FFmpeg存放压缩后的音视频数据的结构体:AVPacket简介,结构体,函数
如下图的解码流程,AVPacket中的位置

FFmpeg源码中通过AVPacket存储压缩后的音视频数据。它通常由解复用器(demuxers)输出,然后作为输入传递给解码器。
或者从编码器作为输出接收,然后传递给多路复用器(muxers)。
对于视频,它通常包含一个压缩帧;对于音频,它可能包含几个压缩帧。编码器允许输出不包含压缩音视频数据、只包含side data(边数据:例如,在编码结束时更新一些流参数)的空的数据包( empty packets)。
AVPacket 结构体 所在的文件名 libavcodec/packet.h
/** AVPacket public API** This file is part of FFmpeg.** FFmpeg is free software; you can redistribute it and/or* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.** FFmpeg is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU* Lesser General Public License for more details.** You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public* License along with FFmpeg; if not, write to the Free Software* Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA*/#ifndef AVCODEC_PACKET_H
#define AVCODEC_PACKET_H#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdint.h>#include "libavutil/attributes.h"
#include "libavutil/buffer.h"
#include "libavutil/dict.h"
#include "libavutil/rational.h"
#include "libavutil/version.h"#include "libavcodec/version_major.h"/*** @defgroup lavc_packet AVPacket** Types and functions for working with AVPacket.* @{*/
enum AVPacketSideDataType {/*** An AV_PKT_DATA_PALETTE side data packet contains exactly AVPALETTE_SIZE* bytes worth of palette. This side data signals that a new palette is* present.*/AV_PKT_DATA_PALETTE,/*** The AV_PKT_DATA_NEW_EXTRADATA is used to notify the codec or the format* that the extradata buffer was changed and the receiving side should* act upon it appropriately. The new extradata is embedded in the side* data buffer and should be immediately used for processing the current* frame or packet.*/AV_PKT_DATA_NEW_EXTRADATA,/*** An AV_PKT_DATA_PARAM_CHANGE side data packet is laid out as follows:* @code* u32le param_flags* if (param_flags & AV_SIDE_DATA_PARAM_CHANGE_CHANNEL_COUNT)* s32le channel_count* if (param_flags & AV_SIDE_DATA_PARAM_CHANGE_CHANNEL_LAYOUT)* u64le channel_layout* if (param_flags & AV_SIDE_DATA_PARAM_CHANGE_SAMPLE_RATE)* s32le sample_rate* if (param_flags & AV_SIDE_DATA_PARAM_CHANGE_DIMENSIONS)* s32le width* s32le height* @endcode*/AV_PKT_DATA_PARAM_CHANGE,/*** An AV_PKT_DATA_H263_MB_INFO side data packet contains a number of* structures with info about macroblocks relevant to splitting the* packet into smaller packets on macroblock edges (e.g. as for RFC 2190).* That is, it does not necessarily contain info about all macroblocks,* as long as the distance between macroblocks in the info is smaller* than the target payload size.* Each MB info structure is 12 bytes, and is laid out as follows:* @code* u32le bit offset from the start of the packet* u8 current quantizer at the start of the macroblock* u8 GOB number* u16le macroblock address within the GOB* u8 horizontal MV predictor* u8 vertical MV predictor* u8 horizontal MV predictor for block number 3* u8 vertical MV predictor for block number 3* @endcode*/AV_PKT_DATA_H263_MB_INFO,/*** This side data should be associated with an audio stream and contains* ReplayGain information in form of the AVReplayGain struct.*/AV_PKT_DATA_REPLAYGAIN,/*** This side data contains a 3x3 transformation matrix describing an affine* transformation that needs to be applied to the decoded video frames for* correct presentation.** See libavutil/display.h for a detailed description of the data.*/AV_PKT_DATA_DISPLAYMATRIX,/*** This side data should be associated with a video stream and contains* Stereoscopic 3D information in form of the AVStereo3D struct.*/AV_PKT_DATA_STEREO3D,/*** This side data should be associated with an audio stream and corresponds* to enum AVAudioServiceType.*/AV_PKT_DATA_AUDIO_SERVICE_TYPE,/*** This side data contains quality related information from the encoder.* @code* u32le quality factor of the compressed frame. Allowed range is between 1 (good) and FF_LAMBDA_MAX (bad).* u8 picture type* u8 error count* u16 reserved* u64le[error count] sum of squared differences between encoder in and output* @endcode*/AV_PKT_DATA_QUALITY_STATS,/*** This side data contains an integer value representing the stream index* of a "fallback" track. A fallback track indicates an alternate* track to use when the current track can not be decoded for some reason.* e.g. no decoder available for codec.*/AV_PKT_DATA_FALLBACK_TRACK,/*** This side data corresponds to the AVCPBProperties struct.*/AV_PKT_DATA_CPB_PROPERTIES,/*** Recommmends skipping the specified number of samples* @code* u32le number of samples to skip from start of this packet* u32le number of samples to skip from end of this packet* u8 reason for start skip* u8 reason for end skip (0=padding silence, 1=convergence)* @endcode*/AV_PKT_DATA_SKIP_SAMPLES,/*** An AV_PKT_DATA_JP_DUALMONO side data packet indicates that* the packet may contain "dual mono" audio specific to Japanese DTV* and if it is true, recommends only the selected channel to be used.* @code* u8 selected channels (0=main/left, 1=sub/right, 2=both)* @endcode*/AV_PKT_DATA_JP_DUALMONO,/*** A list of zero terminated key/value strings. There is no end marker for* the list, so it is required to rely on the side data size to stop.*/AV_PKT_DATA_STRINGS_METADATA,/*** Subtitle event position* @code* u32le x1* u32le y1* u32le x2* u32le y2* @endcode*/AV_PKT_DATA_SUBTITLE_POSITION,/*** Data found in BlockAdditional element of matroska container. There is* no end marker for the data, so it is required to rely on the side data* size to recognize the end. 8 byte id (as found in BlockAddId) followed* by data.*/AV_PKT_DATA_MATROSKA_BLOCKADDITIONAL,/*** The optional first identifier line of a WebVTT cue.*/AV_PKT_DATA_WEBVTT_IDENTIFIER,/*** The optional settings (rendering instructions) that immediately* follow the timestamp specifier of a WebVTT cue.*/AV_PKT_DATA_WEBVTT_SETTINGS,/*** A list of zero terminated key/value strings. There is no end marker for* the list, so it is required to rely on the side data size to stop. This* side data includes updated metadata which appeared in the stream.*/AV_PKT_DATA_METADATA_UPDATE,/*** MPEGTS stream ID as uint8_t, this is required to pass the stream ID* information from the demuxer to the corresponding muxer.*/AV_PKT_DATA_MPEGTS_STREAM_ID,/*** Mastering display metadata (based on SMPTE-2086:2014). This metadata* should be associated with a video stream and contains data in the form* of the AVMasteringDisplayMetadata struct.*/AV_PKT_DATA_MASTERING_DISPLAY_METADATA,/*** This side data should be associated with a video stream and corresponds* to the AVSphericalMapping structure.*/AV_PKT_DATA_SPHERICAL,/*** Content light level (based on CTA-861.3). This metadata should be* associated with a video stream and contains data in the form of the* AVContentLightMetadata struct.*/AV_PKT_DATA_CONTENT_LIGHT_LEVEL,/*** ATSC A53 Part 4 Closed Captions. This metadata should be associated with* a video stream. A53 CC bitstream is stored as uint8_t in AVPacketSideData.data.* The number of bytes of CC data is AVPacketSideData.size.*/AV_PKT_DATA_A53_CC,/*** This side data is encryption initialization data.* The format is not part of ABI, use av_encryption_init_info_* methods to* access.*/AV_PKT_DATA_ENCRYPTION_INIT_INFO,/*** This side data contains encryption info for how to decrypt the packet.* The format is not part of ABI, use av_encryption_info_* methods to access.*/AV_PKT_DATA_ENCRYPTION_INFO,/*** Active Format Description data consisting of a single byte as specified* in ETSI TS 101 154 using AVActiveFormatDescription enum.*/AV_PKT_DATA_AFD,/*** Producer Reference Time data corresponding to the AVProducerReferenceTime struct,* usually exported by some encoders (on demand through the prft flag set in the* AVCodecContext export_side_data field).*/AV_PKT_DATA_PRFT,/*** ICC profile data consisting of an opaque octet buffer following the* format described by ISO 15076-1.*/AV_PKT_DATA_ICC_PROFILE,/*** DOVI configuration* ref:* dolby-vision-bitstreams-within-the-iso-base-media-file-format-v2.1.2, section 2.2* dolby-vision-bitstreams-in-mpeg-2-transport-stream-multiplex-v1.2, section 3.3* Tags are stored in struct AVDOVIDecoderConfigurationRecord.*/AV_PKT_DATA_DOVI_CONF,/*** Timecode which conforms to SMPTE ST 12-1:2014. The data is an array of 4 uint32_t* where the first uint32_t describes how many (1-3) of the other timecodes are used.* The timecode format is described in the documentation of av_timecode_get_smpte_from_framenum()* function in libavutil/timecode.h.*/AV_PKT_DATA_S12M_TIMECODE,/*** HDR10+ dynamic metadata associated with a video frame. The metadata is in* the form of the AVDynamicHDRPlus struct and contains* information for color volume transform - application 4 of* SMPTE 2094-40:2016 standard.*/AV_PKT_DATA_DYNAMIC_HDR10_PLUS,/*** The number of side data types.* This is not part of the public API/ABI in the sense that it may* change when new side data types are added.* This must stay the last enum value.* If its value becomes huge, some code using it* needs to be updated as it assumes it to be smaller than other limits.*/AV_PKT_DATA_NB
};#define AV_PKT_DATA_QUALITY_FACTOR AV_PKT_DATA_QUALITY_STATS //DEPRECATEDtypedef struct AVPacketSideData {uint8_t *data;size_t size;enum AVPacketSideDataType type;
} AVPacketSideData;/*** This structure stores compressed data. It is typically exported by demuxers* and then passed as input to decoders, or received as output from encoders and* then passed to muxers.** For video, it should typically contain one compressed frame. For audio it may* contain several compressed frames. Encoders are allowed to output empty* packets, with no compressed data, containing only side data* (e.g. to update some stream parameters at the end of encoding).** The semantics of data ownership depends on the buf field.* If it is set, the packet data is dynamically allocated and is* valid indefinitely until a call to av_packet_unref() reduces the* reference count to 0.** If the buf field is not set av_packet_ref() would make a copy instead* of increasing the reference count.** The side data is always allocated with av_malloc(), copied by* av_packet_ref() and freed by av_packet_unref().** sizeof(AVPacket) being a part of the public ABI is deprecated. once* av_init_packet() is removed, new packets will only be able to be allocated* with av_packet_alloc(), and new fields may be added to the end of the struct* with a minor bump.** @see av_packet_alloc* @see av_packet_ref* @see av_packet_unref*/
typedef struct AVPacket {/*** A reference to the reference-counted buffer where the packet data is* stored.* May be NULL, then the packet data is not reference-counted.*/AVBufferRef *buf;/*** Presentation timestamp in AVStream->time_base units; the time at which* the decompressed packet will be presented to the user.* Can be AV_NOPTS_VALUE if it is not stored in the file.* pts MUST be larger or equal to dts as presentation cannot happen before* decompression, unless one wants to view hex dumps. Some formats misuse* the terms dts and pts/cts to mean something different. Such timestamps* must be converted to true pts/dts before they are stored in AVPacket.*/int64_t pts;/*** Decompression timestamp in AVStream->time_base units; the time at which* the packet is decompressed.* Can be AV_NOPTS_VALUE if it is not stored in the file.*/int64_t dts;uint8_t *data;int size;int stream_index;/*** A combination of AV_PKT_FLAG values*/int flags;/*** Additional packet data that can be provided by the container.* Packet can contain several types of side information.*/AVPacketSideData *side_data;int side_data_elems;/*** Duration of this packet in AVStream->time_base units, 0 if unknown.* Equals next_pts - this_pts in presentation order.*/int64_t duration;int64_t pos; ///< byte position in stream, -1 if unknown/*** for some private data of the user*/void *opaque;/*** AVBufferRef for free use by the API user. FFmpeg will never check the* contents of the buffer ref. FFmpeg calls av_buffer_unref() on it when* the packet is unreferenced. av_packet_copy_props() calls create a new* reference with av_buffer_ref() for the target packet's opaque_ref field.** This is unrelated to the opaque field, although it serves a similar* purpose.*/AVBufferRef *opaque_ref;/*** Time base of the packet's timestamps.* In the future, this field may be set on packets output by encoders or* demuxers, but its value will be by default ignored on input to decoders* or muxers.*/AVRational time_base;
} AVPacket;#if FF_API_INIT_PACKET
attribute_deprecated
typedef struct AVPacketList {AVPacket pkt;struct AVPacketList *next;
} AVPacketList;
#endif#define AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY 0x0001 ///< The packet contains a keyframe
#define AV_PKT_FLAG_CORRUPT 0x0002 ///< The packet content is corrupted
/*** Flag is used to discard packets which are required to maintain valid* decoder state but are not required for output and should be dropped* after decoding.**/
#define AV_PKT_FLAG_DISCARD 0x0004
/*** The packet comes from a trusted source.** Otherwise-unsafe constructs such as arbitrary pointers to data* outside the packet may be followed.*/
#define AV_PKT_FLAG_TRUSTED 0x0008
/*** Flag is used to indicate packets that contain frames that can* be discarded by the decoder. I.e. Non-reference frames.*/
#define AV_PKT_FLAG_DISPOSABLE 0x0010enum AVSideDataParamChangeFlags {
#if FF_API_OLD_CHANNEL_LAYOUT/*** @deprecated those are not used by any decoder*/AV_SIDE_DATA_PARAM_CHANGE_CHANNEL_COUNT = 0x0001,AV_SIDE_DATA_PARAM_CHANGE_CHANNEL_LAYOUT = 0x0002,
#endifAV_SIDE_DATA_PARAM_CHANGE_SAMPLE_RATE = 0x0004,AV_SIDE_DATA_PARAM_CHANGE_DIMENSIONS = 0x0008,
};/*** Allocate an AVPacket and set its fields to default values. The resulting* struct must be freed using av_packet_free().** @return An AVPacket filled with default values or NULL on failure.** @note this only allocates the AVPacket itself, not the data buffers. Those* must be allocated through other means such as av_new_packet.** @see av_new_packet*/
