移植LVGL8.2以及移植过程的理解
一、LVGL刷新显示(画点 OR 区域刷新颜色)
原来LCD的区域填充,由于没用到DMA就是普通的遍历区域块的坐标,需要传入的坐标就是显示区域的x轴起始与x轴尾部。y轴的起始与y轴的尾部。
怎么实现呢?
SPI不加DMA实现区域填充
首先确定要填充的y轴地址 确定y轴 ,然后在x轴起始位置向spi接口里连续写字节,这时候不用去变寄存器的地址,因为它会自增的。x轴的一行写完了,再写y的下一个像素行。
/******************************************************************************函数说明:在指定区域填充颜色入口数据:xsta,ysta 起始坐标xend,yend 终止坐标color 要填充的颜色返回值: 无
******************************************************************************/
void LCD_Fill(u16 xsta,u16 ysta,u16 xend,u16 yend,u16 color)
{ u16 i,j; LCD_Address_Set(xsta+OFFSET_X,ysta+OFFSET_Y,xend+OFFSET_X-1,yend-1+OFFSET_Y);//设置显示范围for(i=ysta;i<yend;i++){ for(j=xsta;j<xend;j++){LCD_WR_DATA(color);}}
}|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||在LVGL里为了加快数据的传输,启用SPI发送的DMA功能
SPI加DMA实现快速填充
/******************************************************************************函数说明:在指定区域填充颜色入口数据:xsta,ysta 起始坐标xend,yend 终止坐标color 要填充的颜色返回值: 无
******************************************************************************/
void LCD_Color_Fill(u16 xsta,u16 ysta,u16 xend,u16 yend,u16 *color_p)
{u16 width,height; width = xend-xsta+1;height = yend-ysta+1;uint32_t size = width * height;LCD_Address_Set(xsta,ysta+OFFSET_Y,xend,yend+OFFSET_Y);hspi1.Init.DataSize = SPI_DATASIZE_16BIT;//切换成16位hspi1.Instance->CR1|=SPI_CR1_DFF;//切换成16位HAL_SPI_Transmit_DMA(&hspi1,(uint8_t*)color_p,size);//启动DMA传输while(__HAL_DMA_GET_COUNTER(&hdma_spi1_tx)!=0);//没传输完毕就不退出whilehspi1.Init.DataSize = SPI_DATASIZE_8BIT;//切换回8位模式hspi1.Instance->CR1&=~SPI_CR1_DFF;//切换回8位模式}为什么宽或高是end-sta+1 数数 1~3有几个数就知道了 1 2 3 !=3-1
至于为什么采用半字的形式传输 也就是16位 我记得正点原子的LCD驱动芯片好像也是ST7789
这里涉及一个像素565 红绿蓝的问题 刚好组合为16位
然后就是开启SPI DMA传输的函数
HAL_SPI_Transmit_DMA(&hspi1,(uint8_t*)color_p,size);通过 SPI 使用 DMA 方式传输颜色数据到 LCD。这里将指向颜色数据的指针color_p转换为uint8_t*类型,因为 DMA 通常以字节为单位传输数据。参数size指定了要传输的字节数 这是AI的解释,我认为不完全正确

在SPI的驱动里,我们设置了DMA是半字传输方式。但是这里强转成8位是让我摸不到头脑的。地址先不管它了,我理解的是8位指针自增 它就加1个字节,16位自增加2个字节。看来它们并不是完全相关,可能用了什么手法吧。反正传入的是起始地址,在32位中指针大小就为4个字节。强转成8位还是4个字节。
LVGL原文件里的填充函数
/*Flush the content of the internal buffer the specific area on the display*You can use DMA or any hardware acceleration to do this operation in the background but*'lv_disp_flush_ready()' has to be called when finished.*/
static void disp_flush(lv_disp_drv_t * disp_drv, const lv_area_t * area, lv_color_t * color_p)
{/*The most simple case (but also the slowest) to put all pixels to the screen one-by-one*/int32_t x;int32_t y;for(y = area->y1; y <= area->y2; y++) {for(x = area->x1; x <= area->x2; x++) {/*Put a pixel to the display. For example:*//*put_px(x, y, *color_p)*/color_p++;}}/*IMPORTANT!!!*Inform the graphics library that you are ready with the flushing*/lv_disp_flush_ready(disp_drv);
}我们可以看到 LVGL的移植 这就是需要1个画点函数 ,在某个像素16位 进行上色(发送2个字节数据)
画点函数的实现
/******************************************************************************函数说明:在指定位置画点入口数据:x,y 画点坐标color 点的颜色返回值: 无
******************************************************************************/
void LCD_DrawPoint(u16 x,u16 y,u16 color)
{LCD_Address_Set(x,y,x,y);//设置光标位置 LCD_WR_DATA(color);
} 但是这样就慢了啊, 如果我们是对区域操作,可以节省很多时间。画点得不停的换寄存器地址
而这种设置一个区域,再向里面填充会大大提高刷新的速率。

