[OpenGL]使用glsl实现smallpt
一、简介
本文介绍了如何使用 OpenGL,使用 glsl 语言在 Fragment shader 中实现 smallpt。程序完成后可以得到以下渲染结果(samples per pixel, spp = 16)。在程序中按下A,W可以左右平移,按下W,S可以前后平移:

二、smallpt
0. smallpt 介绍
smallpt 是一个简易的路径跟踪程序,仅使用99行代码就实现了简单的路径跟踪。对 smallpt 代码的介绍可以查看[图形学]smallpt代码详解(上)、[图形学]smallpt代码详解(中) 和 [图形学]smallpt代码详解(下);
由于 smallpt 使用递归实现,然而 glsl 中并不支持函数的递归调用,因此需要先将基于递归的smallpt转为基于迭代的smallpt。
1. 基于迭代的 smallpt
在基于递归的 smallpt 中,像素 (x,y) 处的渲染结果 L L L 等于:
L = L e 0 + L c 0 ∗ r a d i a n c e ( r a y 0 ) r a d i a n c e ( r a y 0 ) = L e 1 + L c 1 ∗ r a d i a n c e ( r a y 1 ) r a d i a n c e ( r a y 1 ) = L e 2 + L c 2 ∗ r a d i a n c e ( r a y 2 ) . . . L = L_{e0} + L_{c0}* radiance(ray_{0}) \\ radiance(ray_{0}) = L_{e1} + L_{c1}* radiance(ray_{1}) \\ radiance(ray_{1}) = L_{e2} + L_{c2}* radiance(ray_{2}) \\ ... L=Le0+Lc0∗radiance(ray0)radiance(ray0)=Le1+Lc1∗radiance(ray1)radiance(ray1)=Le2+Lc2∗radiance(ray2)...
其中 L e 0 L_{e0} Le0为光线第一次相交处图元的自发光项emit, L c 0 L_{c0} Lc0是光线第一次相交处图元的颜色项color。 L e 1 L_{e1} Le1为光线第二次相交处图元的自发光项emit, L c 1 L_{c1} Lc1是光线第二次相交处图元的颜色项color。以此类推。
根据上式可以得到:
L = L e 0 + L c 0 ∗ L e 1 + L c 0 ∗ L c 1 ∗ L e 2 + . . . L = L_{e0} + L_{c0}*L_{e1} + L_{c0}*L_{c1}*L_{e2} + ... L=Le0+Lc0∗Le1+Lc0∗Lc1∗Le2+...
我们可以使用迭代(循环)的结构计算上式,在循环中维护变量L和Lf。L是最终的结果,Lf等于 L c 0 ∗ L c 1 . . . L c i L_{c0}*L_{c1}... L_{ci} Lc0∗Lc1...Lci,伪代码如下:
for(i=0;i<max_depth; i++)
{
L = L + Lf * L_ei;
Lf = Lf * L_ci;
}
基于 迭代的smallpt 代码如下:
#include <math.h> // smallpt, a Path Tracer by Kevin Beason, 2008
#include <stdlib.h> // Make : g++ -O3 -fopenmp smallpt.cpp -o smallpt
#include <stdio.h> // Remove "-fopenmp" for g++ version < 4.2
#define double float
struct Vec { // Usage: time ./smallpt 5000 && xv image.ppmdouble x, y, z; // position, also color (r,g,b)Vec(double x_=0, double y_=0, double z_=0){ x=x_; y=y_; z=z_; }Vec operator+(const Vec &b) const { return Vec(x+b.x,y+b.y,z+b.z); }Vec operator-(const Vec &b) const { return Vec(x-b.x,y-b.y,z-b.z); }Vec operator*(double b) const { return Vec(x*b,y*b,z*b); }Vec mult(const Vec &b) const { return Vec(x*b.x,y*b.y,z*b.z); }Vec& norm(){ return *this = *this * (1/sqrt(x*x+y*y+z*z)); }double dot(const Vec &b) const { return x*b.x+y*b.y+z*b.z; } // cross:Vec operator%(Vec&b){return Vec(y*b.z-z*b.y,z*b.x-x*b.z,x*b.y-y*b.x);}
};
struct Ray { Vec o, d; Ray(Vec o_, Vec d_) : o(o_), d(d_) {} };
enum Refl_t { DIFF, SPEC, REFR }; // material types, used in radiance()
struct Sphere {double rad; // radiusVec p, e, c; // position, emission, colorRefl_t refl; // reflection type (DIFFuse, SPECular, REFRactive)Sphere(double rad_, Vec p_, Vec e_, Vec c_, Refl_t refl_):rad(rad_), p(p_), e(e_), c(c_), refl(refl_) {}double intersect(const Ray &r) const { // returns distance, 0 if nohitVec op = p-r.o; // Solve t^2*d.d + 2*t*(o-p).d + (o-p).(o-p)-R^2 = 0double t, eps=1e-4, b=op.dot(r.d), det=b*b-op.dot(op)+rad*rad;if (det<0) return 0; else det=sqrt(det);return (t=b-det)>eps ? t : ((t=b+det)>eps ? t : 0);}
};
Sphere spheres[] = {//Scene: radius, position, emission, color, materialSphere(1e5, Vec( 1e5+1,40.8,81.6), Vec(),Vec(.75,.25,.25),DIFF),//LeftSphere(1e5, Vec(-1e5+99,40.8,81.6),Vec(),Vec(.25,.25,.75),DIFF),//RghtSphere(1e5, Vec(50,40.8, 1e5), Vec(),Vec(.75,.75,.75),DIFF),//BackSphere(1e5, Vec(50,40.8,-1e5+170), Vec(),Vec(), DIFF),//FrntSphere(1e5, Vec(50, 1e5, 81.6), Vec(),Vec(.75,.75,.75),DIFF),//BotmSphere(1e5, Vec(50,-1e5+81.6,81.6),Vec(),Vec(.75,.75,.75),DIFF),//TopSphere(16.5,Vec(27,16.5,47), Vec(),Vec(1,1,1)*.999, SPEC),//MirrSphere(16.5,Vec(73,16.5,78), Vec(),Vec(1,1,1)*.999, REFR),//GlasSphere(600, Vec(50,681.6-.27,81.6),Vec(12,12,12), Vec(), DIFF) //Lite
};
inline double clamp(double x){ return x<0 ? 0 : x>1 ? 1 : x; }
inline int toInt(double x){ return int(pow(clamp(x),1/2.2)*255+.5); }
inline bool intersect(const Ray &r, double &t, int &id){double n=sizeof(spheres)/sizeof(Sphere), d, inf=t=1e20;for(int i=int(n);i--;) if((d=spheres[i].intersect(r))&&d<t){t=d;id=i;}return t<inf;
}
