数据结构之链表笔试题详解
一:移除链表元素

我们很容易就可以想到一个解决方案:再创建一个链表,把不是val的结点拿过来尾插。
这样确实可以但是,我们每次尾插都需要遍历一遍整个链表,这样时间复杂度就变成了O(n^2),
因此我们不妨设置一个tail尾结点来指向它的尾。
画图分析:
这里面还有一个潜在的问题就是,假如最后一个节点的数值==val怎么办,想一想。
完整代码:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {ListNode* newhead;ListNode* newtail;ListNode* pcur = head;newhead=newtail=NULL;while(pcur){if(pcur->val!=val){if(newhead==NULL){newhead=newtail=pcur;}else{newtail->next=pcur;newtail=pcur;}}pcur=pcur->next;}if(newtail!=NULL&&newtail->next!=NULL){newtail->next=NULL;}return newhead;
}二:反转链表

这一题有两种解法:
解法一:
直接反转指向,比如原来二指向三,现在让三指向2.
画图分析:

经过分析我们写出了这样的代码:
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* pprev = NULL;
struct ListNode* pcur = head;
struct ListNode* pnext = head->next;
while(pcur)
{
pcur->next=pprev;
pprev=pcur;
pcur=pnext;
pnext=pnext->next;
}
return pprev;
}
放在力扣上提交

遇到错误不要慌张,我们看一下提示信息,可以发现,原来是对NULL解引用了,所以在17行那要加上判断,那么说到这了万一这个链表原来就是空呢?因此在一开始也要对这种情况处理。
完整代码:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode* pprev = NULL;struct ListNode* pcur = head;struct ListNode* pnext;if(head){pnext = head->next;}while(pcur){pcur->next=pprev;pprev=pcur;pcur=pnext;if(pnext){pnext=pnext->next;}}return pprev;
}解法二:
取原链表中元素,头插到新链表的newhead中。
画图分析: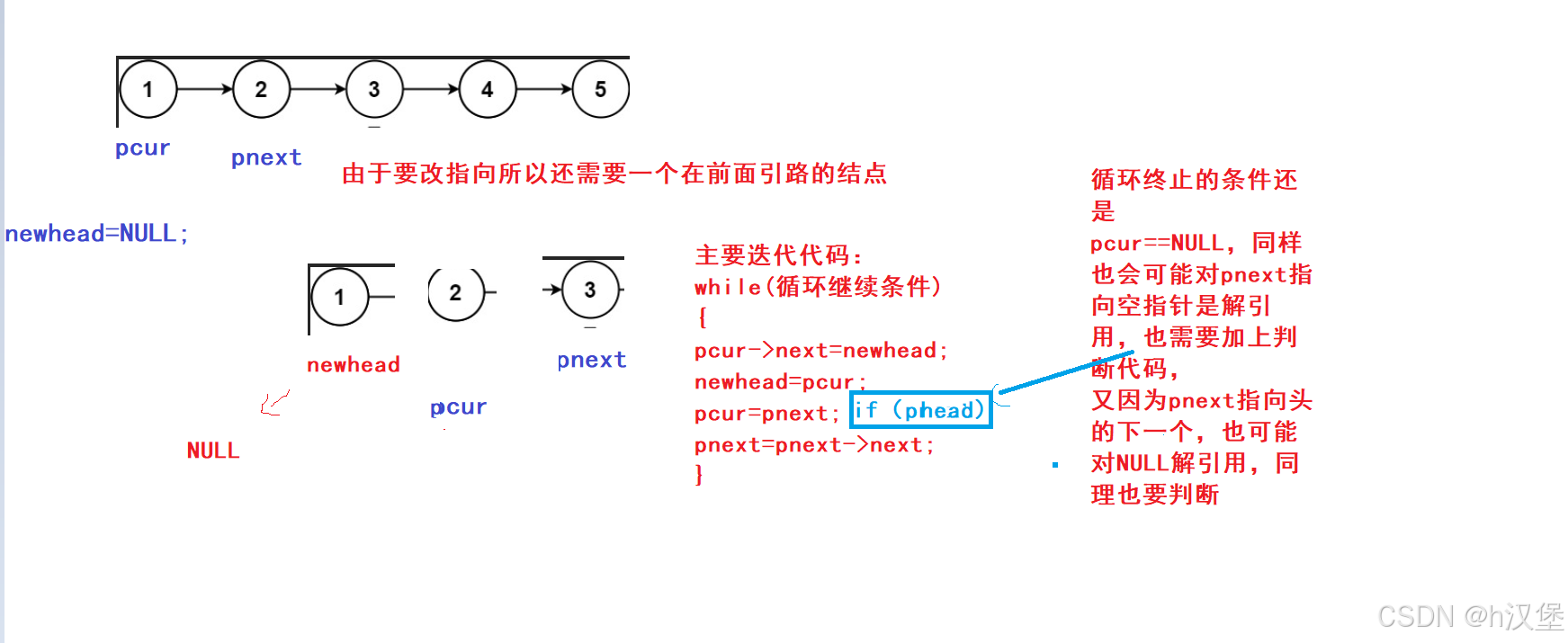
完整代码:
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode* pcur = head;struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;struct ListNode* pnext;if(head){pnext=head->next;}while(pcur){pcur->next = newhead;newhead = pcur;pcur = pnext;if(pnext){pnext = pnext->next;}}return newhead;
}三:链表的倒数k个结点

