观察者模式(sigslot in C++)
大家,我是东风,今天抽点时间整理一下我很久前关注的一个不错的库,可以支持我们在使用标准C++的时候使用信号槽机制进行观察者模式设计,sigslot 官网: http://sigslot.sourceforge.net/
本文较为详尽探讨了一种观察者模式的精妙实现方式,即2002年由Sarah Thompson匠心设计的sigslot库。该库以其高效、灵活的特点,在信号与槽的连接管理上展现出卓越性能,成为事件驱动编程领域中的一大亮点。
1.sigslot 类结构

其中,以 _signal_base_interface 为基类的派生系列主要实现信号的链接与触发机制;以 has_slots_interface 为基类的派生系列主要实现槽对象,提供信号操作的对象;mt_policy、lock_block 则主要实现类似std::lock_guard<>的锁机制,确保线程安全。此外,很重要的一个类 _opaque_connection,它是槽对象的逻辑存储节点,在一定程度上解耦了信号与槽的直接联系。
2.源码疑问注解
2.1.信号与槽

//template <class mt_policy>
//class _signal_base
typedef std::list<_opaque_connection> connections_list;connections_list m_connected_slots; //template <class mt_policy = SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY>
//class has_slots
typedef std::set<_signal_base_interface*> sender_set;sender_set m_senders; 可以这样理解,一个信号可以触发多个槽回调,同样,一个槽对象可以被多个信号触发。
2.2.函数指针 cast
肯定不少人会对_opaque_connection的union实现函数指针 cast 表示疑问
template <typename FromT, typename ToT>
union union_caster {FromT from;ToT to;
}; 我先给出自己的理解:union_caster 实现将 FromT 类型转成 ToT。其中本质是利用以下两个性质:
(1) union 同一时刻只能存储一个值,要么是 from,要么是 to
(2)函数指针在同一平台上的字节大小是一样的
基于这两点,那么执行下列代码时,会有以下效果(见代码)
template <typename FromT, typename ToT>
union union_caster {FromT from;ToT to;
};void fun_t(int a)
{std::cout << "fun_t " << a << std::endl;
}void fun_f(int a,int b)
{std::cout << "fun_f " << a << "," << b << std::endl;
}int main()
{typedef void (*emit_t)(int a);typedef void (*em_t)(int a, int b);union_caster<em_t, emit_t> caster2; // <em_t, emit_t>caster2.from = fun_f;//此时,只看数值,caster2.to == caster2.from == fun_femit_t pemit = caster2.to;union_caster<emit_t,em_t> caster; // <emit_t,em_t> 巧妙完成类型转换caster.from = pemit; //caster的from是caster2的to(caster.to)(30, 20); //caster的to是caster2的from,因此这里等价 fun_f(30, 20)//验证想法std::cout << "sizeof fun_t(): " << sizeof(&fun_t) << " sizeof fun_t(): " << sizeof(&fun_f) << std::endl;std::cout << "caster2.from: " << caster2.from << " caster2.to: " << caster2.to << std::endl;std::cout << "caster.from: " << caster.from << " caster.to: " << caster.to << std::endl;getchar();return 0;
}
3.库使用
这里我们先给一个常规的应用,可以参照作者示例
#include "sigslot.h"
#include <iostream>using namespace sigslot;class Switch
{
public:Switch(){}~Switch(){}public:signal1<int> ToggleLight;};class Light : public has_slots<>
{
public:Light() {};~Light() {};public:void TurnState(int a){std::cout << "Light on/off " << a << std::endl;}};int main()
{Switch s;Light l;s.ToggleLight.connect(&l,&Light::TurnState);//l.signal_disconnect(&(s.ToggleLight));//l.disconnect_all();//s.ToggleLight.disconnect(&l);s.ToggleLight.emit(1000);//s.ToggleLight.emit(1000);getchar();return 0;
}
我认为只需搞明白connect()即可,其他行为就显而易见了。通过调试跟踪,我们可以发现,connect() 大概流程为:
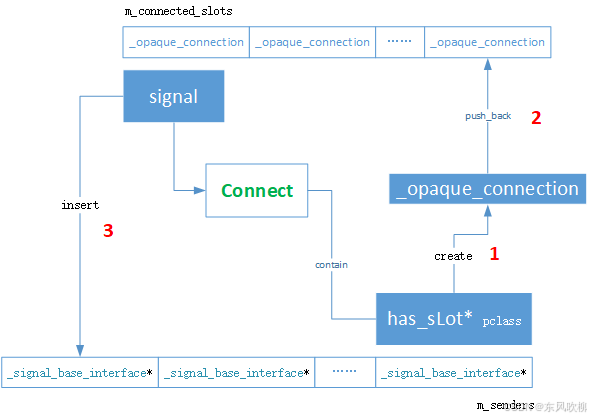
很显然,connect其实就是完成 m_senders 集合和 m_connected_slots 链表的更新,后续 emit() 、 disconnect()等等操作都是基于这两个数据结构来开展的。举个例子,当信号对象执行emit()时,不用查阅代码我们都可以知道,流程大概是:信号对象遍历 m_connected_slots ,针对每一个 _opaque_connection,回调它事先存储的槽对象成员方法。
TIPS:
(1) has_slots<> 的 signal_connect()、signal_disconnect()成员只是操作了 m_senders,并没有更新 m_connected_slots;disconnect_all() 成员更新了 m_senders 和 m_connected_slots;
(2)signal 的 connect()、disconnect() 等基本所有类似成员方法里都同时更新了 m_senders和 m_connected_slots。
若有不对,提醒我啦!
附录:sigslot 源码
//头文件:sigslot.h
//
// sigslot.h: Signal/Slot classes
//
// Written by Sarah Thompson (sarah@telergy.com) 2002.
//
// License: Public domain. You are free to use this code however you like, with
// the proviso that the author takes on no responsibility or liability for any
// use.
//
// QUICK DOCUMENTATION
//
// (see also the full documentation at http://sigslot.sourceforge.net/)
//
// #define switches
// SIGSLOT_PURE_ISO:
// Define this to force ISO C++ compliance. This also disables all of
// the thread safety support on platforms where it is available.
//
// SIGSLOT_USE_POSIX_THREADS:
// Force use of Posix threads when using a C++ compiler other than gcc
// on a platform that supports Posix threads. (When using gcc, this is
// the default - use SIGSLOT_PURE_ISO to disable this if necessary)
//
// SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY:
// Where thread support is enabled, this defaults to
// multi_threaded_global. Otherwise, the default is single_threaded.
// #define this yourself to override the default. In pure ISO mode,
// anything other than single_threaded will cause a compiler error.
//
// PLATFORM NOTES
//
// Win32:
// On Win32, the WEBRTC_WIN symbol must be #defined. Most mainstream
// compilers do this by default, but you may need to define it yourself
// if your build environment is less standard. This causes the Win32
// thread support to be compiled in and used automatically.
//
// Unix/Linux/BSD, etc.:
// If you're using gcc, it is assumed that you have Posix threads
// available, so they are used automatically. You can override this (as
// under Windows) with the SIGSLOT_PURE_ISO switch. If you're using
// something other than gcc but still want to use Posix threads, you
// need to #define SIGSLOT_USE_POSIX_THREADS.
//
// ISO C++:
// If none of the supported platforms are detected, or if
// SIGSLOT_PURE_ISO is defined, all multithreading support is turned
// off, along with any code that might cause a pure ISO C++ environment
// to complain. Before you ask, gcc -ansi -pedantic won't compile this
// library, but gcc -ansi is fine. Pedantic mode seems to throw a lot of
// errors that aren't really there. If you feel like investigating this,
// please contact the author.
//
//
// THREADING MODES
//
// single_threaded:
// Your program is assumed to be single threaded from the point of view
// of signal/slot usage (i.e. all objects using signals and slots are
// created and destroyed from a single thread). Behaviour if objects are
// destroyed concurrently is undefined (i.e. you'll get the occasional
