【k8s深入学习之 event 记录】初步了解 k8s event 记录机制
event 事件记录初始化
- 一般在控制器都会有如下的初始化函数,初始化 event 记录器等参数
1. 创建 EventBroadcaster
record.NewBroadcaster(): 创建事件广播器,用于记录和分发事件。StartLogging(klog.Infof): 将事件以日志的形式输出。StartRecordingToSink: 将事件发送到 Kubernetes API Server,存储为Event资源。
2. 创建 EventRecorder
NewRecorder(scheme, source)从广播器中创建事件记录器。scheme: 用于验证和序列化资源。source: 指定事件的来源(如example-controller)。
import "k8s.io/client-go/tools/record"func (c *controller) Initialize(opt *framework.ControllerOption) error {// ...// 1. 创建事件广播器 eventBroadcastereventBroadcaster := record.NewBroadcaster()// 将 event 记录到 logeventBroadcaster.StartLogging(klog.Infof)// 将 event 记录到 apiserver// c.kubeClient.CoreV1().Events("") 这个是创建一个可以操作任意 ns 下 event 的 clienteventBroadcaster.StartRecordingToSink(&corev1.EventSinkImpl{Interface: c.kubeClient.CoreV1().Events("")})// 2. 基于事件广播器 创建事件记录器 Recorderc.recorder = eventBroadcaster.NewRecorder(versionedscheme.Scheme, v1.EventSource{Component: "example-controller"})
}// 事件的记录
const Create-Reason = "PodCreate"
func (c *controller)Controller_Do_Something(pod *corev1.Pod){newPod:= pod.DeepCopy()// 生成个 event,并记录// 内容为 newPod 创建成功,event等级为 Normal,Reason 是 PodCreate,Message 是 Create Pod succeed// 之后 Recorder 内的 eventBroadcaster 会将此 event 广播出去,然后 eventBroadcaster 之前注册的日志记录和event存储逻辑会执行// 日志记录逻辑,会通过 klog.Infof 将此 event 打印出来// event存储逻辑,会将此 event 存储到 apiserverc.recorder.Event(newPod, v1.EventTypeNormal, Create-Reason, "Create Pod succeed")
}
源码解析
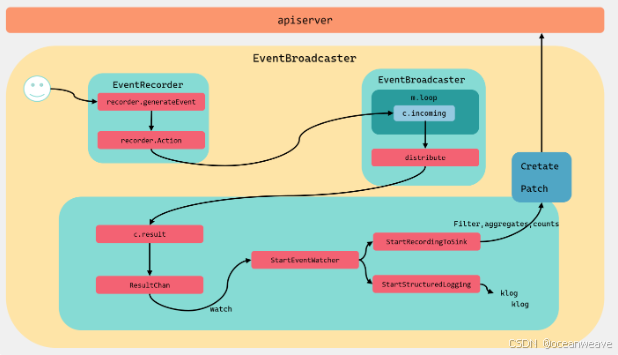
0- 总体逻辑设计
-
控制中心 Broadcaster
-
eventBroadcaster := record.NewBroadcaster()创建一个公共数据源(或理解为总控中心,也可以称之为控制器,但不是k8s 控制器)- 返回的是
eventBroadcasterImpl结构体,其封装了Broadcaster结构体,因此eventBroadcasterImpl结构体的字段很丰富
- 返回的是
-
Broadcaster中的字段主要记录处理 event 的监听者watchers,以及分发的控制等eventBroadcaster.StartLogging(klog.Infof)就是一个watchereventBroadcaster.StartRecordingToSink(&corev1.EventSinkImpl{Interface: c.kubeClient.CoreV1().Events("")})也是个watcher- 这些
watcher都会被记录到Broadcaster结构体的watchers map[int64]*broadcasterWatcher的map 中
-
eventBroadcasterImpl在Broadcaster基础上增加少量配置参数和控制函数
-
-
Event 分发和 watcher 处理逻辑
eventBroadcaster := record.NewBroadcaster()执行过程中会调用watch.NewLongQueueBroadcaster(maxQueuedEvents, watch.DropIfChannelFull)函数,其会开启 event 分发逻辑go m.loop()go m.loop()用于处理 event 的分发,读取eventBroadcasterImpl中incoming chan Event通道传来的 event,分发给各个 watcher 的resultchannelincoming中的 event 是由Recorder写入的,Recorder.Event会生成个 event ,并发送到incomimgchannel 中go m.loop()函数会读取incoming通道中的 Event,发送个各个watcher, 然后各个watcher执行自己的逻辑(如记录为 info级别日志、或写入apiserver等)
- 同时为了避免主进程的结束导致
go m.loop()进程结束,NewLongQueueBroadcaster还利用distributing sync.WaitGroup变量,进行m.distributing.Add(1),让主进程等待(避免主进程快速结束,导致 loop 进程结束)
StartLogging或StartRecordingToSink函数会调用StartEventWatcher函数,StartEventWatcher函数将传入的参数变为一个 event处理函数eventHandler,StartEventWatcher函数同时会开启一个 go 协程,读取各自 watcherresultchannel 中的 event,之后用eventHandler进行处理(如记录为 info级别日志、或写入apiserver等)
-
Event 产生逻辑
-
Recorder是由eventBroadcaster.NewRecorder创建出来的,相当于对eventBroadcasterImpl中Broadcaster的封装 -
Recorder.Event会生成个 event ,并发送到incomimgchannel 中-
Recorder会利用Broadcaster的incomingchannel 写入 event -
Recorder会利用Broadcaster的incomingBlock,控制写入时的并发,避免同一时间写入 event 过多导致错乱(这部分逻辑在blockQueue函数中)
-
-
1- 控制中心的创建 —— NewBroadcaster 函数
- 创建的
eventBroadcaster,实际上就是创建一个eventBroadcasterImpl结构体,并传入一些配置参数进行初始化 - 注意
eventBroadcasterImpl封装了Broadcaster结构体- 注意
Broadcaster中有很多channel、watchers和分发相关控制、并发控制字段等eventBroadcaster.StartLogging(klog.Infof)就是一个watchereventBroadcaster.StartRecordingToSink(&corev1.EventSinkImpl{Interface: c.kubeClient.CoreV1().Events("")})也是个watcher- 这些
watcher都会被记录到watchers map[int64]*broadcasterWatcher的map 中
- 基于
eventBroadcaster创建的Recorder,实际上级就是对eventBroadcasterImpl结构体的封装 - 之后
Recorder创建 event 时,会传入到eventBroadcasterImpl内Broadcaster
- 注意
// 路径 mod/k8s.io/client-go@v0.29.0/tools/record/event.go
const maxQueuedEvents = 1000
type FullChannelBehavior int
const (WaitIfChannelFull FullChannelBehavior = iotaDropIfChannelFull
)// Creates a new event broadcaster.
func NewBroadcaster(opts ...BroadcasterOption) EventBroadcaster {c := config{sleepDuration: defaultSleepDuration,}for _, opt := range opts {opt(&c)}// 重点关注eventBroadcaster := &eventBroadcasterImpl{Broadcaster: watch.NewLongQueueBroadcaster(maxQueuedEvents, watch.DropIfChannelFull),sleepDuration: c.sleepDuration,options: c.CorrelatorOptions,}ctx := c.Contextif ctx == nil {ctx = context.Background()} else {// Calling Shutdown is not required when a context was provided:// when the context is canceled, this goroutine will shut down// the broadcaster.go func() {<-ctx.Done()eventBroadcaster.Broadcaster.Shutdown()}()}eventBroadcaster.cancelationCtx, eventBroadcaster.cancel = context.WithCancel(ctx)// 重点关注return eventBroadcaster
}// 路径 mod/k8s.io/apimachinery@v0.29.0/pkg/watch/mux.go
// NewLongQueueBroadcaster functions nearly identically to NewBroadcaster,
// except that the incoming queue is the same size as the outgoing queues
// (specified by queueLength).
func NewLongQueueBroadcaster(queueLength int, fullChannelBehavior FullChannelBehavior) *Broadcaster {m := &Broadcaster{watchers: map[int64]*broadcasterWatcher{},incoming: make(chan Event, queueLength),stopped: make(chan struct{}),watchQueueLength: queueLength,fullChannelBehavior: fullChannelBehavior,}m.distributing.Add(1) // distributing sync.WaitGroup, 1 个进程go m.loop() // loop 进程,很关键! 处理 event 的分发,分发给 watcher 处理 return m
}
1.1- eventBroadcasterImpl 结构体
// 路径 mod/k8s.io/client-go@v0.29.0/tools/record/event.go
type eventBroadcasterImpl struct {*watch.Broadcaster // 此处引用下面的结构体sleepDuration time.Durationoptions CorrelatorOptionscancelationCtx context.Contextcancel func()
}// 路径 /mod/k8s.io/apimachinery@v0.29.0/pkg/watch/mux.go
// Broadcaster distributes event notifications among any number of watchers. Every event
// is delivered to every watcher.
type Broadcaster struct {watchers map[int64]*broadcasterWatcher // map 结构 id 和 watcher 的映射nextWatcher int64 // 下一个 watcher 该分配的 iddistributing sync.WaitGroup // 用于保证分发函数 loop 正常运行,避免主函数停止,导致 loop 函数停止// incomingBlock allows us to ensure we don't race and end up sending events// to a closed channel following a broadcaster shutdown.incomingBlock sync.Mutex // 避免接收 event 时,event 过多导致的并发,因此需要锁进行控制incoming chan Event // 承接生成的 event,其他 watcher 会从此 channel 中读取 event 进行记录到 apiserver 或日志打印等stopped chan struct{} // 承接关闭广播器 Broadcaster 的停止信号// How large to make watcher's channel.watchQueueLength int// If one of the watch channels is full, don't wait for it to become empty.// Instead just deliver it to the watchers that do have space in their// channels and move on to the next event.// It's more fair to do this on a per-watcher basis than to do it on the// "incoming" channel, which would allow one slow watcher to prevent all// other watchers from getting new events.fullChannelBehavior FullChannelBehavior
