datawhale11月组队学习 模型压缩技术2:PyTorch模型剪枝教程
文章目录
- 一、 prune模块简介
- 1.1 常用方法
- 1.2 剪枝效果
- 1.3 二、三、四章剪枝测试总结
- 二、局部剪枝(Local Pruning)
- 2.1 结构化剪枝
- 2.1.1 对weight进行随机结构化剪枝(random_structured)
- 2.1.2 对weight进行迭代剪枝(范数结构化剪枝,ln_structured)
- 2.2 非结构化剪枝
- 2.2.1 对bias进行随机非结构化剪枝
- 2.2.2 对多层网络进行范数非结构化剪枝(l1_unstructured)
- 2.3 永久化剪枝(remove)
- 三、全局剪枝(GLobal pruning)
- 四、自定义剪枝(Custom pruning)
- 《datawhale2411组队学习之模型压缩技术1:模型剪枝(上)》:介绍模型压缩的几种技术;模型剪枝基本概念、分类方式、剪枝标准、剪枝频次、剪枝后微调等内容
- 《datawhale11月组队学习 模型压缩技术2:PyTorch模型剪枝教程》:介绍PyTorch的prune模块具体用法
- 《datawhale11月组队学习 模型压缩技术3:2:4结构稀疏化BERT模型》:介绍基于模式的剪枝——2:4结构稀疏化及其在BERT模型上的测试效果
项目地址awesome-compression、在线阅读
一、 prune模块简介
PyTorch教程《Pruning Tutorial》、torch.nn.utils.prune文档
1.1 常用方法
Pytorch在1.4.0版本开始,加入了剪枝操作,在torch.nn.utils.prune模块中,主要有以下剪枝方法:
| 剪枝类型 | 子类型 | 剪枝方法 |
|---|---|---|
| 局部剪枝 | 结构化剪枝 | 随机结构化剪枝 (random_structured) |
范数结构化剪枝 (ln_structured) | ||
| 非结构化剪枝 | 随机非结构化剪枝 (random_unstructured) | |
范数非结构化剪枝 (ln_unstructured) | ||
| 全局剪枝 | 非结构化剪枝 | 全局非结构化剪枝 (global_unstructured) |
| 自定义剪枝 | 自定义剪枝 (Custom Pruning) |
除此之外,模块中还有一些其它方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
prune.remove(module, name) | 剪枝永久化 |
prune.apply | 使用指定的剪枝方法对模块进行剪枝。 |
prune.is_pruned(module) | 检查给定模块的某个参数是否已被剪枝。 |
prune.custom_from_mask(module, name, mask) | 基于自定义的掩码进行剪枝,用于定义更加细粒度的剪枝策略。 |
1.2 剪枝效果
-
参数变化:
- 剪枝前,
weight是模型的一个参数,意味着它是模型训练时优化的对象,可以通过梯度更新(通过optimizer.step()来更新它的值)。 - 剪枝过程中,原始权重被保存到新的变量
weight_orig中,便于后续访问原始权重。 - 剪枝后,
weight是剪枝后的权重值(通过原始权重和剪枝掩码计算得出),但此时不再是参数,而是模型的属性(一个普通的变量)。
- 剪枝前,
-
掩码存储:生成一个名为
weight_mask的剪枝掩码,会被保存为模块的一个缓冲区(buffer)。 -
前向传递:PyTorch 使用
forward_pre_hooks来确保每次前向传递时都会应用剪枝处理。每个被剪枝的参数都会在模块中添加一个钩子来实现这一操作。
1.3 二、三、四章剪枝测试总结
- 对
weight进行剪枝,效果见1.2 章节。 - 对
weight进行迭代剪枝,相当于把多个剪枝核(mask)序列化成一个剪枝核, 最终只有一个weight_orig和weight_mask,hook也被更新。 - 对
weight剪枝后,再对bias进行剪枝,weight_orig和weight_mask不变,新增bias_orig和bias_mask,新增bias hook。 - 可以对多个模块同时进行剪枝,最后使用
remove进行剪枝永久化
使用remove函数后,weight_orig和bias_orig被移除,剪枝后的weight和bias成为标准的模型参数。经过remove操作后,剪枝永久化生效。此时,剪枝掩码weight_mask和 hook不再需要,named_buffers和_forward_pre_hooks都被清空。 - 局部剪枝需要根据自己的经验来决定对某一层网络进行剪枝,需要对模型有深入了解,所以全局剪枝(跨不同参数)更通用,即从整体网络的角度进行剪枝。采用全局剪枝时,不同的层被剪掉的百分比可能不同。
parameters_to_prune = ((model.conv1, 'weight'),(model.conv2, 'weight'),(model.fc1, 'weight'),(model.fc2, 'weight'))# 应用20%全局剪枝
prune.global_unstructured(parameters_to_prune, pruning_method=prune.L1Unstructured, amount=0.2)
最终各层剪枝比例为(随机的):
Sparsity in conv1.weight: 5.33%
Sparsity in conv2.weight: 17.25%
Sparsity in fc1.weight: 22.03%
Sparsity in fc2.weight: 14.67%
Global sparsity: 20.00%
- 自定义剪枝需要通过继承class BasePruningMethod()来定义,,其内部有若干方法:
call, apply_mask, apply, prune, remove。其中,必须实现__init__和compute_mask两个函数才能完成自定义的剪枝规则设定。此外,您必须指定要实现的修剪类型( global, structured, and unstructured)。
二、局部剪枝(Local Pruning)
局部剪枝,指的是对网络的单个层或局部范围内进行剪枝。其中,非结构化剪枝会随机地将一些权重参数变为0,结构化剪枝则将某个维度某些通道的权重变成0。
总结一下2.1和2.2的效果:
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.utils.prune as prune
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchsummary import summary# 1.定义一个经典的LeNet网络
class LeNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, num_classes=10):super(LeNet, self).__init__()self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=6, kernel_size=5)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=6, out_channels=16, kernel_size=5)self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features=16 * 4 * 4, out_features=120)self.fc2 = nn.Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84)self.fc3 = nn.Linear(in_features=84, out_features=num_classes)def forward(self, x):x = self.maxpool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))x = self.maxpool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))x = x.view(x.size()[0], -1)x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))x = self.fc3(x)return x
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = LeNet().to(device=device)# 2.打印模型结构
summary(model, input_size=(1, 28, 28))
----------------------------------------------------------------Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
================================================================Conv2d-1 [-1, 6, 24, 24] 156MaxPool2d-2 [-1, 6, 12, 12] 0Conv2d-3 [-1, 16, 8, 8] 2,416MaxPool2d-4 [-1, 16, 4, 4] 0Linear-5 [-1, 120] 30,840Linear-6 [-1, 84] 10,164Linear-7 [-1, 10] 850
================================================================