AVPacket *av_packet_alloc(void);/*** Create a new packet that references the same data as src.** This is a shortcut for av_packet_alloc()+av_packet_ref().** @return newly created AVPacket on success, NULL on error.** @see av_packet_alloc* @see av_packet_ref*/
AVPacket *av_packet_clone(const AVPacket *src);/*** Free the packet, if the packet is reference counted, it will be* unreferenced first.** @param pkt packet to be freed. The pointer will be set to NULL.* @note passing NULL is a no-op.*/
void av_packet_free(AVPacket **pkt);#if FF_API_INIT_PACKET
/*** Initialize optional fields of a packet with default values.** Note, this does not touch the data and size members, which have to be* initialized separately.** @param pkt packet** @see av_packet_alloc* @see av_packet_unref** @deprecated This function is deprecated. Once it's removed,sizeof(AVPacket) will not be a part of the ABI anymore.*/
attribute_deprecated
void av_init_packet(AVPacket *pkt);
#endif/*** Allocate the payload of a packet and initialize its fields with* default values.** @param pkt packet* @param size wanted payload size* @return 0 if OK, AVERROR_xxx otherwise*/
int av_new_packet(AVPacket *pkt, int size);/*** Reduce packet size, correctly zeroing padding** @param pkt packet* @param size new size*/
void av_shrink_packet(AVPacket *pkt, int size);/*** Increase packet size, correctly zeroing padding** @param pkt packet* @param grow_by number of bytes by which to increase the size of the packet*/
int av_grow_packet(AVPacket *pkt, int grow_by);/*** Initialize a reference-counted packet from av_malloc()ed data.** @param pkt packet to be initialized. This function will set the data, size,* and buf fields, all others are left untouched.* @param data Data allocated by av_malloc() to be used as packet data. If this* function returns successfully, the data is owned by the underlying AVBuffer.* The caller may not access the data through other means.* @param size size of data in bytes, without the padding. I.e. the full buffer* size is assumed to be size + AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE.** @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on error*/
int av_packet_from_data(AVPacket *pkt, uint8_t *data, int size);/*** Allocate new information of a packet.** @param pkt packet* @param type side information type* @param size side information size* @return pointer to fresh allocated data or NULL otherwise*/
uint8_t* av_packet_new_side_data(AVPacket *pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type,size_t size);/*** Wrap an existing array as a packet side data.** @param pkt packet* @param type side information type* @param data the side data array. It must be allocated with the av_malloc()* family of functions. The ownership of the data is transferred to* pkt.* @param size side information size* @return a non-negative number on success, a negative AVERROR code on* failure. On failure, the packet is unchanged and the data remains* owned by the caller.*/
int av_packet_add_side_data(AVPacket *pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type,uint8_t *data, size_t size);/*** Shrink the already allocated side data buffer** @param pkt packet* @param type side information type* @param size new side information size* @return 0 on success, < 0 on failure*/
int av_packet_shrink_side_data(AVPacket *pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type,size_t size);/*** Get side information from packet.** @param pkt packet* @param type desired side information type* @param size If supplied, *size will be set to the size of the side data* or to zero if the desired side data is not present.* @return pointer to data if present or NULL otherwise*/
uint8_t* av_packet_get_side_data(const AVPacket *pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type,size_t *size);const char *av_packet_side_data_name(enum AVPacketSideDataType type);/*** Pack a dictionary for use in side_data.** @param dict The dictionary to pack.* @param size pointer to store the size of the returned data* @return pointer to data if successful, NULL otherwise*/
uint8_t *av_packet_pack_dictionary(AVDictionary *dict, size_t *size);
/*** Unpack a dictionary from side_data.** @param data data from side_data* @param size size of the data* @param dict the metadata storage dictionary* @return 0 on success, < 0 on failure*/
int av_packet_unpack_dictionary(const uint8_t *data, size_t size,AVDictionary **dict);/*** Convenience function to free all the side data stored.* All the other fields stay untouched.** @param pkt packet*/
void av_packet_free_side_data(AVPacket *pkt);/*** Setup a new reference to the data described by a given packet** If src is reference-counted, setup dst as a new reference to the* buffer in src. Otherwise allocate a new buffer in dst and copy the* data from src into it.** All the other fields are copied from src.** @see av_packet_unref** @param dst Destination packet. Will be completely overwritten.* @param src Source packet** @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on error. On error, dst* will be blank (as if returned by av_packet_alloc()).*/
int av_packet_ref(AVPacket *dst, const AVPacket *src);/*** Wipe the packet.** Unreference the buffer referenced by the packet and reset the* remaining packet fields to their default values.** @param pkt The packet to be unreferenced.*/
void av_packet_unref(AVPacket *pkt);/*** Move every field in src to dst and reset src.** @see av_packet_unref** @param src Source packet, will be reset* @param dst Destination packet*/
void av_packet_move_ref(AVPacket *dst, AVPacket *src);/*** Copy only "properties" fields from src to dst.** Properties for the purpose of this function are all the fields* beside those related to the packet data (buf, data, size)** @param dst Destination packet* @param src Source packet** @return 0 on success AVERROR on failure.*/
int av_packet_copy_props(AVPacket *dst, const AVPacket *src);/*** Ensure the data described by a given packet is reference counted.** @note This function does not ensure that the reference will be writable.* Use av_packet_make_writable instead for that purpose.** @see av_packet_ref* @see av_packet_make_writable** @param pkt packet whose data should be made reference counted.** @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on error. On failure, the* packet is unchanged.*/
int av_packet_make_refcounted(AVPacket *pkt);/*** Create a writable reference for the data described by a given packet,* avoiding data copy if possible.** @param pkt Packet whose data should be made writable.** @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on failure. On failure, the* packet is unchanged.*/
int av_packet_make_writable(AVPacket *pkt);/*** Convert valid timing fields (timestamps / durations) in a packet from one* timebase to another. Timestamps with unknown values (AV_NOPTS_VALUE) will be* ignored.** @param pkt packet on which the conversion will be performed* @param tb_src source timebase, in which the timing fields in pkt are* expressed* @param tb_dst destination timebase, to which the timing fields will be* converted*/
void av_packet_rescale_ts(AVPacket *pkt, AVRational tb_src, AVRational tb_dst);/*** @}*/#endif // AVCODEC_PACKET_H
AVPacket结构体
AVPacket结构体声明在FFmpeg源码(本文演示用的FFmpeg源码版本为7.0.1)的头文件libavcodec/packet.h中:
/*** @}*//*** @defgroup lavc_packet AVPacket** Types and functions for working with AVPacket.* @{*//*** This structure stores compressed data. It is typically exported by demuxers* and then passed as input to decoders, or received as output from encoders and* then passed to muxers.** For video, it should typically contain one compressed frame. For audio it may* contain several compressed frames. Encoders are allowed to output empty* packets, with no compressed data, containing only side data* (e.g. to update some stream parameters at the end of encoding).** The semantics of data ownership depends on the buf field.* If it is set, the packet data is dynamically allocated and is* valid indefinitely until a call to av_packet_unref() reduces the* reference count to 0.** If the buf field is not set av_packet_ref() would make a copy instead* of increasing the reference count.** The side data is always allocated with av_malloc(), copied by* av_packet_ref() and freed by av_packet_unref().** sizeof(AVPacket) being a part of the public ABI is deprecated. once* av_init_packet() is removed, new packets will only be able to be allocated* with av_packet_alloc(), and new fields may be added to the end of the struct* with a minor bump.** @see av_packet_alloc* @see av_packet_ref* @see av_packet_unref*/
typedef struct AVPacket {/*** A reference to the reference-counted buffer where the packet data is* stored.* May be NULL, then the packet data is not reference-counted.*/AVBufferRef *buf;/*** Presentation timestamp in AVStream->time_base units; the time at which* the decompressed packet will be presented to the user.* Can be AV_NOPTS_VALUE if it is not stored in the file.* pts MUST be larger or equal to dts as presentation cannot happen before* decompression, unless one wants to view hex dumps. Some formats misuse* the terms dts and pts/cts to mean something different. Such timestamps* must be converted to true pts/dts before they are stored in AVPacket.*/int64_t pts;/*** Decompression timestamp in AVStream->time_base units; the time at which* the packet is decompressed.* Can be AV_NOPTS_VALUE if it is not stored in the file.*/int64_t dts;uint8_t *data;int size;int stream_index;/*** A combination of AV_PKT_FLAG values*/int flags;/*** Additional packet data that can be provided by the container.* Packet can contain several types of side information.*/AVPacketSideData *side_data;int side_data_elems;/*** Duration of this packet in AVStream->time_base units, 0 if unknown.* Equals next_pts - this_pts in presentation order.*/int64_t duration;int64_t pos; ///< byte position in stream, -1 if unknown/*** for some private data of the user*/void *opaque;/*** AVBufferRef for free use by the API user. FFmpeg will never check the* contents of the buffer ref. FFmpeg calls av_buffer_unref() on it when* the packet is unreferenced. av_packet_copy_props() calls create a new* reference with av_buffer_ref() for the target packet's opaque_ref field.** This is unrelated to the opaque field, although it serves a similar* purpose.*/AVBufferRef *opaque_ref;/*** Time base of the packet's timestamps.* In the future, this field may be set on packets output by encoders or* demuxers, but its value will be by default ignored on input to decoders* or muxers.*/AVRational time_base;
} AVPacket;成员变量buf:
AVBufferRef类型指针,指向“存储packet(一个数据包的压缩后的音视频)数据的引用计数缓冲区”。如果为NULL,表示该packet数据未被引用计数。AVPacket通过AVBufferRef来管理引用计数缓冲区。通过AVBufferRef结构体里面的AVBuffer里面的成员变量refcount记录资源使用的次数,控制资源的释放。可以通过av_buffer_get_ref_count(const AVBufferRef *buf);方法得到引用计数
关于AVBufferRef类型可以参考:FFmpeg引用计数数据缓冲区相关的结构体:AVBuffer、AVBufferRef。-CSDN博客
成员变量pts:
显示时间戳(presentation time stamp)。即帧显示的时间刻度,用来告诉播放器在哪个时间点显示此帧(可以简单理解为这帧视频或音频数据的播放时间)。其单位不是秒,而是以AVStream->time_base为单位。pts必须大于或等于dts,因为一帧视频或音频数据必须在解码后才能播放,所以一帧视频或音频数据的显示/播放时间必须大于或等于解码时间。
在avpacket中,pts 并不由我们写入,这是因为 pts 的显示时间,那么最初的原始数据YUV在存储到avframe的时候,就需要写入pts,不然后面的avpacket怎么知道呢?
成员变量dts:
解码时间戳(Decompression timestamp)。即帧解码的时间刻度,用来告诉播放器在哪个时间点解码此帧。其单位不是秒,而是以AVStream->time_base为单位。
如果解码 和显示都是按照顺序的,那么dts和pts都是一样的,只有当视频中含有B帧的时候,pts 和dts 会有不同的时候,这是因为B帧会参考 前后的帧显示,因此解码的时候先要解码前面的帧,然后解码后面的帧,才能解码自己,但是显示的时候顺序还是一样的,前面一帧--->自己---》后面一帧
dts是由具体的解码器内部生成的,这也很好理解,例如你用的 H264的解码器,或者H265的解码器,那么不同的解码器算法肯定不同,怎么压缩,那一帧是关键帧,后面的哪些帧依赖于这个关键帧,是不是弄成B帧呀,都是不一样的,因此 解码的顺序也是由具体的解码器说的算的
成员变量data:
指针,指向“存放压缩后的一帧(对于视频通常包含一个压缩帧,对于音频可能包含几个压缩帧)音视频数据的缓冲区”。
成员变量size:
成员变量data指向的缓冲区的大小,单位为字节。
成员变量stream_index:
索引,用来标识该AVPacket所属的视频/音频流的序号,表示这是第几路流。注意:它是从0而不是从1开始的。
成员变量flags:
AV_PKT_FLAG的组合。值有如下选择:
#define AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY 0x0001 ///< The packet contains a keyframe
#define AV_PKT_FLAG_CORRUPT 0x0002 ///< The packet content is corrupted
/*** Flag is used to discard packets which are required to maintain valid* decoder state but are not required for output and should be dropped* after decoding.**/
#define AV_PKT_FLAG_DISCARD 0x0004
/*** The packet comes from a trusted source.** Otherwise-unsafe constructs such as arbitrary pointers to data* outside the packet may be followed.*/
#define AV_PKT_FLAG_TRUSTED 0x0008
/*** Flag is used to indicate packets that contain frames that can* be discarded by the decoder. I.e. Non-reference frames.*/
#define AV_PKT_FLAG_DISPOSABLE 0x0010AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY:数据包包含一个关键帧,即当前AVPacket是关键帧。可以独立显示出来的一张图片,当然一般情况下,这张图片是有做 帧内编码的(参考视频编码原理那一节),这个很重要,在seekg的时候,一定要移动到 关键帧
AV_PKT_FLAG_CORRUPT:数据包内容已损坏。
AV_PKT_FLAG_DISCARD:用于丢弃需要保持有效解码器状态但不需要输出的数据包,并且在解码后应该丢弃。带有该标志的AVPacket所携带的数据为解码器相关的信息,不会被解码出一幅图像。
AV_PKT_FLAG_TRUSTED:该数据包来自一个可信的源。
AV_PKT_FLAG_DISPOSABLE:用于指示包含可以被解码器丢弃的帧的数据包。也就是非参考帧。
成员变量side_data:
存放“容器可以提供的额外数据包数据”的数组的首地址。数据包可以包含多种类型的边信息,比如,在编码结束的时候更新一些流的参数。指针side_data指向的空间存储了用于解码、展现或处理编码流的辅助信息,它通常由解复用器和编码器导出,可以以分组为单位提供给解码器和复用器,也可以作为全局侧数据(应用于整个编码流)。
成员变量side_data_elems:
side_data的数量。
成员变量duration:
该数据包的持续时间,以AVStream->time_base为单位。值为下一个数据包的pts减去当前数据包的pts。如果值为0表示未知。
成员变量pos:
该数据包在流中的位置,单位为字节。值为-1表示未知。
成员变量opaque:
指针,指向“存放用户使用的私有数据的缓冲区”。
成员变量time_base:
AVRational类型,数据包时间戳的时间基准,即pts和dts的时间基。
例如对于视频来说,这个值可能是 1,25 也就是说,1秒钟我们显示
AVPacket 相关函数说明
av_packet_alloc函数
av_packet_alloc函数定义在源文件libavcodec/avpacket.c中:
需要通过av_packet_free() 释放
* @note this only allocates the AVPacket itself, not the data buffers. Those
* must be allocated through other means such as av_new_packet.
需要注意的是: 通过 av_packet_alloc的只能 allocates avpacket自己,里面有写内容给了默认值,有些给了特殊值,//调用 get_packet_defaults(AVPacket *pkt)出了特殊值 的有pts,dts,pos,time_base(time_base在 ffmpeg4.3没有,在5.0以后有)
#define AV_NOPTS_VALUE ((int64_t)UINT64_C(0x8000000000000000))
pkt->pts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;
pkt->dts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;
pkt->pos = -1;
pkt->time_base = av_make_q(0, 1);