}
1.2- EventBroadcaster 接口
// 路径 mod/k8s.io/client-go@v0.29.0/tools/record/event.go
// EventBroadcaster knows how to receive events and send them to any EventSink, watcher, or log.
type EventBroadcaster interface {// StartEventWatcher starts sending events received from this EventBroadcaster to the given// event handler function. The return value can be ignored or used to stop recording, if// desired.StartEventWatcher(eventHandler func(*v1.Event)) watch.Interface// StartRecordingToSink starts sending events received from this EventBroadcaster to the given// sink. The return value can be ignored or used to stop recording, if desired.StartRecordingToSink(sink EventSink) watch.Interface// StartLogging starts sending events received from this EventBroadcaster to the given logging// function. The return value can be ignored or used to stop recording, if desired.StartLogging(logf func(format string, args ...interface{})) watch.Interface// StartStructuredLogging starts sending events received from this EventBroadcaster to the structured// logging function. The return value can be ignored or used to stop recording, if desired.StartStructuredLogging(verbosity klog.Level) watch.Interface// NewRecorder returns an EventRecorder that can be used to send events to this EventBroadcaster// with the event source set to the given event source.NewRecorder(scheme *runtime.Scheme, source v1.EventSource) EventRecorderLogger// Shutdown shuts down the broadcaster. Once the broadcaster is shut// down, it will only try to record an event in a sink once before// giving up on it with an error message.Shutdown()
}
1.3- NewRecorder 接口的实现
- Recorder 封装了 Broadcaster
// 路径 mod/k8s.io/client-go@v0.29.0/tools/record/event.go// NewRecorder returns an EventRecorder that records events with the given event source.
func (e *eventBroadcasterImpl) NewRecorder(scheme *runtime.Scheme, source v1.EventSource) EventRecorderLogger {return &recorderImplLogger{recorderImpl: &recorderImpl{scheme, source, e.Broadcaster, clock.RealClock{}}, logger: klog.Background()}
}type recorderImplLogger struct {*recorderImpllogger klog.Logger
}type recorderImpl struct {scheme *runtime.Schemesource v1.EventSource*watch.Broadcasterclock clock.PassiveClock
}
1.3- loop(event的分发)
// // 路径 /mod/k8s.io/apimachinery@v0.29.0/pkg/watch/mux.go
// loop receives from m.incoming and distributes to all watchers.
func (m *Broadcaster) loop() {// Deliberately not catching crashes here. Yes, bring down the process if there's a// bug in watch.Broadcaster.for event := range m.incoming {if event.Type == internalRunFunctionMarker {event.Object.(functionFakeRuntimeObject)()continue}m.distribute(event) // 将 event 分发给 watcher}m.closeAll()m.distributing.Done()
}// distribute sends event to all watchers. Blocking.
func (m *Broadcaster) distribute(event Event) {if m.fullChannelBehavior == DropIfChannelFull {for _, w := range m.watchers {select {case w.result <- event: // 将 event 发送到 watcher 的 result channel,等待 watcher 进行处理case <-w.stopped:default: // Don't block if the event can't be queued.}}} else {for _, w := range m.watchers {select {case w.result <- event:case <-w.stopped:}}}
}
1.4 event 的产生
// 路径 mod/k8s.io/client-go@v0.29.0/tools/record/event.go// EventRecorder knows how to record events on behalf of an EventSource.
type EventRecorder interface {// Event constructs an event from the given information and puts it in the queue for sending.// 'object' is the object this event is about. Event will make a reference-- or you may also// pass a reference to the object directly.// 'eventtype' of this event, and can be one of Normal, Warning. New types could be added in future// 'reason' is the reason this event is generated. 'reason' should be short and unique; it// should be in UpperCamelCase format (starting with a capital letter). "reason" will be used// to automate handling of events, so imagine people writing switch statements to handle them.// You want to make that easy.// 'message' is intended to be human readable.//// The resulting event will be created in the same namespace as the reference object.Event(object runtime.Object, eventtype, reason, message string)// Eventf is just like Event, but with Sprintf for the message field.Eventf(object runtime.Object, eventtype, reason, messageFmt string, args ...interface{})// AnnotatedEventf is just like eventf, but with annotations attachedAnnotatedEventf(object runtime.Object, annotations map[string]string, eventtype, reason, messageFmt string, args ...interface{})
}func (recorder *recorderImpl) Event(object runtime.Object, eventtype, reason, message string) {recorder.generateEvent(klog.Background(), object, nil, eventtype, reason, message)
}func (recorder *recorderImpl) generateEvent(logger klog.Logger, object runtime.Object, annotations map[string]string, eventtype, reason, message string) {ref, err := ref.GetReference(recorder.scheme, object)if err != nil {logger.Error(err, "Could not construct reference, will not report event", "object", object, "eventType", eventtype, "reason", reason, "message", message)return}if !util.ValidateEventType(eventtype) {logger.Error(nil, "Unsupported event type", "eventType", eventtype)return}event := recorder.makeEvent(ref, annotations, eventtype, reason, message)event.Source = recorder.sourceevent.ReportingInstance = recorder.source.Hostevent.ReportingController = recorder.source.Component// NOTE: events should be a non-blocking operation, but we also need to not// put this in a goroutine, otherwise we'll race to write to a closed channel// when we go to shut down this broadcaster. Just drop events if we get overloaded,// and log an error if that happens (we've configured the broadcaster to drop// outgoing events anyway).sent, err := recorder.ActionOrDrop(watch.Added, event)if err != nil {logger.Error(err, "Unable to record event (will not retry!)")return}if !sent {logger.Error(nil, "Unable to record event: too many queued events, dropped event", "event", event)}
}// Action distributes the given event among all watchers, or drops it on the floor
// if too many incoming actions are queued up. Returns true if the action was sent,
// false if dropped.
func (m *Broadcaster) ActionOrDrop(action EventType, obj runtime.Object) (bool, error) {m.incomingBlock.Lock()defer m.incomingBlock.Unlock()// Ensure that if the broadcaster is stopped we do not send events to it.select {case <-m.stopped:return false, fmt.Errorf("broadcaster already stopped")default:}select {case m.incoming <- Event{action, obj}:return true, nildefault:return false, nil}
