《密码系统设计》实验二 4-6学时
文章目录
- 《密码系统设计》实验
- 实验项目
- 实验二 密码算法实现
- 4-6 学时实践要求(30 分)
- 1. 定义宏
- 2. 使用特定的源文件
- 3. 编译MIRACL库
- 4. 配置KCM和Comba方法
- 5. 编译和运行MEX工具
- 6. 使用config.c工具
- 总结
- 1. 准备环境
- 2. 下载和解压MIRACL库
- 3. 定义宏
- 4. 使用特定的源文件
- 5. 编译MIRACL库
- 6. 配置KCM和Comba方法
- 7. 编译和运行MEX工具
- 8. 使用config.c工具
- 9. 安装库
- 总结
- SM2标准的关键点:
- 代码实现分析:
- 结论:
- 代码实现分析:
- 结论:
- SM2相关标准文档:
- SM3标准的关键点:
- 代码实现分析:
- 结论:
- SM3相关标准文档:
- SM4标准的关键点:
- 代码实现分析:
- 结论:
- SM4相关标准文档:
《密码系统设计》实验
实验项目
| 实验序号 | 实验名称 | 实验学时数 | 实验目的 | 实验内容 | 实验类型 | 学生学习预期成果 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验二 | 密码算法实现 | 6 | 掌握常见商用密码算法的原理与实现 | 基于国产化平台使用C语言编程实现SM2、SM3、SM4等算法; | 验证性 | 1.基于Arm等平台和国产化操作系统使用C语言编程实现SM2、SM3、SM4算法; 2.对比分析算法实现的正确性和效率。 |
实验二 密码算法实现
4-6 学时实践要求(30 分)
- 在 Ubuntu或openEuler中(推荐 openEuler)中调试运行教材提供的源代码,至少运行SM2,SM3,SM4代码,使用GmSSL命令验证你代码的正确性,使用Markdown记录详细记录实践过程,每完成一项功能或者一个函数git commit 一次。(15分)
sm2
//sm2enc.c
#include "miracl/miracl.h"
#include "miracl/mirdef.h"
#include "SM2_ENC.h"
#include "kdf.h"// 定义全局变量
big para_p, para_a, para_b, para_n, para_Gx, para_Gy, para_h;
epoint *G;
miracl *mip;unsigned char SM2_p[32] = { 0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFE,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,
0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF };
unsigned char SM2_a[32] = { 0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFE,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,
0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFC };
unsigned char SM2_b[32] = { 0x28,0xE9,0xFA,0x9E,0x9D,0x9F,0x5E,0x34,0x4D,0x5A,0x9E,0x4B,0xCF,0x65,0x09,0xA7,
0xF3,0x97,0x89,0xF5,0x15,0xAB,0x8F,0x92,0xDD,0xBC,0xBD,0x41,0x4D,0x94,0x0E,0x93 };
unsigned char SM2_n[32] = { 0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFE,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,
0x72,0x03,0xDF,0x6B,0x21,0xC6,0x05,0x2B,0x53,0xBB,0xF4,0x09,0x39,0xD5,0x41,0x23 };
unsigned char SM2_Gx[32] = { 0x32,0xC4,0xAE,0x2C,0x1F,0x19,0x81,0x19,0x5F,0x99,0x04,0x46,0x6A,0x39,0xC9,0x94,
0x8F,0xE3,0x0B,0xBF,0xF2,0x66,0x0B,0xE1,0x71,0x5A,0x45,0x89,0x33,0x4C,0x74,0xC7 };
unsigned char SM2_Gy[32] = { 0xBC,0x37,0x36,0xA2,0xF4,0xF6,0x77,0x9C,0x59,0xBD,0xCE,0xE3,0x6B,0x69,0x21,0x53,
0xD0,0xA9,0x87,0x7C,0xC6,0x2A,0x47,0x40,0x02,0xDF,0x32,0xE5,0x21,0x39,0xF0,0xA0 };
unsigned char SM2_h[32] = { 0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,
0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x01 };/****************************************************************
Function: Test_Point
Description: test if the given point is on SM2 curve
Calls:
Called By: SM2_Decrypt, Test_PubKey
Input: point
Output: null
Return: 0: sucess
3: not a valid point on curve
Others:
****************************************************************/
int Test_Point(epoint* point)
{big x, y, x_3, tmp;x = mirvar(0);y = mirvar(0);x_3 = mirvar(0);tmp = mirvar(0);//test if y^2=x^3+ax+bepoint_get(point, x, y);power(x, 3, para_p, x_3); //x_3=x^3 mod pmultiply(x, para_a, x); //x=a*xdivide(x, para_p, tmp); //x=a*x mod p , tmp=a*x/padd(x_3, x, x); //x=x^3+axadd(x, para_b, x); //x=x^3+ax+bdivide(x, para_p, tmp); //x=x^3+ax+b mod ppower(y, 2, para_p, y); //y=y^2 mod pif (mr_compare(x, y) != 0)return ERR_NOT_VALID_POINT;elsereturn 0;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: SM2_TestPubKey
Description: test if the given point is valid
Calls:
Called By: SM2_Decrypt
Input: pubKey //a point
Output: null
Return: 0: sucess
1: a point at infinity
2: X or Y coordinate is beyond Fq
3: not a valid point on curve
4: not a point of order n
Others:
****************************************************************/
int Test_PubKey(epoint *pubKey)
{big x, y, x_3, tmp;epoint *nP;x = mirvar(0);y = mirvar(0);x_3 = mirvar(0);tmp = mirvar(0);nP = epoint_init();//test if the pubKey is the point at infinityif (point_at_infinity(pubKey))// if pubKey is point at infinity, return error;return ERR_INFINITY_POINT;//test if x<p and y<p both holdepoint_get(pubKey, x, y);if ((mr_compare(x, para_p) != -1) || (mr_compare(y, para_p) != -1))return ERR_NOT_VALID_ELEMENT;if (Test_Point(pubKey) != 0)return ERR_NOT_VALID_POINT;//test if the order of pubKey is equal to necurve_mult(para_n, pubKey, nP); // nP=[n]Pif (!point_at_infinity(nP)) // if np is point NOT at infinity, return error;return ERR_ORDER;return 0;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: Test_Null
Description: test if the given array is all zero
Calls:
Called By: SM2_Encrypt
Input: array[len]
len //byte len of the array
Output: null
Return: 0: the given array is not all zero
1: the given array is all zero
Others:
****************************************************************/
int Test_Null(unsigned char array[], int len)
{int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < len; i++){if (array[i] != 0x00)return 0;}return 1;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: SM2_Init
Description: Initiate SM2 curve
Calls: MIRACL functions
Called By:
Input: null
Output: null
Return: 0: sucess;
7: paremeter error;
4: the given point G is not a point of order n
Others:
****************************************************************/
int SM2_Init()
{epoint *nG;para_p = mirvar(0);para_a = mirvar(0);para_b = mirvar(0);para_n = mirvar(0);para_Gx = mirvar(0);para_Gy = mirvar(0);para_h = mirvar(0);G = epoint_init();nG = epoint_init();bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_p, para_p);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_a, para_a);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_b, para_b);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_n, para_n);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_Gx, para_Gx);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_Gy, para_Gy);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_h, para_h);ecurve_init(para_a, para_b, para_p, MR_PROJECTIVE);//Initialises GF(p) elliptic curve.//MR_PROJECTIVE specifying projective coordinatesif (!epoint_set(para_Gx, para_Gy, 0, G))//initialise point G{return ERR_ECURVE_INIT;}ecurve_mult(para_n, G, nG);if (!point_at_infinity(nG)) //test if the order of the point is n{return ERR_ORDER;}return 0;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: SM2_KeyGeneration
Description: calculate a pubKey out of a given priKey
Calls: SM2_TestPubKey
Called By:
Input: priKey // a big number lies in[1,n-2]
Output: pubKey // pubKey=[priKey]G
Return: 0: sucess
1: fail
Others:
****************************************************************/
int SM2_KeyGeneration(big priKey, epoint *pubKey)
{int i = 0;big x, y;x = mirvar(0);y = mirvar(0);ecurve_mult(priKey, G, pubKey);//ͨ ͻ Կepoint_get(pubKey, x, y);if (Test_PubKey(pubKey) != 0)return 1;elsereturn 0;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: SM2_Encrypt
Description: SM2 encryption
Calls: SM2_KDF,Test_null,Test_Point,SM3_init,SM3_process,SM3_done
Called By:
Input: randK[SM2_NUMWORD] // a random number K lies in [1,n-1]
pubKey // public key of the cipher receiver
M[klen] // original message
klen // byte len of original message
Output: C[klen+SM2_NUMWORD*3] // cipher C1||C3||C2
Return: 0: sucess
1: S is point at infinity
5: the KDF output is all zero
Others:
****************************************************************/
int SM2_Encrypt(unsigned char* randK, epoint *pubKey, unsigned char M[], int klen, unsigned char C[])
{big C1x, C1y, x2, y2, rand;epoint *C1, *kP, *S;int i = 0;unsigned char x2y2[SM2_NUMWORD * 2] = { 0 };SM3_STATE md;C1x = mirvar(0);C1y = mirvar(0);x2 = mirvar(0);y2 = mirvar(0);rand = mirvar(0);C1 = epoint_init();kP = epoint_init();S = epoint_init();//Step2. calculate C1=[k]G=(rGx,rGy)bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, randK, rand);ecurve_mult(rand, G, C1); //C1=[k]Gepoint_get(C1, C1x, C1y);big_to_bytes(SM2_NUMWORD, C1x, C, 1);big_to_bytes(SM2_NUMWORD, C1y, C + SM2_NUMWORD, 1);//Step3. test if S=[h]pubKey if the point at infinityecurve_mult(para_h, pubKey, S);if (point_at_infinity(S))// if S is point at infinity, return error;return ERR_INFINITY_POINT;//Step4. calculate [k]PB=(x2,y2)ecurve_mult(rand, pubKey, kP); //kP=[k]Pepoint_get(kP, x2, y2);//Step5. KDF(x2||y2,klen)big_to_bytes(SM2_NUMWORD, x2, x2y2, 1);big_to_bytes(SM2_NUMWORD, y2, x2y2 + SM2_NUMWORD, 1);SM3_KDF(x2y2, SM2_NUMWORD * 2, klen, C + SM2_NUMWORD * 3);if (Test_Null(C + SM2_NUMWORD * 3, klen) != 0)return ERR_ARRAY_NULL;//Step6. C2=M^tfor (i = 0; i < klen; i++){C[SM2_NUMWORD * 3 + i] = M[i] ^ C[SM2_NUMWORD * 3 + i];}//Step7. C3=hash(x2,M,y2)SM3_init(&md);SM3_process(&md, x2y2, SM2_NUMWORD);SM3_process(&md, M, klen);SM3_process(&md, x2y2 + SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_NUMWORD);SM3_done(&md, C + SM2_NUMWORD * 2);return 0;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: SM2_Decrypt
Description: SM2 decryption
Calls: SM2_KDF,Test_Point,SM3_init,SM3_process,SM3_done
Called By:
Input: dB // a big number lies in [1,n-2]
pubKey // [dB]G
C[Clen] // cipher C1||C3||C2
Clen // byte len of cipher
Output: M[Clen-SM2_NUMWORD*3] // decrypted data
Return: 0: sucess
1: S is a point at finity
3: C1 is not a valid point
5: KDF output is all zero
6: C3 does not match
Others:
****************************************************************/
int SM2_Decrypt(big dB, unsigned char C[], int Clen, unsigned char M[])
{SM3_STATE md;int i = 0;unsigned char x2y2[SM2_NUMWORD * 2] = { 0 };unsigned char hash[SM2_NUMWORD] = { 0 };big C1x, C1y, x2, y2;epoint *C1, *S, *dBC1;C1x = mirvar(0);C1y = mirvar(0);x2 = mirvar(0);y2 = mirvar(0);C1 = epoint_init();S = epoint_init();dBC1 = epoint_init();//Step1. test if C1 fits the curvebytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, C, C1x);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, C + SM2_NUMWORD, C1y);epoint_set(C1x, C1y, 0, C1);i = Test_Point(C1);if (i != 0)return i;//Step2. S=[h]C1 and test if S is the point at infinityecurve_mult(para_h, C1, S);if (point_at_infinity(S))// if S is point at infinity, return error;return ERR_INFINITY_POINT;//Step3. [dB]C1=(x2,y2)ecurve_mult(dB, C1, dBC1);epoint_get(dBC1, x2, y2);big_to_bytes(SM2_NUMWORD, x2, x2y2, 1);big_to_bytes(SM2_NUMWORD, y2, x2y2 + SM2_NUMWORD, 1);//Step4. t=KDF(x2||y2,klen)SM3_KDF(x2y2, SM2_NUMWORD * 2, Clen - SM2_NUMWORD * 3, M);if (Test_Null(M, Clen - SM2_NUMWORD * 3) != 0)return ERR_ARRAY_NULL;//Step5. M=C2^tfor (i = 0; i < Clen - SM2_NUMWORD * 3; i++)M[i] = M[i] ^ C[SM2_NUMWORD * 3 + i];//Step6. hash(x2,m,y2)SM3_init(&md);SM3_process(&md, x2y2, SM2_NUMWORD);SM3_process(&md, M, Clen - SM2_NUMWORD * 3);SM3_process(&md, x2y2 + SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_NUMWORD);SM3_done(&md, hash);if (memcmp(hash, C + SM2_NUMWORD * 2, SM2_NUMWORD) != 0)return ERR_C3_MATCH;elsereturn 0;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: SM2_ENC_SelfTest
Description: test whether the SM2 calculation is correct by comparing the result with the standard data
Calls: SM2_init,SM2_ENC,SM2_DEC
Called By:
Input: NULL
Output: NULL
Return: 0: sucess
1: S is a point at finity