于是我们在LVGL的绑定函数disp(移植的时候需要把template注释掉)里要这么改
//开启DMA以加速数据传输
static void disp_flush(lv_disp_drv_t * disp_drv, const lv_area_t * area, lv_color_t * color_p)
{/*The most simple case (but also the slowest) to put all pixels to the screen one-by-one*/LCD_Color_Fill(area->x1,area->y1,area->x2,area->y2,(u16*)color_p);/*IMPORTANT!!!*Inform the graphics library that you are ready with the flushing*/lv_disp_flush_ready(disp_drv);
}二、LVGL的端口显示初始化
1 首先他告诉我们要初始化我们的显示器 ,当然我们是在LCD里进行初始化。这里就空着
2 接着创建一个内存空间用于画画
他给了很大一段注释
/**
* LVGL 需要一个缓冲区,它在内部在此绘制小部件。
* 稍后,这个缓冲区将传递给你的显示驱动程序的`flush_cb`,以将其内容复制到你的显示器上。
* 缓冲区必须大于 1 个显示行。
* 有三种缓冲配置:
* 1. 创建一个缓冲区:
* LVGL 将在此绘制显示器的内容并将其写入你的显示器。
*
* 2. 创建两个缓冲区:
* LVGL 将显示器的内容绘制到一个缓冲区并写入你的显示器。
* 你应该使用 DMA 将缓冲区的内容写入显示器。
* 这将使 LVGL 在从第一个缓冲区发送数据时能够将屏幕的下一部分绘制到另一个缓冲区。这使得渲染和刷新并行进行。
*
* 3. 双缓冲
* 设置两个屏幕大小的缓冲区,并设置 disp_drv.full_refresh = 1。
* 这样,LVGL 将始终在`flush_cb`中提供整个渲染后的屏幕,
* 而你只需要更改帧缓冲区的地址。
*/
void lv_port_disp_init(void)
{/*-------------------------* Initialize your display* -----------------------*/disp_init();/*-----------------------------* Create a buffer for drawing*----------------------------*//*** LVGL requires a buffer where it internally draws the widgets.* Later this buffer will passed to your display driver's `flush_cb` to copy its content to your display.* The buffer has to be greater than 1 display row** There are 3 buffering configurations:* 1. Create ONE buffer:* LVGL will draw the display's content here and writes it to your display** 2. Create TWO buffer:* LVGL will draw the display's content to a buffer and writes it your display.* You should use DMA to write the buffer's content to the display.* It will enable LVGL to draw the next part of the screen to the other buffer while* the data is being sent form the first buffer. It makes rendering and flushing parallel.** 3. Double buffering* Set 2 screens sized buffers and set disp_drv.full_refresh = 1.* This way LVGL will always provide the whole rendered screen in `flush_cb`* and you only need to change the frame buffer's address.*//* Example for 1) */static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_1;static lv_color_t buf_1[MY_DISP_HOR_RES * 10]; /*A buffer for 10 rows*/lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_1, buf_1, NULL, MY_DISP_HOR_RES * 10); /*Initialize the display buffer*//* Example for 2) */static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_2;static lv_color_t buf_2_1[MY_DISP_HOR_RES * 10]; /*A buffer for 10 rows*/static lv_color_t buf_2_2[MY_DISP_HOR_RES * 10]; /*An other buffer for 10 rows*/lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_2, buf_2_1, buf_2_2, MY_DISP_HOR_RES * 10); /*Initialize the display buffer*//* Example for 3) also set disp_drv.full_refresh = 1 below*/static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_3;static lv_color_t buf_3_1[MY_DISP_HOR_RES * MY_DISP_VER_RES]; /*A screen sized buffer*/static lv_color_t buf_3_2[MY_DISP_HOR_RES * MY_DISP_VER_RES]; /*Another screen sized buffer*/lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_3, buf_3_1, buf_3_2, MY_DISP_VER_RES * LV_VER_RES_MAX); /*Initialize the display buffer*//*-----------------------------------* Register the display in LVGL*----------------------------------*/static lv_disp_drv_t disp_drv; /*Descriptor of a display driver*/lv_disp_drv_init(&disp_drv); /*Basic initialization*//*Set up the functions to access to your display*//*Set the resolution of the display*/disp_drv.hor_res = 480;disp_drv.ver_res = 320;/*Used to copy the buffer's content to the display*/disp_drv.flush_cb = disp_flush;/*Set a display buffer*/disp_drv.draw_buf = &draw_buf_dsc_1;/*Required for Example 3)*///disp_drv.full_refresh = 1/* Fill a memory array with a color if you have GPU.* Note that, in lv_conf.h you can enable GPUs that has built-in support in LVGL.* But if you have a different GPU you can use with this callback.*///disp_drv.gpu_fill_cb = gpu_fill;/*Finally register the driver*/lv_disp_drv_register(&disp_drv);
}这里他给出了三种模式,我们采取第2种,我觉得就是1个备胎,1个正主,俩人轮流当备胎。一个DMA还在搬运的时候,另一个Buffer已经填充了。当这个搬运完就该搬运下一个了。
2.1 首先把他提供的实例初始化了
/*Used to copy the buffer's content to the display*/disp_drv.flush_cb = disp_flush;static lv_disp_drv_t disp_drv; /*Descriptor of a display driver*/lv_disp_drv_init(&disp_drv); /*Basic initialization*/我们在配置IO属性的时候都是把成员全部初始化之后才回去初始化整个实例。这有些不太一样,先初始化实例,再逐个成员进行修改。
2.2 设置函数去获取你的显示器,没太懂什么意思
2.3 设置显示器分辨率
disp_drv.hor_res = LCD_W;disp_drv.ver_res = LCD_H;2.4 用于将缓冲区的内容复制到显示器
/*Used to copy the buffer's content to the display*/disp_drv.flush_cb = disp_flush;2.5 设置一个显示缓冲区
这里利用宏进行条件编译 使用的是模式2 两个Buff缓冲区 每个大小为 整个屏幕的十分之一。当然最小不要小于一行像素的大小
#define BUFFER_METHOD 2 //他这里缓冲区大小是整个分辨率大小除10
#if BUFFER_METHOD == 1/* Example for 1) */static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_1;static lv_color_t buf_1[LCD_W * LCD_H / 10]; /*A buffer for 10 rows*/lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_1, buf_1, NULL, LCD_W * LCD_H / 10); /*Initialize the display buffer*//*Set a display buffer*/disp_drv.draw_buf = &draw_buf_dsc_1;
#elif BUFFER_METHOD == 2/* Example for 2) */static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_2;static lv_color_t buf_2_1[LCD_W * LCD_H / 10]; /*A buffer for 10 rows*/static lv_color_t buf_2_2[LCD_W * LCD_H / 10]; /*An other buffer for 10 rows*/lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_2, buf_2_1, buf_2_2, LCD_W * LCD_H / 10); /*Initialize the display buffer*//*Set a display buffer*/disp_drv.draw_buf = &draw_buf_dsc_2;
#elif BUFFER_METHOD == 3/* Example for 3) also set disp_drv.full_refresh = 1 below*/static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_3;static lv_color_t buf_3_1[LCD_W * LCD_H]; /*A screen sized buffer*/static lv_color_t buf_3_2[LCD_W * LCD_H]; /*An other screen sized buffer*/lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_3, buf_3_1, buf_3_2, LCD_W * LCD_H); /*Initialize the display buffer*//*Required for Example 3)*/disp_drv.full_refresh = 1;/*Set a display buffer*/disp_drv.draw_buf = &draw_buf_dsc_3;
#endif // 0这里的两个静态定义不太懂啊,我们去定义看看
2.5.1 lv_disp_draw_buf_t