// segmentation fault/memory exception).
//
// multi_threaded_global:
// Your program is assumed to be multi threaded. Objects using signals
// and slots can be safely created and destroyed from any thread, even
// when connections exist. In multi_threaded_global mode, this is
// achieved by a single global mutex (actually a critical section on
// Windows because they are faster). This option uses less OS resources,
// but results in more opportunities for contention, possibly resulting
// in more context switches than are strictly necessary.
//
// multi_threaded_local:
// Behaviour in this mode is essentially the same as
// multi_threaded_global, except that each signal, and each object that
// inherits has_slots, all have their own mutex/critical section. In
// practice, this means that mutex collisions (and hence context
// switches) only happen if they are absolutely essential. However, on
// some platforms, creating a lot of mutexes can slow down the whole OS,
// so use this option with care.
//
// USING THE LIBRARY
//
// See the full documentation at http://sigslot.sourceforge.net/
//
// Libjingle specific:
//
// This file has been modified such that has_slots and signalx do not have to be
// using the same threading requirements. E.g. it is possible to connect a
// has_slots<single_threaded> and signal0<multi_threaded_local> or
// has_slots<multi_threaded_local> and signal0<single_threaded>.
// If has_slots is single threaded the user must ensure that it is not trying
// to connect or disconnect to signalx concurrently or data race may occur.
// If signalx is single threaded the user must ensure that disconnect, connect
// or signal is not happening concurrently or data race may occur.#ifndef RTC_BASE_THIRD_PARTY_SIGSLOT_SIGSLOT_H_
#define RTC_BASE_THIRD_PARTY_SIGSLOT_SIGSLOT_H_#include <cstring>
#include <list>
#include <set>// On our copy of sigslot.h, we set single threading as default.
#define SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY single_threaded#if defined(SIGSLOT_PURE_ISO) || \(!defined(WEBRTC_WIN) && !defined(__GNUG__) && \!defined(SIGSLOT_USE_POSIX_THREADS))
#define _SIGSLOT_SINGLE_THREADED
#elif defined(WEBRTC_WIN)
#define _SIGSLOT_HAS_WIN32_THREADS
#include "windows.h"
#elif defined(__GNUG__) || defined(SIGSLOT_USE_POSIX_THREADS)
#define _SIGSLOT_HAS_POSIX_THREADS
#include <pthread.h>
#else
#define _SIGSLOT_SINGLE_THREADED
#endif#ifndef SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY
#ifdef _SIGSLOT_SINGLE_THREADED
#define SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY single_threaded
#else
#define SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY multi_threaded_local
#endif
#endif//
namespace sigslot {class single_threaded {public:void lock() {}void unlock() {}
};#ifdef _SIGSLOT_HAS_WIN32_THREADS
// The multi threading policies only get compiled in if they are enabled.
class multi_threaded_global {public:multi_threaded_global() {static bool isinitialised = false;if (!isinitialised) {InitializeCriticalSection(get_critsec());isinitialised = true;}}void lock() { EnterCriticalSection(get_critsec()); }void unlock() { LeaveCriticalSection(get_critsec()); }private:CRITICAL_SECTION* get_critsec() {static CRITICAL_SECTION g_critsec;return &g_critsec;}
};class multi_threaded_local {public:multi_threaded_local() { InitializeCriticalSection(&m_critsec); }multi_threaded_local(const multi_threaded_local&) {InitializeCriticalSection(&m_critsec);}~multi_threaded_local() { DeleteCriticalSection(&m_critsec); }void lock() { EnterCriticalSection(&m_critsec); }void unlock() { LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critsec); }private:CRITICAL_SECTION m_critsec;
};
#endif // _SIGSLOT_HAS_WIN32_THREADS#ifdef _SIGSLOT_HAS_POSIX_THREADS
// The multi threading policies only get compiled in if they are enabled.
class multi_threaded_global {public:void lock() { pthread_mutex_lock(get_mutex()); }void unlock() { pthread_mutex_unlock(get_mutex()); }private:static pthread_mutex_t* get_mutex();
};class multi_threaded_local {public:multi_threaded_local() { pthread_mutex_init(&m_mutex, nullptr); }multi_threaded_local(const multi_threaded_local&) {pthread_mutex_init(&m_mutex, nullptr);}~multi_threaded_local() { pthread_mutex_destroy(&m_mutex); }void lock() { pthread_mutex_lock(&m_mutex); }void unlock() { pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_mutex); }private:pthread_mutex_t m_mutex;
};
#endif // _SIGSLOT_HAS_POSIX_THREADStemplate <class mt_policy>
class lock_block {public:mt_policy* m_mutex;lock_block(mt_policy* mtx) : m_mutex(mtx) { m_mutex->lock(); }~lock_block() { m_mutex->unlock(); }
};class _signal_base_interface;class has_slots_interface {private:typedef void (*signal_connect_t)(has_slots_interface* self,_signal_base_interface* sender);typedef void (*signal_disconnect_t)(has_slots_interface* self,_signal_base_interface* sender);typedef void (*disconnect_all_t)(has_slots_interface* self);const signal_connect_t m_signal_connect;const signal_disconnect_t m_signal_disconnect;const disconnect_all_t m_disconnect_all;protected:has_slots_interface(signal_connect_t conn,signal_disconnect_t disc,disconnect_all_t disc_all): m_signal_connect(conn),m_signal_disconnect(disc),m_disconnect_all(disc_all) {}// Doesn't really need to be virtual, but is for backwards compatibility// (it was virtual in a previous version of sigslot).virtual ~has_slots_interface() {}public:void signal_connect(_signal_base_interface* sender) {m_signal_connect(this, sender);}void signal_disconnect(_signal_base_interface* sender) {m_signal_disconnect(this, sender);}void disconnect_all() { m_disconnect_all(this); }