2: X or Y coordinate is beyond Fq
3: not a valid point on curve
4: the given point G is not a point of order n
5: KDF output is all zero
6: C3 does not match
8: public key generation error
9: SM2 encryption error
a: SM2 decryption error
Others:
****************************************************************/
int SM2_ENC_SelfTest()
{int tmp = 0, i = 0;unsigned char Cipher[115] = { 0 };unsigned char M[19] = { 0 };unsigned char kGxy[SM2_NUMWORD * 2] = { 0 };big ks, x, y;epoint *kG;//standard dataunsigned char std_priKey[32] = { 0x39,0x45,0x20,0x8F,0x7B,0x21,0x44,0xB1,0x3F,0x36,0xE3,0x8A,0xC6,0xD3,0x9F,0x95,0x88,0x93,0x93,0x69,0x28,0x60,0xB5,0x1A,0x42,0xFB,0x81,0xEF,0x4D,0xF7,0xC5,0xB8 };unsigned char std_pubKey[64] = { 0x09,0xF9,0xDF,0x31,0x1E,0x54,0x21,0xA1,0x50,0xDD,0x7D,0x16,0x1E,0x4B,0xC5,0xC6,0x72,0x17,0x9F,0xAD,0x18,0x33,0xFC,0x07,0x6B,0xB0,0x8F,0xF3,0x56,0xF3,0x50,0x20,0xCC,0xEA,0x49,0x0C,0xE2,0x67,0x75,0xA5,0x2D,0xC6,0xEA,0x71,0x8C,0xC1,0xAA,0x60,0x0A,0xED,0x05,0xFB,0xF3,0x5E,0x08,0x4A,0x66,0x32,0xF6,0x07,0x2D,0xA9,0xAD,0x13 };unsigned char std_rand[32] = { 0x59,0x27,0x6E,0x27,0xD5,0x06,0x86,0x1A,0x16,0x68,0x0F,0x3A,0xD9,0xC0,0x2D,0xCC,0xEF,0x3C,0xC1,0xFA,0x3C,0xDB,0xE4,0xCE,0x6D,0x54,0xB8,0x0D,0xEA,0xC1,0xBC,0x21 };unsigned char std_Message[19] = { 0x65,0x6E,0x63,0x72,0x79,0x70,0x74,0x69,0x6F,0x6E,0x20,0x73,0x74,0x61,0x6E,0x64,0x61,0x72,0x64 };unsigned char std_Cipher[115] = { 0x04,0xEB,0xFC,0x71,0x8E,0x8D,0x17,0x98,0x62,0x04,0x32,0x26,0x8E,0x77,0xFE,0xB6,0x41,0x5E,0x2E,0xDE,0x0E,0x07,0x3C,0x0F,0x4F,0x64,0x0E,0xCD,0x2E,0x14,0x9A,0x73,0xE8,0x58,0xF9,0xD8,0x1E,0x54,0x30,0xA5,0x7B,0x36,0xDA,0xAB,0x8F,0x95,0x0A,0x3C,0x64,0xE6,0xEE,0x6A,0x63,0x09,0x4D,0x99,0x28,0x3A,0xFF,0x76,0x7E,0x12,0x4D,0xF0,0x59,0x98,0x3C,0x18,0xF8,0x09,0xE2,0x62,0x92,0x3C,0x53,0xAE,0xC2,0x95,0xD3,0x03,0x83,0xB5,0x4E,0x39,0xD6,0x09,0xD1,0x60,0xAF,0xCB,0x19,0x08,0xD0,0xBD,0x87,0x66,0x21,0x88,0x6C,0xA9,0x89,0xCA,0x9C,0x7D,0x58,0x08,0x73,0x07,0xCA,0x93,0x09,0x2D,0x65,0x1E,0xFA };mip = mirsys(1000, 16);mip->IOBASE = 16;x = mirvar(0);y = mirvar(0);ks = mirvar(0);kG = epoint_init();bytes_to_big(32, std_priKey, ks); //ks is the standard private key//initiate SM2 curveSM2_Init();//generate key pairtmp = SM2_KeyGeneration(ks, kG);if (tmp != 0)return tmp;epoint_get(kG, x, y);big_to_bytes(SM2_NUMWORD, x, kGxy, 1);big_to_bytes(SM2_NUMWORD, y, kGxy + SM2_NUMWORD, 1);if (memcmp(kGxy, std_pubKey, SM2_NUMWORD * 2) != 0)return ERR_SELFTEST_KG;puts("原文");for (i = 0; i < 19; i++){if (i > 0 && i % 8 == 0) printf("\n");printf("0x%x,", std_Message[i]);}//encrypt data and compare the result with the standard datatmp = SM2_Encrypt(std_rand, kG, std_Message, 19, Cipher);if (tmp != 0)return tmp;if (memcmp(Cipher, std_Cipher, 19 + SM2_NUMWORD * 3) != 0)return ERR_SELFTEST_ENC;puts("\n\n 密文:");for (i = 0; i < 19 + SM2_NUMWORD * 3; i++){if (i > 0 && i % 8 == 0) printf("\n");printf("0x%x,", Cipher[i]);}//decrypt cipher and compare the result with the standard datatmp = SM2_Decrypt(ks, Cipher, 115, M);if (tmp != 0)return tmp;puts("\n\n解密结果:");for (i = 0; i < 19; i++){if (i>0&&i%8 == 0) printf("\n");printf("0x%x,", M[i]);}if (memcmp(M, std_Message, 19) != 0)return ERR_SELFTEST_DEC;puts("\n解密成功");return 0;
}
//sm2_sv.c#include "SM2_sv.h"
#include "kdf.h"big Gx, Gy, p, a, b, n;
epoint *G, *nG;unsigned char SM2_p[32] = { 0xff,0xff,0xff,0xfe,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,
0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00, 0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff, 0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff };
unsigned char SM2_a[32] = { 0xff,0xff,0xff,0xfe,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,
0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00, 0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff, 0xff,0xff,0xff,0xfc };
unsigned char SM2_b[32] = { 0x28,0xe9,0xfa,0x9e, 0x9d,0x9f,0x5e,0x34, 0x4d,0x5a,0x9e,0x4b,0xcf,0x65,0x09,0xa7,
0xf3,0x97,0x89,0xf5, 0x15,0xab,0x8f,0x92, 0xdd,0xbc,0xbd,0x41,0x4d,0x94,0x0e,0x93 };
unsigned char SM2_Gx[32] = { 0x32,0xc4,0xae,0x2c, 0x1f,0x19,0x81,0x19,0x5f,0x99,0x04,0x46,0x6a,0x39,0xc9,0x94,
0x8f,0xe3,0x0b,0xbf,0xf2,0x66,0x0b,0xe1,0x71,0x5a,0x45,0x89,0x33,0x4c,0x74,0xc7 };
unsigned char SM2_Gy[32] = { 0xbc,0x37,0x36,0xa2,0xf4,0xf6,0x77,0x9c,0x59,0xbd,0xce,0xe3,0x6b,0x69,0x21,0x53,0xd0,
0xa9,0x87,0x7c,0xc6,0x2a,0x47,0x40,0x02,0xdf,0x32,0xe5,0x21,0x39,0xf0,0xa0 };
unsigned char SM2_n[32] = { 0xff,0xff,0xff,0xfe,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,
0x72,0x03,0xdf,0x6b,0x21,0xc6,0x05,0x2b,0x53,0xbb,0xf4,0x09,0x39,0xd5,0x41,0x23 };/****************************************************************
Function: SM2_Init
Description: Initiate SM2 curve
Calls: MIRACL functions
Called By: SM2_KeyGeneration,SM2_Sign,SM2_Verify,SM2_SelfCheck
Input: null
Output: null
Return: 0: sucess;
1: parameter initialization error;
4: the given point G is not a point of order n
Others:
****************************************************************/
int SM2_Init()
{Gx = mirvar(0);Gy = mirvar(0);p = mirvar(0);a = mirvar(0);b = mirvar(0);n = mirvar(0);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_Gx, Gx);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_Gy, Gy);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_p, p);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_a, a);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_b, b);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_n, n);ecurve_init(a, b, p, MR_PROJECTIVE);G = epoint_init();nG = epoint_init();if (!epoint_set(Gx, Gy, 0, G))//initialise point G{return ERR_ECURVE_INIT;}ecurve_mult(n, G, nG);if (!point_at_infinity(nG)) //test if the order of the point is n{return ERR_ORDER;}return 0;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: Test_Point
Description: test if the given point is on SM2 curve
Calls:
Called By: SM2_KeyGeneration
Input: point
Output: null
Return: 0: sucess
3: not a valid point on curve
Others:
****************************************************************/
int Test_Point(epoint* point)
{big x, y, x_3, tmp;x = mirvar(0);y = mirvar(0);x_3 = mirvar(0);tmp = mirvar(0);//test if y^2=x^3+ax+bepoint_get(point, x, y);power(x, 3, p, x_3); //x_3=x^3 mod pmultiply(x, a, x); //x=a*xdivide(x, p, tmp); //x=a*x mod p , tmp=a*x/padd(x_3, x, x); //x=x^3+axadd(x, b, x); //x=x^3+ax+bdivide(x, p, tmp); //x=x^3+ax+b mod ppower(y, 2, p, y); //y=y^2 mod pif (mr_compare(x, y) != 0)return ERR_NOT_VALID_POINT;elsereturn 0;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: Test_PubKey
Description: test if the given public key is valid
Calls:
Called By: SM2_KeyGeneration
Input: pubKey //a point
Output: null
Return: 0: sucess
2: a point at infinity
5: X or Y coordinate is beyond Fq
3: not a valid point on curve
4: not a point of order n
Others:
****************************************************************/
int Test_PubKey(epoint *pubKey)
{big x, y, x_3, tmp;epoint *nP;x = mirvar(0);y = mirvar(0);x_3 = mirvar(0);tmp = mirvar(0);nP = epoint_init();//test if the pubKey is the point at infinityif (point_at_infinity(pubKey))// if pubKey is point at infinity, return error;return ERR_INFINITY_POINT;//test if x<p and y<p both holdepoint_get(pubKey, x, y);if ((mr_compare(x, p) != -1) || (mr_compare(y, p) != -1))return ERR_NOT_VALID_ELEMENT;if (Test_Point(pubKey) != 0)return ERR_NOT_VALID_POINT;//test if the order of pubKey is equal to necurve_mult(n, pubKey, nP); // nP=[n]Pif (!point_at_infinity(nP)) // if np is point NOT at infinity, return error;return ERR_ORDER;return 0;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: Test_Zero
Description: test if the big x is zero
Calls:
Called By: SM2_Sign
Input: pubKey //a point
Output: null
Return: 0: x!=0
1: x==0
Others:
****************************************************************/
int Test_Zero(big x)
{big zero;zero = mirvar(0);if (mr_compare(x, zero) == 0)return 1;else return 0;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: Test_n
Description: test if the big x is order n
Calls:
Called By: SM2_Sign
Input: big x //a miracl data type
Output: null
Return: 0: sucess
1: x==n,fail
Others:
****************************************************************/
int Test_n(big x)
{// bytes_to_big(32,SM2_n,n);if (mr_compare(x, n) == 0)return 1;else return 0;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: Test_Range
Description: test if the big x belong to the range[1,n-1]
Calls:
Called By: SM2_Verify
Input: big x ///a miracl data type
Output: null
Return: 0: sucess
1: fail
Others:
****************************************************************/
int Test_Range(big x)
{big one, decr_n;one = mirvar(0);decr_n = mirvar(0);convert(1, one);decr(n, 1, decr_n);if ((mr_compare(x, one) < 0) | (mr_compare(x, decr_n) > 0))return 1;return 0;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: SM2_KeyGeneration
Description: calculate a pubKey out of a given priKey
Calls: SM2_SelfCheck()
Called By: SM2_Init()
Input: priKey // a big number lies in[1,n-2]
Output: pubKey // pubKey=[priKey]G
Return: 0: sucess
2: a point at infinity
5: X or Y coordinate is beyond Fq
3: not a valid point on curve
4: not a point of order n
Others:
****************************************************************/
int SM2_KeyGeneration(unsigned char PriKey[], unsigned char Px[], unsigned char Py[])
{int i = 0;big d, PAx, PAy;epoint *PA;SM2_Init();PA = epoint_init();d = mirvar(0);PAx = mirvar(0);PAy = mirvar(0);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, PriKey, d);ecurve_mult(d, G, PA);epoint_get(PA, PAx, PAy);big_to_bytes(SM2_NUMWORD, PAx, Px, TRUE);big_to_bytes(SM2_NUMWORD, PAy, Py, TRUE);i = Test_PubKey(PA);if (i)return i;elsereturn 0;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: SM2_Sign
Description: SM2 signature algorithm
Calls: SM2_Init(),Test_Zero(),Test_n(), SM3_256()
Called By: SM2_SelfCheck()
Input: message //the message to be signed
len //the length of message
ZA // ZA=Hash(ENTLA|| IDA|| a|| b|| Gx || Gy || xA|| yA)
rand //a random number K lies in [1,n-1]
d //the private key
Output: R,S //signature result
Return: 0: sucess
1: parameter initialization error;
4: the given point G is not a point of order n
6: the signed r equals 0 or r+rand equals n
7 the signed s equals 0
Others:
****************************************************************/
int SM2_Sign(unsigned char *message, int len, unsigned char ZA[], unsigned char rand[], unsigned char d[], unsigned char R[], unsigned char S[])