}
1.5 watcher 的处理
eventBroadcaster.StartLogging(klog.Infof)// StartLogging starts sending events received from this EventBroadcaster to the given logging function.
// The return value can be ignored or used to stop recording, if desired.
func (e *eventBroadcasterImpl) StartLogging(logf func(format string, args ...interface{})) watch.Interface {return e.StartEventWatcher(func(e *v1.Event) { // 对应 下面 eventHandlerlogf("Event(%#v): type: '%v' reason: '%v' %v", e.InvolvedObject, e.Type, e.Reason, e.Message)})
}// StartEventWatcher starts sending events received from this EventBroadcaster to the given event handler function.
// The return value can be ignored or used to stop recording, if desired.
func (e *eventBroadcasterImpl) StartEventWatcher(eventHandler func(*v1.Event)) watch.Interface {watcher, err := e.Watch()if err != nil {klog.FromContext(e.cancelationCtx).Error(err, "Unable start event watcher (will not retry!)")}go func() { // 直接运行了defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()for {select {case <-e.cancelationCtx.Done():watcher.Stop()returncase watchEvent := <-watcher.ResultChan(): // 从 watcher result channel 中取出 event event, ok := watchEvent.Object.(*v1.Event)if !ok {// This is all local, so there's no reason this should// ever happen.continue}eventHandler(event) // 对 event 进行处理 }}}()return watcher
}附录1 | 示例详解
以下是一个完整的 EventRecorder 和 EventBroadcaster 实例化的代码示例,展示如何在 Kubernetes 控制器中记录事件。代码包含详细注释,适合用于实际开发或学习:
代码示例
package mainimport ("context""fmt""time"corev1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1""k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime"metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime/schema""k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes""k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes/fake""k8s.io/client-go/tools/record""k8s.io/client-go/util/workqueue""k8s.io/klog/v2"
)// 主要逻辑的入口
func main() {// 1. 创建 Kubernetes 客户端// 这里我们使用 fake 客户端进行演示,生产环境应替换为真实的 `kubernetes.Clientset`clientset := fake.NewSimpleClientset()// 2. 创建事件广播器(EventBroadcaster)// 事件广播器是事件处理的核心,负责分发事件到日志和 API ServereventBroadcaster := record.NewBroadcaster()// 3. 启动日志记录功能// 通过 `klog.Infof` 输出事件到控制台或日志文件eventBroadcaster.StartLogging(klog.Infof)// 4. 启动事件的 API Server 记录功能// 配置事件接收器,将事件发送到 API Server,通过 `kubeClient.CoreV1().Events` 接口记录事件eventBroadcaster.StartRecordingToSink(&corev1.EventSinkImpl{Interface: clientset.CoreV1().Events(""),})// 5. 创建事件记录器(EventRecorder)// EventRecorder 用于开发者实际记录事件recorder := eventBroadcaster.NewRecorder(scheme(), // 提供资源的模式信息,常用的是 `runtime.NewScheme()` 或自定义的 schemecorev1.EventSource{Component: "example-controller"},)// 6. 模拟一个 Kubernetes 对象(如 Pod)的引用// 事件通常需要与具体的 Kubernetes 资源关联objRef := &corev1.ObjectReference{Kind: "Pod", // 资源类型Namespace: "default", // 命名空间Name: "example-pod", // 资源名称UID: "12345-abcde-67890", // 唯一标识符APIVersion: "v1", // API 版本}// 7. 使用 EventRecorder 记录事件// 记录一个正常类型的事件(EventTypeNormal)recorder.Eventf(objRef, corev1.EventTypeNormal, "PodCreated", "Successfully created Pod %s", objRef.Name)// 模拟一个警告事件(EventTypeWarning)recorder.Eventf(objRef, corev1.EventTypeWarning, "PodFailed", "Failed to create Pod %s due to insufficient resources", objRef.Name)// 模拟一个控制器逻辑的操作processQueue(recorder, objRef)// 等待事件记录完成time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
}// 模拟处理队列的函数
func processQueue(recorder record.EventRecorder, objRef *corev1.ObjectReference) {// 创建一个工作队列queue := workqueue.NewRateLimitingQueue(workqueue.DefaultControllerRateLimiter())// 将任务添加到队列queue.Add("task1")// 模拟处理队列中的任务for queue.Len() > 0 {item, _ := queue.Get()defer queue.Done(item)// 记录一个事件,表明任务已处理recorder.Eventf(objRef, corev1.EventTypeNormal, "TaskProcessed", "Successfully processed task: %v", item)fmt.Printf("Processed task: %v\n", item)}
}// 创建 Scheme 用于事件记录器
// Scheme 是 Kubernetes 中资源的模式定义,用于确定资源类型和序列化方式
func scheme() *runtime.Scheme {s := runtime.NewScheme()// 添加 CoreV1 资源到 Scheme 中corev1.AddToScheme(s)metav1.AddToGroupVersion(s, schema.GroupVersion{Version: "v1"})return s
}
代码详解
1. 创建 EventBroadcaster
record.NewBroadcaster(): 创建事件广播器,用于记录和分发事件。StartLogging(klog.Infof): 将事件以日志的形式输出。StartRecordingToSink: 将事件发送到 Kubernetes API Server,存储为Event资源。
2. 创建 EventRecorder
NewRecorder(scheme, source)从广播器中创建事件记录器。scheme: 用于验证和序列化资源。source: 指定事件的来源(如example-controller)。
3. 创建对象引用
ObjectReference: 用于标识事件关联的 Kubernetes 资源。包括类型、名称、命名空间、UID 等信息。
4. 记录事件
-
- 用于记录事件,包括:
Eventf- 类型:
corev1.EventTypeNormal(正常)或corev1.EventTypeWarning(警告)。 - 原因:事件发生的原因(如
PodCreated)。 - 消息:事件的详细描述。
5. 模拟队列任务
- 使用
workqueue模拟处理任务,记录任务完成时的事件。
运行结果
日志输出
事件将输出到日志(通过 klog):
I1119 12:34:56.123456 12345 example.go:52] Event(v1.ObjectReference{...}): type: 'Normal' reason: 'PodCreated' message: 'Successfully created Pod example-pod'
I1119 12:34:56.123457 12345 example.go:53] Event(v1.ObjectReference{...}): type: 'Warning' reason: 'PodFailed' message: 'Failed to create Pod example-pod due to insufficient resources'
Processed task: task1
事件存储
如果使用真实客户端,事件会存储在集群中,可通过 kubectl 查看:
kubectl get events
事件输出
LAST SEEN TYPE REASON OBJECT MESSAGE
5s Normal PodCreated Pod/example-pod Successfully created Pod example-pod
5s Warning PodFailed Pod/example-pod Failed to create Pod example-pod due to insufficient resources
5s Normal TaskProcessed Pod/example-pod Successfully processed task: task1
代码用途
- 日志记录和事件管理: 帮助开发者跟踪控制器的运行状态和资源变更。
- 任务队列处理: 将业务逻辑与事件机制结合,记录每个关键操作的状态。
以上代码展示了如何使用 EventRecorder 和 EventBroadcaster 实现 Kubernetes 控制器中的事件管理,适合用于开发自定义控制器或调试集群事件处理逻辑。
附录2 | stoped 变量的作用
在 NewBroadcaster 函数中的 stopped 通道用于实现对 Broadcaster 对象的停止和关闭控制。具体来说,它的作用是在广播器的生命周期中进行信号传递,用于通知 Broadcaster 是否已经停止运行。
详细分析:
1. 通道的定义:
stopped: make(chan struct{}),
stopped 是一个无缓冲的通道,类型为 struct{}。无缓冲的通道用于信号传递,表示某个事件的发生,而不需要传递具体数据。这里的 struct{} 是一个空结构体,占用零内存,因此不会传递任何实际数据。
2. 停止广播器的作用:
stopped 通道用于在广播器停止时传递一个信号。通常这种信号用于通知相关的 goroutine 或者处理流程,广播器已经停止工作,可以做一些清理操作或者退出。
3. 与 go m.loop() 的配合:
go m.loop()
在 NewBroadcaster 中,启动了一个新的 goroutine 来执行 m.loop()。这个 loop 方法通常是处理传入事件并进行分发的核心逻辑。loop 方法可能会定期检查 stopped 通道,判断是否已经收到停止信号。
4. 典型的停止逻辑(假设)
func (m *Broadcaster) loop() {for {select {case event := <-m.incoming:// 处理事件逻辑case <-m.stopped:// 收到停止信号后,退出 goroutinereturn}}
}
在这个假设的 loop 实现中,select 语句等待从 m.incoming 通道接收事件,或者等待 stopped 通道的信号。当收到 stopped 通道的信号时,loop 方法退出,从而停止事件的分发。
5. 停止广播器的触发:
在实际代码中,某个外部操作可能会通过 close(m.stopped) 或者发送一个信号到 m.stopped 通道,来通知 Broadcaster 停止工作。比如在处理完所有事件或者发生错误时,可能会调用停止操作:
close(m.stopped)
或者
m.stopped <- struct{}{}
这样 loop 就会检测到停止信号并退出。
总结
stopped 通道在 Broadcaster 中的作用是提供一个停止信号,通知正在运行的 goroutine(如 loop 方法)停止执行。这种设计使得 Broadcaster 能够优雅地处理停止操作,确保所有 goroutine 都能够适时退出并清理资源。
相关文章:

【k8s深入学习之 event 记录】初步了解 k8s event 记录机制
event 事件记录初始化 一般在控制器都会有如下的初始化函数,初始化 event 记录器等参数 1. 创建 EventBroadcaster record.NewBroadcaster(): 创建事件广播器,用于记录和分发事件。StartLogging(klog.Infof): 将事件以日志的形式输出。StartRecording…...

redhat 7.9配置阿里云yum源
1、mv /etc/yum.repos.d/*.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/backup/ 2、添加dns vim/etc/resolv.conf nameserver 8.8.8.8 nameserver 8.8.4.4 nameserver 114.114.114.114 #配置完先检查下通不通 3、vi /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/subscription-manager.conf # 将 “enabled1” 改为 “ena…...

深入探索Flax:一个用于构建神经网络的灵活和高效库
深入探索Flax:一个用于构建神经网络的灵活和高效库 在深度学习领域,TensorFlow 和 PyTorch 作为主流的框架,已被广泛使用。不过,Flax 作为一个较新的库,近年来得到了越来越多的关注。Flax 是一个由Google Research团队…...
Nginx auth_request详解
网上看到多篇先关文章,觉得很不错,这里合并记录一下,仅供学习参考。 模块 nginx-auth-request-module 该模块是nginx一个安装模块,使用配置都比较简单,只要作用是实现权限控制拦截作用。默认高版本nginx(比…...

