要一个全局变量来保存叶子节点的个数,每走到一个节点先判断它是否为空,为空返回,再判断它是否为叶子节点(它的左右子树是否为空),是则leafSize+1,然后再递归的访问它的左右子树。
第二种:每走到一个节点先判断它是否为空,为空返回,再判断它是否为叶子节点(它的左右子树是否为空),是,返回1,否则返回左子树的叶子节点个数 + 右子树的叶子节点个数。
/*获取叶子节点的个数:遍历思路*/public static int leafSize = 0;void getLeafNodeCount1(TreeNode root) {if(root == null){return;}if (root.left == null && root.right == null){leafSize ++;}getLeafNodeCount1(root.left);getLeafNodeCount1(root.right);}/*获取叶子节点的个数:子问题*/int getLeafNodeCount2(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {return 1;}return getLeafNodeCount2(root.left) + getLeafNodeCount2(root.right);}2.8 获取第K层节点的个数
(1)判断根节点是否为空或k是否合法,根节点为空或k不合法返回0
(2)再判断是否到了第k层(k == 1),是,返回1(第k层节点个数+1)
(3)否则(没到第k层)返回根节点的左右子树的叶子节点。
int getKLevelNodeCount(TreeNode root, int k) {if (root == null || k <= 0){return 0;}if (k == 1){return 1;}return getKLevelNodeCount(root.left,k - 1) + getKLevelNodeCount(root.right,k - 1);}2.9 获取二叉树的高度
(1)判断根节点是否为空,根节点为空,直接返回0
(2)再判断根节点的左右子树是否为空(判断树是否只有一个节点),是,返回1
(3)返回 本层高度1 + 根节点的左右子树中高度较大的数(递归的交给getHeigth方法判断)
/*获取二叉树的高度时间复杂度:O(N)*/int getHeight(TreeNode root) {if (root == null){return 0;}if(root.left == null && root.right == null){return 1;}return 1 + Math.max(getHeight(root.left),getHeight(root.right));}2.10 检测值为val的元素是否存在
前序遍历的思路
第一种:
(1)判断根节点是否为空,根节点为空,直接返回null(不存在)
(2)判断根节点的值是否等于val,是,说明找到了该元素,返回根节点
(3)判断左子树中是否存在val,存在,返回该节点;不存在,再到右子树中寻找。
第二种:
与第一种思路一致,但是返回值使用布尔值,代码更简洁了。
// 检测值为value的元素是否存在1TreeNode find(TreeNode root, char val) {if (root == null){return null;}if (root.val == val){return root;}TreeNode node = find(root.left,val);if (node != null){return node;}return find(root.right,val);}
// 检测值为value的元素是否存在2public boolean contains(TreeNode root,char val){if (root == null) {return false;}if (root.val == val){return true;}return contains(root.left,val) || contains(root.right,val);}2.11 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
按照层序遍历的方式遍历完全二叉树
step1:当前完全二叉树的每个节点都是度为2的节点,碰到第一个叶子节点或者只有左子树没有右子树的节点时转入step2;碰到第一个只有右子树没有左子树的节点直接返回false。
step2:当前完全二叉树全是叶子节点
boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);boolean isStep1 = true;while (!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = queue.poll();if(isStep1){if(node.left != null && node.right != null){queue.offer(node.left);queue.offer(node.right);} else if (node.left != null) {queue.offer(node.left);isStep1 = false;} else if (node.right != null){return false;}else {isStep1 = false;}}else {if(node.left != null || node.right != null){return false;}}}return true;}3. 整体代码 + 测试代码
import java.util.Deque;
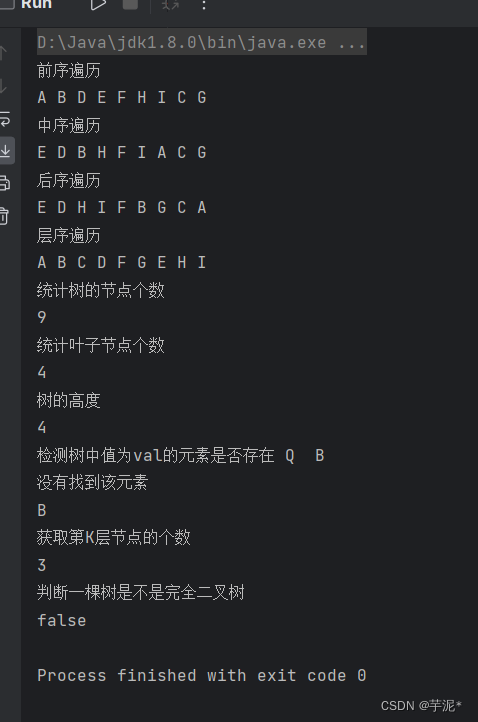
import java.util.LinkedList;public class BinaryTree {static class TreeNode {public char val;public TreeNode left;//左孩子的引用public TreeNode right;//右孩子的引用public TreeNode(char val) {this.val = val;}}/*** 创建一棵二叉树 返回这棵树的根节点** @return*/public TreeNode createTree() {TreeNode root = new TreeNode('A');TreeNode node1 = new TreeNode('B');TreeNode node2 = new TreeNode('C');TreeNode node3 = new TreeNode('D');TreeNode node4 = new TreeNode('E');TreeNode node5 = new TreeNode('F');TreeNode node6 = new TreeNode('G');TreeNode node7 = new TreeNode('H');TreeNode node8 = new TreeNode('I');root.left = node1;root.right = node2;node1.left = node3;node1.right = node5;node2.right = node6;node3.left = node4;node5.left = node7;node5.right = node8;return root;}// 前序遍历public void preOrder(TreeNode root) {if(root == null){return;}System.out.print(root.val + " ");preOrder(root.left);preOrder(root.right);}// 中序遍历void inOrder(TreeNode root) {if(root == null){return;}inOrder(root.left);System.out.print(root.val + " ");inOrder(root.right);}// 后序遍历void