{unsigned char hash[SM3_len / 8];int M_len = len + SM3_len / 8;unsigned char *M = NULL;int i;big dA, r, s, e, k, KGx, KGy;big rem, rk, z1, z2;epoint *KG;i = SM2_Init();if (i) return i;//initiatedA = mirvar(0);e = mirvar(0);k = mirvar(0);KGx = mirvar(0);KGy = mirvar(0);r = mirvar(0);s = mirvar(0);rem = mirvar(0);rk = mirvar(0);z1 = mirvar(0);z2 = mirvar(0);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, d, dA);//cinstr(dA,d);KG = epoint_init();//step1,set M=ZA||MM = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*(M_len + 1));memcpy(M, ZA, SM3_len / 8);memcpy(M + SM3_len / 8, message, len);//step2,generate e=H(M)SM3_256(M, M_len, hash);bytes_to_big(SM3_len / 8, hash, e);//step3:generate kbytes_to_big(SM3_len / 8, rand, k);//step4:calculate kGecurve_mult(k, G, KG);//step5:calculate repoint_get(KG, KGx, KGy);add(e, KGx, r);divide(r, n, rem);//judge r=0 or n+k=n?add(r, k, rk);if (Test_Zero(r) | Test_n(rk))return ERR_GENERATE_R;//step6:generate sincr(dA, 1, z1);xgcd(z1, n, z1, z1, z1);multiply(r, dA, z2);divide(z2, n, rem);subtract(k, z2, z2);add(z2, n, z2);multiply(z1, z2, s);divide(s, n, rem);//judge s=0?if (Test_Zero(s))return ERR_GENERATE_S;big_to_bytes(SM2_NUMWORD, r, R, TRUE);big_to_bytes(SM2_NUMWORD, s, S, TRUE);free(M);return 0;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: SM2_Verify
Description: SM2 verification algorithm
Calls: SM2_Init(),Test_Range(), Test_Zero(),SM3_256()
Called By: SM2_SelfCheck()
Input: message //the message to be signed
len //the length of message
ZA //ZA=Hash(ENTLA|| IDA|| a|| b|| Gx || Gy || xA|| yA)
Px,Py //the public key
R,S //signature result
Output:
Return: 0: sucess
1: parameter initialization error;
4: the given point G is not a point of order n
B: public key error
8: the signed R out of range [1,n-1]
9: the signed S out of range [1,n-1]
A: the intermediate data t equals 0
C: verification fail
Others:
****************************************************************/
int SM2_Verify(unsigned char *message, int len, unsigned char ZA[], unsigned char Px[], unsigned char Py[], unsigned char R[], unsigned char S[])
{unsigned char hash[SM3_len / 8];int M_len = len + SM3_len / 8;unsigned char *M = NULL;int i;big PAx, PAy, r, s, e, t, rem, x1, y1;big RR;epoint *PA, *sG, *tPA;i = SM2_Init();if (i) return i;PAx = mirvar(0);PAy = mirvar(0);r = mirvar(0);s = mirvar(0);e = mirvar(0);t = mirvar(0);x1 = mirvar(0);y1 = mirvar(0);rem = mirvar(0);RR = mirvar(0);PA = epoint_init();sG = epoint_init();tPA = epoint_init();bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, Px, PAx);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, Py, PAy);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, R, r);bytes_to_big(SM2_NUMWORD, S, s);if (!epoint_set(PAx, PAy, 0, PA))//initialise public key{return ERR_PUBKEY_INIT;}//step1: test if r belong to [1,n-1]if (Test_Range(r))return ERR_OUTRANGE_R;//step2: test if s belong to [1,n-1]if (Test_Range(s))return ERR_OUTRANGE_S;//step3,generate MM = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*(M_len + 1));memcpy(M, ZA, SM3_len / 8);memcpy(M + SM3_len / 8, message, len);//step4,generate e=H(M)SM3_256(M, M_len, hash);bytes_to_big(SM3_len / 8, hash, e);//step5:generate tadd(r, s, t);divide(t, n, rem);if (Test_Zero(t))return ERR_GENERATE_T;//step 6: generate(x1,y1)ecurve_mult(s, G, sG);ecurve_mult(t, PA, tPA);ecurve_add(sG, tPA);epoint_get(tPA, x1, y1);//step7:generate RRadd(e, x1, RR);divide(RR, n, rem);free(M);if (mr_compare(RR, r) == 0)return 0;elsereturn ERR_DATA_MEMCMP;
}
/****************************************************************
Function: SM2_SelfCheck
Description: SM2 self check
Calls: SM2_Init(), SM2_KeyGeneration,SM2_Sign, SM2_Verify,SM3_256()
Called By:
Input:
Output:
Return: 0: sucess
1: paremeter initialization error
2: a point at infinity
5: X or Y coordinate is beyond Fq
3: not a valid point on curve
4: not a point of order n
B: public key error
8: the signed R out of range [1,n-1]
9: the signed S out of range [1,n-1]
A: the intermediate data t equals 0
C: verification fail
Others:
****************************************************************/
int SM2_SelfCheck()
{//the private keyunsigned char dA[32] = { 0x39,0x45,0x20,0x8f,0x7b,0x21,0x44,0xb1,0x3f,0x36,0xe3,0x8a,0xc6,0xd3,0x9f,0x95,0x88,0x93,0x93,0x69,0x28,0x60,0xb5,0x1a,0x42,0xfb,0x81,0xef,0x4d,0xf7,0xc5,0xb8 };unsigned char rand[32] = { 0x59,0x27,0x6E,0x27,0xD5,0x06,0x86,0x1A,0x16,0x68,0x0F,0x3A,0xD9,0xC0,0x2D,0xCC,0xEF,0x3C,0xC1,0xFA,0x3C,0xDB,0xE4,0xCE,0x6D,0x54,0xB8,0x0D,0xEA,0xC1,0xBC,0x21 };//the public key/* unsigned char xA[32]={0x09,0xf9,0xdf,0x31,0x1e,0x54,0x21,0xa1,0x50,0xdd,0x7d,0x16,0x1e,0x4b,0xc5,0xc6,0x72,0x17,0x9f,0xad,0x18,0x33,0xfc,0x07,0x6b,0xb0,0x8f,0xf3,0x56,0xf3,0x50,0x20};unsigned char yA[32]={0xcc,0xea,0x49,0x0c,0xe2,0x67,0x75,0xa5,0x2d,0xc6,0xea,0x71,0x8c,0xc1,0xaa,0x60,0x0a,0xed,0x05,0xfb,0xf3,0x5e,0x08,0x4a,0x66,0x32,0xf6,0x07,0x2d,0xa9,0xad,0x13};*/unsigned char xA[32], yA[32];unsigned char r[32], s[32];// Signatureunsigned char IDA[16] = { 0x31,0x32,0x33,0x34,0x35,0x36,0x37,0x38,0x31,0x32,0x33,0x34,0x35,0x36,0x37,0x38 };//ASCII code of userA's identificationint IDA_len = 16;unsigned char ENTLA[2] = { 0x00,0x80 };//the length of userA's identification,presentation in ASCII codeunsigned char *message = "message digest";//the message to be signedint len = strlen(message);//the length of messageunsigned char ZA[SM3_len / 8];//ZA=Hash(ENTLA|| IDA|| a|| b|| Gx || Gy || xA|| yA)unsigned char Msg[210]; //210=IDA_len+2+SM2_NUMWORD*6int temp;miracl *mip = mirsys(10000, 16);mip->IOBASE = 16;temp = SM2_KeyGeneration(dA, xA, yA);if (temp)return temp;// ENTLA|| IDA|| a|| b|| Gx || Gy || xA|| yAmemcpy(Msg, ENTLA, 2);memcpy(Msg + 2, IDA, IDA_len);memcpy(Msg + 2 + IDA_len, SM2_a, SM2_NUMWORD);memcpy(Msg + 2 + IDA_len + SM2_NUMWORD, SM2_b, SM2_NUMWORD);memcpy(Msg + 2 + IDA_len + SM2_NUMWORD * 2, SM2_Gx, SM2_NUMWORD);memcpy(Msg + 2 + IDA_len + SM2_NUMWORD * 3, SM2_Gy, SM2_NUMWORD);memcpy(Msg + 2 + IDA_len + SM2_NUMWORD * 4, xA, SM2_NUMWORD);memcpy(Msg + 2 + IDA_len + SM2_NUMWORD * 5, yA, SM2_NUMWORD);SM3_256(Msg, 210, ZA);temp = SM2_Sign(message, len, ZA, rand, dA, r, s);if (temp)return temp;temp = SM2_Verify(message, len, ZA, xA, yA, r, s);if (temp)return temp;return 0;
}
由于在github中,miracl库只支持32位系统,要是想要使用,
需要配置适合64位系统使用。通过查阅miracl库的win64.txt文件
这是配置所需步骤
概述 在Microsoft Visual C++ (Visual Studio)环境下,Intel
x86-64架构现在已完全支持。然而,需要注意的是,该环境不支持内联汇编,因此必须使用内置的内在函数(如umul128())来替代。
配置头文件 为了在Windows x86-64环境下使用MIRACL库,需要定义一些宏并包含特定的头文件。以下是一个示例头文件配置:
> #define MR_LITTLE_ENDIAN
> #define MIRACL 64
> #define mr_utype __int64
> #define MR_IBITS 32
> #define MR_LBITS 32
> #define mr_unsign32 unsigned int
> #define mr_unsign64 unsigned __int64
> #define MR_FLASH 52
> #define MAXBASE ((mr_small)1<<(MIRACL-1))
> #define BITSINCHAR 8
使用mrmuldv.w64文件 将
mrmuldv.w64文件重命名为mrmuldv.c,以便在编译时使用。 宏文件
还有一个宏文件win64.mcs,相关的说明可以在kcmcomba.txt和makemcs.txt文件中找到。
构建MIRACL库 要构建Windows
x86-64的MIRACL库,可以执行批处理文件ms64doit.bat。这个批处理文件将负责编译和链接必要的源文件,生成最终的库文件。
通过以上步骤,您可以在Microsoft Visual C++环境下成功构建和使用MIRACL库,支持Intel x86-64架构。
综合上述内容,
配置64位的miracl步骤如下
根据您提供的文件内容,配置适合64位操作系统的MIRACL库需要遵循以下步骤:
Windows64
1. 定义宏
首先,您需要定义一组宏,这些宏指定了MIRACL库在64位系统上的配置。根据
win64.txt文件,您可以创建一个头文件(例如mirdef.h),并定义以下宏:#define MR_LITTLE_ENDIAN #define MIRACL 64 #define mr_utype __int64 #define MR_IBITS 32 #define MR_LBITS 32 #define mr_unsign32 unsigned int #define mr_unsign64 unsigned __int64 #define MR_FLASH 52 #define MAXBASE ((mr_small)1<<(MIRACL-1)) #define BITSINCHAR 8这些宏定义了基本的数据类型和位数,以及MIRACL库在64位系统上的行为。
2. 使用特定的源文件
根据
win64.txt文件,您需要使用mrmuldv.w64作为mrmuldv.c。这意味着您应该将mrmuldv.w64文件重命名为mrmuldv.c,以便MIRACL库能够使用这个文件。3. 编译MIRACL库
在Windows
x86-64系统上,您可以通过执行ms64doit.bat批处理文件来构建MIRACL库。这个批处理文件会自动编译MIRACL库的所有源文件,并生成库文件。4. 配置KCM和Comba方法
如果您需要使用KCM(Karatsuba-Comba-Montgomery)方法或Comba方法来提高性能,您需要根据
kcmcomba.txt文件中的说明创建mrkcm.c或mrcomba.c文件。这通常是通过使用MEX工具从模板文件(如mrkcm.tpl或mrcomba.tpl)和宏文件(如win64.mcs)生成的。5. 编译和运行MEX工具
根据
makemcs.txt文件,MEX工具用于从.mcs文件中提取宏并生成用于快速算法的代码。您需要编译并运行MEX工具来生成这些文件。6. 使用config.c工具
config.c工具可以帮助您确定如何配置MIRACL库以及如何使用MEX工具。它提供了关于如何为您的目标处理器配置MIRACL库的参数建议。总结
通过以上步骤,您可以配置和构建一个适合64位操作系统的MIRACL库。确保您的开发环境(如Microsoft Visual
C++)已经设置好,并且您有权限在系统上执行这些操作。如果您遇到任何问题,可以参考MIRACL库的文档和示例代码,或者在MIRACL社区寻求帮助。
Linux64
在Linux系统(如openEuler或Ubuntu)上配置64位的MIRACL库,步骤与Windows系统有所不同,主要是因为Linux使用不同的编译器和构建工具。以下是在Linux系统上配置64位MIRACL库的步骤:1. 准备环境
确保你的Linux系统上安装了GCC编译器和必要的开发工具。你可以通过以下命令安装它们(如果尚未安装):
bash sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install build-essential2. 下载和解压MIRACL库
从MIRACL
GitHub仓库下载MIRACL库的源码,并解压到一个目录。https://github.com/miracl/MIRACL/archive/refs/heads/master.zip unzip master.zip cd MIRACL-master3. 定义宏
创建或修改
mirdef.h文件,定义适合64位系统的宏。根据win64.txt文件,你可以创建一个类似的配置文件,例如mirdef.h:#define MR_LITTLE_ENDIAN #define MIRACL 64 #define mr_utype long #define MR_IBITS 32 #define MR_LBITS 32 #define mr_unsign32 unsigned int #define mr_unsign64 unsigned long #define MR_FLASH 52 #define MAXBASE ((mr_small)1<<(MIRACL-1)) #define BITSINCHAR 8请注意,
mr_utype在Linux上通常是long而不是__int64。4. 使用特定的源文件
在Linux上,你可能不需要像在Windows上那样重命名
mrmuldv.w64文件,因为Linux系统通常不需要这样做。确保源代码目录中有mrmuldv.c文件。5. 编译MIRACL库
在Linux上,你可以使用
make命令来编译MIRACL库。MIRACL库通常包含一个makefile文件,你可以直接使用它来构建库。
bash make6. 配置KCM和Comba方法
如果你需要使用KCM或Comba方法,你需要根据
kcmcomba.txt文件中的说明创建mrkcm.c或mrcomba.c文件。这通常是通过使用MEX工具从模板文件(如mrkcm.tpl或mrcomba.tpl)和宏文件(如linux64.mcs,如果有的话)生成的。7. 编译和运行MEX工具
在Linux上,MEX工具可能需要你自己编写或修改,以适应Linux的汇编语言和编译器语法。编译并运行MEX工具来生成
mrkcm.c或mrcomba.c文件。8. 使用config.c工具
config.c工具可以帮助你确定如何配置MIRACL库以及如何使用MEX工具。它提供了关于如何为你的目标处理器配置MIRACL库的参数建议。9. 安装库
如果一切顺利,
make命令将生成库文件(通常是libmiracl.a)。你可以将这个库文件安装到系统的库目录中,或者在你的项目中直接引用它。总结
在Linux系统上配置64位MIRACL库主要涉及到下载源码、定义宏、编译库以及可能的KCM和Comba方法配置。确保你遵循MIRACL库的文档和指南,以便正确配置和优化库以适应你的特定需求。
注意 还可以寻找开源的适合64位的miracl库
如
git clone https://github.com/lookingforfyf/SMX_Test/tree/master/SMX_Test/miracl-lib-X86_64/SM2ALG/miracl
但github可能出现连接不稳定的情况。所以不一定会成功。
root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:~/exp2/sm2# gcc -o test kdf.c SM2_ENC.c test.c
In file included from kdf.c:1:
kdf.c: In function ‘CF’:
kdf.h:21:31: warning: result of ‘2055708042 << 16’ requires 48
bits to represent, but ‘int’ only has 32 bits [-Wshift-overflow=]
21 | #define SM3_rotl32(x,n) (((x) << n) | ((x) >> (32 - n)))| ^~
kdf.c:89:29: note: in expansion of macro ‘SM3_rotl32’
89 | T = SM3_rotl32(SM3_T2, 16);| ^~~~~~~~~~
test.c: In function ‘main’:
test.c:5:9: warning: implicit declaration of function
‘SM2_ENC_SelfTest’ [-Wimplicit-function-declaration]5 | SM2_ENC_SelfTest();| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:~/exp2/sm2# ./test
原文
0x65,0x6e,0x63,0x72,0x79,0x70,0x74,0x69,
0x6f,0x6e,0x20,0x73,0x74,0x61,0x6e,0x64,
0x61,0x72,0x64,
密文:
0x4,0xeb,0xfc,0x71,0x8e,0x8d,0x17,0x98,
0x62,0x4,0x32,0x26,0x8e,0x77,0xfe,0xb6,
0x41,0x5e,0x2e,0xde,0xe,0x7,0x3c,0xf,
0x4f,0x64,0xe,0xcd,0x2e,0x14,0x9a,0x73,
0xe8,0x58,0xf9,0xd8,0x1e,0x54,0x30,0xa5,
0x7b,0x36,0xda,0xab,0x8f,0x95,0xa,0x3c,
0x64,0xe6,0xee,0x6a,0x63,0x9,0x4d,0x99,
0x28,0x3a,0xff,0x76,0x7e,0x12,0x4d,0xf0,
0x59,0x98,0x3c,0x18,0xf8,0x9,0xe2,0x62,
0x92,0x3c,0x53,0xae,0xc2,0x95,0xd3,0x3,
0x83,0xb5,0x4e,0x39,0xd6,0x9,0xd1,0x60,
0xaf,0xcb,0x19,0x8,0xd0,0xbd,0x87,0x66,
0x21,0x88,0x6c,0xa9,0x89,0xca,0x9c,0x7d,
0x58,0x8,0x73,0x7,0xca,0x93,0x9,0x2d,
0x65,0x1e,0xfa,
解密结果:
0x65,0x6e,0x63,0x72,0x79,0x70,0x74,0x69,
0x6f,0x6e,0x20,0x73,0x74,0x61,0x6e,0x64,
0x61,0x72,0x64,
解密成功
root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:~/exp2/sm2# gcc -o test test.c SM2_sv.c kdf.c
