设计模式 - 行为模式
行为模式
观察者模式,策略模式,命令模式,中介者模式,备忘录模式,模板方法模式,迭代器模式,状态模式,责任链模式,解释器模式,访问者模式
| 保存/封装 行为/请求 | |
|---|---|
| Strategy 模式 | 抽象出同一的接口,执行不同的算法 |
| Command 模式 | 封装一个请求,从而决定何时、怎样满足请求 |
| Visitor 模式 | 某些可作用于一个(组)对象上的操作,但不修改这些对象的类 |
| x对多的依赖关系 | |
| Observer 模式 | (一对多)对多个对象依赖于另外一个对象,而这些对象又如何保持一致 |
| Mediator 模式 | (多对多)对象间怎样交互、和谁交互 |
| 组件协作 | |
| Template 模式 | 对算法中的某些步骤 |
| 状态变化 | |
| State 模式 | 对象的状态 |
| Memento 模式 | 对一个对象中哪些私有信息存放在该对象之外,以及在对什么时候进行存储 |
| 数据结构 | |
| Chain of Responsibility 模式 | 满足一个请求的对象链 |
| Iterator 模式 | 如何遍历、访问一个聚合的各元素 |
| 领域问题 | |
| Interpreter 模式 | 对一个语言的文法及解释 |
保存/封装 行为/请求
Strategy
结构化设计 分而治之
ifelse switch case中 if else绝对不变,可以用面相对象 抽象来解决。
code
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>class Strategy {
public:virtual ~Strategy() = default;virtual void excute() = 0;
};class Strategy_allin : public Strategy {
public:void excute() {printf("塔塔开!\n");}
};class Strategy_giveup : public Strategy {
public:void excute() {printf("点了点了点了.\n");}
};class ChasingGame {
public:void play() {if (this->mStrategy) {mStrategy->excute();} else {printf("挂机,等着输.\n");}}void set_strategy(Strategy* strategy) {if (this->mStrategy) {delete this->mStrategy;}this->mStrategy = strategy;}Strategy* mStrategy = nullptr;
};int main() {ChasingGame* mGame = new ChasingGame;mGame->play();Strategy* mStrategy = new Strategy_allin;mGame->set_strategy(mStrategy);mGame->play();mStrategy = new Strategy_giveup;mGame->set_strategy(mStrategy);mGame->play();return 1;
}command (保存)
将 请求/行为 封装成对象。
基类 Command 虚方法 excute,子类继承后实现excute方法。到此为止的话 和策略模式特别类似,但区别是 存在一个容器(复合命令对象)存放cmd对象,执行其中所有的命令。
-
策略模式,往往需要工厂模式创建一个对象 执行该对象的方法。
-
cmd模式,一般自行创建cmd对象,将请求放入队列中。怎么执行这个请求,是队列决定的
函数对象和cmd模式存在相似。
-
函数对象
-
执行函数对象是通过重载()操作符,
-
函数对象以函数签名来定义行为接口规范,
-
编译时绑定(泛型编程 使用模板,编译时解析类型)
更灵活,性能更高。
-
-
cmd模式
- 以面相对象的 “接口 实现”来定义行为接口规范,更严格
- 有性能损失
- 运行时绑定 > 编译时绑定
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <vector>class Command {
public:virtual ~Command() = default;virtual void excute() = 0;
};class Command_EatApple : public Command {
public:void excute() {printf("eat an Apple\n");}
};class Command_DrinkTea : public Command {
public:void excute() {printf("drink a cup of tea\n");}
};class CmdQueue {
public:void enqueueCmd(Command* cmd) {this->cmds.push_back(cmd);}void handleCmd() {for (auto cmd : this->cmds) {cmd->excute();}cmds.clear();}std::vector<Command*> cmds;
};int main() {CmdQueue* mQueue = new CmdQueue;Command_DrinkTea* cmd1 = new Command_DrinkTea;Command_EatApple* cmd2 = new Command_EatApple;mQueue->enqueueCmd(cmd1);mQueue->enqueueCmd(cmd2);printf("容器决定什么时候执行cmd");mQueue->handleCmd();delete cmd1;delete cmd2;delete mQueue;return 0;
}visitor (升维)
概念
对 Strategy模式 的维度提升——
原先,Strategy :
- 实现处 基类定义 子类实现,一个方法
excute。 - 使用处 调用。
后来,Command:更进一步
- 将 Strategy 视为一个可移动的对象
- 使用处决定 执行/不执行 什么时候执行 其中的
excute方法。
**现在,visitor :**作用与对象结构的二次辨析(dispatch)
- 实现处同时实现多个不同的动作
- 不同的使用处,选择执行其中一个动作
体现在使用上:
-
实现处 visitor 类
- 基类:要求各个方法的接口足够稳定
- 定义若干虚函数
actionA, actionB ...
- 定义若干虚函数
- 子类:
- 实现虚函数
actionA, actionB ...
- 实现虚函数
- 基类:要求各个方法的接口足够稳定
-
使用处 element类:层次结构稳定,其中面临的操作面临频繁的变化。
-
基类 element:以下接口稳定
- 虚函数
action,不同的子类对其进行实现
否则一旦基类element添加新的虚函数,就需要修改所有子类。
- 方法accept(&visitor)
接收&保存一个 visitor 对象(不用保存若干不同的 Strategy/Command 对象—— all in one)
- 虚函数
-
子类:要求数量稳定
- 实现接口
action - 实现的方法是:调用 所保存的 visitor 对象的不同
actionX。例如- elementA 的方法action执行visitor.actionA
- elementB 的方法action执行visitor.actionB