基于Java Springboot个人财务APP且微信小程序
一、作品包含 源码数据库设计文档万字PPT全套环境和工具资源部署教程 二、项目技术 前端技术:Html、Css、Js、Vue、Element-ui 数据库:MySQL 后端技术:Java、Spring Boot、MyBatis 三、运行环境 开发工具:IDEA/eclipse 微信…...
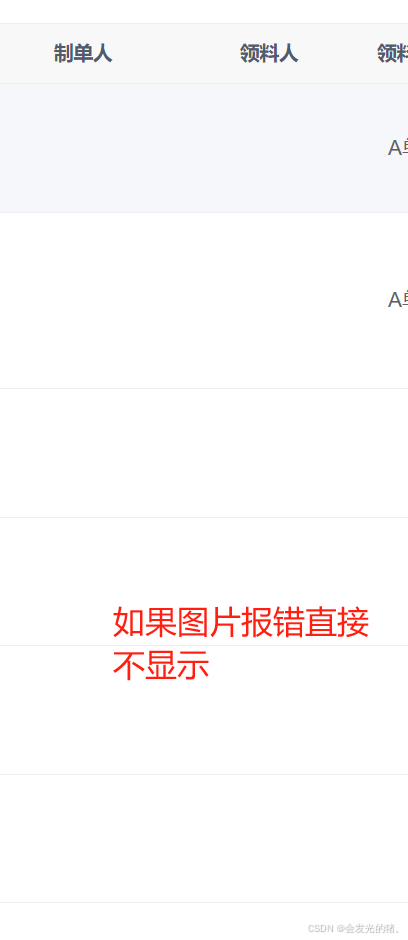
vue3图片报错转换为空白不显示的方法
vue3图片报错转换为空白不显示的方法 直接上代码: <el-table-column label"领料人" align"center"><template #default"scope"><el-imagev-if"scope.row.receiver":src"scope.row.receiver"style…...
mysq之快速批量的插入生成数据
mysq之快速批量的插入生成数据 1.insert inot select2.存储过程3.借助工具 在日常测试工作时,有时候需要某张表有大量的数据,如:需要有几百个系统中的用户账号等情况;因此,记录整理,如何快速的在表中插入生…...