Total params: 44,426
Trainable params: 44,426
Non-trainable params: 0
----------------------------------------------------------------
Input size (MB): 0.00
Forward/backward pass size (MB): 0.04
Params size (MB): 0.17
Estimated Total Size (MB): 0.22
----------------------------------------------------------------
# 3.打印模型的状态字典,状态字典里包含了所有的参数
print(model.state_dict().keys())
odict_keys(['conv1.weight', 'conv1.bias', 'conv2.weight', 'conv2.bias', 'fc1.weight', 'fc1.bias', 'fc2.weight', 'fc2.bias', 'fc3.weight', 'fc3.bias'])
# 4.打印第一个卷积层的参数
module = model.conv1
print(list(module.named_parameters()))
[('weight', Parameter containing:
tensor([[[[ 0.1529, 0.1660, -0.0469, 0.1837, -0.0438],[ 0.0404, -0.0974, 0.1175, 0.1763, -0.1467],[ 0.1738, 0.0374, 0.1478, 0.0271, 0.0964],[-0.0282, 0.1542, 0.0296, -0.0934, 0.0510],[-0.0921, -0.0235, -0.0812, 0.1327, -0.1579]]],......[[[-0.1167, -0.0685, -0.1579, 0.1677, -0.0397],[ 0.1721, 0.0623, -0.1694, 0.1384, -0.0550],[-0.0767, -0.1660, -0.1988, 0.0572, -0.0437],[ 0.0779, -0.1641, 0.1485, -0.1468, -0.0345],[ 0.0418, 0.1033, 0.1615, 0.1822, -0.1586]]]], device='cuda:0',requires_grad=True)), ('bias', Parameter containing:
tensor([ 0.0503, -0.0860, -0.0219, -0.1497, 0.1822, -0.1468], device='cuda:0',requires_grad=True))]
# 5.打印module中属性张量named_buffers,此时为空列表
print(list(module.named_buffers()))
[]
2.1 结构化剪枝
2.1.1 对weight进行随机结构化剪枝(random_structured)
对LeNet的conv1层的weight参数进行随机结构化剪枝,其中 amount是一个介于0.0-1.0的float数值,代表比例, 或者一个正整数,代表剪裁掉多少个参数.
prune.random_structured(module, name="weight", amount=2, dim=0)
# 1.再次打印模型的状态字典,发现conv1层多了weight_orig和weight_mask
print(model.state_dict().keys())
odict_keys(['conv1.bias', 'conv1.weight_orig', 'conv1.weight_mask', 'conv2.weight', 'conv2.bias', 'fc1.weight', 'fc1.bias', 'fc2.weight', 'fc2.bias', 'fc3.weight', 'fc3.bias'])
Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
# 2. 剪枝后,原始的weight变成了weight_orig,并存放在named_parameters中
print(list(module.named_parameters()))
[('bias', Parameter containing:
tensor([ 0.0503, -0.0860, -0.0219, -0.1497, 0.1822, -0.1468], device='cuda:0',requires_grad=True)), ('weight_orig', Parameter containing:
tensor([[[[ 0.1529, 0.1660, -0.0469, 0.1837, -0.0438],[ 0.0404, -0.0974, 0.1175, 0.1763, -0.1467],[ 0.1738, 0.0374, 0.1478, 0.0271, 0.0964],[-0.0282, 0.1542, 0.0296, -0.0934, 0.0510],[-0.0921, -0.0235, -0.0812, 0.1327, -0.1579]]],......[[[-0.1167, -0.0685, -0.1579, 0.1677, -0.0397],[ 0.1721, 0.0623, -0.1694, 0.1384, -0.0550],[-0.0767, -0.1660, -0.1988, 0.0572, -0.0437],[ 0.0779, -0.1641, 0.1485, -0.1468, -0.0345],[ 0.0418, 0.1033, 0.1615, 0.1822, -0.1586]]]], device='cuda:0',requires_grad=True))]
# 3. 剪枝掩码矩阵weight_mask存放在模块的buffer中
print(list(module.named_buffers()))
[('weight_mask', tensor([[[[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]]],[[[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]]],[[[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]]],[[[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]]],[[[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]]],[[[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]]]]))]
# 4. 剪枝操作后的weight已经不再是module的参数, 而只是module的一个属性.
print(module.weight)
tensor([[[[ 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[ 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[ 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000],[-0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[ 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000]]],[[[-0.0540, -0.1928, -0.0355, -0.0075, -0.1481],[ 0.0135, 0.0192, 0.0082, -0.0120, -0.0164],[-0.0435, -0.1488, 0.1092, -0.0041, 0.1960],[-0.1045, -0.0136, 0.0398, -0.1286, 0.0617],[-0.0091, 0.0466, 0.1827, 0.1655, 0.0727]]],[[[ 0.1216, -0.0833, -0.1491, -0.1143, 0.0113],[ 0.0452, 0.1662, -0.0425, -0.0904, -0.1235],[ 0.0565, 0.0933, -0.0721, 0.0909, 0.1837],[-0.1739, 0.0263, 0.1339, 0.0648, -0.0382],[-0.1667, 0.1478, 0.0448, -0.0892, 0.0815]]],[[[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[-0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000],[-0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[-0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[ 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000]]],[[[ 0.1278, 0.1037, -0.0323, -0.1504, 0.1080],[ 0.0266, -0.0996, 0.1499, -0.0845, 0.0609],[-0.0662, -0.1405, -0.0586, -0.0615, -0.0462],[-0.1118, -0.0961, -0.1325, -0.0417, -0.0741],[ 0.1842, -0.1040, -0.1786, -0.0593, 0.0186]]],[[[-0.0889, -0.0737, -0.1655, -0.1708, -0.0988],[-0.1787, 0.1127, 0.0706, -0.0352, 0.1238],[-0.0985, -0.1929, -0.0062, 0.0488, -0.1152],[-0.1659, -0.0448, 0.0821, -0.0956, -0.0262],[ 0.1928, 0.1767, -0.1792, -0.1364, 0.0507]]]],grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