我们确实可以先遍历一遍拿到链表长度,然后就可以找到倒数k个结点了。但是如果只能这么做就没有拿出来的必要了qwq。
快慢指针法:两个指针先让一个走k,然后一起走,等到k指向空(具体看下面画图分析)结束。
画图分析: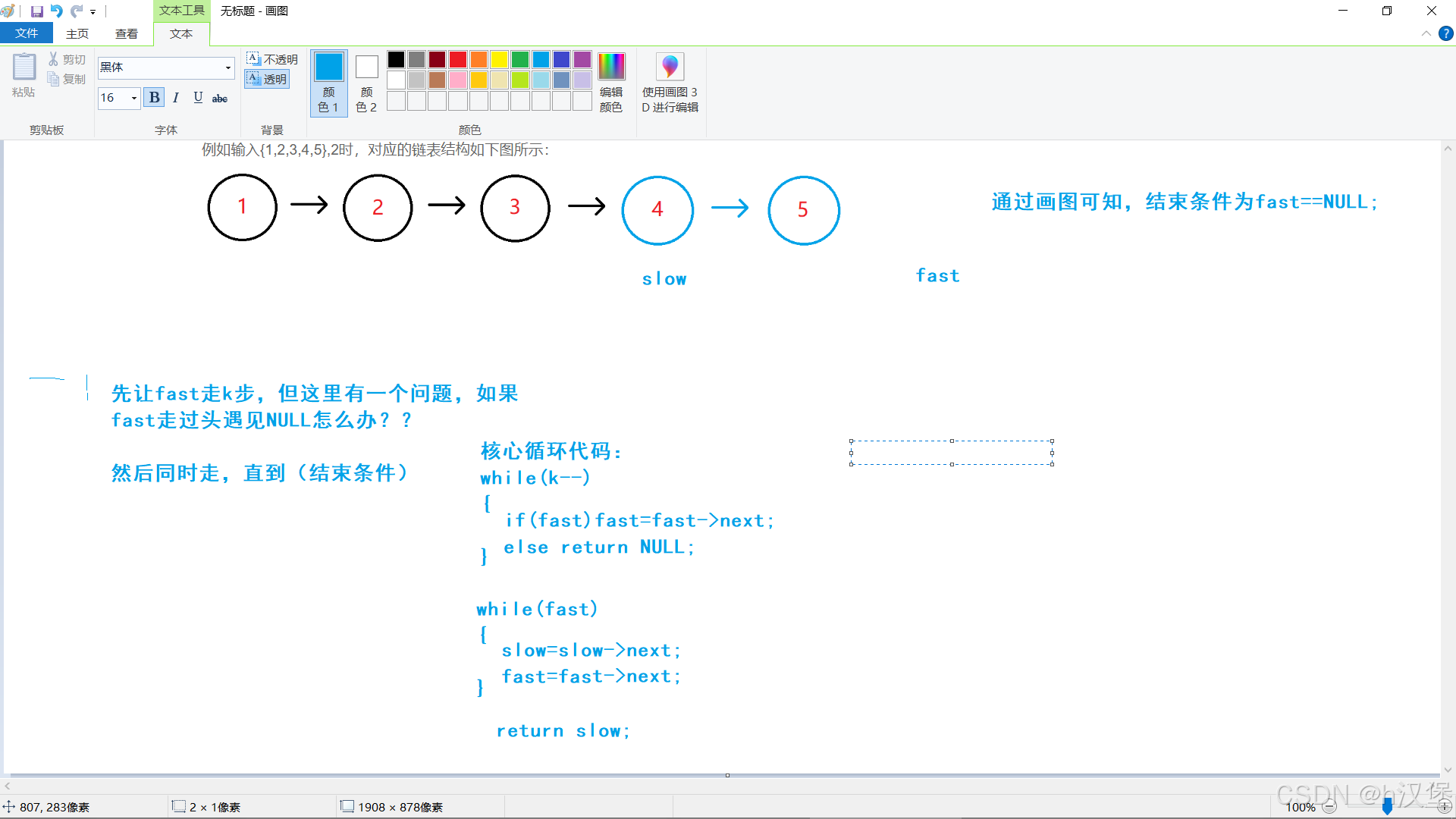
完整代码:
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pHead, int k ) {struct ListNode* slow;struct ListNode* fast;slow=fast=pHead;while(k--){if(fast){fast=fast->next;}else {return NULL;}}while(fast){slow=slow->next;fast=fast->next;}return slow;
}四:链表的中间结点

