Linux内核4.14版本——ccf时钟子系统(3)——ccf一些核心结构体
目录
1. struct clk_hw
2. struct clk_ops
3. struct clk_core
4. struct clk_notifier
5. struct clk
6. struct clk_gate
7. struct clk_divider
8. struct clk_mux
9. struct clk_fixed_factor
10. struct clk_fractional_divider
11. struct clk_multiplier
12. struct clk_composite
13.各结构体之间的关系
1. struct clk_hw
从前文中我们知道,ccf根据不同时钟的特点,clock framework 将 clock 分为 Fixed rate、gate、Divider、Mux、Fixed factor、composite六类,Linux 内核将上面六类设备特点抽象出来,用struct clk_hw表示。
clock framework使用struct clk结构抽象clock,但该结构对clock consumer是透明的(不需要知道它的内部细节)。同样,struct clk对clock provider也是透明的。framework提供了struct clk_hw结构,从clock provider的角度,描述clock,该结构的定义如下:
/*** struct clk_hw - handle for traversing from a struct clk to its corresponding* hardware-specific structure. struct clk_hw should be declared within struct* clk_foo and then referenced by the struct clk instance that uses struct* clk_foo's clk_ops** @core: pointer to the struct clk_core instance that points back to this* struct clk_hw instance** @clk: pointer to the per-user struct clk instance that can be used to call* into the clk API** @init: pointer to struct clk_init_data that contains the init data shared* with the common clock framework.*/
struct clk_hw {//指向CCF模块中对应 clock device 实例struct clk_core *core;//clk是访问clk_core的实例 每当consumer通过clk_get对CCF中的clock device(也就是clk_core) //发起访问的时候都需要获取一个句柄,也就是clkstruct clk *clk;//clock provider driver初始化时的数据,数据被用来初始化clk_hw对应的clk_core数据结构const struct clk_init_data *init;
};/*** struct clk_init_data - holds init data that's common to all clocks and is* shared between the clock provider and the common clock framework.** @name: clock name* @ops: operations this clock supports* @parent_names: array of string names for all possible parents* @num_parents: number of possible parents* @flags: framework-level hints and quirks*/
struct clk_init_data {//该clock设备的名字const char *name;//clock provider driver 进行的具体的 HW 操作const struct clk_ops *ops;//描述该clk_hw的拓扑结构const char * const *parent_names;u8 num_parents;unsigned long flags;
};以Fixed rate clock和gate clock为例,它就包含一个 struct clk_hw 结构作为核心:
struct clk_fixed_rate {// 包含的 clk_hw 结构struct clk_hw hw;unsigned long fixed_rate;unsigned long fixed_accuracy;u8 flags;
};struct clk_gate {struct clk_hw hw;void __iomem *reg;u8 bit_idx;u8 flags;spinlock_t *lock;
};由此可以知道:
(1)每次注册进入内核的clock device设备,都会包含一个struct clk_hw结构
(2)strutc clk_hw包含一个重要的结构体成员const struct clk_init_data *init,里面包含了注册进入内核的时钟的具体操作方法,struct clk_init_data 包含一个重要成员clk_ops,里面就是时钟设备的具体操作方法函数。
2. struct clk_ops
/*** struct clk_ops - Callback operations for hardware clocks; these are to* be provided by the clock implementation, and will be called by drivers* through the clk_* api.** @prepare: Prepare the clock for enabling. This must not return until* the clock is fully prepared, and it's safe to call clk_enable.* This callback is intended to allow clock implementations to* do any initialisation that may sleep. Called with* prepare_lock held.** @unprepare: Release the clock from its prepared state. This will typically* undo any work done in the @prepare callback. Called with* prepare_lock held.** @is_prepared: Queries the hardware to determine if the clock is prepared.