这个是个结构体的别名 用于保存显示缓冲区信息的结构。
static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_2;static lv_color_t buf_2_1[LCD_W * LCD_H / 10]; /*A buffer for 10 rows*/static lv_color_t buf_2_2[LCD_W * LCD_H / 10]; /*An other buffer for 10 rows*/lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_2, buf_2_1, buf_2_2, LCD_W * LCD_H / 10); /*Initialize the display buffer*/最后通过初始化函数将这个实例初始化了,参数一结构体地址,参数二buff1,参数三buff2,参数4
估计是1个buff的像素个数
/*** Initialize a display buffer* @param draw_buf pointer `lv_disp_draw_buf_t` variable to initialize* @param buf1 A buffer to be used by LVGL to draw the image.* Always has to specified and can't be NULL.* Can be an array allocated by the user. E.g. `static lv_color_t disp_buf1[1024 * 10]`* Or a memory address e.g. in external SRAM* @param buf2 Optionally specify a second buffer to make image rendering and image flushing* (sending to the display) parallel.* In the `disp_drv->flush` you should use DMA or similar hardware to send* the image to the display in the background.* It lets LVGL to render next frame into the other buffer while previous is being* sent. Set to `NULL` if unused.* @param size_in_px_cnt size of the `buf1` and `buf2` in pixel count.*/
void lv_disp_draw_buf_init(lv_disp_draw_buf_t * draw_buf, void * buf1, void * buf2, uint32_t size_in_px_cnt)
{lv_memset_00(draw_buf, sizeof(lv_disp_draw_buf_t));draw_buf->buf1 = buf1;draw_buf->buf2 = buf2;draw_buf->buf_act = draw_buf->buf1;draw_buf->size = size_in_px_cnt;
}
2.5.2 lv_color_t
typedef LV_CONCAT3(lv_color, LV_COLOR_DEPTH, _t) lv_color_t;![]()
x ## y ## z:这是宏的具体实现。在 C 和 C++ 中,##是预处理器的连接运算符。它将前后的两个标记(token)连接成一个新的标记。这里的作用是将参数 x、y 和 z 连接在一起。
结果就是 将这三个参数 lv_colorLV_COLOR_DEPTH _t