SM2_sv.c:3:10: fatal error: KDF.h: No such file or directory3 | #include "KDF.h"| ^~~~~~~
compilation terminated.
In file included from kdf.c:1:
kdf.c: In function ‘CF’:
kdf.h:22:31: warning: result of ‘2055708042 << 16’ requires 48
bits to represent, but ‘int’ only has 32 bits [-Wshift-overflow=]
22 | #define SM3_rotl32(x,n) (((x) << n) | ((x) >> (32 - n)))| ^~
kdf.c:92:29: note: in expansion of macro ‘SM3_rotl32’
92 | T = SM3_rotl32(SM3_T2, 16);| ^~~~~~~~~~
root@Youer:~/shiyan/shiyan02/shiyan2-2/sm2/14-3# nano SM2_sv.c
root@Youer:~/shiyan/shiyan02/shiyan2-2/sm2/14-3# gcc -o test
test.c SM2_sv.c kdf.c -lmiracl_32 -m32
In file included from kdf.c:1:
kdf.c: In function ‘CF’:
kdf.h:22:31: warning: result of ‘2055708042 << 16’ requires 48
bits to represent, but ‘int’ only has 32 bits [-Wshift-overflow=]
22 | #define SM3_rotl32(x,n) (((x) << n) | ((x) >> (32 - n)))
root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:~/exp2/sm2# ./test
SM2 签名验签成功sm3
一段式算法实现
// test.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//#include "pch.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <memory>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdint> // 包含标准整数类型unsigned char IV[256 / 8] = { 0x73,0x80,0x16,0x6f,0x49,0x14,0xb2,0xb9,0x17,0x24,0x42,0xd7,0xda,0x8a,0x06,0x00,0xa9,0x6f,0x30,0xbc,0x16,0x31,0x38,0xaa,0xe3,0x8d,0xee,0x4d,0xb0,0xfb,0x0e,0x4e };// 循环左移
unsigned long SL(unsigned long X, int n)
{uint64_t x = X; // 修改为标准类型x = x << (n % 32);unsigned long l = (unsigned long)(x >> 32);return x | l;
}unsigned long Tj(int j)
{if (j <= 15){return 0x79cc4519;}else{return 0x7a879d8a;}
}unsigned long FFj(int j, unsigned long X, unsigned long Y, unsigned long Z)
{if (j <= 15){return X ^ Y ^ Z;}else{return (X & Y) | (X & Z) | (Y & Z);}
}unsigned long GGj(int j, unsigned long X, unsigned long Y, unsigned long Z)
{if (j <= 15){return X ^ Y ^ Z;}else{return (X & Y) | (~X & Z);}
}unsigned long P0(unsigned long X)
{return X ^ SL(X, 9) ^ SL(X, 17);
}unsigned long P1(unsigned long X)
{return X ^ SL(X, 15) ^ SL(X, 23);
}// 扩展
void EB(unsigned char Bi[512 / 8], unsigned long W[68], unsigned long W1[64])
{// Bi 分为W0~W15for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i){W[i] = Bi[i * 4] << 24 | Bi[i * 4 + 1] << 16 | Bi[i * 4 + 2] << 8 | Bi[i * 4 + 3];}for (int j = 16; j <= 67; ++j){W[j] = P1(W[j - 16] ^ W[j - 9] ^ SL(W[j - 3], 15)) ^ SL(W[j - 13], 7) ^ W[j - 6];}for (int j = 0; j <= 63; ++j){W1[j] = W[j] ^ W[j + 4];}
}// 压缩函数
void CF(unsigned char Vi[256 / 8], unsigned char Bi[512 / 8], unsigned char Vi1[256 / 8])
{// Bi 扩展为132个字unsigned long W[68] = { 0 };unsigned long W1[64] = { 0 };EB(Bi, W, W1);// 串联 ABCDEFGH = Viunsigned long R[8] = { 0 };for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i){R[i] = ((unsigned long)Vi[i * 4]) << 24 | ((unsigned long)Vi[i * 4 + 1]) << 16 | ((unsigned long)Vi[i * 4 + 2]) << 8 | ((unsigned long)Vi[i * 4 + 3]);}unsigned long A = R[0], B = R[1], C = R[2], D = R[3], E = R[4], F = R[5], G = R[6], H = R[7];unsigned long SS1, SS2, TT1, TT2;for (int j = 0; j <= 63; ++j){SS1 = SL(SL(A, 12) + E + SL(Tj(j), j), 7);SS2 = SS1 ^ SL(A, 12);TT1 = FFj(j, A, B, C) + D + SS2 + W1[j];TT2 = GGj(j, E, F, G) + H + SS1 + W[j];D = C;C = SL(B, 9);B = A;A = TT1;H = G;G = SL(F, 19);F = E;E = P0(TT2);}// Vi1 = ABCDEFGH 串联R[0] = A, R[1] = B, R[2] = C, R[3] = D, R[4] = E, R[5] = F, R[6] = G, R[7] = H;for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i){Vi1[i * 4] = (R[i] >> 24) & 0xFF;Vi1[i * 4 + 1] = (R[i] >> 16) & 0xFF;Vi1[i * 4 + 2] = (R[i] >> 8) & 0xFF;Vi1[i * 4 + 3] = (R[i]) & 0xFF;}// Vi1 = ABCDEFGH ^ Vifor (int i = 0; i < 256 / 8; ++i){Vi1[i] ^= Vi[i];}
}//参数 m 是原始数据,ml 是数据长度,r 是输出参数,存放hash结果
void SM3Hash(unsigned char* m, int ml, unsigned char r[32])
{int l = ml * 8;int k = 448 - 1 - l % 512; // 添加k个0,k 是满足 l + 1 + k ≡ 448mod512 的最小的非负整数if (k <= 0){k += 512;}int n = (l + k + 65) / 512;int m1l = n * 512 / 8; // 填充后的长度,512位的倍数unsigned char* m1 = new unsigned char[m1l];memset(m1, 0, m1l);memcpy(m1, m, l / 8);m1[l / 8] = 0x80; // 消息后补1// 再添加一个64位比特串,该比特串是长度l的二进制表示unsigned long l1 = l;for (int i = 0; i < 64 / 8 && l1 > 0; ++i){m1[m1l - 1 - i] = l1 & 0xFF;l1 = l1 >> 8;}//将填充后的消息m′按512比特进行分组:m′ = B(0)B(1)· · · B(n−1),其中n=(l+k+65)/512。unsigned char** B = new unsigned char*[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){B[i] = new unsigned char[512 / 8];memcpy(B[i], m1 + (512 / 8)*i, 512 / 8);}delete[] m1;unsigned char** V = new unsigned char*[n + 1];for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i){V[i] = new unsigned char[256 / 8];memset(V[i], 0, 256 / 8);}// 初始化 V0 = VImemcpy(V[0], IV, 256 / 8);// 压缩函数,V 与扩展的Bfor (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){CF(V[i], B[i], V[i + 1]);}for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){delete[] B[i];}delete[] B;// V[n]是结果memcpy(r, V[n], 32);for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i){delete[] V[i];}delete[] V;
}// 打印缓冲区内容
void dumpbuf(unsigned char* buf, int len)
{for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {printf("%02x", buf[i]);if ((i + 1) % 16 == 0) printf("\n");elseprintf(" ");}printf("\n");
}int main()
{// 输入数据unsigned char message[] = "abc";int message_len = strlen((char*)message);// 输出缓冲区unsigned char hash_result[32] = { 0 };// 调用 SM3 哈希函数SM3Hash(message, message_len, hash_result);// 输出哈希结果printf("SM3 Hash:\n");dumpbuf(hash_result, 32);return 0;
}[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm3]$ g++ -o test test.cpp pch.cpp
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm3]$ ./test
SM3 Hash:
02 f1 cf ea 2d 3b c7 e3 a8 fa ee 95 07 f1 fb e0
04 a3 7c 94 cf 08 5a 52 56 7b 87 ea 0d 06 a1 f1
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm3]$ git init
/home/wzy/exp2/test2/sm3/.git: Permission denied
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm3]$ git add test
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm3]$ git commit -m "sm3一段式实现"
[master 039e899] sm3一段式实现1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)create mode 100755 exp2/test2/sm3/test
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm3]$ git log
commit 039e899857a7ee26a670b5f1e7ab030b57a10e7f (HEAD -> master)
Author: wei-zhengyi <https://gitee.com/wei-zhengyi/projects>
Date: Sun Nov 3 17:18:31 2024 +0800sm3一段式实现手工实现三段式
// test.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//#include "pch.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "sm3.h"int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{unsigned char *input = (unsigned char*)"abc";int ilen = 3;unsigned char output[32];int i;sm3_context ctx;printf("Message: ");printf("%s\n", input);sm3(input, ilen, output);printf("Hash: ");for (i = 0; i < 32; i++){printf("%02x", output[i]);if (((i + 1) % 4) == 0) printf(" ");}printf("\n");printf("Message: ");for (i = 0; i < 16; i++)printf("abcd");printf("\n");sm3_starts(&ctx);for (i = 0; i < 16; i++)sm3_update(&ctx, (unsigned char*)"abcd", 4);sm3_finish(&ctx, output);memset(&ctx, 0, sizeof(sm3_context));printf("Hash: ");for (i = 0; i < 32; i++){printf("%02x", output[i]);if (((i + 1) % 4) == 0) printf(" ");}printf("\n");//getch();
}[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C pra2]$ ./test
Message: abc
Hash: 37bc43d1 1cab393d 7899ef62 24f568ec 18a8fd85 1d165c50 0c375402 0f466a04
Message: abcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcd
Hash: a8f95215 08e03054 1325267f d822077a e5c2fd1f 32b54ebb bf8c1c79 064c9b6d
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C pra2]$ git add test
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C pra2]$ git commit -m "sm3三段式实现"
[master 576f081] sm3三段式实现6 files changed, 489 insertions(+)create mode 100644 exp2/test2/sm3/pra2/pch.cppcreate mode 100644 exp2/test2/sm3/pra2/pch.hcreate mode 100644 exp2/test2/sm3/pra2/sm3.cppcreate mode 100644 exp2/test2/sm3/pra2/sm3.hcreate mode 100755 exp2/test2/sm3/pra2/testcreate mode 100644 exp2/test2/sm3/pra2/test.cpp
openssl实现sm3
// test.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//#include "pch.h"#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "sm3hash.h"int main(void)
{const unsigned char sample1[] = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 0 };unsigned int sample1_len = strlen((char *)sample1);const unsigned char sample2[] = { 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64,0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64,0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64,0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64,0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64,0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64,0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64,0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64 };unsigned int sample2_len = sizeof(sample2);unsigned char hash_value[64];unsigned int i, hash_len;sm3_hash(sample1, sample1_len, hash_value, &hash_len);printf("raw data: %s\n", sample1);printf("hash length: %d bytes.\n", hash_len);printf("hash value:\n");for (i = 0; i < hash_len; i++){printf("0x%x ", hash_value[i]);}printf("\n\n");sm3_hash(sample2, sample2_len, hash_value, &hash_len);printf("raw data:\n");for (i = 0; i < sample2_len; i++){printf("0x%x ", sample2[i]);}printf("\n");printf("hash length: %d bytes.\n", hash_len);printf("hash value:\n");for (i = 0; i < hash_len; i++){printf("0x%x ", hash_value[i]);}printf("\n");return 0;
}root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:/home/wzy/sm3/sm3_3# git init
hint: Using 'master' as the name for the initial branch. This default branch name
hint: is subject to change. To configure the initial branch name to use in all
hint: of your new repositories, which will suppress this warning, call:
hint:
hint: git config --global init.defaultBranch <name>
hint:
hint: Names commonly chosen instead of 'master' are 'main', 'trunk' and
hint: 'development'. The just-created branch can be renamed via this command:
hint:
hint: git branch -m <name>
root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:/home/wzy/sm3/sm3_3# g++ -o test test.cpp sm3hash.cpp pch.cpp -lcrypto
root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:/home/wzy/sm3/sm3_3# ./test
raw data: abc
hash length: 32 bytes.
hash value:
0x66 0xc7 0xf0 0xf4 0x62 0xee 0xed 0xd9 0xd1 0xf2 0xd4 0x6b 0xdc 0x10 0xe4 0xe2 0x41 0x67 0xc4 0x87 0x5c 0xf2 0xf7 0xa2 0x29 0x7d 0xa0 0x2b 0x8f 0x4b 0xa8 0xe0raw data:
0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64 0x61 0x62 0x63 0x64
hash length: 32 bytes.
hash value:
0xde 0xbe 0x9f 0xf9 0x22 0x75 0xb8 0xa1 0x38 0x60 0x48 0x89 0xc1 0x8e 0x5a 0x4d 0x6f 0xdb 0x70 0xe5 0x38 0x7e 0x57 0x65 0x29 0x3d 0xcb 0xa3 0x9c 0xc 0x57 0x32
root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:/home/wzy/sm3/sm3_3# git add .
root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:/home/wzy/sm3/sm3_3# git commit -m "openssl实现sm3算法-编译"
[master (root-commit) 86980de] openssl实现sm3算法-编译Committer: root <root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C>
Your name and email address were configured automatically based
