Java中List、ArrayList与顺序表
List、ArrayList与顺序表
- List
- 什么是List
- 常用方法介绍
- List的使用
- ArrayList与顺序表
- 线性表
- 顺序表
- 接口的实现
- ArrayList简介
- ArrayList的使用
- ArrayList的构造
- ArrayList的常见操作
- ArrayList的遍历
- ArrayList的扩容机制
- ArrayList的具体使用
- 杨辉三角
- 简单的洗牌算法
- ArrayList的问题及思考
List
什么是List
在集合框架中,List是一个接口,继承自Collection。

Collection 也是一个接口,该接口中规范了后序容器中常用的一些方法,具体如下所示:

Iterable 也是一个接口,表示实现该接口的类是可以逐个元素进行遍历的,具体如下:

List的官方文档
在数据结构的角度看,List就是一个线性表,即n个具有相同类型元素的有限序列,在该序列上可以进行增删查改以及变量等操作。
常用方法介绍
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 尾插 e |
| void add(int index, E element) | 将 e 插入到 index 位置 |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | 尾插 c 中的元素 |
| E remove(int index) | 删除 index 位置元素 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 删除遇到的第一个 o |
| E get(int index) | 获取下标 index 位置元素 |
| E set(int index, E element) | 将下标 index 位置元素设置为 element |
| void clear() | 清空 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断 o 是否在线性表中 |
| int indexOf(Object o) | 返回第一个 o 所在下标 |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回最后一个 o 的下标 |
| List< E > subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 截取部分 list |
List的使用
注意:List是一个接口,并不能直接用来实例化。
如果要使用,必须去实例化List的实现类。在集合框架中,ArrayList和LinkedList都实现了List接口。
ArrayList与顺序表
线性表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。线性表实际上是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表有:顺序表、链表、栈、队列…
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就是说是一条连续的直线,但是在物理结构上并不是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。