};class _signal_base_interface {private:typedef void (*slot_disconnect_t)(_signal_base_interface* self,has_slots_interface* pslot);typedef void (*slot_duplicate_t)(_signal_base_interface* self,const has_slots_interface* poldslot,has_slots_interface* pnewslot);const slot_disconnect_t m_slot_disconnect;const slot_duplicate_t m_slot_duplicate;protected:_signal_base_interface(slot_disconnect_t disc, slot_duplicate_t dupl): m_slot_disconnect(disc), m_slot_duplicate(dupl) {}~_signal_base_interface() {}public:void slot_disconnect(has_slots_interface* pslot) {m_slot_disconnect(this, pslot);}void slot_duplicate(const has_slots_interface* poldslot,has_slots_interface* pnewslot) {m_slot_duplicate(this, poldslot, pnewslot);}
};class _opaque_connection {private:typedef void (*emit_t)(const _opaque_connection*);template <typename FromT, typename ToT>union union_caster {FromT from;ToT to;};emit_t pemit;has_slots_interface* pdest;// Pointers to member functions may be up to 16 bytes (24 bytes for MSVC)// for virtual classes, so make sure we have enough space to store it.
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && !defined(__clang__)unsigned char pmethod[24];
#elseunsigned char pmethod[16];
#endifpublic:template <typename DestT, typename... Args>_opaque_connection(DestT* pd, void (DestT::*pm)(Args...)) : pdest(pd) {typedef void (DestT::*pm_t)(Args...);static_assert(sizeof(pm_t) <= sizeof(pmethod),"Size of slot function pointer too large.");std::memcpy(pmethod, &pm, sizeof(pm_t));typedef void (*em_t)(const _opaque_connection* self, Args...);union_caster<em_t, emit_t> caster2;caster2.from = &_opaque_connection::emitter<DestT, Args...>;pemit = caster2.to;}has_slots_interface* getdest() const { return pdest; }_opaque_connection duplicate(has_slots_interface* newtarget) const {_opaque_connection res = *this;res.pdest = newtarget;return res;}// Just calls the stored "emitter" function pointer stored at construction// time.template <typename... Args>void emit(Args... args) const {typedef void (*em_t)(const _opaque_connection*, Args...);union_caster<emit_t, em_t> caster;caster.from = pemit;(caster.to)(this, args...);}private:template <typename DestT, typename... Args>static void emitter(const _opaque_connection* self, Args... args) {typedef void (DestT::*pm_t)(Args...);pm_t pm;static_assert(sizeof(pm_t) <= sizeof(pmethod),"Size of slot function pointer too large.");std::memcpy(&pm, self->pmethod, sizeof(pm_t));(static_cast<DestT*>(self->pdest)->*(pm))(args...);}
};template <class mt_policy>
class _signal_base : public _signal_base_interface, public mt_policy {protected:typedef std::list<_opaque_connection> connections_list;_signal_base(): _signal_base_interface(&_signal_base::do_slot_disconnect,&_signal_base::do_slot_duplicate),m_current_iterator(m_connected_slots.end()) {}~_signal_base() { disconnect_all(); }private:_signal_base& operator=(_signal_base const& that);public:_signal_base(const _signal_base& o): _signal_base_interface(&_signal_base::do_slot_disconnect,&_signal_base::do_slot_duplicate),m_current_iterator(m_connected_slots.end()) {lock_block<mt_policy> lock(this);for (const auto& connection : o.m_connected_slots) {connection.getdest()->signal_connect(this);m_connected_slots.push_back(connection);}}bool is_empty() {lock_block<mt_policy> lock(this);return m_connected_slots.empty();}void disconnect_all() {lock_block<mt_policy> lock(this);while (!m_connected_slots.empty()) {has_slots_interface* pdest = m_connected_slots.front().getdest();m_connected_slots.pop_front();pdest->signal_disconnect(static_cast<_signal_base_interface*>(this));}// If disconnect_all is called while the signal is firing, advance the// current slot iterator to the end to avoid an invalidated iterator from// being dereferenced.m_current_iterator = m_connected_slots.end();}#if !defined(NDEBUG)bool connected(has_slots_interface* pclass) {lock_block<mt_policy> lock(this);connections_list::const_iterator it = m_connected_slots.begin();connections_list::const_iterator itEnd = m_connected_slots.end();while (it != itEnd) {if (it->getdest() == pclass)return true;++it;}return false;}
#endifvoid disconnect(has_slots_interface* pclass) {lock_block<mt_policy> lock(this);connections_list::iterator it = m_connected_slots.begin();connections_list::iterator itEnd = m_connected_slots.end();while (it != itEnd) {if (it->getdest() == pclass) {// If we're currently using this iterator because the signal is firing,// advance it to avoid it being invalidated.if (m_current_iterator == it) {m_current_iterator = m_connected_slots.erase(it);} else {m_connected_slots.erase(it);}pclass->signal_disconnect(static_cast<_signal_base_interface*>(this));return;}++it;}}private:static void do_slot_disconnect(_signal_base_interface* p,has_slots_interface* pslot) {_signal_base* const self = static_cast<_signal_base*>(p);lock_block<mt_policy> lock(self);connections_list::iterator it = self->m_connected_slots.begin();connections_list::iterator itEnd = self->m_connected_slots.end();while (it != itEnd) {connections_list::iterator itNext = it;++itNext;if (it->getdest() == pslot) {// If we're currently using this iterator because the signal is firing,// advance it to avoid it being invalidated.if (self->m_current_iterator == it) {self->m_current_iterator = self->m_connected_slots.erase(it);} else {self->m_connected_slots.erase(it);}}it = itNext;}}static void do_slot_duplicate(_signal_base_interface* p,const has_slots_interface* oldtarget,has_slots_interface* newtarget) {_signal_base* const self = static_cast<_signal_base*>(p);lock_block<mt_policy> lock(self);connections_list::iterator it = self->m_connected_slots.begin();connections_list::iterator itEnd = self->m_connected_slots.end();while (it != itEnd) {if (it->getdest() == oldtarget) {self->m_connected_slots.push_back(it->duplicate(newtarget));}++it;}}protected:connections_list m_connected_slots;// Used to handle a slot being disconnected while a signal is// firing (iterating m_connected_slots).connections_list::iterator m_current_iterator;bool m_erase_current_iterator = false;