这题同样也是快慢指针法,大体思路是让fast走两步,slow走一步,但是直觉告诉我们结点数的奇偶性会影响结束条件。
画图分析:

完整代码:
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode* slow;struct ListNode* fast;fast=slow=head;while(fast&&fast->next){slow=slow->next;fast=fast->next->next;}return slow;
}五:合并两个有序链表

思路:依次比较链表中的结点,然后插入小的结点
画图分析:

完整代码:
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {struct ListNode* newhead;struct ListNode* newtail;newhead=newtail=NULL;struct ListNode* pcur1=list1;struct ListNode* pcur2=list2;if(pcur1==NULL)return pcur2;if(pcur2==NULL)return pcur1;while(pcur1&&pcur2){if(pcur1->val<pcur2->val){if(newhead==NULL){ newhead=newtail=pcur1;}else{newtail->next=pcur1;newtail=pcur1;}pcur1=pcur1->next;}else{if(newhead==NULL){ newhead=newtail=pcur2;}else{newtail->next=pcur2;newtail=pcur2;}pcur2=pcur2->next;}}if(pcur1!=NULL){newtail->next=pcur1;}if(pcur2!=NULL){newtail->next=pcur2;}return newhead;
}
优化:
我们每次都要对新创建的头结点判断是否为空。
有没有一种方法可以不用判断呢?:设置一个哨兵位就可以了
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {struct ListNode* pcur1=list1;struct ListNode* pcur2=list2;if(pcur1==NULL)return pcur2;if(pcur2==NULL)return pcur1;struct ListNode* head = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));struct ListNode* tail = head;while(pcur1&&pcur2){if(pcur1->val<pcur2->val){tail->next=pcur1;tail=pcur1;pcur1=pcur1->next;}else{tail->next=pcur2;tail=pcur2;pcur2=pcur2->next;}}if(pcur1!=NULL){tail->next=pcur1;}else{tail->next=pcur2;}struct ListNode* newhead=head->next;free(head);return newhead;
}
六:链表分割
这题没给图,直接画图分析:
画图分析:

完整代码:
class Partition {
public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {ListNode* lesshead =(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));ListNode* lesstail=lesshead;ListNode* greaterhead=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));ListNode* greatertail=greaterhead;ListNode* pcur=pHead;if(pcur==NULL)return NULL;while(pcur){if(pcur->val<x){lesstail->next=pcur;lesstail=pcur;}else {greatertail->next=pcur;greatertail=pcur;}pcur=pcur->next;}lesstail->next=greaterhead->next;greatertail->next=NULL;ListNode* newhead=lesshead->next;free(lesshead);free(greaterhead);return newhead;}
};七:链表回文

首先这一题开一个900的数组也可以过,但是他并不符合空间复杂度O(1)。
然后我们说一下这一题的思路:先找中间结点,然后逆置,最后一一比较。
具体细节,请看下
画图分析:

完整代码:
/*
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* A)
{ListNode* slow = A;ListNode* fast = A;while(fast && fast->next){fast=fast->next->next;slow=slow->next;}return slow;
}
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{struct ListNode* pprev = NULL;struct ListNode* pcur = head;struct ListNode* pnext;if(head){pnext = head->next;}while(pcur){pcur->next = pprev;pprev = pcur;pcur = pnext;if(pnext){pnext = pnext->next;}}return pprev;
}
class PalindromeList {
public:bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {ListNode* mid = middleNode(A);ListNode* rhead = reverseList(mid);ListNode* curA = A;ListNode* curR = rhead;while(curA && curR){if(curA->val != curR->val){return false; }else{curA=curA->next;curR=curR->next;}}return true;}
};八:链表相交

思路:遍历一遍求长度(同时判断是否会相交),长的走差值步,然后一起走直到两指针相同
这一题不可以用逆置做,想一想为什么??
画图分析:

完整代码:
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {struct ListNode* curA = headA;struct ListNode* curB = headB;int lenA = 1; int lenB = 1;while(curA->next){lenA++;curA=curA->next;}while(curB->next){lenB++;curB=curB->next;}if(curA!=curB)return NULL;int gap = abs(lenA-lenB);struct ListNode* longlist = headA;struct ListNode* shortlist = headB;if(lenA < lenB){longlist = headB;shortlist = headA;}while(gap--){longlist=longlist->next;}while(longlist!=shortlist){longlist=longlist->next;shortlist=shortlist->next;}return longlist;
}九:环形链表1

思路:快慢指针法,slow走1步fast走2步。如果相遇则带环,否则不带环
画图分析: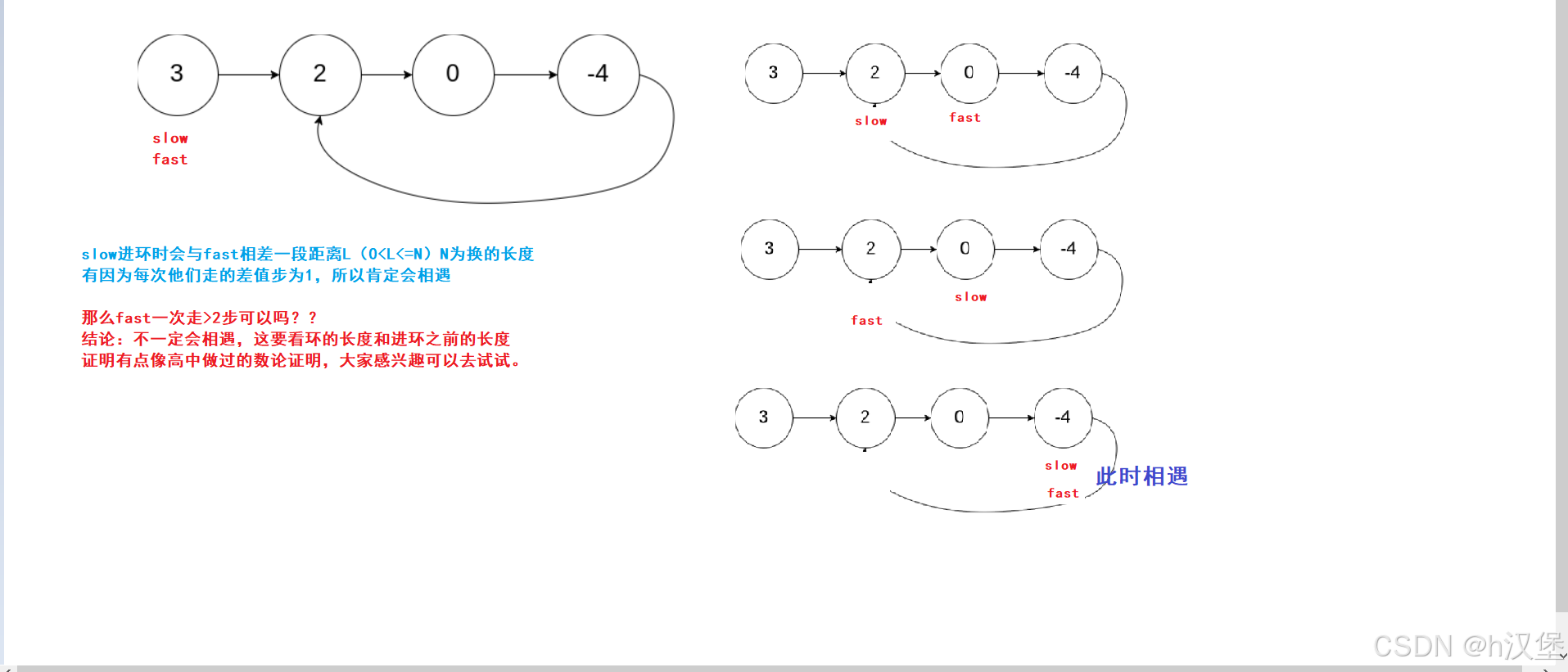
完整代码:
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;while(fast && fast->next){fast=fast->next->next;slow=slow->next;if(fast==slow)return true;}return false;
}十:环形链表2