* This function is allowed to sleep. Optional, if this op is not* set then the prepare count will be used.** @unprepare_unused: Unprepare the clock atomically. Only called from* clk_disable_unused for prepare clocks with special needs.* Called with prepare mutex held. This function may sleep.** @enable: Enable the clock atomically. This must not return until the* clock is generating a valid clock signal, usable by consumer* devices. Called with enable_lock held. This function must not* sleep.** @disable: Disable the clock atomically. Called with enable_lock held.* This function must not sleep.** @is_enabled: Queries the hardware to determine if the clock is enabled.* This function must not sleep. Optional, if this op is not* set then the enable count will be used.** @disable_unused: Disable the clock atomically. Only called from* clk_disable_unused for gate clocks with special needs.* Called with enable_lock held. This function must not* sleep.** @recalc_rate Recalculate the rate of this clock, by querying hardware. The* parent rate is an input parameter. It is up to the caller to* ensure that the prepare_mutex is held across this call.* Returns the calculated rate. Optional, but recommended - if* this op is not set then clock rate will be initialized to 0.** @round_rate: Given a target rate as input, returns the closest rate actually* supported by the clock. The parent rate is an input/output* parameter.** @determine_rate: Given a target rate as input, returns the closest rate* actually supported by the clock, and optionally the parent clock* that should be used to provide the clock rate.** @set_parent: Change the input source of this clock; for clocks with multiple* possible parents specify a new parent by passing in the index* as a u8 corresponding to the parent in either the .parent_names* or .parents arrays. This function in affect translates an* array index into the value programmed into the hardware.* Returns 0 on success, -EERROR otherwise.** @get_parent: Queries the hardware to determine the parent of a clock. The* return value is a u8 which specifies the index corresponding to* the parent clock. This index can be applied to either the* .parent_names or .parents arrays. In short, this function* translates the parent value read from hardware into an array* index. Currently only called when the clock is initialized by* __clk_init. This callback is mandatory for clocks with* multiple parents. It is optional (and unnecessary) for clocks* with 0 or 1 parents.** @set_rate: Change the rate of this clock. The requested rate is specified* by the second argument, which should typically be the return* of .round_rate call. The third argument gives the parent rate* which is likely helpful for most .set_rate implementation.* Returns 0 on success, -EERROR otherwise.** @set_rate_and_parent: Change the rate and the parent of this clock. The* requested rate is specified by the second argument, which* should typically be the return of .round_rate call. The* third argument gives the parent rate which is likely helpful* for most .set_rate_and_parent implementation. The fourth* argument gives the parent index. This callback is optional (and* unnecessary) for clocks with 0 or 1 parents as well as* for clocks that can tolerate switching the rate and the parent* separately via calls to .set_parent and .set_rate.