对于每一次剪枝操作,PyTorch 会为剪枝的参数(如 weight)添加一个 forward_pre_hook。这个钩子会在每次进行前向传递计算之前,自动应用剪枝掩码(即将某些权重置为零),这保证了剪枝后的权重在模型计算时被正确地使用。
# 5.打印_forward_pre_hooks
print(module._forward_pre_hooks)
OrderedDict([(0, <torch.nn.utils.prune.RandomStructured object at 0x7f04012f8ca0>)])
简单总结就是:
weight不再是参数,它变成了一个属性,表示剪枝后的权重。weight_orig保存原始未剪枝的权重。weight_mask是一个掩码,表示哪些权重被剪去了(即哪些位置变为零)。- 钩子会保证每次前向传递时,
weight会根据weight_mask来计算出剪枝后的版本。
2.1.2 对weight进行迭代剪枝(范数结构化剪枝,ln_structured)
一个模型的参数可以执行多次剪枝操作,这种操作被称为迭代剪枝(Iterative Pruning)。上述步骤已经对conv1进行了随机结构化剪枝,接下来对其再进行范数结构化剪枝,看看会发生什么?
# n代表范数,这里n=2表示l2范数
prune.ln_structured(module, name="weight", amount=0.5, n=2, dim=0)# 再次打印模型参数
print(" model state_dict keys:")
print(model.state_dict().keys())
print('*'*50)print(" module named_parameters:")
print(list(module.named_parameters()))
print('*'*50)print(" module named_buffers:")
print(list(module.named_buffers()))
print('*'*50)print(" module weight:")
print(module.weight)
print('*'*50)print(" module _forward_pre_hooks:")
print(module._forward_pre_hooks)
model state_dict keys:
odict_keys(['conv1.bias', 'conv1.weight_orig', 'conv1.weight_mask', 'conv2.weight', 'conv2.bias', 'fc1.weight', 'fc1.bias', 'fc2.weight', 'fc2.bias', 'fc3.weight', 'fc3.bias'])
**************************************************
module named_parameters: # 原始参数weight_orig不变
...
...
module named_buffers:
[('weight_mask', tensor([[[[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]]],[[[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]]],[[[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]]],[[[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]]],[[[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]]],[[[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]]]]))]
**************************************************module weight:......
module _forward_pre_hooks:
OrderedDict([(1, <torch.nn.utils.prune.PruningContainer object at 0x7f04c86756d0>)])
可见迭代剪枝相当于把多个剪枝核序列化成一个剪枝核, 新的 mask 矩阵与旧的 mask 矩阵的结合由PruningContainer的compute_mask方法处理,最后只有一个weight_orig和weight_mask。
module._forward_pre_hooks是一个用于在模型的前向传播之前执行自定义操作的机制,这里记录了执行过的剪枝方法:
# 打印剪枝历史
for hook in module._forward_pre_hooks.values():if hook._tensor_name == "weight": breakprint(list(hook))
[<torch.nn.utils.prune.RandomStructured object at 0x7f04012f8ca0>, <torch.nn.utils.prune.LnStructured object at 0x7f04c8675b80>]
2.2 非结构化剪枝
2.2.1 对bias进行随机非结构化剪枝
此时,我们也可以继续对偏置bias进行剪枝,看看module的参数、缓冲区、钩子和属性是如何变化的。
prune.random_unstructured(module, name="bias", amount=1)
# 再次打印模型参数
print(" model state_dict keys:")
print(model.state_dict().keys())
print('*'*50)print(" module named_parameters:")
print(list(module.named_parameters()))
print('*'*50)print(" module named_buffers:")
print(list(module.named_buffers()))
print('*'*50)print(" module bias:")
print(module.bias)
print('*'*50)print(" module _forward_pre_hooks:")
print(module._forward_pre_hooks)
model state_dict keys:
odict_keys(['conv1.weight_orig', 'conv1.bias_orig', 'conv1.weight_mask', 'conv1.bias_mask', 'conv2.weight', 'conv2.bias', 'fc1.weight', 'fc1.bias', 'fc2.weight', 'fc2.bias', 'fc3.weight', 'fc3.bias'])
**************************************************
# weight_orig不变,添加了bias_origmodule named_parameters:
[('weight_orig', Parameter containing:...
, requires_grad=True)), ('bias_orig', Parameter containing:
tensor([-0.0893, -0.1464, -0.1101, -0.0076, 0.1493, -0.0418],requires_grad=True))]
**************************************************
# weight_mask不变,添加了bias_maskmodule named_buffers:
[('weight_mask',
...('bias_mask', tensor([1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1.]))]
**************************************************module bias:
tensor([-0.0893, -0.1464, -0.0000, -0.0076, 0.1493, -0.0418],grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
**************************************************module _forward_pre_hooks:
OrderedDict([(1, <torch.nn.utils.prune.PruningContainer object at 0x7f04c86756d0>), (2, <torch.nn.utils.prune.RandomUnstructured object at 0x7f04013a7d30>)])