};template <class mt_policy = SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY>
class has_slots : public has_slots_interface, public mt_policy {private:typedef std::set<_signal_base_interface*> sender_set;typedef sender_set::const_iterator const_iterator;public:has_slots(): has_slots_interface(&has_slots::do_signal_connect,&has_slots::do_signal_disconnect,&has_slots::do_disconnect_all) {}has_slots(has_slots const& o): has_slots_interface(&has_slots::do_signal_connect,&has_slots::do_signal_disconnect,&has_slots::do_disconnect_all) {lock_block<mt_policy> lock(this);for (auto* sender : o.m_senders) {sender->slot_duplicate(&o, this);m_senders.insert(sender);}}~has_slots() { this->disconnect_all(); }private:has_slots& operator=(has_slots const&);static void do_signal_connect(has_slots_interface* p,_signal_base_interface* sender) {has_slots* const self = static_cast<has_slots*>(p);lock_block<mt_policy> lock(self);self->m_senders.insert(sender);}static void do_signal_disconnect(has_slots_interface* p,_signal_base_interface* sender) {has_slots* const self = static_cast<has_slots*>(p);lock_block<mt_policy> lock(self);self->m_senders.erase(sender);}static void do_disconnect_all(has_slots_interface* p) {has_slots* const self = static_cast<has_slots*>(p);lock_block<mt_policy> lock(self);while (!self->m_senders.empty()) {std::set<_signal_base_interface*> senders;senders.swap(self->m_senders);const_iterator it = senders.begin();const_iterator itEnd = senders.end();while (it != itEnd) {_signal_base_interface* s = *it;++it;s->slot_disconnect(p);}}}private:sender_set m_senders;
};template <class mt_policy, typename... Args>
class signal_with_thread_policy : public _signal_base<mt_policy> {private:typedef _signal_base<mt_policy> base;protected:typedef typename base::connections_list connections_list;public:signal_with_thread_policy() {}template <class desttype>void connect(desttype* pclass, void (desttype::*pmemfun)(Args...)) {lock_block<mt_policy> lock(this);this->m_connected_slots.push_back(_opaque_connection(pclass, pmemfun));pclass->signal_connect(static_cast<_signal_base_interface*>(this));}void emit(Args... args) {lock_block<mt_policy> lock(this);this->m_current_iterator = this->m_connected_slots.begin();while (this->m_current_iterator != this->m_connected_slots.end()) {_opaque_connection const& conn = *this->m_current_iterator;++(this->m_current_iterator);conn.emit<Args...>(args...);}}void operator()(Args... args) { emit(args...); }
};// Alias with default thread policy. Needed because both default arguments
// and variadic template arguments must go at the end of the list, so we
// can't have both at once.
template <typename... Args>
using signal = signal_with_thread_policy<SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY, Args...>;// The previous verion of sigslot didn't use variadic templates, so you would
// need to write "sigslot::signal2<Arg1, Arg2>", for example.
// Now you can just write "sigslot::signal<Arg1, Arg2>", but these aliases
// exist for backwards compatibility.
template <typename mt_policy = SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY>
using signal0 = signal_with_thread_policy<mt_policy>;template <typename A1, typename mt_policy = SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY>
using signal1 = signal_with_thread_policy<mt_policy, A1>;template <typename A1,typename A2,typename mt_policy = SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY>
using signal2 = signal_with_thread_policy<mt_policy, A1, A2>;template <typename A1,typename A2,typename A3,typename mt_policy = SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY>
using signal3 = signal_with_thread_policy<mt_policy, A1, A2, A3>;template <typename A1,typename A2,typename A3,typename A4,typename mt_policy = SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY>
using signal4 = signal_with_thread_policy<mt_policy, A1, A2, A3, A4>;template <typename A1,typename A2,typename A3,typename A4,typename A5,typename mt_policy = SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY>
using signal5 = signal_with_thread_policy<mt_policy, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5>;template <typename A1,typename A2,typename A3,typename A4,typename A5,typename A6,typename mt_policy = SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY>
using signal6 = signal_with_thread_policy<mt_policy, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6>;template <typename A1,typename A2,typename A3,typename A4,typename A5,typename A6,typename A7,typename mt_policy = SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY>
using signal7 =signal_with_thread_policy<mt_policy, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7>;template <typename A1,typename A2,typename A3,typename A4,typename A5,typename A6,typename A7,typename A8,typename mt_policy = SIGSLOT_DEFAULT_MT_POLICY>
using signal8 =signal_with_thread_policy<mt_policy, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8>;} // namespace sigslot#endif /* RTC_BASE_THIRD_PARTY_SIGSLOT_SIGSLOT_H_ */
//实现文件:sigslot.cc
//
// sigslot.h: Signal/Slot classes
//
// Written by Sarah Thompson (sarah@telergy.com) 2002.
//
// License: Public domain. You are free to use this code however you like, with
// the proviso that the author takes on no responsibility or liability for any
// use.#include "sigslot.h"namespace sigslot {#ifdef _SIGSLOT_HAS_POSIX_THREADSpthread_mutex_t* multi_threaded_global::get_mutex() {static pthread_mutex_t g_mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;return &g_mutex;
}#endif // _SIGSLOT_HAS_POSIX_THREADS} // namespace sigslot
相关文章:

观察者模式(sigslot in C++)
大家,我是东风,今天抽点时间整理一下我很久前关注的一个不错的库,可以支持我们在使用标准C的时候使用信号槽机制进行观察者模式设计,sigslot 官网: http://sigslot.sourceforge.net/ 本文较为详尽探讨了一种观察者模…...

python使用pip进行库的下载
前言 现如今有太多的python编译软件,其库的下载也是五花八门,但在作者看来,无论是哪种方法都是万变不离其宗,即pip下载。 pip是python的包管理工具,无论你是用的什么python软件,都可以用pip进行库的下载。 …...
)
C#(委托)
一、基本定义 在C#中,委托(Delegate)是一种引用类型,它用于封装一个方法(具有特定的参数列表和返回类型)。可以把委托想象成一个能存储方法的变量,这个变量能够像调用普通方法一样来调用它所存…...

《点点之歌》“意外”诞生记
世界是“点点”的,“点点”是世界的。 (笔记模板由python脚本于2024年12月23日 19:28:25创建,本篇笔记适合喜欢诗文的coder翻阅) 【学习的细节是欢悦的历程】 Python 官网:https://www.python.org/ Free:大咖免费“圣经”教程《 …...
ue5 pcg(程序内容生成)真的简单方便,就5个节点
总结: 前情提示 鼠标单击右键平移节点 1.编辑-》插件-》procedural->勾选两个插件 2.右键-》pcg图表-》拖拽进入场景 3.先看点point 右键-》调试(快捷键d)->右侧设置粒子数 3.1调整粒子数 可以在右侧输入框,使用加减乘除 4.1 表面采样器 …...

32岁前端干了8年,是继续做前端开发,还是转其它工作
前端发展有瓶颈,变来变去都是那一套,只是换了框架换了环境。换了框架后又得去学习,虽然很快上手,但是那些刚毕业的也很快上手了,入门门槛越来越低,想转行或继续卷,该如何破圈 这是一位网友的自述…...
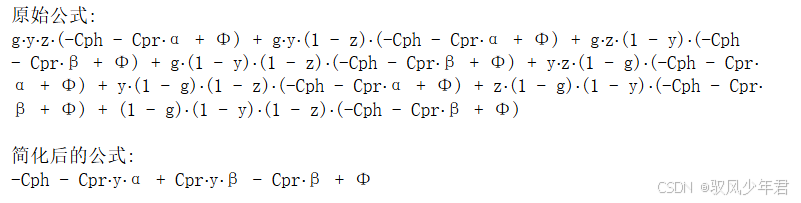
【演化博弈】期望收益函数公式、复制动态方程——化简功能技巧
期望化简 在演化博弈论的研究中,期望收益函数和复制动态方程是核心工具。化简这些公式的功能技巧具有以下几个重要作用: 提高公式的可读性和理解度 复杂的数学表达式可能让人感到困惑。通过化简,公式变得更加简单和易读,使研究者…...

opencv中的各种滤波器简介
在 OpenCV 中,滤波器是图像处理中的重要工具,用于对图像进行平滑、去噪、边缘检测等操作。以下是几种常见滤波器的简单介绍。 1. 均值滤波 (Mean Filter) 功能: 对图像进行平滑处理,减少噪声。 应用场景: 去除图像…...