/*** Allocate an AVPacket and set its fields to default values. The resulting* struct must be freed using av_packet_free().** @return An AVPacket filled with default values or NULL on failure.** @note this only allocates the AVPacket itself, not the data buffers. Those* must be allocated through other means such as av_new_packet.** @see av_new_packet*/
AVPacket *av_packet_alloc(void);实现
AVPacket *av_packet_alloc(void)
{AVPacket *pkt = av_malloc(sizeof(AVPacket));if (!pkt)return pkt;get_packet_defaults(pkt);return pkt;
}//调用 get_packet_defaults(AVPacket *pkt)出了默认值 的有pts,dts,pos,time_base
static void get_packet_defaults(AVPacket *pkt)
{// 清空值,都是0,这意味着后面学习的 av_init_packet(AVPacket * pkt)方法作用不大,因此在ffmpeg5.0之后,将av_init_packet这个方法 标志成了 过时的。memset(pkt, 0, sizeof(*pkt));pkt->pts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;pkt->dts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;pkt->pos = -1;pkt->time_base = av_make_q(0, 1);
}测试,我们看到在 av_packet_alloc之后,除了avpacket自己有值外,里面的数据都是0或者特殊值。

void av_init_packet(AVPacket* pkt); 已过时
从前面我们使用 av_packet_alloc的源码可以看到,在alloc的时候 memset 了0,然后给了pts,dts,timebase,pos 特殊值,我们看到 av_inti_packet方法除了给 pos,pts,dts,timebase特殊值外,其他值也是0,
这说明:av_init_packet方法干了 av_packet_alloc的部分工作,如果user 是先调用了av_packet_alloc();然后再调用 av_init_packet,就会显得很 冗余,这可能也是ffmpeg在5.0上将此方法标识为过时的原因。
那么这个方法到底有没有应用场景呢?应该是有的,当我们不通过 av_packet_alloc()去 create一个AVPacket *的时候,而是直接在 栈上使用一个 AVPacket,那么这个方法就可以初始化avpacket的内容。
#if FF_API_INIT_PACKET
/*** Initialize optional fields of a packet with default values.** Note, this does not touch the data and size members, which have to be* initialized separately.** @param pkt packet** @see av_packet_alloc* @see av_packet_unref** @deprecated This function is deprecated. Once it's removed,sizeof(AVPacket) will not be a part of the ABI anymore.*/
attribute_deprecated
void av_init_packet(AVPacket *pkt);
#endif实现
#if FF_API_INIT_PACKET
void av_init_packet(AVPacket *pkt)
{pkt->pts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;pkt->dts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;pkt->pos = -1;pkt->duration = 0;pkt->flags = 0;pkt->stream_index = 0;pkt->buf = NULL;pkt->side_data = NULL;pkt->side_data_elems = 0;pkt->opaque = NULL;pkt->opaque_ref = NULL;pkt->time_base = av_make_q(0, 1);
}
#endif测试:
无作用版:
void createAVPacketandInit1() {AVPacket* avpacket = av_packet_alloc();if (avpacket == nullptr) {cout << "av_packet_alloc error" << endl;}cout << "debug point 0" << endl;av_init_packet(avpacket);cout << "debug point 1" << endl;
}
有点作用版:
void createAVPacketandInit() {AVPacket avpacket;cout << "debug point 0" << endl;av_init_packet(&avpacket);cout << "debug point 1" << endl;
}

av_packet_alloc 和 av_init_packet的区别是?
初始化的区别在于没有给size赋值。
我们再来回顾一下前面关于 这个 size是啥?
成员变量size:成员变量data指向的缓冲区的大小,单位为字节。
有啥用? 在后面 av_packet_clone函数中就可以看到,如果这个size的值没有被赋值过,则clone的new avpacket 会失败,也就是返回nullptr。

void av_packet_free(AVPacket **pkt);
/*** Free the packet, if the packet is reference counted, it will be* unreferenced first.** @param pkt packet to be freed. The pointer will be set to NULL.* @note passing NULL is a no-op.*/
void av_packet_free(AVPacket **pkt);实现
从实现可以看到,这个不管是不ptk 是不是nullptr,都不会有错误
void av_packet_free(AVPacket **pkt)
{if (!pkt || !*pkt)return;av_packet_unref(*pkt);av_freep(pkt);
}从这个方法来看,是将pkt的内部数据都释放了,并且给内部数据重新给了默认值
av_packet_unref(*pkt);void av_packet_unref(AVPacket *pkt)
{av_packet_free_side_data(pkt);av_buffer_unref(&pkt->opaque_ref);av_buffer_unref(&pkt->buf);get_packet_defaults(pkt);
}从 av_freep 方法来看,是 将 &pkt,的值赋值给&val,然后将&pkg赋值为null,最后再free &val。
为什么写的这么复杂呢?
直接free &pkt 不行吗? 这个好处是啥呢?知道的童鞋可以回复一下,感谢!!!
void av_freep(void *arg)
{void *val;memcpy(&val, arg, sizeof(val));memcpy(arg, &(void *){ NULL }, sizeof(val));av_free(val);
}void av_free(void *ptr)
{
#if HAVE_ALIGNED_MALLOC_aligned_free(ptr);
#elsefree(ptr);
#endif
}使用测试
void createAVpacketandFreeAVPacket() {AVPacket* avpacket = av_packet_alloc();if (avpacket == nullptr) {cout << "av_packet_alloc error" << endl;}cout << "debugpoint1" << endl;av_packet_free(&avpacket);cout << "debugpoint2" << endl;
}

AVPacket* av_packet_clone(const AVPacket* src);
This is a shortcut for av_packet_alloc()+av_packet_ref().
/*** Create a new packet that references the same data as src.** This is a shortcut for av_packet_alloc()+av_packet_ref().** @return newly created AVPacket on success, NULL on error.** @see av_packet_alloc* @see av_packet_ref*/
AVPacket* av_packet_clone(const AVPacket* src);实现可以看到 :是先 ret = av_packet_alloc,然后调用 (av_packet_ref(ret, src)),最后返回 新建的这个ret。
这里的关键是 av_packet_ref(AVPacket *dst, const AVPacket *src) 方法
AVPacket *av_packet_clone(const AVPacket *src)
{AVPacket *ret = av_packet_alloc();if (!ret)return ret;if (av_packet_ref(ret, src))av_packet_free(&ret);return ret;
}int av_packet_ref(AVPacket *dst, const AVPacket *src)
{int ret;dst->buf = NULL;ret = av_packet_copy_props(dst, src);if (ret < 0)goto fail;if (!src->buf) {ret = packet_alloc(&dst->buf, src->size);if (ret < 0)goto fail;av_assert1(!src->size || src->data);if (src->size)memcpy(dst->buf->data, src->data, src->size);dst->data = dst->buf->data;} else {dst->buf = av_buffer_ref(src->buf);if (!dst->buf) {ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);goto fail;}dst->data = src->data;}dst->size = src->size;return 0;
fail:av_packet_unref(dst);return ret;
}实验测试1 :如果在 src 是不是通过 av_packet_clone出来的,或者 没有通过 av_init_packet初始化过packet 的会有 runtime error
/***
*
* 实验测试当 AVPacket 没有赋值的时候,使用 av_packet_clone会报error
***/
void avpacketclone() {AVPacket avpacket1 ;//实验测试当 AVPacket 没有赋值的时候,使用 av_packet_clone会报errorAVPacket* newavpacket = av_packet_clone(&avpacket1);if (newavpacket == nullptr) {cout << "newavpacket = nullptr" << endl;}cout << "debug point" << endl;
}实验测试2:
* 实验测试当 AVPacket 在栈空间,且通过 av_init_packet初始化,
* 返回的newavpacket是nullptr
* root case 是 av_packet_ref(ret, src) ,packet_alloc(&dst->buf, src->size) ;src->size 的值是 < 0的,因此返回nullptr
/***
*
* 实验测试当 AVPacket 在栈空间,且通过 av_init_packet初始化,
* 返回的newavpacket是nullptr
* root case 是 av_packet_ref(ret, src) ,packet_alloc(&dst->buf, src->size) ;src->size 的值是 < 0的,因此返回nullptr
*
***/
void avpacketclone1() {AVPacket avpacket1;//实验测试当 AVPacket 没有赋值的时候,使用 av_packet_clone会报errorav_init_packet(&avpacket1);//那么通过av_packet_alloc方法是否OK呢?AVPacket* newavpacket = av_packet_clone(&avpacket1);if (newavpacket == nullptr) {cout << "newavpacket = nullptr" << endl;}cout << "debug point" << endl;
}实验测试3:
/// <summary>
/// 上述 通过 av_packet_clone方法 不是有 runtime exception就是 clone出来的newpacket为nullpptr
/// clone出来的newpacket 为nullptr 的root case 是 因为size 为一个默认值,很大的负数,没有被赋值为0或者其他值
/// 那我们下来手动的将这个 size这个值设置为 一个具体的数,行不行呢?
/// 如何设置这个值,我们查看 .h文件,发现有一个api说明比较像
/// int av_new_packet(AVPacket *pkt, int size);
/// 先来测试一下,我们再来研究这个 av_new_packet 函数
/// <summary>
/// 上述 通过 av_packet_clone方法 不是有 runtime exception就是 clone出来的newpacket为nullpptr
/// clone出来的newpacket 为nullptr 的root case 是 因为size 为一个默认值,很大的负数,没有被赋值为0或者其他值
/// 那我们下来手动的将这个 size这个值设置为 一个具体的数,行不行呢?
/// 如何设置这个值,我们查看 .h文件,发现有一个api说明比较像
/// int av_new_packet(AVPacket *pkt, int size);
/// 先来测试一下,我们再来研究这个 av_new_packet 函数
/// </summary>
void avpacketclone2() {AVPacket* avpacket = av_packet_alloc();int ret = 0;ret = av_new_packet(avpacket, 10);AVPacket* newavpacket = av_packet_clone(avpacket);if (newavpacket == nullptr) {cout << "newavpacket = nullptr" << endl;}cout << "debug point" << endl;
}结论是:成功,且两个packet 的buf的指针是一样的。