对bias进行剪枝后,会发现state_dict和named_parameters中不仅仅有了weight_orig,也有了bias_orig。在named_buffers中, 也同时出现了weight_mask和bias_mask。最后,因为我们在两种参数上进行剪枝,因此会生成两个钩子。
2.2.2 对多层网络进行范数非结构化剪枝(l1_unstructured)
前面介绍了对指定的conv1层的weight和bias进行了不同方法的剪枝,那么能不能支持同时对多层网络的特定参数进行剪枝呢?
# 对于模型多个模块进行bias剪枝
for n, m in model.named_modules():# 对模型中所有的卷积层执行l1_unstructured剪枝操作, 选取20%的参数剪枝if isinstance(m, torch.nn.Conv2d):prune.l1_unstructured(m, name="bias", amount=0.2)# 对模型中所有全连接层执行ln_structured剪枝操作, 选取40%的参数剪枝# elif isinstance(module, torch.nn.Linear):# prune.random_structured(module, name="weight", amount=0.4,dim=0)# 再次打印模型参数
print(" model state_dict keys:")
print(model.state_dict().keys())
print('*'*50)print(" module named_parameters:")
print(list(module.named_parameters()))
print('*'*50)print(" module named_buffers:")
print(list(module.named_buffers()))
print('*'*50)print(" module weight:")
print(module.weight)
print('*'*50)print(" module bias:")
print(module.bias)
print('*'*50)print(" module _forward_pre_hooks:")
print(module._forward_pre_hooks)
model state_dict keys:
odict_keys(['conv1.weight_orig', 'conv1.bias_orig', 'conv1.weight_mask', 'conv1.bias_mask', 'conv2.weight', 'conv2.bias_orig', 'conv2.bias_mask', 'fc1.weight', 'fc1.bias', 'fc2.weight', 'fc2.bias', 'fc3.weight', 'fc3.bias'])
**************************************************module named_parameters:[('weight_orig', Parameter containing:...('bias_orig', Parameter containing:...
**************************************************
# # weight_mask不变,bias_mask更新
module named_buffers:
[('weight_mask', ...
('bias_mask', tensor([1., 1., 0., 0., 1., 1.]))]
**************************************************
# module weight不变
module weight:...
**************************************************
module bias:
tensor([-0.0893, -0.1464, -0.0000, -0.0000, 0.1493, -0.0418],grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
**************************************************
module _forward_pre_hooks:
OrderedDict([(1, <torch.nn.utils.prune.PruningContainer object at 0x7f04c86756d0>), (3, <torch.nn.utils.prune.PruningContainer object at 0x7f04010c1100>)])
2.3 永久化剪枝(remove)
接下来对模型的weight和bias参数进行永久化剪枝操作prune.remove。
# 对module的weight执行剪枝永久化操作remove
for n, m in model.named_modules():if isinstance(m, torch.nn.Conv2d):prune.remove(m, 'bias')# 对conv1的weight执行剪枝永久化操作remove
prune.remove(module, 'weight')
print('*'*50)# 将剪枝后的模型的状态字典打印出来
print(" model state_dict keys:")
print(model.state_dict().keys())
print('*'*50)# 再次打印模型参数
print(" model named_parameters:")
print(list(module.named_parameters()))
print('*'*50)# 再次打印模型mask buffers参数
print(" model named_buffers:")
print(list(module.named_buffers()))
print('*'*50)# 再次打印模型的_forward_pre_hooks
print(" model forward_pre_hooks:")
print(module._forward_pre_hooks)
**************************************************model state_dict keys:
odict_keys(['conv1.bias', 'conv1.weight', 'conv2.weight', 'conv2.bias', 'fc1.weight', 'fc1.bias', 'fc2.weight', 'fc2.bias', 'fc3.weight', 'fc3.bias'])
**************************************************model named_parameters:
[('bias', Parameter containing:
tensor([-0.0893, -0.1464, -0.0000, -0.0000, 0.1493, -0.0418],requires_grad=True)), ('weight', Parameter containing:
tensor([[[[ 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[ 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[ 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000],[-0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[ 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000]]],[[[-0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000],[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000],[-0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[-0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[-0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]]],[[[ 0.1216, -0.0833, -0.1491, -0.1143, 0.0113],[ 0.0452, 0.1662, -0.0425, -0.0904, -0.1235],[ 0.0565, 0.0933, -0.0721, 0.0909, 0.1837],[-0.1739, 0.0263, 0.1339, 0.0648, -0.0382],[-0.1667, 0.1478, 0.0448, -0.0892, 0.0815]]],[[[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[-0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000],[-0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[-0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[ 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000]]],[[[ 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[ 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000],[-0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000],[-0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000],[ 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000]]],[[[-0.0889, -0.0737, -0.1655, -0.1708, -0.0988],[-0.1787, 0.1127, 0.0706, -0.0352, 0.1238],[-0.0985, -0.1929, -0.0062, 0.0488, -0.1152],[-0.1659, -0.0448, 0.0821, -0.0956, -0.0262],[ 0.1928, 0.1767, -0.1792, -0.1364, 0.0507]]]], requires_grad=True))]