浅谈C#库之DevExpress
一、DevExpress库介绍 DevExpress是一个功能强大、界面美观的UI组件库,广泛应用于桌面应用程序和Web应用程序的开发中。它提供了丰富的控件和工具,帮助开发人员快速构建现代化的用户界面。DevExpress控件库以其功能丰富、应用简便、界面华丽以及方便定制…...
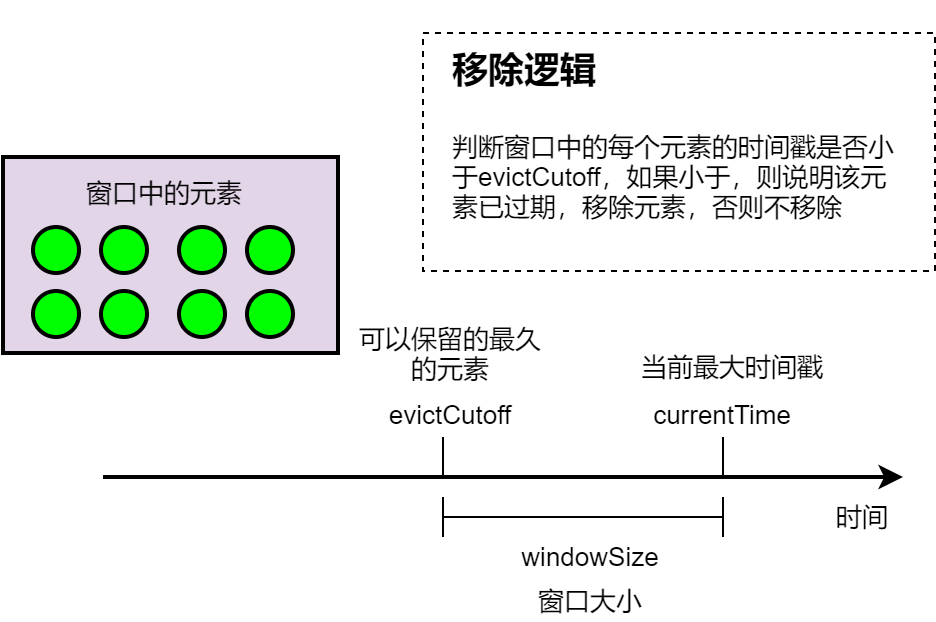
聊聊Flink:这次把Flink的触发器(Trigger)、移除器(Evictor)讲透
一、触发器(Trigger) Trigger 决定了一个窗口(由 window assigner 定义)何时可以被 window function 处理。 每个 WindowAssigner 都有一个默认的 Trigger。 如果默认 trigger 无法满足你的需要,你可以在 trigger(…) 调用中指定自定义的 tr…...

一款支持80+语言,包括:拉丁文、中文、阿拉伯文、梵文等开源OCR库
大家好,今天给大家分享一个基于PyTorch的OCR库EasyOCR,它允许开发者通过简单的API调用来读取图片中的文本,无需复杂的模型训练过程。 项目介绍 EasyOCR 是一个基于Python的开源项目,它提供了一个简单易用的光学字符识别ÿ…...
Flink四大基石之CheckPoint(检查点) 的使用详解
目录 一、Checkpoint 剖析 State 与 Checkpoint 概念区分 设置 Checkpoint 实战 执行代码所需的服务与遇到的问题 二、重启策略解读 重启策略意义 代码示例与效果展示 三、SavePoint 与 Checkpoint 异同 操作步骤详解 四、总结 在大数据流式处理领域,Ap…...
)
JVM 常见面试题及解析(2024)
目录 一、JVM 基础概念 二、JVM 内存结构 三、类加载机制 四、垃圾回收机制 五、性能调优 六、实战问题 七、JVM 与其他技术结合 八、JVM 内部机制深化 九、JVM 相关概念拓展 十、故障排查与异常处理 一、JVM 基础概念 1、什么是 JVM?它的主要作用是…...
Python 调用 Umi-OCR API 批量识别图片/PDF文档数据
目录 一、需求分析 二、方案设计(概要/详细) 三、技术选型 四、OCR 测试 Demo 五、批量文件识别完整代码实现 六、总结 一、需求分析 市场部同事进行采购或给客户报价时,往往基于过往采购合同数据,给出现在采购或报价的金额…...

K8S资源之secret资源
secret资源介绍 secret用于敏感数据存储,底层基于base64编码,数据存储在etcd数据库中 应用场景举例: 数据库的用户名,密码,tls的证书ssh等服务的相关证书 secret的基础管理 1 在命令行响应式创建 1.响应式创建 …...

QT:信号和槽01
QT中什么是信号和槽 概念解释 在 Qt 中,信号(Signals)和槽(Slots)是一种用于对象间通信的机制。信号是对象发出的事件通知,而槽是接收并处理这些通知的函数。 例如,当用户点击一个按钮时&#…...

针对Qwen-Agent框架的Function Call及ReAct的源码阅读与解析:Agent基类篇
文章目录 Agent继承链Agent类总体架构初始化方法`__init__` 方法:`_init_tool` 方法:对话生成方法`_call_llm` 方法:工具调用方法`_call_tool` 方法:`_detect_tool` 方法:整体执行方法`run` 方法:`_run` 方法:`run_nonstream` 方法总结回顾本文在 基于Qwen-Agent框架的Functio…...

XML 查看器:深入理解与高效使用
XML 查看器:深入理解与高效使用 XML(可扩展标记语言)是一种用于存储和传输数据的标记语言。它通过使用标签来定义数据结构,使得数据既易于人类阅读,也易于机器解析。在本文中,我们将探讨 XML 查看器的功能、重要性以及如何高效使用它们。 什么是 XML 查看器? XML 查看…...

《Vue零基础入门教程》第十五课:样式绑定
往期内容 《Vue零基础入门教程》第六课:基本选项 《Vue零基础入门教程》第八课:模板语法 《Vue零基础入门教程》第九课:插值语法细节 《Vue零基础入门教程》第十课:属性绑定指令 《Vue零基础入门教程》第十一课:事…...

以AI算力助推转型升级,暴雨亮相CCF中国存储大会
2024年11月29日-12月1日,CCF中国存储大会(CCF ChinaStorage 2024)在广州市长隆国际会展中心召开。本次会议以“存力、算力、智力”为主题,由中国计算机学会(CCF)主办,中山大学计算机学院、CCF信…...