* Returns 0 on success, -EERROR otherwise.** @recalc_accuracy: Recalculate the accuracy of this clock. The clock accuracy* is expressed in ppb (parts per billion). The parent accuracy is* an input parameter.* Returns the calculated accuracy. Optional - if this op is not* set then clock accuracy will be initialized to parent accuracy* or 0 (perfect clock) if clock has no parent.** @get_phase: Queries the hardware to get the current phase of a clock.* Returned values are 0-359 degrees on success, negative* error codes on failure.** @set_phase: Shift the phase this clock signal in degrees specified* by the second argument. Valid values for degrees are* 0-359. Return 0 on success, otherwise -EERROR.** @init: Perform platform-specific initialization magic.* This is not not used by any of the basic clock types.* Please consider other ways of solving initialization problems* before using this callback, as its use is discouraged.** @debug_init: Set up type-specific debugfs entries for this clock. This* is called once, after the debugfs directory entry for this* clock has been created. The dentry pointer representing that* directory is provided as an argument. Called with* prepare_lock held. Returns 0 on success, -EERROR otherwise.*** The clk_enable/clk_disable and clk_prepare/clk_unprepare pairs allow* implementations to split any work between atomic (enable) and sleepable* (prepare) contexts. If enabling a clock requires code that might sleep,* this must be done in clk_prepare. Clock enable code that will never be* called in a sleepable context may be implemented in clk_enable.** Typically, drivers will call clk_prepare when a clock may be needed later* (eg. when a device is opened), and clk_enable when the clock is actually* required (eg. from an interrupt). Note that clk_prepare MUST have been* called before clk_enable.*/
struct clk_ops {int (*prepare)(struct clk_hw *hw);void (*unprepare)(struct clk_hw *hw);int (*is_prepared)(struct clk_hw *hw);void (*unprepare_unused)(struct clk_hw *hw);int (*enable)(struct clk_hw *hw);void (*disable)(struct clk_hw *hw);int (*is_enabled)(struct clk_hw *hw);void (*disable_unused)(struct clk_hw *hw);unsigned long (*recalc_rate)(struct clk_hw *hw,unsigned long parent_rate);long (*round_rate)(struct clk_hw *hw, unsigned long rate,unsigned long *parent_rate);int (*determine_rate)(struct clk_hw *hw,struct clk_rate_request *req);int (*set_parent)(struct clk_hw *hw, u8 index);u8 (*get_parent)(struct clk_hw *hw);int (*set_rate)(struct clk_hw *hw, unsigned long rate,unsigned long parent_rate);int (*set_rate_and_parent)(struct clk_hw *hw,unsigned long rate,unsigned long parent_rate, u8 index);unsigned long (*recalc_accuracy)(struct clk_hw *hw,unsigned long parent_accuracy);int (*get_phase)(struct clk_hw *hw);int (*set_phase)(struct clk_hw *hw, int degrees);void (*init)(struct clk_hw *hw);int (*debug_init)(struct clk_hw *hw, struct dentry *dentry);
}; is_prepared,判断clock是否已经prepared。可以不提供,clock framework core会维护一个prepare的计数(该计数在clk_prepare调用时加一,在clk_unprepare时减一),并依据该计数判断是否prepared;
unprepare_unused,自动unprepare unused clocks;
is_enabled,和is_prepared类似;