**************************************************model named_buffers:
[]
**************************************************model forward_pre_hooks:
OrderedDict()
可见,执行remove操作后:
weight_orig和bias_orig被移除,剪枝后的weight和bias成为标准的模型参数。经过remove操作后,剪枝永久化生效。- 剪枝掩码
weight_mask和bias_mask不再需要,named_buffers被清空 _forward_pre_hooks也被清空(由于剪枝后的权重和偏置将直接反映在最终模型中,所以无须再借助外部的掩码或钩子函数来维护剪枝过程)。
三、全局剪枝(GLobal pruning)
前面已经介绍了局部剪枝的四种方法,但这很大程度上需要根据自己的经验来决定对某一层网络进行剪枝。 更通用的剪枝策略是采用全局剪枝,即从整体网络的角度进行剪枝。采用全局剪枝时,不同的层被剪掉的百分比可能不同。
model = LeNet().to(device=device)# 1.打印初始化模型的状态字典
print(model.state_dict().keys())
print('*'*50)# 2.构建参数集合, 决定哪些层, 哪些参数集合参与剪枝
parameters_to_prune = ((model.conv1, 'weight'),(model.conv2, 'weight'),(model.fc1, 'weight'),(model.fc2, 'weight'))# 3. 全局剪枝
prune.global_unstructured(parameters_to_prune, pruning_method=prune.L1Unstructured, amount=0.2)# 4. 打印剪枝后模型的状态字典
print(model.state_dict().keys())
odict_keys(['conv1.weight', 'conv1.bias', 'conv2.weight', 'conv2.bias', 'fc1.weight', 'fc1.bias', 'fc2.weight', 'fc2.bias', 'fc3.weight', 'fc3.bias'])
**************************************************
odict_keys(['conv1.bias', 'conv1.weight_orig', 'conv1.weight_mask', 'conv2.bias', 'conv2.weight_orig', 'conv2.weight_mask', 'fc1.bias', 'fc1.weight_orig', 'fc1.weight_mask', 'fc2.bias', 'fc2.weight_orig', 'fc2.weight_mask', 'fc3.weight', 'fc3.bias'])
打印一下各层被剪枝的比例:
print("Sparsity in conv1.weight: {:.2f}%".format(100. * float(torch.sum(model.conv1.weight == 0))/ float(model.conv1.weight.nelement())))print("Sparsity in conv2.weight: {:.2f}%".format(100. * float(torch.sum(model.conv2.weight == 0))/ float(model.conv2.weight.nelement())))print("Sparsity in fc1.weight: {:.2f}%".format(100. * float(torch.sum(model.fc1.weight == 0))/ float(model.fc1.weight.nelement())))print("Sparsity in fc2.weight: {:.2f}%".format(100. * float(torch.sum(model.fc2.weight == 0))/ float(model.fc2.weight.nelement())))print("Global sparsity: {:.2f}%".format(100. * float(torch.sum(model.conv1.weight == 0)+ torch.sum(model.conv2.weight == 0)+ torch.sum(model.fc1.weight == 0)+ torch.sum(model.fc2.weight == 0))/ float(model.conv1.weight.nelement()+ model.conv2.weight.nelement()+ model.fc1.weight.nelement()+ model.fc2.weight.nelement())))Sparsity in conv1.weight: 5.33%
Sparsity in conv2.weight: 17.25%
Sparsity in fc1.weight: 22.03%
Sparsity in fc2.weight: 14.67%
Global sparsity: 20.00%
四、自定义剪枝(Custom pruning)
剪枝模型通过继承class BasePruningMethod()来执行剪枝, 内部有若干方法: call, apply_mask, apply, prune, remove等等。其中,必须实现__init__构造函数和compute_mask两个函数才能完成自定义的剪枝规则设定。 此外,您必须指定要实现的修剪类型( global, structured, and unstructured)。
# 自定义剪枝方法的类, 一定要继承prune.BasePruningMethod
class custom_prune(prune.BasePruningMethod):# 指定此技术实现的修剪类型(支持的选项为global、 structured和unstructured)PRUNING_TYPE = "unstructured"# 内部实现compute_mask函数, 定义剪枝规则, 本质上就是如何去mask掉权重参数def compute_mask(self, t, default_mask):mask = default_mask.clone()# 此处定义的规则是每隔一个参数就遮掩掉一个, 最终参与剪枝的参数的50%被mask掉mask.view(-1)[::2] = 0return mask# 自定义剪枝方法的函数, 内部直接调用剪枝类的方法apply
def custome_unstructured_pruning(module, name):custom_prune.apply(module, name)return module
import time
# 实例化模型类
model = LeNet().to(device=device)start = time.time()
# 调用自定义剪枝方法的函数, 对model中的第1个全连接层fc1中的偏置bias执行自定义剪枝
custome_unstructured_pruning(model.fc1, name="bias")# 剪枝成功的最大标志, 就是拥有了bias_mask参数
print(model.fc1.bias_mask)# 打印一下自定义剪枝的耗时
duration = time.time() - start
print(duration * 1000, 'ms')
tensor([0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1.,0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1.,0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1.,0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1.,0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1.,0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1.,0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1.])
5.576610565185547 ms
相关文章:

datawhale11月组队学习 模型压缩技术2:PyTorch模型剪枝教程
文章目录 一、 prune模块简介1.1 常用方法1.2 剪枝效果1.3 二、三、四章剪枝测试总结 二、局部剪枝(Local Pruning)2.1 结构化剪枝2.1.1 对weight进行随机结构化剪枝(random_structured)2.1.2 对weight进行迭代剪枝(范…...

SOL链上Meme生态的崛起与未来#Dapp开发#链游#交易所#公链搭建
近年来,随着区块链技术的普及和NFT文化的流行,meme(网络迷因)逐渐成为区块链生态中的重要组成部分。meme不仅是一种互联网文化符号,更逐步渗透进了去中心化金融(DeFi)、NFT和元宇宙等多个领域&a…...

部署Apache Doris
官方文档:https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/installing/compilation.html 一、编译 使用 Docker 开发镜像编译(推荐) 1.拉取镜像 #下载 Docker 最新主干版本代码,会随主干版本不断更新。 $ docker pull apache/incubator-doris:…...

ElasticSearch-全文检索(一)基本介绍
简介 Elasticsearch:官方分布式搜索和分析引擎 | Elastic 全文搜索属于最常见的需求,开源的Elasticsearch是目前全文搜索引擎的首选。 它可以快速地储存、搜索和分析海量数据。维基百科、StackOverflow、Github都采用它 Elastic的底层是开源库Lucene。但…...