这一题有点数学题的意思。还是先说思路:还是先slow与fast走,等到两指针相遇,在再让一个指针从都走,另一个指针从相遇位置走,直到二者再次相遇即为如环点。
画图分析:

完整代码:
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;while(fast && fast->next){fast=fast->next->next;slow=slow->next;if(slow==fast){struct ListNode* cur = head;struct ListNode* curC = fast;while(cur!=curC){cur=cur->next;curC=curC->next;}return cur;}}return NULL;
}十一:复杂随机链表的拷贝
 这一次最难搞的是random指针。思路也不好想,大家还是借鉴一下大佬的思路吧。
这一次最难搞的是random指针。思路也不好想,大家还是借鉴一下大佬的思路吧。
思路:在每个节点后面插入一个一样的节点,定义cur 和 next指针 cur->next->radom=cur->radom->next,然后迭代往后。最后解开插入的结点。
画图分析:

完整代码:
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {struct Node* cur = head;//插入新节点while(cur){struct Node* newnode = (struct Node* )malloc(sizeof(struct Node));newnode->val = cur->val;newnode->next = cur->next;cur->next = newnode;cur = newnode->next;}//处理randomcur = head;while(cur){struct Node* newnode = cur -> next;if(cur->random==NULL){newnode->random = NULL;}else{newnode->random = cur->random->next;}cur = newnode->next;}//取新节点尾插,同时恢复原链表cur = head;struct Node* newhead = NULL;struct Node* newtail = NULL;while(cur){struct Node* newnode = cur->next;struct Node* next = newnode->next;if(newhead==NULL){newhead = newtail = cur->next;}else{newtail->next = newnode;newtail = newnode;}cur->next = newnode->next;cur = newnode->next;}return newhead;
}完
相关文章:

数据结构之链表笔试题详解
一:移除链表元素 我们很容易就可以想到一个解决方案:再创建一个链表,把不是val的结点拿过来尾插。 这样确实可以但是,我们每次尾插都需要遍历一遍整个链表,这样时间复杂度就变成了O(n^2), 因此我们不妨设…...
结构化的Prompt
资源库: AI 提示词-WayToAGI精选高效的AI提示词库,助力创作者和开发者解锁人工智能的潜力。通过我们的提示词和策略,优化您的AI工具使用效率,激发创意思维,提升产出质量。https://www.waytoagi.com/prompts?tag6 结构…...