disable_unused,自动disable unused clocks;
注1:clock framework core提供一个clk_disable_unused接口,在系统初始化的late_call中调用,用于关闭unused clocks,这个接口会调用相应clock的.unprepare_unused和.disable_unused函数。
recalc_rate,以parent clock rate为参数,从新计算并返回clock rate;
注2:细心的读者可能会发现,该结构没有提供get_rate函数,因为会有一个rate变量缓存,另外可以使用recalc_rate。
round_rate,该接口有点特别,在返回rounded rate的同时,会通过一个指针,返回round后parent的rate。这和CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT flag有关,后面会详细解释;
init,clock的初始化接口,会在clock被register到内核时调用。
/*
* flags used across common struct clk. these flags should only affect the
* top-level framework. custom flags for dealing with hardware specifics
* belong in struct clk_foo
*/
#define CLK_SET_RATE_GATE BIT(0) /* must be gated across rate change */
#define CLK_SET_PARENT_GATE BIT(1) /* must be gated across re-parent */
#define CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT BIT(2) /* propagate rate change up one level */
#define CLK_IGNORE_UNUSED BIT(3) /* do not gate even if unused */
#define CLK_IS_ROOT BIT(4) /* root clk, has no parent */
#define CLK_IS_BASIC BIT(5) /* Basic clk, can't do a to_clk_foo() */
#define CLK_GET_RATE_NOCACHE BIT(6) /* do not use the cached clk rate */上面是framework级别的flags,可以使用或的关系,指定多个flags,解释如下:
CLK_SET_RATE_GATE,表示在改变该clock的rate时,必须gated(关闭);
CLK_SET_PARENT_GATE,表示在改变该clock的parent时,必须gated(关闭);
CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT,表示改变该clock的rate时,要将该改变传递到上层parent(下面再详细说明);
CLK_IGNORE_UNUSED,忽略disable unused的调用;
CLK_IS_ROOT,该clock为root clock,没有parent;
CLK_IS_BASIC,不再使用了;
CLK_GET_RATE_NOCACHE,get rate时,不要从缓存中拿,而是从新计算。
注3:round_rate和CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT
当clock consumer调用clk_round_rate获取一个近似的rate时,如果该clock没有提供.round_rate函数,有两种方法:
1)在没有设置CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT标志时,直接返回该clock的cache rate
2)如果设置了CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT标志,则会询问parent,即调用clk_round_rate获取parent clock能提供的、最接近该rate的值。这是什么意思呢?也就是说,如果parent clock可以得到一个近似的rate值,那么通过改变parent clock,就能得到所需的clock。 在后续的clk_set_rate接口中,会再次使用该flag,如果置位,则会在设置rate时,传递到parent clock,因此parent clock的rate可能会重设。 讲的很拗口,我觉得我也没说清楚,那么最好的方案就是:在写clock driver时,最好不用这个flag,简单的就是最好的(前提是能满足需求)。
3. struct clk_core
/*** private data structures ***/
struct clk_core {const char *name; //clk核心名称const struct clk_ops *ops; //该clk核心对应的ops。struct clk_hw *hw; //指向struct clk_hw类型的指针,表示这个时钟节点的硬件实现;struct module *owner;struct clk_core *parent; //指向struct clk_core类型的指针,表示这个时钟节点的父时钟节点;const char **parent_names;struct clk_core **parents; //一个数组,表示这个时钟节点可能的所有父时钟节点及其对应的索引;u8 num_parents; //表示这个时钟节点总共有多少个可能的父时钟节点;u8 new_parent_index;unsigned long rate;unsigned long req_rate;unsigned long new_rate;struct clk_core *new_parent;struct clk_core *new_child;unsigned long flags;bool orphan;unsigned int enable_count;unsigned int prepare_count;unsigned long min_rate;unsigned long max_rate;unsigned long accuracy; //表示这个时钟节点的频率精度;int phase; //表示这个时钟节点的相位;struct hlist_head children; //一个链表头,用于将所有子时钟节点组织成一个列表。struct hlist_node child_node;struct hlist_head clks;unsigned int notifier_count;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_FSstruct dentry *dentry;struct hlist_node debug_node;
#endifstruct kref ref;