on your username and hostname. Please check that they are accurate.
You can suppress this message by setting them explicitly. Run the
following command and follow the instructions in your editor to edit
your configuration file:git config --global --editAfter doing this, you may fix the identity used for this commit with:git commit --amend --reset-author6 files changed, 104 insertions(+)create mode 100644 pch.cppcreate mode 100644 pch.hcreate mode 100644 sm3hash.cppcreate mode 100644 sm3hash.hcreate mode 100755 testcreate mode 100644 test.cppHMAC-SM3(sm3.cpp参考教材源代码)
// test.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//#include "pch.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "sm3.h"int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{unsigned char *input = (unsigned char*)"abc";unsigned char *key = (unsigned char*)"123456";int ilen = 3;unsigned char output[32];int i;sm3_context ctx;printf("Message: ");printf("%s\n", input);sm3_hmac(key, 6, input, 3, output);printf("HMAC: ");for (i = 0; i < 32; i++){printf("%02x", output[i]);if (((i + 1) % 4) == 0) printf(" ");}printf("\n");}root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:/home/wzy/sm3/sm3_4# g++ -o test test.cpp sm3.cpp pch.cpp -lcrypto
root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:/home/wzy/sm3/sm3_4# ./test
Message: abc
HMAC: 740e5559 6015660c 17020fc6 da9f207a 43c4a59f cf00eedf d2c533fb f9abc0c4root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:/home/wzy/sm3/sm3_4# git init
hint: Using 'master' as the name for the initial branch. This default branch name
hint: is subject to change. To configure the initial branch name to use in all
hint: of your new repositories, which will suppress this warning, call:
hint:
hint: git config --global init.defaultBranch <name>
hint:
hint: Names commonly chosen instead of 'master' are 'main', 'trunk' and
hint: 'development'. The just-created branch can be renamed via this command:
hint:
hint: git branch -m <name>
Initialized empty Git repository in /home/wzy/sm3/sm3_4/.git/
root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:/home/wzy/sm3/sm3_4# git add .
root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:/home/wzy/sm3/sm3_4# git commit -m "Hmac-sm3实现"
[master (root-commit) 51078fe] Hmac-sm3实现Committer: root <root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C>
Your name and email address were configured automatically based
on your username and hostname. Please check that they are accurate.
You can suppress this message by setting them explicitly. Run the
following command and follow the instructions in your editor to edit
your configuration file:git config --global --editAfter doing this, you may fix the identity used for this commit with:git commit --amend --reset-author6 files changed, 586 insertions(+)create mode 100644 pch.cppcreate mode 100644 pch.hcreate mode 100644 sm3.cppcreate mode 100644 sm3.hcreate mode 100755 testcreate mode 100644 test.cpp
root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:/home/wzy/sm3/sm3_4# git log
commit 51078fef1acdcdf09c4f5242a414e0d0fbe16d84 (HEAD -> master)
Author: root <root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C>
Date: Sun Nov 3 17:15:12 2024 +0800Hmac-sm3实现
sm4
sm4算法16字节实现
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm4_1]$ sudo g++ -o test test.cpp pch.cpp sm4.cpp
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm4_1]$ ./test
sm4(16字节)自检成功
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm4_1]$ git add test
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm4_1]$ git commit -m "实现sm4算法16字节版"
[master f64aac4] 实现sm4算法16字节版1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)create mode 100755 exp2/test2/sm4/sm4_1/test
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm4_1]$ git log
commit f64aac488dcbb99304171c7f62cf65365e5c5f95 (HEAD -> master)
Author: wei-zhengyi <https://gitee.com/wei-zhengyi/projects>
Date: Sun Nov 3 18:17:09 2024 +0800实现sm4算法16字节版
实现SM4-ECBCBCCFBOFB 算法
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm4_2]$ sudo vim sm4.cpp
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm4_2]$ sudo g++ -o test test.cpp sm4check.cpp sm4.cpp pch.cpp
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm4_2]$ ./test
ecb enc(len=16) memcmp ok
ecb dec(len=16) memcmp ok
ecb enc/dec(len=32) memcmp ok
ecb enc/dec(len=64) memcmp ok
ecb enc/dec(len=128) memcmp ok
ecb enc/dec(len=256) memcmp ok
ecb enc/dec(len=512) memcmp ok
ecb enc/dec(len=1024) memcmp ok
ecb enc/dec(len=2048) memcmp ok
ecb enc/dec(len=4096) memcmp ok
cbc enc(len=32) memcmp ok
cbc dec(len=32) memcmp ok
cbc enc/dec(len=32) memcmp ok
cbc enc/dec(len=64) memcmp ok
cbc enc/dec(len=128) memcmp ok
cbc enc/dec(len=256) memcmp ok
cbc enc/dec(len=512) memcmp ok
cbc enc/dec(len=1024) memcmp ok
cbc enc/dec(len=2048) memcmp ok
cbc enc/dec(len=4096) memcmp ok
cfb enc/dec(len=16) memcmp ok
cfb enc/dec(len=32) memcmp ok
cfb enc/dec(len=64) memcmp ok
cfb enc/dec(len=128) memcmp ok
cfb enc/dec(len=256) memcmp ok
cfb enc/dec(len=512) memcmp ok
cfb enc/dec(len=1024) memcmp ok
cfb enc/dec(len=2048) memcmp ok
cfb enc/dec(len=4096) memcmp ok
ofb enc/dec(len=16) memcmp ok
ofb enc/dec(len=32) memcmp ok
ofb enc/dec(len=64) memcmp ok
ofb enc/dec(len=128) memcmp ok
ofb enc/dec(len=256) memcmp ok
ofb enc/dec(len=512) memcmp ok
ofb enc/dec(len=1024) memcmp ok
ofb enc/dec(len=2048) memcmp ok
ofb enc/dec(len=4096) memcmp ok
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm4_2]$ sudo git add test
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm4_2]$ sudo git commit -m "实现sm4 ECB CBC CFB OFB算法"
- 在密标委网站http://www.gmbz.org.cn/main/bzlb.html查找SM2,SM3,SM4相关标准,分析代码实现与标准的对应关系。(10分)
SM2标准的关键点:
椭圆曲线参数:
- SM2标准定义了特定的椭圆曲线参数,包括素数( p )、系数( a )和( b )、基点( G )的坐标( (x, y) )、阶( n )和加密参数( h )。
密钥生成:
- 用户随机选择一个私钥( d_A ),然后计算对应的公钥( Q_A = d_A \cdot G )。
加密过程:
- 加密过程包括生成随机数( k ),计算点( C_1 = k \cdot G )和( C_3 = k \cdot Q_B ),以及使用KDF(密钥派生函数)和哈希函数生成密文。
解密过程:
- 解密过程涉及使用私钥( d_A )来计算( C_2 ),然后使用KDF和哈希函数验证密文的完整性。
签名和验证:
- 签名过程包括使用私钥和哈希函数生成签名,验证过程则使用公钥来验证签名的有效性。
sm2加密解密
SM2是中国国家密码管理局发布的公钥密码标准,主要用于椭圆曲线加密、签名等。它基于椭圆曲线密码学,使用特定的椭圆曲线参数。以下是SM2标准的一些关键点,以及如何根据您提供的代码分析其实现:
代码实现分析:
椭圆曲线参数初始化:
- 代码中的全局变量
SM2_p、SM2_a、SM2_b、SM2_n、SM2_Gx、SM2_Gy和SM2_h分别存储了SM2标准的椭圆曲线参数。这些参数在SM2_Init函数中被初始化。密钥生成:
SM2_KeyGeneration函数实现了密钥生成过程,它接受私钥priKey并计算对应的公钥pubKey。加密过程:
SM2_Encrypt函数实现了SM2的加密过程,包括计算( C_1 )、( C_2 )和( C_3 ),以及使用SM3哈希函数和KDF。解密过程:
SM2_Decrypt函数实现了SM2的解密过程,包括验证( C_1 )的有效性、计算( C_2 )和使用SM3哈希函数验证密文的完整性。点的有效性测试:
Test_Point和Test_PubKey函数用于验证椭圆曲线上的点是否有效,这是SM2标准中的重要部分。自测试:
SM2_ENC_SelfTest函数提供了一个自测试,用于验证实现的正确性,通过比较加密和解密的结果与标准数据。结论:
提供的代码实现了SM2标准的核心功能,包括密钥生成、加密、解密和自测试。代码中的函数和逻辑与SM2标准的要求相匹配,表明它是一个符合SM2标准的实现。需要注意的是,代码的正确性和安全性还需要通过详细的安全审计和测试来验证。
sm2签名验签
代码实现分析:
椭圆曲线参数初始化:
SM2_Init函数初始化了SM2所需的椭圆曲线参数,包括( p )、( a )、( b )、( n )、( Gx )、( Gy ),并检查了基点( G )的阶是否为( n )。密钥生成:
SM2_KeyGeneration函数实现了密钥生成过程,接受私钥并计算对应的公钥。签名算法:
SM2_Sign函数实现了SM2签名算法,包括生成随机数( k ),计算( kG ),计算签名( (r, s) ),并进行了必要的错误检查。验证算法:
SM2_Verify函数实现了SM2验证算法,包括检查( r )和( s )的范围,计算( t ),验证签名的有效性。自检测试:
SM2_SelfCheck函数提供了一个自测试,用于验证实现的正确性,通过比较签名和验证的结果。结论:
提供的代码实现了SM2标准的核心功能,包括密钥生成、签名、验证和自测试。代码中的函数和逻辑与SM2标准的要求相匹配,表明它是一个符合SM2标准的实现。需要注意的是,代码的正确性和安全性还需要通过详细的安全审计和测试来验证。
SM2相关标准文档:
- GM/T 0003.1-2012《椭圆曲线公钥密码算法 第1部分:总则》
- GM/T 0003.2-2012《椭圆曲线公钥密码算法 第2部分:SM2密码算法》
- GM/T 0003.3-2012《椭圆曲线公钥密码算法 第3部分:SM2密码算法使用规范》
这些标准文档详细描述了SM2算法的技术细节和使用规范,是理解和实现SM2算法的重要参考。
SM3
SM3是中国国家密码管理局发布的密码散列函数标准,用于生成消息的摘要或哈希值。SM3算法的设计目标是确保安全性,同时满足高效性、抗碰撞性和抗预像性等要求。以下是SM3标准的关键点和您提供的代码实现的分析:
SM3标准的关键点:
算法描述:
- SM3算法采用Merkle-Damgård结构,基于512位的块处理和1024位的消息摘要。
消息填充:
- 消息被填充到512位的倍数,最后附加一个64位的消息长度。
IV值:
- 算法使用一个固定的初始值(IV),用于初始化压缩函数的内部状态。
压缩函数:
- 压缩函数处理512位的消息块,生成一个256位的输出。
消息分组:
- 消息被分成512位的块,每个块通过压缩函数处理。
最终处理:
- 最后一个块处理完后,将最后一个块的输出与前一个状态进行异或,得到最终的哈希值。
代码实现分析:
初始化向量(IV):
- 代码中的
IV数组正确地初始化了SM3算法的初始值。消息填充:
SM3Hash函数中,消息被填充到512位的倍数,并附加了一个64位的消息长度,符合SM3标准的要求。压缩函数:
CF函数实现了SM3的压缩函数,包括消息扩展、循环左移、T函数、F和G函数、P0和P1函数,以及最终的状态更新。消息分组:
- 代码将填充后的消息分成512位的块,并逐块通过压缩函数处理。
最终输出:
- 最终的哈希值通过将最后一个块的输出与前一个状态进行异或得到,并输出。
代码优化:
- 代码中使用了循环左移函数
SL和T函数Tj来简化操作,这些是SM3算法中的关键操作。代码结构:
- 代码结构清晰,函数分工明确,易于理解和维护。
结论:
提供的代码实现了SM3标准的核心功能,包括消息填充、压缩函数、消息分组和最终输出。代码中的函数和逻辑与SM3标准的要求相匹配,表明它是一个符合SM3标准的实现。需要注意的是,代码的正确性和安全性还需要通过详细的安全审计和测试来验证。
SM3相关标准文档:
- GM/T 0004-2012《密码散列函数 SM3》
- GB/T 32092-2015《信息安全技术 SM3密码杂凑函数》
这些标准文档详细描述了SM3算法的技术细节和使用规范,是理解和实现SM3算法的重要参考。
SM4
SM4是中国国家密码管理局发布的对称加密标准,也称为SMS4或WCDMA,是一种基于AES架构的块密码算法,主要用于无线通信系统的数据加密。以下是SM4标准的关键点和您提供的代码实现的分析:
SM4标准的关键点:
算法描述:
- SM4算法是一种分组密码,分组大小为128位,密钥长度也为128位。
密钥调度:
- 算法使用一个128位的密钥生成32轮的轮密钥。
加密过程:
- 加密过程包括一个初始轮、32轮的加密轮次和一个最终轮。
解密过程:
- 解密过程与加密过程类似,但轮密钥的应用顺序相反。
S盒:
- 算法使用一个固定的S盒进行非线性变换。
轮函数:
- 轮函数包括一个非线性变换和一个线性变换。
代码实现分析:
密钥调度:
SM4_KeySchedule函数实现了密钥调度算法,生成32轮的轮密钥。加密和解密:
SM4_Encrypt和SM4_Decrypt函数分别实现了加密和解密过程。非线性变换:
- 代码中的S盒(
SM4_Sbox)用于非线性变换。线性变换:
- 线性变换包括循环左移操作,由
SM4_Rotl32宏实现。轮函数:
- 代码中的
FK和CK数组用于轮函数的计算。模式操作:
- 代码提供了ECB、CBC、CFB和OFB四种工作模式的实现。
自检测试:
SM4_SelfCheck函数提供了自检测试,用于验证算法的正确性。结论:
提供的代码实现了SM4标准的核心功能,包括密钥调度、加密、解密以及多种工作模式。代码中的函数和逻辑与SM4标准的要求相匹配,表明它是一个符合SM4标准的实现。需要注意的是,代码的正确性和安全性还需要通过详细的安全审计和测试来验证。
SM4相关标准文档:
- GM/T 0002-2012《对称加密算法 SM4》
- GB/T 32907-2016《信息安全技术 SM4分组密码算法》
这些标准文档详细描述了SM4算法的技术细节和使用规范,是理解和实现SM4算法的重要参考。
-
使用GmSSL,UKey 交叉验证实现的正确性(5 分)
-
实验记录中提交 gitee 课程项目链接,提交本次实验相关 git log运行结果
[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm2]$ git log
commit a029d38ce29b02927eee5b3989b11031e6ae903f (HEAD -> master)
Author: wei-zhengyi <https://gitee.com/wei-zhengyi/projects>
Date: Sun Nov 3 19:10:49 2024 +0800sm2算法实现2[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm3]$ git log
commit 039e899857a7ee26a670b5f1e7ab030b57a10e7f (HEAD -> master)
Author: wei-zhengyi <https://gitee.com/wei-zhengyi/projects>
Date: Sun Nov 3 17:18:31 2024 +0800sm3一段式实现[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C pra2]$ git log
commit 576f081146ac546a1bc3e29236317ffe903c6774 (HEAD -> master)
Author: wei-zhengyi <https://gitee.com/wei-zhengyi/projects>
Date: Sun Nov 3 18:04:22 2024 +0800sm3三段式实现root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C:/home/wzy/sm3/sm3_3# git log
commit 86980decb2ad991fc75a5e2bd62cff81273a56bd (HEAD -> master)
Author: root <root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C>
Date: Sun Nov 3 17:08:48 2024 +0800openssl实现sm3算法-编译commit 51078fef1acdcdf09c4f5242a414e0d0fbe16d84 (HEAD -> master)
Author: root <root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C>
Date: Sun Nov 3 17:15:12 2024 +0800Hmac-sm3实现[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm4_1]$ sudo git log
commit f64aac488dcbb99304171c7f62cf65365e5c5f95 (HEAD -> master)
Author: wei-zhengyi <https://gitee.com/wei-zhengyi/projects>
Date: Sun Nov 3 18:17:09 2024 +0800实现sm4算法16字节版[wzy@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C sm4_2]$ sudo git log
commit 870255cebff57f7c22b72a1bc726487805c43cf1 (HEAD -> master)
Author: Super User <root@LAPTOP-PRC71A0C>
Date: Sun Nov 3 18:25:19 2024 +0800实现sm4 ECB CBC CFB OFB算法
- 提交要求:
- 提交实践过程Markdown和转化的PDF文件
- 代码,文档托管到gitee或github等,推荐 gitclone
- 记录实验过程中遇到的问题,解决过程,反思等内容,用于后面实验报告
相关文章:

《密码系统设计》实验二 4-6学时
文章目录 《密码系统设计》实验实验项目实验二 密码算法实现4-6 学时实践要求(30 分)1. 定义宏2. 使用特定的源文件3. 编译MIRACL库4. 配置KCM和Comba方法5. 编译和运行MEX工具6. 使用config.c工具总结1. 准备环境2. 下载和解压MIRACL库3. 定义宏4. 使用…...

Zypher Network:全栈式 Web3 游戏引擎,服务器抽象叙事的引领者
近期,《黑神话:悟空》的爆火不仅让 AAA 游戏重回焦点,也引发了玩家与开发者的热议。Web2 游戏的持续成功导致部分 Web3 玩家们的倒戈,对比之下 Web3 游戏存在生命周期短且商业模式难以明确的问题,尤其在当前加密市场环…...

2025生物发酵展(济南)为生物制造产业注入新活力共谱行业新篇章
2025第十四届国际生物发酵展将于3月3-5日济南盛大举办!产业链逐步完整,展会面积再创历史新高,展览面积较上届增涨至60000平方米,专业观众40000,品牌展商800,同期活动会议增加至50场,展会同期将举…...

git入门教程14:Git与其他工具的集成
一、Git与代码托管平台的集成 GitHub 集成方式: 在GitHub上创建或克隆仓库。在本地使用Git命令进行代码提交和推送(如git push)。GitHub提供Web界面进行代码浏览、协作和持续集成配置。 特点: 支持Pull Request,便于代…...