【数字化】华为数字化转型架构蓝图
导读:华为的数字化转型规划团队在2016年年底基于对愿景的系统诠释,整合出了数字化转型架构蓝图。该蓝图共分为5层,旨在通过数字化转型实现客户交互方式的转变、作战方式的转变、公司各平台业务能力的数字化、服务化以及运营模式的转变。 目录…...

最新全开源IM即时通讯系统源码(PC+WEB+IOS+Android)部署指南
全开源IM(即时通讯)系统源码部署是一个复杂但系统的过程,涉及多个组件和步骤。以下是一个详细的部署指南,旨在帮助开发者或系统管理员成功部署一个全开源的IM系统,如OpenIM。 IM即时通讯系统源码准备工作 …...

go 跨平台打包
GOARCH是Go语言中的一个环境变量,用于指定目标平台的底层架构。在Go的交叉编译过程中,GOARCH决定了编译出的二进制文件将在哪种硬件架构上运行。 GOARCH的常见值 amd64:64位 x86 架构386:32位 x86 架构arm&am…...

C++ 给定字符串,然后给出开始要取的位置,返回取到的信息
3 happy new year 7 year 1 new 4 new year year error input #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> void strmcpy(char* s, char* t, int m); int main() {int repeat, m;char t[1000], s[1000];scanf("%d", &repeat);getchar(); //吸收换行符in…...

【树莓派4B】MindSpore lite 部署demo
一个demo,mindspore lite 部署在树莓派4B ubuntu22.04中,为后续操作开个门! 环境 开发环境:wsl-ubuntu22.04分发版部署环境:树莓派4B,操作系统为ubuntu22.04mindspore lite版本:mindspore-li…...

Idea汉化插件Datagrip汉化插件
汉化插件 Chinese (Simplified) Language Pack / 中文语言包 插件地址 安装完了之后,如果还不是中文的怎么办 需要手动设置 Seetings -> Appearance & Behavior -> System Settings -> Language and Region -> Language 修改为 [ Chi…...

精彩回顾|Cocos开发者沙龙长沙站
长沙-不一样 Cocos 开发者沙龙长沙站,完全超出了我们的预期,一开始还担心没有太多人报名。最后发现,全场爆满,座无虚席。 <<< 左右滑动见更多 >>> 许多小伙伴曾反馈过,在以往的开发者沙龙回顾文章中…...

算法日记 49 day 图论(A*算法)
这算是算法的最后一篇了,原本A*之前还有一些相关的最短路径算法的,比如dijkstra的堆优化,SPFA等等,但是有些我没看懂,就不写了,用A*做个结尾。 题目:骑士的攻击 127. 骑士的攻击 (kamacoder.co…...

服务器批量清理redis keys,无法适用客户端必须直连的情况
在 Redis 中,批量清理指定模式的键(例如 memberCardData:*)可以通过多种方法来实现。需要注意的是,Redis 的命令执行是单线程的,因此对大量键进行操作时可能会阻塞服务器。以下是几种常见的方法: shell K…...

Grafana配置告警规则推送企微机器人服务器资源告警
前提 已经部署Grafana,并且dashboard接入数据 大屏编号地址:Node Exporter Full | Grafana Labs 创建企微机器人 备注:群里若有第三方外部人员不能创建 机器人创建完成,记录下来Webhook地址 Grafana配置告警消息模板 {{ define &…...
)
数字货币金融研究,深度学习虚拟币价格预测 数据集 市值top20 (2014年—2024年)
比特币,以太坊,狗狗币,屎币,模因币 声明 此数据集的目的是 用于数字货币金融研究,深度学习虚拟币价格预测 1、数据集 2014年——2024年 市值top20 比特币,以太坊,屎币,狗狗币交易…...

druid.properties图标是齿轮
一、问题 在IDEA中, druid.properties图标是齿轮 二、原因 2023版本开始,IDEA新的UI的问题 三、解决方法 1、点击右上角的齿轮图标 2、点击Settings 3、Appearance & Behavior---->New UI---->取消勾选“Enable new UI”---->右下角OK 4…...