【VMware】Ubuntu 虚拟机硬盘扩容教程(Ubuntu 22.04)
引言 想装个 Anaconda,发现 Ubuntu 硬盘空间不足。 步骤 虚拟机关机 编辑虚拟机设置 扩展硬盘容量 虚拟机开机 安装 gparted sudo apt install gparted启动 gparted sudo gparted右键sda3,调整分区大小 新大小拉满 应用全部操作 调整完成...
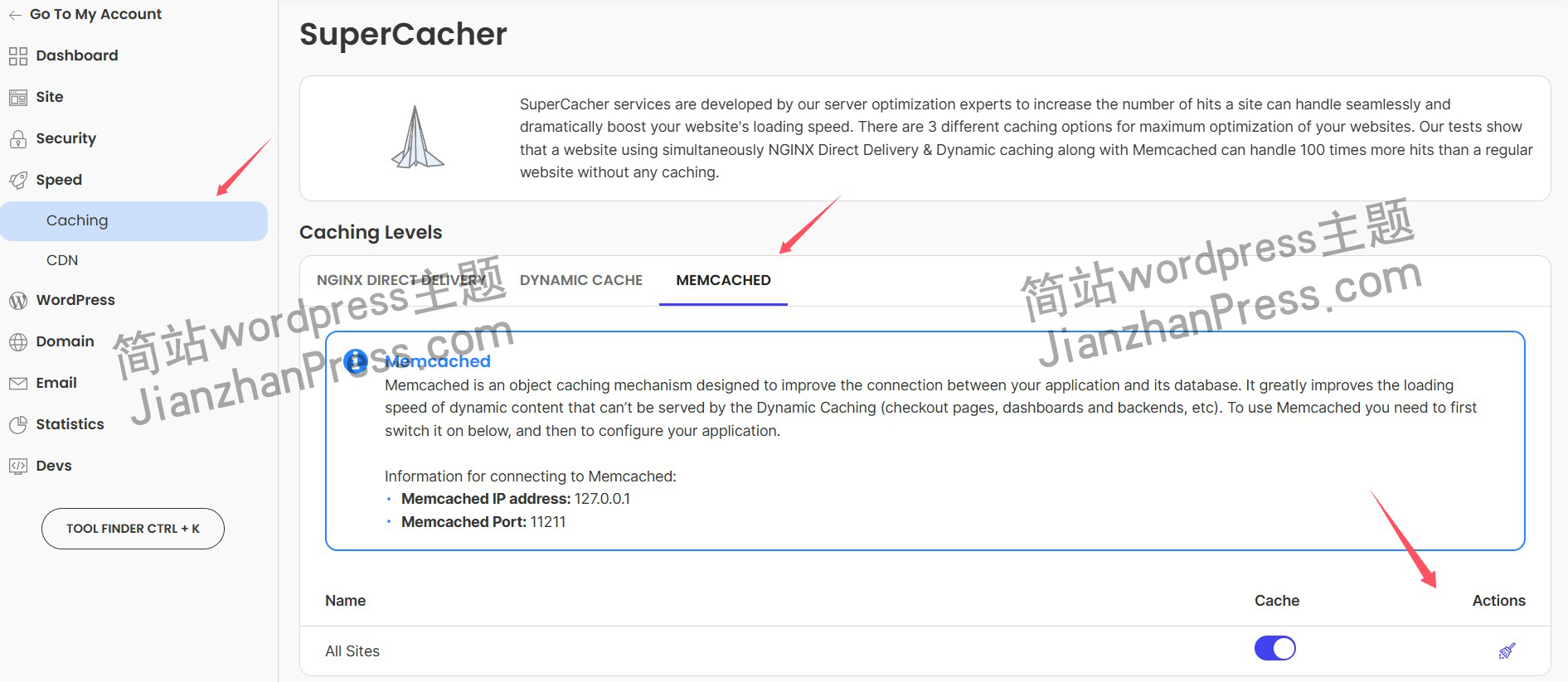
wordpress后台更新后 前端没变化的解决方法
使用siteground主机的wordpress网站,会出现更新了网站内容和修改了php模板文件、js文件、css文件、图片文件后,网站没有变化的情况。 不熟悉siteground主机的新手,遇到这个问题,就很抓狂,明明是哪都没操作错误&#x…...
springboot 百货中心供应链管理系统小程序
一、前言 随着我国经济迅速发展,人们对手机的需求越来越大,各种手机软件也都在被广泛应用,但是对于手机进行数据信息管理,对于手机的各种软件也是备受用户的喜爱,百货中心供应链管理系统被用户普遍使用,为方…...
python/java环境配置
环境变量放一起 python: 1.首先下载Python Python下载地址:Download Python | Python.org downloads ---windows -- 64 2.安装Python 下面两个,然后自定义,全选 可以把前4个选上 3.环境配置 1)搜高级系统设置 2…...

vue3 定时器-定义全局方法 vue+ts
1.创建ts文件 路径:src/utils/timer.ts 完整代码: import { onUnmounted } from vuetype TimerCallback (...args: any[]) > voidexport function useGlobalTimer() {const timers: Map<number, NodeJS.Timeout> new Map()// 创建定时器con…...
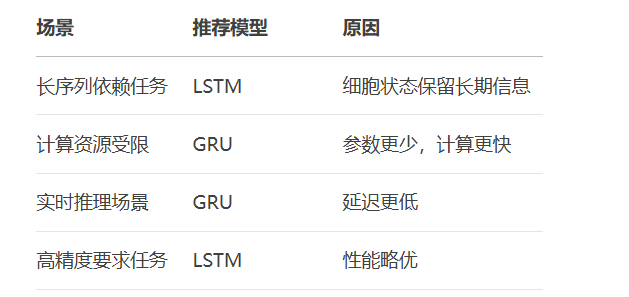
RNN避坑指南:从数学推导到LSTM/GRU工业级部署实战流程
本文较长,建议点赞收藏,以免遗失。更多AI大模型应用开发学习视频及资料,尽在聚客AI学院。 本文全面剖析RNN核心原理,深入讲解梯度消失/爆炸问题,并通过LSTM/GRU结构实现解决方案,提供时间序列预测和文本生成…...