Vec radiance(const Ray &r_, int depth_, unsigned short *Xi){double t; // distance to intersectionint id=0; // id of intersected objectRay r=r_;int depth=depth_;// L0 = Le0 + f0*(L1)// = Le0 + f0*(Le1 + f1*L2)// = Le0 + f0*(Le1 + f1*(Le2 + f2*(L3))// = Le0 + f0*(Le1 + f1*(Le2 + f2*(Le3 + f3*(L4)))// = ...// = Le0 + f0*Le1 + f0*f1*Le2 + f0*f1*f2*Le3 + f0*f1*f2*f3*Le4 + ...// // So:// F = 1// while (1){// L += F*Lei// F *= fi// }Vec cl(0,0,0); // accumulated colorVec cf(1,1,1); // accumulated reflectancewhile (1){if (!intersect(r, t, id)) return cl; // if miss, return blackconst Sphere &obj = spheres[id]; // the hit objectVec x=r.o+r.d*t, n=(x-obj.p).norm(), nl=n.dot(r.d)<0?n:n*-1, f=obj.c;double p = f.x>f.y && f.x>f.z ? f.x : f.y>f.z ? f.y : f.z; // max reflcl = cl + cf.mult(obj.e);if (++depth>5) if (erand48(Xi)<p) f=f*(1/p); else return cl; //R.R.cf = cf.mult(f);if (obj.refl == DIFF){ // Ideal DIFFUSE reflectiondouble r1=2*M_PI*erand48(Xi), r2=erand48(Xi), r2s=sqrt(r2);Vec w=nl, u=((fabs(w.x)>.1?Vec(0,1):Vec(1))%w).norm(), v=w%u;Vec d = (u*cos(r1)*r2s + v*sin(r1)*r2s + w*sqrt(1-r2)).norm();//return obj.e + f.mult(radiance(Ray(x,d),depth,Xi));r = Ray(x,d);continue;} else if (obj.refl == SPEC){ // Ideal SPECULAR reflection//return obj.e + f.mult(radiance(Ray(x,r.d-n*2*n.dot(r.d)),depth,Xi));r = Ray(x,r.d-n*2*n.dot(r.d));continue;}Ray reflRay(x, r.d-n*2*n.dot(r.d)); // Ideal dielectric REFRACTIONbool into = n.dot(nl)>0; // Ray from outside going in?double nc=1, nt=1.5, nnt=into?nc/nt:nt/nc, ddn=r.d.dot(nl), cos2t;if ((cos2t=1-nnt*nnt*(1-ddn*ddn))<0){ // Total internal reflection//return obj.e + f.mult(radiance(reflRay,depth,Xi));r = reflRay;continue;}Vec tdir = (r.d*nnt - n*((into?1:-1)*(ddn*nnt+sqrt(cos2t)))).norm();double a=nt-nc, b=nt+nc, R0=a*a/(b*b), c = 1-(into?-ddn:tdir.dot(n));double Re=R0+(1-R0)*c*c*c*c*c,Tr=1-Re,P=.25+.5*Re,RP=Re/P,TP=Tr/(1-P);// return obj.e + f.mult(erand48(Xi)<P ?// radiance(reflRay, depth,Xi)*RP:// radiance(Ray(x,tdir),depth,Xi)*TP);if (erand48(Xi)<P){cf = cf*RP;r = reflRay;} else {cf = cf*TP;r = Ray(x,tdir);}continue;}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){int w=512, h=384, samps = argc==2 ? atoi(argv[1])/4 : 1; // # samplesRay cam(Vec(50,52,295.6), Vec(0,-0.042612,-1).norm()); // cam pos, dirVec cx=Vec(w*.5135/h), cy=(cx%cam.d).norm()*.5135, r, *c=new Vec[w*h];
#pragma omp parallel for schedule(dynamic, 1) private(r) // OpenMPfor (int y=0; y<h; y++){ // Loop over image rowsfprintf(stderr,"\rRendering (%d spp) %5.2f%%",samps*4,100.*y/(h-1));for (unsigned short x=0, Xi[3]={0,0,y*y*y}; x<w; x++) // Loop colsfor (int sy=0, i=(h-y-1)*w+x; sy<2; sy++) // 2x2 subpixel rowsfor (int sx=0; sx<2; sx++, r=Vec()){ // 2x2 subpixel colsfor (int s=0; s<samps; s++){double r1=2*erand48(Xi), dx=r1<1 ? sqrt(r1)-1: 1-sqrt(2-r1);double r2=2*erand48(Xi), dy=r2<1 ? sqrt(r2)-1: 1-sqrt(2-r2);Vec d = cx*( ( (sx+.5 + dx)/2 + x)/w - .5) +cy*( ( (sy+.5 + dy)/2 + y)/h - .5) + cam.d;r = r + radiance(Ray(cam.o+d*140,d.norm()),0,Xi)*(1./samps);} // Camera rays are pushed ^^^^^ forward to start in interiorc[i] = c[i] + Vec(clamp(r.x),clamp(r.y),clamp(r.z))*.25;}}FILE *f = fopen("image.ppm", "w"); // Write image to PPM file.fprintf(f, "P3\n%d %d\n%d\n", w, h, 255);for (int i=0; i<w*h; i++)fprintf(f,"%d %d %d ", toInt(c[i].x), toInt(c[i].y), toInt(c[i].z));
}
2. 使用 glsl 实现 smallpt
使用 glsl 实现 smallpt 时,在 Fragment shader 中实现上述的基于迭代的smallpt。在 Fragment shader 中,每个片段(片元)为一个像素点(x,y),在该像素点发射一根光线,调用函数radianc(Ray r)计算该像素处的着色值。
2.1. Vertex shader 代码
smallpt.vert:
#version 430
layout(location = 0) in vec3 position;
void main() { gl_Position = vec4(position, 1.0f); }
2.2. Fragment shader 代码
smallpt.frag:
#version 430
out vec4 frag_colour;
uniform ivec2 image_size; // 窗口的宽、高
uniform vec3 cam_position; // 相机的位置
uniform int spp; // samples per pixel/* 用于生成随机数 */
int erand_i = 1;
int erand_j = 1;
double erand08() {int k;k = (erand_i + erand_j) % 16777216;erand_i = erand_j;erand_j = k;return double(erand_i) / 16777216.0;
}
uint hash(uint x) {x += (x << 10u);x ^= (x >> 6u);x += (x << 3u);x ^= (x >> 11u);x += (x << 15u);return x;
}
double floatConstruct(uint m) {const uint ieeeMantissa = 0x007FFFFFu; // binary32 mantissa bitmask\nconst uint ieeeOne = 0x3F800000u; // 1.0 in IEEE binary32\nm &= ieeeMantissa; // Keep only mantissa bits (fractional part)\nm |= ieeeOne; // Add fractional part to 1.0\ndouble f = double(uintBitsToFloat(m)); // Range [1:2]\nreturn f - 1.0; // Range [0:1]\n
}
double random(float x) { return floatConstruct(hash(floatBitsToUint(x))); }
/********************/struct Ray {dvec3 o, d;
};
int DIFF = 0;
int SPEC = 1;
int REFR = 2;
struct Sphere {double rad;dvec3 p, e, c;int refl;
};