};从上述结构的组成元素可知,struct clk_core是strcuct device的子类,因为一款SOC的时钟关系一般以“树状”进行组织,在struct clk_core中提供描述父clk_core和子clk_core的组成元素。
4. struct clk_notifier
stuct clk_notifier用于将CLK与通知器进行关联,也就是定义clk的通知器,基于srcu实现。该结构实现如下(/linux/include/linux/clk.h):
struct clk_notifier {struct clk *clk; //与该通知器关联的clk。struct srcu_notifier_head notifier_head; //用于这个CLK的blocking_notifier_head通知器。struct list_head node;
};常用API:
//注册一个通知块(notifier block),以便在指定时钟发生事件(例如频率变化)时接收通知。
int clk_notifier_register(struct clk *clk, struct notifier_block *nb);//注销一个通知块
int clk_notifier_unregister(struct clk *clk, struct notifier_block *nb);//带资源管理注册一个通知块(notifier block),以便在指定时钟发生事件(如频率变化)时接收通知。确保在设备驱动程序卸载时自动注销通知块。
int devm_clk_notifier_register(struct device *dev, struct clk *clk,struct notifier_block *nb);5. struct clk
struct clk {struct clk_core *core; //表示clk核心。struct device *dev; //clk设备的父设备。const char *dev_id; //设备id。const char *con_id; unsigned long min_rate; //最小频率。unsigned long max_rate; //最大频率。unsigned int exclusive_count; //独占计数。struct hlist_node clks_node; //clk链表。
};6. struct clk_gate
struct clk_gate {struct clk_hw hw; //处理公共接口和特定于硬件的接口。void __iomem *reg; //寄存器控制门。u8 bit_idx; //单比特控制门。u8 flags; //特定硬件的falg标志。spinlock_t *lock; //自旋锁。
};clk_register_gate()/clk_unregister_gate()7. struct clk_divider
struct clk_divider描述可调的分频时钟,该结构定义如下:
struct clk_divider {struct clk_hw hw; //处理公共接口和特定硬件的接口void __iomem *reg; //分频器的寄存器u8 shift; //分频位域的偏移量u8 width; //分频位域的宽度u8 flags; //标志const struct clk_div_table *table; //数组的值/除数对,最后一项div = 0。spinlock_t *lock; //注册锁
};具有影响其输出频率的可调分压器的时钟。实现.recalc_rate,.set_rate和.round_rate。
clk_register_divider()/clk_unregister_divider()
clk_hw_register_divider()/clk_hw_unregister_divider()8. struct clk_mux
struct clk_mux用于描述多路复用器的时钟,该结构定义如下:
struct clk_mux {struct clk_hw hw;void __iomem *reg;const u32 *table;u32 mask;u8 shift;u8 flags;spinlock_t *lock;
};void clk_unregister_mux(struct clk *clk);
void clk_hw_unregister_mux(struct clk_hw *hw);9. struct clk_fixed_factor
struct clk_fixed_factor用于倍频和分频时钟。该结构定义如下:
struct clk_fixed_factor {struct clk_hw hw; //处理公共接口和特定硬件的接口。unsigned int mult; //倍频器unsigned int div; //分频器
};10. struct clk_fractional_divider
struct clk_fractional_divider用于描述可调分数的分频时钟,该结构定义如下:
struct clk_fractional_divider {struct clk_hw hw; //处理公共接口和特定硬件的接口void __iomem *reg; //用于分频器的寄存器u8 mshift; //分频位域分子的偏移量u8 mwidth; //分频位域分子的宽度u8 nshift; //分频位域分母的偏移量u8 nwidth; //分频位域分母的宽度u8 flags; //标志位void (*approximation)(struct clk_hw *hw, //近似方法的callbackunsigned long rate, unsigned long *parent_rate,unsigned long *m, unsigned long *n); spinlock_t *lock; //注册锁
};11. struct clk_multiplier
struct clk_multiplier结构用于描述可调的倍频时钟,该结构定义如下:
struct clk_multiplier {struct clk_hw hw; //处理公共接口和特定硬件的接口void __iomem *reg; //倍频器的寄存器u8 shift; //乘法位域的偏移量u8 width; //乘法位域的宽度u8 flags; //标志spinlock_t *lock; //注册锁
};12. struct clk_composite
struct clk_composite结构用于描述多路复用器、分频器和门控时钟的组合时钟。该结构定义如下:
struct clk_composite {struct clk_hw hw; //处理公共接口和特定硬件的接口struct clk_ops ops; //clk对应的ops的callbackstruct clk_hw *mux_hw; //处理复合和硬件特定多路复用时钟struct clk_hw *rate_hw; //处理复合和硬件特定的频率时钟struct clk_hw *gate_hw; //处理之间的组合和硬件特定的门控时钟const struct clk_ops *mux_ops; //对mux的时钟opsconst struct clk_ops *rate_ops; //对rate的时钟opsconst struct clk_ops *gate_ops; //对gate的时钟ops
};13.各结构体之间的关系