[Effective C++]条款36-37 两个绝不
本文初发于 “天目中云的小站”,同步转载于此。 条款36 : 绝不重新定义继承而来的non-virtual函数 本条款很容易理解, 援引以前的条款就可以说明为什么 : 条款34中就提到过 : non-virtual函数意味着接口 强制性实现继承, 它不应当被改变. 重新定义继承而来的non-…...
)
各种网站(学习资源及其他)
欢迎围观笔者的个人博客~ 也欢迎通过RSS网址https://kangaroogao.github.io/atom.xml进行订阅~ 大学指南 上海交通大学生存手册中国科学技术大学人工智能与数据科学学院本科进阶指南USTC不完全入学指南大学生活质量指北科研论 信息搜集 AI信息搜集USTC飞跃网站计算机保研 技…...

docker怎么部署高斯数据库
部署高斯数据库(openGauss)到Docker的步骤如下: 安装Docker: 如果您的系统尚未安装Docker,需要先进行安装。以CentOS为例,可以使用以下命令安装Docker: yum install -y docker拉取镜像ÿ…...
VScode中配置ESlint+Prettier详细步骤(图文详情)
VScode中配置ESlintPrettier详细步骤(图文详情) 前置环境: node 18.19.0 vite 3.2.11 vue 3.2.47 本文将不在演示vue3基础工程创建,如果还没有vue3项目工程请参考文章: Vite创建Vue3工程并引入ElementPlus&#x…...
Leetcode打卡:考场就坐
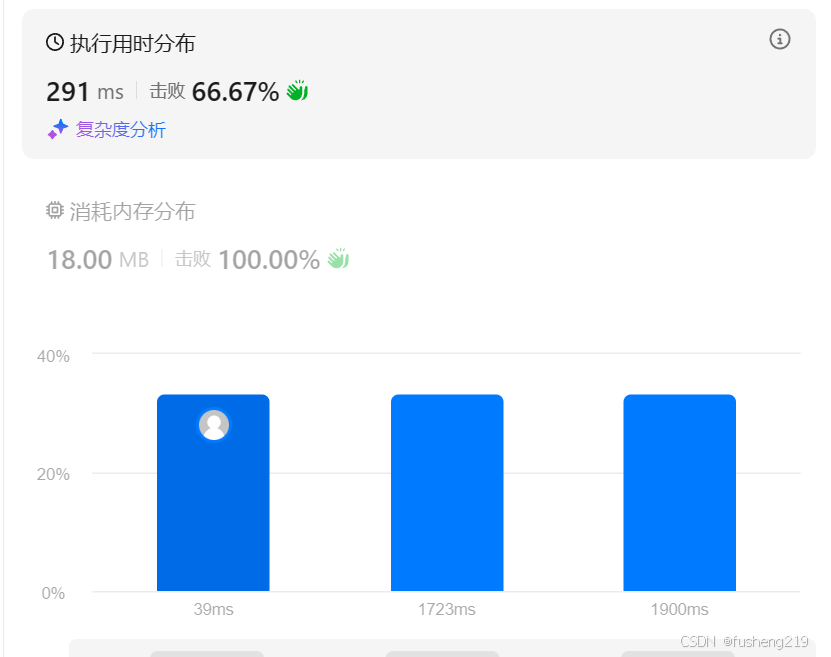
执行结果:通过 题目: 855 考场就坐 在考场里,有 n 个座位排成一行,编号为 0 到 n - 1。 当学生进入考场后,他必须坐在离最近的人最远的座位上。如果有多个这样的座位,他会坐在编号最小的座位上。(另外&am…...
数据库压力测试详解
🍅 点击文末小卡片,免费获取软件测试全套资料,资料在手,涨薪更快 很多人提到 jmeter 时,只会说到 jmeter进行接口自动化或接口性能测试,其实jmeter还能对数据库进行自动化操作。个人常用的场景有以下&#…...

项目测试方案流程详解
🍅 点击文末小卡片,免费获取软件测试全套资料,资料在手,涨薪更快 作为一名软件测试工程师,为项目制作完成的测试方案并执行,是我们日常工作的重要部分,同时,也是一名合格的软件测试工…...
以二进制形式创建gitea仓库
1、官方文档: 数据库准备 | Gitea Documentation 使用二进制文件安装 | Gitea Documentation 2、具体操作 1)创建gitea数据库 2)检查是否安装 Git。要求 Git 版本 > 2.0。 如需升级git请参考以下链接:linux升级git版本-C…...
Spring(七)Spring Cloud----Feign、Zuul和Apollo
文章目录 一、服务调用Feign1.1 Feign的基本使用1.2 Feign的属性配置1.2.1 Ribbon配置1.2.2 Hystrix配置 二、网关服务Zuul2.1 Zuul的基本使用2.1.1 请求路由2.1.2 请求过滤 2.2 路由详解2.2.1 传统路由配置2.2.2 服务路由配置2.2.3 服务路由的默认规则2.2.4 自定义路由映射规则…...

*【每日一题 提高题】[蓝桥杯 2022 国 A] 选素数
选素数 小蓝有一个数 x,每次操作小蓝会选择一个小于 x 的素数 p,然后在 x 成为 p 的倍数前不断将 x 加 1,(如果 x 一开始就是 p 的倍数则 x 不变)。 小乔看到了小蓝进行了 2 次上述操作后得到的结果 n,他想…...
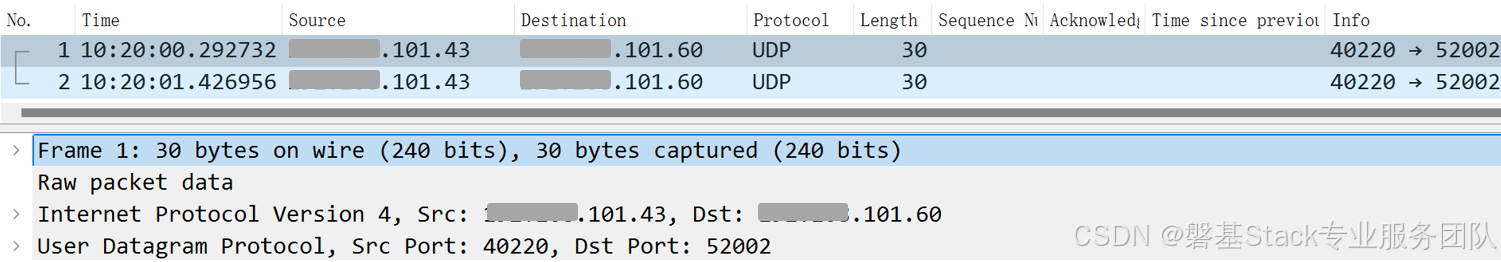
华为云环境下LVS/DR架构的故障诊断优化
本文作者:刘涛 文章目录 前言1.LVS/DR集群的问题2.华为云环境3.问题排查3.1 检查LVS/DR模式配置3.1.1 RS服务器3.1.2 DS服务器 3.2 继续分析抓包结果3.2.1 调整tcpdump抓包过滤条件3.2.2 client向集群VIP发包3.2.3 DS服务器arp消息 3.3 查看丢包3.3.1 监控DS和RS服…...