- 实现接口
-
code
// 作用与对象结构的二次辨析
#include <cstdio>class Visitor {
public:virtual ~Visitor() = default;virtual void action_lunch() = 0;virtual void action_dinner() = 0;
};class Visitor_Shanghai : public Visitor {
public:virtual void action_lunch() {printf("山西午餐吃炸酱面\n");}virtual void action_dinner() {printf("山西晚餐吃刀削面\n");}
};class Visitor_ShanXi : public Visitor {
public:virtual void action_lunch() {printf("上海午餐吃酱鸭子\n");}virtual void action_dinner() {printf("上海晚餐吃剩下的酱鸭子\n");}
};class Element {
public:virtual ~Element() = default;virtual void eat_meal() = 0;virtual void accept(Visitor* visitor) {mVisitor = visitor;}Visitor* mVisitor;
};class Element_Lunch : public Element {
public:virtual void eat_meal() {if (mVisitor) {mVisitor->action_lunch();}}
};class Element_dinner : public Element {
public:virtual void eat_meal() {if (mVisitor) {mVisitor->action_dinner();}}
};int main() {Visitor* mShanxi = new Visitor_ShanXi;Visitor* mShanghai = new Visitor_Shanghai;Element* meal = new Element_Lunch;meal->accept(mShanghai);meal->eat_meal();delete meal;meal = new Element_dinner;meal->accept(mShanxi);meal->eat_meal();delete meal;delete mShanghai;delete mShanxi;return 1;
}
x对多的依赖关系
Observer 观察者模式(单向)
Observer 模式要解决的问题为:
指多个对象间存在一对多的依赖关系,当一个对象的状态发生改变 “一”变化的时候,所有依赖于这个“一”的多对象都得到通知并被自动更新。
Subject 提供
-
依赖于它的观察者 Observer 的
- 注册(registerObserver)
- 注销(remove)操作,
-
使依赖于它的所有观察者同步的操作(notifyObserver),
观察者 Observer 提供
- Update 操作
- 注意这里的 Observer 的 Update 操作并不在 Observer 改变了 Subject 目标状态的时候就对自己进行更新,这个更新操作要延迟到 Subject 对象发出 Notify 通知所有Observer 进行修改(调用 Update)。
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>class Observer;
class Subscriber;class Subject {
public:virtual ~Subject() = default;virtual void registObserver(Observer*) = 0;virtual void removeObserver(Observer*) = 0;virtual void notifyObserver() = 0;std::list<Observer*> mObservers;
};class Subscriber {
public:Subscriber(std::string name) : name(name){};std::string name;void watchVideo() {printf("%s start watching . \n", this->name.c_str());}
};class Observer {
public:void addSubscriber(Subscriber*);void removeSubscriber(Subscriber*);void notifySubscriber();std::list<Subscriber*> mSubcribers;
};class Subject_Bilibili : public Subject {
public:virtual void registObserver(Observer* observer) {this->mObservers.push_back(observer);};virtual void removeObserver(Observer* observer) {this->mObservers.remove(observer);};virtual void notifyObserver() {printf("bilibili update! \n");for (auto observer : this->mObservers) {observer->notifySubscriber();}}
};void Observer::addSubscriber(Subscriber* subscriber) {this->mSubcribers.push_back(subscriber);
}
void Observer::removeSubscriber(Subscriber* subscriber) {this->mSubcribers.remove(subscriber);
}
void Observer::notifySubscriber() {printf("好的,这就通知\n");for (auto subscriber : this->mSubcribers) {subscriber->watchVideo();}
}int main() {Subject* biblibili = new Subject_Bilibili;Observer* mObserver = new Observer;Subscriber* A = new Subscriber("张三");Subscriber* B = new Subscriber("李四");Subscriber* C = new Subscriber("王五");biblibili->registObserver(mObserver);mObserver->addSubscriber(A);mObserver->addSubscriber(B);mObserver->addSubscriber(C);mObserver->removeSubscriber(C);biblibili->notifyObserver();return 1;
}
Mediator 中介模式(双向/多向)
Mediator 解耦系统内多个类之间需要大量密集复杂的相互交互,对他们进行集中管理。
- 依赖倒置原则 在多对象模型中的体现
- 类似交换机,要求 通信规范
- 实现
- 让这些类继承相同的接口/成为某一基类的子类
- 子类都持有中介的指针