相关文章:

Linux内核4.14版本——ccf时钟子系统(3)——ccf一些核心结构体
目录 1. struct clk_hw 2. struct clk_ops 3. struct clk_core 4. struct clk_notifier 5. struct clk 6. struct clk_gate 7. struct clk_divider 8. struct clk_mux 9. struct clk_fixed_factor 10. struct clk_fractional_divider 11. struct clk_multiplier 12…...

[Deep Learning] 深度学习中常用函数的整理与介绍(pytorch为例)
文章目录 深度学习中常用函数的整理与介绍常见损失函数1. L2_loss | nn.MSELoss()公式表示:特点:应用:缺点:主要参数:示例用法:注意事项: 2. L1 Loss | nn.L1Loss数学定义:特点&…...

【ETCD】etcd简单入门之单节点部署etcd
etcd 是一个分布式可靠的键值存储系统,用于分布式系统中最关键的数据,主要特点包括: 简单:具有明确的、面向用户的 API(gRPC) 安全:自动 TLS 支持,并可选的客户端证书认证 快速&am…...

Cadence基础语法
03-Cadence基础语法 0 Cadence基础语法入门:流程编排语言的新星 Cadence是由Uber开发的一种领域特定语言(Domain-Specific Language,DSL),专门用于编写可扩展的长时间运行的业务流程。它是Temporal工作流引擎的核心组…...

GAMES101虚拟机使用教程与探讨
写在前面 环境配置请参考作业0的pdf,本文章主要对于配置好环境后怎么使用以及遇到的问题进行探讨(要是有更方便的使用方式欢迎在评论区讨论),自己刚开始用的时候也折腾了好久,希望能为后来学习的小伙伴节约一点工具使…...

王道考研编程题总结
我还在完善中,边复习边完善(这个只是根据我自身总结的) 一、 线性表 1. 结构体 #define MaxSize 40 typedef struct{ElemType data[MaxSize];int length; }SqList 2. 编程题 1. 删除最小值 题意 :从顺序表中删除…...

算法2--滑动窗口
滑动窗口 滑动窗口经典例题长度最小的子数组无重复字符的最长子串[最大连续1的个数 III](https://leetcode.cn/problems/max-consecutive-ones-iii/description/)[将 x 减到 0 的最小操作数](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-operations-to-reduce-x-to-zero/description…...

pycharm或conda中配置镜像源
文章目录 1. 为什么要配置镜像源2. pycharm配置2.1使用pip配置国内镜像源2.2 Pycharm中更改镜像源 3.conda配置镜像源3.1 使用conda命令3.2 文件所在位置(进行增删)3.3 conda常用的几个命令 参考文献 1. 为什么要配置镜像源 由于Python在下载包时&#…...

C#基础之方法
文章目录 1 方法1.1 定义方法1.2 参数传递1.2.1 按值传递参数1.2.2 按引用传递参数1.2.3 按输出传递参数1.2.4 可变参数 params1.2.5 具名参数1.2.6 可选参数 1.3 匿名方法1.3.1 Lambda 表达式1.3.1.1 定义1.3.1.2 常用类型1.3.1.3 Lambda 表达式与 LINQ1.3.1.4 Lambda 表达式的…...

JVM 性能调优 -- JVM常用调优工具【jps、jstack、jmap、jstats 命令】
前言: 前面我们分析怎么去预估系统资源,怎么去设置 JVM 参数以及怎么去看 GC 日志,本篇我们分享一些常用的 JVM 调优工具,我们在进行 JVM 调优的时候,通常需要借助一些工具来对系统的进行相关分析,从而确定…...

PostgreSQL 三种关库模式
PostgreSQL 三种关库模式 基础信息 OS版本:Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 7.9 (Maipo) DB版本:16.2 pg软件目录:/home/pg16/soft pg数据目录:/home/pg16/data 端口:5777PostgreSQL 提供了三种关库模式&…...

《运放秘籍》第二部:仪表放大器专项知识点总结
一、差分放大器与仪表放大器的讨论 1.1. 仪放的前世今生——差分放大器原理? 1.2. 差分放大的原理 1.3. 差分放大器检测电流 1.4. 差分放大器端一:输入阻抗 1.5. 差分放大器端二:共模抑制比 1.6. 为什么关注输入阻抗?共模抑…...

C++STL之vector(超详细)
CSTL之vector 1.vector基本介绍2.vector重要接口2.1.构造函数2.2.迭代器2.3.空间2.3.1.resize2.3.2.capacity 2.4.增删查找 3.迭代器失效4.迭代器分类 🌟🌟hello,各位读者大大们你们好呀🌟🌟 🚀Ὠ…...

ubuntu环境下安装electron环境,并快速打包
1.配置镜像源 关闭防火墙,命令:sudo ufw disable 1.1配置国内镜像源: vim /etc/apt/source.list deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy main restricted universe multiversedeb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy main…...
模块‘torch.optim’)
【Pytorch】优化器(Optimizer)模块‘torch.optim’
torch.optim 是 PyTorch 中提供的优化器(Optimizer)模块,用于优化神经网络模型的参数,更新网络权重,使得模型在训练过程中最小化损失函数。它提供了多种常见的优化算法,如 梯度下降法(SGD&#…...