int av_new_packet(AVPacket *pkt, int size);
给pkt 赋初始值(这个赋初值包含size吗?包含且为0,在后面的源码中可以看到);然后再给data 分配大小为size。
/*** Allocate the payload of a packet and initialize its fields with* default values.** @param pkt packet* @param size wanted payload size* @return 0 if OK, AVERROR_xxx otherwise*/
int av_new_packet(AVPacket *pkt, int size);源码:
从代码中可以看到 apcket_alloc的时候,这个size就很关键了,size的大小决定了到底赋值还是不赋值
int av_new_packet(AVPacket *pkt, int size)
{AVBufferRef *buf = NULL;int ret = packet_alloc(&buf, size);if (ret < 0)return ret;get_packet_defaults(pkt);pkt->buf = buf;pkt->data = buf->data;pkt->size = size;return 0;
}//即使size的值是符合预期的,分配的大小 还要加上一个 AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE(64)
//为啥要多弄出来一个64 呢?这是因为有些解码器,编码器为了算法优化,会有一些多余的buffer(这个buffer一般都是小于等于64的),因此ffmpeg在设计的时候,就多加了个64
static int packet_alloc(AVBufferRef **buf, int size)
{int ret;// 错误判断if (size < 0 || size >= INT_MAX - AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE)return AVERROR(EINVAL);/// 真的分配空间ret = av_buffer_realloc(buf, size + AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE);if (ret < 0)return ret;
///清空空间memset((*buf)->data + size, 0, AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE);return 0;
}///这里看一下,ffmpeg中分配空间的方法
void *av_realloc(void *ptr, size_t size)
{
/// error判断void *ret;if (size > atomic_load_explicit(&max_alloc_size, memory_order_relaxed))return NULL;
/// HAVE_ALIGNED_MALLOC=1,因此代码会走到 _aligned_realloc这一行
#if HAVE_ALIGNED_MALLOCret = _aligned_realloc(ptr, size + !size, ALIGN);
#elseret = realloc(ptr, size + !size);
#endif
/// CONFIG_MEMORY_POISONING =0; 因此下面的代码不会走。
#if CONFIG_MEMORY_POISONINGif (ret && !ptr)memset(ret, FF_MEMORY_POISON, size);
#endifreturn ret;
}///_aligned_realloc 方法的详细说明
https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/cpp/c-runtime-library/reference/aligned-realloc?view=msvc-170_aligned_realloc(ptr, size + !size, ALIGN);ALIGN是32
给ptr 分配 (size + !size)的大小 ,这个大小为啥是 (size + !size)为什么这么写呢?
在c语言中 !0 = 1, !1=0, 猜测ffmpeg的开发者 这么写是为了保证这个值最少是1,可能是为了某个bug,也可能是为了保证这个值的必须 >0.void * _aligned_realloc(void *memblock,size_t size,size_t alignment
);memblock
当前的内存块指针。size
请求的内存分配的大小。alignment
对齐值,必须是 2 的整数次幂。static void get_packet_defaults(AVPacket *pkt)
{memset(pkt, 0, sizeof(*pkt));pkt->pts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;pkt->dts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;pkt->pos = -1;pkt->time_base = av_make_q(0, 1);
}在看完源码之后,能想到这个api使用的时机是什么吗?
猜测是我们知道了要传入的packet 的data 大小,可以提前设定这个大小?
void av_shrink_packet(AVPacket *pkt, int size);
成员变量data:
指针,指向“存放压缩后的一帧(对于视频通常包含一个压缩帧,对于音频可能包含几个压缩帧)音视频数据的缓冲区”。
成员变量size:
成员变量data指向的缓冲区的大小,单位为字节。
shrink 是收缩,缩小的意思,从字面意思来是,是将pkt data 的size 变成现在的值。
将当前pkt 中的 data的大小变成size,如果当前pkt->size本身就比要设置的size小,则直接return,
例如原先pkt->size的值是8,user 想要改成,16,那就不变还是8
例如原先pkt->size的值是8,user 想要改成6,那么就会变成6.
然后还会将 pkt->data + size 后的 AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE大小的空间清零
这也很好理解,size 变化了,本身就在size后面多加了AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE,要保证 AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE 这段空间是清零的。
/*** Reduce packet size, correctly zeroing padding** @param pkt packet* @param size new size*/
void av_shrink_packet(AVPacket *pkt, int size);实现
void av_shrink_packet(AVPacket *pkt, int size)
{if (pkt->size <= size)return;pkt->size = size;memset(pkt->data + size, 0, AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE);
}问题是:在哪里使用呢?什么时机使用呢?
int av_grow_packet(AVPacket* pkt, int grow_by);
增加数据包大小,正确归零填充
/*** Increase packet size, correctly zeroing padding** @param pkt packet* @param grow_by number of bytes by which to increase the size of the packet*/
int av_grow_packet(AVPacket *pkt, int grow_by);实现:
从实现来看,
增加数据包(pkt->data指向的缓冲区)的大小,让该大小增至(pkt->size + grow_by)字节。让地址为(pkt->data + pkt->size + grow_by)后的数据字节归零。执行该函数后,pkt->size会增至(pkt->size + grow_by)字节。返回0表示成功,返回负数表示失败。
int av_grow_packet(AVPacket *pkt, int grow_by)
{int new_size;av_assert0((unsigned)pkt->size <= INT_MAX - AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE);if ((unsigned)grow_by >INT_MAX - (pkt->size + AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE))return AVERROR(ENOMEM);new_size = pkt->size + grow_by + AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE;if (pkt->buf) {size_t data_offset;uint8_t *old_data = pkt->data;if (pkt->data == NULL) {data_offset = 0;pkt->data = pkt->buf->data;} else {data_offset = pkt->data - pkt->buf->data;if (data_offset > INT_MAX - new_size)return AVERROR(ENOMEM);}if (new_size + data_offset > pkt->buf->size ||!av_buffer_is_writable(pkt->buf)) {int ret;// allocate slightly more than requested to avoid excessive// reallocationsif (new_size + data_offset < INT_MAX - new_size/16)new_size += new_size/16;ret = av_buffer_realloc(&pkt->buf, new_size + data_offset);if (ret < 0) {pkt->data = old_data;return ret;}pkt->data = pkt->buf->data + data_offset;}} else {pkt->buf = av_buffer_alloc(new_size);if (!pkt->buf)return AVERROR(ENOMEM);if (pkt->size > 0)memcpy(pkt->buf->data, pkt->data, pkt->size);pkt->data = pkt->buf->data;}pkt->size += grow_by;memset(pkt->data + pkt->size, 0, AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE);return 0;
}int av_packet_from_data(AVPacket *pkt, uint8_t *data, int size)
使用已经分配好的buffer初始化一个AVPacket,会设置AVPacket的data和size成员。传入的size参数是减去了AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE的,也就是size + AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE等于buffer总的大小。
代码实现,从实现上来看,会将 pkt->data指向传进来的data,大小为size,注意的 pkt的data 赋值并没有 copy,而是直接将指针赋值给了pkt的data,也就是说,在pkt 的data没有使用的时候,不要释放data空间,释放了意味着pkt的data也就变化了 ;;如果覆盖了传递进来的data空间,也意味着pkt的data的内容变化了。
/*** Initialize a reference-counted packet from av_malloc()ed data.** @param pkt packet to be initialized. This function will set the data, size,* and buf fields, all others are left untouched.* @param data Data allocated by av_malloc() to be used as packet data. If this* function returns successfully, the data is owned by the underlying AVBuffer.* The caller may not access the data through other means.* @param size size of data in bytes, without the padding. I.e. the full buffer* size is assumed to be size + AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE.** @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on error*/
int av_packet_from_data(AVPacket *pkt, uint8_t *data, int size);int av_packet_from_data(AVPacket *pkt, uint8_t *data, int size)
{if (size >= INT_MAX - AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE)return AVERROR(EINVAL);pkt->buf = av_buffer_create(data, size + AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE,av_buffer_default_free, NULL, 0);if (!pkt->buf)return AVERROR(ENOMEM);pkt->data = data;pkt->size = size;return 0;
}int av_buffer_get_ref_count(const AVBufferRef *buf);
得到avpacket或者 avframe的 引用计数
int av_buffer_get_ref_count(const AVBufferRef *buf)
{return atomic_load(&buf->buffer->refcount);
}cout<<av_buffer_get_ref_count(avpacket->buf)<<endl;
cout<<av_buffer_get_ref_count(avframe->buf)<<endl;
uint8_t* av_packet_new_side_data(AVPacket* pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type, size_t size);
返回值是要存储的 size_data的指针。
AVPacket->side_data是AVPacket携带的side数据数组,AVPacket->side_data_elems是数组的长度。av_packet_new_side_data和av_packet_add_side_data函数都提供了向AVPacket添加指定类型side data的能力,只是参数略有差异,每次都会把新side data添加到数组的尾部。 av_packet_get_side_data函数提供了从AVPacket获取指定类型side data的能力。
/*** Allocate new information of a packet.** @param pkt packet* @param type side information type* @param size side information size* @return pointer to fresh allocated data or NULL otherwise*/
uint8_t* av_packet_new_side_data(AVPacket* pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type,size_t size);uint8_t *av_packet_new_side_data(AVPacket *pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type,size_t size)
{int ret;uint8_t *data;if (size > SIZE_MAX - AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE)return NULL;data = av_mallocz(size + AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE);if (!data)return NULL;ret = av_packet_add_side_data(pkt, type, data, size);if (ret < 0) {av_freep(&data);return NULL;}return data;
}int av_packet_add_side_data(AVPacket *pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type, uint8_t *data, size_t size);
/*** Wrap an existing array as a packet side data.** @param pkt packet* @param type side information type* @param data the side data array. It must be allocated with the av_malloc()* family of functions. The ownership of the data is transferred to* pkt.* @param size side information size* @return a non-negative number on success, a negative AVERROR code on* failure. On failure, the packet is unchanged and the data remains* owned by the caller.*/
int av_packet_add_side_data(AVPacket *pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type,uint8_t *data, size_t size);int av_packet_add_side_data(AVPacket *pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type,uint8_t *data, size_t size)
{AVPacketSideData *tmp;int i, elems = pkt->side_data_elems;for (i = 0; i < elems; i++) {AVPacketSideData *sd = &pkt->side_data[i];if (sd->type == type) {av_free(sd->data);sd->data = data;sd->size = size;return 0;}}if ((unsigned)elems + 1 > AV_PKT_DATA_NB)return AVERROR(ERANGE);tmp = av_realloc(pkt->side_data, (elems + 1) * sizeof(*tmp));if (!tmp)return AVERROR(ENOMEM);pkt->side_data = tmp;pkt->side_data[elems].data = data;pkt->side_data[elems].size = size;pkt->side_data[elems].type = type;pkt->side_data_elems++;return 0;
}参考ffmpeg源码中的一些使用。
如下的例子都是ffmpeg在编码的时候用到,再回看关于 字段size_data的说明: 存放“容器可以提供的额外数据包数据”的数组的首地址。数据包可以包含多种类型的边信息,比如,在编码结束的时候更新一些流的参数。指针side_data指向的空间存储了用于解码、展现或处理编码流的辅助信息,它通常由解复用器和编码器导出,可以以分组为单位提供给解码器和复用器,也可以作为全局侧数据(应用于整个编码流)。
flac.enc中的使用
static int flac_encode_frame(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVPacket *avpkt,const AVFrame *frame, int *got_packet_ptr)
{FlacEncodeContext *s;int frame_bytes, out_bytes, ret;s = avctx->priv_data;/* when the last block is reached, update the header in extradata */if (!frame) {s->max_framesize = s->max_encoded_framesize;av_md5_final(s->md5ctx, s->md5sum);write_streaminfo(s, avctx->extradata);if (!s->flushed) {uint8_t *side_data = av_packet_new_side_data(avpkt, AV_PKT_DATA_NEW_EXTRADATA,avctx->extradata_size);if (!side_data)return AVERROR(ENOMEM);memcpy(side_data, avctx->extradata, avctx->extradata_size);avpkt->pts = s->next_pts;*got_packet_ptr = 1;s->flushed = 1;}return 0;}从img2dec.c中看到
要结合 av_packet_pack_dictionary方法使用
static int add_filename_as_pkt_side_data(char *filename, AVPacket *pkt) {AVDictionary *d = NULL;char *packed_metadata = NULL;size_t metadata_len;int ret;av_dict_set(&d, "lavf.image2dec.source_path", filename, 0);av_dict_set(&d, "lavf.image2dec.source_basename", av_basename(filename), 0);packed_metadata = av_packet_pack_dictionary(d, &metadata_len);av_dict_free(&d);if (!packed_metadata)return AVERROR(ENOMEM);ret = av_packet_add_side_data(pkt, AV_PKT_DATA_STRINGS_METADATA,packed_metadata, metadata_len);if (ret < 0) {av_freep(&packed_metadata);return ret;}return 0;
}总结一下:一般这玩意在 特定的编码器的时候使用,表明我们要给avpacket中添加一些特殊的信息,信息的类型由 AVPacketSideDataType 决定,那么 AVPacketSideDataType 有哪些?这些翻译出来也不知道真正的意思是啥,应该是对于 每一种特殊的编码学习的时候,会用到这个,我们假设mp4编码器有特殊的值,那么就在这个 AVPacketSideDataType 里面找。