Sphere spheres[] = {// Scene: radius, position, emission, color, material\nSphere(1e5, dvec3(1e5 + 1, 40.8, 81.6), dvec3(0, 0, 0),dvec3(.75, .25, .25),DIFF), // Left\nSphere(1e5, dvec3(-1e5 + 99, 40.8, 81.6), dvec3(0, 0, 0),dvec3(.25, .25, .75),DIFF), // Rght\nSphere(1e5, dvec3(50, 40.8, 1e5), dvec3(0, 0, 0), dvec3(.75, .75, .75),DIFF), // Back\n// Sphere(1e5, dvec3(50, 40.8, -1e5 + 170), dvec3(0, 0, 0), dvec3(0, 0, 0),// DIFF), // Frnt\nSphere(1e5, dvec3(50, 1e5, 81.6), dvec3(0, 0, 0), dvec3(.75, .75, .75),DIFF), // Botm\nSphere(1e5, dvec3(50, -1e5 + 81.6, 81.6), dvec3(0, 0, 0),dvec3(.75, .75, .75),DIFF), // Top\nSphere(16.5, dvec3(27, 16.5, 47), dvec3(0, 0, 0), dvec3(1, 1, 1) * .999,SPEC), // Mirr\nSphere(16.5, dvec3(73, 16.5, 78), dvec3(0, 0, 0), dvec3(1, 1, 1) * .999,REFR), // Glas\nSphere(600, dvec3(50, 681.6 - .27, 81.6), dvec3(12, 12, 12), dvec3(0, 0, 0),DIFF) // Lite\n
};
double intersect(Sphere s, Ray r) { // returns distance, 0 if nohit\ndvec3 op = s.p - r.o; // Solve t^2*d.d + 2*t*(o-p).d + (o-p).(o-p)-R^2 = 0\ndouble t, eps = 4e-2, b = dot(op, r.d),det = b * b - dot(op, op) + s.rad * s.rad;if (det < 0)return 0;elsedet = sqrt(det);return (t = b - det) > eps ? t : ((t = b + det) > eps ? t : 0);
}
// int numSpheres = 9; // sizeof(spheres)/sizeof(Sphere);\n
int numSpheres = 8; // sizeof(spheres)/sizeof(Sphere);\n
struct TID {double t;int id;
} tid;
bool Intersect(Ray r) { // closest intersecting sphere\ndouble d, inf = tid.t = 1e20;int i;for (i = 0; i < numSpheres; i++) {d = intersect(spheres[i], r);if ((d > 0) && (d < tid.t)) {tid.t = d;tid.id = i;}}return tid.t < inf;
}
double M_PI = 3.14159265358979323846;
double M_1_PI = 0.31830988618379067154;
int depth;
dvec3 radiance(Ray r) {double t; // distance to intersection\nint id; // id of intersected object\ndvec3 cl = dvec3(0, 0, 0); // accumulated color\ndvec3 cf = dvec3(1, 1, 1); // accumulated reflectance\nfor (depth = 0; depth < 5; depth++) {if (!Intersect(r))return cl; // if miss, return black\nt = tid.t;id = tid.id;Sphere obj = spheres[id];dvec3 x = r.o + r.d * t, n = normalize(x - obj.p),nl = ((dot(n, r.d) < 0) ? n : n * -1), f = obj.c;double p = (((f.x > f.y) && (f.x > f.z))? f.x: ((f.y > f.z) ? f.y : f.z)); // max refl\ncl = cl + cf * obj.e;if (depth > 3) {if (erand08() < p)f = f * (1 / p);elsereturn cl;} // R.R.\ncf = cf * f;if (obj.refl == DIFF) { // Ideal DIFFUSE reflection\ndouble r1 = 2 * M_PI * erand08(), r2 = erand08(), r2s = sqrt(r2);dvec3 w = nl,u = normalize(cross(((abs(w.x) > .1) ? dvec3(0, 1, 0) : dvec3(1, 0, 0)), w)),v = cross(w, u);dvec3 d = normalize(u * cos(float(r1)) * r2s + v * sin(float(r1)) * r2s +w * sqrt(1 - r2));r = Ray(x, d);continue;} else if (obj.refl == SPEC) { // Ideal SPECULAR reflection\nr = Ray(x, r.d - n * 2 * dot(n, r.d));continue;}Ray reflRay =Ray(x, r.d - n * 2 * dot(n, r.d)); // Ideal dielectric REFRACTION\nbool into = (dot(n, nl) > 0); // Ray from outside going in?\ndouble nc = 1, nt = 1.5, nnt = (into ? nc / nt : nt / nc),ddn = dot(r.d, nl), cos2t = 1 - nnt * nnt * (1 - ddn * ddn);if (cos2t < 0) { // Total internal reflection\nr = reflRay;continue;}dvec3 tdir = normalize(r.d * nnt -n * ((into ? 1 : -1) * (ddn * nnt + sqrt(cos2t))));double a = nt - nc, b = nt + nc, R0 = a * a / (b * b),c = 1 - (into ? -ddn : dot(tdir, n));double Re = R0 + (1 - R0) * c * c * c * c * c, Tr = 1 - Re,P = .25 + .5 * Re, RP = Re / P, TP = Tr / (1 - P);if (erand08() < P) {cf = cf * RP;r = reflRay;} else {cf = cf * TP;r = Ray(x, tdir);}}return cl;
}
double clamp(double x) { return ((x < 0) ? 0 : ((x > 1) ? 1 : x)); }
void main() {int w = image_size.x, h = image_size.y;int samps = int(spp / 4 <= 0 ? 1 : spp / 4); // # samples\nRay cam = Ray(dvec3(50, 52, 295.6),normalize(dvec3(0, -0.042612, -1))); // cam pos, dir\ncam = Ray(dvec3(cam_position),normalize(dvec3(0, -0.042612, -1))); // cam pos, dir\ndvec3 cx = dvec3(w * .5135 / h, 0, 0);dvec3 cy = normalize(cross(cx, cam.d)) * .5135;dvec3 r = dvec3(0, 0, 0);dvec3 c = dvec3(0, 0, 0);int x, y; // 屏幕像素位置/** 屏幕像素坐标示意图:* ^* y|* (0,h)......(w,h)* | |* | |* | |* (0,0)......(w,0)---> x*/x = int(gl_FragCoord[0]);// y = int(h - gl_FragCoord[1] - 1);y = int(gl_FragCoord[1]);erand_i = int(random(y * w + x) * 16777216);erand_j = int(random(x * h + y) * 16777216);int sx, sy, s;for (sy = 0; sy < 2; sy++) { // 2x2 subpixel rows\nfor (sx = 0; sx < 2; sx++) { // 2x2 subpixel cols\nfor (s = 0; s < samps; s++) {double r1 = 2 * erand08(),dx = ((r1 < 1) ? sqrt(r1) - 1 : 1 - sqrt(2 - r1));double r2 = 2 * erand08(),dy = ((r2 < 1) ? sqrt(r2) - 1 : 1 - sqrt(2 - r2));dvec3 d = cx * (((sx + .5 + dx) / 2 + x) / w - .5) +cy * (((sy + .5 + dy) / 2 + y) / h - .5) + cam.d;r = r + radiance(Ray(cam.o + d * 140, normalize(d))) * (1. / samps);} // Camera rays are pushed ^^^^^ forward to start in interior\nc = c + dvec3(clamp(r.x), clamp(r.y), clamp(r.z)) * .25;r.x = 0;r.y = 0;r.z = 0;}}// gamma 矫正c.x = pow(float(clamp(c.x)), 1 / 2.2);c.y = pow(float(clamp(c.y)), 1 / 2.2);c.z = pow(float(clamp(c.z)), 1 / 2.2);frag_colour = vec4(c.x, c.y, c.z, 1);