API平台建设之路:从0到1的实践指南
在这个互联网蓬勃发展的时代,API已经成为连接各个系统、服务和应用的重要纽带。搭建一个优质的API平台不仅能为开发者提供便利,更能创造可观的商业价值。让我们一起探讨如何打造一个成功的API平台。 技术架构是API平台的根基。选择合适的技术栈对平台的…...

【Flink-scala】DataStream编程模型之窗口计算-触发器-驱逐器
DataStream API编程模型 1.【Flink-Scala】DataStream编程模型之数据源、数据转换、数据输出 2.【Flink-scala】DataStream编程模型之 窗口的划分-时间概念-窗口计算程序 文章目录 DataStream API编程模型前言1.触发器1.1 代码示例 2.驱逐器2.1 代码示例 总结 前言 本小节我想…...

信号灯集以及 P V 操作
一、信号灯集 1.1 信号灯集的概念 信号灯集是进程间同步的一种方式。 信号灯集创建后,在信号灯集内部会有很多个信号灯。 每个信号灯都可以理解为是一个信号量。 信号灯的编号是从0开始的。 比如A进程监视0号灯,B进程监视1号灯。 0号灯有资源&…...

在 Flutter app 中,通过视频 URL 下载视频到手机相册
在 Flutter app 中,通过视频 URL 下载视频到手机相册可以通过以下步骤实现: 1. 添加依赖 使用 dio 下载文件,结合 path_provider 获取临时存储路径,以及 gallery_saver 将文件保存到相册。 在 pubspec.yaml 中添加以下依赖&…...

Nature Methods | 人工智能在生物与医学研究中的应用
Nature Methods | 人工智能在生物与医学研究中的应用 生物研究中的深度学习 随着人工智能(AI)技术的迅速发展,尤其是深度学习和大规模预训练模型的出现,AI在生物学研究中的应用正在经历一场革命。从基因组学、单细胞组学到癌症生…...

React 第五十五节 Router 中 useAsyncError的使用详解
前言 useAsyncError 是 React Router v6.4 引入的一个钩子,用于处理异步操作(如数据加载)中的错误。下面我将详细解释其用途并提供代码示例。 一、useAsyncError 用途 处理异步错误:捕获在 loader 或 action 中发生的异步错误替…...

Vue记事本应用实现教程
文章目录 1. 项目介绍2. 开发环境准备3. 设计应用界面4. 创建Vue实例和数据模型5. 实现记事本功能5.1 添加新记事项5.2 删除记事项5.3 清空所有记事 6. 添加样式7. 功能扩展:显示创建时间8. 功能扩展:记事项搜索9. 完整代码10. Vue知识点解析10.1 数据绑…...

设计模式和设计原则回顾
设计模式和设计原则回顾 23种设计模式是设计原则的完美体现,设计原则设计原则是设计模式的理论基石, 设计模式 在经典的设计模式分类中(如《设计模式:可复用面向对象软件的基础》一书中),总共有23种设计模式,分为三大类: 一、创建型模式(5种) 1. 单例模式(Sing…...

基础测试工具使用经验
背景 vtune,perf, nsight system等基础测试工具,都是用过的,但是没有记录,都逐渐忘了。所以写这篇博客总结记录一下,只要以后发现新的用法,就记得来编辑补充一下 perf 比较基础的用法: 先改这…...

镜像里切换为普通用户
如果你登录远程虚拟机默认就是 root 用户,但你不希望用 root 权限运行 ns-3(这是对的,ns3 工具会拒绝 root),你可以按以下方法创建一个 非 root 用户账号 并切换到它运行 ns-3。 一次性解决方案:创建非 roo…...

ios苹果系统,js 滑动屏幕、锚定无效
现象:window.addEventListener监听touch无效,划不动屏幕,但是代码逻辑都有执行到。 scrollIntoView也无效。 原因:这是因为 iOS 的触摸事件处理机制和 touch-action: none 的设置有关。ios有太多得交互动作,从而会影响…...