顺序表
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储,在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
接口的实现
我们通过模拟实现来进一步学习ArrayList
public interface IList {// 新增元素,默认在数组最后新增public void add(int data);// 在 pos 位置新增元素public void add(int pos, int data);// 判定是否包含某个元素public boolean contains(int toFind);// 查找某个元素对应的位置public int indexOf(int toFind);// 获取 pos 位置的元素public int get(int pos);// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 valuepublic void set(int pos, int value);//删除第一次出现的关键字keypublic void remove(int toRemove);// 获取顺序表长度public int size();// 清空顺序表public void clear();// 打印顺序表,注意:该方法并不是顺序表中的方法,为了方便看测试结果给出的public void display();
}
public class MyArrayList implements IList{public int[] array;public int usedSize;public static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 5;public MyArrayList() {this.array = new int[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];}
}
接下来对接口中的方法进行重写
首先从最简单的打印顺序表和获取顺序表长度开始
@Override
public int size() {return this.usedSize;
}
@Override
public void display() {for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {System.out.print(array[i] + " ");}
}
接下来实现add(新增元素,默认在数组最后新增)
在实现之前,我们需要思考该数组会不会已经放满了,我们需要对其检查,若是放满我们还需要对其扩容,我们默认大小只有5,代码并不是简简单单的插入元素这么简单。
public boolean isFull(int[] array){return this.usedSize == array.length;
}private void grow(){this.array = Arrays.copyOf(this.array,this.array.length * 2);
}@Override
public void add(int data) {if(isFull(this.array)){grow();}array[usedSize] = data;usedSize++;
}
在 pos 位置新增元素,我们需要对pos及后面的元素往后移,从而空出位置来插入,我们需要从usedSize-1开始往后移,而不是pos,因为从pos往后会将后面的元素进行覆盖,从而丢失数据。还有我们依然需要对数组是否已经放满进行检查,而且需要对pos是否合法进行检查,负数是不可以的,超过数组usedSize是不可以插入的。usedSize这个位置是可以插入的,因为规定每次插入数据的位置,前驱必须存在,也就是说插入位置的前一个不能是空的。
public class PosIllegal extends RuntimeException{public PosIllegal() {}public PosIllegal(String msg) {super(msg);}
}
private void checkPosOfAdd(int pos) throws PosIllegal{if(pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize){throw new PosIllegal("插入位置不合法");}
}
@Override
public void add(int pos, int data) {try{checkPosOfAdd(pos);if(isFull(this.array)){grow();}for (int i = usedSize - 1; i >= pos ; i--) {this.array[i + 1] = this.array[i];}array[pos] = data;usedSize++;}catch(PosIllegal e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
接下来实现判定是否包含某个元素和查找某个元素对应的位置的方法。
@Overridepublic boolean contains(int toFind) {for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {if(array[i] == toFind){return true;}//如果存放的不是整型元素,而是引用类型的元素,则需要使用equals方法来比较,并且重写该方法。}return false;}@Overridepublic int indexOf(int toFind) {for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {if(array[i] == toFind){return i;}//如果存放的不是整型元素,而是引用类型的元素,则需要使用equals方法来比较,并且重写该方法。}return -1;}
获取 pos 位置的元素,对于获取元素,我们依然需要对pos位置是否合法进行检查,但是这一次pos位置不能小于0,而且不能大于usedSize -1,因为数组从0开始,usedSize不可能存放元素,对于获取元素我们还应该考虑一点,就是当数组为空时,我们是不能获取到任何元素的,所以我们需要对数组是否为空进行检查,当我们发现其为空时,我们需要抛出异常,因为无论我们返回何整数,都有可能在数组中存在,所以抛出异常是最好的。
public boolean isEmpty(){return this.usedSize == 0;
}private void checkEmpty(){if(isEmpty()){throw new EmptyException("顺序表为空");}
}private void checkPosOfGet(int pos){if(pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize -1){throw new PosIllegal("获取元素的位置不合法");}
}@Override
public int get(int pos) {try{checkEmpty();checkPosOfGet(pos);return array[pos];}catch(PosIllegal e){e.printStackTrace();}catch(EmptyException e){e.printStackTrace();}return -1;
}
给 pos 位置的元素设为 value,这就是更新的意思,也就是与得到元素类似需要对其位置进行检查,不能不能小于0,而且不能大于usedSize -1,也要对数组是否为空进行检查。
@Override
public void set(int pos, int value) {try{checkEmpty();checkPosOfGet(pos);array[pos] = value;}catch(PosIllegal e){e.printStackTrace();}catch(EmptyException e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
删除第一次出现的关键字key,首先要对顺序表是否为空进行判断,空是没办法删除的。不为空之后我们可以通过遍历查找该元素的下标,找不到直接返回,找到对其后的元素进行挪动来覆盖,最后不要忘了usedSize进行减一。
@Overridepublic void remove(int toRemove) {try{checkEmpty();int pos = indexOf(toRemove);if(pos == -1){return;}for (int i = pos; i < this.usedSize - 1; i++) {this.array[i] = this.array[i+1];}this.usedSize--;}catch(EmptyException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
清空顺序表,对于清空顺序表,在int数组中我们可以对其usedSize置为0,后面在add也只是覆盖,但是如果是引用类型,这样会造成内存泄漏,因为数组中依然有一段地址指向一个空间,而这个空间并没有什么作用,所以应该将其置为null。
@Override
public void clear() {this.usedSize = 0;/*for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {this.array[i] = null;}*/
}
到这里我们就将ArrayList中常用的方法模拟实现了。下面为完整代码和测试代码
public interface IList {// 新增元素,默认在数组最后新增public void add(int data);// 在 pos 位置新增元素public void add(int pos, int data);// 判定是否包含某个元素public boolean contains(int toFind);// 查找某个元素对应的位置public int indexOf(int toFind);// 获取 pos 位置的元素public int get(int pos);// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 valuepublic void set(int pos, int value);//删除第一次出现的关键字keypublic void remove(int toRemove);// 获取顺序表长度public int size();// 清空顺序表public void clear();// 打印顺序表,注意:该方法并不是顺序表中的方法,为了方便看测试结果给出的public void display();
}
public class PosIllegal extends RuntimeException{public PosIllegal() {}public PosIllegal(String msg) {super(msg);}
}
public class EmptyException extends RuntimeException{public EmptyException() {}public EmptyException(String message) {super(message);}
}
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyArrayList implements IList{public int[] array;public int usedSize;public static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 5;public MyArrayList() {this.array = new int[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];}public boolean isFull(int[] array){return this.usedSize == array.length;}private void grow(){this.array = Arrays.copyOf(this.array,this.array.length * 2);}@Overridepublic void add(int data) {if(isFull(this.array)){grow();}array[usedSize] = data;usedSize++;}private void checkPosOfAdd(int pos) throws PosIllegal{if(pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize){throw new PosIllegal("插入位置不合法");}}@Overridepublic void add(int pos, int data) {try{checkPosOfAdd(pos);if(isFull(this.array)){grow();}for (int i = usedSize - 1; i >= pos ; i--) {this.array[i + 1] = this.array[i];}array[pos] = data;usedSize++;}catch(PosIllegal e){e.printStackTrace();}}@Overridepublic boolean contains(int toFind) {for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {if(array[i] == toFind){return true;}//如果存放的不是整型元素,而是引用类型的元素,则需要使用equals方法来比较,并且重写该方法。}return false;}@Overridepublic int indexOf(int toFind) {for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {if(array[i] == toFind){return i;}//如果存放的不是整型元素,而是引用类型的元素,则需要使用equals方法来比较,并且重写该方法。}return -1;}public boolean isEmpty(){return this.usedSize == 0;}private void checkEmpty(){if(isEmpty()){throw new EmptyException("顺序表为空");}}private void checkPosOfGet(int pos){if(pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize -1){throw new PosIllegal("获取元素的位置不合法");}}@Overridepublic int get(int pos) {try{checkEmpty();checkPosOfGet(pos);return array[pos];}catch(PosIllegal e){e.printStackTrace();}catch(EmptyException e){e.printStackTrace();}return -1;}@Overridepublic void set(int pos, int value) {try{checkEmpty();checkPosOfGet(pos);array[pos] = value;}catch(PosIllegal e){e.printStackTrace();}catch(EmptyException e){e.printStackTrace();}}@Overridepublic void remove(int toRemove) {try{checkEmpty();int pos = indexOf(toRemove);if(pos == -1){return;}for (int i = pos; i < this.usedSize - 1; i++) {this.array[i] = this.array[i+1];}this.usedSize--;}catch(EmptyException e){e.printStackTrace();}}@Overridepublic int size() {return this.usedSize;}@Overridepublic void clear() {this.usedSize = 0;/*for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {this.array[i] = null;}*/}@Overridepublic void display() {for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {System.out.print(array[i] + " ");}System.out.println();}
}
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {MyArrayList list1 = new MyArrayList();IList list2 = new MyArrayList();System.out.println("初始有效元素个数:");System.out.println(list1.usedSize);System.out.println("打印初始顺序表");list1.display();System.out.println("打印初始数组大小");System.out.println(list1.size());list1.add(1);list1.add(2);list1.add(3);list1.add(4);System.out.println("打印插入元素后的顺序表");list1.display();System.out.println("打印插入元素后的顺序表大小");System.out.println(list1.size());list1.add(2,33);System.out.println("打印在指定位置插入元素后的顺序表");list1.display();//list1.add(44,4);System.out.println("顺序表是否包含某个元素");System.out.println(list1.contains(2));System.out.println(list1.contains(55));System.out.println("查找某个元素的指定位置");System.out.println(list1.indexOf(2));System.out.println(list1.indexOf(44));System.out.println("获取某个位置的元素");System.out.println(list1.get(1));//System.out.println(list1.get(100));System.out.println("更新某个位置的元素");list1.set(0,11);list1.display();System.out.println("删除第一次出现的关键字key");list1.remove(33);list1.display();System.out.println("清空顺序表");list1.clear();list1.display();//结果为://初始有效元素个数://0//打印初始顺序表////打印初始数组大小//0//打印插入元素后的顺序表//1 2 3 4 //打印插入元素后的顺序表大小//4//打印在指定位置插入元素后的顺序表//1 2 33 3 4 //顺序表是否包含某个元素//true//false//查找某个元素的指定位置//1//-1//获取某个位置的元素//2//更新某个位置的元素//11 2 33 3 4 //删除第一次出现的关键字key//11 2 3 4 //清空顺序表}
}
ArrayList简介
在集合框架中,ArrayList是一个普通的类,实现了List接口,具体框架图如下:

说明:
- ArrayList是以泛型的方式实现的,使用时必须要先实例化
- ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,表明ArrayList支持随机访问
- ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口,表明ArrayList是可以clone的
- ArrayList实现了Serializable接口,表明ArrayList是支持序列化的
- 和Vector不同,ArrayList不是线程安全的,在单线程下可以使用,在多线程中可以选择Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList
- ArrayList底层是一段连续的空间,并且可以动态扩容,是一个动态类型的顺序表。
ArrayList的使用
ArrayList的构造
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| ArrayList () | 无参构造 |
| ArrayList (Collection<? extends E> c) | 利用其他 Collection 构建 ArrayList |
| ArrayList (int initialCapacity) | 指定顺序表初始容量 |
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {//ArrayList创建//构造一个空的列表List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();//构造一个具有10个容量的列表List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>(10);list2.add(1);list2.add(2);list2.add(3);//list2.add("hello"); //编译失败,List<Integer>本身就限定了list2中只能存储整型元素//list3构造好之后,与list中的元素一致ArrayList<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>(list2);//避免省略类型,否则:任意类型的元素都可以存放,使用时很麻烦List list4 = new ArrayList();list4.add(1);list4.add("hello");}
}
ArrayList的常见操作
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 尾插 e |
| void add(int index, E element) | 将 e 插入到 index 位置 |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | 尾插 c 中的元素 |
| E remove(int index) | 删除 index 位置元素 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 删除遇到的第一个 o |
| E get(int index) | 获取下标 index 位置元素 |
| E set(int index, E element) | 将下标 index 位置元素设置为 element |
| void clear() | 清空 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断 o 是否在线性表中 |
| int indexOf(Object o) | 返回第一个 o 所在下标 |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回最后一个 o 的下标 |
| List< E > subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 截取部分 list |
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("food");list.add("book");list.add("clothes");list.add("drink");System.out.println(list); //[food, book, clothes, drink]//获取list中有效元素的个数System.out.println(list.size()); //4//获取和设置index位置上的元素,注意index必须介于[0,size)间System.out.println(list.get(1)); //booklist.set(1,"BOOK");System.out.println(list.get(1)); //BOOK//在list的index位置插入指定元素,index及后续的元素统一往后搬移一个位置list.add(1,"shoes");System.out.println(list); //[food, shoes, BOOK, clothes, drink]//删除指定元素,找到了就删除,该元素之后的元素统一往前搬移一个位置list.remove("shoes");System.out.println(list); //[food, BOOK, clothes, drink]//删除list中的index位置上的元素,注意index不用超过list中有效元素个数,否则会抛出下标越界异常list.remove(list.size() - 1); System.out.println(list); //[food, BOOK, clothes]//检测list中是否包含指定元素,包含返回true,否则返回falseif(!list.contains("drink")){list.add("drink");}System.out.println(list); //[food, BOOK, clothes, drink]//查找指定元素第一次出现的位置:indexOf从前往后找,lastIndexOf从后往前找list.add("bag");System.out.println(list); //[food, BOOK, clothes, drink, bag]System.out.println(list.indexOf("bag")); //4System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("bag")); //4//使用list中[0,4)之间的元素构成一个新的subList返回,但是和ArrayList共用一个elementData数组,//也就的引用指向同一个空间,当你修改subList中的元素,List指向的空间中的元素自然也改变了。List<String> ret = list.subList(0,4);System.out.println(ret); //[food, BOOK, clothes, drink]System.out.println(list); //[food, BOOK, clothes, drink, bag]ret.set(0,"FOOD");System.out.println(list); //[FOOD, BOOK, clothes, drink, bag]System.out.println(ret); //[FOOD, BOOK, clothes, drink]list.clear();System.out.println(list.size()); //0}
}
ArrayList的遍历
ArrayList可以使用三种方式遍历:for循环+下标、foreach、使用迭代器
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);list.add(4);System.out.println(list);System.out.println("=== for循环遍历 ===");for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("=== foreach遍历 ===");for (Integer x : list) {System.out.print(x + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("=== 使用迭代器Iterator输出 ===");Iterator<Integer> it1 = list.iterator();while(it1.hasNext()){System.out.print(it1.next() + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("=== 使用迭代器ListIterator输出 ===");ListIterator<Integer> it2 = list.listIterator();while(it2.hasNext()){System.out.print(it2.next() + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("=== 使用迭代器ListIterator输出 拓展 ===");ListIterator<Integer> it3 = list.listIterator(list.size());while(it3.hasPrevious()){System.out.print(it3.previous() + " ");}}//结果为://[1, 2, 3, 4]//=== for循环遍历 ===//1 2 3 4 //=== foreach遍历 ===//1 2 3 4 //=== 使用迭代器Iterator输出 ===//1 2 3 4 //=== 使用迭代器ListIterator输出 ===//1 2 3 4 //=== 使用迭代器ListIterator输出 拓展 ===//4 3 2 1
}
ArrayList的扩容机制
ArrayList是一个动态类型的顺序表,即:在插入元素的过程中会自动扩容。以下是ArrayList源码中扩容方式:
Object[] elementData; // 存放元素的空间
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 默认空间
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 默认容量大小
public boolean add(E e) {ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!elementData[size++] = e;return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);}return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {modCount++;// overflow-conscious codeif (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)grow(minCapacity);
}
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private void grow(int minCapacity) {// 获取旧空间大小int oldCapacity = elementData.length;// 预计按照1.5倍方式扩容int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);// 如果用户需要扩容大小 超过 原空间1.5倍,按照用户所需大小扩容if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;// 如果需要扩容大小超过MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,重新计算容量大小if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);// 调用copyOf扩容elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {// 如果minCapacity小于0,抛出OutOfMemoryError异常if (minCapacity < 0)throw new OutOfMemoryError();return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
总结:
- 检测是否真正需要扩容,如果是调用grow准备扩容
- 预估需要容量的大小
初步预估按照1.5倍大小扩容
如果用户所需大小超过预估1.5倍大小,则按照用户所需大小扩容
真正扩容之前检测是否能扩容成功,防止太大导致扩容失败 - 使用copyOf进行扩容
ArrayList的具体使用
杨辉三角
杨辉三角
给定一个非负整数 numRows,生成「杨辉三角」的前 numRows 行。
在「杨辉三角」中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。