我们找到 #define LV_COLOR_DEPTH 16 宏定义
于是就有 lv_color16 _t
然后我们找到这是个内联函数

#elif LV_COLOR_DEPTH == 16return color.full;这个名为lv_color_to16的函数是一个内联函数,用于将输入的lv_color_t类型的颜色值转换为 16 位颜色值。 然后我们用这个lv_color_t定义的变量 如果是1,8,等等都被转换成16位的。
当LV_COLOR_DEPTH为 16 时:直接返回输入颜色的full成员,因为输入颜色已经是 16 位深度,无需进行转换。
2.6 如果你的芯片支持GPU的话
/* Fill a memory array with a color if you have GPU.* Note that, in lv_conf.h you can enable GPUs that has built-in support in LVGL.* But if you have a different GPU you can use with this callback.*///disp_drv.gpu_fill_cb = gpu_fill;2.7 最后注册这个驱动
/*Finally register the driver*/lv_disp_drv_register(&disp_drv);整个流程下来,这个显示函数的内容就这么多,按照注释也可以一步步操作,下面给出整个C文件
lv_port_disp.c
/*** @file lv_port_disp_templ.c**///这段代码是用于将 LVGL(Light and Versatile Graphics Library)//图形库与特定的显示设备进行适配的初始化代码。它主要完成了显示设备的初始化、//为 LVGL 创建用于绘图的缓冲区、设置将缓冲区内容刷新到显示设备的函数//以及将显示驱动注册到 LVGL 等一系列操作,
// 以便能够在该显示设备上正确地显示 LVGL 绘制的图形界面。
//把像素分辨率、画点函数和申请的内存大小填充就ok了/*Copy this file as "lv_port_disp.c" and set this value to "1" to enable content*/
#if 1/********************** INCLUDES*********************/
#include "lv_port_disp.h"
#include "lvgl.h"#include "lcd.h"
#include "lcd_init.h"/********************** DEFINES*********************//*********************** TYPEDEFS**********************//*********************** STATIC PROTOTYPES**********************/
static void disp_init(void);static void disp_flush(lv_disp_drv_t * disp_drv, const lv_area_t * area, lv_color_t * color_p);
//static void gpu_fill(lv_disp_drv_t * disp_drv, lv_color_t * dest_buf, lv_coord_t dest_width,
// const lv_area_t * fill_area, lv_color_t color);/*********************** STATIC VARIABLES**********************//*********************** MACROS**********************//*********************** GLOBAL FUNCTIONS**********************/void lv_port_disp_init(void)
{/*-------------------------* Initialize your display* -----------------------*/// 这里进行你的屏幕初始化disp_init();/*-----------------------------* Create a buffer for drawing*----------------------------*//*** LVGL requires a buffer where it internally draws the widgets.* Later this buffer will passed to your display driver's `flush_cb` to copy its content to your display.* The buffer has to be greater than 1 display row** There are 3 buffering configurations:* 1. Create ONE buffer:* LVGL will draw the display's content here and writes it to your display** 2. Create TWO buffer:* LVGL will draw the display's content to a buffer and writes it your display.* You should use DMA to write the buffer's content to the display.* It will enable LVGL to draw the next part of the screen to the other buffer while* the data is being sent form the first buffer. It makes rendering and flushing parallel.** 3. Double buffering* Set 2 screens sized buffers and set disp_drv.full_refresh = 1.* This way LVGL will always provide the whole rendered screen in `flush_cb`* and you only need to change the frame buffer's address.*/static lv_disp_drv_t disp_drv; /*Descriptor of a display driver*/lv_disp_drv_init(&disp_drv); /*Basic initialization*//*Set up the functions to access to your display*//*Set the resolution of the display*/disp_drv.hor_res = LCD_W;disp_drv.ver_res = LCD_H;/*Used to copy the buffer's content to the display*/// disp_flush的函数实现看下面disp_drv.flush_cb = disp_flush;// 这里是LVGL画面渲染所使用的缓存空间分配,总共有三种方式// 你也可以改为malloc分配空间
#define BUFFER_METHOD 2 //他这里缓冲区大小是整个分辨率大小除10
#if BUFFER_METHOD == 1/* Example for 1) */static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_1;static lv_color_t buf_1[LCD_W * LCD_H / 10]; /*A buffer for 10 rows*/lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_1, buf_1, NULL, LCD_W * LCD_H / 10); /*Initialize the display buffer*//*Set a display buffer*/disp_drv.draw_buf = &draw_buf_dsc_1;
#elif BUFFER_METHOD == 2/* Example for 2) */static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_2;static lv_color_t buf_2_1[LCD_W * LCD_H / 10]; /*A buffer for 10 rows*/static lv_color_t buf_2_2[LCD_W * LCD_H / 10]; /*An other buffer for 10 rows*/lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_2, buf_2_1, buf_2_2, LCD_W * LCD_H / 10); /*Initialize the display buffer*//*Set a display buffer*/disp_drv.draw_buf = &draw_buf_dsc_2;
#elif BUFFER_METHOD == 3/* Example for 3) also set disp_drv.full_refresh = 1 below*/static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_3;static lv_color_t buf_3_1[LCD_W * LCD_H]; /*A screen sized buffer*/static lv_color_t buf_3_2[LCD_W * LCD_H]; /*An other screen sized buffer*/lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_3, buf_3_1, buf_3_2, LCD_W * LCD_H); /*Initialize the display buffer*//*Required for Example 3)*/disp_drv.full_refresh = 1;/*Set a display buffer*/disp_drv.draw_buf = &draw_buf_dsc_3;
#endif // 0/*-----------------------------------* Register the display in LVGL*----------------------------------*//* Fill a memory array with a color if you have GPU.* Note that, in lv_conf.h you can enable GPUs that has built-in support in LVGL.* But if you have a different GPU you can use with this callback.*///disp_drv.gpu_fill_cb = gpu_fill;/*Finally register the driver*/lv_disp_drv_register(&disp_drv);
}/*********************** STATIC FUNCTIONS**********************//*Initialize your display and the required peripherals.*/
static void disp_init(void)
{/*You code here*/
}/*Flush the content of the internal buffer the specific area on the display*You can use DMA or any hardware acceleration to do this operation in the background but*'lv_disp_flush_ready()' has to be called when finished.*/
//开启DMA以加速数据传输
static void disp_flush(lv_disp_drv_t * disp_drv, const lv_area_t * area, lv_color_t * color_p)
{/*The most simple case (but also the slowest) to put all pixels to the screen one-by-one*/LCD_Color_Fill(area->x1,area->y1,area->x2,area->y2,(u16*)color_p);/*IMPORTANT!!!*Inform the graphics library that you are ready with the flushing*/lv_disp_flush_ready(disp_drv);
}/*OPTIONAL: GPU INTERFACE*//*If your MCU has hardware accelerator (GPU) then you can use it to fill a memory with a color*/
//static void gpu_fill(lv_disp_drv_t * disp_drv, lv_color_t * dest_buf, lv_coord_t dest_width,
// const lv_area_t * fill_area, lv_color_t color)
//{
// /*It's an example code which should be done by your GPU*/
// int32_t x, y;
// dest_buf += dest_width * fill_area->y1; /*Go to the first line*/
//
// for(y = fill_area->y1; y <= fill_area->y2; y++) {
// for(x = fill_area->x1; x <= fill_area->x2; x++) {
// dest_buf[x] = color;
// }
// dest_buf+=dest_width; /*Go to the next line*/
// }
//}#else /*Enable this file at the top*//*This dummy typedef exists purely to silence -Wpedantic.*/
typedef int keep_pedantic_happy;
#endif
三、图形库与触摸输入设备(这里具体是 CST816 触摸屏)进行适配
源文件
/*** @file lv_port_indev_templ.c**//*Copy this file as "lv_port_indev.c" and set this value to "1" to enable content*/
#if 0/********************** INCLUDES*********************/
#include "lv_port_indev_template.h"
#include "../../lvgl.h"/********************** DEFINES*********************//*********************** TYPEDEFS**********************//*********************** STATIC PROTOTYPES**********************/static void touchpad_init(void);
static void touchpad_read(lv_indev_drv_t * indev_drv, lv_indev_data_t * data);
static bool touchpad_is_pressed(void);
static void touchpad_get_xy(lv_coord_t * x, lv_coord_t * y);static void mouse_init(void);
static void mouse_read(lv_indev_drv_t * indev_drv, lv_indev_data_t * data);
static bool mouse_is_pressed(void);
static void mouse_get_xy(lv_coord_t * x, lv_coord_t * y);static void keypad_init(void);
static void keypad_read(lv_indev_drv_t * indev_drv, lv_indev_data_t * data);
static uint32_t keypad_get_key(void);static void encoder_init(void);
static void encoder_read(lv_indev_drv_t * indev_drv, lv_indev_data_t * data);
static void encoder_handler(void);static void button_init(void);
static void button_read(lv_indev_drv_t * indev_drv, lv_indev_data_t * data);
static int8_t button_get_pressed_id(void);
static bool button_is_pressed(uint8_t id);/*********************** STATIC VARIABLES**********************/
lv_indev_t * indev_touchpad;
lv_indev_t * indev_mouse;
lv_indev_t * indev_keypad;
lv_indev_t * indev_encoder;
lv_indev_t * indev_button;static int32_t encoder_diff;
static lv_indev_state_t encoder_state;/*********************** MACROS**********************//*********************** GLOBAL FUNCTIONS**********************/void lv_port_indev_init(void)