postOrder(TreeNode root) {if(root == null){return;}postOrder(root.left);postOrder(root.right);System.out.print(root.val + " ");}public static int nodeSize;/*** 获取树中节点的个数:遍历思路*/void size(TreeNode root) {if (root == null){return;}nodeSize ++;size(root.left);size(root.right);}/*** 获取节点的个数:子问题的思路** @param root* @return*/int size2(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;return size2(root.left) + size2(root.right) + 1;}/*获取叶子节点的个数:遍历思路*/public static int leafSize = 0;void getLeafNodeCount1(TreeNode root) {if(root == null){return;}if (root.left == null && root.right == null){leafSize ++;}getLeafNodeCount1(root.left);getLeafNodeCount1(root.right);}/*获取叶子节点的个数:子问题*/int getLeafNodeCount2(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {return 1;}return getLeafNodeCount2(root.left) + getLeafNodeCount2(root.right);}/*获取第K层节点的个数*/int getKLevelNodeCount(TreeNode root, int k) {if (root == null || k <= 0){return 0;}if (k == 1){return 1;}return getKLevelNodeCount(root.left,k - 1) + getKLevelNodeCount(root.right,k - 1);}/*获取二叉树的高度时间复杂度:O(N)*/int getHeight(TreeNode root) {if (root == null){return 0;}if(root.left == null && root.right == null){return 1;}return 1 + Math.max(getHeight(root.left),getHeight(root.right));}// 检测值为value的元素是否存在1TreeNode find(TreeNode root, char val) {if (root == null){return null;}if (root.val == val){return root;}TreeNode node = find(root.left,val);if (node != null){return node;}return find(root.right,val);}// 检测树中值为val的元素是否存在2public boolean contains(TreeNode root,char val){if (root == null) {return false;}if (root.val == val){return true;}return contains(root.left,val) || contains(root.right,val);}//层序遍历void levelOrder(TreeNode root) {if (root == null){System.out.println("这是颗空树!!!");return;}Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNode cur = queue.pop();System.out.print(cur.val + " ");if (cur.left != null){queue.offer(cur.left);}if (cur.right != null){queue.offer(cur.right);}}}// 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);boolean isStep1 = true;while (!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = queue.poll();if(isStep1){if(node.left != null && node.right != null){queue.offer(node.left);queue.offer(node.right);} else if (node.left != null) {queue.offer(node.left);isStep1 = false;} else if (node.right != null){return false;}else {isStep1 = false;}}else {if(node.left != null || node.right != null){return false;}}}return true;}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();TreeNode root = tree.createTree();System.out.println("前序遍历");tree.preOrder(root);System.out.println();System.out.println("中序遍历");tree.inOrder(root);System.out.println();System.out.println("后序遍历");tree.postOrder(root);System.out.println();System.out.println("层序遍历");tree.levelOrder(root);System.out.println();System.out.println("统计树的节点个数");tree.size(root);System.out.println(nodeSize);System.out.println("统计叶子节点个数");tree.getLeafNodeCount1(root);System.out.println(leafSize);System.out.println("树的高度");System.out.println(tree.getHeight(root));System.out.println("检测树中值为val的元素是否存在");
// System.out.println(tree.find(root,'x').val);if (tree.find(root,'Q') == null){System.out.println("没有找到该元素");}else {System.out.println(tree.find(root,'x').val);}if (tree.find(root,'B') == null){System.out.println("没有找到该元素");}else {System.out.println(tree.find(root,'B').val);}System.out.println("获取第K层节点的个数");System.out.println(tree.getKLevelNodeCount(root,3));System.out.println("判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树");System.out.println(tree.isCompleteTree(root));}}
测试结果:
相关文章:

【数据结构】实现二叉树的基本操作
目录 1. 二叉树的基本操作 2. 具体实现 2.1 创建BinaryTree类以及简单创建一棵树 2.2 前序遍历 2.3 中序遍历 2.4 后序遍历 2.5 层序遍历 2.6 获取树中节点的个数 2.7 获取叶子节点的个数 2.8 获取第K层节点的个数 2.9 获取二叉树的高度 2.10 检测值为val的元素是否…...
代码随想录算法训练营第五十二天| ● 300.最长递增子序列 ● 674. 最长连续递增序列 ● 718. 最长重复子数组
300.最长递增子序列 看完题后的思路 dp[i] [0,i]子数组中,以nums[i]结尾的子序列的长度 dp[i]dp[j]1 j从i-1向0遍历,在所有nums[j]<nums[i]中dp[j]最大 初始化 dp[0]1 代码 class Solution {public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {if (nums.length0){return 0;}int[] dpne…...

手机验证发送及其验证(基于springboot+redis)保姆级
在Java开发中,发送手机验证码时需要考虑以下几个问题: 验证码的有效期:验证码应该有一定的有效期,一般设置为几分钟或者十几分钟。过期的验证码应该被认为是无效的,不能用于验证用户身份。手机号码格式的校验…...

【JavaScript 逆向】数美滑块逆向分析
声明本文章中所有内容仅供学习交流,相关链接做了脱敏处理,若有侵权,请联系我立即删除!案例目标验证码:aHR0cHM6Ly93d3cuaXNodW1laS5jb20vbmV3L3Byb2R1Y3QvdHcvY29kZQ以上均做了脱敏处理,Base64 编码及解码方…...