leetcode hot100除自身以外的数组的乘积
238. 除自身以外数组的乘积 已解答 中等 相关标签 相关企业 提示 给你一个整数数组 nums,返回 数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 等于 nums 中除 nums[i] 之外其余各元素的乘积 。 题目数据 保证 数组 nums之中任意元素的全部前缀元素和后缀的乘积都在…...
:にする)
日语学习-日语知识点小记-构建基础-JLPT-N4阶段(33):にする
日语学习-日语知识点小记-构建基础-JLPT-N4阶段(33):にする 1、前言(1)情况说明(2)工程师的信仰2、知识点(1) にする1,接续:名词+にする2,接续:疑问词+にする3,(A)は(B)にする。(2)復習:(1)复习句子(2)ために & ように(3)そう(4)にする3、…...
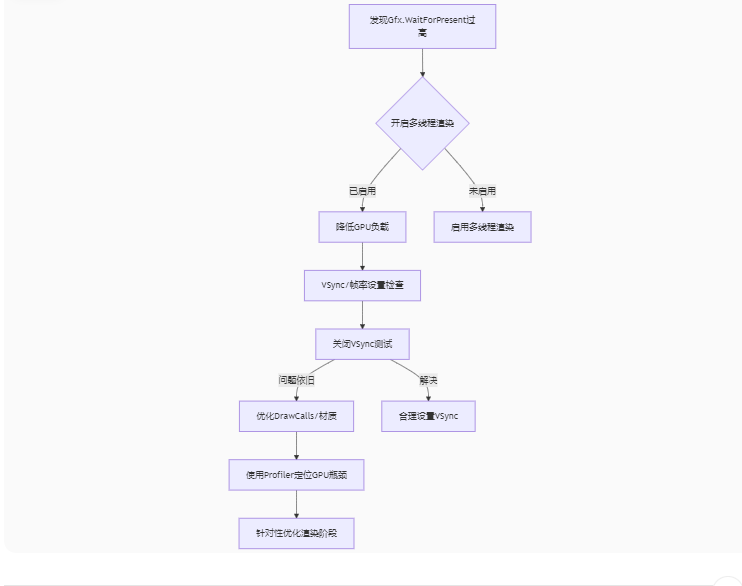
Unity3D中Gfx.WaitForPresent优化方案
前言 在Unity中,Gfx.WaitForPresent占用CPU过高通常表示主线程在等待GPU完成渲染(即CPU被阻塞),这表明存在GPU瓶颈或垂直同步/帧率设置问题。以下是系统的优化方案: 对惹,这里有一个游戏开发交流小组&…...
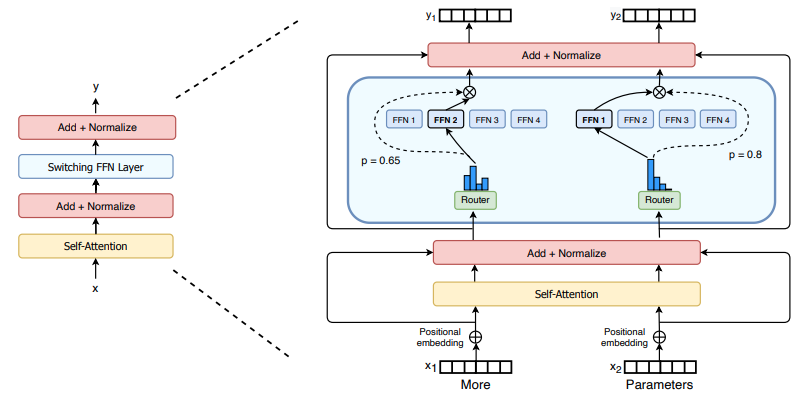
(二)TensorRT-LLM | 模型导出(v0.20.0rc3)
0. 概述 上一节 对安装和使用有个基本介绍。根据这个 issue 的描述,后续 TensorRT-LLM 团队可能更专注于更新和维护 pytorch backend。但 tensorrt backend 作为先前一直开发的工作,其中包含了大量可以学习的地方。本文主要看看它导出模型的部分&#x…...
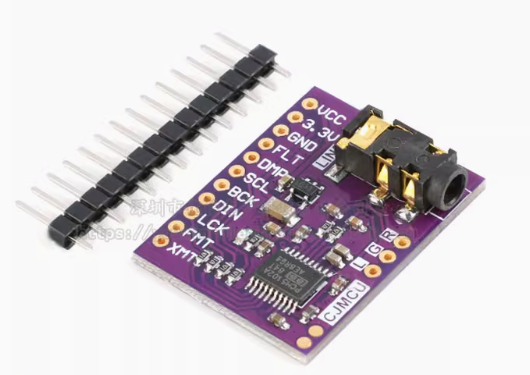
ESP32 I2S音频总线学习笔记(四): INMP441采集音频并实时播放
简介 前面两期文章我们介绍了I2S的读取和写入,一个是通过INMP441麦克风模块采集音频,一个是通过PCM5102A模块播放音频,那如果我们将两者结合起来,将麦克风采集到的音频通过PCM5102A播放,是不是就可以做一个扩音器了呢…...
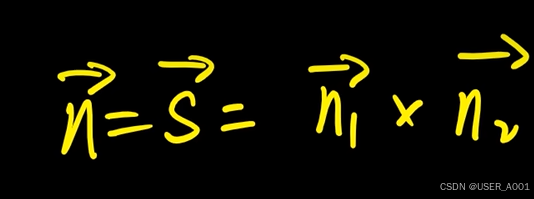
高等数学(下)题型笔记(八)空间解析几何与向量代数
目录 0 前言 1 向量的点乘 1.1 基本公式 1.2 例题 2 向量的叉乘 2.1 基础知识 2.2 例题 3 空间平面方程 3.1 基础知识 3.2 例题 4 空间直线方程 4.1 基础知识 4.2 例题 5 旋转曲面及其方程 5.1 基础知识 5.2 例题 6 空间曲面的法线与切平面 6.1 基础知识 6.2…...