【图像处理】利用numpy、opencv、python实现车牌检测
| 利用opencv实现车牌检测 整体流程涉及5个部分 图像通道转换对比度增强边缘连接二值化边界区域裁剪 图像通道转换 将RGB图像转换为HSV图像,仅保留V通道。V通道表示颜色的明暗,常用于图像对比度拉伸、直方图均衡化等流程。 原图像: V通…...

ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘torchvision.transforms.functional_tensor‘
问题: 运行代码时,报错: … File “/home/xzy/anaconda3/envs/groundinggpt/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pytorchvideo/transforms/augmix.py”, line 6, in from pytorchvideo.transforms.augmentations import ( File “/home/xzy/anac…...

Android无障碍服务监听实现自动点击按钮
原理: 通过监听窗口改变事件,监听目标应用,通过视图ID(或文本、或描述、或其他如坐标之类的)找到目标视图,使用无障碍动作点击方法点击它 无障碍服务实现: 1、写一个自己的无障碍服务继承Acc…...

Deveco Studio首次编译项目初始化失败
编译项目失败 Ohpm install失败的时候重新使用管理者打开程序 build init 初始化失败遇到了以下报错信息 Installing pnpm8.13.1... npm ERR! code CERT_HAS_EXPIRED npm ERR! errno CERT_HAS_EXPIRED npm ERR! request to https://registry.npm.taobao.org/pnpm failed, r…...

Redis缓存应用场景【Redis场景上篇】
文章目录 1.缓存基础2.缓存异步场景1.缓存穿透2.缓存击穿3.缓存雪崩总结 3.缓存一致性 1.缓存基础 Redis由于性能高效,通常可以做数据库存储的缓存。一般而言,缓存分为服务端缓存和客户端缓存。缓存有以下三种模式: Cache Aside(…...

线程与进程基础
文章目录 前言一、 线程与进程1.1 什么是线程与进程?1.2 并发与并行1.3 同步调用与异步调用1.4 为什么要使用多线程? 前言 在学习juc前,需要先对进程和线程之间整体有一个认知。我们之前或多或少接触过,一些特别高大上的概念&…...
51c自动驾驶~合集58
我自己的原文哦~ https://blog.51cto.com/whaosoft/13967107 #CCA-Attention 全局池化局部保留,CCA-Attention为LLM长文本建模带来突破性进展 琶洲实验室、华南理工大学联合推出关键上下文感知注意力机制(CCA-Attention),…...
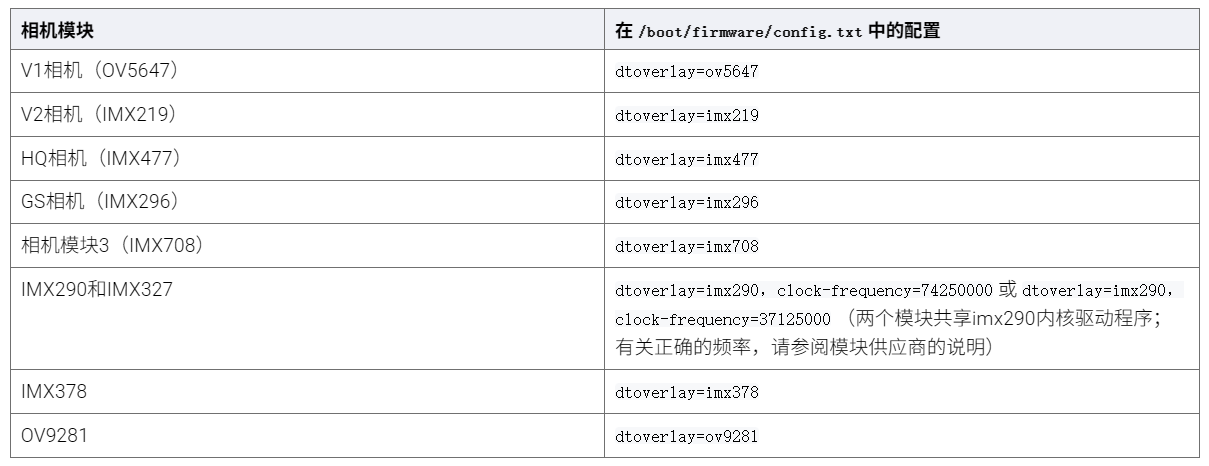
树莓派超全系列教程文档--(61)树莓派摄像头高级使用方法
树莓派摄像头高级使用方法 配置通过调谐文件来调整相机行为 使用多个摄像头安装 libcam 和 rpicam-apps依赖关系开发包 文章来源: http://raspberry.dns8844.cn/documentation 原文网址 配置 大多数用例自动工作,无需更改相机配置。但是,一…...