多任务之线程
文章目录一、多任务是什么?二、多任务-线程四、通过继承Tread类完成创建线程五、资源竞争六、同步与互斥锁七、对峙与避免死锁一、多任务是什么? 多个函数同时执行一件事情就是多任务,没有多任务的时候任务执行都是按照顺序的,而…...
(数字图像处理MATLAB+Python)第二章数字图像处理基础-第二节:色度学基础与颜色模型
文章目录一:颜色匹配二:CIE 1931-RGB系统三:CIE 1931标准色度系统四:CIE 1976Lab均匀颜色空间五:孟塞尔表色系统(1)孟塞尔明度(Value,记为V)(2)孟塞尔彩度(Ch…...
)
【华为OD机试 2023最新 】 网上商城优惠活动(C++)
文章目录 题目描述输入描述输出描述备注用例题目解析C++题目描述 某网上商场举办优惠活动,发布了满减、打折、无门槛3种优惠券,分别为: 每满100元优惠10元,无使用数限制,如100199元可以使用1张减10元,200299可使用2张减20元,以此类推;92折券,1次限使用1张,如100元,…...

记一次CentOS 8 部署packstack部署OpenStack失败案例,请直接看最后
首先你需要一台安装好CentOS8 的虚拟机,相关参数如图。两块网卡,网卡1 NAT IP 192.168.100.100 GW192.168.100.2 网卡2 可不做配置。能ping通百度。创建完成虚拟机记得打好快照。 开机编辑基本配置环境变量 [rootlocalhost ~]# nmcli connection show NA…...

【2023春招】美团技术岗笔试10min+AK
随手投递了前端&移动端,笔试2道算法+选择+行测题(为什么笔试会有行测题?) 目录 T1-火车栈结构 题意 输入描述 输出描述 样例 AC_Code T2-春游...

Echarts实现图表自适应屏幕分辨率
一:简介 之前做项目的时候要实现echarts图表随浏览器窗口大小变化而改变,echarts本身提供了一个resize()方法,然后我们需要用一个函数实现浏览器窗口监听,最初我选用的是window.onresize方法,当页面只有一个图表时可以…...

【2023年第十一届泰迪杯数据挖掘挑战赛】B题:产品订单的数据分析与需求预测 建模及python代码详解 问题一
相关链接 【2023年第十一届泰迪杯数据挖掘挑战赛】B题:产品订单的数据分析与需求预测 建模及python代码详解 问题一 【2023年第十一届泰迪杯数据挖掘挑战赛】B题:产品订单的数据分析与需求预测 建模及python代码详解 问题二 1 题目 一.问题…...

【蓝桥杯嵌入式】第十三届蓝桥杯嵌入式国赛客观题以及详细题解
题1 概念题。 USRAT:异步串口通信,常用于数据传输;SW-DP:SWD 的全称应该是 The Serial Wire Debug Port (SW-DP),也就是串行调试端口,是 >ARM 目前支持的两种调试端口之一;JTAG-DP:另一个调试…...