在Zetero中调用腾讯云API的输入密钥的问题
也是使用了Translate插件了,但是需要调用腾讯云翻译,一直没成功。 第一步就是,按照这上面方法做:百度、阿里、腾讯、有道各平台翻译API申请教程 之后就是:Zotero PDF translat翻译:申请腾讯翻译接口 主要是…...

【AD】1-8 AD24软件工程创建
1.点击文件,新建项目 2.如图进行设置工程名称和文件路径 3.创建原理图库及原理图,并保存 4.新建PCB库及PCB,并保存 5.单击右键工程保存 注意:先新建工程,在新建文件...

RT-Thread学习
文章目录 前言一、rtt的启动流程二、移植工作总结 前言 RT-Thread学习,这里记录对bsp的移植 一、rtt的启动流程 RT-Thread 支持多种平台和多种编译器,而 rtthread_startup() 函数是 RT-Thread 规定的统一启动入口。一般执行顺序是:系统先从…...

20241102在荣品PRO-RK3566开发板使用荣品预编译的buildroot通过iperf2测试AP6256的WIFI网速
20241102在荣品PRO-RK3566开发板使用荣品预编译的buildroot通过iperf2测试AP6256的WIFI网速 2024/11/2 14:18 客户端:荣耀手机HONOR 70【iPerf2 for Android】 服务器端:荣品PRO-RK3566开发板 预编译固件:update-pro-rk3566-buildroot-hdmi-2…...

网络模型——二层转发原理
网课地址:网络模型_二层转发原理(三)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 一、路由交换 网络:用来信息通信,信息共享的平台。 网络节点(交换机,路由器,防火墙,AP)介质&#…...

【编程技巧】C++如何使用std::map管理std::function函数指针
一、问题背景 开发过程中遇到了需要根据const字符串调用不同函数的要求。在开发过程中为了快速实现功能,实际使用了if else等判断实现了不同函数的调用,徒增了不少代码行数。 明知道可以采用map管理函数指针,但是没有具体实现过,…...

导航栏小案例
实现类似于这样的效果 <!DOCTYPE html> <html><head><meta charset"utf-8"><title>导航栏</title><style>*{margin: 0;padding: 0;}.div1{width: 100%;height: 60px;/* border: 1px solid blue; */background-color:rgb(…...
)
MyBatis一文入门精通,面试题(含答案)
一、MyBatis详细介绍 MyBatis 是一个流行的 Java 持久层框架,主要用于简化 SQL 数据库操作。它的设计初衷是通过 XML 或注解的方式配置和执行 SQL 语句,使得数据库操作更加灵活、方便和高效。相比于传统的 JDBC,MyBatis 提供了一些关键优势&…...

Ubuntu18.04服务器非root用户在虚拟环境下的python版本设定
最近需要跑一个python3.9.16版本的代码,Ubuntu18.04服务器上是上次博客中已经定死的python3.8.0版本 需要创建一个虚拟环境,并且在虚拟环境中配置python3.9.16版本 只需要创建一个虚拟环境 conda create -n yyy python3.9.16yyy是你的虚拟环境名字 创建…...
CodeS:构建用于文本到 SQL 的开源语言模型
发布于:2024 年 10 月 29 日 #RAG #Text2 SQL #NL2 SQL 语言模型在将自然语言问题转换为 SQL 查询(文本到 SQL )的任务中显示出良好的性能。然而,大多数最先进的 (SOTA) 方法都依赖于强大但闭源的大型语言…...

HTML 基础概念:什么是 HTML ? HTML 的构成 与 HTML 基本文档结构
文章目录 什么是 HTML ?HTML 的构成 ?什么是 HTML 元素?HTML 元素的组成部分HTML 元素的特点 HTML 基本文档结构如何打开新建的 HTML 文件代码查看 什么是 HTML ? HTML(超文本标记语言,HyperText Markup L…...

18 Docker容器集群网络架构:一、etcd 概述
文章目录 Docker容器集群网络架构:一、etcd概述1.1 etcd 的基本概念和特点1.1.1 定义1.1.2 特点1.2 etcd 在 Docker 集群网络中的作用1.3 etcd 集群的架构和原理1.3.1 架构1.3.2 原理Docker容器集群网络架构:一、etcd概述 etcd是一个高可用的分布式键值存储系统,它主要用于…...