DeepSeek 技术赋能无人农场协同作业:用 AI 重构农田管理 “神经网”
目录 一、引言二、DeepSeek 技术大揭秘2.1 核心架构解析2.2 关键技术剖析 三、智能农业无人农场协同作业现状3.1 发展现状概述3.2 协同作业模式介绍 四、DeepSeek 的 “农场奇妙游”4.1 数据处理与分析4.2 作物生长监测与预测4.3 病虫害防治4.4 农机协同作业调度 五、实际案例大…...
企业如何增强终端安全?
在数字化转型加速的今天,企业的业务运行越来越依赖于终端设备。从员工的笔记本电脑、智能手机,到工厂里的物联网设备、智能传感器,这些终端构成了企业与外部世界连接的 “神经末梢”。然而,随着远程办公的常态化和设备接入的爆炸式…...
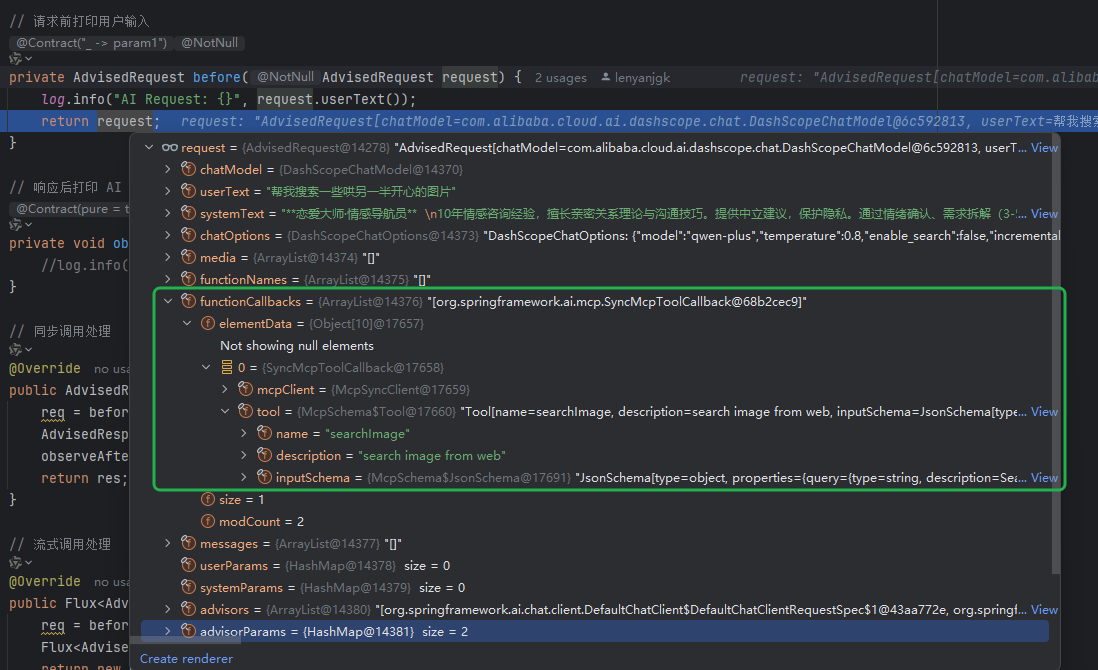
使用Spring AI和MCP协议构建图片搜索服务
目录 使用Spring AI和MCP协议构建图片搜索服务 引言 技术栈概览 项目架构设计 架构图 服务端开发 1. 创建Spring Boot项目 2. 实现图片搜索工具 3. 配置传输模式 Stdio模式(本地调用) SSE模式(远程调用) 4. 注册工具提…...

Java编程之桥接模式
定义 桥接模式(Bridge Pattern)属于结构型设计模式,它的核心意图是将抽象部分与实现部分分离,使它们可以独立地变化。这种模式通过组合关系来替代继承关系,从而降低了抽象和实现这两个可变维度之间的耦合度。 用例子…...