}
2.3. main.cpp 代码
main.cpp
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include "Shader.hpp"
#include <cstdint>
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>// 用于处理窗口大小改变的回调函数
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow *window, int width, int height);
void window_close_callback(GLFWwindow *window);// 用于处理用户输入的函数
void process_input_callback(GLFWwindow *window, int key, int scancode, int action, int mods);// 指定窗口默认width和height像素大小
unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800;
unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
// 相机位置
glm::vec3 camera_position = glm::vec3(50, 52, 295.6);
/************************************/int main()
{/****** 1. 初始化 glfw, glad, 窗口 *******/// glfw 初始化 + 配置 glfw 参数glfwInit();glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 4);glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);// glfw 生成窗口GLFWwindow *window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", NULL, NULL);if (window == NULL){// 检查是否成功生成窗口,如果没有成功打印出错信息并且退出std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;glfwTerminate();return -1;}// 设置窗口window的上下文glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);// 配置window变化时的回调函数glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback);// 设置窗口关闭回调glfwSetWindowCloseCallback(window, window_close_callback);// 设置按键回调函数glfwSetKeyCallback(window, process_input_callback);// 使用 glad 加载 OpenGL 中的各种函数if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress)){std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;return -1;}/************************************//****** 2. 初始化 shader ******/Shader smallptShader("../resources/smallpt.vert", "../resources/smallpt.frag");/************************************//****** 3. 准备输入数据 ******//* vertices* 0 ----- 3* | \ |* | \_ |* | \_ |* 1 ----- 2*/float vertices[] = {// x,y,z-1.0, 1.0, 0.0, // 0-1.0, -1.0, 0.0, // 11.0, -1.0, 0.0, // 21.0, 1.0, 0.0 // 3};unsigned int indices[] = {0, 1, 2, 2, 3, 0};GLuint VAO, VBO, EBO;glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);glGenBuffers(1, &EBO);glBindVertexArray(VAO);glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_READ);glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof(float), (void *)(0 * sizeof(float)));glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, EBO);glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(indices), indices, GL_STATIC_READ);/************************************//****** 4.开始渲染 ******/while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window)){// render// ------glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);smallptShader.use();smallptShader.setiVec2("image_size", glm::ivec2(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT));smallptShader.setInt("spp", 16);smallptShader.setVec3("cam_position", camera_position);glBindVertexArray(VAO); // 绑定VAO,指定当前绘制使用的VAO对象glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, 6, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0);glfwSwapBuffers(window); // 在gfw中启用双缓冲,确保绘制的平滑和无缝切换glfwPollEvents(); // 用于处理所有挂起的事件,例如键盘输入、鼠标移动、窗口大小变化等事件}/************************************//****** 5. 释放资源 ******/// glfw 释放 glfw使用的所有资源glfwTerminate();/************************************/return 0;
}// 用于处理用户输入的函数
void process_input_callback(GLFWwindow *window, int key, int scancode, int action, int mods)
{switch (key){case GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE:// 当按下 Esc 按键时调用 glfwSetWindowShouldClose() 函数,关闭窗口glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);break;case GLFW_KEY_A:camera_position.x -= 1;break;case GLFW_KEY_D:camera_position.x += 1;break;case GLFW_KEY_W:camera_position.z -= 1;break;case GLFW_KEY_S:camera_position.z += 1;break;default:break;}
}// 在使用 OpenGL 和 GLFW 库时,处理窗口大小改变的回调函数
// 当窗口大小发生变化时,确保 OpenGL 渲染的内容能够适应新的窗口大小,避免图像被拉伸、压缩或出现其他比例失真的问题
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow *window, int width, int height)
{SCR_WIDTH = width;SCR_HEIGHT = height;glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
}
void window_close_callback(GLFWwindow *window)
{// 这里可以做一些额外的清理工作// 例如释放资源、记录日志等std::cout << "Window is closing..." << std::endl;
}2.4. 运行结果
spp=16:

spp=256:

spp=1024(很耗时):

3. 全部代码
使用 glsl 实现 smallpt 的全部代码以及模型文件可以在 [OpenGL]使用glsl实现smallpt 中下载。
4. 改进思路
当spp比较大时,程序运行会比较卡顿。为了提高程序的流畅性,下面几条是可以用于优化程序的方向(如果有时间的话我以后可能会实现一下):
- 使用预计算的随机数纹理生成随机数,而不是使用 Fragment shader 中的函数 on the fly 地生成随机数;
- 基于时间的连续性,在前后两帧间进行插值;
- 基于空间的连续性,对结果进行滤波处理;
三、参考
[1.]smallpt
[2.]smallpt-glsl
相关文章:

[OpenGL]使用glsl实现smallpt
一、简介 本文介绍了如何使用 OpenGL,使用 glsl 语言在 Fragment shader 中实现 smallpt。程序完成后可以得到以下渲染结果(samples per pixel, spp 16)。在程序中按下A,W可以左右平移,按下W,S可以前后平移: 二、s…...

elementui的默认样式修改
今天用element ui ,做了个消息提示,发现提示的位置总是在上面,如图: 可是我想让提示的位置到下面来,该怎么办? 最后还是看了官方的api 原来有个自定义样式属性 customClass 设置下就好了 js代码 css代码…...

mysql的主从配置
#mysql数据库 #主从 MySQL数据库主从配置 1.MySQL主从介绍 MySQL 主从又叫做 Replication、AB 复制。简单讲就是 A 和 B 两台机器做主 从后,在 A 上写数据,另外一台 B 也会跟着写数据,两者数据实时同步的。 MySQL 主从是基于 binlog 的&…...