R语言贝叶斯分层、层次(Hierarchical Bayesian)模型房价数据空间分析
原文链接:https://tecdat.cn/?p38077 本文主要探讨了贝叶斯分层模型在分析区域数据方面的应用,以房价数据为例,详细阐述了如何帮助客户利用R进行模型拟合、分析及结果解读,展示了该方法在处理空间相关数据时的灵活性和有效性。&a…...

SpringBoot 在初始化加载无法使用@Value的时候读取配置文件教程
怀旧网个人博客地址:怀旧网,博客详情:SpringBoot 在初始化加载无法使用Value的时候读取配置文件教程 读取数据库数据案例 // 创建YamlPropertiesFactoryBean对象 YamlPropertiesFactoryBean factory new YamlPropertiesFactoryBean(); // …...

基于MATLAB的身份证号码识别系统
课题介绍 本课题为基于连通域分割和模板匹配的二代居民身份证号码识别系统,带有一个GUI人机交互界面。可以识别数十张身份证图片。 首先从身份证图像上获取0~9和X共十一个号码字符的样本图像作为后续识别的字符库样本,其次将待测身份证图像…...

【人工智能-初级】练习题:matplotlib基础练习30例
练习 1: 画折线图 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] y = [10, 20, 25, 30, 40] 使用 plt.plot() 画出折线图,适用于连续数据的可视化 plt.plot(x, y) plt.xlabel(‘X 轴’) plt.ylabel(‘Y 轴’) plt.title(‘简单折线图’) plt.show() 练习 2: 画散…...
)
浏览器访问 AWS ECS 上部署的 Docker 容器(监听 80 端口)
✅ 一、ECS 服务配置 Dockerfile 确保监听 80 端口 EXPOSE 80 CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]或 EXPOSE 80 CMD ["python3", "-m", "http.server", "80"]任务定义(Task Definition&…...
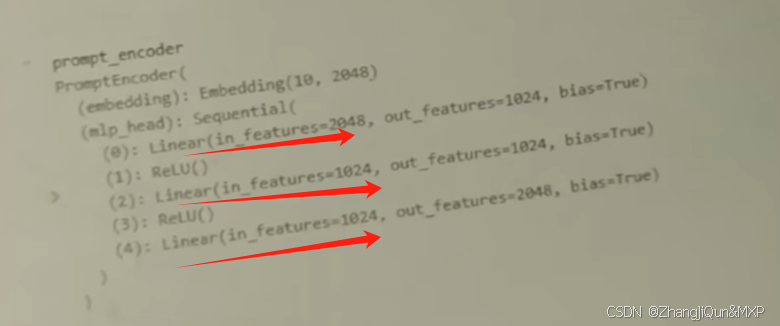
Prompt Tuning、P-Tuning、Prefix Tuning的区别
一、Prompt Tuning、P-Tuning、Prefix Tuning的区别 1. Prompt Tuning(提示调优) 核心思想:固定预训练模型参数,仅学习额外的连续提示向量(通常是嵌入层的一部分)。实现方式:在输入文本前添加可训练的连续向量(软提示),模型只更新这些提示参数。优势:参数量少(仅提…...

前端导出带有合并单元格的列表
// 导出async function exportExcel(fileName "共识调整.xlsx") {// 所有数据const exportData await getAllMainData();// 表头内容let fitstTitleList [];const secondTitleList [];allColumns.value.forEach(column > {if (!column.children) {fitstTitleL…...

【ROS】Nav2源码之nav2_behavior_tree-行为树节点列表
1、行为树节点分类 在 Nav2(Navigation2)的行为树框架中,行为树节点插件按照功能分为 Action(动作节点)、Condition(条件节点)、Control(控制节点) 和 Decorator(装饰节点) 四类。 1.1 动作节点 Action 执行具体的机器人操作或任务,直接与硬件、传感器或外部系统…...

【配置 YOLOX 用于按目录分类的图片数据集】
现在的图标点选越来越多,如何一步解决,采用 YOLOX 目标检测模式则可以轻松解决 要在 YOLOX 中使用按目录分类的图片数据集(每个目录代表一个类别,目录下是该类别的所有图片),你需要进行以下配置步骤&#x…...

在web-view 加载的本地及远程HTML中调用uniapp的API及网页和vue页面是如何通讯的?
uni-app 中 Web-view 与 Vue 页面的通讯机制详解 一、Web-view 简介 Web-view 是 uni-app 提供的一个重要组件,用于在原生应用中加载 HTML 页面: 支持加载本地 HTML 文件支持加载远程 HTML 页面实现 Web 与原生的双向通讯可用于嵌入第三方网页或 H5 应…...

音视频——I2S 协议详解
I2S 协议详解 I2S (Inter-IC Sound) 协议是一种串行总线协议,专门用于在数字音频设备之间传输数字音频数据。它由飞利浦(Philips)公司开发,以其简单、高效和广泛的兼容性而闻名。 1. 信号线 I2S 协议通常使用三根或四根信号线&a…...
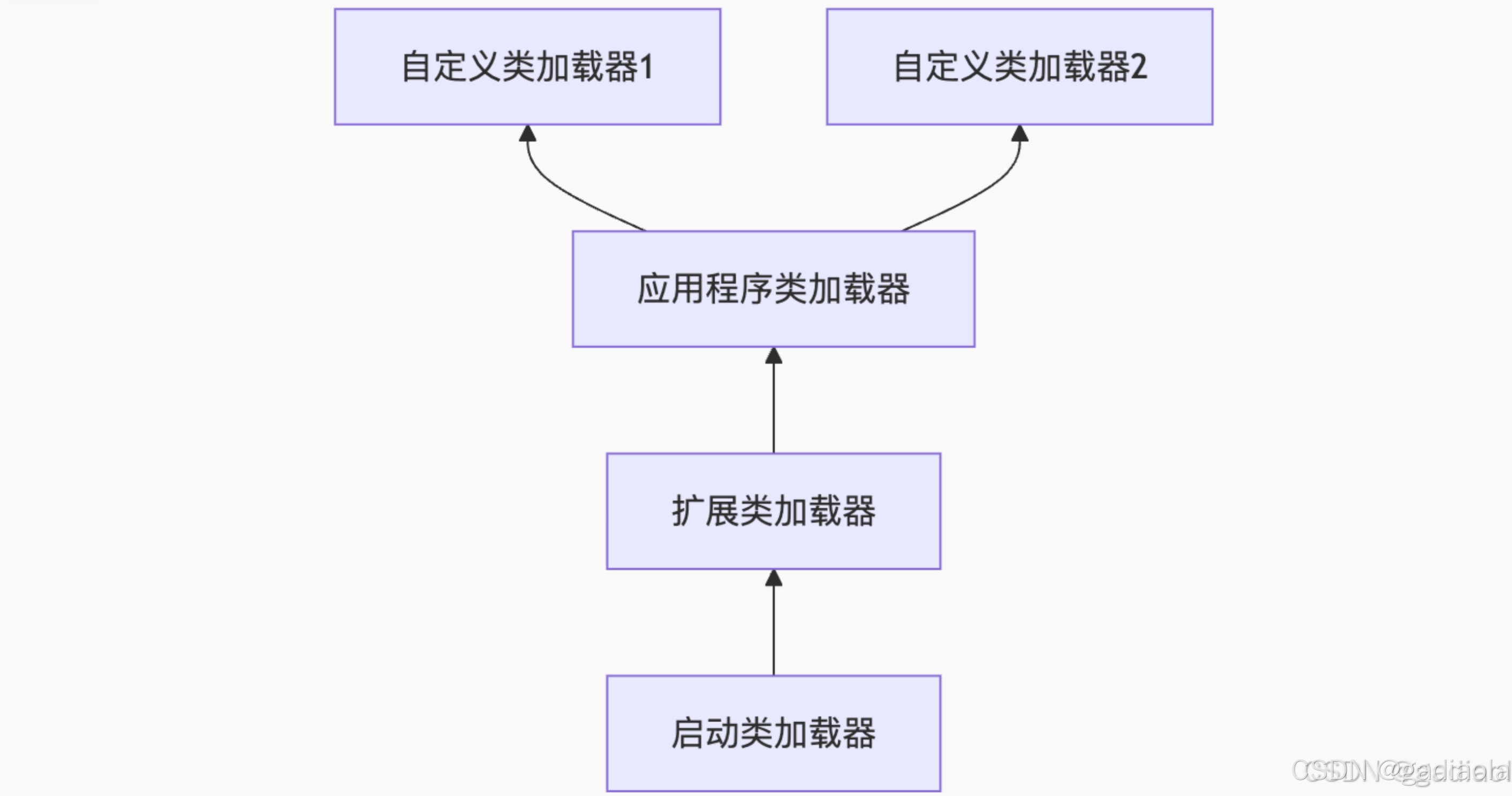
【JVM面试篇】高频八股汇总——类加载和类加载器
目录 1. 讲一下类加载过程? 2. Java创建对象的过程? 3. 对象的生命周期? 4. 类加载器有哪些? 5. 双亲委派模型的作用(好处)? 6. 讲一下类的加载和双亲委派原则? 7. 双亲委派模…...
: 一刀斩断视频片头广告)
快刀集(1): 一刀斩断视频片头广告
一刀流:用一个简单脚本,秒杀视频片头广告,还你清爽观影体验。 1. 引子 作为一个爱生活、爱学习、爱收藏高清资源的老码农,平时写代码之余看看电影、补补片,是再正常不过的事。 电影嘛,要沉浸,…...
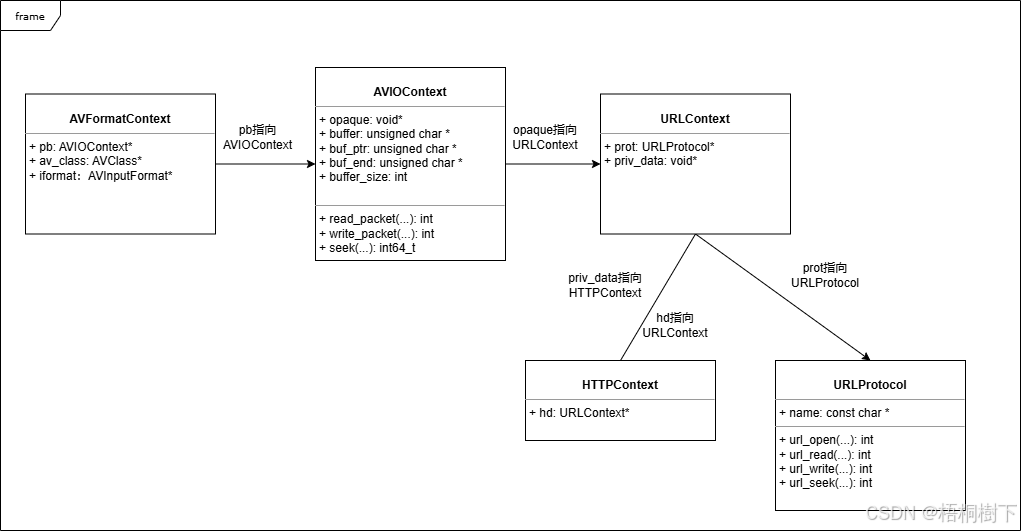
FFmpeg avformat_open_input函数分析
函数内部的总体流程如下: avformat_open_input 精简后的代码如下: int avformat_open_input(AVFormatContext **ps, const char *filename,ff_const59 AVInputFormat *fmt, AVDictionary **options) {AVFormatContext *s *ps;int i, ret 0;AVDictio…...