java中Map遍历的4种方式
目录 1、map.entrySet()方式 2、map.keySet()方式 3、map.values()方式 4、forEach方式 本文以如下map案例: Map<String, String> map new HashMap<>(); map.put("student1", "张三"); map.put("student2", "…...
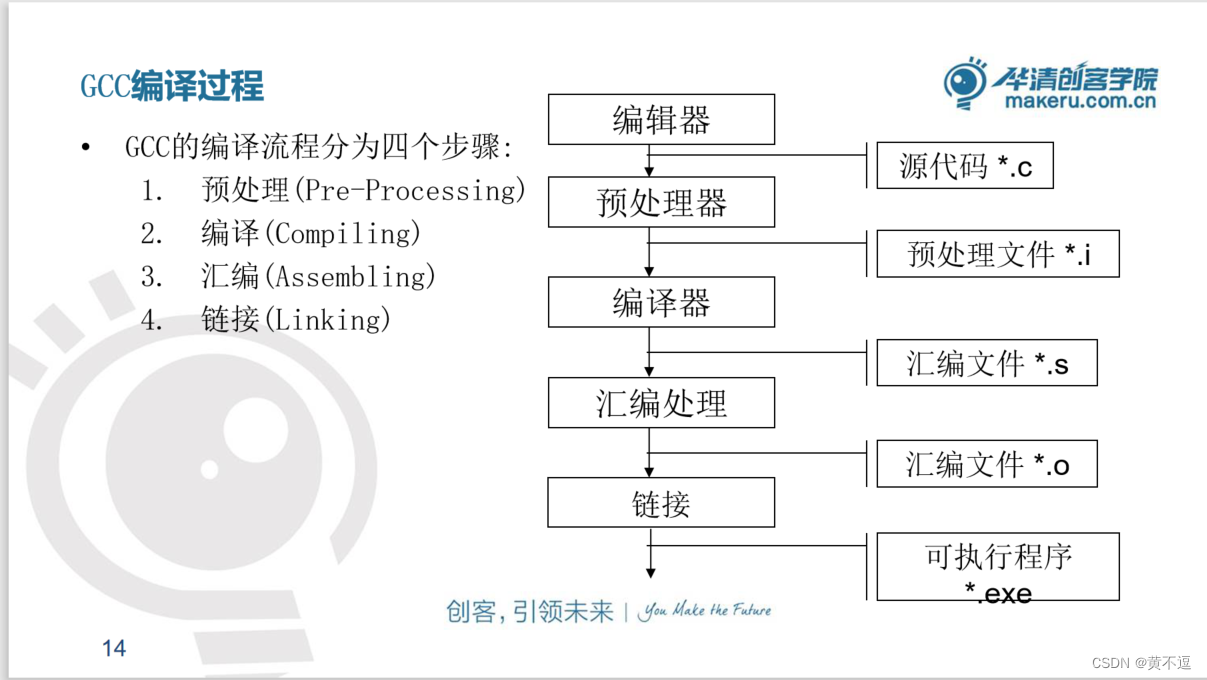
GCC 编译器的主要组件和编译过程
主要组件: 分析器:分析器将源语言程序代码转换为汇编语言。因为要从一种格式转换为另一种格式(C到汇编),所以分析器需要知道目标机器的汇编语言。 汇编器:汇编器将汇编语言代码转换为CPU可以执行字节码。 …...

蓝桥杯冲刺 - week2
文章目录💬前言🌲day1最大和 (DP质因数分解)901. 滑雪 - 记忆化搜索🌲day21227. 分巧克力 - 二分🌲day31221. 四平方和 - 空间换时间1230. K倍区间🌲day41076. 迷宫问题 - 路径2017-迷宫-填空🌲day5848. 有…...
第十四届蓝桥杯三月真题刷题训练——第 20 天
目录 第 1 题:纸张尺寸 问题描述 输入格式 输出格式 样例输入1 样例输出1 样例输入 2 样例输出 2 运行限制 代码: 解析: 第 2 题:最大数字 第 3 题:全排列的价值_递推公式 问题描述 输入格式 输出格式…...
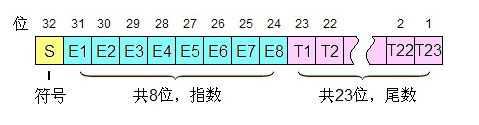
【C++】科普:C++中的浮点数怎么在计算机中表示?
这里我们以8.25这个数为例说明计算机时如何存取float类型的数据的: float a 8.25;引言 1. 所占位数 首先,明确一个概念,float类型的数据在常规计算机中通常占4个字节,也就是32位。其内存分布如图: 位字段说明所占位…...

Linux 多线程:多线程和多进程的对比
目录一、多进程优缺点二、多线程优缺点三、使用多执行流的场景在多任务处理中,我们既可以使用多进程,也可以使用多线程。但多进程和多线程并不是随意选择的,因为它们应对的场景不同,优缺点也不同。 一、多进程优缺点 多进程就是在…...
IO流你了解多少
IO流你了解多少 🏠个人主页:shark-Gao 🧑个人简介:大家好,我是shark-Gao,一个想要与大家共同进步的男人😉😉 🎉目前状况:23届毕业生,目前在某公…...