- 中介持有所有子类的指针
基类成员 基类::成员名,与子类成员进行区分。
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>class Mediator;class Client {
public:virtual ~Client() = default;void registMediator(Mediator* mediator);void callSomeTeam(int type);virtual void responce() = 0;Mediator* mMediator;int type;std::string name;
};class Client_Boss : public Client {
public:virtual ~Client_Boss() = default;Client_Boss(std::string name, Mediator* mediator) {Client::name = name;Client::type = 99;registMediator(mediator);}virtual void responce() {printf("Boss %s here! what do u want?\n", name.c_str());}
};class Client_Engineer : public Client {
public:virtual ~Client_Engineer() = default;Client_Engineer(std::string name, Mediator* mediator) {Client::name = name;Client::type = 1;registMediator(mediator);}virtual void responce() {printf("Engineer %s here! how can i help u?\n", name.c_str());}
};class Mediator {
public:void registClient(Client* client) {this->mClient.push_back(client);}void removeClient(Client* client) {this->mClient.remove(client);}void callClient(int type) {printf("callClient type = %d \n", type);for (auto client : this->mClient) {if (client->type == type) {client->responce();}}}std::list<Client*> mClient;
};void Client::callSomeTeam(int type) {if (this->mMediator)this->mMediator->callClient(type);elseprintf("unset Mediator\n");
}void Client::registMediator(Mediator* mediator){this->mMediator = mediator;mediator->registClient(this);
}int main() {Mediator* mMediator = new Mediator;Client_Boss* mBoss = new Client_Boss("fajie", mMediator);Client_Engineer* mEngineer1 = new Client_Engineer("pengyi 1", mMediator);Client_Engineer* mEngineer2 = new Client_Engineer("pengyi 2", mMediator);mBoss->callSomeTeam(1);printf("10mins after\n");mEngineer1->callSomeTeam(99);return 1;
}
组件协作
Template 模板模式
对于某一个业务逻辑(算法实现)在不同的对象中有不同的细节实现,但是逻辑(算法)的框架(或通用的应用算法)是相同的。
Template 模式,采用继承的方式实现这一点
-
抽象基类:
定义细节的接口,定义逻辑(算法)框架
-
子类
实现逻辑细节。
在子类实现详细的处理算法时并不会改变算法中的执行次序。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;//做饮料模板
class TemplateDrink {
public:virtual ~TemplateDrink() = default;//煮水virtual void BoildWater() = 0;//冲泡virtual void Brew() = 0;//倒入杯中virtual void PourInCup() = 0;//加辅助材料virtual void AddSomething() = 0;//模板方法void Make() {BoildWater();Brew();PourInCup();AddSomething();}
};class Coffee : public TemplateDrink {virtual void BoildWater() {cout << "煮纯净水" << endl;}virtual void Brew() {cout << "冲泡咖啡" << endl;}virtual void PourInCup() {cout << "咖啡倒入杯中" << endl;}virtual void AddSomething() {cout << "加牛奶" << endl;}
};class Tea :public TemplateDrink {virtual void BoildWater() {cout << "煮山泉水" << endl;}virtual void Brew() {cout << "冲泡铁观音" << endl;}virtual void PourInCup() {cout << "茶水倒入杯中" << endl;}virtual void AddSomething() {}
};int main()
{Tea* tea = new Tea;tea->Make();Coffee* coffee = new Coffee;coffee->Make();delete tea;delete coffee;
}
状态变化
State 状态模式
主要解决:Switch/Case 的爆炸
Switch/Case 的缺点
-
当状态数目很多的时候,维护一大组的Switch/Case 语句将是一件异常困难并且容易出错的事情。
-
状态逻辑和动作实现没有分离。
-
动作的实现代码直接写在状态的逻辑当中。
后果是系统的扩展性和维护得不到保证。
概念
和策略模式类似
每个人、事物在不同的状态下会有不同表现(动作),而一个状态又会在不同的表现下转移到下一个不同的状态(State)。
状态机
- 不同状态的operation,高度相似,相对固定。
- operation依据某个变量state,发生变化。
优点
State类:枚举可能的状态,
-
可以方便地增加新的状态,只需要改变对象状态即可改变对象的行为。
-
封装了转换规则。在枚举状态之前需要确定状态种类。
Process:将所有与某个状态有关的行为放到一个类中,
- 允许状态转换逻辑与状态对象合成一体,而不是某一个巨大的条件语句块。
系统资源
- 通常与单例模式一起使用
- 可以让多个环境对象共享一个状态对象,从而减少系统中对象的个数。
实现上
State
-
State基类 除虚析构外,还持有