CPO-CNN-GRU-Attention、CNN-GRU-Attention、CPO-CNN-GRU、CNN-GRU四模型多变量时序预测对比
CPO-CNN-GRU-Attention、CNN-GRU-Attention、CPO-CNN-GRU、CNN-GRU四模型多变量时序预测对比 目录 CPO-CNN-GRU-Attention、CNN-GRU-Attention、CPO-CNN-GRU、CNN-GRU四模型多变量时序预测对比预测效果基本介绍程序设计参考资料 预测效果 基本介绍 基于CPO-CNN-GRU-Attention、…...
)
深入了解PINN:物理信息神经网络(Physics-Informed Neural Networks)
1. 什么是PINN(物理信息神经网络)? 物理信息神经网络(PINN,Physics-Informed Neural Networks)是一类通过结合神经网络和物理方程的深度学习方法。其主要特点是将物理系统的约束条件(如偏微分方…...

人形机器人全身运动规划相关资料与文章
1.HumanPlus: Humanoid Shadowing and Imitation from Humans 文章地址:[2406.10454] HumanPlus: Humanoid Shadowing and Imitation from Humans 代码地址:MarkFzp/humanplus: [CoRL 2024] HumanPlus: Humanoid Shadowing and Imitation from Humans …...

使用uWSGI将Flask应用部署到生产环境
使用uWSGI将Flask应用部署到生产环境: 1、安装uWSGI conda install -c conda-forge uwsgi(pip install uwsgi会报错) 2、配置uWSGI 在python程序的同一文件夹下创建 uwsgi.ini文件,文件内容如下表。 需要按照实际情况修改文件名称…...

微服务监控工具Grafana
目录 前言 服务介绍 Grafana:数据可视化和展示 Prometheus:时序数据监控 Loki:日志管理 工具使用 安装 配置 Grafana 数据源编辑 Go Web 项目上报数据 Prometheus 指标上报 Loki 日志上报 数据查看 前言 随着微服务的盛行&…...

用户界面的UML建模06
4.1 抽象表示层的结构(Abstract Presentation Structure) 如图6 所示,抽象表示层模型具有一个顶层的容器(container),《apm》AbstractForm,其包含了许多组件,《apm》AbstractCompon…...

【力扣刷题第一天】63.不同路径Ⅱ
63.不同路径Ⅱ 🚀 题目 题目来源:leetcode 63. 不同路径Ⅱ:63. 不同路径 II - 力扣(LeetCode); 给定一个 m x n 的整数数组 grid。一个机器人初始位于 左上角(即 obstacleGrid[0][0]…...

如何优化Python网络爬虫的数据清洗流程,以提升数据质量并有效应对网站反爬虫机制?
优化爬虫数据清洗流程,应对反爬虫机制 一、数据清洗的重要性 在网络爬虫中,数据清洗是关键环节。打个比方,我们从网页抓取到的原始数据就像一堆杂乱的杂物,里面有各种格式、错误和重复信息。比如抓取到的文本可能包含HTML标签、…...

svn 相关应用与管理
文章目录 SVN 概要svn 权限控制svn 实操实例svn 备份 SVN 概要 一、SVN简介 Subversion(SVN)是一个开放源代码的版本控制系统,用于管理文件和目录的版本。它采用集中式的版本控制方式,即有一个中央仓库存储所有文件的版本信息&a…...

THM:Mouse Trap[WriteUP]
目录 连接至THM服务器并启动靶机 信息收集 使用rustscan对靶机TCP端口进行开放扫描 提取扫描结果中的端口号 使用nmap对靶机TCP开放端口进行脚本、服务扫描 使用nmap对靶机TCP开放端口进行漏洞、系统扫描 使用nmap对靶机UDP常用端口进行开放扫描 使用smbmap尝试枚举靶机…...

Nginx详细安装配置过程
目录 1.nginx环境准备 1.1 在配置好yum源之后,安装如下的编译工具 1.2 安装nginx所需的依赖库 1.3 关闭防火墙,selinux,并确保网络正常 2.nginx的编译安装 2.1从nginx官网复制下载链接,wget 下载 2.2? 解压nginx源代码 2…...
目标检测入门指南:从原理到实践
目录 1. 数据准备与预处理 2. 模型架构设计 2.1 特征提取网络原理 2.2 区域提议网络(RPN)原理 2.3 特征金字塔网络(FPN)原理 2.4 边界框回归原理 2.5 非极大值抑制(NMS)原理 2.6 多尺度训练与测试原理 2.7 损失函数设计原理 3. 损失函数设计 4. 训练策略优化 5. 后…...