示例 1:
输入: numRows = 5
输出: [[1],[1,1],[1,2,1],[1,3,3,1],[1,4,6,4,1]]


public class Test{//List<List<Integer>> 为二维数组public static List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> list0 = new ArrayList<>();list0.add(1);ret.add(list0);for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {List<Integer> curRow = new ArrayList<>();//处理第一个元素curRow.add(1);//中间for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {Integer data = ret.get(i-1).get(j-1) + ret.get(i-1).get(j);curRow.add(data);}//尾部curRow.add(1);ret.add(curRow);}return ret;}public static void main(String[] args) {List<List<Integer>> ret = generate(4);/*System.out.println(ret);*/for (int i = 0; i < ret.size(); i++) {for (int j = 0; j < ret.get(i).size(); j++) {System.out.print(ret.get(i).get(j) + " ");}System.out.println();}//结果为://1 //1 1 //1 2 1 //1 3 3 1 }
}
简单的洗牌算法
要求:
- 买52张牌
- 洗牌
- 3个人,每个人轮流拿五张
public class Card {public int rank; //牌面值public String suit; //花色public Card(int rank, String suit) {this.rank = rank;this.suit = suit;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "{" + rank + suit + '}';}
}
public class CardDemo {public static final String[] suits = {"♦","♣","♥","♠"};public List<Card> buyCard(){List<Card> cardList = new ArrayList<>(52);for (int i = 1; i <= 13 ; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {int rank = i;String suit = suits[j];cardList.add(new Card(rank,suit));}}return cardList;}public void shuffle(List<Card> cardlist){Random random = new Random();for (int i = cardlist.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {int index = random.nextInt(i);swap(cardlist,i,index);}}private void swap(List<Card> cardList, int i, int j){/*Card tmp = cardList[i];cardList[i] = cardList[j];cardList[j] = tmp;*/Card tmp = cardList.get(i);cardList.set(i,cardList.get(j));cardList.set(j,tmp);}public List<List<Card>> play(List<Card> cardList){List<List<Card>> ret = new ArrayList<>();List<Card> hand0 = new ArrayList<>();List<Card> hand1 = new ArrayList<>();List<Card> hand2 = new ArrayList<>();ret.add(hand0);ret.add(hand1);ret.add(hand2);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {ret.get(j).add(cardList.remove(0));}}return ret;}
}
public class Test{public static void main(String[] args) {//买一副52张的牌CardDemo cards = new CardDemo();List<Card> cardList = cards.buyCard();System.out.println(cardList);//洗牌cards.shuffle(cardList);System.out.println(cardList);//3个人,每个人轮流拿五张List<List<Card>> players = cards.play(cardList);for (int i = 0; i < players.size(); i++) {System.out.println("第"+(i+1) +"个人的牌:" + players.get(i));}//剩下的牌:System.out.print("剩下的牌:");System.out.println(cardList);}//结果为://[{1♦}, {1♣}, {1♥}, {1♠}, {2♦}, {2♣}, {2♥}, {2♠}, {3♦}, {3♣}, {3♥}, {3♠}, {4♦}, {4♣}, {4♥}, {4♠}, {5♦}, {5♣}, {5♥}, {5♠}, {6♦}, {6♣}, {6♥}, {6♠}, {7♦}, {7♣}, {7♥}, {7♠}, {8♦}, {8♣}, {8♥}, {8♠}, {9♦}, {9♣}, {9♥}, {9♠}, {10♦}, {10♣}, {10♥}, {10♠}, {11♦}, {11♣}, {11♥}, {11♠}, {12♦}, {12♣}, {12♥}, {12♠}, {13♦}, {13♣}, {13♥}, {13♠}]//[{4♠}, {9♥}, {5♣}, {1♦}, {12♣}, {13♥}, {3♦}, {8♣}, {4♦}, {5♠}, {2♠}, {5♦}, {10♥}, {13♦}, {12♥}, {10♦}, {7♥}, {10♠}, {7♣}, {11♦}, {9♦}, {5♥}, {1♠}, {8♠}, {11♥}, {13♣}, {4♥}, {12♦}, {3♥}, {6♠}, {8♦}, {6♥}, {3♠}, {13♠}, {6♦}, {1♥}, {1♣}, {2♦}, {4♣}, {10♣}, {7♠}, {3♣}, {2♣}, {7♦}, {9♠}, {6♣}, {9♣}, {2♥}, {8♥}, {12♠}, {11♣}, {11♠}]//第1个人的牌:[{4♠}, {1♦}, {3♦}, {5♠}, {10♥}]//第2个人的牌:[{9♥}, {12♣}, {8♣}, {2♠}, {13♦}]//第3个人的牌:[{5♣}, {13♥}, {4♦}, {5♦}, {12♥}]//剩下的牌:[{10♦}, {7♥}, {10♠}, {7♣}, {11♦}, {9♦}, {5♥}, {1♠}, {8♠}, {11♥}, {13♣}, {4♥}, {12♦}, {3♥}, {6♠}, {8♦}, {6♥}, {3♠}, {13♠}, {6♦}, {1♥}, {1♣}, {2♦}, {4♣}, {10♣}, {7♠}, {3♣}, {2♣}, {7♦}, {9♠}, {6♣}, {9♣}, {2♥}, {8♥}, {12♠}, {11♣}, {11♠}]
}
ArrayList的问题及思考
- ArrayList底层使用连续的空间,任意位置插入或者删除元素时,需要将该位置后序元素整体往前或者往后搬移,故时间复杂度为O(N)
- 增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间,会有不小的消耗。
- 增容一般是呈1.5倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到150,我们只想继续插入5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了45个数据空间。
关于ArrayList我们先了解和学习到这,希望这篇文章能帮助到你,谢谢你的阅读。
相关文章:

Java中List、ArrayList与顺序表
List、ArrayList与顺序表 List什么是List常用方法介绍List的使用 ArrayList与顺序表线性表顺序表接口的实现 ArrayList简介ArrayList的使用ArrayList的构造ArrayList的常见操作ArrayList的遍历ArrayList的扩容机制 ArrayList的具体使用杨辉三角简单的洗牌算法 ArrayList的问题及…...

缓存技巧 · Spring Cache Caffeine 高性能缓存库
Caffeine 背景 Caffeine是一个高性能的Java缓存库,它基于Guava Cache进行了增强,提供了更加出色的缓存体验。Caffeine的主要特点包括: 高性能:Caffeine使用了Java 8最新的StampedLock乐观锁技术,极大地提高了缓存的并…...
、队列(Queue)和路由键(Routing Key))
RabbitMq中交换机(Exchange)、队列(Queue)和路由键(Routing Key)
RabbitMQ 是一个消息代理系统,使用交换机(Exchange)、队列(Queue)和路由键(Routing Key)来管理消息的传递。它们分别起到不同的作用,构成了消息从生产者到消费者的传递路径。 以下是…...

解码 OpenAI 的 o1 系列大型语言模型
OpenAI 表示,其 Strawberry 项目已升级为新的大型语言模型 (LLM) 系列,公司将其命名为 OpenAI o1。 该公司表示,新系列模型还包括一个 o1-mini 版本,以提高成本效益,可根据其推理能力与最新的GPT-4o 模型进行区分。 …...

大小端字节序 和 内存高低地址顺序
目录 1. 大小端字节序 1.1 什么是大小端字节序? 1.2 为什么有大小端字节序? 1.3 习题:用程序结果判断大端小端 2. 各种易混淆的高低地址顺序 2.1 监视窗口的地址表示【计算机标准展示方式】 2.2 横向地址表示 2.3 一个字节 与 多个字节 的地址…...

Spring扩展点系列-MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
文章目录 简介源码分析示例示例一:Spring中Autowire注解的依赖注入 简介 spring容器中Bean的生命周期内所有可扩展的点的调用顺序 扩展接口 实现接口ApplicationContextlnitializer initialize AbstractApplicationContext refreshe BeanDefinitionRegistryPos…...

Centos 7.9 使用 crontab 实现开机启动
[rootlocalhost ~]# crontab -e [rootlocalhost ~]# reboot # crontab -e reboot /path/to/my/program # reboot 表示重启开机的时候运行一次 reboot /test/hello.sh 参考: Linux crontab 命令 https://www.runoob.com/linux/linux-comm-crontab.html Run prog…...