- 一系列operation虚函数
- 看情况
- process指针(使用该指针,更改process中的下一个state)
- state指针(指向下一个状态),(上下文指针)
-
State子类继承State基类
- 重写operarion函数。
Process
-
Process 基类
- 持有State指针
- 一系列operation虚函数。
-
Process 子类
-
重写operation
-
调用State指针的operation
让State更新为下一个状态 state = state->next。
-
code
// main.cpp#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include "processImpl.cpp"
#include "stateImpl.cpp"int main() {Process* mProcess = new Process(10);mProcess->buy(101);mProcess->buy(1);mProcess->recharge(10);mProcess->buy(1);mProcess->recharge(1000);mProcess->buy(100);delete mProcess;return 1;
}
// process.h#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include "state.h"
#pragma onceclass Process {
public:Process(int = 10);void set_state(State* state);void recharge(int money);void buy(int price);int query_money();int balance;State* mState = nullptr;
};// processImpl.cpp#include "process.h"
#include "state.h"
#include <cstdio>
#pragma onceProcess::Process(int init_money) {this->balance = init_money;if (init_money > 0) {this->set_state(new State_rich);} else {this->set_state(new State_poor);}
}int Process::query_money() {return this->balance;
}void Process::set_state(State* state) {if (mState)delete this->mState;this->mState = state;this->mState->set_process(this);
}void Process::recharge(int money) {bool result = this->mState->recharge(money);this->balance += money;if (result) {printf("尊贵的用户: 充值后,余额 %d\n", this->query_money());} else {printf("欠费的用户: 充值后,余额 %d\n", this->query_money());}
}void Process::buy(int price) {if (this->mState->buy(price))printf("购买成功, 余额 %d\n", this->query_money());elseprintf("购买失败 请充值, 余额 %d\n", this->query_money());
}
// state.h
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#pragma once
class Process;class State {
public:virtual ~State() = default;void set_process(Process* process) {this->process = process;}Process* get_process() {return this->process;}virtual bool buy(int) = 0; virtual bool recharge(int) = 0; Process* process;
};class State_rich : public State {
public:bool buy(int) override;bool recharge(int) override;
};class State_poor : public State {
public:bool buy(int) override;bool recharge(int) override;
};
// stateImpl.cpp#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include "state.h"
#include "process.h"
#pragma oncebool State_rich::buy(int price) {this->process->balance -= price;int balance = this->process->query_money();if (balance <= 0) {this->process->set_state(new State_poor);}return true;
}bool State_rich::recharge(int money) {int balance = this->process->query_money();if (money + balance > 0) {return true;}return false;
}bool State_poor::buy(int price) {// int balance = this->process->query_money();return false;
}bool State_poor::recharge(int money) {int balance = this->process->query_money();if (money + balance > 0) {this->process->set_state(new State_rich);return true;}return false;
}
Memento (过时)
Memento 备忘录模式
信息隐藏条件下,对对象的快照。
原发器,持有state,保存快照时 根据state创建并返回一个memnto对象。恢复时,传入memnto对象,设置 原发器的state对象。 实现对原发器对外的信息隐藏。
现在来看太低级了 java c#等具有高效成熟容易正确实现的对象序列化支持,有更容易正确实现的序列化方案。
不怎么介绍也没关系
迭代器
从性能角度讲——编译期多态好过运行时多态
-
泛型编程的迭代器 > 面相对象的迭代器
-
虚函数成本过高
但在 java c# php等等语言,不支持编译时多态,仍然在使用运行时多态
责任链模式
运行时的类型判断。一个请求者可能有多个接受者,但最后真正的接受者或者说处理者只有一个。运行时动态添加 修改请求的处理职责。
避免请求的发送者和接受者之间的耦合关系。
数据结构构成的处理模型。链表
行为变化,将组件的行为与组件本身进行解耦
非虚函数,静态函数 地址在编译时绑定的方式。
虚函数是运行时,使用虚函数表指针绑定的。
Interpreter 模式
对一个语言的文法及解释
相关文章:

设计模式 - 行为模式
行为模式 观察者模式,策略模式,命令模式,中介者模式,备忘录模式,模板方法模式,迭代器模式,状态模式,责任链模式,解释器模式,访问者模式 保存/封装 行为/请求…...

InstructGPT的四阶段:预训练、有监督微调、奖励建模、强化学习涉及到的公式解读
1. 预训练 1. 语言建模目标函数(公式1): L 1 ( U ) ∑ i log P ( u i ∣ u i − k , … , u i − 1 ; Θ ) L_1(\mathcal{U}) \sum_{i} \log P(u_i \mid u_{i-k}, \dots, u_{i-1}; \Theta) L1(U)i∑logP(ui∣ui−k,…,ui−1;Θ…...

没有HTTPS 证书时,像这样实现多路复用
在没有 HTTPS 证书的情况下,HTTP/2 通常不能直接通过 HTTP 协议使用。虽然 HTTP/2 协议的规范是可以支持纯 HTTP 连接(即通过 http:// 协议),但大多数主流浏览器(如 Chrome、Firefox)都 强制要求 HTTP/2 必须在 HTTPS 上运行。这是出于安全和隐私的考虑。 因此,如果你没…...

2.1.ReactOS系统NtReadFile函数的实现。
ReactOS系统NtReadFile函数的实现。 ReactOS系统NtReadFile函数的实现。 文章目录 ReactOS系统NtReadFile函数的实现。NtReadFile函数的定义NtReadFile函数的实现 NtReadFile()是windows的一个系统调用,内核中有一个叫NtReadFile的函数 NtReadFile函数的定义 NTS…...

2020-11-06《04丨人工智能时代,新的职业机会在哪里?》
《香帅中国财富报告25讲》 04丨人工智能时代,新的职业机会在哪里? 1、新机会的三个诞生方向 前两讲我们都在说,人工智能的出现会极大地冲击现有的职业,从2020年开始,未来一二十年,可能有一半以上的职业都会…...

TensorRT-LLM七日谈 Day5
模型加载 在day2, 我们尝试了对于llama8B进行转换和推理,可惜最后因为OOM而失败,在day4,我们详细的过了一遍tinyllama的推理,值得注意的是,这两个模型的推理走的是不同的流程。llama8b需要显式的进行模型的转换,引擎的…...

使用Java Socket实现简单版本的Rpc服务
通过如下demo,希望大家可以快速理解RPC的简单案例。如果对socket不熟悉的话可以先看下我的上篇文章 Java Scoket实现简单的时间服务器-CSDN博客 对socket现有基础了解。 RPC简介 RPC(Remote Procedure Call,远程过程调用)是一种…...

P2P 网络 简单研究 1
起因, 目的: P2P 网络, 一道题。题目描述, 在下面。 P2P 网络,我以前只是听说过,并不深入。如果我有5台电脑的话,我也想深入研究一下。 P2P 简介: P2P(Peer-to-Peer)网络是一种分…...

RAG(检索增强生成)面经(1)
1、RAG有哪几个步骤? 1.1、文本分块 第一个步骤是文本分块(chunking),这是一个重要的步骤,尤其在构建与处理文档的大型文本的时候。分块作为一种预处理技术,将长文档拆分成较小的文本块,这些文…...

卫爱守护|守护青春,送出温暖
2024年10月10日,艾多美爱心志愿者来到校园。艾多美“卫艾守护”项目于吉林省白山市政务大厅会议室举办了捐赠仪式,东北区外事部经理黄山出席了捐赠仪式仪式,为全校女同学捐赠了青春关爱包。 此次捐赠,面向吉林省自山市第十八中学、…...

ubuntu-24.04.1 系统安装
使用VMware虚拟机上进行实现 官网下载地址: https://cn.ubuntu.com/download https://releases.ubuntu.com 操作系统手册: https://ubuntu.com/server/docs/ (里面包含安装文档) 安装指南(详细):…...