paramiko 库实现的暴力破解 SSH 密码
import paramiko import optparse import threading import time from threading import Thread, BoundedSemaphore# 用paramiko暴力破解SSH密码 # 最大并发连接尝试的数量,可根据实际情况调整,适当减小可降低对目标服务器的压力以及减少多线程同步问题出…...

Python 操作 Elasticsearch 全指南:从连接到数据查询与处理
文章目录 Python 操作 Elasticsearch 全指南:从连接到数据查询与处理引言安装 elasticsearch-py连接到 Elasticsearch创建索引插入数据查询数据1. 简单查询2. 布尔查询 更新文档删除文档和索引删除文档删除索引 批量插入数据处理分页结果总结 Python 操作 Elasticse…...
)
Jarvis March算法详解及Python实现(附设计模式案例)
目录 Jarvis March算法详解及Python实现(附设计模式案例)第一部分:Jarvis March算法概述与原理1.1 什么是Jarvis March算法?1.2 算法原理1.3 算法流程1.4 时间复杂度第二部分:Jarvis March算法的Python实现(面向对象设计)2.1 面向对象设计2.2 代码实现2.3 代码解释第三部…...

AIGC中的文本风格迁移:基于深度学习的实现
引言 文本风格迁移是自然语言处理领域的一个重要研究方向,它可以将文本从一种风格转换为另一种风格,同时保留其原有的内容。随着深度学习技术的发展,文本风格迁移的方法变得越来越先进和高效。本文将探讨基于序列到序列模型(Seq2…...

丹摩征文活动 |【前端开发】HTML+CSS+JavaScript前端三剑客的基础知识体系了解
前言 🌟🌟本期讲解关于HTMLCSSJavaScript的基础知识,小编带领大家简单过一遍~~~ 🌈感兴趣的小伙伴看一看小编主页:GGBondlctrl-CSDN博客 🔥 你的点赞就是小编不断更新的最大动力 …...

响应“一机两用”政策 落实政务外网安全
在数字化时代,政务办公外网安全的重要性日益凸显,特别是在“一机两用”的背景下,即同一台终端既要处理政务内网的数据,又要访问互联网,这对网络安全提出了更高的要求。深信达SPN安全上网方案,即反向沙箱技术…...
通过JS删除当前域名中的全部COOKIE教程
有时候需要通过JS来控制一下网站的登录状态,就例如:网站登出功能,我们可以直接通过JS将所有COOKIE删除,COOKIE删除之后,网站自然也就退出了。 那么今天我就给大家分享一段JS的函数,通过调用这段函数就可以实现删除COO…...

Flutter:Widget生命周期
StatelessWidget:无状态部件的生命周期 import package:flutter/material.dart;void main() {runApp(App()); }class App extends StatelessWidget {overrideWidget build(BuildContext context) {return MaterialApp(home: MyHomePage(title: MyHome),);} }class M…...

Flutter:Dio下载文件到本地
import dart:io; import package:dio/dio.dart;main(){// 创建dio对象final dio Dio();// 下载地址var url https://*******.org/files/1.0.0.apk;// 手机端路径String savePath Directory.systemTemp.path/ceshi.apk;print(savePath);downLoad(dio,url,savePath); }downLo…...

[⑧5G NR]: PBCH payload生成
本篇博客记录下5G PBCH信道中payload数据的生成方式。PBCH payload一共32个比特,基本结构如下图: 根据SSB PDU中bchPayloadFlag的值有三种方式得到PBCH payload。 bchPayloadFlag 0:全部32比特由MAC层提供。 bchPayloadFlag 1:M…...

查看解决端口占用,以及docker解决端口占用的原理
在软件开发和部署过程中,端口占用是一个常见的问题。以下是查看和解决端口占用问题的完整解决方案: 一、查看端口占用情况 1. 在 Linux 系统中 方法一:使用 lsof 命令 sudo lsof -i:<端口号>输出信息中会显示占用端口的进程名称、PI…...

力扣-Hot100-链表其一【算法学习day.34】
前言 ###我做这类文档一个重要的目的还是给正在学习的大家提供方向(例如想要掌握基础用法,该刷哪些题?)我的解析也不会做的非常详细,只会提供思路和一些关键点,力扣上的大佬们的题解质量是非常非常高滴&am…...

centos7 升级openssl 与升级openssh 安装卸载 telnet-server
前言: 服务器被安全扫描,扫出了漏洞需要修复,根据提示将openssh升级为9.8p1的版本,同时需要升级openssl,但是升级openssh可能会导致ssh连接失败,从而无法继续操作,特别是远程机房尤为危险&#…...
:STL综合)
C++知识点总结(57):STL综合
STL综合 一、数据结构1. 队列2. 映射 二、队列例题1. 约瑟夫环(数据加强)2. 打印队列3. 小组队列4. 日志统计 2.0 三、映射真题1. 眼红的 Medusa2. 美食评委 一、数据结构 1. 队列 功能代码定义queue<tp>q入队.push(x)出队.pop()队头.front()队尾…...

mac2019环境 Airflow+hive+spark+hadoop本地环境安装
1 环境介绍 本地安装可分为两个部分,mac软件环境, python开发环境 ps: 安装过程参考chatgpt、csdn文章 1.1 mac软件环境 目标安装的的软件是hive、apache-spark、hadoop,但是这三个软件又依赖java(spark依赖)、ssh(…...