基于微信的设备故障报修管理系统设计与实现+ssm论文源码调试讲解
2相关技术 2.1微信小程序 小程序是一种新的开放能力,开发者可以快速地开发一个小程序。小程序可以在微信内被便捷地获取和传播,同时具有出色的使用体验。尤其拥抱微信生态圈,让微信小程序更加的如虎添翼,发展迅猛。 2.2 MYSQL数据…...

yolo自动化项目实例解析(二)ui页面整理 1.78
我们在上一章整理main.py 的if __name__ __main__: 内容还留下面这一段, from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *from lanrenauto.moni.moni import *from PyQt5.QtGui import *app QApplication(sys.argv) # 初始化Qt应用ratio screen_width / 2560 # 分辨率比例# 设…...
PyQt / PySide + Pywin32 + ctypes 自定义标题栏窗口 + 完全还原 Windows 原生窗口边框特效项目
项目地址: GitHub - github201014/PyQt-NativeWindow: A class of window include nativeEvent, use PySide or PyQt and Pywin32 and ctypesA class of window include nativeEvent, use PySide or PyQt and Pywin32 and ctypes - github201014/PyQt-NativeWindow…...

面试时遇见的项目问题
汽车在线销售平台项目 项目的甲方是谁? 甲方是一家汽车销售公司,他们希望通过互联网技术提升销售效率和服务质量 为什么要做这个项目? 很多消费者越来越倾向于在线上完成购车之前的大部分决策。所以甲方找到我们希望通过建立一个在线的销…...

在线骑行网站设计与实现
摘 要 传统办法管理信息首先需要花费的时间比较多,其次数据出错率比较高,而且对错误的数据进行更改也比较困难,最后,检索数据费事费力。因此,在计算机上安装在线骑行网站软件来发挥其高效地信息处理的作用,…...
)
大批量查询方案简记(Mybatis流式查询)
Mybatis的流式查询 摘要: 介绍使用mybatis流式查询解决大数据量查询问题. 1 业务背景 开发中遇到一个业务,说起来也很无奈:公司用的数据库MySQL,一张表里只保留了一个月的数据,但是数据量竟然高达2000W还要多,然后用户有个需求也很恶心,为了完成这个业务我需要定时任务每一个月…...
python - 子类为什么调用父类的方法
菜鸟教程 - 面向对象https://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-class.html为什么写这个呢 ,因为很多时候,事情很简单,但我往往记住了使用方式,忘记了使用原因,也因为自己看到super()时,也想问为什么要用supe…...

【JavaScript】数据结构之字典 哈希表
字典 键值对存储的,类似于js的对象,但在js对象中键[key]都是字符串类型或者会转换成字符串类型,因此后声明的键值会覆盖之前声明的值。字典以map表示,map的键不会转换类型。 let map new Map() map.set(a, 1) map.set(b, 2) ma…...

Adobe出现This unlicensed Photoshop app has been disabled
Adobe Acrobat或Photoshop软件突然出现This unlicensed Photoshop app has been disabled 症状 解决方法 删除软件安装目录下的AcroCEF和acrocef_1l两个子文件夹。主要是为了删除AcroCEF.exe。 如果存在复发,则删除xxxxxxx\AdobeGCClient\AdobeGCClient.exe。 不…...

elementui 单元格添加样式的两种方法
方法一 <el-table-column fixed prop"name" label"姓名" width"120"> <<template scope"scope"> <span :class"{red:scope.row.color1,yell:scope.row.color2,green:scope.row.col…...

如何有效管理技术债务:IT项目中的长期隐患
如何有效管理技术债务:IT项目中的长期隐患 在软件开发和IT项目管理中,技术债务(Technical Debt)是一个经常被忽视却又至关重要的概念。技术债务就像金融债务一样,当我们在项目开发中选择了某些“捷径”来快速交付&…...

2024 “华为杯” 中国研究生数学建模竞赛(D题)深度剖析|大数据驱动的地理综合问题|数学建模完整代码+建模过程全解全析
当大家面临着复杂的数学建模问题时,你是否曾经感到茫然无措?作为2022年美国大学生数学建模比赛的O奖得主,我为大家提供了一套优秀的解题思路,让你轻松应对各种难题! CS团队倾注了大量时间和心血,深入挖掘解…...

Linux 清空redis缓存及查询key值
1.登录redis redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379# 如果有密码需要下面这一步 auth 你的密码直接带密码登录 redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379 -a 密码出现ok表示登录成功 2.标题查看所有key keys *3.查看某个key 的值 get keyName4.清空整个Redis服务器的数据 flushall5.查看…...

iOS 26 携众系统重磅更新,但“苹果智能”仍与国行无缘
美国西海岸的夏天,再次被苹果点燃。一年一度的全球开发者大会 WWDC25 如期而至,这不仅是开发者的盛宴,更是全球数亿苹果用户翘首以盼的科技春晚。今年,苹果依旧为我们带来了全家桶式的系统更新,包括 iOS 26、iPadOS 26…...