2024 高通边缘智能创新应用大赛智能边缘计算赛道冠军方案解读
2024 高通边缘智能创新应用大赛聚焦不同细分领域的边缘智能创新应用落地,共设立三大热门领域赛道——工业智能质检赛道、智能边缘计算赛道和智能机器人赛道。本文为智能边缘计算赛道冠军项目《端侧大模型智能翻译机》的开发思路与成果分享。 赛题要求 聚焦边缘智能…...

tcpdump 网络数据包分析工具
简介 用简单的话来定义tcpdump,就是:dump the traffic on a network,根据使用者的定义对网络上的数据包进行截获的包分析工具。 tcpdump可以将网络中传送的数据包的“头”完全截获下来提供分析。它支持针对网络层、协议、主机、网络或端口的…...
鱼眼相机模型与去畸变实现
1.坐标系说明 鱼眼相机模型涉及到世界坐标系、相机坐标系、图像坐标系、像素坐标系之间的转换关系。对于分析鱼眼相机模型,假定世界坐标系下的坐标点,经过外参矩阵的变换转到相机坐标系,相机坐标再经过内参转换到像素坐标,具体如下 进一步进…...

【Unity功能集】TextureShop纹理工坊(七)魔棒工具
项目源码:在终章发布 索引 魔棒工具PS魔棒工具魔棒工具功能点提炼TextureShop魔棒工具根据色差选取非连续区域中间镂空边框的流动虚线取消选区魔棒工具 魔棒工具,也既是通过颜色色差,在图像上选出自定义选区的工具(了解PS魔棒工具)。 PS魔棒工具 我们先来看看PS中的魔棒…...

ASP.NET Core Web API Hangfire
ASP.NET Core Web API Hangfire 前言一、安装二、相关代码1.代码片段2.代码片段3.运行效果 三、测试代码1.即发即弃作业2.延迟作业3.重复作业4.延续作业5.页面调度作业 前言 👨💻👨🌾📝记录学习成果,以…...

Python爬虫实战:研究MechanicalSoup库相关技术
一、MechanicalSoup 库概述 1.1 库简介 MechanicalSoup 是一个 Python 库,专为自动化交互网站而设计。它结合了 requests 的 HTTP 请求能力和 BeautifulSoup 的 HTML 解析能力,提供了直观的 API,让我们可以像人类用户一样浏览网页、填写表单和提交请求。 1.2 主要功能特点…...

生成xcframework
打包 XCFramework 的方法 XCFramework 是苹果推出的一种多平台二进制分发格式,可以包含多个架构和平台的代码。打包 XCFramework 通常用于分发库或框架。 使用 Xcode 命令行工具打包 通过 xcodebuild 命令可以打包 XCFramework。确保项目已经配置好需要支持的平台…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个医院挂号小程序
一、开发准备 环境搭建: 安装DevEco Studio 3.0或更高版本配置HarmonyOS SDK申请开发者账号 项目创建: File > New > Create Project > Application (选择"Empty Ability") 二、核心功能实现 1. 医院科室展示 /…...
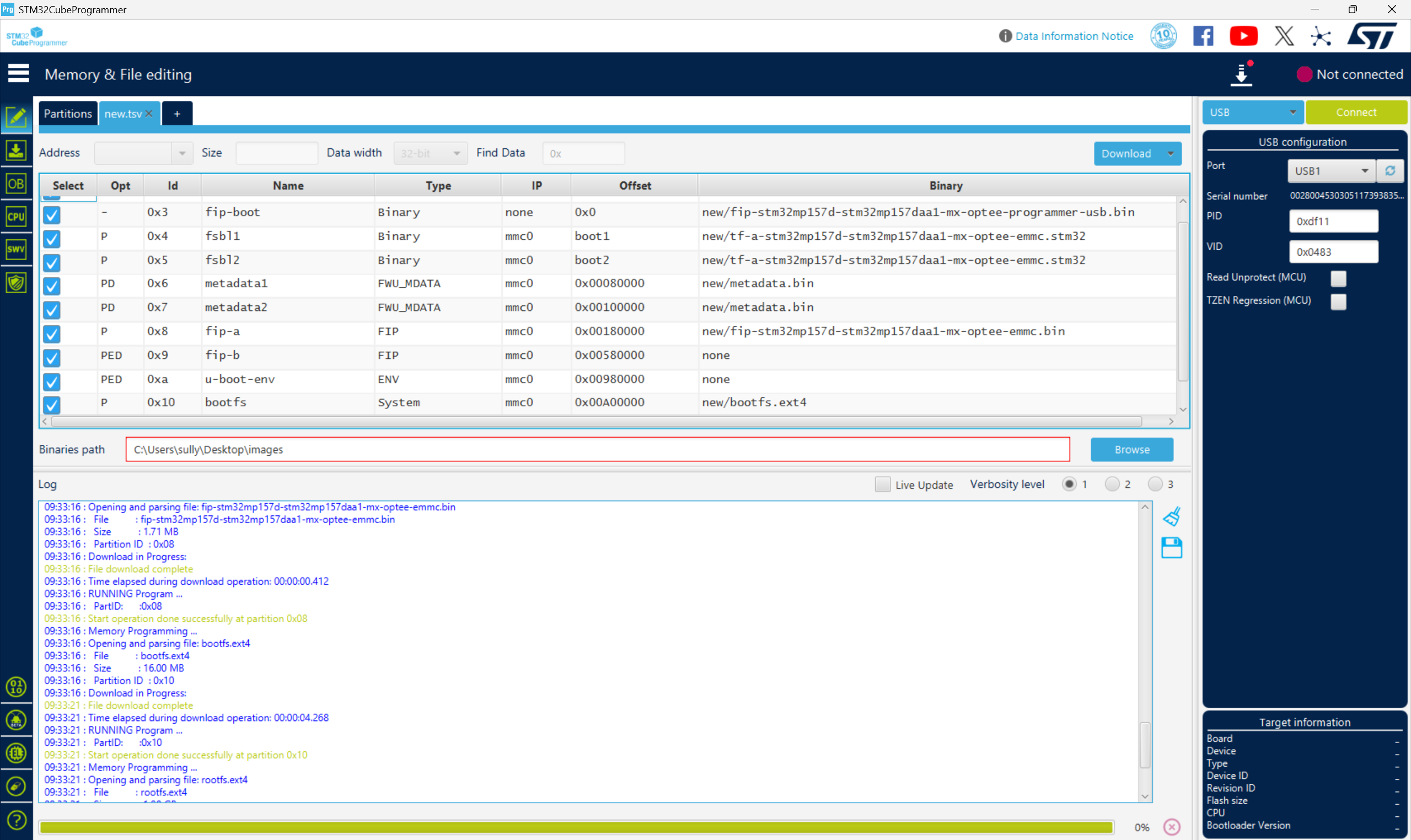
从零开始打造 OpenSTLinux 6.6 Yocto 系统(基于STM32CubeMX)(九)
设备树移植 和uboot设备树修改的内容同步到kernel将设备树stm32mp157d-stm32mp157daa1-mx.dts复制到内核源码目录下 源码修改及编译 修改arch/arm/boot/dts/st/Makefile,新增设备树编译 stm32mp157f-ev1-m4-examples.dtb \stm32mp157d-stm32mp157daa1-mx.dtb修改…...