{/*** Here you will find example implementation of input devices supported by LittelvGL:* - Touchpad* - Mouse (with cursor support)* - Keypad (supports GUI usage only with key)* - Encoder (supports GUI usage only with: left, right, push)* - Button (external buttons to press points on the screen)** The `..._read()` function are only examples.* You should shape them according to your hardware*/static lv_indev_drv_t indev_drv;/*------------------* Touchpad* -----------------*//*Initialize your touchpad if you have*/touchpad_init();/*Register a touchpad input device*/lv_indev_drv_init(&indev_drv);indev_drv.type = LV_INDEV_TYPE_POINTER;indev_drv.read_cb = touchpad_read;indev_touchpad = lv_indev_drv_register(&indev_drv);/*------------------* Mouse* -----------------*//*Initialize your mouse if you have*/mouse_init();/*Register a mouse input device*/lv_indev_drv_init(&indev_drv);indev_drv.type = LV_INDEV_TYPE_POINTER;indev_drv.read_cb = mouse_read;indev_mouse = lv_indev_drv_register(&indev_drv);/*Set cursor. For simplicity set a HOME symbol now.*/lv_obj_t * mouse_cursor = lv_img_create(lv_scr_act());lv_img_set_src(mouse_cursor, LV_SYMBOL_HOME);lv_indev_set_cursor(indev_mouse, mouse_cursor);/*------------------* Keypad* -----------------*//*Initialize your keypad or keyboard if you have*/keypad_init();/*Register a keypad input device*/lv_indev_drv_init(&indev_drv);indev_drv.type = LV_INDEV_TYPE_KEYPAD;indev_drv.read_cb = keypad_read;indev_keypad = lv_indev_drv_register(&indev_drv);/*Later you should create group(s) with `lv_group_t * group = lv_group_create()`,*add objects to the group with `lv_group_add_obj(group, obj)`*and assign this input device to group to navigate in it:*`lv_indev_set_group(indev_keypad, group);`*//*------------------* Encoder* -----------------*//*Initialize your encoder if you have*/encoder_init();/*Register a encoder input device*/lv_indev_drv_init(&indev_drv);indev_drv.type = LV_INDEV_TYPE_ENCODER;indev_drv.read_cb = encoder_read;indev_encoder = lv_indev_drv_register(&indev_drv);/*Later you should create group(s) with `lv_group_t * group = lv_group_create()`,*add objects to the group with `lv_group_add_obj(group, obj)`*and assign this input device to group to navigate in it:*`lv_indev_set_group(indev_encoder, group);`*//*------------------* Button* -----------------*//*Initialize your button if you have*/button_init();/*Register a button input device*/lv_indev_drv_init(&indev_drv);indev_drv.type = LV_INDEV_TYPE_BUTTON;indev_drv.read_cb = button_read;indev_button = lv_indev_drv_register(&indev_drv);/*Assign buttons to points on the screen*/static const lv_point_t btn_points[2] = {{10, 10}, /*Button 0 -> x:10; y:10*/{40, 100}, /*Button 1 -> x:40; y:100*/};lv_indev_set_button_points(indev_button, btn_points);
}/*********************** STATIC FUNCTIONS**********************//*------------------* Touchpad* -----------------*//*Initialize your touchpad*/
static void touchpad_init(void)
{/*Your code comes here*/
}/*Will be called by the library to read the touchpad*/
static void touchpad_read(lv_indev_drv_t * indev_drv, lv_indev_data_t * data)
{static lv_coord_t last_x = 0;static lv_coord_t last_y = 0;/*Save the pressed coordinates and the state*/if(touchpad_is_pressed()) {touchpad_get_xy(&last_x, &last_y);data->state = LV_INDEV_STATE_PR;} else {data->state = LV_INDEV_STATE_REL;}/*Set the last pressed coordinates*/data->point.x = last_x;data->point.y = last_y;
}/*Return true is the touchpad is pressed*/
static bool touchpad_is_pressed(void)
{/*Your code comes here*/return false;
}/*Get the x and y coordinates if the touchpad is pressed*/
static void touchpad_get_xy(lv_coord_t * x, lv_coord_t * y)
{/*Your code comes here*/(*x) = 0;(*y) = 0;
}/*------------------* Mouse* -----------------*//*Initialize your mouse*/
static void mouse_init(void)
{/*Your code comes here*/
}/*Will be called by the library to read the mouse*/
static void mouse_read(lv_indev_drv_t * indev_drv, lv_indev_data_t * data)
{/*Get the current x and y coordinates*/mouse_get_xy(&data->point.x, &data->point.y);/*Get whether the mouse button is pressed or released*/if(mouse_is_pressed()) {data->state = LV_INDEV_STATE_PR;} else {data->state = LV_INDEV_STATE_REL;}
}/*Return true is the mouse button is pressed*/
static bool mouse_is_pressed(void)
{/*Your code comes here*/return false;
}/*Get the x and y coordinates if the mouse is pressed*/
static void mouse_get_xy(lv_coord_t * x, lv_coord_t * y)
{/*Your code comes here*/(*x) = 0;(*y) = 0;
}/*------------------* Keypad* -----------------*//*Initialize your keypad*/
static void keypad_init(void)
{/*Your code comes here*/
}/*Will be called by the library to read the mouse*/
static void keypad_read(lv_indev_drv_t * indev_drv, lv_indev_data_t * data)
{static uint32_t last_key = 0;/*Get the current x and y coordinates*/mouse_get_xy(&data->point.x, &data->point.y);/*Get whether the a key is pressed and save the pressed key*/uint32_t act_key = keypad_get_key();if(act_key != 0) {data->state = LV_INDEV_STATE_PR;/*Translate the keys to LVGL control characters according to your key definitions*/switch(act_key) {case 1:act_key = LV_KEY_NEXT;break;case 2:act_key = LV_KEY_PREV;break;case 3:act_key = LV_KEY_LEFT;break;case 4:act_key = LV_KEY_RIGHT;break;case 5:act_key = LV_KEY_ENTER;break;}last_key = act_key;} else {data->state = LV_INDEV_STATE_REL;}data->key = last_key;
}/*Get the currently being pressed key. 0 if no key is pressed*/
static uint32_t keypad_get_key(void)
{/*Your code comes here*/return 0;
}/*------------------* Encoder* -----------------*//*Initialize your keypad*/
static void encoder_init(void)
{/*Your code comes here*/
}/*Will be called by the library to read the encoder*/
static void encoder_read(lv_indev_drv_t * indev_drv, lv_indev_data_t * data)
{data->enc_diff = encoder_diff;data->state = encoder_state;
}/*Call this function in an interrupt to process encoder events (turn, press)*/
static void encoder_handler(void)
{/*Your code comes here*/encoder_diff += 0;encoder_state = LV_INDEV_STATE_REL;
}/*------------------* Button* -----------------*//*Initialize your buttons*/
static void button_init(void)
{/*Your code comes here*/
}/*Will be called by the library to read the button*/
static void button_read(lv_indev_drv_t * indev_drv, lv_indev_data_t * data)
{static uint8_t last_btn = 0;/*Get the pressed button's ID*/int8_t btn_act = button_get_pressed_id();if(btn_act >= 0) {data->state = LV_INDEV_STATE_PR;last_btn = btn_act;} else {data->state = LV_INDEV_STATE_REL;}/*Save the last pressed button's ID*/data->btn_id = last_btn;
}/*Get ID (0, 1, 2 ..) of the pressed button*/
static int8_t button_get_pressed_id(void)
{uint8_t i;/*Check to buttons see which is being pressed (assume there are 2 buttons)*/for(i = 0; i < 2; i++) {/*Return the pressed button's ID*/if(button_is_pressed(i)) {return i;}}/*No button pressed*/return -1;
}/*Test if `id` button is pressed or not*/
static bool button_is_pressed(uint8_t id)
{/*Your code comes here*/return false;
}#else /*Enable this file at the top*//*This dummy typedef exists purely to silence -Wpedantic.*/
typedef int keep_pedantic_happy;
#endif
3.1 lv_port_indev_init函数
/**
* 在此处,您将找到 LittlevGL 支持的输入设备的示例实现:
* - 触摸板
* - 鼠标(支持光标)
* - 小键盘(仅使用按键支持 GUI 使用)
* - 编码器(仅支持以下操作来使用 GUI:左、右、按下)
* - 按钮(用于在屏幕上按下点的外部按钮)
*
* `..._read()`函数仅为示例。
* 您应根据您的硬件对其进行调整。
*/
我们只用到了触摸IC的功能 也就是触摸板
只需要这部分就可以 其他的都可以条件编译或者注释或者删除掉
void lv_port_indev_init(void)
{/*** Here you will find example implementation of input devices supported by LittelvGL:* - Touchpad* - Mouse (with cursor support)* - Keypad (supports GUI usage only with key)* - Encoder (supports GUI usage only with: left, right, push)* - Button (external buttons to press points on the screen)** The `..._read()` function are only examples.* You should shape them according to your hardware*/static lv_indev_drv_t indev_drv;/*------------------* Touchpad* -----------------*//*Initialize your touchpad if you have*/touchpad_init();/*Register a touchpad input device*/lv_indev_drv_init(&indev_drv);indev_drv.type = LV_INDEV_TYPE_POINTER;indev_drv.read_cb = touchpad_read;indev_touchpad = lv_indev_drv_register(&indev_drv);}初始化的操作依然实在驱动那块就做了。
/*Initialize your touchpad*/
static void touchpad_init(void)
{/*Your code comes here*/
}然后就是注册一个触摸板输入设备(注册设备可让我想起来学linux驱动开发那会了)
LVGL帮我们实现了这个读取回调函数
/*Will be called by the library to read the touchpad*/
static void touchpad_read(lv_indev_drv_t * indev_drv, lv_indev_data_t * data)
{static lv_coord_t last_x = 0;static lv_coord_t last_y = 0;/*Save the pressed coordinates and the state*/if(touchpad_is_pressed()) {touchpad_get_xy(&last_x, &last_y);data->state = LV_INDEV_STATE_PR;} else {data->state = LV_INDEV_STATE_REL;}/*Set the last pressed coordinates*/data->point.x = last_x;data->point.y = last_y;
}3.2 我么需要实现的另外两个函数
/*Return true is the touchpad is pressed*/
static bool touchpad_is_pressed(void)
{/*Your code comes here*/return false;
}/*Get the x and y coordinates if the touchpad is pressed*/
static void touchpad_get_xy(lv_coord_t * x, lv_coord_t * y)
{/*Your code comes here*/(*x) = 0;(*y) = 0;
}
返回触摸状态(是否按压) 和 坐标位置
我们在驱动中定义了一个位置结构体并实例化了,其中保存的就是x和y的坐标
3.2.1 touchpad_is_pressed
/*Return true is the touchpad is pressed*/
static bool touchpad_is_pressed(void)
{//通过调用CST816_Get_FingerNum函数获取 CST816 触摸屏上当前触摸的手指个数信息/*Your code comes here*///如果获取到的手指个数既不是 0x00(可能表示没有触摸)//也不是 0xFF(可能表示触摸屏处于睡眠状态等特殊情况)//则返回true,表示触摸设备被按下if(CST816_Get_FingerNum()!=0x00 && CST816_Get_FingerNum()!=0xFF){return true;}else{return false;}
}
3.2.2 touchpad_get_xy
/*Get the x and y coordinates if the touchpad is pressed*/
static void touchpad_get_xy(lv_coord_t * x, lv_coord_t * y)
{/*Your code comes here*/ //这个函数用于获取触摸设备被按下时触摸点的坐标值CST816_Get_XY_AXIS();(*x) = CST816_Instance.X_Pos;(*y) = CST816_Instance.Y_Pos;
}
到这关于触摸输入设备就完了。
当然8.2版本的LVGL还有一个文件 是跟文件系统有关的。
![]()
由于暂时没有使用到,就不做过多的了解。
四、lvgl的裁剪文件lv_conf.h
这个文件从哪找呢,就在你下载的源代码的根目录