应用升级/灾备测试时使用guarantee 闪回点迅速回退
1.场景 应用要升级,当升级失败时,数据库回退到升级前. 要测试系统,测试完成后,数据库要回退到测试前。 相对于RMAN恢复需要很长时间, 数据库闪回只需要几分钟。 2.技术实现 数据库设置 2个db_recovery参数 创建guarantee闪回点,不需要开启数据库闪回。…...
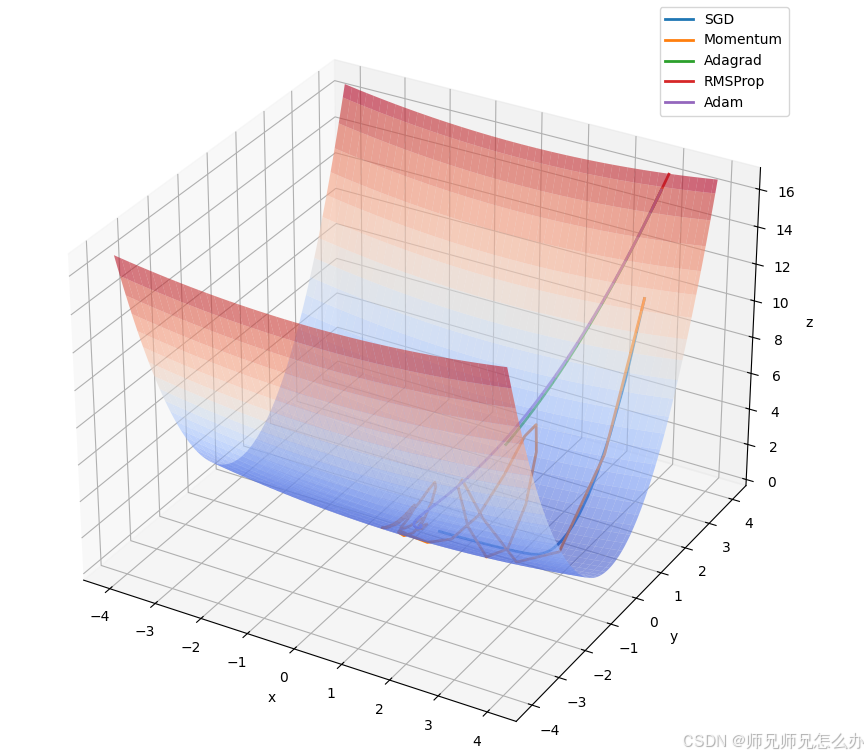
【人工智能】神经网络的优化器optimizer(二):Adagrad自适应学习率优化器
一.自适应梯度算法Adagrad概述 Adagrad(Adaptive Gradient Algorithm)是一种自适应学习率的优化算法,由Duchi等人在2011年提出。其核心思想是针对不同参数自动调整学习率,适合处理稀疏数据和不同参数梯度差异较大的场景。Adagrad通…...
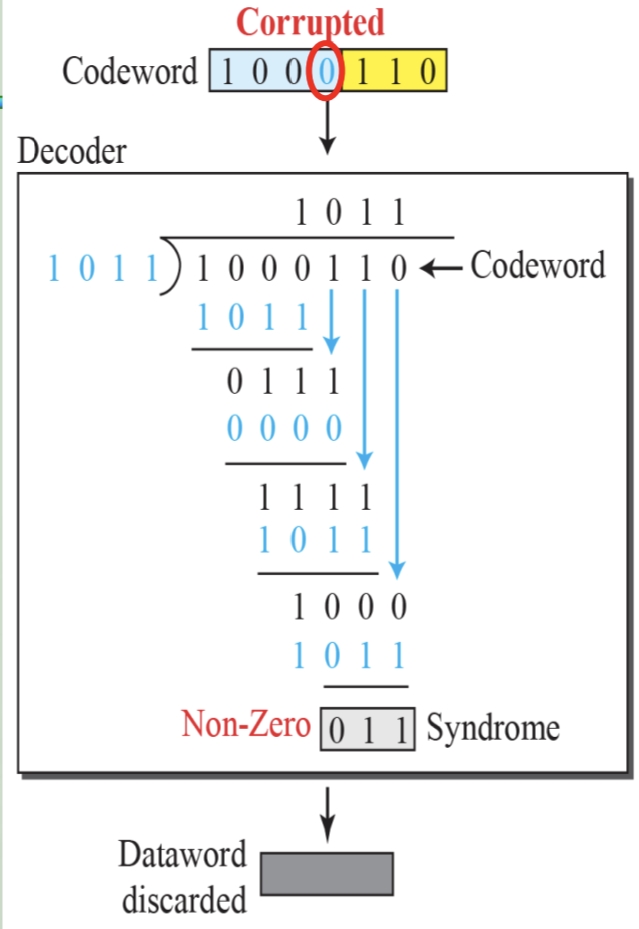
循环冗余码校验CRC码 算法步骤+详细实例计算
通信过程:(白话解释) 我们将原始待发送的消息称为 M M M,依据发送接收消息双方约定的生成多项式 G ( x ) G(x) G(x)(意思就是 G ( x ) G(x) G(x) 是已知的)࿰…...
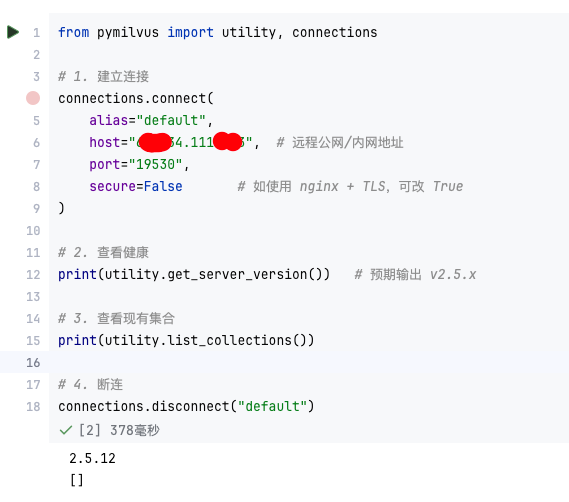
【大模型RAG】Docker 一键部署 Milvus 完整攻略
本文概要 Milvus 2.5 Stand-alone 版可通过 Docker 在几分钟内完成安装;只需暴露 19530(gRPC)与 9091(HTTP/WebUI)两个端口,即可让本地电脑通过 PyMilvus 或浏览器访问远程 Linux 服务器上的 Milvus。下面…...
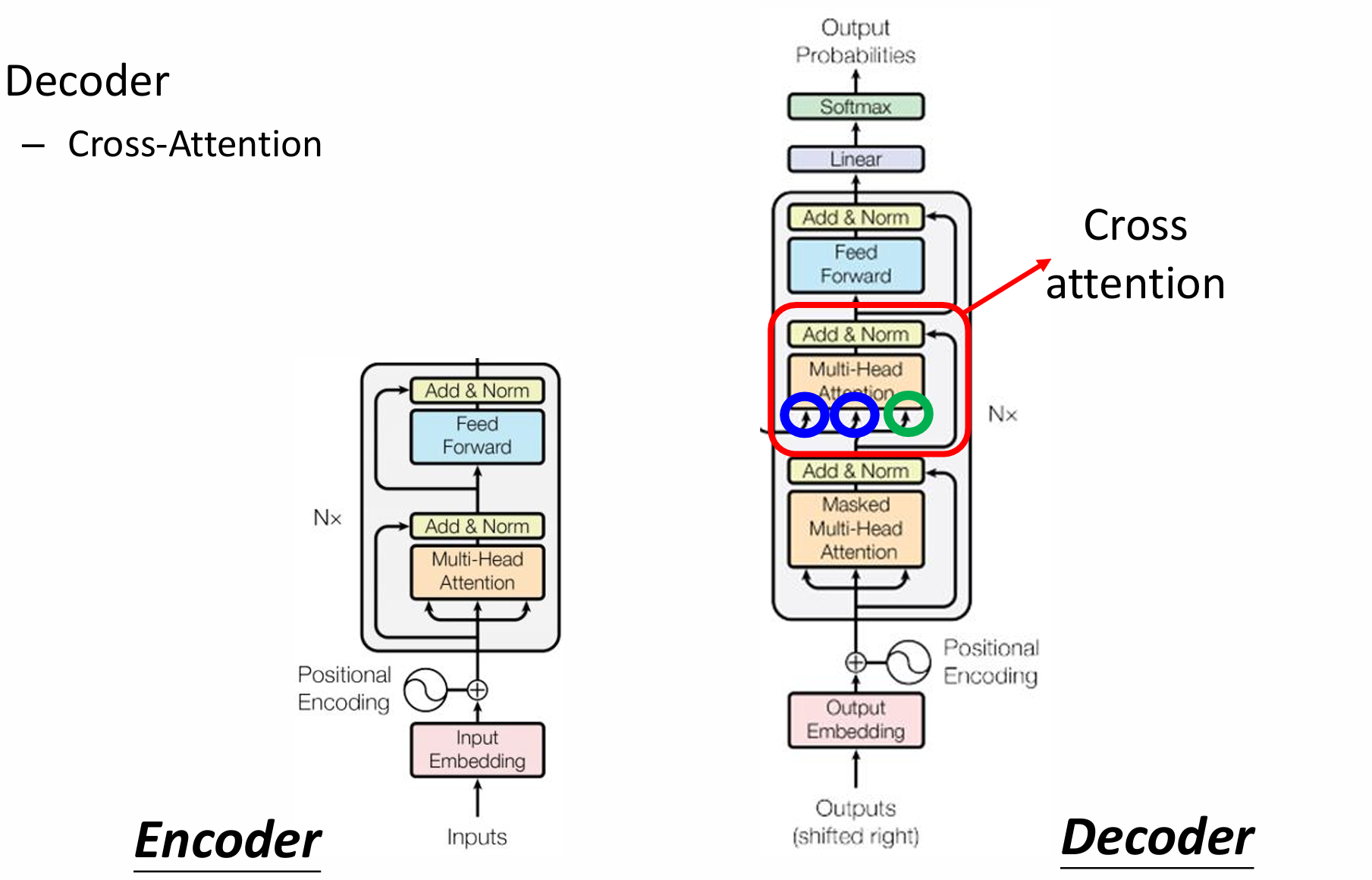
自然语言处理——Transformer
自然语言处理——Transformer 自注意力机制多头注意力机制Transformer 虽然循环神经网络可以对具有序列特性的数据非常有效,它能挖掘数据中的时序信息以及语义信息,但是它有一个很大的缺陷——很难并行化。 我们可以考虑用CNN来替代RNN,但是…...