size_t size : 应该是 要设置的AVPacket->side_data的大小。在实际开发中遇到后,应该多测试,看是否要减去这个 AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE
uint8_t* av_packet_get_side_data(const AVPacket* pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type, size_t* size);
这个看起来就在解码的时候用到,得到avpacket中存储的值
/*** Get side information from packet.** @param pkt packet* @param type desired side information type* @param size If supplied, *size will be set to the size of the side data* or to zero if the desired side data is not present.* @return pointer to data if present or NULL otherwise*/
uint8_t* av_packet_get_side_data(const AVPacket* pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type,size_t* size);源码实现
uint8_t *av_packet_get_side_data(const AVPacket *pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type,size_t *size)
{int i;for (i = 0; i < pkt->side_data_elems; i++) {if (pkt->side_data[i].type == type) {if (size)*size = pkt->side_data[i].size;return pkt->side_data[i].data;}}if (size)*size = 0;return NULL;
}源码中的使用
static int h264_decode_frame(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVFrame *pict,int *got_frame, AVPacket *avpkt)
{const uint8_t *buf = avpkt->data;int buf_size = avpkt->size;H264Context *h = avctx->priv_data;int buf_index;int ret;h->flags = avctx->flags;h->setup_finished = 0;h->nb_slice_ctx_queued = 0;ff_h264_unref_picture(h, &h->last_pic_for_ec);/* end of stream, output what is still in the buffers */if (buf_size == 0)return send_next_delayed_frame(h, pict, got_frame, 0);if (av_packet_get_side_data(avpkt, AV_PKT_DATA_NEW_EXTRADATA, NULL)) {size_t side_size;uint8_t *side = av_packet_get_side_data(avpkt, AV_PKT_DATA_NEW_EXTRADATA, &side_size);ff_h264_decode_extradata(side, side_size,&h->ps, &h->is_avc, &h->nal_length_size,avctx->err_recognition, avctx);}if (h->is_avc && buf_size >= 9 && buf[0]==1 && buf[2]==0 && (buf[4]&0xFC)==0xFC) {if (is_avcc_extradata(buf, buf_size))return ff_h264_decode_extradata(buf, buf_size,&h->ps, &h->is_avc, &h->nal_length_size,avctx->err_recognition, avctx);}buf_index = decode_nal_units(h, buf, buf_size);if (buf_index < 0)return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;if (!h->cur_pic_ptr && h->nal_unit_type == H264_NAL_END_SEQUENCE) {av_assert0(buf_index <= buf_size);return send_next_delayed_frame(h, pict, got_frame, buf_index);}if (!(avctx->flags2 & AV_CODEC_FLAG2_CHUNKS) && (!h->cur_pic_ptr || !h->has_slice)) {if (avctx->skip_frame >= AVDISCARD_NONREF ||buf_size >= 4 && !memcmp("Q264", buf, 4))return buf_size;av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "no frame!\n");return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;}if (!(avctx->flags2 & AV_CODEC_FLAG2_CHUNKS) ||(h->mb_y >= h->mb_height && h->mb_height)) {if ((ret = ff_h264_field_end(h, &h->slice_ctx[0], 0)) < 0)return ret;/* Wait for second field. */if (h->next_output_pic) {ret = finalize_frame(h, pict, h->next_output_pic, got_frame);if (ret < 0)return ret;}}av_assert0(pict->buf[0] || !*got_frame);ff_h264_unref_picture(h, &h->last_pic_for_ec);return get_consumed_bytes(buf_index, buf_size);
}int av_packet_shrink_side_data(AVPacket* pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type, size_t size);
/*** Shrink the already allocated side data buffer** @param pkt packet* @param type side information type* @param size new side information size* @return 0 on success, < 0 on failure*/
int av_packet_shrink_side_data(AVPacket* pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type,size_t size);源码
int av_packet_shrink_side_data(AVPacket *pkt, enum AVPacketSideDataType type,size_t size)
{int i;for (i = 0; i < pkt->side_data_elems; i++) {if (pkt->side_data[i].type == type) {if (size > pkt->side_data[i].size)return AVERROR(ENOMEM);pkt->side_data[i].size = size;return 0;}}return AVERROR(ENOENT);
}使用,看到只有在mpegvideo_enc.c中有使用,应该和上述的 av_packet_new_side_data和 av_packet_add_side_data 相关,
int ff_mpv_encode_picture(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVPacket *pkt,const AVFrame *pic_arg, int *got_packet)
{MpegEncContext *s = avctx->priv_data;int i, stuffing_count, ret;int context_count = s->slice_context_count;s->vbv_ignore_qmax = 0;s->picture_in_gop_number++;if (load_input_picture(s, pic_arg) < 0)return -1;if (select_input_picture(s) < 0) {return -1;}/* output? */if (s->new_picture->data[0]) {int growing_buffer = context_count == 1 && !s->data_partitioning;size_t pkt_size = 10000 + s->mb_width * s->mb_height *(growing_buffer ? 64 : (MAX_MB_BYTES + 100));if (CONFIG_MJPEG_ENCODER && avctx->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MJPEG) {ret = ff_mjpeg_add_icc_profile_size(avctx, s->new_picture, &pkt_size);if (ret < 0)return ret;}if ((ret = ff_alloc_packet(avctx, pkt, pkt_size)) < 0)return ret;pkt->size = avctx->internal->byte_buffer_size - AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE;if (s->mb_info) {s->mb_info_ptr = av_packet_new_side_data(pkt,AV_PKT_DATA_H263_MB_INFO,s->mb_width*s->mb_height*12);s->prev_mb_info = s->last_mb_info = s->mb_info_size = 0;}for (i = 0; i < context_count; i++) {int start_y = s->thread_context[i]->start_mb_y;int end_y = s->thread_context[i]-> end_mb_y;int h = s->mb_height;uint8_t *start = pkt->data + (size_t)(((int64_t) pkt->size) * start_y / h);uint8_t *end = pkt->data + (size_t)(((int64_t) pkt->size) * end_y / h);init_put_bits(&s->thread_context[i]->pb, start, end - start);}s->pict_type = s->new_picture->pict_type;//emms_c();ret = frame_start(s);if (ret < 0)return ret;
vbv_retry:ret = encode_picture(s);if (growing_buffer) {av_assert0(s->pb.buf == avctx->internal->byte_buffer);pkt->data = s->pb.buf;pkt->size = avctx->internal->byte_buffer_size;}if (ret < 0)return -1;frame_end(s);if ((CONFIG_MJPEG_ENCODER || CONFIG_AMV_ENCODER) && s->out_format == FMT_MJPEG)ff_mjpeg_encode_picture_trailer(&s->pb, s->header_bits);if (avctx->rc_buffer_size) {RateControlContext *rcc = &s->rc_context;int max_size = FFMAX(rcc->buffer_index * avctx->rc_max_available_vbv_use, rcc->buffer_index - 500);int hq = (avctx->mb_decision == FF_MB_DECISION_RD || avctx->trellis);int min_step = hq ? 1 : (1<<(FF_LAMBDA_SHIFT + 7))/139;if (put_bits_count(&s->pb) > max_size &&s->lambda < s->lmax) {s->next_lambda = FFMAX(s->lambda + min_step, s->lambda *(s->qscale + 1) / s->qscale);if (s->adaptive_quant) {int i;for (i = 0; i < s->mb_height * s->mb_stride; i++)s->lambda_table[i] =FFMAX(s->lambda_table[i] + min_step,s->lambda_table[i] * (s->qscale + 1) /s->qscale);}s->mb_skipped = 0; // done in frame_start()// done in encode_picture() so we must undo itif (s->pict_type == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_P) {if (s->flipflop_rounding ||s->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H263P ||s->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4)s->no_rounding ^= 1;}if (s->pict_type != AV_PICTURE_TYPE_B) {s->time_base = s->last_time_base;s->last_non_b_time = s->time - s->pp_time;}for (i = 0; i < context_count; i++) {PutBitContext *pb = &s->thread_context[i]->pb;init_put_bits(pb, pb->buf, pb->buf_end - pb->buf);}s->vbv_ignore_qmax = 1;av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_VERBOSE, "reencoding frame due to VBV\n");goto vbv_retry;}av_assert0(avctx->rc_max_rate);}if (avctx->flags & AV_CODEC_FLAG_PASS1)ff_write_pass1_stats(s);for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {avctx->error[i] += s->encoding_error[i];}ff_side_data_set_encoder_stats(pkt, s->current_picture.f->quality,s->encoding_error,(avctx->flags&AV_CODEC_FLAG_PSNR) ? MPEGVIDEO_MAX_PLANES : 0,s->pict_type);if (avctx->flags & AV_CODEC_FLAG_PASS1)assert(put_bits_count(&s->pb) == s->header_bits + s->mv_bits +s->misc_bits + s->i_tex_bits +s->p_tex_bits);flush_put_bits(&s->pb);s->frame_bits = put_bits_count(&s->pb);stuffing_count = ff_vbv_update(s, s->frame_bits);s->stuffing_bits = 8*stuffing_count;if (stuffing_count) {if (put_bytes_left(&s->pb, 0) < stuffing_count + 50) {av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "stuffing too large\n");return -1;}switch (s->codec_id) {case AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG1VIDEO:case AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG2VIDEO:while (stuffing_count--) {put_bits(&s->pb, 8, 0);}break;case AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4:put_bits(&s->pb, 16, 0);put_bits(&s->pb, 16, 0x1C3);stuffing_count -= 4;while (stuffing_count--) {put_bits(&s->pb, 8, 0xFF);}break;default:av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "vbv buffer overflow\n");s->stuffing_bits = 0;}flush_put_bits(&s->pb);s->frame_bits = put_bits_count(&s->pb);}/* update MPEG-1/2 vbv_delay for CBR */if (avctx->rc_max_rate &&avctx->rc_min_rate == avctx->rc_max_rate &&s->out_format == FMT_MPEG1 &&90000LL * (avctx->rc_buffer_size - 1) <=avctx->rc_max_rate * 0xFFFFLL) {AVCPBProperties *props;size_t props_size;int vbv_delay, min_delay;double inbits = avctx->rc_max_rate *av_q2d(avctx->time_base);int minbits = s->frame_bits - 8 *(s->vbv_delay_pos - 1);double bits = s->rc_context.buffer_index + minbits - inbits;uint8_t *const vbv_delay_ptr = s->pb.buf + s->vbv_delay_pos;if (bits < 0)av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR,"Internal error, negative bits\n");av_assert1(s->repeat_first_field == 0);vbv_delay = bits * 90000 / avctx->rc_max_rate;min_delay = (minbits * 90000LL + avctx->rc_max_rate - 1) /avctx->rc_max_rate;vbv_delay = FFMAX(vbv_delay, min_delay);av_assert0(vbv_delay < 0xFFFF);vbv_delay_ptr[0] &= 0xF8;vbv_delay_ptr[0] |= vbv_delay >> 13;vbv_delay_ptr[1] = vbv_delay >> 5;vbv_delay_ptr[2] &= 0x07;vbv_delay_ptr[2] |= vbv_delay << 3;props = av_cpb_properties_alloc(&props_size);if (!props)return AVERROR(ENOMEM);props->vbv_delay = vbv_delay * 300;ret = av_packet_add_side_data(pkt, AV_PKT_DATA_CPB_PROPERTIES,(uint8_t*)props, props_size);if (ret < 0) {av_freep(&props);return ret;}}s->total_bits += s->frame_bits;pkt->pts = s->current_picture.f->pts;pkt->duration = s->current_picture.f->duration;if (!s->low_delay && s->pict_type != AV_PICTURE_TYPE_B) {if (!s->current_picture.coded_picture_number)pkt->dts = pkt->pts - s->dts_delta;elsepkt->dts = s->reordered_pts;s->reordered_pts = pkt->pts;} elsepkt->dts = pkt->pts;// the no-delay case is handled in generic codeif (avctx->codec->capabilities & AV_CODEC_CAP_DELAY) {ret = ff_encode_reordered_opaque(avctx, pkt, s->current_picture.f);if (ret < 0)return ret;}if (s->current_picture.f->key_frame)pkt->flags |= AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY;if (s->mb_info)av_packet_shrink_side_data(pkt, AV_PKT_DATA_H263_MB_INFO, s->mb_info_size);} else {s->frame_bits = 0;}/* release non-reference frames */for (i = 0; i < MAX_PICTURE_COUNT; i++) {if (!s->picture[i].reference)ff_mpeg_unref_picture(avctx, &s->picture[i]);}av_assert1((s->frame_bits & 7) == 0);pkt->size = s->frame_bits / 8;*got_packet = !!pkt->size;return 0;
}const char *av_packet_side_data_name(enum AVPacketSideDataType type);
const char *av_packet_side_data_name(enum AVPacketSideDataType type);实现:
const char *av_packet_side_data_name(enum AVPacketSideDataType type)