打开文件会出现
```
/*
* 将此文件复制为`lv_conf.h`
* 1. 紧邻`lvgl`文件夹
* 2. 或者其他任何位置,并
* - 定义`LV_CONF_INCLUDE_SIMPLE`
* - 将路径添加为包含路径
*/
```
其中的内容就是对lvgl的功能进行裁剪,比如什么滑块,支不支持gif,png,各种东西。我想先用lvgl做个鸡哥的gif出来,哈哈
大致手表的配置如下
//做一些LVGL的配置,裁剪的功能
//改了字体,改了刷新频率10ms,改了小组件的开关,额外组件,主题

支持更多字体大小

修改了刷新率,原来是30ms一刷,现在是10ms 毕竟开了DMA,必须加快刷新

取消了一些没用到的小组件

不使用基础主题和单色主题。
下一篇文章,我打算先移植玩玩,然后对lvgl8.2的各种c文件具体干什么打个标签,方便以后裁剪。
五、移植LVGL全过程
5.1 github或镜像或压缩包下载并解压得到源代码
https://github.com/lvgl/lvgl/tree/release/v8.2

版本选择在这release

5.2 得到源代码

5.3 保留如下文件及文件夹,或者不对文件做任何操作,毕竟我们只是后期可以裁剪,只对需要的文件编译


再次进入examples文件夹内 只保留这个接口文件夹 porting
当然examples里面是丰富的例程,以后需要还是可以看看的
把内部文件全部剪切走,在根目录下新建lvgl_porting文件夹


并将裁剪头文件改名

src里面包含的就是一些组件等功能的实现,当然也可以头文件与c文件分离,但是也可以不做。
然后就是把接口文件改名,并删除掉不需要的接口

这样一份可以加入LVGL工程的模板就以基本完工,然后就是前面的裁剪,添加绘制函数和缓冲模式,与触摸的坐标与状态获取。
相关文章:

移植LVGL8.2以及移植过程的理解
一、LVGL刷新显示(画点 OR 区域刷新颜色) 原来LCD的区域填充,由于没用到DMA就是普通的遍历区域块的坐标,需要传入的坐标就是显示区域的x轴起始与x轴尾部。y轴的起始与y轴的尾部。 怎么实现呢? SPI不加DMA实现区域填充…...

动态规划-背包问题——1049.最后一块石头的重量II
1.题目解析 题目来源 1049.最后一块石头的重量II——力扣 测试用例 2.算法原理 首先需要将该问题转化为0-1背包问题后再做分析 1.状态表示 根据数学中的知识我们知道将一个数字分为两个子数后求这两个子数的最小差值,那么就要求这两个子数尽可能接近于原数字的一…...
】并发性模式:如生产者-消费者、读写锁等。 架构模式:如MVC、MVVM等。属于23 种设计模式吗? RAII 的关系?)
【C++学习(37)】并发性模式:如生产者-消费者、读写锁等。 架构模式:如MVC、MVVM等。属于23 种设计模式吗? RAII 的关系?
并发性模式(如生产者-消费者、读写锁等)和架构模式(如 MVC、MVVM 等)并不属于 Gang of Four(GoF) 提出的 23 种经典设计模式 中。这些模式是其他领域中的设计模式,虽然它们和 GoF 的设计模式有交集,尤其是在程序架构和资源管理方面,但并不直接包含在 GoF 的 23 种设计…...

[Mysql] Mysql的多表查询----多表关系(下)
4、操作 方式二:创建表之后设置外键约束 外键约束也可以在修改表时添加,但是添加外键约束的前提是:从表中外键列中的数据必须与主表中主键列中的数据一致或者是没有数据。 语法: alter table <从表名> add constr…...

命名空间(namespace)详解(一)
域 在学习命名空间之前,我们首先要了解几种常见的域 一、域的种类 1、类作用域 类作用域是指定义在类内部的成员(包括数据成员和成员函数)的可见性和访问权限的范围 代码示例: #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include &…...

HarmonyOS ArkTs 解决流式传输编码问题
工作日志 日期:2024-11-15 标题:HarmonyOS ArkTs 解决流式传输编码问题 问题描述 问题:在处理流式数据的 HTTP 请求时,服务器返回的数据存在编码问题,导致数据无法正确地解码为字符串。部分数据在解码后出现了乱码…...

NPOI 实现Excel模板导出
记录一下使用NPOI实现定制的Excel导出模板,已下实现需求及主要逻辑 所需Json数据 对应参数 List<PurQuoteExportDataCrInput> listData [{"ItemName": "电缆VV3*162*10","Spec": "电缆VV3*162*10","Uom":…...