06 Deep learning神经网络编程基础 激活函数 --吴恩达
深度学习激活函数详解 一、核心作用 引入非线性:使神经网络可学习复杂模式控制输出范围:如Sigmoid将输出限制在(0,1)梯度传递:影响反向传播的稳定性二、常见类型及数学表达 Sigmoid σ ( x ) = 1 1 +...

CSS设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整
width: fit-content 是 CSS 中的一个属性值,用于设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整,确保宽度刚好容纳内容而不会超出。 效果对比 默认情况(width: auto): 块级元素(如 <div>)会占满父容器…...
技术栈RabbitMq的介绍和使用
目录 1. 什么是消息队列?2. 消息队列的优点3. RabbitMQ 消息队列概述4. RabbitMQ 安装5. Exchange 四种类型5.1 direct 精准匹配5.2 fanout 广播5.3 topic 正则匹配 6. RabbitMQ 队列模式6.1 简单队列模式6.2 工作队列模式6.3 发布/订阅模式6.4 路由模式6.5 主题模式…...

华为OD机试-最短木板长度-二分法(A卷,100分)
此题是一个最大化最小值的典型例题, 因为搜索范围是有界的,上界最大木板长度补充的全部木料长度,下界最小木板长度; 即left0,right10^6; 我们可以设置一个候选值x(mid),将木板的长度全部都补充到x,如果成功…...