【C++】C++ 11 新特性之auto关键字
文章目录类型别名的思考auto简介auto关键字的特性类型别名的思考 随着程序越来越复杂,程序中用到的类型也越来越复杂,经常体现在: 类型难于拼写含义不明确导致容易出错 #include <string> #include <map> int main() {std::ma…...
)
Java 语言特性(面试系列2)
一、SQL 基础 1. 复杂查询 (1)连接查询(JOIN) 内连接(INNER JOIN):返回两表匹配的记录。 SELECT e.name, d.dept_name FROM employees e INNER JOIN departments d ON e.dept_id d.dept_id; 左…...

1688商品列表API与其他数据源的对接思路
将1688商品列表API与其他数据源对接时,需结合业务场景设计数据流转链路,重点关注数据格式兼容性、接口调用频率控制及数据一致性维护。以下是具体对接思路及关键技术点: 一、核心对接场景与目标 商品数据同步 场景:将1688商品信息…...
【单片机期末】单片机系统设计
主要内容:系统状态机,系统时基,系统需求分析,系统构建,系统状态流图 一、题目要求 二、绘制系统状态流图 题目:根据上述描述绘制系统状态流图,注明状态转移条件及方向。 三、利用定时器产生时…...

sqlserver 根据指定字符 解析拼接字符串
DECLARE LotNo NVARCHAR(50)A,B,C DECLARE xml XML ( SELECT <x> REPLACE(LotNo, ,, </x><x>) </x> ) DECLARE ErrorCode NVARCHAR(50) -- 提取 XML 中的值 SELECT value x.value(., VARCHAR(MAX))…...

成都鼎讯硬核科技!雷达目标与干扰模拟器,以卓越性能制胜电磁频谱战
在现代战争中,电磁频谱已成为继陆、海、空、天之后的 “第五维战场”,雷达作为电磁频谱领域的关键装备,其干扰与抗干扰能力的较量,直接影响着战争的胜负走向。由成都鼎讯科技匠心打造的雷达目标与干扰模拟器,凭借数字射…...
基于SpringBoot在线拍卖系统的设计和实现
摘 要 随着社会的发展,社会的各行各业都在利用信息化时代的优势。计算机的优势和普及使得各种信息系统的开发成为必需。 在线拍卖系统,主要的模块包括管理员;首页、个人中心、用户管理、商品类型管理、拍卖商品管理、历史竞拍管理、竞拍订单…...
Windows安装Miniconda
一、下载 https://www.anaconda.com/download/success 二、安装 三、配置镜像源 Anaconda/Miniconda pip 配置清华镜像源_anaconda配置清华源-CSDN博客 四、常用操作命令 Anaconda/Miniconda 基本操作命令_miniconda创建环境命令-CSDN博客...

怎么让Comfyui导出的图像不包含工作流信息,
为了数据安全,让Comfyui导出的图像不包含工作流信息,导出的图像就不会拖到comfyui中加载出来工作流。 ComfyUI的目录下node.py 直接移除 pnginfo(推荐) 在 save_images 方法中,删除或注释掉所有与 metadata …...
MacOS下Homebrew国内镜像加速指南(2025最新国内镜像加速)
macos brew国内镜像加速方法 brew install 加速formula.jws.json下载慢加速 🍺 最新版brew安装慢到怀疑人生?别怕,教你轻松起飞! 最近Homebrew更新至最新版,每次执行 brew 命令时都会自动从官方地址 https://formulae.…...
)
【LeetCode】3309. 连接二进制表示可形成的最大数值(递归|回溯|位运算)
LeetCode 3309. 连接二进制表示可形成的最大数值(中等) 题目描述解题思路Java代码 题目描述 题目链接:LeetCode 3309. 连接二进制表示可形成的最大数值(中等) 给你一个长度为 3 的整数数组 nums。 现以某种顺序 连接…...