【OpenGL】OpenGL简介
文章目录 OpenGL概述OpenGL的本质OpenGL相关库核心库窗口管理glutfreeglutglfw 函数加载glewGLAD OpenGL概述 OpenGL(Open Graphics Library) 严格来说,本身并不是一个API,它是一个由Khronos组织制定并维护的规范(Specification)。OpenGL规范严格规定了…...

shell命令笔记
一、shell基本基础知识 1. shell命令中捕获上一个命令执行是否成功,通过判断 $? 是否为0,为0则表示成功,其他错误码则表示执行失败。 2. sheel命令中,变量赋值时默认都是字符串类型。赋值时须注意单引号与双引号的区别…...

qml显示OpenCV mat图片
文章目录 方式一QQuickPaintedItem 类介绍主要特点使用方法示例代码在 QML 中使用主要方法和属性注意事项编写OpenCV mat显示代码方式二本篇博客介绍在Qt6.5.3 qml项目里介绍如何显示OpenCV mat图片。视频:https://edu.csdn.net/learn/40003/654043?spm=3001.4143 在qml里显示…...

类与对象(2)---类的6个默认成员函数
1.类的6个默认成员函数 任何类在什么都不写时,编译器会自动生成以下6个默认成员函数。 默认成员函数:用户没有显式实现,编译器会生成的成员函数称为默认成员函数。 2.构造函数 2.1构造函数特性 构造函数的主要任务是初始化对象。 它有如下特…...

华为云租户网络-用的是隧道技术
1.验证租户网络是vxlan 2.验证用OVS 2.1控制节点VXLAN 本端ip(local ip)192.168.31.8 2.2计算节点VXLAN 本端ip(local ip)192.168.31.11 计算节点用的是bond0做隧道网络 2.3查看bond文件是否主备模式...

手搓神经网络(MLP)解决MNIST手写数字识别问题 | 数学推导+代码实现 | 仅用numpy,tensor和torch基本计算 | 含正反向传播数学推导
手写数字识别(神经网络入门) 文章目录 手写数字识别(神经网络入门)实验概述实验过程数据准备模型实现线性变换层前向传播反向传播更新参数整体实现 激活函数层(ReLU)前向传播反向传播整体实现 Softmax层&am…...

esp32c3安装micropython环境
esp32c3竟然支持micropython环境,真的太让人高兴了。主要是python开发比较友好,开发速度要快于C和C, 可以用来快速创意验证。 下载 首先到官网:MicroPython - Python for microcontrollers 点击“download”进入下载页面&#…...

ES6的Iterator 和 for...of 循环
写在前面 在JavaScript中,Iterator(遍历器)是一种接口,用于遍历数据结构(如数组、对象等)中的元素。它提供了一种统一的方式来访问集合中的每个项,包括值和位置。 默认 Iterator 接口 许多内…...

《C语言程序设计现代方法》note-4 基本类型 强制类型转换 类型定义
文章目录 助记提要7章 基本类型7.1 整数类型有符号整数和无符号整数整数类型的说明符整数类型的范围整型常量整数溢出读/写整数 7.2 浮点类型浮点数的范围浮点常量读/写浮点数 7.3 字符类型字符被当做整数来操作转义序列大小写转换scanf和printf读/写字符getchar和putchar读写字…...
【数据类型 —— 数值类型】)
MySQL(4)【数据类型 —— 数值类型】
阅读导航 引言一、数据类型分类二、数值类型取值范围三、tinyint 类型1. 💻数值越界测试⭕有符号案例⭕无符号案例 四、bit 类型1. 基本语法2. 使用示例✅创建表并插入数据✅使用 BIT 存储多个设置✅查询和格式化 BIT 数据✅更新 BIT 数据 五、小数类型1. float&…...
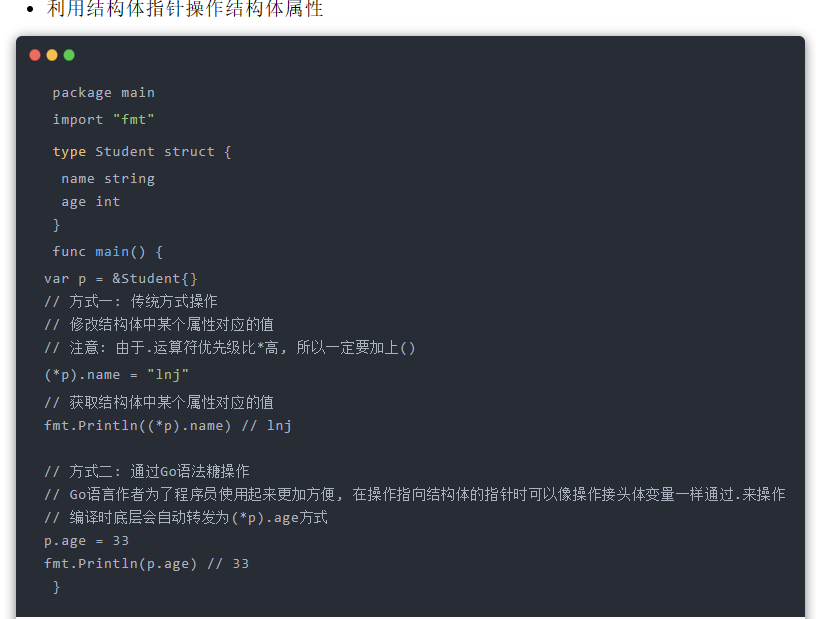
Golang超详细入门教程
Golang超详细入门教程 部分图片可能加载不出来,所以这里我上传到了自己的个人网站上也可以查看:http://dahua.bloggo.chat/testimonials/490.html 一、数据类型转换 C语言中数据可以隐式转换或显示转换, 但是Go语言中数据只能显示转换格式: 数据类型(…...

鸿蒙NEXT自定义组件:太极Loading
【引言】(完整代码在最后面) 本文将介绍如何在鸿蒙NEXT中创建一个自定义的“太极Loading”组件,为你的应用增添独特的视觉效果。 【环境准备】 电脑系统:windows 10 开发工具:DevEco Studio NEXT Beta1 Build Vers…...

FPGA 第7讲 简单组合逻辑译码器
时间:2024.11.15 一、学习内容 1.译码器 译码是编码的逆过程,在编码时,每一种二进制代码,都赋予了特定的含义,即都表示了一个确定的信号或者对象。把代码状态的特定含义翻译出来的过程叫做译码,实现译码操…...