{switch(type) {case AV_PKT_DATA_PALETTE: return "Palette";case AV_PKT_DATA_NEW_EXTRADATA: return "New Extradata";case AV_PKT_DATA_PARAM_CHANGE: return "Param Change";case AV_PKT_DATA_H263_MB_INFO: return "H263 MB Info";case AV_PKT_DATA_REPLAYGAIN: return "Replay Gain";case AV_PKT_DATA_DISPLAYMATRIX: return "Display Matrix";case AV_PKT_DATA_STEREO3D: return "Stereo 3D";case AV_PKT_DATA_AUDIO_SERVICE_TYPE: return "Audio Service Type";case AV_PKT_DATA_QUALITY_STATS: return "Quality stats";case AV_PKT_DATA_FALLBACK_TRACK: return "Fallback track";case AV_PKT_DATA_CPB_PROPERTIES: return "CPB properties";case AV_PKT_DATA_SKIP_SAMPLES: return "Skip Samples";case AV_PKT_DATA_JP_DUALMONO: return "JP Dual Mono";case AV_PKT_DATA_STRINGS_METADATA: return "Strings Metadata";case AV_PKT_DATA_SUBTITLE_POSITION: return "Subtitle Position";case AV_PKT_DATA_MATROSKA_BLOCKADDITIONAL: return "Matroska BlockAdditional";case AV_PKT_DATA_WEBVTT_IDENTIFIER: return "WebVTT ID";case AV_PKT_DATA_WEBVTT_SETTINGS: return "WebVTT Settings";case AV_PKT_DATA_METADATA_UPDATE: return "Metadata Update";case AV_PKT_DATA_MPEGTS_STREAM_ID: return "MPEGTS Stream ID";case AV_PKT_DATA_MASTERING_DISPLAY_METADATA: return "Mastering display metadata";case AV_PKT_DATA_CONTENT_LIGHT_LEVEL: return "Content light level metadata";case AV_PKT_DATA_SPHERICAL: return "Spherical Mapping";case AV_PKT_DATA_A53_CC: return "A53 Closed Captions";case AV_PKT_DATA_ENCRYPTION_INIT_INFO: return "Encryption initialization data";case AV_PKT_DATA_ENCRYPTION_INFO: return "Encryption info";case AV_PKT_DATA_AFD: return "Active Format Description data";case AV_PKT_DATA_PRFT: return "Producer Reference Time";case AV_PKT_DATA_ICC_PROFILE: return "ICC Profile";case AV_PKT_DATA_DOVI_CONF: return "DOVI configuration record";case AV_PKT_DATA_S12M_TIMECODE: return "SMPTE ST 12-1:2014 timecode";case AV_PKT_DATA_DYNAMIC_HDR10_PLUS: return "HDR10+ Dynamic Metadata (SMPTE 2094-40)";}return NULL;
}
uint8_t* av_packet_pack_dictionary(AVDictionary* dict, size_t* size);
将AVDictioary中的数据放到一整块内存并返回;
返回值是 avpacket->data_side_data 的指针。
实际开发中 需要再给返回值 copy 数据才算完成
/*** Pack a dictionary for use in side_data.** @param dict The dictionary to pack.* @param size pointer to store the size of the returned data* @return pointer to data if successful, NULL otherwise*/
uint8_t* av_packet_pack_dictionary(AVDictionary* dict, size_t* size);源码实现
uint8_t *av_packet_pack_dictionary(AVDictionary *dict, size_t *size)
{uint8_t *data = NULL;*size = 0;if (!dict)return NULL;for (int pass = 0; pass < 2; pass++) {const AVDictionaryEntry *t = NULL;size_t total_length = 0;while ((t = av_dict_iterate(dict, t))) {for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {const char *str = i ? t->value : t->key;const size_t len = strlen(str) + 1;if (pass)memcpy(data + total_length, str, len);else if (len > SIZE_MAX - total_length)return NULL;total_length += len;}}if (pass)break;data = av_malloc(total_length);if (!data)return NULL;*size = total_length;}return data;
}参考 av_packet_add_side_data 中例子。
int av_packet_unpack_dictionary(const uint8_t* data, size_t size,
AVDictionary** dict);
从一整块数据中解析出一个AVDictionary;
实际上主要是给 dict 中传递数据解析 AVDictionary中 。
/*** Unpack a dictionary from side_data.** @param data data from side_data* @param size size of the data* @param dict the metadata storage dictionary* @return 0 on success, < 0 on failure*/
int av_packet_unpack_dictionary(const uint8_t* data, size_t size,AVDictionary** dict);int av_packet_unpack_dictionary(const uint8_t *data, size_t size,AVDictionary **dict)
{const uint8_t *end;int ret;if (!dict || !data || !size)return 0;end = data + size;if (size && end[-1])return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;while (data < end) {const uint8_t *key = data;const uint8_t *val = data + strlen(key) + 1;if (val >= end || !*key)return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;ret = av_dict_set(dict, key, val, 0);if (ret < 0)return ret;data = val + strlen(val) + 1;}return 0;
}
void av_packet_free_side_data(AVPacket* pkt);
/*** Convenience function to free all the side data stored.* All the other fields stay untouched.** @param pkt packet*/
void av_packet_free_side_data(AVPacket* pkt);实现
void av_packet_free_side_data(AVPacket *pkt)
{int i;for (i = 0; i < pkt->side_data_elems; i++)av_freep(&pkt->side_data[i].data);av_freep(&pkt->side_data);pkt->side_data_elems = 0;
}int av_packet_ref(AVPacket* dst, const AVPacket* src);
引用计数加一
/*** Setup a new reference to the data described by a given packet** If src is reference-counted, setup dst as a new reference to the* buffer in src. Otherwise allocate a new buffer in dst and copy the* data from src into it.** All the other fields are copied from src.** @see av_packet_unref** @param dst Destination packet. Will be completely overwritten.* @param src Source packet** @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on error. On error, dst* will be blank (as if returned by av_packet_alloc()).*/
int av_packet_ref(AVPacket* dst, const AVPacket* src);源码
int av_packet_ref(AVPacket *dst, const AVPacket *src)
{int ret;dst->buf = NULL;ret = av_packet_copy_props(dst, src);if (ret < 0)goto fail;if (!src->buf) {ret = packet_alloc(&dst->buf, src->size);if (ret < 0)goto fail;av_assert1(!src->size || src->data);if (src->size)memcpy(dst->buf->data, src->data, src->size);dst->data = dst->buf->data;} else {dst->buf = av_buffer_ref(src->buf);if (!dst->buf) {ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);goto fail;}dst->data = src->data;}dst->size = src->size;return 0;
fail:av_packet_unref(dst);return ret;
}void av_packet_unref(AVPacket* pkt);
引用计数减一
/*** Wipe the packet.** Unreference the buffer referenced by the packet and reset the* remaining packet fields to their default values.** @param pkt The packet to be unreferenced.*/
void av_packet_unref(AVPacket* pkt);void av_packet_unref(AVPacket *pkt)
{av_packet_free_side_data(pkt);av_buffer_unref(&pkt->opaque_ref);av_buffer_unref(&pkt->buf);get_packet_defaults(pkt);
}void av_packet_move_ref(AVPacket* dst, AVPacket* src);
引用计数不变,将src 的所有东西都转移给dst,然后将src 的值都恢复成默认值
那么move 之后,src就不能使用了
/*** Move every field in src to dst and reset src.** @see av_packet_unref** @param src Source packet, will be reset* @param dst Destination packet*/
void av_packet_move_ref(AVPacket* dst, AVPacket* src);void av_packet_move_ref(AVPacket *dst, AVPacket *src)
{*dst = *src;get_packet_defaults(src);
}int av_packet_copy_props(AVPacket *dst, const AVPacket *src);
将src 中 "properties" 的字段拷贝给 dst,那么哪些属于是 "properties"呢?---》参考源码
/*** Copy only "properties" fields from src to dst.** Properties for the purpose of this function are all the fields* beside those related to the packet data (buf, data, size)** @param dst Destination packet* @param src Source packet** @return 0 on success AVERROR on failure.*/
int av_packet_copy_props(AVPacket *dst, const AVPacket *src);实现:
int av_packet_copy_props(AVPacket *dst, const AVPacket *src)
{int i, ret;dst->pts = src->pts;dst->dts = src->dts;dst->pos = src->pos;dst->duration = src->duration;dst->flags = src->flags;dst->stream_index = src->stream_index;dst->opaque = src->opaque;dst->time_base = src->time_base;dst->opaque_ref = NULL;dst->side_data = NULL;dst->side_data_elems = 0;ret = av_buffer_replace(&dst->opaque_ref, src->opaque_ref);if (ret < 0)return ret;for (i = 0; i < src->side_data_elems; i++) {enum AVPacketSideDataType type = src->side_data[i].type;size_t size = src->side_data[i].size;uint8_t *src_data = src->side_data[i].data;uint8_t *dst_data = av_packet_new_side_data(dst, type, size);if (!dst_data) {av_buffer_unref(&dst->opaque_ref);av_packet_free_side_data(dst);return AVERROR(ENOMEM);}memcpy(dst_data, src_data, size);}return 0;
}int av_packet_make_writable(AVPacket *pkt);
从实现来看:如果传递的参数pkt 的 字段 ------ AVBufferRef *buf 不为null 且是可以写的,则直接返回0. AVPacket是否可写:对应的flags 非AV_BUFFER_FLAG_READONLY
如果buf 是null 或者不可写,则重新 alloc buf,并且传递给 pkt,总的来说,这个函数就是让 你传进来的pkt 的 buf字段变成可写的,将引用计数变为1
/*** Create a writable reference for the data described by a given packet,* avoiding data copy if possible.** @param pkt Packet whose data should be made writable.** @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on failure. On failure, the* packet is unchanged.*/
int av_packet_make_writable(AVPacket *pkt);实现
int av_packet_make_writable(AVPacket *pkt)
{AVBufferRef *buf = NULL;int ret;if (pkt->buf && av_buffer_is_writable(pkt->buf))return 0;ret = packet_alloc(&buf, pkt->size);if (ret < 0)return ret;av_assert1(!pkt->size || pkt->data);if (pkt->size)memcpy(buf->data, pkt->data, pkt->size);av_buffer_unref(&pkt->buf);pkt->buf = buf;pkt->data = buf->data;return 0;
}int av_packet_make_refcounted(AVPacket* pkt);
如果没有buf字段为null,则根据size 重新create buf,并将这个buf赋值给pkt的字段,最后将将引用计数变为1
/*** Ensure the data described by a given packet is reference counted.** @note This function does not ensure that the reference will be writable.* Use av_packet_make_writable instead for that purpose.** @see av_packet_ref* @see av_packet_make_writable** @param pkt packet whose data should be made reference counted.** @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on error. On failure, the* packet is unchanged.*/
int av_packet_make_refcounted(AVPacket* pkt);int av_packet_make_refcounted(AVPacket *pkt)
{int ret;if (pkt->buf)return 0;ret = packet_alloc(&pkt->buf, pkt->size);if (ret < 0)return ret;av_assert1(!pkt->size || pkt->data);if (pkt->size)memcpy(pkt->buf->data, pkt->data, pkt->size);pkt->data = pkt->buf->data;return 0;
}void av_packet_rescale_ts(AVPacket* pkt, AVRational tb_src, AVRational tb_dst);
/*** Convert valid timing fields (timestamps / durations) in a packet from one* timebase to another. Timestamps with unknown values (AV_NOPTS_VALUE) will be* ignored.** @param pkt packet on which the conversion will be performed* @param tb_src source timebase, in which the timing fields in pkt are* expressed* @param tb_dst destination timebase, to which the timing fields will be* converted*/
void av_packet_rescale_ts(AVPacket* pkt, AVRational tb_src, AVRational tb_dst);实现:
void av_packet_rescale_ts(AVPacket *pkt, AVRational src_tb, AVRational dst_tb)
{if (pkt->pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE)pkt->pts = av_rescale_q(pkt->pts, src_tb, dst_tb);if (pkt->dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE)pkt->dts = av_rescale_q(pkt->dts, src_tb, dst_tb);if (pkt->duration > 0)pkt->duration = av_rescale_q(pkt->duration, src_tb, dst_tb);
}参考
从零到一学FFmpeg:av_packet_rescale_ts 函数详析与实战_avpacket 时间戳-CSDN博客
av_packet_rescale_ts是FFmpeg库中的一个函数,用于重新缩放或转换媒体流中的时间戳(timestamp),以适配不同的时间基(timebase)。
在处理多媒体数据时,特别是当数据在不同组件间传递,或者在编码、解码、转封装等操作中,时间戳经常需要调整以匹配当前上下文的时间基。
参数说明
pkt: 指向AVPacket结构体的指针,该结构体包含了要调整时间戳的媒体数据包。
tb_src: 原始时间基,即pkt中时间戳所依据的时间基。
通常,这来自于数据包来源的AVStream的time_base。
tb_dst: 目标时间基,即你想将时间戳转换到的时间基。
这通常与你打算将数据包发送到的目标组件(如解码器、输出格式上下文等)的时间基相匹配。
二、功能描述
时间戳转换: 该函数通过计算两个时间基之间的比例,对AVPacket中的pts(显示时间戳)和dts(解码时间戳)进行相应的缩放。这对于确保媒体处理管道中各环节的时间戳一致性至关重要。
同步与播放: 时间戳的正确调整对于视频和音频的同步播放非常重要,尤其是在涉及不同速率或格式转换的场景下。
三、使用实例
仅调整时间戳,不对数据包内的数据进行任何修改。
确保tb_src和tb_dst都是有效的AVRational结构体,避免除以零的错误。
在进行解复用、编码、解码或复用等操作前后,通常需要调用此函数来适配不同的时间基需求。
AVPacket pkt;
// 假设pkt是从某个输入流中获取的,已带有基于该流时间基的时间戳
AVRational in_timebase = (AVRational){1, 25}; // 假设输入时间基为25fps
AVRational out_timebase = (AVRational){1, 1000}; // 假设目标时间基为毫秒单位// 调整时间戳
av_packet_rescale_ts(&pkt, in_timebase, out_timebase);// 现在pkt的时间戳已转换为目标时间基,可以安全地用于输出或进一步处理
相关文章:

FFmpeg存放压缩后的音视频数据的结构体:AVPacket简介,结构体,函数
如下图的解码流程,AVPacket中的位置 FFmpeg源码中通过AVPacket存储压缩后的音视频数据。它通常由解复用器(demuxers)输出,然后作为输入传递给解码器。 或者从编码器作为输出接收,然后传递给多路复用器(mux…...

用接地气的例子趣谈 WWDC 24 全新的 Swift Testing 入门(三)
概述 从 WWDC 24 开始,苹果推出了全新的测试机制:Swift Testing。利用它我们可以大幅度简化之前“老态龙钟”的 XCTest 编码范式,并且使得单元测试更加灵动自由,更符合 Swift 语言的优雅品味。 在这里我们会和大家一起初涉并领略…...

#渗透测试#SRC漏洞挖掘#深入挖掘CSRF漏洞02
免责声明 本教程仅为合法的教学目的而准备,严禁用于任何形式的违法犯罪活动及其他商业行为,在使用本教程前,您应确保该行为符合当地的法律法规,继续阅读即表示您需自行承担所有操作的后果,如有异议,请立即停…...
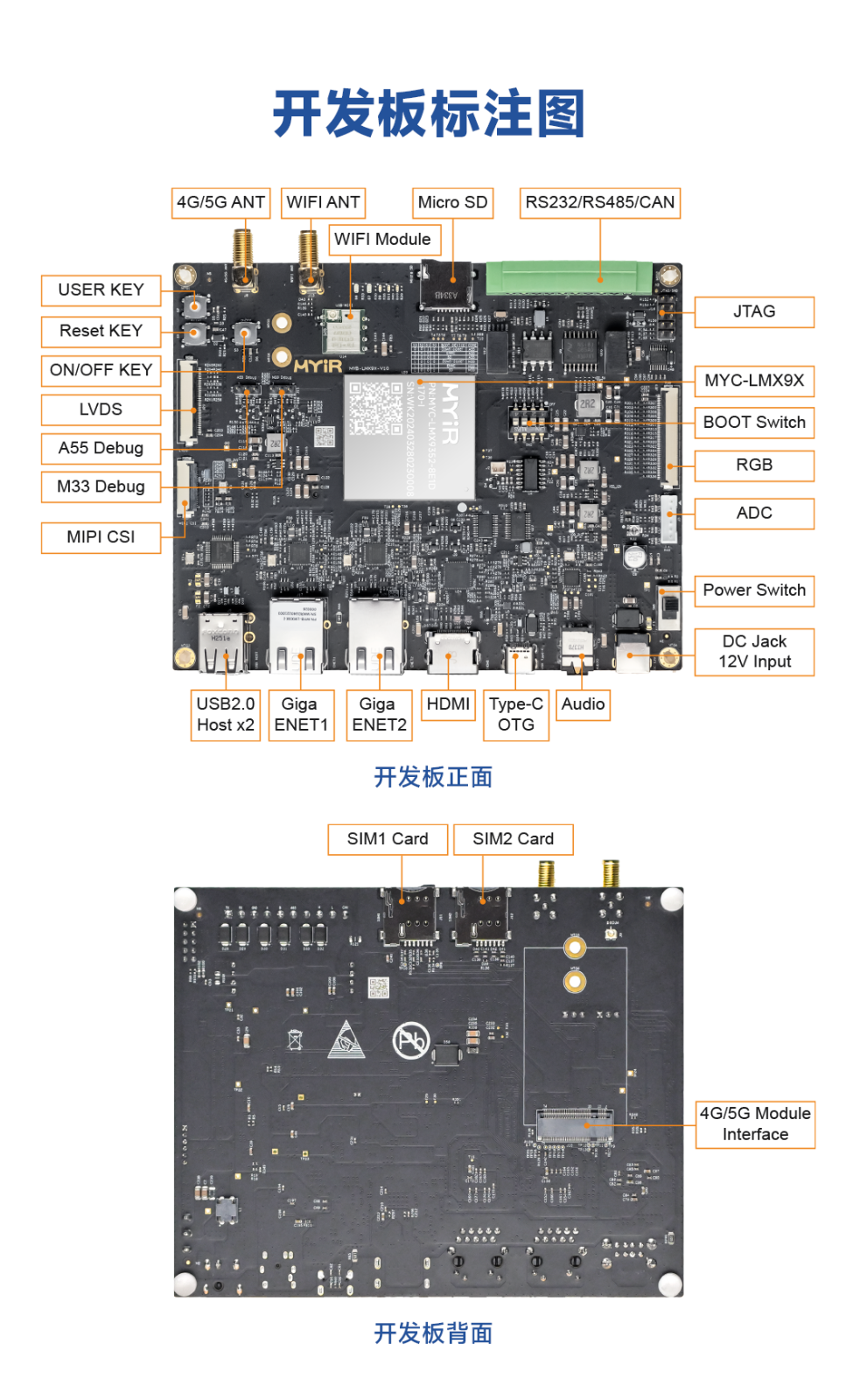
基于OpenCV的相机捕捉视频进行人脸检测--米尔NXP i.MX93开发板
本篇测评由优秀测评者“eefocus_3914144”提供。 本文将介绍基于米尔电子MYD-LMX93开发板(米尔基于NXP i.MX93开发板)的基于OpenCV的人脸检测方案测试。 OpenCV提供了一个非常简单的接口,用于相机捕捉一个视频(我用的电脑内置摄像头) 1、安…...

【Node-Red】使用文件或相机拍摄实现图像识别
使用相机拍照实现图像识别 首先需要下载节点 node-red-contrib-tfjs-coco-ssd,下载不上的朋友可以根据【Node-Red】最新版coco-ssd 1.0.6安装方法(windows)文章进行安装。 1、智能识别图片 使用本地文件的形式对图像进行识别 时间戳&…...

【Arcpy】提示需要深度学习框架代码
try:import torchimport arcgis相关库HAS_DEPS True except:HAS_DEPS Falsedef _raise_conda_import_error():arcpy.AddIDMessage("ERROR", 260005)exit(260005)if not HAS_DEPS:_raise_conda_import_error()...

【蓝桥杯 2021 省 B2】特殊年份
题目描述: 今年是 2021 年,2021 这个数字非常特殊, 它的千位和十位相等, 个位比百位大 1,我们称满足这样条件的年份为特殊年份。 输入 5 个年份,请计算这里面有多少个特殊年份。 输入格式 输入 5 行,每行一个 4 位十…...

【云原生开发】namespace管理的后端开发设计与实现
✨✨ 欢迎大家来到景天科技苑✨✨ 🎈🎈 养成好习惯,先赞后看哦~🎈🎈 🏆 作者简介:景天科技苑 🏆《头衔》:大厂架构师,华为云开发者社区专家博主,…...

威联通Docker Compose搭建NAS媒体库资源工具NAS Tools
文章目录 一、环境配置1-1 需要的配件1-2 环境安装及配置注意:获取PUID/PGID1-3 目录位置准备总结,这里我们要做5件事备注:Docker无法下载解决办法二、登录配件,进行配件连接和配置2-1 jackett设置2-2 qBittorrent设置!!!设置文件下载地址2-3 jellyfin设置2-4 NASTools设…...

【JAVA基础】MAVEN的安装及idea的引用说明
本篇文章主要讲解,maven的安装及集成在idea中进行构建项目的详细操作教程。 日期:2024年11月11日 作者:任聪聪 所需材料: 1、idea 2024版本及以上 2、maven 3.9.9安装包 3、一个空java springBoot项目,可以使用阿里云…...

【go从零单排】Rate Limiting限流
🌈Don’t worry , just coding! 内耗与overthinking只会削弱你的精力,虚度你的光阴,每天迈出一小步,回头时发现已经走了很远。 📗概念 在 Go 中,速率限制(Rate Limiting)是一种控制…...

解析Eureka的架构
1. 引言 1.1 Eureka的定义与背景 Eureka是由Netflix开发的一个RESTful服务,用于服务发现。它是微服务架构中的一个核心组件,主要用于管理服务的注册和发现。Eureka允许服务提供者注册自己的服务信息,同时也允许服务消费者查询可用的服务&am…...

AI变现,做数字游民
在数字化时代,AI技术的迅猛发展不仅改变了各行各业的生产方式,还为普通人提供了前所未有的变现机会。本文将探讨如何利用AI技术实现变现,成为一名数字游民,享受自由职业带来的便利与乐趣。 一、AI技术的变现潜力 AI技术以其强大…...

linux-vlan
# VLAN # 1.topo # 2.创建命名空间 ip netns add ns1 ip netns add ns2 ip netns add ns3 # 3.创建veth设备 ip link add ns1-veth0 type veth peer name ns21-veth0 ip link add ns3-veth0 type veth peer name ns23-veth0 # 4.veth设备放入命名空间,启动接口 ip link set n…...

前端跨域~简述
前言 :绿蚁新醅酒,红泥小火炉 第一:前端跨域(粗谈概念) 1. 疑惑 当前端请求后端接口不通,浏览器控制台出现类似信息,则需要解决跨域 Access to XMLHttpRequest at ‘http://47.100.214.160:10…...