如何使用EasyExcel生成多列表组合填充的复杂Excel示例
作者:Funky_oaNiu 一、(需求)生成的表格效果:二、搞一个模板文件三、建立对应的表格实体类四、开始填充五、Vue3前端发起请求下载六、官方文档及AI问答 一、(需求)生成的表格效果: 其中只有顶部…...

利用最小二乘法找圆心和半径
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cmath> #include <Eigen/Dense> // 需安装Eigen库用于矩阵运算 // 定义点结构 struct Point { double x, y; Point(double x_, double y_) : x(x_), y(y_) {} }; // 最小二乘法求圆心和半径 …...

Chapter03-Authentication vulnerabilities
文章目录 1. 身份验证简介1.1 What is authentication1.2 difference between authentication and authorization1.3 身份验证机制失效的原因1.4 身份验证机制失效的影响 2. 基于登录功能的漏洞2.1 密码爆破2.2 用户名枚举2.3 有缺陷的暴力破解防护2.3.1 如果用户登录尝试失败次…...
51c自动驾驶~合集58
我自己的原文哦~ https://blog.51cto.com/whaosoft/13967107 #CCA-Attention 全局池化局部保留,CCA-Attention为LLM长文本建模带来突破性进展 琶洲实验室、华南理工大学联合推出关键上下文感知注意力机制(CCA-Attention),…...
理解 MCP 工作流:使用 Ollama 和 LangChain 构建本地 MCP 客户端
🌟 什么是 MCP? 模型控制协议 (MCP) 是一种创新的协议,旨在无缝连接 AI 模型与应用程序。 MCP 是一个开源协议,它标准化了我们的 LLM 应用程序连接所需工具和数据源并与之协作的方式。 可以把它想象成你的 AI 模型 和想要使用它…...

Unit 1 深度强化学习简介
Deep RL Course ——Unit 1 Introduction 从理论和实践层面深入学习深度强化学习。学会使用知名的深度强化学习库,例如 Stable Baselines3、RL Baselines3 Zoo、Sample Factory 和 CleanRL。在独特的环境中训练智能体,比如 SnowballFight、Huggy the Do…...
自然语言处理——循环神经网络
自然语言处理——循环神经网络 循环神经网络应用到基于机器学习的自然语言处理任务序列到类别同步的序列到序列模式异步的序列到序列模式 参数学习和长程依赖问题基于门控的循环神经网络门控循环单元(GRU)长短期记忆神经网络(LSTM)…...
ArcGIS Pro制作水平横向图例+多级标注
今天介绍下载ArcGIS Pro中如何设置水平横向图例。 之前我们介绍了ArcGIS的横向图例制作:ArcGIS横向、多列图例、顺序重排、符号居中、批量更改图例符号等等(ArcGIS出图图例8大技巧),那这次我们看看ArcGIS Pro如何更加快捷的操作。…...
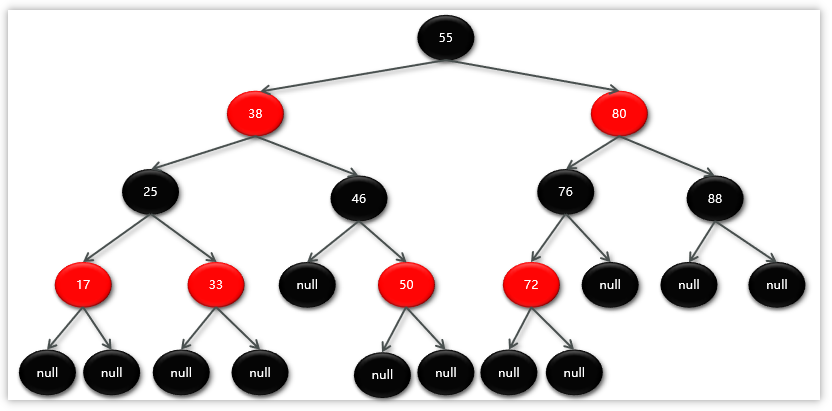
Map相关知识
数据结构 二叉树 二叉树,顾名思义,每个节点最多有两个“叉”,也就是两个子节点,分别是左子 节点和右子节点。不过,二叉树并不要求每个节点都有两个子节点,有的节点只 有左子节点,有的节点只有…...
python执行测试用例,allure报乱码且未成功生成报告
allure执行测试用例时显示乱码:‘allure’ �����ڲ����ⲿ���Ҳ���ǿ�&am…...

OD 算法题 B卷【正整数到Excel编号之间的转换】
文章目录 正整数到Excel编号之间的转换 正整数到Excel编号之间的转换 excel的列编号是这样的:a b c … z aa ab ac… az ba bb bc…yz za zb zc …zz aaa aab aac…; 分别代表以下的编号1 2 3 … 26 27 28 29… 52 53 54 55… 676 677 678 679 … 702 703 704 705;…...