华为OD机试真题---生成哈夫曼树
华为OD机试中关于生成哈夫曼树的题目通常要求根据给定的叶子节点权值数组,构建一棵哈夫曼树,并按照某种遍历方式(如中序遍历)输出树中节点的权值序列。以下是对这道题目的详细解析和解答思路: 一、题目要求 给定一个…...

小红书新ID保持项目StoryMaker,面部特征、服装、发型和身体特征都能保持一致!(已开源)
继之前和大家介绍的小红书在ID保持以及风格转换方面相关的优秀工作,感兴趣的小伙伴可以点击以下链接阅读~ 近期,小红书又新开源了一款文生图身份保持项目:StoryMaker,是一种个性化解决方案,它不仅保留了面部的一致性&…...

Docker 环境下 GPU 监控实战:使用 Prometheus 实现 DCGM Exporter 部署与 GPU 性能监控
Docker 环境下 GPU 监控实战:使用 Prometheus 实现 DCGM Exporter 部署与 GPU 性能监控 文章目录 Docker 环境下 GPU 监控实战:使用 Prometheus 实现 DCGM Exporter 部署与 GPU 性能监控一 查看当前 GPU 信息二 dcgm-exporter 部署1)Docker r…...

联想小新打印机M7328w如何解决卡纸,卡了一个小角在里面,然后再次打印的时候,直接卡住,不能动了。灯显示红色。
1、今天打印一张纸,应该是不小心放歪了,打出来的也是有些斜,然后打出来缺少了个角。 图中的小纸就是从打印机的左边的角,用镊子取出来的,手不太好拿,所以拿个工具比较合适。 2、那么碰到这种卡纸应该如何处…...

软件可靠性之MTTR、MTBF、MTTF、MTTD区别
一.概念解释 1.MTBF(Mean Time Between Failures):指两次故障之间的平均时间,通常用于衡量设备或系统的可靠性。 2.MTTF(Mean Time to Failure):指设备或系统的平均无故障运行时间。 3.MTTR&am…...

Qt-QDockWidget浮动窗口相关操作(49)
目录 描述 使用 描述 在 Qt 中,浮动窗⼝也称之为铆接部件。浮动窗⼝是通过 QDockWidget类 来实现浮动的功能。浮动窗口⼀般是位于核心部件的周围,可以有多个。 使用 创建我们可以参考下面的语法格式 使用起来也很简单,不过只能创建一个 Q…...

图形用户界面-GUI的基本概念和组件之一
前言 GUI(Graphical User Interface,图形用户界面,简称图形界面)编程实际是引用java.awt或javax.swing类包中的窗口类、控制组件类、布局类、事件类等,通过将控制组件类,如菜单、按钮、文本框等,…...

【MATLAB代码】基于RSSI原理的蓝牙定位程序(N个锚点、三维空间),源代码可直接复制
文章目录 介绍主要功能技术细节适用场景程序结构运行截图源代码详细教程:基于RSSI的蓝牙定位程序1. 准备工作2. 代码结构2.1 清理工作环境2.2 定义参数2.3 生成锚点坐标2.4 定义信号强度与距离的关系2.5 模拟未知点的位置2.6 定位函数2.7 绘图2.8 输出结果2.9 定义定位函数3. …...

Pyenv 介绍和安装指南 - Ubuntu 24
原文: https://www.qiulin-dev.top/articles/81aab753-0d0e-470c-b08f-2643c876841b 1. Pyenv 介绍 Pyenv 是一个非常流行的 Python 版本管理工具,它可以让你在同一台机器上安装并管理多个不同的 Python 版本,解决了不同项目需要不同 Python…...
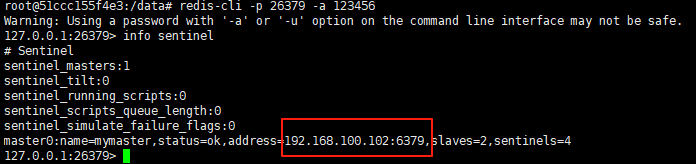
使用docker在3台服务器上搭建基于redis 6.x的一主两从三台均是哨兵模式
一、环境及版本说明 如果服务器已经安装了docker,则忽略此步骤,如果没有安装,则可以按照一下方式安装: 1. 在线安装(有互联网环境): 请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 2. 离线安装(内网环境):请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 说明:假设每台服务器已…...