从零实现富文本编辑器#5-编辑器选区模型的状态结构表达
先前我们总结了浏览器选区模型的交互策略,并且实现了基本的选区操作,还调研了自绘选区的实现。那么相对的,我们还需要设计编辑器的选区表达,也可以称为模型选区。编辑器中应用变更时的操作范围,就是以模型选区为基准来…...

FFmpeg 低延迟同屏方案
引言 在实时互动需求激增的当下,无论是在线教育中的师生同屏演示、远程办公的屏幕共享协作,还是游戏直播的画面实时传输,低延迟同屏已成为保障用户体验的核心指标。FFmpeg 作为一款功能强大的多媒体框架,凭借其灵活的编解码、数据…...

前端导出带有合并单元格的列表
// 导出async function exportExcel(fileName "共识调整.xlsx") {// 所有数据const exportData await getAllMainData();// 表头内容let fitstTitleList [];const secondTitleList [];allColumns.value.forEach(column > {if (!column.children) {fitstTitleL…...
【机器视觉】单目测距——运动结构恢复
ps:图是随便找的,为了凑个封面 前言 在前面对光流法进行进一步改进,希望将2D光流推广至3D场景流时,发现2D转3D过程中存在尺度歧义问题,需要补全摄像头拍摄图像中缺失的深度信息,否则解空间不收敛…...

电脑插入多块移动硬盘后经常出现卡顿和蓝屏
当电脑在插入多块移动硬盘后频繁出现卡顿和蓝屏问题时,可能涉及硬件资源冲突、驱动兼容性、供电不足或系统设置等多方面原因。以下是逐步排查和解决方案: 1. 检查电源供电问题 问题原因:多块移动硬盘同时运行可能导致USB接口供电不足&#x…...
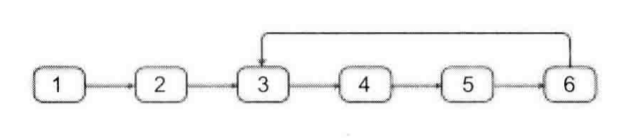
剑指offer20_链表中环的入口节点
链表中环的入口节点 给定一个链表,若其中包含环,则输出环的入口节点。 若其中不包含环,则输出null。 数据范围 节点 val 值取值范围 [ 1 , 1000 ] [1,1000] [1,1000]。 节点 val 值各不相同。 链表长度 [ 0 , 500 ] [0,500] [0,500]。 …...

PL0语法,分析器实现!
简介 PL/0 是一种简单的编程语言,通常用于教学编译原理。它的语法结构清晰,功能包括常量定义、变量声明、过程(子程序)定义以及基本的控制结构(如条件语句和循环语句)。 PL/0 语法规范 PL/0 是一种教学用的小型编程语言,由 Niklaus Wirth 设计,用于展示编译原理的核…...

Caliper 配置文件解析:config.yaml
Caliper 是一个区块链性能基准测试工具,用于评估不同区块链平台的性能。下面我将详细解释你提供的 fisco-bcos.json 文件结构,并说明它与 config.yaml 文件的关系。 fisco-bcos.json 文件解析 这个文件是针对 FISCO-BCOS 区块链网络的 Caliper 配置文件,主要包含以下几个部…...