稳定币的深度剖析与展望
一、引言 在当今数字化浪潮席卷全球的时代,加密货币作为一种新兴的金融现象,正以前所未有的速度改变着我们对传统货币和金融体系的认知。然而,加密货币市场的高度波动性却成为了其广泛应用和普及的一大障碍。在这样的背景下,稳定…...

Web 架构之 CDN 加速原理与落地实践
文章目录 一、思维导图二、正文内容(一)CDN 基础概念1. 定义2. 组成部分 (二)CDN 加速原理1. 请求路由2. 内容缓存3. 内容更新 (三)CDN 落地实践1. 选择 CDN 服务商2. 配置 CDN3. 集成到 Web 架构 …...
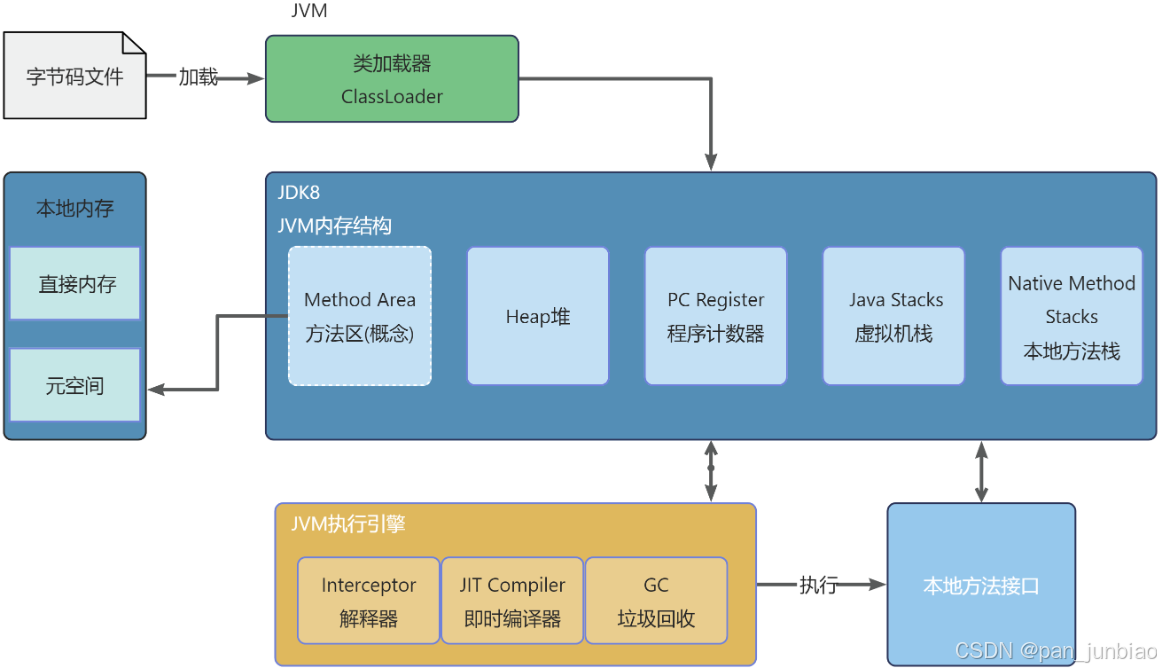
JVM虚拟机:内存结构、垃圾回收、性能优化
1、JVM虚拟机的简介 Java 虚拟机(Java Virtual Machine 简称:JVM)是运行所有 Java 程序的抽象计算机,是 Java 语言的运行环境,实现了 Java 程序的跨平台特性。JVM 屏蔽了与具体操作系统平台相关的信息,使得 Java 程序只需生成在 JVM 上运行的目标代码(字节码),就可以…...
人机融合智能 | “人智交互”跨学科新领域
本文系统地提出基于“以人为中心AI(HCAI)”理念的人-人工智能交互(人智交互)这一跨学科新领域及框架,定义人智交互领域的理念、基本理论和关键问题、方法、开发流程和参与团队等,阐述提出人智交互新领域的意义。然后,提出人智交互研究的三种新范式取向以及它们的意义。最后,总结…...
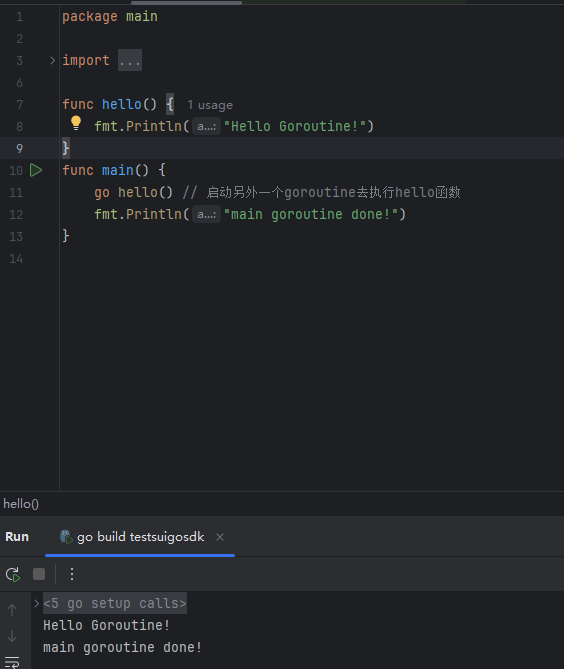
GO协程(Goroutine)问题总结
在使用Go语言来编写代码时,遇到的一些问题总结一下 [参考文档]:https://www.topgoer.com/%E5%B9%B6%E5%8F%91%E7%BC%96%E7%A8%8B/goroutine.html 1. main()函数默认的Goroutine 场景再现: 今天在看到这个教程的时候,在自己的电…...