Android Wi-Fi 连接失败日志分析
1. Android wifi 关键日志总结 (1) Wi-Fi 断开 (CTRL-EVENT-DISCONNECTED reason3) 日志相关部分: 06-05 10:48:40.987 943 943 I wpa_supplicant: wlan0: CTRL-EVENT-DISCONNECTED bssid44:9b:c1:57:a8:90 reason3 locally_generated1解析: CTR…...

Golang 面试经典题:map 的 key 可以是什么类型?哪些不可以?
Golang 面试经典题:map 的 key 可以是什么类型?哪些不可以? 在 Golang 的面试中,map 类型的使用是一个常见的考点,其中对 key 类型的合法性 是一道常被提及的基础却很容易被忽视的问题。本文将带你深入理解 Golang 中…...

《Qt C++ 与 OpenCV:解锁视频播放程序设计的奥秘》
引言:探索视频播放程序设计之旅 在当今数字化时代,多媒体应用已渗透到我们生活的方方面面,从日常的视频娱乐到专业的视频监控、视频会议系统,视频播放程序作为多媒体应用的核心组成部分,扮演着至关重要的角色。无论是在个人电脑、移动设备还是智能电视等平台上,用户都期望…...
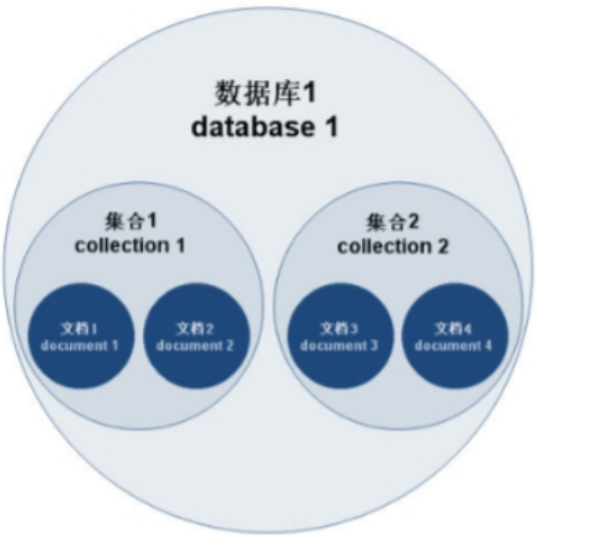
MongoDB学习和应用(高效的非关系型数据库)
一丶 MongoDB简介 对于社交类软件的功能,我们需要对它的功能特点进行分析: 数据量会随着用户数增大而增大读多写少价值较低非好友看不到其动态信息地理位置的查询… 针对以上特点进行分析各大存储工具: mysql:关系型数据库&am…...

【SpringBoot】100、SpringBoot中使用自定义注解+AOP实现参数自动解密
在实际项目中,用户注册、登录、修改密码等操作,都涉及到参数传输安全问题。所以我们需要在前端对账户、密码等敏感信息加密传输,在后端接收到数据后能自动解密。 1、引入依赖 <dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId...