GIN:逼近WL-test的GNN架构
Introduction 在 图卷积网络GCN 中我们已经知道图神经网络在结点分类等任务上的作用,但GIN(图同构神经网络)给出了一个对于图嵌入(graph embedding)更强的公式。 GIN,图同构神经网络,致力于解…...

NIST密码学未来展望:Naughty Step 上的 SHA-1、3DES 和 SHA-224
1. 引言 NIST 几十年来一直致力于推动密码学标准的发展,2024年10月,其发布了Transitioning the Use of Cryptographic Algorithms and Key Lengths 草案: 概述了 SHA-1(为160位哈希算法) 将在不久的将来退役…...

go 集成gorm 数据库操作
一、什么是gorm GORM 是一个用于 Go 语言的 ORM(对象关系映射)库,它提供了一种简单而强大的方式来与数据库进行交互。GORM 支持多种数据库,包括 MySQL、PostgreSQL、SQLite、SQL Server 等,并且提供了丰富的功能&…...

进程 线程 和go协程的区别
进程和线程是操作系统中两个重要的执行单元,理解它们的区别对于编程和系统设计非常重要。以下是它们的主要区别: ### 进程(Process) 定义:进程是一个正在执行的程序的实例,具有独立的地址空间。 资源&…...

STM32获取SHT3X温湿度芯片数据
目录 一、概述 二、单次数据采集模式的测量 1、配置说明 2、代码实现方式 三、周期性数据采集模式的测量 1、配置说明 2、代码实现方式 四、完整代码下载链接 一、概述 SHT3X是Sensirion公司推出的一款高精度、完全校准的温湿度传感器,基于CMOSens技术。它提…...

【大模型RAG】拍照搜题技术架构速览:三层管道、两级检索、兜底大模型
摘要 拍照搜题系统采用“三层管道(多模态 OCR → 语义检索 → 答案渲染)、两级检索(倒排 BM25 向量 HNSW)并以大语言模型兜底”的整体框架: 多模态 OCR 层 将题目图片经过超分、去噪、倾斜校正后,分别用…...

<6>-MySQL表的增删查改
目录 一,create(创建表) 二,retrieve(查询表) 1,select列 2,where条件 三,update(更新表) 四,delete(删除表…...
)
Java 语言特性(面试系列1)
一、面向对象编程 1. 封装(Encapsulation) 定义:将数据(属性)和操作数据的方法绑定在一起,通过访问控制符(private、protected、public)隐藏内部实现细节。示例: public …...
练习(含atoi的模拟实现,自定义类型等练习)
一、结构体大小的计算及位段 (结构体大小计算及位段 详解请看:自定义类型:结构体进阶-CSDN博客) 1.在32位系统环境,编译选项为4字节对齐,那么sizeof(A)和sizeof(B)是多少? #pragma pack(4)st…...
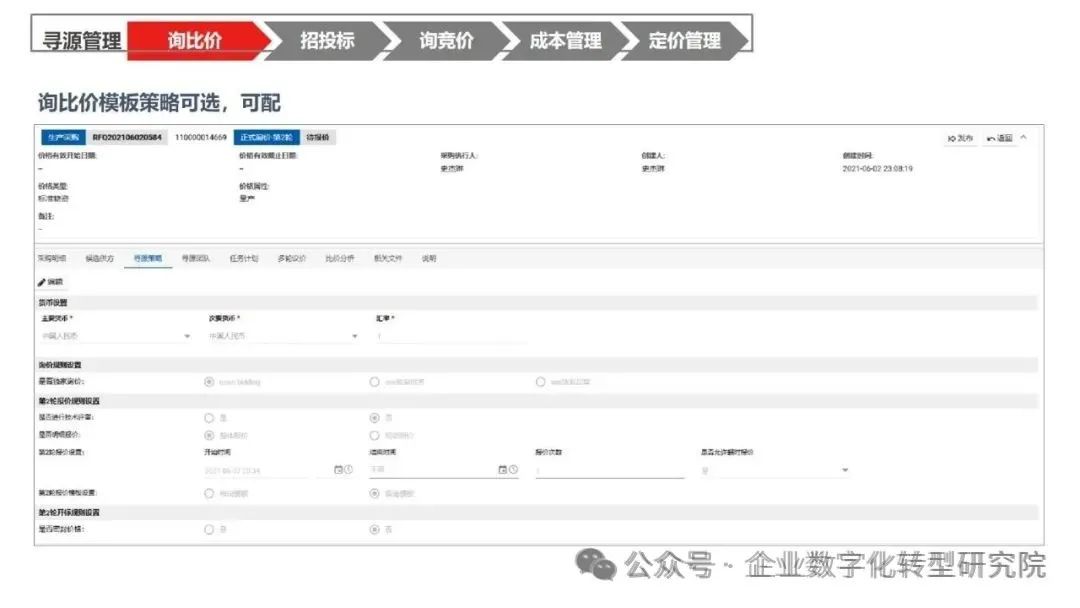
PPT|230页| 制造集团企业供应链端到端的数字化解决方案:从需求到结算的全链路业务闭环构建
制造业采购供应链管理是企业运营的核心环节,供应链协同管理在供应链上下游企业之间建立紧密的合作关系,通过信息共享、资源整合、业务协同等方式,实现供应链的全面管理和优化,提高供应链的效率和透明度,降低供应链的成…...

【SpringBoot】100、SpringBoot中使用自定义注解+AOP实现参数自动解密
在实际项目中,用户注册、登录、修改密码等操作,都涉及到参数传输安全问题。所以我们需要在前端对账户、密码等敏感信息加密传输,在后端接收到数据后能自动解密。 1、引入依赖 <dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId...
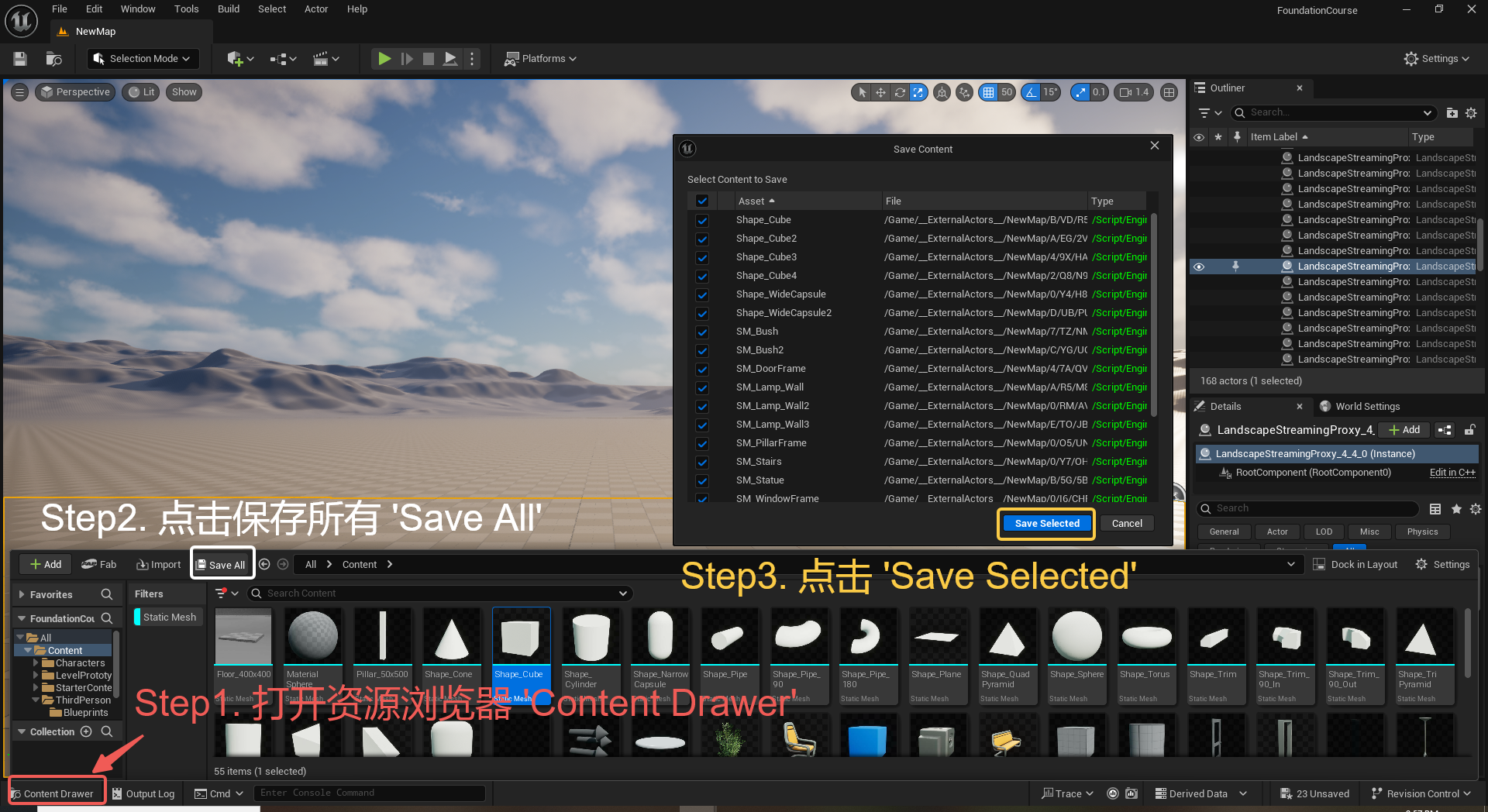
UE5 学习系列(三)创建和移动物体
这篇博客是该系列的第三篇,是在之前两篇博客的基础上展开,主要介绍如何在操作界面中创建和拖动物体,这篇博客跟随的视频链接如下: B 站视频:s03-创建和移动物体 如果你不打算开之前的博客并且对UE5 比较熟的话按照以…...
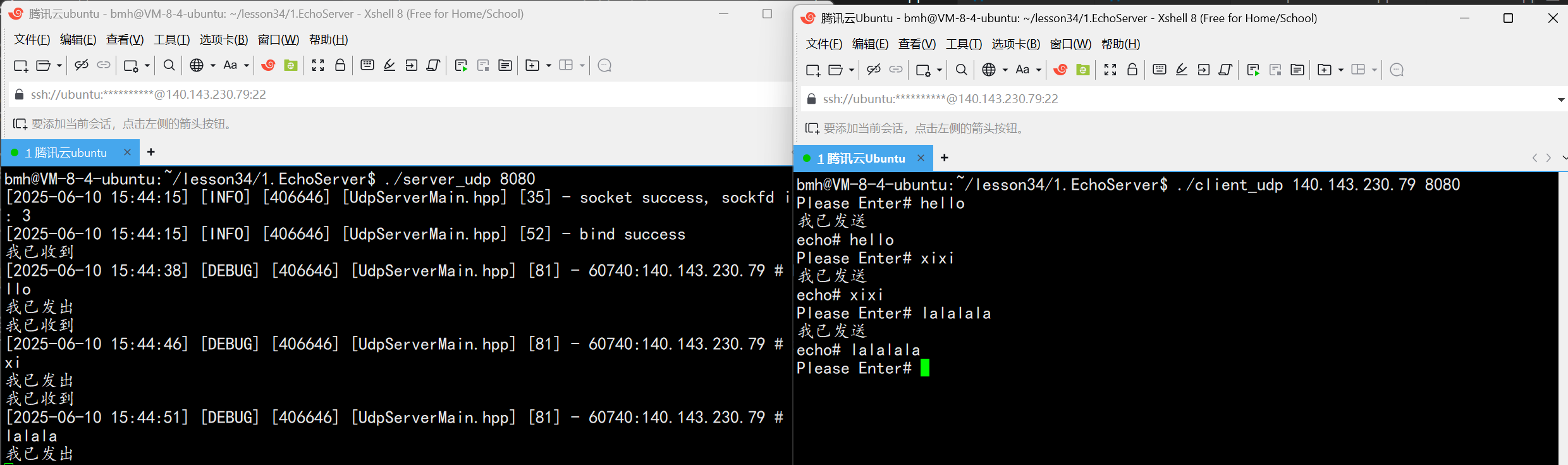
UDP(Echoserver)
网络命令 Ping 命令 检测网络是否连通 使用方法: ping -c 次数 网址ping -c 3 www.baidu.comnetstat 命令 netstat 是一个用来查看网络状态的重要工具. 语法:netstat [选项] 功能:查看网络状态 常用选项: n 拒绝显示别名&#…...

Java - Mysql数据类型对应
Mysql数据类型java数据类型备注整型INT/INTEGERint / java.lang.Integer–BIGINTlong/java.lang.Long–––浮点型FLOATfloat/java.lang.FloatDOUBLEdouble/java.lang.Double–DECIMAL/NUMERICjava.math.BigDecimal字符串型CHARjava.lang.String固定长度字符串VARCHARjava.lang…...

[10-3]软件I2C读写MPU6050 江协科技学习笔记(16个知识点)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16...