Java 加密常用的各种算法及其选择
在数字化时代,数据安全至关重要,Java 作为广泛应用的编程语言,提供了丰富的加密算法来保障数据的保密性、完整性和真实性。了解这些常用加密算法及其适用场景,有助于开发者在不同的业务需求中做出正确的选择。 一、对称加密算法…...

用机器学习破解新能源领域的“弃风”难题
音乐发烧友深有体会,玩音乐的本质就是玩电网。火电声音偏暖,水电偏冷,风电偏空旷。至于太阳能发的电,则略显朦胧和单薄。 不知你是否有感觉,近两年家里的音响声音越来越冷,听起来越来越单薄? —…...
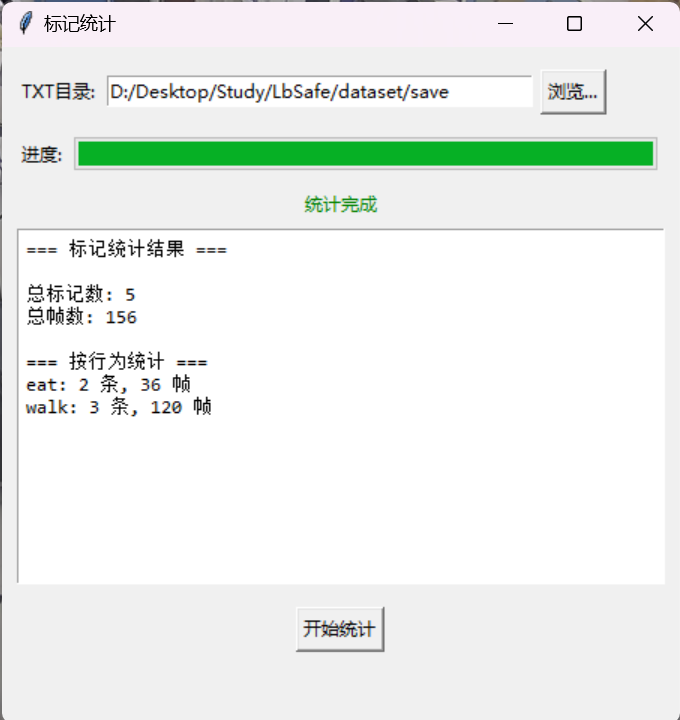
视频行为标注工具BehaviLabel(源码+使用介绍+Windows.Exe版本)
前言: 最近在做行为检测相关的模型,用的是时空图卷积网络(STGCN),但原有kinetic-400数据集数据质量较低,需要进行细粒度的标注,同时粗略搜了下已有开源工具基本都集中于图像分割这块,…...

AGain DB和倍数增益的关系
我在设置一款索尼CMOS芯片时,Again增益0db变化为6DB,画面的变化只有2倍DN的增益,比如10变为20。 这与dB和线性增益的关系以及传感器处理流程有关。以下是具体原因分析: 1. dB与线性增益的换算关系 6dB对应的理论线性增益应为&…...
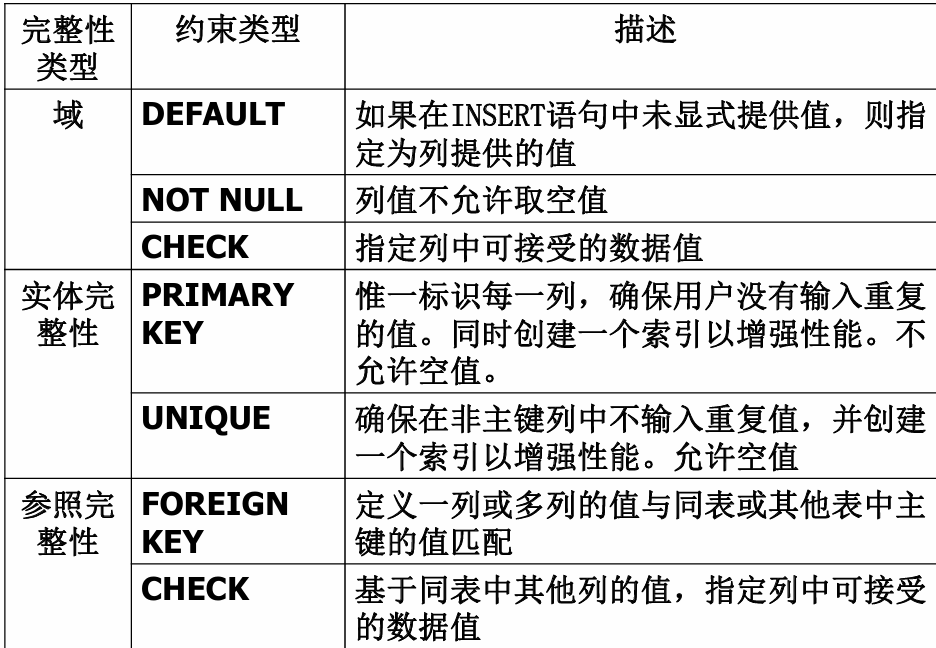
七、数据库的完整性
七、数据库的完整性 主要内容 7.1 数据库的完整性概述 7.2 实体完整性 7.3 参照完整性 7.4 用户定义的完整性 7.5 触发器 7.6 SQL Server中数据库完整性的实现 7.7 小结 7.1 数据库的完整性概述 数据库完整性的含义 正确性 指数据的合法性 有效性 指数据是否属于所定…...