系统设计 --- MongoDB亿级数据查询优化策略
系统设计 --- MongoDB亿级数据查询分表策略 背景Solution --- 分表 背景 使用audit log实现Audi Trail功能 Audit Trail范围: 六个月数据量: 每秒5-7条audi log,共计7千万 – 1亿条数据需要实现全文检索按照时间倒序因为license问题,不能使用ELK只能使用…...
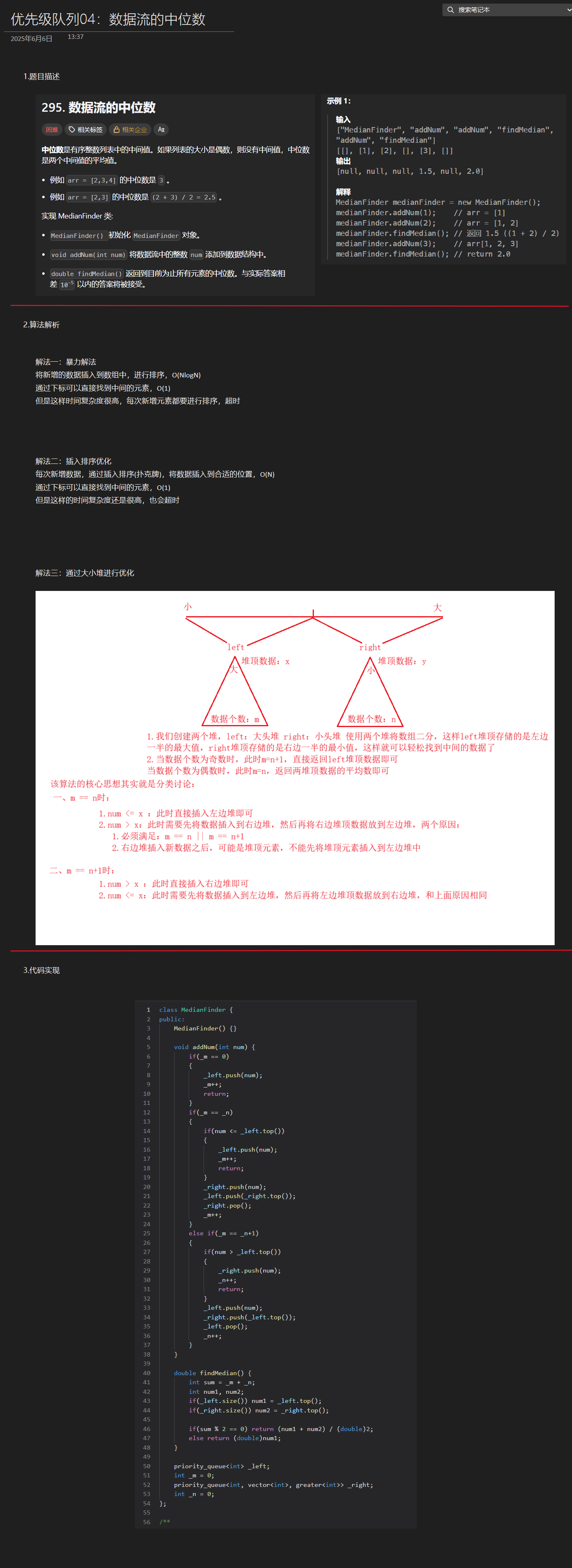
优选算法第十二讲:队列 + 宽搜 优先级队列
优选算法第十二讲:队列 宽搜 && 优先级队列 1.N叉树的层序遍历2.二叉树的锯齿型层序遍历3.二叉树最大宽度4.在每个树行中找最大值5.优先级队列 -- 最后一块石头的重量6.数据流中的第K大元素7.前K个高频单词8.数据流的中位数 1.N叉树的层序遍历 2.二叉树的锯…...
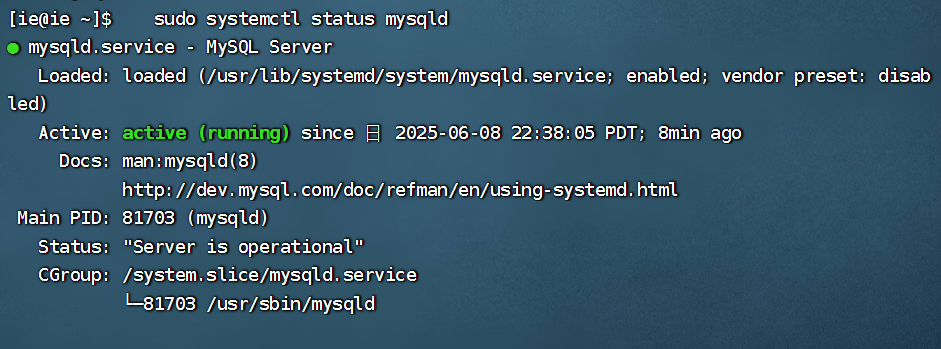
项目部署到Linux上时遇到的错误(Redis,MySQL,无法正确连接,地址占用问题)
Redis无法正确连接 在运行jar包时出现了这样的错误 查询得知问题核心在于Redis连接失败,具体原因是客户端发送了密码认证请求,但Redis服务器未设置密码 1.为Redis设置密码(匹配客户端配置) 步骤: 1).修…...

分布式增量爬虫实现方案
之前我们在讨论的是分布式爬虫如何实现增量爬取。增量爬虫的目标是只爬取新产生或发生变化的页面,避免重复抓取,以节省资源和时间。 在分布式环境下,增量爬虫的实现需要考虑多个爬虫节点之间的协调和去重。 另一种思路:将增量判…...