地震勘探——干扰波识别、井中地震时距曲线特点
目录 干扰波识别反射波地震勘探的干扰波 井中地震时距曲线特点 干扰波识别 有效波:可以用来解决所提出的地质任务的波;干扰波:所有妨碍辨认、追踪有效波的其他波。 地震勘探中,有效波和干扰波是相对的。例如,在反射波…...

css实现圆环展示百分比,根据值动态展示所占比例
代码如下 <view class""><view class"circle-chart"><view v-if"!!num" class"pie-item" :style"{background: conic-gradient(var(--one-color) 0%,#E9E6F1 ${num}%),}"></view><view v-else …...

Leetcode 3576. Transform Array to All Equal Elements
Leetcode 3576. Transform Array to All Equal Elements 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3576. Transform Array to All Equal Elements 1. 解题思路 这一题思路上就是分别考察一下是否能将其转化为全1或者全-1数组即可。 至于每一种情况是否可以达到…...
visual studio 2022更改主题为深色
visual studio 2022更改主题为深色 点击visual studio 上方的 工具-> 选项 在选项窗口中,选择 环境 -> 常规 ,将其中的颜色主题改成深色 点击确定,更改完成...

MODBUS TCP转CANopen 技术赋能高效协同作业
在现代工业自动化领域,MODBUS TCP和CANopen两种通讯协议因其稳定性和高效性被广泛应用于各种设备和系统中。而随着科技的不断进步,这两种通讯协议也正在被逐步融合,形成了一种新型的通讯方式——开疆智能MODBUS TCP转CANopen网关KJ-TCPC-CANP…...

Ascend NPU上适配Step-Audio模型
1 概述 1.1 简述 Step-Audio 是业界首个集语音理解与生成控制一体化的产品级开源实时语音对话系统,支持多语言对话(如 中文,英文,日语),语音情感(如 开心,悲伤)&#x…...

面向无人机海岸带生态系统监测的语义分割基准数据集
描述:海岸带生态系统的监测是维护生态平衡和可持续发展的重要任务。语义分割技术在遥感影像中的应用为海岸带生态系统的精准监测提供了有效手段。然而,目前该领域仍面临一个挑战,即缺乏公开的专门面向海岸带生态系统的语义分割基准数据集。受…...

elementUI点击浏览table所选行数据查看文档
项目场景: table按照要求特定的数据变成按钮可以点击 解决方案: <el-table-columnprop"mlname"label"名称"align"center"width"180"><template slot-scope"scope"><el-buttonv-if&qu…...
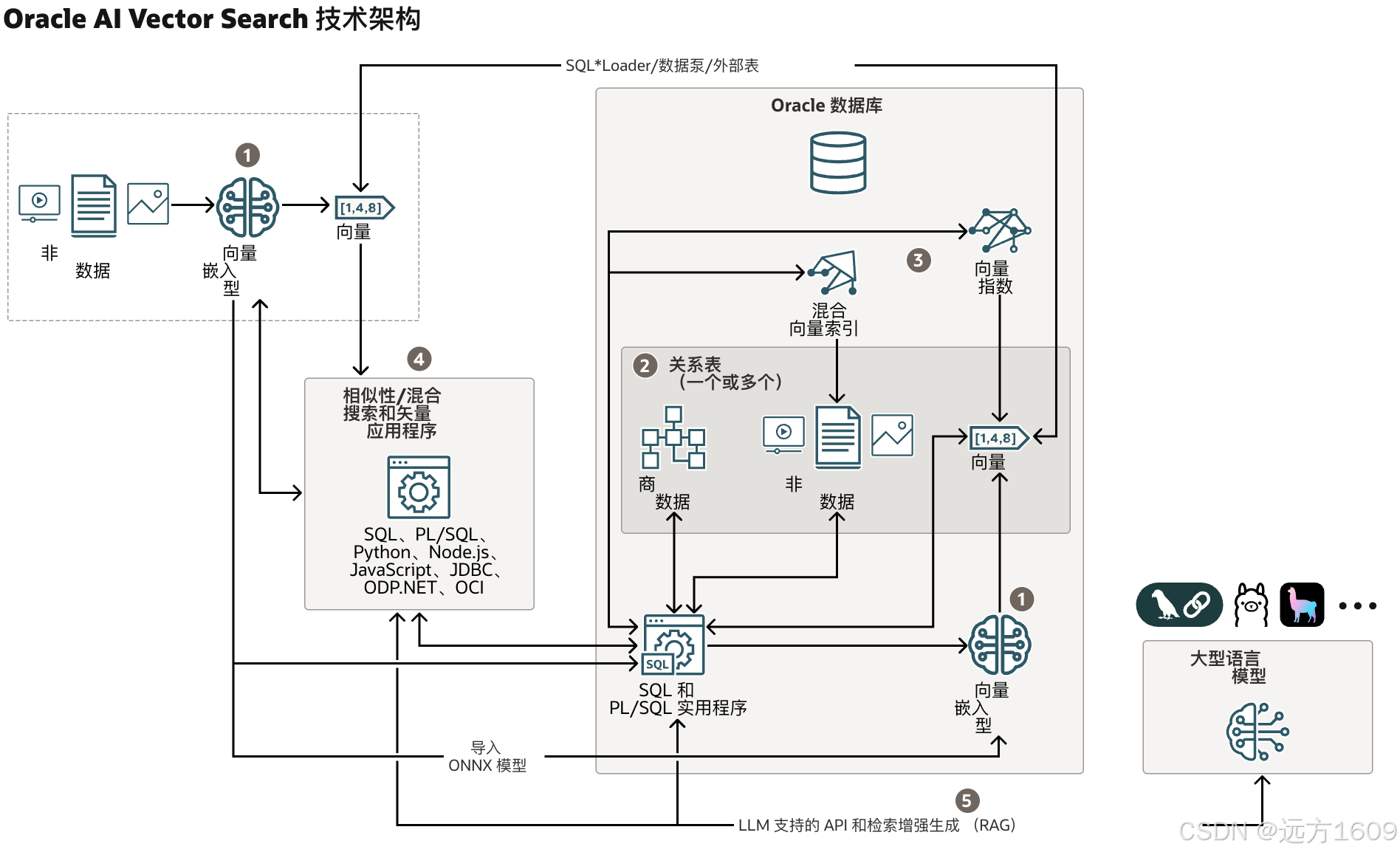
9-Oracle 23 ai Vector Search 特性 知识准备
很多小伙伴是不是参加了 免费认证课程(限时至2025/5/15) Oracle AI Vector Search 1Z0-184-25考试,都顺利拿到certified了没。 各行各业的AI 大模型的到来,传统的数据库中的SQL还能不能打,结构化和非结构的话数据如何和…...

信息收集:从图像元数据(隐藏信息收集)到用户身份的揭秘 --- 7000
目录 🌐 访问Web服务 💻 分析源代码 ⬇️ 下载图片并保留元数据 🔍 提取元数据(重点) 👤 生成用户名列表 🛠️ 技术原理 图片元数据(EXIF 数据) Username-Anarch…...