Python ROS2【机器人中间件框架】 简介
销量过万TEEIS德国护膝夏天用薄款 优惠券冠生园 百花蜂蜜428g 挤压瓶纯蜂蜜巨奇严选 鞋子除臭剂360ml 多芬身体磨砂膏280g健70%-75%酒精消毒棉片湿巾1418cm 80片/袋3袋大包清洁食品用消毒 优惠券AIMORNY52朵红玫瑰永生香皂花同城配送非鲜花七夕情人节生日礼物送女友 热卖妙洁棉…...

python爬虫——气象数据爬取
一、导入库与全局配置 python 运行 import json import datetime import time import requests from sqlalchemy import create_engine import csv import pandas as pd作用: 引入数据解析、网络请求、时间处理、数据库操作等所需库。requests:发送 …...

vue3 daterange正则踩坑
<el-form-item label"空置时间" prop"vacantTime"> <el-date-picker v-model"form.vacantTime" type"daterange" start-placeholder"开始日期" end-placeholder"结束日期" clearable :editable"fal…...
实现跳一跳小游戏)
鸿蒙(HarmonyOS5)实现跳一跳小游戏
下面我将介绍如何使用鸿蒙的ArkUI框架,实现一个简单的跳一跳小游戏。 1. 项目结构 src/main/ets/ ├── MainAbility │ ├── pages │ │ ├── Index.ets // 主页面 │ │ └── GamePage.ets // 游戏页面 │ └── model │ …...
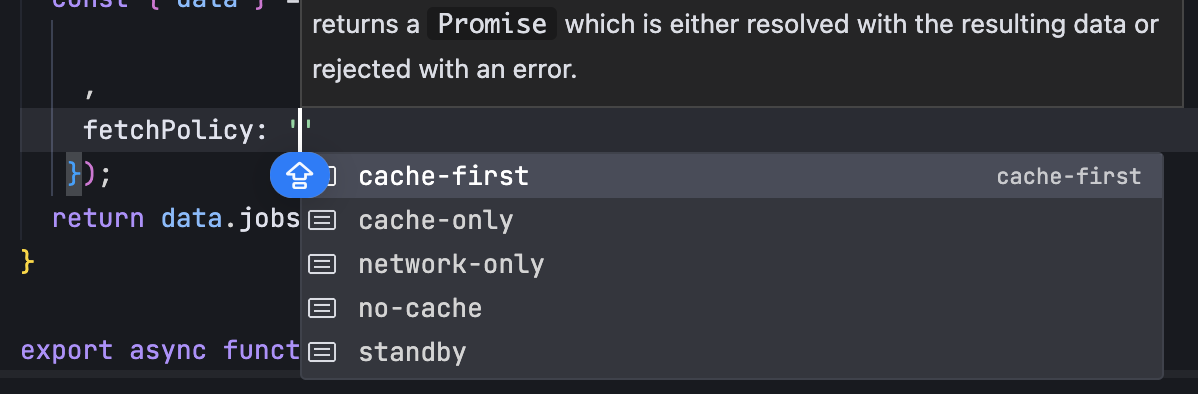
GraphQL 实战篇:Apollo Client 配置与缓存
GraphQL 实战篇:Apollo Client 配置与缓存 上一篇:GraphQL 入门篇:基础查询语法 依旧和上一篇的笔记一样,主实操,没啥过多的细节讲解,代码具体在: https://github.com/GoldenaArcher/graphql…...

webpack面试题
面试题:webpack介绍和简单使用 一、webpack(模块化打包工具)1. webpack是把项目当作一个整体,通过给定的一个主文件,webpack将从这个主文件开始找到你项目当中的所有依赖文件,使用loaders来处理它们&#x…...
